Majungasaurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Majungasaurus'' (; ) is a
 French
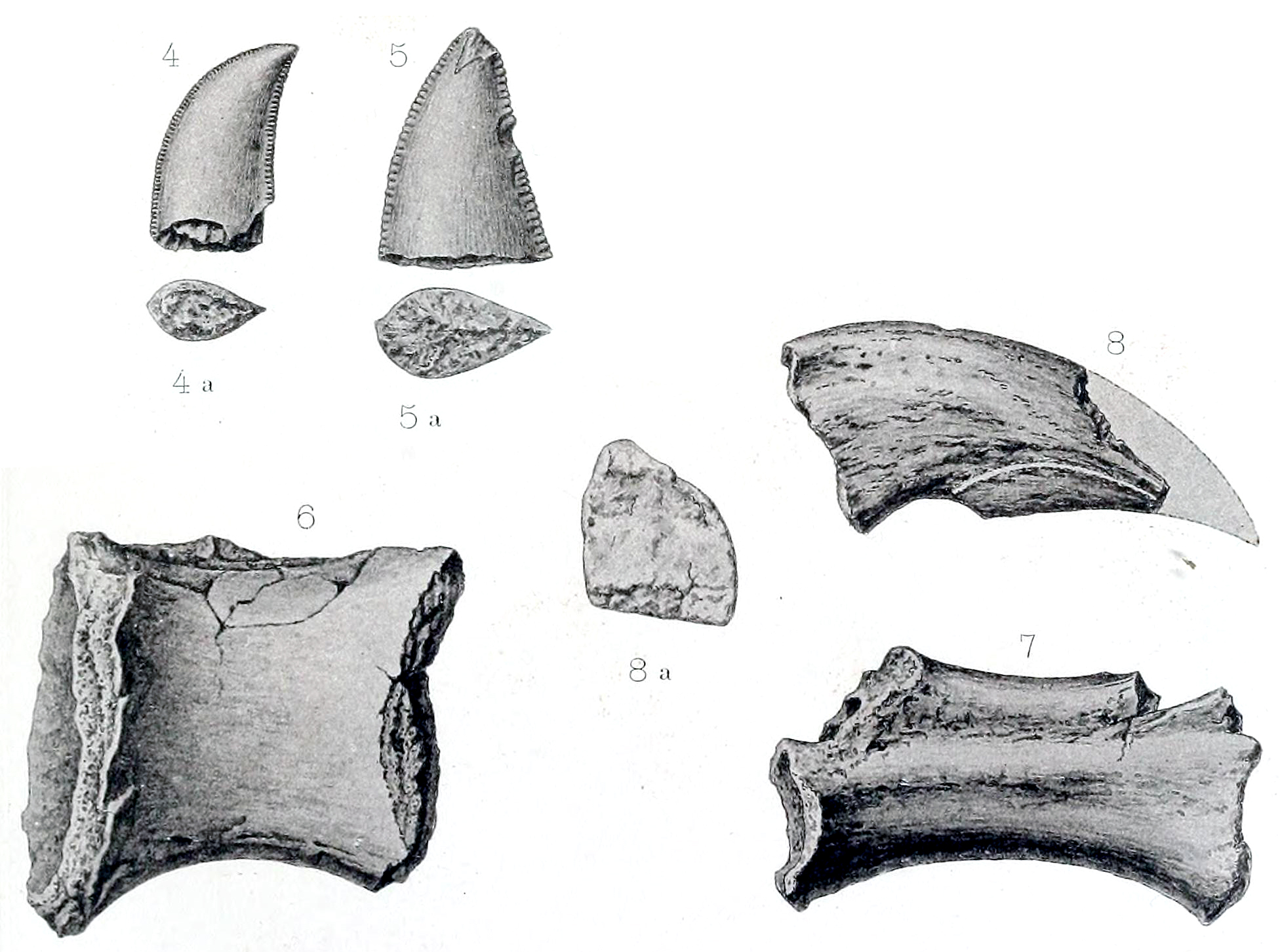
French  Numerous fragmentary remains from
Numerous fragmentary remains from  Fieldwork in 1996 turned up a spectacularly complete theropod skull preserved in exquisite detail ( FMNH PR 2100). On top of this skull was a dome-shaped swelling nearly identical to the one described by Sues and Taquet as ''Majungatholus atopus''. ''Majungatholus'' was redescribed as an abelisaurid rather than a pachycephalosaur in 1998. Although the name ''Majungasaurus crenatissimus'' was older than ''Majungatholus atopus'', the authors judged the type dentary of ''Majungasaurus'' too fragmentary to confidently assign to the same species as the skull. Further fieldwork over the next decade turned up a series of less complete skulls, as well as dozens of partial skeletons of individuals ranging from juveniles to adults. Project members also collected hundreds of isolated bones and thousands of shed ''Majungasaurus'' teeth. Taken together, these remains represent nearly all the bones of the skeleton, although most of the forelimbs, most of the
Fieldwork in 1996 turned up a spectacularly complete theropod skull preserved in exquisite detail ( FMNH PR 2100). On top of this skull was a dome-shaped swelling nearly identical to the one described by Sues and Taquet as ''Majungatholus atopus''. ''Majungatholus'' was redescribed as an abelisaurid rather than a pachycephalosaur in 1998. Although the name ''Majungasaurus crenatissimus'' was older than ''Majungatholus atopus'', the authors judged the type dentary of ''Majungasaurus'' too fragmentary to confidently assign to the same species as the skull. Further fieldwork over the next decade turned up a series of less complete skulls, as well as dozens of partial skeletons of individuals ranging from juveniles to adults. Project members also collected hundreds of isolated bones and thousands of shed ''Majungasaurus'' teeth. Taken together, these remains represent nearly all the bones of the skeleton, although most of the forelimbs, most of the
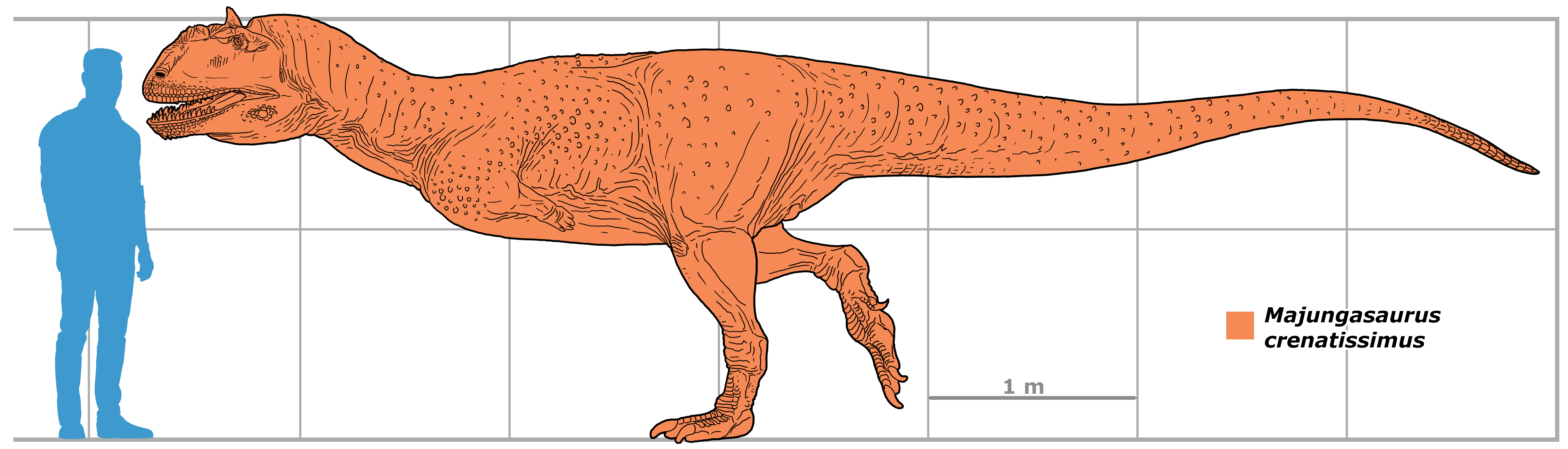 ''Majungasaurus'' was a medium-sized theropod that typically reached in length and weighed . Fragmentary remains of larger individuals indicate that some adults could have been similar in size to its relative '' Carnotaurus'', possibly exceeding in length.
The skull of ''Majungasaurus'' is exceptionally well-known compared to most theropods and generally similar to that of other abelisaurids. Like other abelisaurid skulls, its length was proportionally short for its height, although not as short as in ''Carnotaurus''. The skulls of large individuals measured long. The tall
''Majungasaurus'' was a medium-sized theropod that typically reached in length and weighed . Fragmentary remains of larger individuals indicate that some adults could have been similar in size to its relative '' Carnotaurus'', possibly exceeding in length.
The skull of ''Majungasaurus'' is exceptionally well-known compared to most theropods and generally similar to that of other abelisaurids. Like other abelisaurid skulls, its length was proportionally short for its height, although not as short as in ''Carnotaurus''. The skulls of large individuals measured long. The tall  The
The
 A cladogram by Tortosa ''et al.'' 2013 places ''Majungasaurus'' in a new subfamily, Majungasaurinae. A simplified version showing the taxa within the group is shown below.
A cladogram by Tortosa ''et al.'' 2013 places ''Majungasaurus'' in a new subfamily, Majungasaurinae. A simplified version showing the taxa within the group is shown below.
 ''Majungasaurus'' is perhaps most distinctive for its skull ornamentation, including the swollen and fused nasals and the frontal horn. Other ceratosaurs, including ''Carnotaurus'', ''Rajasaurus'', and ''
''Majungasaurus'' is perhaps most distinctive for its skull ornamentation, including the swollen and fused nasals and the frontal horn. Other ceratosaurs, including ''Carnotaurus'', ''Rajasaurus'', and ''
 Scientists have suggested that the unique skull shape of ''Majungasaurus'' and other abelisaurids indicate different predatory habits than other theropods. Whereas most theropods were characterized by long, low skulls of narrow width, abelisaurid skulls were taller and wider, and often shorter in length as well. The narrow skulls of other theropods were well equipped to withstand the vertical stress of a powerful bite, but not as good at withstanding torsion (twisting). In comparison to modern mammalian predators, most theropods may have used a strategy similar in some ways to that of long- and narrow-snouted
Scientists have suggested that the unique skull shape of ''Majungasaurus'' and other abelisaurids indicate different predatory habits than other theropods. Whereas most theropods were characterized by long, low skulls of narrow width, abelisaurid skulls were taller and wider, and often shorter in length as well. The narrow skulls of other theropods were well equipped to withstand the vertical stress of a powerful bite, but not as good at withstanding torsion (twisting). In comparison to modern mammalian predators, most theropods may have used a strategy similar in some ways to that of long- and narrow-snouted  ''Majungasaurus'' was the largest predator in its environment, while the only known large herbivores at the time were sauropods like ''Rapetosaurus''. Scientists have suggested that ''Majungasaurus'', and perhaps other abelisaurids, specialized on hunting sauropods. Adaptations to strengthen the head and neck for a bite-and-hold type of attack might have been very useful against sauropods, which would have been tremendously powerful animals. This hypothesis may also be supported by the hindlegs of ''Majungasaurus'', which were short and stocky, as opposed to the longer and more slender legs of most other theropods. While ''Majungasaurus'' would not have moved as fast as other similar-sized theropods, it would have had no trouble keeping up with slow-moving sauropods. The robust hindlimb bones suggest very powerful legs, and their shorter length would have lowered the animal's center of gravity. Thus ''Majungasaurus'' may have sacrificed speed for power. ''Majungasaurus'' tooth marks on ''Rapetosaurus'' bones confirm that it at least fed on these sauropods, whether or not it actually killed them.
''Majungasaurus'' was the largest predator in its environment, while the only known large herbivores at the time were sauropods like ''Rapetosaurus''. Scientists have suggested that ''Majungasaurus'', and perhaps other abelisaurids, specialized on hunting sauropods. Adaptations to strengthen the head and neck for a bite-and-hold type of attack might have been very useful against sauropods, which would have been tremendously powerful animals. This hypothesis may also be supported by the hindlegs of ''Majungasaurus'', which were short and stocky, as opposed to the longer and more slender legs of most other theropods. While ''Majungasaurus'' would not have moved as fast as other similar-sized theropods, it would have had no trouble keeping up with slow-moving sauropods. The robust hindlimb bones suggest very powerful legs, and their shorter length would have lowered the animal's center of gravity. Thus ''Majungasaurus'' may have sacrificed speed for power. ''Majungasaurus'' tooth marks on ''Rapetosaurus'' bones confirm that it at least fed on these sauropods, whether or not it actually killed them.
 Scientists have reconstructed the
Scientists have reconstructed the
 ''Majungasaurus'', being known from many well-preserved specimens of different ages, is well studied in regards to its growth and development. Throughout ontogeny, the skull of ''Majungasaurus'' (more specifically, the
''Majungasaurus'', being known from many well-preserved specimens of different ages, is well studied in regards to its growth and development. Throughout ontogeny, the skull of ''Majungasaurus'' (more specifically, the
 All specimens of ''Majungasaurus'' have been recovered from the Maevarano Formation in the
All specimens of ''Majungasaurus'' have been recovered from the Maevarano Formation in the
Press release
about the ''Majungasaurus'' mount erected in 2006 at
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of abelisaurid theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived in Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
from 70 to 66 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago ...
, at the end of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
Period, making it one of the last known non-avian dinosaurs that went extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
. The genus contains a single species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
, ''Majungasaurus crenatissimus''. This dinosaur is also called ''Majungatholus'', a name which is considered a junior synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
* In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linn ...
of ''Majungasaurus''.
Like other abelisaurids, ''Majungasaurus'' was a biped
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
al predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
with a short snout. Although the forelimbs are not completely known, they were very short, while the hind limbs were longer and very stocky. It can be distinguished from other abelisaurids by its wider skull, the very rough texture and thickened bone on the top of its snout, and the single rounded horn on the roof of its skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
, which was originally mistaken for the dome of a pachycephalosaur
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachyc ...
. It also had more teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, ...
in both upper and lower jaws than most abelisaurids.
Known from several well-preserved skulls and abundant skeletal material, ''Majungasaurus'' has recently become one of the best-studied theropod dinosaurs from the Southern Hemisphere. It appears to be most closely related to abelisaurids from India rather than South America or continental Africa, a fact that has important biogeographical
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
implications. ''Majungasaurus'' was the apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
in its ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
, mainly preying on sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', ' lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their ...
s like '' Rapetosaurus'', and is also one of the few dinosaurs for which there is direct evidence of cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
.
Discovery and naming
 French
French paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
Charles Depéret described the first theropod remains from northwestern Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
in 1896. These included two teeth, a claw, and some vertebrae discovered along the Betsiboka River
Betsiboka River is a long river in central-north Madagascar. It flows northwestward and empties to Bombetoka Bay, forming a large delta. It originates to the east of Antananarivo. The river is surrounded in mangroves. The river is distinctive f ...
by a French army officer and deposited in the collection of what is now the Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1. Depéret referred these fossils to the genus ''Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic period (Bathonian stage, 166 million years ...
'', which at the time was a wastebasket taxon
Wastebasket taxon (also called a wastebin taxon, dustbin taxon or catch-all taxon) is a term used by some taxonomists to refer to a taxon that has the sole purpose of classifying organisms that do not fit anywhere else. They are typically defined ...
containing any number of unrelated large theropods, as the new species ''M. crenatissimus''. This name is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
word ''crenatus'' ("notched") and the suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carr ...
''-issimus'' ("most"), in reference to the numerous serrations on both front and rear edges of the teeth. Depéret later reassigned the species to the North American genus '' Dryptosaurus'', another poorly known taxon.
 Numerous fragmentary remains from
Numerous fragmentary remains from Mahajanga Province
Mahajanga was a former province of Madagascar that had an area of 150,023 km². It had a population of 1,896,000 (2004). Its capital was Mahajanga, the second largest city in Madagascar.
Except for Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga Province bordere ...
in northwestern Madagascar were recovered by French collectors over the next 100 years, many of which were deposited in the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle
The French National Museum of Natural History, known in French as the ' (abbreviation MNHN), is the national natural history museum of France and a ' of higher education part of Sorbonne Universities. The main museum, with four galleries, is loc ...
in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
. In 1955, René Lavocat described a theropod dentary (MNHN
The French National Museum of Natural History, known in French as the ' (abbreviation MNHN), is the national natural history museum of France and a ' of higher education part of Sorbonne Universities. The main museum, with four galleries, is loc ...
.MAJ 1) with teeth from the Maevarano Formation in the same region where the original material was found. The teeth matched those first described by Depéret, but the strongly curved jaw bone was very different from both ''Megalosaurus'' and ''Dryptosaurus''. Based on this dentary, Lavocat created the new genus ''Majungasaurus'', using an older spelling of Mahajanga as well as the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word (meaning "lizard"). Hans-Dieter Sues
Hans-Dieter Sues (born January 13, 1956) is a German-born American paleontologist who is Senior Scientist and Curator of Vertebrate Paleontology at the National Museum of Natural History of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC.
He receiv ...
and Philippe Taquet described a dome-shaped skull fragment (MNHN.MAJ 4) as a new genus of pachycephalosaur (''Majungatholus atopus'') in 1979. This was the first report of a pachycephalosaur in the Southern Hemisphere.
In 1993, scientists from the State University of New York at Stony Brook
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York system' ...
and the University of Antananarivo
University of Antananarivo (french: Université d'Antananarivo) is the primary public university of Madagascar, located in the capital Antananarivo.
History
The university traces its founding to 16 December 1955 and the formation of the Instit ...
began the Mahajanga Basin Project, a series of expeditions to examine the fossils and geology of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
sediments near the village of Berivotra, in Mahajanga Province. Among these scientists was paleontologist David W. Krause of Stony Brook. The first expedition turned up hundreds of theropod teeth identical to those of ''Majungasaurus'', some of which were attached to an isolated premaxilla that was described in 1996. The following seven expeditions would turn up tens of thousands of fossils, many of which belonged to species new to science. The Mahajanga Basin Project claims credit for quintupling the known diversity of fossil taxa in the region.
 Fieldwork in 1996 turned up a spectacularly complete theropod skull preserved in exquisite detail ( FMNH PR 2100). On top of this skull was a dome-shaped swelling nearly identical to the one described by Sues and Taquet as ''Majungatholus atopus''. ''Majungatholus'' was redescribed as an abelisaurid rather than a pachycephalosaur in 1998. Although the name ''Majungasaurus crenatissimus'' was older than ''Majungatholus atopus'', the authors judged the type dentary of ''Majungasaurus'' too fragmentary to confidently assign to the same species as the skull. Further fieldwork over the next decade turned up a series of less complete skulls, as well as dozens of partial skeletons of individuals ranging from juveniles to adults. Project members also collected hundreds of isolated bones and thousands of shed ''Majungasaurus'' teeth. Taken together, these remains represent nearly all the bones of the skeleton, although most of the forelimbs, most of the
Fieldwork in 1996 turned up a spectacularly complete theropod skull preserved in exquisite detail ( FMNH PR 2100). On top of this skull was a dome-shaped swelling nearly identical to the one described by Sues and Taquet as ''Majungatholus atopus''. ''Majungatholus'' was redescribed as an abelisaurid rather than a pachycephalosaur in 1998. Although the name ''Majungasaurus crenatissimus'' was older than ''Majungatholus atopus'', the authors judged the type dentary of ''Majungasaurus'' too fragmentary to confidently assign to the same species as the skull. Further fieldwork over the next decade turned up a series of less complete skulls, as well as dozens of partial skeletons of individuals ranging from juveniles to adults. Project members also collected hundreds of isolated bones and thousands of shed ''Majungasaurus'' teeth. Taken together, these remains represent nearly all the bones of the skeleton, although most of the forelimbs, most of the pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
and the tip of the tail are still unknown. This fieldwork culminated in a 2007 monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject.
In library cataloging, ''monogra ...
consisting of seven scientific paper
: ''For a broader class of literature, see Academic publishing.''
Scientific literature comprises scholarly publications that report original empirical and theoretical work in the natural and social sciences. Within an academic field, scienti ...
s on all aspects of the animal's biology, published in the ''Society of Vertebrate Paleontology
The Society of Vertebrate Paleontology (SVP) is a professional organization that was founded in the United States in 1940 to advance the science of vertebrate paleontology around the world.
Mission and Activities
SVP has about 2,300 members inte ...
Memoirs''. The papers are in English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, although each has an abstract written in Malagasy. In this volume, the dentary described by Lavocat was re-evaluated and determined to be diagnostic for this species. Therefore, the name ''Majungatholus'' was replaced by the older name ''Majungasaurus''. Although the monograph is comprehensive, the editors noted that it describes only material recovered from 1993 through 2001. A significant quantity of specimens, some very complete, were excavated in 2003 and 2005 and await preparation and description in future publications. The dentary was made the neotype
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the ...
specimen after a 2009 petition to the ICZN
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the I ...
.
Description
 ''Majungasaurus'' was a medium-sized theropod that typically reached in length and weighed . Fragmentary remains of larger individuals indicate that some adults could have been similar in size to its relative '' Carnotaurus'', possibly exceeding in length.
The skull of ''Majungasaurus'' is exceptionally well-known compared to most theropods and generally similar to that of other abelisaurids. Like other abelisaurid skulls, its length was proportionally short for its height, although not as short as in ''Carnotaurus''. The skulls of large individuals measured long. The tall
''Majungasaurus'' was a medium-sized theropod that typically reached in length and weighed . Fragmentary remains of larger individuals indicate that some adults could have been similar in size to its relative '' Carnotaurus'', possibly exceeding in length.
The skull of ''Majungasaurus'' is exceptionally well-known compared to most theropods and generally similar to that of other abelisaurids. Like other abelisaurid skulls, its length was proportionally short for its height, although not as short as in ''Carnotaurus''. The skulls of large individuals measured long. The tall premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
(frontmost upper jaw bone), which made the tip of the snout very blunt, was also typical of the family. However, the skull of ''Majungasaurus'' was markedly wider than in other abelisaurids. All abelisaurids had a rough, sculptured texture on the outside faces of the skull bones, and ''Majungasaurus'' was no exception. This was carried to an extreme on the nasal bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose.
Ea ...
s of ''Majungasaurus'', which were extremely thick and fused together, with a low central ridge running along the half of the bone closest to the nostrils. A distinctive dome-like horn protruded from the fused frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, ...
s on top of the skull as well. In life, these structures would have been covered with some sort of integument
In biology, an integument is the tissue surrounding an organism's body or an organ within, such as skin, a husk, shell, germ or rind.
Etymology
The term is derived from ''integumentum'', which is Latin for "a covering". In a transferred, or ...
, possibly made of keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail ...
. Computed tomography (CT scanning) of the skull shows that both the nasal structure and the frontal horn contained hollow sinus cavities, perhaps to reduce weight. The teeth were typical of abelisaurids in having short crowns, although ''Majungasaurus'' bore seventeen teeth in both the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
of the upper jaw and the dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
of the lower jaw, more than in any other abelisaurid except '' Rugops''.
 The
The postcrania Postcrania (postcranium, adjective: postcranial) in zoology and vertebrate paleontology is all or part of the skeleton apart from the skull. Frequently, fossil remains, e.g. of dinosaurs or other extinct tetrapods, consist of partial or isolated sk ...
l skeleton of ''Majungasaurus'' closely resembles those of ''Carnotaurus'' and ''Aucasaurus
''Aucasaurus'' is a genus of medium-sized abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from Argentina that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Santonian to Campanian stage) of the Anacleto Formation. It was smaller than the related ''Carnotaurus'', although m ...
'', the only other abelisaurid genera for which complete skeletal material is known. ''Majungasaurus'' was bipedal, with a long tail to balance out the head and torso, putting the center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ...
over the hips. Although the cervical (neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In ...
) vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
e had numerous cavities and excavations ( pleurocoels) to reduce their weight, they were robust, with exaggerated muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of mus ...
attachment sites and rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
s that interlocked for strength. Ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s attached to the cervical ribs, giving them a forked appearance, as seen in ''Carnotaurus''. All of these features resulted in a very strong and muscular neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In ...
. Uniquely, the cervical ribs of ''Majungasaurus'' had long depressions along the sides for weight reduction. The humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a r ...
(upper arm bone) was short and curved, closely resembling those of ''Aucasaurus'' and ''Carnotaurus''. Also like related dinosaurs, ''Majungasaurus'' had very short forelimbs with four extremely reduced digits, first reported with only two very short external fingers and no claws. The hand and finger bones of ''Majungasaurus'', like other majungasaurines, lacked the characteristic pits and grooves where claws and tendons would normally attach, and its finger bones were fused together, indicating that the hand was immobile. In 2012, a better specimen was described, showing that the lower arm was robust, though short, and that the hand contained four metatarsals and four, probably inflexible and very reduced, fingers, possibly with no claws. The minimum phalanx formula was 1-2-1-1.
Like other abelisaurids, the hindlimbs were stocky and short compared to body length. The tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it conn ...
(lower leg bone) of ''Majungasaurus'' was even stockier than that of its relative ''Carnotaurus'', with a prominent crest on the knee. The astragalus
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to tempe ...
and calcaneum
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
S ...
(ankle bones) were fused together, and the feet bore three functional digits, with a smaller first digit that did not contact the ground.
Classification and systematics
''Majungasaurus'' is classified as a member of the theropodclade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter ...
Abelisauridae, which is considered a family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
in Linnaean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus t ...
. Along with the family Noasauridae, abelisaurids are included in the superfamily Abelisauroidea
Abelisauroidea is typically regarded as a Cretaceous group, though the earliest abelisauridae remains are known from the Middle Jurassic of Argentina (classified as the species Eoabelisaurus mefi) and possibly Madagascar (fragmentary remains o ...
, which is in turn a subdivision of the infraorder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and ...
Ceratosauria. Abelisaurids are known for their tall skulls with blunt snouts, extensive sculpturing on the outer surfaces of the facial bones ( convergent with carcharodontosaurids), very reduced ( atrophied) forelimbs (convergent with tyrannosaurids), and stocky hindlimb proportions, among other features.
As with many dinosaur families, the systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic t ...
(evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
ary relationships) within the family Abelisauridae are confused. Several cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived char ...
studies have indicated that ''Majungasaurus'' shares a close relationship with ''Carnotaurus'' from South America, while others were unable to firmly place it in the phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological s ...
. The most recent analysis, using the most complete information, instead recovered ''Majungasaurus'' in a clade with ''Rajasaurus
''Rajasaurus'' (meaning "princely lizard") is a genus of carnivorous abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of India, containing one species: ''Rajasaurus narmadensis''. The bones were excavated from the Lameta Formation in th ...
'' and ''Indosaurus
''Indosaurus'' () is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now India, about 69 to 66 million years ago during the Maastrichtian division of the Late Cretaceous. The species I. matleyi weighed roughly 700 kg (1540&nbs ...
'' from India, but excluding South American genera like ''Carnotaurus'', ''Ilokelesia
''Ilokelesia'' is an extinct genus of abelisaurid theropod,Coria, R.A.; Salgado, L. & Calvo, J.O. (1991) "Primeros restos de dinosaurios Theropoda del Miembro Huincul, Formación Río Limay (Cretácico Tardío Presenoniano), Neuquén, Argentina." ...
'', '' Ekrixinatosaurus'', ''Aucasaurus'' and ''Abelisaurus
''Abelisaurus'' (; "Abel's lizard") is a genus of predatory abelisaurid theropod dinosaur alive during the Late Cretaceous Period (Campanian) of what is now South America. It was a bipedal carnivore that probably reached about in length, alth ...
'', as well as ''Rugops'' from mainland Africa. This leaves open the possibility of separate clades of abelisaurids in western and eastern Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
.
 A cladogram by Tortosa ''et al.'' 2013 places ''Majungasaurus'' in a new subfamily, Majungasaurinae. A simplified version showing the taxa within the group is shown below.
A cladogram by Tortosa ''et al.'' 2013 places ''Majungasaurus'' in a new subfamily, Majungasaurinae. A simplified version showing the taxa within the group is shown below.
Paleobiology
Skull ornamentation
 ''Majungasaurus'' is perhaps most distinctive for its skull ornamentation, including the swollen and fused nasals and the frontal horn. Other ceratosaurs, including ''Carnotaurus'', ''Rajasaurus'', and ''
''Majungasaurus'' is perhaps most distinctive for its skull ornamentation, including the swollen and fused nasals and the frontal horn. Other ceratosaurs, including ''Carnotaurus'', ''Rajasaurus'', and ''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek κέρας/κέρατος, ' meaning "horn" and σαῦρος ' meaning "lizard") was a carnivorous theropod dinosaur in the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to Tithonian). The genus was first described in 1 ...
'' itself bore crests on the head. These structures are likely to have played a role in intraspecific competition, although their exact function within that context is unknown. The hollow cavity inside the frontal horn of ''Majungasaurus'' would have weakened the structure and probably precluded its use in direct physical combat, although the horn may have served a display purpose. While there is variation in the ornamentation of ''Majungasaurus'' individuals, there is no evidence for sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
.
Feeding
 Scientists have suggested that the unique skull shape of ''Majungasaurus'' and other abelisaurids indicate different predatory habits than other theropods. Whereas most theropods were characterized by long, low skulls of narrow width, abelisaurid skulls were taller and wider, and often shorter in length as well. The narrow skulls of other theropods were well equipped to withstand the vertical stress of a powerful bite, but not as good at withstanding torsion (twisting). In comparison to modern mammalian predators, most theropods may have used a strategy similar in some ways to that of long- and narrow-snouted
Scientists have suggested that the unique skull shape of ''Majungasaurus'' and other abelisaurids indicate different predatory habits than other theropods. Whereas most theropods were characterized by long, low skulls of narrow width, abelisaurid skulls were taller and wider, and often shorter in length as well. The narrow skulls of other theropods were well equipped to withstand the vertical stress of a powerful bite, but not as good at withstanding torsion (twisting). In comparison to modern mammalian predators, most theropods may have used a strategy similar in some ways to that of long- and narrow-snouted canid
Canidae (; from Latin, '' canis'', " dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found withi ...
s, with the delivery of many bites weakening the prey animal.
Abelisaurids, especially ''Majungasaurus'', may instead have been adapted for a feeding strategy more similar to modern felid
Felidae () is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a felid (). The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the dom ...
s, with short and broad snouts, that bite once and hold on until the prey is subdued. ''Majungasaurus'' had an even broader snout than other abelisaurids, and other aspects of its anatomy may also support the bite-and-hold hypothesis. The neck was strengthened, with robust vertebrae, interlocking ribs and ossified tendons, as well as reinforced muscle attachment sites on the vertebrae and the back of the skull. These muscles would have been able to hold the head steady despite the struggles of its prey. Abelisaurid skulls were also strengthened in many areas by bone mineralized out of the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, creating the characteristic rough texture of the bones. This is particularly true of ''Majungasaurus'', where the nasal bones were fused and thickened for strength. On the other hand, the lower jaw of ''Majungasaurus'' sported a large fenestra
A fenestra (fenestration; plural fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomical st ...
(opening) on each side, as seen in other ceratosaurs, as well as synovial joint
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articul ...
s between certain bones that allowed a high degree of flexibility in the lower jaw, although not to the extent seen in snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more ...
s. This may have been an adaptation to prevent the fracture of the lower jaw when holding onto a struggling prey animal. The front teeth of the upper jaw were more robust than the rest, to provide an anchor point for the bite, while the low crown height of ''Majungasaurus'' teeth prevented them from breaking off during a struggle. Finally, unlike the teeth of ''Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' () is a genus of large carnosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic epoch ( Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian). The name "''Allosaurus''" means "different lizard" alludin ...
'' and most other theropods, which were curved on both the front and back, abelisaurids like ''Majungasaurus'' had teeth curved on the front edge but straighter on the back (cutting) edge. This structure may have served to prevent slicing, and instead holding the teeth in place when biting. Examination of the teeth of ''Majungasaurus'' indicates that the theropod replaced its teeth anywhere from 2-13 times faster than other theropods, replacing the entire set within a span of two months. Gnawing on bone may have been a significant reason for such rapid tooth replacement.
 ''Majungasaurus'' was the largest predator in its environment, while the only known large herbivores at the time were sauropods like ''Rapetosaurus''. Scientists have suggested that ''Majungasaurus'', and perhaps other abelisaurids, specialized on hunting sauropods. Adaptations to strengthen the head and neck for a bite-and-hold type of attack might have been very useful against sauropods, which would have been tremendously powerful animals. This hypothesis may also be supported by the hindlegs of ''Majungasaurus'', which were short and stocky, as opposed to the longer and more slender legs of most other theropods. While ''Majungasaurus'' would not have moved as fast as other similar-sized theropods, it would have had no trouble keeping up with slow-moving sauropods. The robust hindlimb bones suggest very powerful legs, and their shorter length would have lowered the animal's center of gravity. Thus ''Majungasaurus'' may have sacrificed speed for power. ''Majungasaurus'' tooth marks on ''Rapetosaurus'' bones confirm that it at least fed on these sauropods, whether or not it actually killed them.
''Majungasaurus'' was the largest predator in its environment, while the only known large herbivores at the time were sauropods like ''Rapetosaurus''. Scientists have suggested that ''Majungasaurus'', and perhaps other abelisaurids, specialized on hunting sauropods. Adaptations to strengthen the head and neck for a bite-and-hold type of attack might have been very useful against sauropods, which would have been tremendously powerful animals. This hypothesis may also be supported by the hindlegs of ''Majungasaurus'', which were short and stocky, as opposed to the longer and more slender legs of most other theropods. While ''Majungasaurus'' would not have moved as fast as other similar-sized theropods, it would have had no trouble keeping up with slow-moving sauropods. The robust hindlimb bones suggest very powerful legs, and their shorter length would have lowered the animal's center of gravity. Thus ''Majungasaurus'' may have sacrificed speed for power. ''Majungasaurus'' tooth marks on ''Rapetosaurus'' bones confirm that it at least fed on these sauropods, whether or not it actually killed them.
Cannibalism
Although sauropods may have been the prey of choice for ''Majungasaurus'', discoveries published in 2007 detail finds in Madagascar that indicate the presence of other ''Majungasaurus'' in their diet. Numerous bones of ''Majungasaurus'' have been discovered bearing tooth marks identical to those found on sauropod bones from the same localities. These marks have the same spacing as teeth in ''Majungasaurus'' jaws, are of the same size as ''Majungasaurus'' teeth, and contain smaller notches consistent with the serrations on those teeth. As ''Majungasaurus'' is the only large theropod known from the area, the simplest explanation is that it was feeding on other members of its own species. Suggestions that theTriassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest per ...
'' Coelophysis'' was a cannibal have been recently disproven, leaving ''Majungasaurus'' as the only non-avian theropod with confirmed cannibalistic tendencies, although there is some evidence that cannibalism may have occurred in other species as well.
It is unknown if ''Majungasaurus'' actively hunted their own kind or only scavenged
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feeding ...
their carcasses. However, some researchers have noted that modern Komodo monitors sometimes kill each other when competing for access to carcasses. The lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia altho ...
s will then proceed to cannibalize the remains of their rivals, which may suggest similar behavior in ''Majungasaurus'' and other theropods.
Respiratory system
 Scientists have reconstructed the
Scientists have reconstructed the respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies g ...
of ''Majungasaurus'' based on a superbly preserved series of vertebrae ( UA 8678) recovered from the Maevarano Formation. Most of these vertebrae and some of the ribs contained cavities (pneumatic foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
) that may have resulted from the infiltration of in
avian
Avian may refer to:
* Birds or Aves, winged animals
*Avian (given name) (russian: Авиа́н, link=no), a male forename
Aviation
*Avro Avian, a series of light aircraft made by Avro in the 1920s and 1930s
*Avian Limited, a hang glider manufactur ...
-style lungs and air sacs. In birds, the neck vertebrae and ribs are hollowed out by the cervical air sac, the upper back vertebrae by the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
, and the lower back and sacral (hip) vertebrae by the abdominal air sac. Similar features in ''Majungasaurus'' vertebrae imply the presence of these air sacs. These air sacs may have allowed for a basic form of avian-style 'flow-through ventilation,' where air flow through the lungs is one-way, so that oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
-rich air inhaled from outside the body is never mixed with exhaled air laden with carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
. This method of respiration, while complicated, is highly efficient.
The recognition of pneumatic foramina in ''Majungasaurus'', besides providing an understanding of its respiratory biology, also has larger-scale implications for evolutionary biology. The split between the ceratosaur line, which led to ''Majungasaurus'', and the tetanuran line, to which birds belong, occurred very early in the history of theropods. The avian respiratory system, present in both lines, must therefore have evolved before the split, and well before the evolution of birds themselves. This provides further evidence of the dinosaurian origin of birds
The scientific question of within which larger group of animals birds evolved has traditionally been called the "origin of birds". The present scientific consensus is that birds are a group of maniraptoran theropod dinosaurs that originated ...
.
Brain and inner ear structure
Computed tomography, also known as CT scanning, of a complete ''Majungasaurus'' skull (FMNH PR 2100) allowed a rough reconstruction of itsbrain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
and inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in th ...
structure. Overall, the brain was very small relative to body size, but otherwise similar to many other non-coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, t ...
n theropods, with a very conservative form closer to modern crocodilia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest livi ...
ns than to birds. One difference between ''Majungasaurus'' and other theropods was its smaller flocculus
The flocculus (Latin: ''tuft of wool'', diminutive) is a small lobe of the cerebellum at the posterior border of the middle cerebellar peduncle anterior to the biventer lobule. Like other parts of the cerebellum, the flocculus is involved in moto ...
, a region of the cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebe ...
that helps to coordinate movements of the eye with movements of the head. This suggests that ''Majungasaurus'' and other abelisaurids like ''Indosaurus
''Indosaurus'' () is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now India, about 69 to 66 million years ago during the Maastrichtian division of the Late Cretaceous. The species I. matleyi weighed roughly 700 kg (1540&nbs ...
'', which also had a small flocculus, did not rely on quick head movements to sight and capture prey.
Inferences about behavior can also be drawn from examination of the inner ear. The semicircular canal
In mathematics (and more specifically geometry), a semicircle is a one-dimensional locus of points that forms half of a circle. The full arc of a semicircle always measures 180° (equivalently, radians, or a half-turn). It has only one line o ...
s within the inner ear aid in balance, and the lateral semicircular canal is usually parallel to the ground when the animal holds its head in an alert posture. When the skull of ''Majungasaurus'' is rotated so that its lateral canal is parallel to the ground, the entire skull is nearly horizontal. This contrasts with many other theropods, where the head was more strongly downturned when in the alert position. The lateral canal is also significantly longer in ''Majungasaurus'' than in its more basal relative ''Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek κέρας/κέρατος, ' meaning "horn" and σαῦρος ' meaning "lizard") was a carnivorous theropod dinosaur in the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to Tithonian). The genus was first described in 1 ...
'', indicating a greater sensitivity to side-to-side motions of the head.
Pathology
A 2007 report describedpathologies
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
in the bones of ''Majungasaurus''. Scientists examined the remains of at least 21 individuals and discovered four with noticeable pathologies. While pathology had been studied in large tetanuran theropods like allosaurids and tyrannosaurids, this was the first time an abelisauroid had been examined in this manner. No wounds were found on any skull elements, in contrast to tyrannosaurids where sometimes gruesome facial bites were common. One of the specimens was a phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly ...
(toe bone) of the foot, which had apparently been broken and subsequently healed.
Most of the pathologies occurred on the vertebrae. For example, a dorsal (back) vertebra from a juvenile animal showed an exostosis
An exostosis, also known as bone spur, is the formation of new bone on the surface of a bone. Exostoses can cause chronic pain ranging from mild to debilitatingly severe, depending on the shape, size, and location of the lesion. It is most commonl ...
(bony growth) on its underside. The growth probably resulted from the conversion of cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck ...
or a ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal l ...
to bone during development, but the cause of the ossification was not determined. Hypervitaminosis A
Hypervitaminosis A refers to the toxic effects of ingesting too much preformed vitamin A (retinyl esters, retinol, and retinal). Symptoms arise as a result of altered bone metabolism and altered metabolism of other fat-soluble vitamins. Hypervi ...
and bone spur
An exostosis, also known as bone spur, is the formation of new bone on the surface of a bone. Exostoses can cause chronic pain ranging from mild to debilitatingly severe, depending on the shape, size, and location of the lesion. It is most common ...
s were ruled out, and an osteoma
An osteoma (plural: "osteomata") is a new piece of bone usually growing on another piece of bone, typically the skull. It is a benign tumor.
When the bone tumor grows on other bone it is known as "homoplastic osteoma"; when it grows on other tissu ...
(benign bone tumor) was deemed unlikely. Another specimen, a small caudal (tail) vertebra, was also found to have an abnormal growth, this time on the top of its neural spine, which projects upwards from the vertebrae, allowing muscle attachment. Similar growths from the neural spine have been found in specimens of ''Allosaurus'' and ''Masiakasaurus'', probably resulting from the ossification of a ligament running either between the neural spines ( interspinal ligament) or along their tops ( supraspinal ligament).
The most serious pathology discovered was in a series of five large tail vertebrae. The first two vertebrae showed only minor abnormalities with the exception of a large groove that extended along the left side of both bones. However, the next three vertebrae were completely fused together at many different points, forming a solid bony mass. There is no sign of any other vertebrae after the fifth in the series, indicating that the tail ended there prematurely. From the size of the last vertebrae, scientists judged that about ten vertebrae were lost. One explanation for this pathology is severe physical trauma
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or ...
resulting in the loss of the tail tip, followed by osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
(infection) of the last remaining vertebrae. Alternatively, the infection may have come first and led to the end of the tail becoming necrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
and falling off. This is the first example of tail truncation known in a non-avian theropod dinosaur.
The small number of specimens preserved with pathologies in ''Majungasaurus'' suggest that the multitude of injuries that occurred were obtained over the course of the lives of the individuals studied. Furthermore, the small number of injured ''Majungasaurus'' specimens observed amongst those recovered indicates most well preserved individuals generally lack observable pathologies, while a few select individuals were shown to have possessed multiple pathologies, a general pattern also noted in other large, nonavian theropods. Such patterns may be the result of a snowball effect where one injury or an infection increased the likelihood of additional maladies and injuries due to functional impairment or compromised immune systems in individuals once an initial injury had occurred.
Ontogeny and growth
 ''Majungasaurus'', being known from many well-preserved specimens of different ages, is well studied in regards to its growth and development. Throughout ontogeny, the skull of ''Majungasaurus'' (more specifically, the
''Majungasaurus'', being known from many well-preserved specimens of different ages, is well studied in regards to its growth and development. Throughout ontogeny, the skull of ''Majungasaurus'' (more specifically, the jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anatomy ...
, postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ...
, and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians.
Anatomy and function
In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ...
) seems to have become taller and more robust; additionally, the skull bones became more fused and the eye sockets became proportionally smaller. This indicates a shift in dietary preferences between juveniles and adults.
Research by Michael D'Emic ''et al'' indicates that it was among the slowest-growing theropods. Based on studies of the lines of arrested growth in several bones, it was found that ''Majungasaurus'' took twenty years to reach maturity, which may have been a result of the harsh environment in which it lived. However, other abelisaurids have also been found to have comparably slow growth rates.
Paleoecology
 All specimens of ''Majungasaurus'' have been recovered from the Maevarano Formation in the
All specimens of ''Majungasaurus'' have been recovered from the Maevarano Formation in the Mahajanga Province
Mahajanga was a former province of Madagascar that had an area of 150,023 km². It had a population of 1,896,000 (2004). Its capital was Mahajanga, the second largest city in Madagascar.
Except for Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga Province bordere ...
in northwestern Madagascar. Most of these, including all of the most complete material, came from the Anembalemba Member, although ''Majungasaurus'' teeth have also been found in the underlying Masorobe Member and the overlying Miadana Member. While these sediments have not been dated radiometrically, evidence from biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of ...
and paleomagnetism
Paleomagnetism (or palaeomagnetismsee ), is the study of magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called ''paleomagnetists.''
Certain magnetic minerals in roc ...
suggest that they were deposited during the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the inte ...
stage, which lasted from 70 to 66 Ma (million years ago). ''Majungasaurus'' teeth are found up until the very end of the Maastrichtian, when all non-avian dinosaurs became extinct.
Then as now, Madagascar was an island, having separated from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
less than 20 million years earlier. It was drifting northwards but still 10–15 ° more southerly in latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
than it is today. The prevailing climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
of the time was semi-arid, with pronounced season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and ...
ality in temperature and rainfall. ''Majungasaurus'' inhabited a coastal flood plain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
cut by many sandy river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of ...
channels. Strong geological evidence suggests the occurrence of periodic debris flow
Debris flows are geological phenomena in which water-laden masses of soil and fragmented rock rush down mountainsides, funnel into stream channels, entrain objects in their paths, and form thick, muddy deposits on valley floors. They generally ...
s through these channels at the beginning of the wet season, burying the carcasses of organisms killed during the preceding dry season and providing for their exceptional preservation as fossils. Sea levels in the area were rising throughout the Maastrichtian, and would continue to do so into the Paleocene Epoch, so ''Majungasaurus'' may have roamed coastal environments like tidal flats
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal f ...
as well. The neighboring Berivotra Formation represents the contemporaneous marine
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean.
Marine or marines may refer to:
Ocean
* Maritime (disambiguation)
* Marine art
* Marine biology
* Marine debris
* Marine habitats
* Marine life
* Marine pollution
Military ...
environment.
Besides ''Majungasaurus'', fossil taxa recovered from the Maevarano include fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
, frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-f ...
s, lizards, snakes, seven distinct species of crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction.
During Mesozoic and early Cenozoic times, cro ...
s, five or six species of mammals, '' Vorona'' and several other birds, the possibly flighted dromaeosaurid
Dromaeosauridae () is a family of feathered theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from Greek ('), meaning ...
''Rahonavis
''Rahonavis'' is a genus of bird-like theropods from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian, about 70 mya) of what is now northwestern Madagascar. It is known from a partial skeleton ( UA 8656) found by Catherine Forster and colleagues in Maevarano ...
'', the noasaurid '' Masiakasaurus'' and two titanosaurian sauropods, including ''Rapetosaurus''. ''Majungasaurus'' was by far the largest carnivore and probably the dominant predator on land, although large crocodylomorphs like ''Mahajangasuchus
''Mahajangasuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodyliform which had blunt, conical teeth. The type species, ''M. insignis'', lived during the Late Cretaceous; its fossils have been found in the Maevarano Formation in northern Madagascar. It was a ...
'' and '' Trematochampsa'' might have competed with it closer to water.
See also
* Timeline of ceratosaur research *Evolution of dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the ...
References
External links
*Press release
about the ''Majungasaurus'' mount erected in 2006 at
Stony Brook University
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York system' ...
.
{{Taxonbar, from1=Q18511009, from2=Q131173
Majungasaurines
Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Africa
Dinosaurs of India and Madagascar
Maevarano fauna
Prehistoric animals of Madagascar
Maastrichtian genera
Fossil taxa described in 1955
Taxa named by René Lavocat