Ogallala Aquifer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Ogallala Aquifer () is a shallow
The Ogallala Aquifer () is a shallow
 The regions overlying the Ogallala Aquifer are some of the most productive regions in the United States for ranching
The regions overlying the Ogallala Aquifer are some of the most productive regions in the United States for ranching
Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts. Retrieved 2/10/14. During the 1990s, the aquifer held some three billion acre-feet of groundwater used for crop irrigation as well as drinking water in urban areas. The demand for the water outstrips its replenishment. The water level is particularly on the decline in Texas and New Mexico. Continued long-term use of the aquifer is "troublesome and in need of major reevaluation," according to the
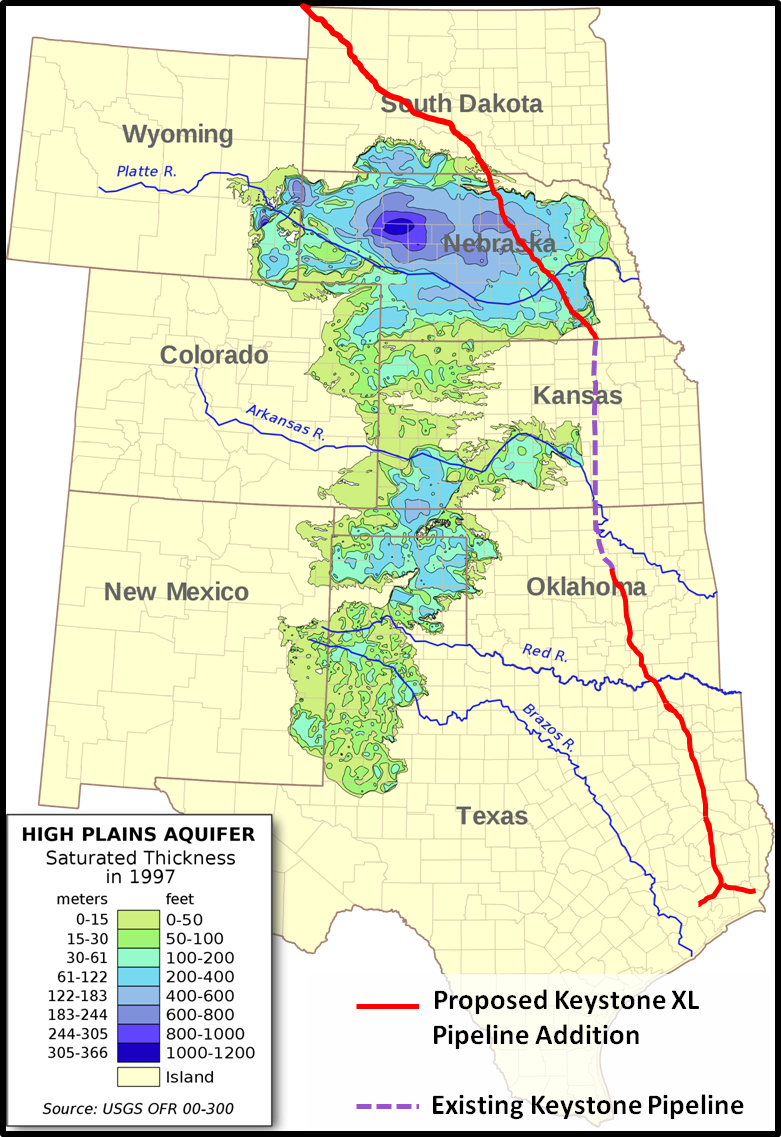 In 2008,
In 2008,
"Report: Sand Hills route best".
Omaha World-Herald.
' 2011-08-27. Retrieved 2011-08-27. Pipeline industry spokesmen have noted that thousands of miles of existing pipelines carrying crude oil and refined liquid hydrocarbons have crossed over the Ogallala Aquifer for years, in southeast Wyoming, eastern Colorado and New Mexico, western Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. The Pioneer crude oil pipeline crosses east-west across Nebraska, and the Pony Express pipeline, which crosses the Ogallala Aquifer in Colorado, Nebraska, and Kansas, was being converted as of 2013 from natural gas to crude oil, under a permit from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. As the lead agency in the transboundary pipeline project, the U.S. State Department commissioned an environmental-impact assessment as required by the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969. The ''Environmental Impact Statement'' concluded that the project posed little threat of "adverse environmental impacts", the report was drafted by Cardno Entrix, a company that assisted both the Department of State and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission in preparing environmental impact statements for other proposed TransCanada projects. Although it is "common for companies applying to build government projects to be involved in assigning and paying for the impact analysis", several opponents of the project suggested there could be a conflict of interest. In response to that concern, the Department of State's Office of the Inspector General conducted an investigation of the potential conflict of interest. The February 2012 report of that investigation states no conflict of interest existed either in the selection of the contractor or in the preparation of the environmental impact statement. U.S. President Barack Obama "initially rejected the Keystone XL pipeline in January 2012, saying he wanted more time for an environmental review." On February 17, 2013, a rally at the National Mall drew an estimated 40,000 in protest of Keystone XL. In January 2014, the U.S. State Department released its Keystone pipeline ''Final Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement for the Keystone XL Project Executive Summary'', which concluded that, according to models, a large crude oil spill from the pipeline that reached the Ogallala could spread as far as , with dissolved components spreading as much as further. Early in his presidency, U.S President Donald Trump overturned U.S. President Barack Obama's decision by signing executive memos in support of the Keystone XL pipeline in January 2017. On January 20, 2021, President Joe Biden signed an
"The Ogallala Aquifer"
Manjula V. Guru, Agricultural Policy Specialist and James E. Horne, President & CEO, The Kerr Center for Sustainable Agriculture, Poteau, Oklahoma
USGS High Plains Regional Groundwater StudyA Legal Fight in Texas over the Ogallala AquiferKansas Geological Survey information on the High Plains / Ogallala AquiferRapid Recharge of Parts of the High Plains Aquifer Indicated by a Reconnaissance Study in Oklahoma
{{Coord, 36, 59, 26, N, 101, 26, 52, W, region:US_type:waterbody, display=title Aquifers in the United States Great Plains Regions of the Western United States Geology of Oklahoma Geology of South Dakota Geology of Nebraska Geology of Kansas Geology of Wyoming Geology of Texas Geology of Colorado Geology of New Mexico
water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteris ...
surrounded by sand, silt, clay, and gravel located beneath the Great Plains in the United States. One of the world's largest aquifers, it underlies an area of approximately in portions of eight states (South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
, Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the sout ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the s ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, Oklahoma, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
). It was named in 1898 by geologist N. H. Darton from its type locality near the town of Ogallala, Nebraska
Ogallala is a city in and the county seat of Keith County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 4,737 at the 2010 census. In the days of the Nebraska Territory, the city was a stop on the Pony Express and later along the transcontinental ...
. The aquifer is part of the High Plains Aquifer System, and resides in the Ogallala Formation, which is the principal geologic unit underlying 80% of the High Plains.
Large-scale extraction for agricultural purposes started after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
due partially to center pivot irrigation
Center-pivot irrigation (sometimes called central pivot irrigation), also called water-wheel and circle irrigation, is a method of crop irrigation in which equipment rotates around a pivot and crops are watered with sprinklers. A circular area ...
and to the adaptation of automotive engines for groundwater wells. Today about 27% of the irrigated land in the entire United States lies over the aquifer, which yields about 30% of the ground water used for irrigation in the United States. The aquifer is at risk of over-extraction and pollution. Since 1950, agricultural irrigation has reduced the saturated volume of the aquifer by an estimated 9%. Once depleted, the aquifer will take over 6,000 years to replenish naturally through rainfall.
The aquifer system supplies drinking water to 82% of the 2.3 million people (1990 census) who live within the boundaries of the High Plains study area.
General characteristics
The deposition of aquifer material dates back two to six million years, from the lateMiocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
to early Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
were still tectonically active. From the uplands to the west, rivers and streams cut channels in a generally west to east or southeast direction. Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
of the Rockies provided alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. All ...
and aeolian sediment that filled the ancient channels and eventually covered the entire area of the present-day aquifer, forming the water-bearing Ogallala Formation. In that respect, the process is similar to those currently prevailing in other modern rivers of the area, such as the Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
and its tributaries. The major differences are time and depth.
The depth of the Ogallala varies with the shape of then-prevailing surface, being deepest where it fills ancient valleys and channels. The Ogallala Formation consists mostly of coarse sedimentary rocks in its deeper sections, which transition upward into finer-grained material.
The water-saturated thickness of the Ogallala Formation ranges from a few feet to more than 1,000 feet. Its deepest part is 1200 ft. (300 m) and is generally greater in the Northern Plains. The depth of the water below the surface of the land ranges from almost in parts of the north to between throughout much of the south. Present-day recharge of the aquifer with fresh water occurs at an exceedingly slow rate, suggesting that much of the water in its pore
Pore may refer to:
Biology Animal biology and microbiology
* Sweat pore, an anatomical structure of the skin of humans (and other mammals) used for secretion of sweat
* Hair follicle, an anatomical structure of the skin of humans (and other m ...
spaces is paleowater, dating back to the most recent ice age and probably earlier.
Groundwater within the Ogallala generally flows from west to east at an average rate of a foot per day. Hydraulic conductivity, or the ability for a fluid (water) to move through porous material, ranges from per day. Water quality within the Ogallala varies with the highest quality for drinking and irrigation in the northern region while the southern region had the poorest.Gurdak, J. J, McMahon, P. B, Dennehy, K, Qi, S. L. (2009). "Water quality in the High Plains Aquifer, Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas, and Wyoming". ''National Water-Quality Assessment Program, USGS Circular 1337''. Retrieved from http://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/1337/pdf/C1337.pdf Human and natural processes over the past 60 to 70 years, including irrigation density, climate, and nitrogen applications, have caused higher concentrations of contaminants including nitrates. Nitrate levels generally meet USGS water quality standards, but continue to gradually increase over time. This trend can impact the future groundwater sustainability for portions of the aquifer.
Aquifer water balance
An aquifer is a groundwater storage reservoir in thewater cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
. While groundwater is a renewable source, reserves replenish relatively slowly. The USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, a ...
has performed several studies of the aquifer, to determine what is coming in (groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs ...
from the surface), what is leaving (water pumped out and baseflow
Baseflow (also called drought flow, groundwater recession flow, low flow, low-water flow, low-water discharge and sustained or fair-weather runoff) is the portion of the streamflow that is sustained between precipitation events, fed to streams by d ...
to streams), and what the net changes in storage are (rise, fall or no change).
The USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, a ...
estimated that total water storage was about in 2005. Withdrawals from the Ogallala Aquifer for irrigation amounted to in 2000. Since major groundwater pumping began in the late 1940s, overdraft from the High Plains Aquifer has amounted to , 85% of the volume of Lake Erie. Many farmers in the Texas High Plains, which rely particularly on groundwater, are now turning away from irrigated agriculture as pumping costs have risen and as they have become aware of the hazards of overpumping.
Groundwater recharge
The rate at which groundwater is recharged is limited by several factors. Much of the plains region issemiarid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
, with steady winds that hasten evaporation of surface water and precipitation. In many locations, the aquifer is overlain, in the vadose zone
The vadose zone, also termed the unsaturated zone, is the part of Earth between the land surface and the top of the phreatic zone, the position at which the groundwater (the water in the soil's pores) is at atmospheric pressure ("vadose" is f ...
, with a shallow layer of caliche
Caliche () is a sedimentary rock, a hardened natural cement of calcium carbonate that binds other materials—such as gravel, sand, clay, and silt. It occurs worldwide, in aridisol and mollisol soil orders—generally in arid or semiarid regions ...
that is practically impermeable; this limits the amount of water able to recharge the aquifer from the land surface. However, the soil of the playa lakes is different and not lined with caliche, making these some of the few areas where the aquifer can recharge. The destruction of playas by farmers and development decreases the available recharge area. The prevalence of the caliche is partly due to the ready evaporation of soil moisture and the semiarid climate; the aridity increases the amount of evaporation, which in turn increases the amount of caliche in the soil. Both mechanisms reduce the amount of recharge water that reaches the water table.
Recharge in the aquifer ranges from per year in parts of Texas and New Mexico to per year in south-central Kansas.
Groundwater discharge
 The regions overlying the Ogallala Aquifer are some of the most productive regions in the United States for ranching
The regions overlying the Ogallala Aquifer are some of the most productive regions in the United States for ranching livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animal ...
, and growing corn, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, and soybeans. The success of large-scale farming in areas that do not have adequate precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
and do not always have perennial surface water for diversion has depended heavily on pumping groundwater for irrigation.
Early settlers of the semiarid High Plains were plagued by crop failures due to cycles of drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
, culminating in the disastrous Dust Bowl
The Dust Bowl was a period of severe dust storms that greatly damaged the ecology and agriculture of the American and Canadian prairies during the 1930s. The phenomenon was caused by a combination of both natural factors (severe drought) a ...
of the 1930s. Only after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, when center pivot irrigation became available, was the land mass of the High Plains aquifer system transformed into one of the most agriculturally productive regions in the world.
Change in groundwater storage
Ground water levels decline when the rate of extraction by irrigation exceeds the rate of recharge. At places, the water table was measured to drop more than 5 ft (1.5 m) per year at the time of maximum extraction. In extreme cases, the deepening of wells was required to reach the steadily falling water table. In the 21st century, recognition of the significance of the aquifer has led to increased coverage from regional and international journalists. Water conservation practices ( terracing andcrop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. It reduces reliance on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, and the probability of developing resistant ...
), more efficient irrigation methods (center pivot and drip), and reduced area under irrigation have helped to slow depletion of the aquifer, but levels are generally still dropping in areas including southwestern Kansas and the Texas Panhandle
The Texas Panhandle is a region of the U.S. state of Texas consisting of the northernmost 26 counties in the state. The panhandle is a square-shaped area bordered by New Mexico to the west and Oklahoma to the north and east. It is adjacent to ...
. In other areas, such as parts of eastern and central Nebraska and of the region south of Lubbock, Texas, water levels have risen since 1980.
The center-pivot irrigator was described as the "villain" in a 2013 ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' article, "Wells Dry, Fertile Plains Turn to Dust" recounting the relentless decline of parts of the Ogallala Aquifer. Sixty years of intensive farming
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ...
using huge center-pivot irrigators has emptied parts of the High Plains Aquifer. Hundreds to thousands of years of rainfall would be needed to replace the groundwater in the depleted aquifer. In Kansas in 1950, irrigated cropland covered ; with the use of center-pivot irrigation, nearly three million acres of land were irrigated. In some places in the Texas Panhandle, the water table has been drained (dewatered). "Vast stretches of Texas farmland lying over the aquifer no longer support irrigation. In west-central Kansas, up to a fifth of the irrigated farmland along a of the aquifer has already gone dry."
The center-pivot irrigation system is considered to be a highly efficient system which helps conserve water. However, by 2013, as the water consumption efficiency of the center-pivot irrigator improved over the years, farmers chose to plant more intensively, irrigate more land, and grow thirstier crops rather than reduce water consumption--an example of the Jevons Paradox
In economics, the Jevons paradox (; sometimes Jevons effect) occurs when technological progress or government policy increases the efficiency with which a resource is used (reducing the amount necessary for any one use), but the falling cost of ...
in practice. One approach to reducing the amount of groundwater used is to employ treated recycled water for irrigation; another approach is to change to crops that require less water, such as sunflowers.
Several rivers, such as the Platte, run below the water level of the aquifer. Because of this, the rivers receive groundwater flow (baseflow), carrying it out of the region rather than recharging the aquifer.
The $46.1-million Optima Lake
Optima Lake was built to be a reservoir in Texas County, Oklahoma. The site is just north of Hardesty and east of Guymon in the Oklahoma Panhandle.
The earthen Optima Lake Dam (National ID # OK20510) was completed in by the United States Arm ...
dam in western Oklahoma was rendered useless when the dropping level of the aquifer drastically reduced flow of the Beaver River, the lake's intended source of water.
Accelerated decline in aquifer storage
The depletion between 2001 and 2008, inclusive, is about 32% of the cumulative depletion during the entire 20th century. In the United States, the biggest users of water from aquifers include agricultural irrigation and oil and coal extraction. "Cumulative total groundwater depletion in the United States accelerated in the late 1940s and continued at an almost steady linear rate through the end of the century. In addition to widely recognized environmental consequences, groundwater depletion also adversely impacts the long-term sustainability of groundwater supplies to help meet the nation’s water needs." Since the 1940s, pumping from the Ogallala has drawn the aquifer down by more than in some areas. Producers have taken steps to reduce their reliance on irrigated water. Streamlined operations allow them to produce significantly greater yield using roughly the same amount of water needed four decades ago. Still, losses to the aquifer between 2001 and 2011 equated to a third of its cumulative depletion during the entire 20th century. The Ogallala is recharged primarily by rainwater, but only about one inch of precipitation actually reaches the aquifer annually. Rainfall in most of the Texas High Plains is minimal, evaporation is high, and infiltration rates are slow.Texas Water Report: Going Deeper for the SolutionTexas Comptroller of Public Accounts. Retrieved 2/10/14. During the 1990s, the aquifer held some three billion acre-feet of groundwater used for crop irrigation as well as drinking water in urban areas. The demand for the water outstrips its replenishment. The water level is particularly on the decline in Texas and New Mexico. Continued long-term use of the aquifer is "troublesome and in need of major reevaluation," according to the
historian
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the st ...
Paul H. Carlson, professor-emeritus from Texas Tech University
Texas Tech University (Texas Tech, Tech, or TTU) is a public research university in Lubbock, Texas. Established on , and called Texas Technological College until 1969, it is the main institution of the five-institution Texas Tech University Sy ...
in Lubbock
Lubbock ( )
is the 10th-most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and the seat of government of Lubbock County. With a population of 260,993 in 2021, the city is also the 85th-most populous in the United States. The city is in the northw ...
. It was reported in 2020 that the aquifer would be "dry" within twenty years.
Environmental controversies
Proposed Keystone XL Pipeline
 In 2008,
In 2008, TransCanada Corporation
TC Energy Corporation (formerly TransCanada Corporation) is a major North American energy company, based in the TC Energy Tower building in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, that develops and operates energy infrastructure in Canada, the United States, ...
proposed the construction of the Keystone XL pipeline to carry oil from the Athabasca oil sands of Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
to refineries near Houston, Texas.
The proposed route of the pipeline crosses the eastern part of the Nebraska Sandhills; opponents of the route cite the risk to the Ogallala Aquifer posed by the possibility of contamination from spilled dilute bitumen.Morton, Joseph, and Paul Hammel"Report: Sand Hills route best".
Omaha World-Herald.
' 2011-08-27. Retrieved 2011-08-27. Pipeline industry spokesmen have noted that thousands of miles of existing pipelines carrying crude oil and refined liquid hydrocarbons have crossed over the Ogallala Aquifer for years, in southeast Wyoming, eastern Colorado and New Mexico, western Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. The Pioneer crude oil pipeline crosses east-west across Nebraska, and the Pony Express pipeline, which crosses the Ogallala Aquifer in Colorado, Nebraska, and Kansas, was being converted as of 2013 from natural gas to crude oil, under a permit from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. As the lead agency in the transboundary pipeline project, the U.S. State Department commissioned an environmental-impact assessment as required by the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969. The ''Environmental Impact Statement'' concluded that the project posed little threat of "adverse environmental impacts", the report was drafted by Cardno Entrix, a company that assisted both the Department of State and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission in preparing environmental impact statements for other proposed TransCanada projects. Although it is "common for companies applying to build government projects to be involved in assigning and paying for the impact analysis", several opponents of the project suggested there could be a conflict of interest. In response to that concern, the Department of State's Office of the Inspector General conducted an investigation of the potential conflict of interest. The February 2012 report of that investigation states no conflict of interest existed either in the selection of the contractor or in the preparation of the environmental impact statement. U.S. President Barack Obama "initially rejected the Keystone XL pipeline in January 2012, saying he wanted more time for an environmental review." On February 17, 2013, a rally at the National Mall drew an estimated 40,000 in protest of Keystone XL. In January 2014, the U.S. State Department released its Keystone pipeline ''Final Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement for the Keystone XL Project Executive Summary'', which concluded that, according to models, a large crude oil spill from the pipeline that reached the Ogallala could spread as far as , with dissolved components spreading as much as further. Early in his presidency, U.S President Donald Trump overturned U.S. President Barack Obama's decision by signing executive memos in support of the Keystone XL pipeline in January 2017. On January 20, 2021, President Joe Biden signed an
executive order
In the United States, an executive order is a directive by the president of the United States that manages operations of the federal government. The legal or constitutional basis for executive orders has multiple sources. Article Two of t ...
to revoke the permit that was granted to TC Energy Corporation for the Keystone XL Pipeline (Phase 4). On June 9, 2021, TC Energy abandoned plans for the Keystone XL Pipeline.
Conservation
Since 2010, the North Plains Groundwater Conservation District, which encompasses eight counties north ofAmarillo
Amarillo ( ; Spanish for " yellow") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the seat of Potter County. It is the 14th-most populous city in Texas and the largest city in the Texas Panhandle. A portion of the city extends into Randall Cou ...
, including Moore and Dallam Counties, has offered a $300,000 annual demonstration project to conserve water that farmers pump from the Ogallala Aquifer. Participating farmers grow corn with just over half of the water that they would normally require to irrigate the fields, or they plant several weeks later than customary. Pivot sprinklers are used in the project, rather than the more expensive drip irrigation. According to district manager Steve Walthour, conservation is essential considering declining levels of the aquifer. The local non-profit organization Ogallala Commons, named for the aquifer itself, which not only collaborates and supports the local communicates, also works to conserve the Ogallala Aquifer and the surrounding area.
Eleven farmers in 2013 participated in the conservation program, with some planting in dry earth, rather than watered soil. They are leaving more space between plants, a technique that retains moisture for a longer period of time. Soil sensors permit farmers to gather accurate information about the moisture level of their crops. The motivation to save water comes from the district's regulations on extracting water from the aquifer. The United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
determined the water level in the aquifer has dropped more in Texas than in any other state in the basin.
Farmers on their own land may draw water from the aquifer without charge. Pumping costs are low because the fuel used, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, is inexpensive. The North Plains district first established limits on pumping in 2005 and tightened the regulations four years later. Certain wells are now required to have meters. Yet another challenge facing the district is that higher prices for crops have prompted some to plant additional fields and further increase the use of water from the aquifer.
See also
*Aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteris ...
* Environmental science
*Fossil water
Fossil water or paleowater is an ancient body of water that has been contained in some undisturbed space, typically groundwater in an aquifer, for millennia. Other types of fossil water can include subglacial lakes, such as Antarctica's Lake Vos ...
*Great Recycling and Northern Development Canal
The Great Recycling and Northern Development (GRAND) Canal of North America or GCNA is a water management proposal designed by Newfoundland engineer Thomas Kierans to alleviate North American freshwater shortage problems. It proposed damming J ...
*Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
* Guarani Aquifer
*Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (''hydro-'' meaning water, and ''-geology'' meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust (commonly in aqui ...
*Irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
*Laurentide Ice Sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million year ...
* Llano Estacado
*Water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
*Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea ...
, the salt-water strait that once covered the area of today's Ogalalla Aquifer.
References
External links
"The Ogallala Aquifer"
Manjula V. Guru, Agricultural Policy Specialist and James E. Horne, President & CEO, The Kerr Center for Sustainable Agriculture, Poteau, Oklahoma
USGS High Plains Regional Groundwater Study
{{Coord, 36, 59, 26, N, 101, 26, 52, W, region:US_type:waterbody, display=title Aquifers in the United States Great Plains Regions of the Western United States Geology of Oklahoma Geology of South Dakota Geology of Nebraska Geology of Kansas Geology of Wyoming Geology of Texas Geology of Colorado Geology of New Mexico