|
Debelt
Debelt ( Bulgarian: Дебелт) is a village in Burgas Province in southeastern Bulgaria. It is located in the municipality of Sredets. History Debelt is located near the ruins of the city of Develtos. During the Russo-Turkish War of 1828-1829, the region was occupied by Russia with the support of the Christian population. However, after the Treaty of Adrianople in 1829, the Christian population of Debelt abandoned the village and travelled with the Russian army as it withdrew from Ottoman territory. The former inhabitants of Debelt mostly settled in Bessarabia. In 1864, the Ottoman government repopulated Debelt with Circassians, after which the village became known as Yakezli (Bulgarian: Якезли).Raychevski (2002), p. 255 Following the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-1878, the Circassians abandoned the village. In 1903, during the Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising, the village served as an important logistical base of the IMRO and training camps were established.Karayotov e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Develtos
Develtos ( el, Δεβελτός, Δηβελτός, Δεουελτòς, Δεούελτος, Διβηλτóς) or Deultum was an ancient city and bishopric in Thrace. It was located at the mouth of the River Sredetska on the west coast of Lake Mandrensko, previously part of the Gulf of Burgas, and near the modern village of Debelt. History Classical period Develton ( Thracian: ''Debelton'', "two-swamp area") was founded as an '' emporium'' of Apollonia Pontica in the 7th century BC.Boer (2002), pp. 131-133 From the 6th century to the 4th century BC, the settlement served as an important place of trade between Thracians and Greeks. Develton was annexed to the Roman Empire in 46 AD and became part of the province of Thrace. The construction of a '' colonia'' for veterans of the VIII ''Augusta'' legion at Develton was likely planned prior to 69 AD, but was delayed due to the eruption of civil war of 69 AD.Campbell (2006), p. 218 The veterans may have been settled at Develton d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
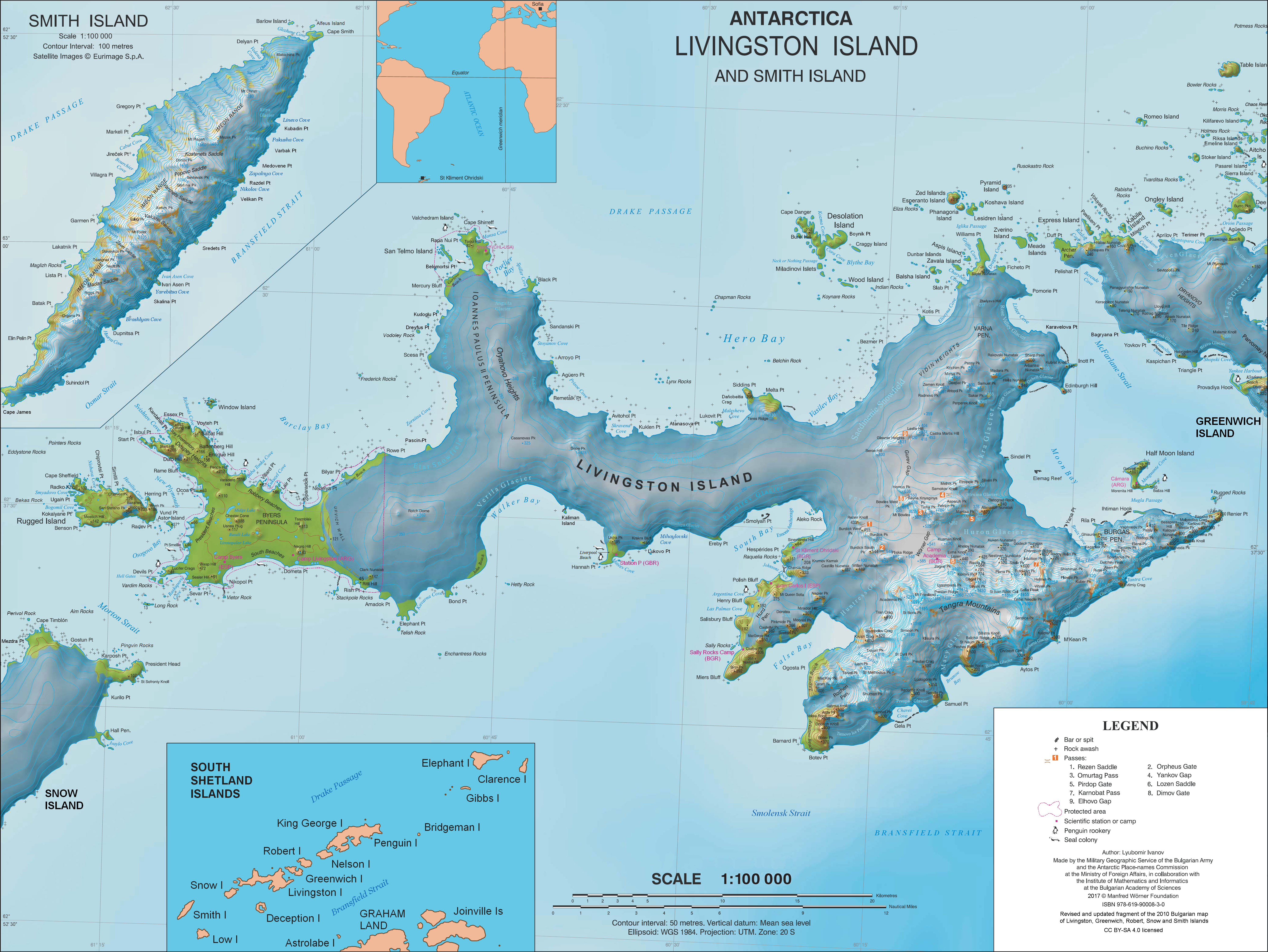
Debelt Glacier
The Debelt Glacier ( bg, ледник Дебелт, lednik Debelt, ) on Varna Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is situated southeast of Rose Valley Glacier and northeast of Panega Glacier. It drains the southeastern slopes of Vidin Heights and flows into Moon Bay between Edinburgh Hill and Helis Nunatak. The glacier extends three km in an east-west direction, and 1.5 km in north-south direction. Debelt glacier is centred at (62.5319° S; 60.0628° W). Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05 and mapping in 2005 and 2009. The feature is named after the settlement of Debelt in Southeastern Bulgaria, successor of the ancient town of Deultum. Registered in the SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
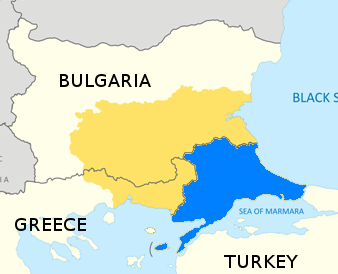
Burgas Province
Burgas Province ( bg, Област Бургас, translit=Oblast Burgas, formerly the Burgas okrug) is a province in southeastern Bulgaria, including the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. The province is named after its administrative and industrial centre, the city of Burgas, the fourth biggest town in the country. It is the largest province by area, embracing a territory of Bulgarian Provinces area and population 1999 — National Center for Regional Development — page 90-91 that is divided into 13 municipalities with a total population, as of December 2009, of 422,319 inhabitants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia in the North Caucasus. As a consequence of the Circassian genocide, which was perpetrated by the Russian Empire in the 19th century during the Russo-Circassian War, most Circassians were exiled from their homeland in Circassia to modern-day Turkey and the rest of the Middle East, where the majority of them are concentrated today. The Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization estimated in the early 1990s that there are as many as 3.7 million Circassians in diaspora in over 50 countries. The Circassian language is the ancestral language of the Circassian people, and Islam has been the dominant religion among them since the 17th century. Circassia has been subject to repeated invasions since ancient times; its isolated terrain couple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes. The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei. There are sixteen research stations in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livingston Island
Livingston Island (Russian name ''Smolensk'', ) is an Antarctic island in the Southern Ocean, part of the South Shetlands Archipelago, a group of Antarctic islands north of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was the first land discovered south of 60° south latitude in 1819, a historic event that marked the end of a centuries-long pursuit of the mythical ''Terra Australis Incognita'' and the beginning of the exploration and utilization of real Antarctica. The name Livingston, although of unknown derivation, has been well established in international usage since the early 1820s. Geography Livingston Island is situated in West Antarctica northwest of Cape Roquemaurel on the Antarctic mainland, south-southeast of Cape Horn in South America, southeast of the Diego Ramírez Islands (the southernmost land of South America), due south of the Falkland Islands, southwest of South Georgia Islands, and from the South Pole.L. IvanovGeneral Geography and History of Livingston Island.In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace ( tr, Doğu Trakya or simply ''Trakya''; el, Ανατολική Θράκη, ''Anatoliki Thraki''; bg, Източна Тракия, ''Iztochna Trakiya''), also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically a part of Southeast Europe. It accounts for 3.4% of Turkey's land area but comprises 15% of its total population. The largest city of the region is Istanbul, which straddles the Bosporus between Europe and Asia. East Thrace is of historic importance as it is next to a major sea trade corridor and constitutes what remains of the once-vast Ottoman region of Rumelia. It is currently also of specific geostrategic importance because the sea corridor, which includes two narrow straits, provides access to the Mediterranean Sea from the Black Sea for the navies of five countries: Russia, Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, and Georgia. The region also serves as a future connector of existing Turkish, Bulgarian, and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracian Bulgarians
Thracians or Thracian Bulgarians ( Bulgarian: Тракийски българи or Тракийци) are a regional, ethnographic group of ethnic Bulgarians, inhabiting or native to Thrace. Today, the larger part of this population is concentrated in Northern Thrace, but much is spread across the whole of Bulgaria and the diaspora. Until the beginning of the twentieth century the Thracian Bulgarians were scattered in the whole of Thrace, then part of the Ottoman Empire. After the persecutions during the Preobrazhenie Uprising and the ethnic cleansing, caused to the Bulgarian population in Eastern Thrace after the Second Balkan War, these people were expelled from the area. After World War I, Bulgaria was required to cede Western Thrace to Greece. A whole population of Bulgarians in Western Thrace was expelled into Bulgaria-controlled Northern Thrace. This was followed by a further population exchange between Bulgaria and Greece (under the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine), which rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies repulsed the Bulgarian offensive and counter-attacked, entering Bulgaria. With Bulgaria also having previously engaged in territorial disputes with Romania and the bulk of Bulgarian forces engaged in the south, the prospect of an easy victory incited Romanian intervention against Bulgaria. The Ottoman Empire also took advantage of the situation to regain some lost territories from the previous war. When Romanian troops approached the capital Sofia, Bulgaria asked for an armistice, resulting in the Treaty of Bucharest, in which Bulgaria had to cede portions of its First Balkan War gains to Serbia, Greece and Romania. In the Treaty of Constantinople, it lost Adrianople to the Ottomans. The political developments and military preparations f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organisation
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO; bg, Вътрешна Македонска Революционна Организация (ВМРО), translit=Vatrešna Makedonska Revoljucionna Organizacija (VMRO); mk, Внатрешна Македонска Револуционерна Организација, translit=Vnatrešna Makedonska Revolucionerna Organizacija), was a secret revolutionary society founded in the Ottoman territories in Europe, that operated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Founded in 1893 in Salonica, initially, it aimed to gain autonomy for Macedonia and Adrianople regions in the Ottoman Empire, however, later it became an agent serving Bulgarian interests in Balkan politics. IMRO group modeled itself after the Internal Revolutionary Organization of Vasil Levski and accepted its motto "Freedom or Death" ( Свобода или смърть). Starting in 1896 it fought the Ottomans using guerrilla tactics, and in this they wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising
The Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising, or simply the Ilinden Uprising of August–October 1903 ( bg, Илинденско-Преображенско въстание, Ilindensko-Preobrazhensko vastanie; mk, Илинденско востание, Ilindensko vostanie; el, Εξέγερση του Ίλιντεν, Eksegersi tou Ilinden), was an organized revolt against the Ottoman Empire, which was prepared and carried out by the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization, with the support of the Supreme Macedonian-Adrianople Committee. The name of the uprising refers to ''Ilinden'', a name for Elijah's day, and to ''Preobrazhenie'' which means Transfiguration. Some historians describe the rebellion in the Serres revolutionary district as a separate uprising, calling it the Krastovden Uprising ( Holy Cross Day Uprising), because on September 14 the revolutionaries there also rebelled. The revolt lasted from the beginning of August to the end of October and covered a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |