Isle of Dogs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Isle of Dogs is a large
accessed: 9 February 2007
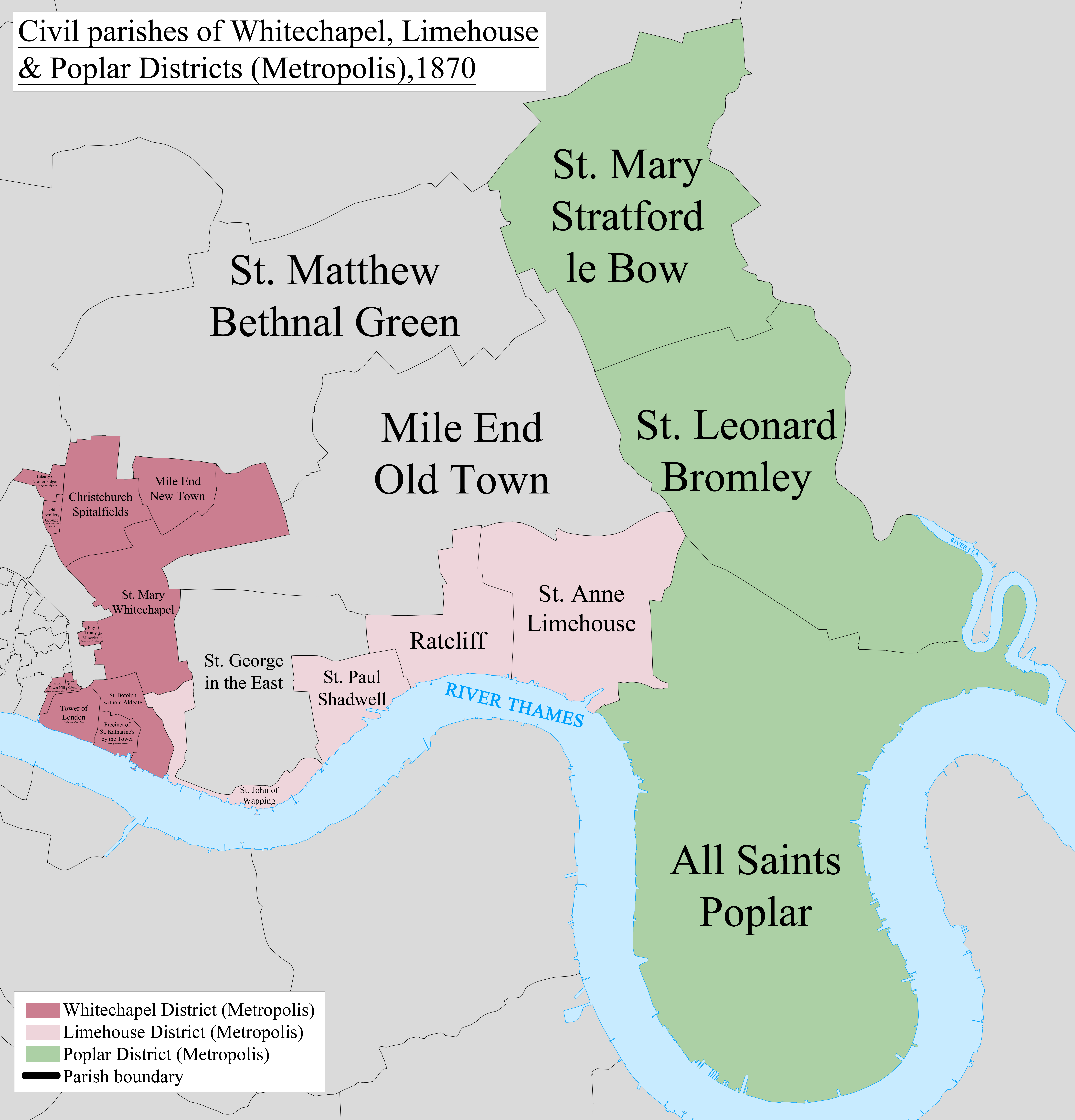
. Laura Wright in a 2015 essay showed that in the Elizabethan era the term "Isle of Dogges" was applied to a small eyot (mud island) lying offshore the present-day Isle of Dogs. It was across the river from the royal
Laura Wright in a 2015 essay showed that in the Elizabethan era the term "Isle of Dogges" was applied to a small eyot (mud island) lying offshore the present-day Isle of Dogs. It was across the river from the royal


 In 1802, the
In 1802, the
 The
The
Island Heritage & History Trust
(archived 24 January 2001)
(archived 17 October 2007) {{Authority control Districts of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets Areas of London Peninsulas of England Former islands of England Geography of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets Districts of London on the River Thames Port of London Islands of London
peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
bounded on three sides by a large meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the Channel (geography), channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erosion, erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank (cut bank, cut bank or river cl ...
in the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
in East London
East London is the part of London, England, east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames as it begins to widen. East London developed as London Docklands, London's docklands and the primary industrial centre. The expansion of ...
, England. It includes the Cubitt Town, Millwall and Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf is a financial area of London, England, located in the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The Greater London Authority defines it as part of London's central business district, alongside Central London. Alongside ...
districts. The area was historically part of the Manor, Hamlet, Parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish pries ...
and, for a time, the wider borough of Poplar. The name had no official status until the 1987 creation of the Isle of Dogs Neighbourhood by Tower Hamlets London Borough Council
Tower Hamlets London Borough Council, also known as Tower Hamlets Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under ...
. It has been known locally as simply "the Island" since the 19th century.
The whole area was once known as Stepney Marsh; Anton van den Wyngaerde's "Panorama of London" dated 1543 depicts and refers to the Isle of Dogs. Records show that ships preparing to carry the English royal household to Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
in 1520 docked at the southern bank of the island. The name ''Isle of Dogges'' occurs in the ''Thamesis Descriptio'' of 1588, applied to a small island in the south-western part of the peninsula. The name is next applied to the ''Isle of Dogs Farm'' (originally known as ''Pomfret Manor'') shown on a map of 1683. At the same time, the area was variously known as ''Isle of Dogs'' or the ''Blackwell levels''. By 1855, it was incorporated within the parish of Poplar under the aegis of the Poplar Board of Works. This was incorporated into the Metropolitan Borough of Poplar on its formation in 1900.
Geology
Thesoil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
is alluvial
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
and silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually ...
y in nature, underlaid by clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
or mud
Mud (, or Middle Dutch) is loam, silt or clay mixed with water. Mud is usually formed after rainfall or near water sources. Ancient mud deposits hardened over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone (generally cal ...
, with a peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most ...
layer in places.The Isle of Dogs: Introduction, Survey of London: volumes 43 and 44: Poplar, Blackwall and Isle of Dogs (1994), pp. 375-87accessed: 9 February 2007
Etymology and heraldry
The first known written mention of the Isle of Dogs is in the '' Letters and Papers of the Reign of Henry VIII''. In Volume 3, entry 1009 "Shipping" dated 2 October 1520, there is a list of purchases, which includes "A hose for the Mary George, in dock at the Isle of Dogs, 10 d." The 1898 edition of ''Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase and Fable
''Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase and Fable'', sometimes referred to simply as ''Brewer's'', is a reference work containing definitions and explanations of many famous phrases, allusions, and figures, whether historical or mythical.
The "New Edi ...
'' attributes the name: "So called from being the receptacle of the greyhound
The English Greyhound, or simply the Greyhound, is a dog breed, breed of dog, a sighthound which has been bred for coursing, greyhound racing and hunting. Some are kept as show dogs or pets.
Greyhounds are defined as a tall, muscular, smooth-c ...
s of Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
. Some say it is a corruption of the Isle of Ducks, and that it is so called in ancient records from the number of wild fowl inhabiting the marshes." Other sources discount this, believing these stories to all derive from the antiquarian John Strype
John Strype (1 November 1643 – 11 December 1737) was an English clergyman, historian and biographer from London. He became a merchant when settling in Petticoat Lane Market, Petticoat Lane. In his twenties, he became perpetual curate of Theydo ...
, and believe it might come from one of the following:
*a nickname of contempt: Ben Jonson
Benjamin Jonson ( 11 June 1572 – ) was an English playwright, poet and actor. Jonson's artistry exerted a lasting influence on English poetry and stage comedy. He popularised the comedy of humours; he is best known for the satire, satirical ...
and Thomas Nashe
Thomas Nashe (also Nash; baptised 30 November 1567 – c. 1601) was an English Elizabethan playwright, poet, satirist and a significant pamphleteer. He is known for his novel '' The Unfortunate Traveller'', his pamphlets including '' Pierce P ...
wrote a satirical play in 1597, which was a mocking attack on the island of Great Britain, titled '' The Isle of Dogs'', which offended some in the nobility. Jonson was imprisoned for a year; Nashe avoided arrest by fleeing the area. Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys ( ; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English writer and Tories (British political party), Tory politician. He served as an official in the Navy Board and Member of Parliament (England), Member of Parliament, but is most r ...
referred to the "unlucky Isle of Doggs."
*the presence of Dutch engineers reclaiming the land from a disastrous flood.
*the presence of gibbet
Gibbeting is the use of a gallows-type structure from which the dead or dying bodies of criminals were hanged on public display to deter other existing or potential criminals. Occasionally, the gibbet () was also used as a method of public ex ...
s on the foreshore facing Greenwich.
*a yeoman
Yeoman is a noun originally referring either to one who owns and cultivates land or to the middle ranks of Serfdom, servants in an Peerage of England, English royal or noble household. The term was first documented in Kingdom of England, mid-1 ...
farmer called ''Brache'', this being an old word for a type of hunting dog.
*the dogs of a later king, Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
, who also kept deer in Greenwich Park
Greenwich Park is a former hunting park in Greenwich and one of the largest single green spaces in south-east London. One of the eight Royal Parks of London, and the first to be enclosed (in 1433), it covers , and is part of the Greenwich World H ...
. Again it is thought that his hunting dogs might have been kept in derelict farm buildings on the island. Now known as the area West Ferry Circus.
* Isle of Dykes, which then got corrupted over the years.The Isle of Dogs and Docklands.
 Laura Wright in a 2015 essay showed that in the Elizabethan era the term "Isle of Dogges" was applied to a small eyot (mud island) lying offshore the present-day Isle of Dogs. It was across the river from the royal
Laura Wright in a 2015 essay showed that in the Elizabethan era the term "Isle of Dogges" was applied to a small eyot (mud island) lying offshore the present-day Isle of Dogs. It was across the river from the royal Deptford dockyard
Deptford Dockyard was an important Royal Navy Dockyard, naval dockyard and base at Deptford on the River Thames, operated by the Royal Navy from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries. It built and maintained warships for 350 years, and man ...
, whose vessels being outfitted were moored at the eyot; the first record of the name appears about the time the dockyard was established. The peninsula itself at that time was always known as Stepney Marsh. A government map, prepared in connection with the Thames defences at the time of the Spanish Armada, suggests the eyot was a recognised navigational landmark alongside an otherwise featureless marsh. Later, the name was extended to a farm on the peninsula, and then to the peninsula itself. That the name referred to the site of royal kennels, she argued, was unsupported speculation 200 years after the first attested usage. Dr Wright offered a speculation of her own: that the name "dogs" was bestowed by the Deptford dockyard workers as a punning reference to the barks (naval vessels) moored at this eyot.
The lost Ben Jonson/Thomas Nashe play (above) was vigorously pursued by the authorities, who even employed a torturer to track down its authors. "The severity of the response seems too great to have been triggered by an attack on a mere individual"; it has been hypothesised that what the play satirised was the then appalling state of England's defences, the play's title ''Isle of Dogs'' being taken to mean the place where the Queen's ships were outfitted.
It is said that Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf is a financial area of London, England, located in the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The Greater London Authority defines it as part of London's central business district, alongside Central London. Alongside ...
, located in the Isle of Dogs, took its name from sea trade with the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, which were named in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
as (). However the name Canary Wharf does not appear until 1936.
The Talbot dog in the coat of arms of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets represents the Isle of Dogs.
Society
Following the building of the Docks (especially theWest India Docks
The West India Docks are a series of three docks, quaysides, and warehouses built to import goods from, and export goods and occasionally passengers to, the British West Indies. Located on the Isle of Dogs in London, the first dock opened in 18 ...
and the adjacent City Canal
The City Canal was a short, and short-lived, canal excavated across the Isle of Dogs in east London, linking two reaches of the River Thames. Today, it has been almost completely reconstructed to form the South Dock of the West India Docks.
...
), and with an increasing population, locals increasingly referred to the area as ''The Island''. This area includes Millwall, Cubitt Town, and Blackwall. The south of the isle opposite Greenwich
Greenwich ( , , ) is an List of areas of London, area in south-east London, England, within the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Greater London, east-south-east of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime hi ...
was once known as ''North Greenwich'', now applied to the area around the Millennium Dome
The Millennium Dome was the original name of the large dome-shaped building on the Greenwich Peninsula in South East (London sub region), South East London, England, which housed a major exhibition celebrating the beginning of the third millen ...
on the Greenwich Peninsula. Between 1986 and 1992 it enjoyed a brief formal existence, as the name ''Isle of Dogs'' was applied to one of seven neighbourhoods to which power was devolved from the council. The neighbourhood was later abolished.
It was the site of the highest concentration of council housing
Public housing in the United Kingdom, also known as council housing or social housing, provided the majority of rented accommodation until 2011, when the number of households in private rental housing surpassed the number in social housing. D ...
in England but is now best known as the location of the Canary Wharf office complex. One Canada Square
One Canada Square is a skyscraper in Canary Wharf, London. It is the third tallest building in the United Kingdom at above ground level,Aviation charts issued by the Civil Aviation Authority and contains 50 storeys. It achieved the title of ...
, also known as the Canary Wharf Tower, is the second tallest habitable building in Britain at . The peninsula is an area of social extremes, comprising some of the most prosperous and most deprived areas of the country; in 2004, nearby Blackwall was the 81st most deprived ward
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a pris ...
in England out of over 8,000, while the presence of Canary Wharf gives the area one of the highest average incomes in the UK. Lincoln Plaza was the 2016 winner of the Carbuncle Cup for the year's "worst new building" and ''The Times'' described it as "mediocre at best, ugly at worst".
History


Origins
The Isle of Dogs is situated some distance downriver from theCity of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, his ...
. It was originally marsh, being several feet below water at high tide. In the Middle Ages it was made available for human habitation by a process known in the Thames estuary as inning
In baseball, softball, and similar games, an inning is the basic unit of play, consisting of two halves or frames, the "top" (first half) and the "bottom" (second half). In each half, one team bats until three outs are made, with the other tea ...
. The reclaimed land was below high water, protected by earthen banks. These banks if not properly kept up were liable to be breached. This happened in 1448, drowning the land for 40 years.
In 1660, the river started to break through the neck of the peninsula, initiating meander cutoff. This was arrested by human intervention, but it left a 5-acre lake called Poplar Gut. It appears on John Rocque
John Rocque (originally Jean; –1762) was a French-born British surveyor and cartographer, best known for his detailed John Rocque's Map of London, 1746, map of London published in 1746.
Life and career
Rocque was born in France in about 1704 ...
's 1746 ''Map of London and ten miles around'', in the extract reproduced in this article.
One road led across the Marshes to an ancient ferry, at Ferry Road. There was rich grazing on the marsh, and cattle were slaughtered in fields known as the ''Killing Fields'', south of Poplar High Street.
The western side of the island was known as ''Marsh Wall'', and the district became known as ''Millwall'' with the building of the docks, and from the number of windmill
A windmill is a machine operated by the force of wind acting on vanes or sails to mill grain (gristmills), pump water, generate electricity, or drive other machinery.
Windmills were used throughout the high medieval and early modern period ...
s constructed along the top of the flood defence.
Industry
 In 1802, the
In 1802, the West India Docks
The West India Docks are a series of three docks, quaysides, and warehouses built to import goods from, and export goods and occasionally passengers to, the British West Indies. Located on the Isle of Dogs in London, the first dock opened in 18 ...
began to be developed on the Isle of Dogs. Beginning in 1812 the Poplar and Greenwich Ferry Roads Company installed tolls on the East Ferry Road. These proved to be unpopular and after many years of lobbying the Metropolitan Board of Works bought the company and abolished the tolls in 1885.
The Docks brought with them many associated industries, such as flour and sugar processing, and also ship building. On 31 January 1858 the largest ship of that time, the SS ''Great Eastern'' designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel ( ; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was an English civil engineer and mechanical engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history", "one of the 19th-century engi ...
, was launched from the yard of Messrs Scott, Russell & Co, of Millwall. The length was too big for the river so the ship had to be launched sideways. Due to the technical difficulties of the launch this was the last big ship to be built on the Island and the industry fell into a decline. However, parts of the launching slipway and plate works have been preserved in situ and may be seen close to Masthouse Terrace Pier.
Docks
 The
The urbanisation
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also ...
of the Isle of Dogs took place in the 19th century following the construction of the West India Docks, which opened in 1802. This heralded the area's most successful period, when it became an important centre for trade. The East India Docks were subsequently opened in 1806, followed by Millwall Dock in 1868.
By the 1880s, the casual employment system caused Dock workers to unionise under Ben Tillett
Benjamin Tillett (11 September 1860 – 27 January 1943) was a British socialist, trade union leader and politician. He was a leader of the "new unionism" of 1889, that focused on organizing unskilled workers. He played a major role in foundin ...
and John Burns
John Elliot Burns (20 October 1858 – 24 January 1943) was an English trade unionist and politician, particularly associated with London politics and Battersea. He was a socialist and then a Liberal Member of Parliament and Minister. He was ...
. This led to a demand for ''6d per hour'' (2.5p), and an end to casual labour in the docks. After a bitter struggle, the London Dock Strike of 1889 was settled with victory for the strikers, and established a national movement for the unionisation of casual workers.
The three dock systems were unified in 1909 when the Port of London Authority
The Port of London Authority (PLA) is a self-funding public trust established on 31 March 1909 in accordance with the Port of London Act 1908 to govern the Port of London. Its responsibility extends over the Tideway of the River Thames and its ...
took control of the docks. With the docks stretching across from East to West with locks at each end, the Isle of Dogs could now almost be described as a genuine island.
Dock workers settled on the "island" as the docks grew in importance, and by 1901, 21,000 people lived there, largely dependent on the river trade on the Isle as well as in Greenwich and Deptford
Deptford is an area on the south bank of the River Thames in southeast London, in the Royal Borough of Greenwich and London Borough of Lewisham. It is named after a Ford (crossing), ford of the River Ravensbourne. From the mid 16th century ...
across the river to the south and west. The Isle of Dogs was connected to the rest of London by the London and Blackwall Railway, opened in 1840 and progressively extended thereafter. In 1902, the ferry to Greenwich was replaced by the construction of the Greenwich foot tunnel, and Island Gardens park was laid out in 1895, providing views across the river. The London and Blackwall Railway closed in 1926. Until the building of the Docklands Light Railway in 1987, the only public transport accessing and exiting the Island consisted of buses using its perimeter roads. These were frequently and substantially delayed by the movement of up to four bridges which allowed ships access to the West India Docks and Millwall Docks. The insular nature of the Island caused its separateness from the rest of London, and its unique nature.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the docks were a key target for the German Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
and were heavily bombed. A number of local civilians were killed in the bombing and extensive destruction was caused on the ground, with many warehouses being destroyed and much of the dock system being put out of action for an extended period. Unexploded bombs from this period continue to be discovered today. Anti-aircraft batteries were based on Mudchute Farm; their concrete bases remain today.
After the war, the docks underwent a brief resurgence and were even upgraded in 1967. However, with the advent of containerisation
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers, or ISO containers). Containerization, also referred as container stuffing or container loading, is the process of uni ...
, which the docks could not handle, they became obsolete soon afterwards. The docks closed progressively during the 1970s, with the last – the West India and Millwall docks – closing down in 1980. This left the area in a severely dilapidated state, with large areas being derelict and abandoned.
'Unilateral declaration of independence'
Local residents resented the scarcity of schools and supermarkets and inadequate transport to neighbourhoods that did have them. On 1 March 1970 a group of activists led by Ted John and John Westfallen, in a reference to the Republic of Rhodesia's recentunilateral declaration of independence
A unilateral declaration of independence (UDI) or "unilateral secession" is a formal process leading to the establishment of a new state by a subnational entity which declares itself independent and sovereign without a formal agreement with the ...
or UDI, issued a UDI for the Isle of Dogs. For two hours (though some reports say a day, others a week) they blocked the two swing-bridges providing the only access to the area by road. According to Johns the intent was semi-jocular and the purpose was only to achieve independence from the rest of London, a right already enjoyed by the nearby City
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
: it was the Press who dubbed him "President Ted of the Isle of Dogs'. Nevertheless, and though a body of local opinion resented the stunt, it achieved wide national and international publicity. It featured on the front page of the ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'', and Johns was interviewed by satellite by Walter Cronkite
Walter Leland Cronkite Jr. (November 4, 1916 – July 17, 2009) was an American broadcast journalist who served as anchorman for the ''CBS Evening News'' from 1962 to 1981. During the 1960s and 1970s, he was often cited as "the most trust ...
for ''CBS Evening News
The ''CBS Evening News'' is the flagship evening News broadcasting#Television, television news program of CBS News, the news division of the CBS television network in the United States. The ''CBS Evening News'' is a daily evening broadcast featu ...
''. A new secondary school and improvements in public transport materialised. According to one source it even served as the catalyst for the eventual development of Canary Wharf.
Patricia Cornwell
Patricia Cornwell (born Patricia Carroll Daniels; June 9, 1956) is an American crime writer. She is known for her best-selling novels featuring medical examiner Kay Scarpetta, of which the first was inspired by a series of sensational murders ...
's 2002 novel ''Isle of Dogs'' features an island off the coast of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
that declares UDI, "claiming its independence lies with those who set sail from the Isle of Dogs in 1607".,
London Docklands Development Corporation
Successive Labour andConservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
governments proposed a number of action plans during the 1970s but it was not until 1981 that the London Docklands Development Corporation (LDDC) was established to redevelop the area. The Isle of Dogs became part of an enterprise zone
An urban enterprise zone is an area in which policies to encourage economic growth and development are implemented. Urban enterprise zone policies generally offer tax concessions, infrastructure incentives, and reduced regulations to attract invest ...
, which covered 1.95 km2 of land and encompassed the West India, Millwall and East India Docks. New housing, office space and transport infrastructure were built. This included the Docklands Light Railway
The Docklands Light Railway (DLR) is an automated medium-capacity rail system, light metro system primarily serving the redeveloped London Docklands, Docklands area of London and providing a direct connection between London's two major financi ...
and later the Jubilee line
The Jubilee line is a London Underground line that runs between in suburban north-west London and in east London, via the West End of London, West End, South Bank and London Docklands, Docklands. Opened in 1979, it is the newest line on the ...
extension, which eventually brought access to the London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or as the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent home counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The Undergro ...
to the area for the first time.
Since its construction in 1987–1991, the area has been dominated by the expanding Canary Wharf development with over of office and retail space having been created; 93,000 now work in Canary Wharf alone.
Politics
The Island achieved notoriety in 1993 when Derek Beackon of theBritish National Party
The British National Party (BNP) is a Far-right politics, far-right, British fascism, fascist list of political parties in the United Kingdom, political party in the United Kingdom. It is headquartered in Wigton, Cumbria, and is led by Adam ...
became a councillor for Millwall ward, in a by-election
A by-election, also known as a special election in the United States and the Philippines, or a bypoll in India, is an election used to fill an office that has become vacant between general elections.
A vacancy may arise as a result of an incumben ...
. This was the culmination of years when race was a prominent issue in local politics, especially with regards to allocation of housing. Labour regained the ward in the full council election of May 1994, and held all three seats until a further by-election in September 2004.
Incidents
On 9 February 1996, the IRA detonated a truck bomb near South Quay DLR station on the Isle of Dogs that killed two people and injured more than a hundred others.Education
There are four stateprimary school
A primary school (in Ireland, India, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, South Africa, and Singapore), elementary school, or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ...
s located on the Isle of Dogs – Cubitt Town Junior School, Arnhem Wharf, Harbinger School and St Edmunds. There was also an independent primary school, River House Montessori.
Canary Wharf College is a free school on the Island which covers primary and secondary education.
Transport
London Underground, DLR, and Elizabeth line stations
The nearest London Underground station isCanary Wharf
Canary Wharf is a financial area of London, England, located in the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The Greater London Authority defines it as part of London's central business district, alongside Central London. Alongside ...
on the Jubilee line. Key areas including Regent's Park
Regent's Park (officially The Regent's Park) is one of the Royal Parks of London. It occupies in north-west Inner London, administratively split between the City of Westminster and the London Borough of Camden, Borough of Camden (and historical ...
, The West End, Westminster
Westminster is the main settlement of the City of Westminster in Central London, Central London, England. It extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street and has many famous landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, ...
, South Bank
The South Bank is an entertainment and commercial area on the south bank of the River Thames, in the London Borough of Lambeth, central London, England.
The South Bank is not formally defined, but is generally understood to be situated betwe ...
, Millennium Dome
The Millennium Dome was the original name of the large dome-shaped building on the Greenwich Peninsula in South East (London sub region), South East London, England, which housed a major exhibition celebrating the beginning of the third millen ...
and the Queen Elizabeth Olympic Park
Queen Elizabeth Olympic Park is a sporting complex and public park in Stratford, Hackney Wick, Leyton and Bow, in east London. It was purpose-built for the 2012 Summer Olympics and Paralympics, situated adjacent to the Stratford City devel ...
, are all within 20 minutes of Canary Wharf by Tube.
The DLR runs north–south through the Isle of Dogs. DLR stations are Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf is a financial area of London, England, located in the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The Greater London Authority defines it as part of London's central business district, alongside Central London. Alongside ...
, Heron Quays, South Quay, Crossharbour, Mudchute and Island Gardens. Key areas including the City of London, Tower Hill
Tower Hill is the area surrounding the Tower of London in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is infamous for the public execution of high status prisoners from the late 14th to the mid 18th century. The execution site on the higher gro ...
and Greenwich are all within 20 minutes of the Isle of Dogs by DLR.
The Elizabeth line
The Elizabeth line is a railway line that runs across Greater London and nearby towns, operating similarly to the Réseau Express Régional, RER in Paris and the S-Bahn systems of German-speaking countries. It runs services on dedicated infras ...
's Canary Wharf station opened in 2022. Situated at the north of the Island, it provides high-frequency, fast connections to the heart of the West End, Paddington Station
Paddington, also known as London Paddington, is a London station group, London railway station and London Underground station complex, located on Praed Street in the Paddington area. The site has been the London terminus of services provided by ...
, Heathrow Airport
Heathrow Airport , also colloquially known as London Heathrow Airport and named ''London Airport'' until 1966, is the primary and largest international airport serving London, the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdo ...
and Abbey Wood
Abbey Wood is an List of areas of London, area in southeast London, England, in the Royal Borough of Greenwich and bordering the London Borough of Bexley. It is located east of Charing Cross. According to the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 ...
.
London bus routes
* London Buses route 135 *London Buses route 277
London is the capital and largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Tha ...
* London Buses route D3
This is a list of Transport for London (TfL) contracted London Buses, bus routes in London, England, as well as commercial services that enter the Greater London area (except Coach (vehicle), coaches).
Bus services in London are operated by A ...
* London Buses route D6
* London Buses route D7
* London Buses route D8
* London Buses route N550
River bus services
Regular commuter boat services serve both Masthouse Terrace Pier and Canary Wharf Pier on the Isle of Dogs. TheThames Clippers
Uber Boat by Thames Clippers is a set of river bus services on the River Thames in London, England.
The company operates both commuter services between eastern and Central London and tourist services under licence from London River Services. ...
provides regular commuter services to Woolwich Arsenal Pier, Greenwich Pier in the east, and the City of London including St. Katherine Docks, Tower Bridge
Tower Bridge is a Listed building#Grade I, Grade I listed combined Bascule bridge, bascule, Suspension bridge, suspension, and, until 1960, Cantilever bridge, cantilever bridge in London, built between 1886 and 1894, designed by Horace Jones ...
, , Greater London Authority
The Greater London Authority (GLA), colloquially known by the Metonymy, metonym City Hall, is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved Regions of England, regional governance body of Greater London, England. It consists of two political ...
building, Tate Modern
Tate Modern is an art gallery in London, housing the United Kingdom's national collection of international Modern art, modern and contemporary art (created from or after 1900). It forms part of the Tate group together with Tate Britain, Tate Live ...
, Blackfriars, as well as the West End of London in the west on the commuter service. There is also a connecting shuttle service to Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe ( ) is a district of South London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, with the Isle of Dogs to the ea ...
and the Tate to Tate service from Tate Modern
Tate Modern is an art gallery in London, housing the United Kingdom's national collection of international Modern art, modern and contemporary art (created from or after 1900). It forms part of the Tate group together with Tate Britain, Tate Live ...
to Tate Britain via London Eye
The London Eye, originally the Millennium Wheel, is a cantilevered observation wheel on the South Bank of the River Thames in London. It is the world's tallest cantilevered observation wheel, and the most popular paid Tourist attractions in the ...
.
From Summer 2007, the service has been enhanced with express boats from central London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
to the O2 Arena (former Millennium Dome).
Airport and helipad
The nearest airport isLondon City Airport
London City Airport is an international airport in London, England. It is located in the Royal Docks in the London Borough of Newham, Borough of Newham, about east of the City of London and east of Canary Wharf. These are the two centres ...
, which is 25 minutes away from Canary Wharf by DLR.
There is also a helipad
A helipad is the landing area of a heliport, in use by helicopters, powered lift, and vertical lift aircraft to land on surface.
While helicopters and powered lift aircraft are able to operate on a variety of relatively flat surfaces, a fa ...
situated on the west of the Island and next to Ferguson's Wharf, which is privately run by Vanguard.
Sailing and watersports activities
The presence of docks, some of a considerable size, has enabled a practice of various watersports, likesailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
, kayaking
Kayaking is the use of a kayak for moving over water. It is distinguished from canoeing by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. A kayak is a low-to-the-water, canoe-like boat in which the paddler sits fac ...
, windsurfing
Windsurfing is a wind-propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the Californian aerospace and surf culture. Windsurfing gain ...
and standup paddleboarding
Standup paddleboarding (SUP) is a water sport born from surfing with modern roots in Hawaii. Standup paddleboarders stand on boards that are floating on the water and use a paddle to propel themselves through the water. The sport was documen ...
.
Docklands Sailing and Watersports Centre is one of the main reference spots for watersports fans.
The Duchess of Cambridge
Duke of Cambridge is a hereditary title of nobility in the British royal family, one of several royal dukedoms in the United Kingdom. The title is named after the city of Cambridge in England. It is heritable by male descendants by primogeni ...
visited the centre in 2017.
In the media
T.S. Eliot
Thomas Stearns Eliot (26 September 18884 January 1965) was a poet, essayist and playwright.Bush, Ronald. "T. S. Eliot's Life and Career", in John A Garraty and Mark C. Carnes (eds), ''American National Biography''. New York: Oxford University ...
's ''The Waste Land
''The Waste Land'' is a poem by T. S. Eliot, widely regarded as one of the most important English-language poems of the 20th century and a central work of modernist poetry. Published in 1922, the 434-line poem first appeared in the United ...
'' contains the lines "The barges wash / Drifting logs / Down Greenwich reach / Past the Isle of Dogs."
In modern times the Isle of Dogs has provided locations for many blockbuster films, including the opening scenes of the James Bond film ''The World Is Not Enough
''The World Is Not Enough'' is a 1999 spy film, the nineteenth in the List of James Bond films, ''James Bond'' series produced by Eon Productions and the third to star Pierce Brosnan as the fictional Secret Intelligence Service, MI6 agent Jam ...
'', ''Full Metal Jacket
''Full Metal Jacket'' is a 1987 war film directed and produced by Stanley Kubrick from a screenplay he co-wrote with Michael Herr and Gustav Hasford. The film is based on Hasford's 1979 autobiographical novel '' The Short-Timers''. It stars ...
'', and more recently ''Batman Begins
''Batman Begins'' is a 2005 superhero film directed by Christopher Nolan, who co-wrote the screenplay with David S. Goyer. Based on the DC Comics character Batman, it stars Christian Bale as Bruce Wayne (Dark Knight trilogy), Bruce Wayne / B ...
'', '' The Constant Gardener'', '' Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix'', and ''Love Actually
''Love Actually'' is a 2003 Christmas film, Christmas romantic comedy film written and directed by Richard Curtis. The film features an ensemble cast, composed predominantly of British actors, many of whom had worked with Curtis in previous pro ...
''. The Isle of Dogs featured heavily in the 1980 British film '' The Long Good Friday'', and the Isle of Dogs is the primary location of the 2007 horror film ''28 Weeks Later
''28 Weeks Later'' is a 2007 post-apocalyptic horror film directed by Juan Carlos Fresnadillo, who co-wrote the screenplay with Rowan Joffé, Enrique López Lavigne and Jesus Olmo. It serves as a standalone sequel to '' 28 Days Later'' (20 ...
'', where it is the only secure and quarantined area in all of Britain suitable for recivilisation after a virus epidemic kills the population of Britain.
The Isle of Dogs was the setting for the 1986 Channel 4 comedy-drama '' Prospects'' starring Gary Olsen and Brian Bovell.
While shooting in East London for his film '' Fantastic Mr. Fox'', Wes Anderson
Wesley Wales Anderson (born May 1, 1969) is an American filmmaker. Wes Anderson filmography, His films are known for themes of grief, loss of innocence, and dysfunctional families. Due to his films' eccentricity, distinctive visual and narrative ...
spotted a road sign directing to the Isle of Dogs. This sparked his imagination, becoming an eponymous source of inspiration for his animated 2018 film '' Isle of Dogs''.
In a 2024 episode of British drama series ''Call the Midwife
''Call the Midwife'' is a British period drama television series about a group of nurse midwives working in the East End of London in the late 1950s, 1960s and 1970s. The principal cast of the show has included Jessica Raine, Miranda Hart, ...
'' set in March 1970, blockades as part of the declared independence of the Isle impede the ability of midwives in Poplar to transport a high risk pregnancy to hospital.
See also
* Burrells Wharf *Crossrail
Crossrail is a completed railway project centred on London. It provides a high-frequency hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit system, akin to the Réseau Express Régional, RER in Paris and the S-Bahn systems of German-speaking countries, kn ...
* Honourable East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
* Island History Trust
* Islands in the River Thames
This article lists the islands in the River Thames, or at the mouth of a tributary (marked †), in England. It excludes human-made islands built as part of the building of forty-five two-gate locks which each accompany a weir, and islets subordi ...
* London Museum Docklands
* Samuda Estate
* SS ''Robin''
References and notes
Bibliography
*Eve Hostettler, ''The Isle of Dogs: 1066–1918: A Brief History, Volume I'' (London: Island History Trust, 2000) *Eve Hostettler, ''The Isle of Dogs: The Twentieth Century: A Brief History, Volume II'' (London: Island History Trust, 2001) *Mick Lemmerman, ''The Isle of Dogs During World War II'' (Amazon, 2015) *Mike Seaborne, ''The Isle of Dogs - Before The Big Money'' (London: Hoxton Mini Press, 2019) *Con Maloney, ''Boozers, Bompers & Bridgers - The History of the Public Houses of the Isle of Dogs'' (London: Friends of Island History Trust, 2020) *Ann Regan-Atherton, ''Heavy Rescue Work on the Isle of Dogs'' (Amazon, 2015)External links
Island Heritage & History Trust
(archived 24 January 2001)
(archived 17 October 2007) {{Authority control Districts of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets Areas of London Peninsulas of England Former islands of England Geography of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets Districts of London on the River Thames Port of London Islands of London