Michael IX Palaiologos on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, image = 154 - Michael IX Palaiologos (Mutinensis - color).png
, caption = 15th-century portrait of Michael IX (from a 15th-century codex containing a copy of the ''Extracts of History'' by
12 October 1320 , coronation = 21 May 1294,
Andronikos III ( in Macedonia) , spouse = , issue = , dynasty = Palaiologos , father =
(now
 During 1303–1304
During 1303–1304
 In 1288 Michael IX was betrothed with Catherine of Courtenay, titular
In 1288 Michael IX was betrothed with Catherine of Courtenay, titular
Joannes Zonaras
Joannes or John Zonaras ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης Ζωναρᾶς ; 1070 – 1140) was a Byzantine Greek historian, chronicler and theologian who lived in Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, Turkey). Under Emperor Alexios I Komnenos he hel ...
)
, succession = Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
, reign = 21 May 1294 –12 October 1320 , coronation = 21 May 1294,
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
, regent = Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg
, caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia''
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 11 December 1282 –24 May 1328
, coronation = 8 Novemb ...
, reg-type = Co-emperor
, predecessor = Andronikos II (alone)
, successor = Andronikos II (alone),Andronikos III ( in Macedonia) , spouse = , issue = , dynasty = Palaiologos , father =
Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg
, caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia''
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 11 December 1282 –24 May 1328
, coronation = 8 Novemb ...
, mother = Anna of Hungary
, birth_date = 17 April 1277
, birth_place = Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
(now
Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
)
, death_date =
, death_place = Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, place of burial =
, , title=Emperor and Autocrat of the Romans
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
Michael IX Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Μιχαήλ Δούκας Ἄγγελος Κομνηνός Παλαιολόγος, ''Mikhaēl Doukas Angelos Komnēnos Palaiologos''; 17 April 1277 – 12 October 1320), was Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
together with his father Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg
, caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia''
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 11 December 1282 –24 May 1328
, coronation = 8 Novemb ...
from 1294 until his death. Andronikos II and Michael IX ruled as equal co-rulers, both using the title ''autokrator
''Autokrator'' or ''Autocrator'' ( grc-gre, αὐτοκράτωρ, autokrátōr, , self-ruler," "one who rules by himself," whence English "autocrat, from grc, αὐτός, autós, self, label=none + grc, κράτος, krátos, dominion, power ...
''.
A man of impeccable morals and a good helper to his father, he was also known as a brave and energetic soldier, willing to make personal sacrifices to pay or encourage his troops; the Catalan military chronicler Ramon Muntaner said about him: "''Emperor Michael was one of the bravest knights in the world''". Despite his military prestige, he suffered several defeats, for unclear reasons: his inability as a commander, the deplorable state of the Byzantine army or just simply bad luck.
The only Palaiologan emperor to predecease his father, his premature death at age 43 was attributed in part to grief over the accidental murder of his younger son Manuel Palaiologos by retainers of his older son and later co-emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos_III_Palaiologos.jpg
, caption = 14th-century miniature.Stuttgart, Württembergische Landesbibliothek.
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 24 May 1328 – 15 June 1341
, coronation = ...
.
In the memory of the Byzantines, Michael IX remained "''the most pious lord''" and "''a true emperor in name and deeds''".
Birth and early years
Michael IX was the eldest son of theByzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg
, caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia''
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 11 December 1282 –24 May 1328
, coronation = 8 Novemb ...
and his first wife Anna
Anna may refer to:
People Surname and given name
* Anna (name)
Mononym
* Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke
* Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773)
* Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century)
* Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 1221) ...
, daughter of King Stephen V of Hungary
Stephen V ( hu, V. István, hr, Stjepan V., sk, Štefan V; before 18 October 1239 – 6 August 1272, Csepel Island) was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1270 and 1272, and Duke of Styria from 1258 to 1260. He was the oldest son of ...
. He was born at noon on Easter Sunday
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the ''Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel P ...
(17 April) of 1277, which was recognized by the people as a miracle.''Georges Pachymérès relations historiques'', p. 99. The Emperor doted on his firstborn son, which became a great consolation for him after the untimely death of his beloved wife Anna in 1281. Michael IX had only one younger full-brother, Constantine, who was born sometime between 1278 and 1281.Nicephorus Gregoras, ''Byzantine History'', Book 6.2.
Andronikos II declared Michael IX an emperor shortly before the death of Michael VIII in 1282, and after his son became an adult, he confirmed his authority. On 21 May 1294 at Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
, Michael IX was crowned by Patriarch John XII of Constantinople. In subsequent years, Andronikos II entrusted his son with the conduct of wars against internal and external enemies.
Military activity
Clash at Magnesia (1302)
In early spring of 1302, Michael IX made his first campaign against theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, which he was very proud of in advance, for he had long wanted (as the historian George Pachymeres reports) to get a chance to prove himself in battle. Under his command, up to 16,000 soldiers were collected, 10,000 of whom were a detachment of mercenary Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
;Nicephorus Gregoras, ''Byzantine History'', Book 6.10. the latter, however, performed their duty badly and plundered both the Turkish population and the Greek with equal zeal. Michael IX camped at the fortress of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
(modern day Manisa
Manisa (), historically known as Magnesia, is a city in Turkey's Aegean Region and the administrative seat of Manisa Province.
Modern Manisa is a booming center of industry and services, advantaged by its closeness to the international port ci ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
), not far from Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prom ...
, where in ancient times a great battle between the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
and the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
had taken place. Seeing the low morale of his people, Michael IX didn't dare to start the battle first, since the Turks managed to take all advantageous positions —the peaks of the surrounding mountains and shelters in the forests— and at the very first collision he would have easily repulsed the onslaught of Greek militia and light Alanian cavalry. Another reason why the young emperor gave his enemies the opportunity to attack first was the problems in his own army. Wayward mercenaries didn't want to carry out his orders, and, according to Nicephorus Gregoras
Meanwhile, the Turks chose the moment and descended from the mountains. Michael IX ordered to prepare for battle, but no one listened to him — the timid soldiers didn't want to start the battle and thought only about flight, as was recalled by Nicephorus Gregoras:
After defeat and a short stay in the fortress of Magnesia, Michael IX retreated to Pergamum and then went to Adramyttium, where he met the New Year
New Year is the time or day currently at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count increments by one. Many cultures celebrate the event in some manner. In the Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system ...
of 1303, and by the summer he was in the city of Cyzicus
Cyzicus (; grc, Κύζικος ''Kúzikos''; ota, آیدینجق, ''Aydıncıḳ'') was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peni ...
.''Georges Pachymérès relations historiques'', p. 427. He still didn't give up his attempts to gather a new army to replace the disintegrated old one and to improve the situation. But by that time the Turks had already seized the area along the lower reaches of the (Sangarius) Sakarya River and defeated another Greek army in the town of Bapheus, near Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
(27 July 1302). It was becoming clear to everyone that the Byzantines had lost the war. To top it all off, Michael IX fell seriously ill; having reached the Pegai fortress, he could not continue and went to bed. Many felt that his days were numbered; dying, he sadly watched as the conquerors divided the Byzantine lands that they had captured to the very coast of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi ( Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
. A year later, the Turkish commander Aydin captured the city of Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
(24 October 1304) and, briefly, the island of Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
.
Michael IX was ill during the last months of 1303. His health recovered only by January 1304, so that he was finally able to leave the fortress and return to Constantinople with his wife Rita, who, after learning about his illness, hurried to Pegai and was devotedly at the side of her husband during all his illness.
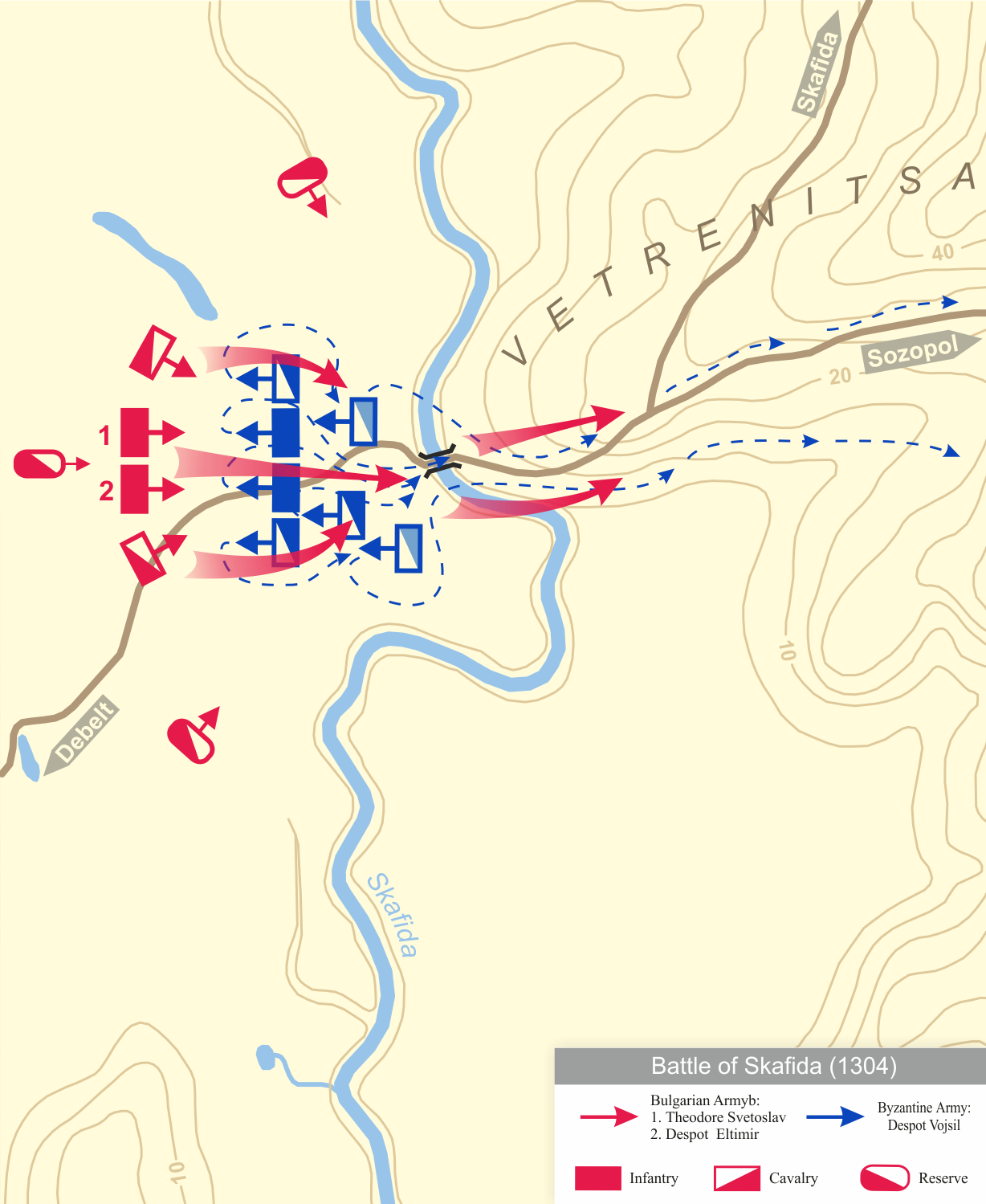
Battle of Skafida (1304)
 During 1303–1304
During 1303–1304 Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
Theodore Svetoslav of Bulgaria invaded Eastern Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
. Michael IX at this time was engaged in a war with the rebellious Catalan Company
The Catalan Company or the Great Catalan Company (Spanish: ''Compañía Catalana'', Catalan: ''Gran Companyia Catalana'', Latin: ''Exercitus francorum'', ''Societas exercitus catalanorum'', ''Societas cathalanorum'', ''Magna Societas Catalanorum' ...
(see below), whose leader, Roger de Flor, refused to fight the Bulgarians if Michael IX and his father didn't pay him the agreed sum of money. In order to prevent the unification of the Catalans and Bulgarians, Michael IX had to oppose the latter, sharing authority over the army with the experienced commander Michael Glaber, who, however, fell seriously ill by the decisive battle and was removed from military affairs. By that time, the Bulgarians had already managed to conquer the fortresses of Kopsis, Kryn, Meglij, Vereya, Diavena, Ichera, Mokren, Sliven
Sliven ( bg, Сливен ) is the eighth-largest city in Bulgaria and the administrative and industrial centre of Sliven Province and municipality in Northern Thrace.
Sliven is famous for its heroic Haiduts who fought against the Ottoman Turk ...
, Sotir, Pyrgitsion, Diampol, Ktenia, Debelt
Debelt ( Bulgarian: Дебелт) is a village in Burgas Province in southeastern Bulgaria. It is located in the municipality of Sredets.
History
Debelt is located near the ruins of the city of Develtos. During the Russo-Turkish War of 1828-1829 ...
, Rusokastro, Lardea
Lardea or Lardeya ( bg, Лардея, gr, Λαρδέα) is a ruined late Roman and medieval fortress, situated near the village of Lozenets in Straldzha Municipality, Yambol Province, south-eastern Bulgaria. In the Middle Ages, Lardea often chan ...
, Markeli, Aytos, Mesembria
Mesembria ( grc, Μεσημβρία; grc-x-doric, Μεσαμβρία, Mesambria) was an important Greek city in ancient Thrace
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who in ...
, Anchialos, Pyrgos, Apolonia and Ahtopol, all along the southern Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coast. However, subsequent events were initially favorable for the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
.
Michael IX defeated the enemies in several skirmishes, after which many fortresses captured by the Bulgarians surrendered to him without a fight. His successes made an impression in Constantinople, where Patriarch Athanasius I Athanasius I may refer to:
*Athanasius of Alexandria
Athanasius I of Alexandria, ; cop, ⲡⲓⲁⲅⲓⲟⲥ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲡⲓⲁⲡⲟⲥⲧⲟⲗⲓⲕⲟⲥ or Ⲡⲁⲡⲁ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲁ̅; (c. 296� ...
, during a sermon, said a word of praise about Michael IX and his victories. There is also a panegyric in which an unknown poet extols the victories of the Byzantine army at that time.
In early autumn 1304 the Byzantines counter-attacked and the two armies met near Skafida river. At the beginning of the battle, Michael IX, who fought bravely in the forefront, had an advantage over the enemy. He forced the Bulgarians to retreat along the road to Apolonia, but he was unable to keep his own soldiers heated up in pursuit. Between the Byzantines and the fleeing Bulgarians, there was the deep and very turbulent Skafida river, with the only bridge across which was damaged by the Bulgarians before the battle. When the Byzantine soldiers in a large crowd tried to cross the bridge, it collapsed. Many of the soldiers drowned, the rest began to panic. At that moment, the Bulgarians returned to the bridge and decided the outcome of the battle, snatching victory from the enemies.
Several hundred Byzantines were captured. To ransom the captives and recruit a new army, Emperor Andronikos II and his son were forced to sell their own jewelry. With varying degrees of success, hostilities continued for several more years until 1307, when a peace that was clearly unfavorable for the Byzantine Empire was concluded, which remained for the next 15 years; as part of the agreement, Michael IX had to give his daughter Theodora in marriage to the Bulgarian Tsar Theodore Svetoslav, his successful enemy.
Battle of Apros (1305)
In the spring of 1305 Michael IX, on his father's instructions, conducted negotiations inAdrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis ( Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian border ...
with the rebellious Catalan condottieri
''Condottieri'' (; singular ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian captains in command of mercenary companies during the Middle Ages and of multinational armies during the early modern period. They notably served popes and other Europ ...
Roger de Flor. According to Nicephorus Gregoras, Roger tried to play a dishonest game: he plundered Greek settlements, made sure that he was given ownership of all of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
with the islands and incomes with the right to distribute fiefs to his vassals and maintain a personal army, and demanded from the Byzantine emperors a salary for his soldiers in the amount of 100,000 gold and extorted another 300,000. (For comparison: during the " War of the Two Andronikos" Andronikos the Younger needed only 45,000 gold to maintain his army):
According to other sources, the Catalan condottieri was insidiously killed in a palace in Adrianople during a night drinking with the Byzantine commanders by an Alan teenager named Hyrkon, whose father had been killed by Roger de Flor a few weeks earlier. Ramon Muntaner, unlike Nicephorus Gregoras, speaks only of the three Catalans who survived and names them by name, adding that before the massacre, Michael IX envied Roger de Flor because of his impressive victories over the Turks. It's also known that Michael IX and Roger de Flor were in conflict with each other: so, back in 1303, de Flor with his people arrived in Pegai, where the sick Michael IX was, but he ordered not to let the Catalans into the fortress and refused to accept their leader. It is unclear, however, whether Michael IX was guilty of the murder, or whether everything happened spontaneously and without preparation. In favor of the latter, was the fact that the Catalans and Byzantines drank almost the entire week before the fatal incident happened (30 April 1305). However, for the several thousand angry Catalans who remained in Gallipoli, the details of the massacre didn't matter. Their new leaders, the "megadux" Berenguer VI de Entenza and the brave warrior Bernat de Rocafort, like monarchs of an independent power, sent a proud embassy to Constantinople declaring war, as demanded by knightly etiquette. Andronikos II, who did not want war, had to make excuses before two seekers of glory and asking him to believe that de Flor was not killed by his order. But his opponents didn't want to listen to anything. 5,000 Catalans, angry with the Byzantines, united with a Turkish detachment of 500 warriors, fortified in Gallipoli, instantly cutting off all the Greek townspeople, and began to raid Thrace, plundering it day and night. Rocafort took the fortresses of Rodosto and Panido: their population was killed or sold into slavery. Other leaders of the mercenaries settled in Gallipoli — Ramon Muntaner, the future historiographer of the "great campaign", and Fernando Jimenez, who later went over with his detachment to the Byzantines. Since their insolence at that time seemed completely unbearable, Michael IX, taking all the Thracian and Macedonian regiments, the Alan auxiliary cavalry and also adding to them about 1,000 Turcopoles (baptized Turks), led by their commander Melekh, approached the Apros fortress (ancient Theodosiopolis), the plain east of which was occupied by the enemy. In total, under his leadership, about 14,000 soldiers were collected (according to other sources 40,000) against 5 or 6,000 Catalans and several hundred Turks:
But as soon as the signal for battle was given, the Catalans rushed into battle with the cry "''Aragon! Aragon! Saint George
Saint George ( Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
!''", as the memorable defeat at Magnesia was repeated. The Turcopoles and Alans suddenly left the battlefield. Such a surprise took all the courage from the Byzantines. Michael IX, seeing that the ranks of his soldiers were mingled, with tears turned to them, begging them to stand firm. But they didn't listen to him at all and rushed to run without looking back. Only about a hundred knights remained with the emperor. Most of the infantry was badly battered by the Catalans, who rushed to pursue the Byzantines.
In the middle of such desperate situation, Michael IX carried himself with great courage:
Michael IX retreated to Didymoteicho, where he met Andronikos II, who gave his son a long and severe reprimand, since he unnecessarily exposed himself to mortal risk. At the same time, the co-Emperor became the object of brutal attacks from his stepmother the Empress Irene
Irene is a name derived from εἰρήνη (eirēnē), the Greek for "peace".
Irene, and related names, may refer to:
* Irene (given name)
Places
* Irene, Gauteng, South Africa
* Irene, South Dakota, United States
* Irene, Texas, United State ...
(born Yolanda of Montferrato), who hated him, since he was the heir in detriment of her sons. As for the victorious Catalans, for the next two years they freely plundered Thrace, then devastated Macedonia and, finally, left to seek glory in Greece.
The state of affairs in Asia, where the Turks managed to cut the line of communication between Nicomedia and Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
(1307), was not the best either.
Turkish fortress (1314)
After the Catalans left in 1314Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, in turn, began to be devastated by the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
. At one time, they accompanied the Catalans, who ravaged Macedonia and Central Greece with fire and sword, and now with their share of the booty were returning home. The Turks asked permission to pass through the Byzantine regions, which they were allowed, but Andronikos II, amazed by the amount of booty and the small number of Turks, decided, without stopping to talk about friendship and alliance, to suddenly hit them and take away all the booty. The plan failed due to the negligence of the Byzantine generals, who acted too slowly and openly. The Turks, once were revealed the intentions of the Byzantines, without hesitation, attacked the nearest fortress, fortified it and, having received help from Asia, began to plunder the country.Nicephorus Gregoras, ''Byzantine History'', Book 7.8.
Michael IX had to gather an army (they collected everyone they could, including ordinary peasants who made up most of the Byzantine army) and lay siege to the fortress. The Byzantines were confident of their success, since they far outnumbered their enemies: the Turks were only 1,300 cavalry and 800 infantry, but as soon as the Turkish horsemen appeared, led by their chief named Halil, the peasants suddenly fled. Then, little by little, the rest of the Byzantine soldiers began to scatter. When Michael IX tried to put the army in order, there was absolutely no one who could listen to him. In despair, he himself, in tears, took to flight, trembling with impotent rage and thinking that ''all this was God's clear punishment for old and new sins''. The adversaries captured many Byzantine nobles, the imperial treasury, crown (the so-called ''calipra'') and tent; sneering at the defeated Emperor, the Turkish chief Halil placed the crown of the Byzantine Basileus on his own head.
The young talented military leader Philes Palaeologus saved the situation, asking the Emperors for permission to independently recruit troops and commanders to fight the Turks. Having selected a small detachment of the most combat-ready and brave, Philes, a warrior weak in body but strong in spirit, near the river Xirogypsus successfully destroyed 1,200 Ottomans who were returning to the fortress with booty and Greek captives, and after the arrival of reinforcements from the Genoese allied to Constantinople with small losses forced the fortress to surrender.
Michael IX as unsuccessful commander
Alanian, Turkish, Catalan, Serbian mercenary detachments and at times simple peasant militias were the only warriors at the head of which Michael IX had to repulse the enemy. The fact is that the military organization of theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
by that time was actually destroyed after the initiatives carried out by Andronikos II.
Andronikos II, a purely civilian man, considered it unreasonably expensive (taking into account the impoverishment of the treasury) and inexpedient (taking into account the greatly reduced empire within the borders) the maintenance of a regular national army. In theory, her role could be handled by a professional detachment of mercenaries, which (again in theory) was much cheaper to maintain. Andronikos II and his advisers didn't confine themselves to mere arguments. Their own armed forces were soon disbanded, and instead of them, mercenaries were entrusted to guard the borders of the Byzantine Empire. But the commanders were unable to curb cowardice, greed and rebelliousness in their new soldiers, turning into open rebellion and disobedience in a number of cases, which strongly questioned the empire's ability to repel enemies and ultimately led to its destruction.
Obedient to his father, Michael IX turned out to be not the person who could radically change the existing system and win victories, commanding the peasant militia and the multi-tribal mercenary rabble, with whom even an outstanding commander could hardly cope and achieve much. It is curious that Philes Palaeologus, the only Byzantine military leader who achieved victory under Michael IX, began by completely refusing to deal with mercenaries and peasant "warriors". Therefore, Michael IX was hardly to blame for his own military failures: they seem to be a natural consequence of the suicidal military transformations carried out in the Byzantine Empire at that time.
Private life
Betrothals and marriage. Issue
 In 1288 Michael IX was betrothed with Catherine of Courtenay, titular
In 1288 Michael IX was betrothed with Catherine of Courtenay, titular Latin Empress of Constantinople
The following is a list of the Latin empresses consort of Constantinople. Yolanda of Flanders and Marie of Brienne were not only empresses consort but also empresses regent. Catherine I and Catherine II were empresses regnant, not empresses con ...
. The marriage was proposed by Andronikos II in the hope of reducing the threat of restoring the power of the Latins in the Byzantine Empire and reconciling with both the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
and the European monarchs, who frightened Constantinople with a new Crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
; however, after several years of fruitless negotiations and the decisive objection from the French king, the purposed union was abandoned by 1295, when Michael IX was already married.
In addition to Catherine of Courtenay, Andronikos II considered a number of other possibles brides for his eldest son: marriage proposals from Constantinople went to the Sicilian and Cypriot courts.Nicephorus Gregoras, ''Byzantine History'', Book 6.8. At one time everyone thought that Michael IX would become the husband of Yolande of Aragon (sister of King Frederick III of Sicily
Frederick II (or III) (13 December 1272 – 25 June 1337) was the regent of the Kingdom of Sicily from 1291 until 1295 and subsequently King of Sicily from 1295 until his death. He was the third son of Peter III of Aragon and served in th ...
), but this was also not destined to come true. In addition, Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, Despot of Epirus proposed his daughter Thamar as a bride for Michael IX, but the matter did not go beyond words.
Finally, Andronikos II sent an embassy to Levon II, King of Armenia; although the ambassadors were captured by pirates, the Emperor was not deterred, and very soon he sent a new embassy mission, led by Theodore Metochites
Theodore Metochites ( el, Θεόδωρος Μετοχίτης; 1270–1332) was a Byzantine Greek statesman, author, gentleman philosopher, and patron of the arts. From c. 1305 to 1328 he held the position of personal adviser ('' mesazōn'') to e ...
and Patriarch John XII, to ask the hand of the Armenian princess Rita
Rita may refer to:
People
* Rita (given name)
* Rita (Indian singer) (born 1984)
* Rita (Israeli singer) (born 1962)
* Rita (Japanese singer)
* Eliza Humphreys (1850–1938), wrote under the pseudonym Rita
Places
* Djarrit, also known as R ...
. The ambassadors returned with the young princess, and on their return to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, on 16 January 1294 at Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
, the marriage between Michael IX and Rita (renamed Maria upon her wedding) took place. At that time, both groom and bride are 16-years-old. They had four children, two sons and two daughters:Nicephorus Gregoras, ''Byzantine History'', Book 8.1.
* Andronikos III Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos_III_Palaiologos.jpg
, caption = 14th-century miniature.Stuttgart, Württembergische Landesbibliothek.
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 24 May 1328 – 15 June 1341
, coronation = ...
(25 March 1297 — 15 June 1341), who became Emperor after dethroning his grandfather in 1328.
* Manuel Palaiologos (died 1320). He was killed by soldiers of his older brother, who had allegedly mistaken him as a rival for the affections of a girl whom young Andronikos III was courting.
* Anna Palaiologina (died 1320), who married firstly in 1307 with Thomas I Komnenos Doukas
Thomas I Komnenos Doukas ( Latinized as Comnenus Ducas) ( el, Θωμάς Α΄ Κομνηνός Δούκας, translit=Thōmas I Komnēnos Doukas) (c. 1285–1318) ruler of Epirus from c. 1297 until his death in 1318.
Thomas was the son of N ...
, Despot of Epirus, and secondly in 1318 with Nicholas Orsini
Nicholas Orsini ( gr, Νικόλαος Ορσίνι, ''Nikolaos Orsini'') was count palatine of Cephalonia from 1317 to 1323 and ruler of Epirus from 1318 to 1323.
Nicholas was the son of Count John I Orsini of Cephalonia by Maria, a daughter ...
, Count Palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos and Despot of Epirus.
* Theodora Palaiologina (died aft. 1330), who married firstly in 1308 with Tsar Theodore Svetoslav of Bulgaria and secondly in 1324 with Tsar Michael Asen III of Bulgaria.
Relationship with stepmother
After the death of his first wife Anna of Hungary in 1281, Andronikos II entered into a new marriage in 1284, choosing as his wife the 10-year-old Yolanda of Montferrato, who was renamed Ireneirene
Irene is a name derived from εἰρήνη (eirēnē), the Greek for "peace".
Irene, and related names, may refer to:
* Irene (given name)
Places
* Irene, Gauteng, South Africa
* Irene, South Dakota, United States
* Irene, Texas, United State ...
upon her wedding (as was customary for foreign princess with strange names in the Byzantine fashion); Michael IX and his brother Constantine were only a few years younger than their stepmother. As it turned out later, this girl became in an ambitious and intriguing woman. From her marriage with Andronikos II, Irene had seven children, of whom only survive four, three sons — John Palaiologos (born in 1286), Theodore Palaiologos (born in 1291) and Demetrios Palaiologos (born in 1297)— and a daughter — Simonis Palaiologina (born in 1294), later wife of King Stefan Uroš II Milutin of Serbia—, so she didn't like the prospect that her stepson Michael IX, to the detriment of the interests of her own children, would inherit the entire Empire after his father's death. Over time, Irene was possessed by a deep hatred against her stepson and an obsessive desire to bring her children to the throne:
After one of the quarrels with her husband, Irene, along with her sons, had to leave Constantinople and retire to Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
. The conflict between Irene and Michael IX ended only after the death of the Empress in 1317, who, however, before her death had time to disgrace herself and become famous for her unworthy behavior, like her attempts to "wash dirty linen in public" and tell everyone intimate and shameful details of her married life to everyone she met.
Death
In October 1319, Michael IX was appointed by his father to govern Thessalonica, where, according to Nicephorus Gregoras, he had to try to put an end to the enmity between the Thessalians and thePelasgians
The name Pelasgians ( grc, Πελασγοί, ''Pelasgoí'', singular: Πελασγός, ''Pelasgós'') was used by classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the emergenc ...
, which had lasted for many years. He humbly accepted his father's will and, together with his wife Rita-Maria, went to live in this city, despite the well-known prophecy at that time, according to which Michael IX was destined to die in Thessaloniki, and which, as they say, worried him greatly.
Michael IX died on 12 October 1320 in the city of Thessalonica; reportedly, the cause of his death was because he couldn't stand the news of the successive deaths of his daughter Anna and son Manuel, who was mistakenly killed by soldiers of his older brother Andronikos III:
According to a Byzantine chronicler whose name has not reached today, Michael IX was buried in the same place where he died — in Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
.
Michael and the Church
Michael IX was also known for his piety and devotion to the Church. In the last period of his life in Thessalonica, he ordened the restoration of theHagios Demetrios
The Church of Saint Demetrius, or Hagios Demetrios ( el, Άγιος Δημήτριος), is the main sanctuary dedicated to Saint Demetrius, the patron saint of Thessaloniki (in Central Macedonia, Greece), dating from a time when it was the s ...
(church dedicated to Saint Demetrius
Saint Demetrius (or Demetrios) of Thessalonica ( el, Ἅγιος Δημήτριος τῆς Θεσσαλονίκης, (); bg, Димитър Солунски (); mk, Свети Димитрија Солунски (); ro, Sfântul Dumitru; sr ...
, the patron saint of Thessaloniki) after being almost completely destroyed by the Normans in 1185. In particular, under his leadership, the vaults were re-painted, the roof made and the temple columns renovated.
Over the years, he issued a large number of church decrees —known as ''chrysobull'' (Golden seal)—. Of greatest interest are his ''chrysobull'' of Iviron (1310) and Hilandar (March 1305) monasteries —by that time plundered by the Catalans after the memorable defeat at Apros— and the Brontochion Monastery
Brontochion Monastery ( el, Βροντόχιον, Μονή Βροντοχίου) is a monastery in Mystras, Greece.
The abbot Pachomius incorporated into it the small church of the Hodegetria
A Hodegetria , ; russian: Одиги́трия, Odi ...
(November 1318). According to these documents, the monks of these monasteries were exempted from many duties and taxes, including the delivery of food and drinks to the state. In the ''chrysobull'' of Iviron Monastery, Michael IX defined his role in the country and society as "Patron saint of subjects in the interests of the common good".
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * ''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium
The ''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'' (ODB) is a three-volume historical dictionary published by the English Oxford University Press. With more than 5,000 entries, it contains comprehensive information in English on topics relating to the Byzant ...
'', Oxford University Press, 1991.
ged 43
{{DEFAULTSORT:Palaiologos, Michael 09
1278 births
1320 deaths
Michael 09
Eastern Orthodox monarchs
13th-century Byzantine emperors
Michael 09
Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars
Byzantine junior emperors
Byzantine–Turkish wars
Sons of Byzantine emperors