Huigu on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Uyghur Khaganate (also Uyghur Empire or Uighur Khaganate, self defined as Toquz-Oghuz country; otk, 𐱃𐰆𐰴𐰕:𐰆𐰍𐰕:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Toquz Oγuz budun,

 In 779 Tengri Bögü planned to invade the Tang dynasty based on the advice of his Sogdian courtiers. However, Tengri Bögü's uncle,
In 779 Tengri Bögü planned to invade the Tang dynasty based on the advice of his Sogdian courtiers. However, Tengri Bögü's uncle,  In 822, the Uyghurs sent troops to help the Tang in quelling rebels. The Tang refused the offer but had to pay them 70,000 pieces of silk to go home.
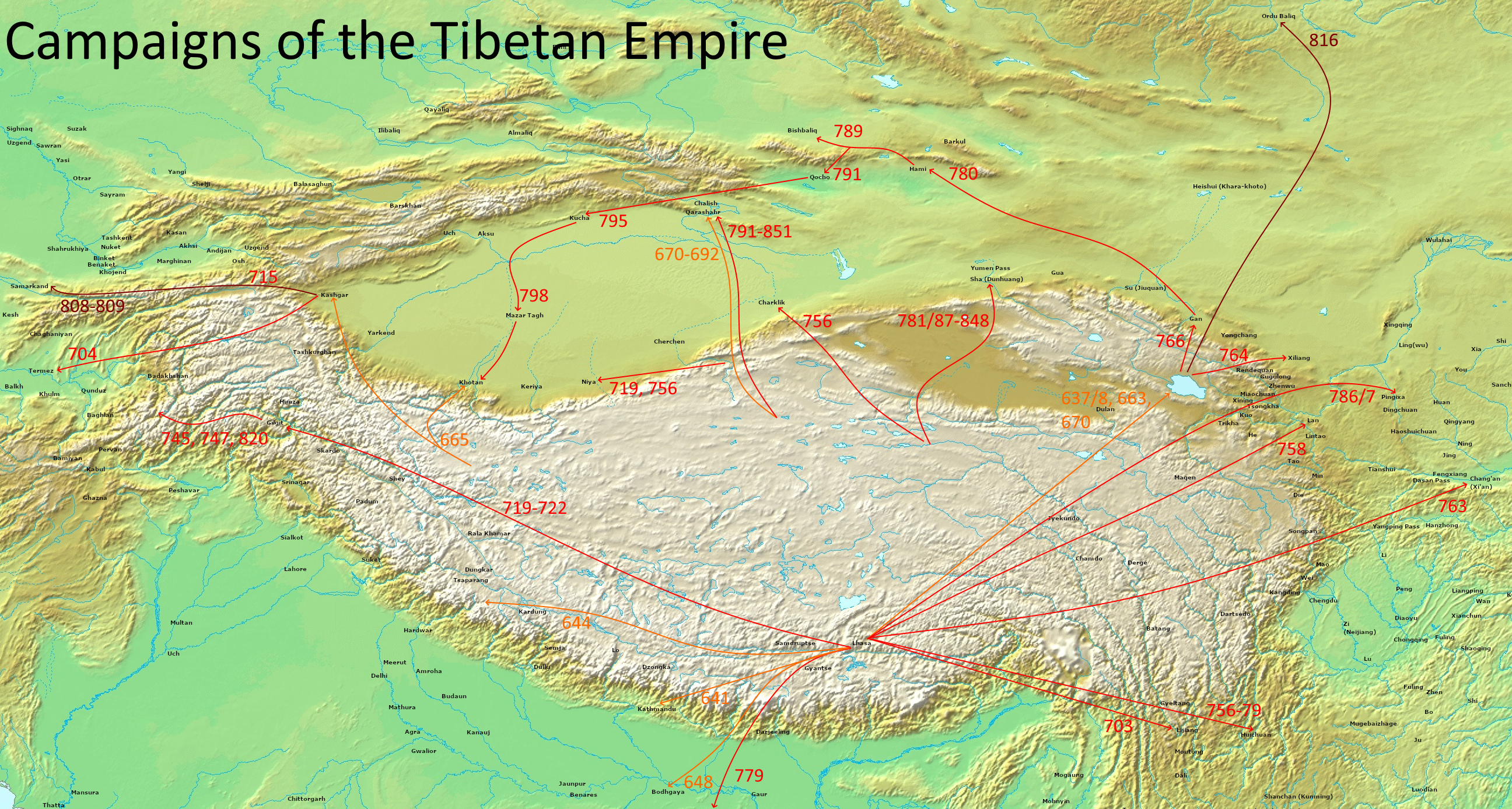
In 823, the Tibetan Empire waged war on the Uyghurs.
In 824, Chongde died and was succeeded by a brother, Qasar.
In 832, Qasar was murdered. He was succeeded by the son of Chongde, Hu. In the same year the Tibetan Empire ceased to make war on the Uyghurs.
In 822, the Uyghurs sent troops to help the Tang in quelling rebels. The Tang refused the offer but had to pay them 70,000 pieces of silk to go home.
In 823, the Tibetan Empire waged war on the Uyghurs.
In 824, Chongde died and was succeeded by a brother, Qasar.
In 832, Qasar was murdered. He was succeeded by the son of Chongde, Hu. In the same year the Tibetan Empire ceased to make war on the Uyghurs.
 The Yenisei Kyrgyz who replaced the Uyghur Khaganate were unsophisticated and had little interest in running the empire which they had destroyed. They held the territory from
The Yenisei Kyrgyz who replaced the Uyghur Khaganate were unsophisticated and had little interest in running the empire which they had destroyed. They held the territory from
 The Uyghurs created an empire with clear Persian influences, particularly in areas of government. Soon after the empire was founded, they emulated sedentary states by establishing a permanent, settled capital, Karabalghasun ( Ordu-Baliq), built on the site of the former Göktürk imperial capital, northeast of the later Mongol capital, Karakorum. The city was a fully fortified commercial center, typical along the Silk Road, with concentric walls and lookout towers, stables, military and commercial stores, and administrative buildings. Certain areas of the town were allotted for trade and handcrafts, while in the center of the town were palaces and temples, including a monastery. The palace had fortified walls and two main gates, as well as moats filled with water and watchtowers.
The khaghan maintained his court there and decided the policies of the empire. With no fixed settlement, the
The Uyghurs created an empire with clear Persian influences, particularly in areas of government. Soon after the empire was founded, they emulated sedentary states by establishing a permanent, settled capital, Karabalghasun ( Ordu-Baliq), built on the site of the former Göktürk imperial capital, northeast of the later Mongol capital, Karakorum. The city was a fully fortified commercial center, typical along the Silk Road, with concentric walls and lookout towers, stables, military and commercial stores, and administrative buildings. Certain areas of the town were allotted for trade and handcrafts, while in the center of the town were palaces and temples, including a monastery. The palace had fortified walls and two main gates, as well as moats filled with water and watchtowers.
The khaghan maintained his court there and decided the policies of the empire. With no fixed settlement, the
(in Chinese) *Xin Tangshu ()
part 1
an
part 2
(in Chinese). Translation in English her
(most of part 1 and beginning of part 2).
Die chinesische Inschrift auf dem uigurischen Denkmal in Kara Balgassun (1896)
{{Empires Historical Turkic states Turkic peoples of Asia Former countries in Chinese history Former monarchies of Asia 744 establishments States and territories established in the 740s 847 disestablishments Khanates States and territories disestablished in the 9th century Former empires
Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) b ...
-era names, with modern Hanyu Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally written in Chinese for ...
: or ) was a Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
empire that existed for about a century between the mid 8th and 9th centuries. They were a tribal confederation under the Orkhon Uyghur () nobility, referred to by the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
as the ''Jiu Xing'' ("Nine Clans"), a calque of the name ''Toquz Oghuz
The Toquz Oghuz ( otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰆𐰔:𐰆𐰍𐰔, Toquz Oγuz; ; "Turks of Nine Seok (clan), Bones") was a political alliance of nine Turkic languages, Turkic-speaking Tiele people, Tiele Turkic tribal confederations, tribes in Inner Asia, dur ...
'' or ''Toquz Tughluq''.
History

Rise
In 657, the Western Turkic Khaganate was defeated by the Tang dynasty, after which the Uyghurs defected to the Tang. Prior to this the Uyghurs had already shown an inclination towards alliances with the Tang when they fought with them against the Tibetan Empire and Turks in 627. In 742, the Uyghurs, Karluks, and Basmyls rebelled against the Second Turkic Khaganate. In 744, the Basmyls captured the Turk capital of Ötüken and killed the reigning Özmiş Khagan. Later that year a Uyghur-Karluk alliance formed against the Basmyls and defeated them. Their khagan was killed and the Basmyls ceased to exist as a people. Hostilities between the Uyghurs and Karluks then forced the Karluks to migrate west into Zhetysu and conflict with the Türgesh, whom they defeated and conquered in 766. The Uyghur khagan's personal name was ''Qullığ Boyla'' (). He took the title '' Kutlug Bilge Kol Khagan'' (''Glorious, wise, mighty khagan''), claiming to be the supreme ruler of all the tribes. He built his capital at Ordu-Baliq. According to Chinese sources, the territory of the Uyghur Empire then reached "on its eastern extremity, the territory ofShiwei Shiwei may refer to:
*Shiwei people, a historic Mongolic people
*Shiwei, Inner Mongolia, a township in Ergun City, Inner Mongolia
Given names
*Che Shiwei (born 1996), Chinese footballer
*Chen Shiwei, Chinese track and field athlete
*Pan Shiwei (bo ...
, on the west the Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The m ...
, on the south it controlled the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
, so it covered the entire territory of the ancient Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
".
In 745, the Uyghurs killed the last khagan of the Göktürks, Báiméikèhán Gǔlǒng fú (), and sent his head to the Tang.
Tribal Composition
Tang Huiyao, vol. 98, listed nine Toquz Oghuz surname tribes (姓部 ''xìngbù''); another list of tribes (部落 ''bùluò'') was recorded in the ''Old Book of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
'' and the ''New Book of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the So ...
''. According to Japanese scholars Hashimoto, Katayama, and Senga, each name in the lists in the Books of Tang recorded each subtribal surname of each chief, while the other list in Tang Huiyao recorded the names of the Toquz Oghuz tribes proper. Walter Bruno Henning (1938) linked nine names recorded in the Saka language " Staël-Holstein Scroll" with those recorded by Han Chinese authors.
; Notes
Golden Age
In 747, Qutlugh Bilge Köl Kaghan died, leaving his youngest son,Bayanchur Khan )''Heavenborn State Founding Wise Qaghan'', birth_name=Yàolúogě Mòyánchùo (藥羅葛磨延啜)
Mo-yun Chur (磨延啜) (b. 713 - d.759) or Eletmish Bilge Qaghan was second qaghan of Uyghur Khaganate. His Tang dynasty invested title was Yingwu ...
to reign as Khagan ''El etmish bilge'' "State settled, wise". After building a number of trading outposts with the Tang, Bayanchur Khan used the profits to construct the capital, Ordu-Baliq, and another city further up the Selenga River
The Selenga or Selenge ( ; bua, Сэлэнгэ гол / Сэлэнгэ мүрэн, translit=Selenge gol / Selenge müren; russian: Селенга́, ) is a major river in Mongolia and Buryatia, Russia. Originating from its headwater tributarie ...
, Bai Baliq
BAI or Bai may refer to:
BAI
Organizations
*BAI Communications, telecommunications infrastructure company
*BAI (organization), professional organization for financial services in the United States
*Badminton Association of India, India's gove ...
. The new khagan then embarked on a series of campaigns to bring all the steppe peoples under his banner. During this time the Empire expanded rapidly and brought the Sekiz Oghuz, Kyrgyz, Karluks, Turgesh, Toquz Tatars, Chiks and the remnants of the Basmyls under Uyghur rule.
In 755 An Lushan instigated a rebellion
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
against the Tang dynasty and Emperor Suzong of Tang turned to Bayanchur Khan for assistance in 756. The khagan agreed and ordered his eldest son to provide military service to the Tang emperor. Approximately 4,000 Uyghur horsemen assisted Tang armies in retaking Chang'an and Luoyang in 757. After the battle at Luoyang the Uyghurs looted the city for three days and only stopped after large quantities of silk were extracted. For their aid, the Tang sent 20,000 rolls of silk and bestowed them with honorary titles. In addition the horse trade was fixed at 40 rolls of silk for every horse and Uyghurs were given "guest" status while staying in Tang China. The Tang and Uyghurs conducted an exchange marriage. Bayanchur Khan married Princess Ninguo while a Uyghur princess was married to a Tang prince. The Uyghur Khaganate exchanged princesses in marriage with Tang dynasty China in 756 to seal the alliance against An Lushan. The Uyghur Khagan Bayanchur Khan )''Heavenborn State Founding Wise Qaghan'', birth_name=Yàolúogě Mòyánchùo (藥羅葛磨延啜)
Mo-yun Chur (磨延啜) (b. 713 - d.759) or Eletmish Bilge Qaghan was second qaghan of Uyghur Khaganate. His Tang dynasty invested title was Yingwu ...
had his daughter Uyghur Princess Pijia (毗伽公主) married to Tang dynasty Chinese Prince Li Chengcai ( 李承采), Prince of Dunhuang (敦煌王李承采), son of Li Shouli, Prince of Bin. while the Tang dynasty Chinese princess Ningguo 寧國公主, daughter of Emperor Suzong, married Uyghur Khagan Bayanchur.
In 758, the Uyghurs turned their attention to the northern Yenisei Kyrgyz. Bayanchur Khan destroyed several of their trading outposts before slaughtering a Kyrgyz army and executing their Khan.
In 759 the Uyghurs attempted to assist the Tang in stamping out the rebels but failed. Bayanchur Khan died and his son Tengri Bögü succeeded him as Khagan ''Qutlugh Tarkhan sengün''.
In 762 Tengri Bögü planned to invade the Tang with 4,000 soldiers but after negotiations switched sides and assisted them in defeating the rebels at Luoyang. After the battle the Uyghurs looted the city. When the people fled to Buddhist temples for protection, the Uyghurs burnt them down, killing over 10,000. For their aid, the Tang was forced to pay 100,000 pieces of silk to get them to leave. During the campaign the khagan encountered Manichaean priests who converted him to Manichaeism. From then on the official religion of the Uyghur Khaganate became Manichaeism.
Decline

 In 779 Tengri Bögü planned to invade the Tang dynasty based on the advice of his Sogdian courtiers. However, Tengri Bögü's uncle,
In 779 Tengri Bögü planned to invade the Tang dynasty based on the advice of his Sogdian courtiers. However, Tengri Bögü's uncle, Tun Baga Tarkhan
)''Brave, Blessed, Wise Qaghan'', birth_name=Yàoluógé Dùnmòhè (藥羅葛顿莫賀), religion= Tengriism
, posthumous name=Bögü Bilge Tengri Qaghan ( otk, 𐰋𐰇𐰏𐰇∶𐰋𐰃𐰠𐰏𐰀∶𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃∶𐰴𐰍𐰣, label=none) ...
, opposed this plan and killed him and "nearly two thousand people from among the kaghan's family, his clique and the Sogdians." Tun Bagha Tarkhan ascended the throne, with the title ''Alp Qutlugh Bilge'' "Victorious, glorious, wise", and enforced a new set of laws, which he designed to secure the unity of the khaganate. During his reign Manichaeism was suppressed, but his successors restored it as the official religion.
In 780 a group of Uyghurs and Sogdians was killed while leaving Chang'an with tribute. Tun demanded 1,800,000 strings of cash in compensation and the Tang agreed to pay this amount in gold and silk.
In 789 Tun Bagha Tarkhan died and his son succeeded him as Külüg Qaghan )''Moon Godborn Glorious Wise Qaghan'', birth_name=Yàoluógé Duōluósī (藥羅葛多邏斯), religion=Tengriism, posthumous name=Külüg Bilge Qaghan — 5th leader of Uyghur Khaganate. His Tang invested title was Zhongzhen Qaghan (忠貞可汗) ...
. The Karluks took this opportunity to encroach on Uyghur territory and annexed Futu Valley.
In 790, the Uyghurs and Tang forces were defeated by Tibetan Empire at Tingzhou (Beshbalik
Beshbalik () is an ancient archaeological site, now located in Jimsar County, Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. The ancient city was initially called Beiting () or Ting Prefecture (), and was the headquarters of the Beiting Protec ...
). Külüg Qaghan died and his son, A-ch'o, succeeded him as Qutluq Bilge Qaghan
)''Blessed Wise Qaghan'', birth_name=Yàoluógé Āchuài (藥羅葛阿啜), religion=Tengriism, posthumous name=
Qutluq Bilge Qaghan (died 795 CE) was the sixth khagan of the Uyghur Khaganate and the last one from the Yaglakar clan. His Tang inves ...
.
In 791 the Tibetans attacked Lingzhou but were driven off by the Uyghurs, who presented captured prisoners and cattle to Emperor Dezong of Tang. The Tibetans and Karluks suffered another defeat against the Uyghurs at Beiting
The Beiting Protectorate-General, initially the Beiting Protectorate, was a Protectorate (imperial China), Chinese protectorate established by the Tang dynasty in 702 to control the Beiting region north of Gaochang in contemporary Xinjiang ...
. The captured Tibetan general Zan Rgyal sum was sent to Dezong.
In 792 the Uyghurs, led by Baoyi Qaghan
Baoyi Qaghan or Alp Bilge Qaghan was the eighth ruler of Uyghurs. His personal name is not known, therefore he is often referred as his Tang dynasty invested title Baoyi () which was invested on 22 June 808.
Reign
He was known as a zealous Manic ...
, defeated the Tibetans and Karluks, taking Gaochang. Not long after the Tibetans attacked Yushu, a fortified town 560 ''li'' east of Kucha. They were besieged by Baoyi there and destroyed.
In 795, Qutluq Bilge Qaghan died and the Yaghlakar dynasty came to an end. A general, Qutluq II, declared himself the new qaghan under the title ''Ay Tängridä ülüg bulmïsh alp qutlugh ulugh bilgä qaghan'' "Greatly born in moon heaven, victorious, glorious, great and wise qaghan", founding a new dynasty, the Ädiz ().
In 803, the Uyghurs captured Qocho.
In 808, Qutluq II died and his son, Baoyi, succeeded him. In the same year the Uyghurs seized Liang Province
Liang Province or Liangzhou () was a province in the northwest of ancient China, in the approximate location of the modern-day province of Gansu. It was bordered in the east by Sili Province.
History
Establishment
The province was first con ...
from the Tibetans.
In 816 a Tibetan raid reached within two days' journey of the Uyghur capital, Ordu-Baliq.
In 821, Baoyi Qaghan died and his son Chongde
Tongxiang City () is a county-level city, part of Jiaxing, in northern Zhejiang Province, China, bordering Jiangsu province to the north. It had a population of 1,029,754 as of the 2020 census even though its built-up (''or metro'') area is sm ...
succeeded him. Chongde was considered the last great khagan of the Uyghur Khaganate and bore the title ''Kün tengride ülüg bulmïsh alp küchlüg bilge'' "Greatly born in sun heaven, victorious, strong and wise". His achievements included improved trade up with the region of Sogdia
Sogdia (Sogdian language, Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also ...
, and on the battlefield he repulsed a force of invading Tibetans in 821. After defeating the Tibetan and Karluk force, the Uyghurs entered the Principality of Ushrusana and plundered the region.
 In 822, the Uyghurs sent troops to help the Tang in quelling rebels. The Tang refused the offer but had to pay them 70,000 pieces of silk to go home.
In 823, the Tibetan Empire waged war on the Uyghurs.
In 824, Chongde died and was succeeded by a brother, Qasar.
In 832, Qasar was murdered. He was succeeded by the son of Chongde, Hu. In the same year the Tibetan Empire ceased to make war on the Uyghurs.
In 822, the Uyghurs sent troops to help the Tang in quelling rebels. The Tang refused the offer but had to pay them 70,000 pieces of silk to go home.
In 823, the Tibetan Empire waged war on the Uyghurs.
In 824, Chongde died and was succeeded by a brother, Qasar.
In 832, Qasar was murdered. He was succeeded by the son of Chongde, Hu. In the same year the Tibetan Empire ceased to make war on the Uyghurs.
Fall
In 839 Hu was forced to commit suicide and a minister named Kürebir seized the throne with the help of 20,000Shatuo
The Shatuo, or the Shatuo Turks (; also transcribed as Sha-t'o, Sanskrit SartZuev Yu.A., ''"Horse Tamgas from Vassal Princedoms (Translation of Chinese composition "Tanghuyao" of 8-10th centuries)"'', Kazakh SSR Academy of Sciences, Alma-Ata, I ...
horsemen from Ordos. In the same year there was a famine and an epidemic, with a particularly severe winter that killed much of the livestock the Uyghur economy was based on.
In 840, one of nine Uyghur ministers, Kulug Bagha, rival of Kurebir, fled to the Yenisei Kyrgyz and invited them to invade from the north. With a force of around 80,000 horsemen, they sacked the Uyghur capital at Ordu-Baliq, razing it to the ground. The Kyrgyz captured the Uyghur Khagan, Kürebir (''Hesa/Qasar''), and promptly beheaded him. They went on to destroy other cities throughout the Uyghur empire, burning them to the ground. The Uyghurs fled in two groups. A 30,000-strong group led by the aristocrat Ormïzt sought refuge in Tang territory but Emperor Wuzong of Tang
Emperor Wuzong of Tang (July 2, 814 – April 22, 846), né Li Chan, later changed to Li Yan just before his death, was an emperor of the Tang Dynasty of China, reigning from 840 to 846. Emperor Wuzong is mainly known in modern times for the r ...
ordered the borders to be closed. The other group, 100,000 strong, led by Öge, son of Baoyi and the new khagan of the defeated Uyghur khaganate, also fled to Tang territory. However Öge demanded a Tang city for residence as well as the protection of Manichaeans and food. Wuzong found the demands unacceptable and refused. He granted Ormïzt asylum in return for the use of his troops against Öge. Two years later, Wuzong extended the order to Christianity, Zoroastrianism, and especially Buddhism.
The Yenisei Kyrgyz and Tang dynasty launched a successful war between 840-848 against the Uyghur Khaganate using their claimed familial ties as justification for an alliance.
In 841 Öge led the Uyghurs in an invasion of today Shaanxi.
In 843 a Tang army led by Shi Xiong
Shi Xiong () (died 848?''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 248.) was a Chinese military general and politician of the Chinese Tang Dynasty, most known for his participation in two campaigns during the reign of Emperor Wuzong — against the remnants of the ...
attacked the Uyghurs led by Öge and slaughtered 10,000 Uyghurs on February 13, 843 at "Kill the Barbarians" Mountain (Shahu). Öge was wounded. After the defeat of Öge, Wuzong ordered Ormïzt's troops to be broken up and dispersed among different units. Ormïzt refused to obey. His troops were massacred by general Liu Mian. With the defeat of the two major Uyghur groups, Wuzong saw his chance to get rid of the Manichaeans. He ordered Manichaean temples in several cities to be destroyed, the confiscation of their estates, and the execution of the clergy.
In 846 the penultimate Uyghur khagan, Öge, was killed after having spent his six-year reign fighting the Kyrgyz, the supporters of his rival Ormïzt, a brother of Kürebir, and Tang dynasty troops in Ordos and today Shaanxi. His brother, Enian Qaghan
Enian Qaghan (遏捻可汗) was the last effective ruler (''khagan'') of the Uyghur Khaganate.
Life
He was a younger brother of Wujie Qaghan and succeeded him in 846. He had 5000 Uyghur followers under his command and lived among Tatabi and de ...
, was decisively defeated by Tang forces in 847.
Successors
 The Yenisei Kyrgyz who replaced the Uyghur Khaganate were unsophisticated and had little interest in running the empire which they had destroyed. They held the territory from
The Yenisei Kyrgyz who replaced the Uyghur Khaganate were unsophisticated and had little interest in running the empire which they had destroyed. They held the territory from Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
in the east to the Irtysh River
The Irtysh ( otk, 𐰼𐱅𐰾:𐰇𐰏𐰕𐰏, Ertis ügüzüg, mn, Эрчис мөрөн, ''Erchis mörön'', "erchleh", "twirl"; russian: Иртыш; kk, Ертіс, Ertis, ; Chinese: 额尔齐斯河, pinyin: ''É'ěrqísī hé'', Xiao'erj ...
in the west and left Kulug Bagha, the Uyghur who defected to them, in charge of the Orkhon Valley. During the reign of Emperor Yizong of Tang (860–873), there were three recorded contacts between the Tang and Kyrgyz, but the nature of their relationship remains unclear. Tang policy makers argued that there was no point in building any relations with the Kyrgyz since the Uyghurs no longer threatened them. The Khitans seized the Orkhon Valley from the Kyrgyz in 890 and no further opposition from the Kyrgyz is recorded.
After the fall of the Uyghur Khaganate, the Uyghurs migrated south and established the Ganzhou Uyghur Kingdom
The Ganzhou Uyghur Kingdom (), also referred to as the Hexi Uyghurs, was established in 894 around Ganzhou in modern Zhangye. The kingdom lasted from 894 to 1036; during that time, many of Ganzhou's residents converted to Buddhism.
The Hexi Corri ...
in modern Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
and the Kingdom of Qocho near modern Turpan. The Uyghurs in Qocho converted to Buddhism, and, according to Mahmud al-Kashgari
Mahmud ibn Husayn ibn Muhammed al-Kashgari, ''Maḥmūd ibnu 'l-Ḥusayn ibn Muḥammad al-Kāšġarī'', , tr, Kaşgarlı Mahmûd, ug, مەھمۇد قەشقىرى, ''Mehmud Qeshqiri'' / Мәһмуд Қәшқири uz, Mahmud Qashg'ariy / М ...
, were "the strongest of the infidels", while the Ganzhou Uyghurs were conquered by the Tangut people in the 1030s. Even so, Kashgari praised contemporary Uyghurs as bilingual Turkophones whose Turkic dialect remained "pure" and "most correct" (just like dialects spoken by monolingual Yagmas, and Tuhsi
The Tuhsis were a Middle Turkic, medieval Turkic-speaking tribe, who lived alongside the Chigil, Yagma, and other tribes, in Zhetysu and today southern Kazakhstan. Tuhsi were also considered remnants of the Türgesh people. Turkologist Yury Zuev n ...
s); meanwhile, Kashgari derided other bilingual Turkophones ( Qay, Tatars, Basmyls, Chömüls, Yabakus, etc.), for incorporating foreign loanwords and "slurring" in their speeches In 1134, Qocho became a vassal of Yelü Dashi's nascent Qara Khitai empire. In 1209, the Qocho ruler Idiqut ( " Lord of happiness" ) Barchuk Art Tegin declared his allegiance to Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
, and the Uyghurs became important civil servants in the later Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
, which adapted the Old Uyghur alphabet
The Old Uyghur alphabet was a Turkic script used for writing the Old Uyghur, a variety of Old Turkic spoken in Turpan and Gansu that is the ancestor of the modern Western Yugur language. The term "Old Uyghur" used for this alphabet is misleading ...
as its official script. According to the ''New Book of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the So ...
'', a third group went to seek refuge among the Karluks.
The Karluks, together with other tribes such as the Chigils and Yagmas, later founded the Kara-Khanid Khanate (940–1212). Some historians associate the Karakhanids with the Uyghurs as the Yaghmas were linked to the Toquz Oghuz
The Toquz Oghuz ( otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰆𐰔:𐰆𐰍𐰔, Toquz Oγuz; ; "Turks of Nine Seok (clan), Bones") was a political alliance of nine Turkic languages, Turkic-speaking Tiele people, Tiele Turkic tribal confederations, tribes in Inner Asia, dur ...
. Sultan Satuq Bughra Khan, believed to be a Yagma from Artux
Artux, Artush ( ug, ئاتۇش شەھىرى; ky, ارتىش, Артыш, Artysh), and officially rendered as Atuş ( zh, s=阿图什市, p=Ātúshí Shì),The official spelling according to is a county-level city and the capital of the Kyrgyz au ...
, converted to Islam in 932 and seized control of Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
in 940, giving rise to the new dynasty, known as '' Karakhanids''.
Relationship with the Sogdians
In order to control trade along theSilk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
, the Uyghurs established a trading relationship with the Sogdian merchants who controlled some oases of Central Asia. As described above, the Uyghur adoption of Manichaeism was one aspect of this relationship—choosing Manichaeism over Buddhism may have been motivated by a desire to show independence from Tang influence. Not all Uyghurs supported conversion—an inscription at Ordu-Baliq states that Manichaens tried to divert people from their ancient shamanistic beliefs. A rather partisan account from a Uyghur-Manichean text of that period demonstrates the unbridled enthusiasm of the khaghan for Manichaeism:
As conversion was based on political and economic concerns regarding trade with the Sogdians, it was driven by the rulers and often encountered resistance in lower societal strata. Furthermore, as the khaghan's political power depended on his ability to provide economically for his subjects, "alliance with the Sogdians through adopting their religion was an important way of securing this objective." Both the Sogdians and the Uyghurs benefited enormously from this alliance. The Sogdians enabled the Uyghurs to trade in the Western Regions and exchange silk from China for other goods. For the Sogdians it provided their Chinese trading communities with Uyghur protection. The 5th and 6th centuries saw a large emigration of Sogdians to China. The Sogdians were main traders along the Silk Roads, and China was always their biggest market. Among the paper clothing found in the Astana cemetery near Turfan is a list of taxes paid on caravan trade in the Gaochang kingdom in the 620s. The text is incomplete, but out of the 35 commercial operations it lists, 29 involve a Sogdian trader. Ultimately both rulers of nomadic origin and sedentary states recognized the importance of merchants like the Sogdians and made alliances to further their own agendas in controlling the Silk Roads.
Karabalghasun
 The Uyghurs created an empire with clear Persian influences, particularly in areas of government. Soon after the empire was founded, they emulated sedentary states by establishing a permanent, settled capital, Karabalghasun ( Ordu-Baliq), built on the site of the former Göktürk imperial capital, northeast of the later Mongol capital, Karakorum. The city was a fully fortified commercial center, typical along the Silk Road, with concentric walls and lookout towers, stables, military and commercial stores, and administrative buildings. Certain areas of the town were allotted for trade and handcrafts, while in the center of the town were palaces and temples, including a monastery. The palace had fortified walls and two main gates, as well as moats filled with water and watchtowers.
The khaghan maintained his court there and decided the policies of the empire. With no fixed settlement, the
The Uyghurs created an empire with clear Persian influences, particularly in areas of government. Soon after the empire was founded, they emulated sedentary states by establishing a permanent, settled capital, Karabalghasun ( Ordu-Baliq), built on the site of the former Göktürk imperial capital, northeast of the later Mongol capital, Karakorum. The city was a fully fortified commercial center, typical along the Silk Road, with concentric walls and lookout towers, stables, military and commercial stores, and administrative buildings. Certain areas of the town were allotted for trade and handcrafts, while in the center of the town were palaces and temples, including a monastery. The palace had fortified walls and two main gates, as well as moats filled with water and watchtowers.
The khaghan maintained his court there and decided the policies of the empire. With no fixed settlement, the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 ...
had been limited in their acquisition of Chinese goods to what they could carry. As stated by Thomas Barfield, "the more goods a nomadic society acquired the less mobility it had, hence, at some point, one was more vulnerable trying to protect a rich treasure house by moving it than by fortifying it." By building a fixed city, the Uyghurs created a protected storage space for trade goods from China. They could hold a stable, fixed court, receive traders, and effectively cement their central role in Silk Road exchange. However, the vulnerability that came with having a fixed city was to be the downfall of the Uyghurs.
List of Uyghur Khagans
The following list is based on Yihong Pan's "Sui-Tang Foreign Policy: Four case studies". Menglig Qaghan (r. 848-?), ( personal name, Mang/Pang Te-qin 厖特勤), sovereign title: Ay Tengride Qut Bolmiş Alp Kutlugh Bilge Qaghan 溫祿登里邏汩沒密施合俱錄毗伽, Chinese title: Huaijian Qaghan 懷建可汗. Moved his political centre to the west.Images of Buddhist and Manichean Uyghurs
Images of Buddhist and Manichean Uyghurs from the Bezeklik caves and Mogao grottoes.See also
*List of Turkic dynasties and countries
The following is a list of dynasties, states or empires which are Turkic-speaking, of Turkic origins, or both. There are currently six recognised Turkic sovereign states. Additionally, there are six federal subjects of Russia in which a Turkic ...
* History of Turkic people
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to the ...
* History of the Uyghur people
* An Lushan Rebellion
* Ethnic groups in Chinese history
* Guo Ziyi
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *. Volume 13 of Brill's Inner Asian Library. * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*Jiu Tangshu ()Old Book of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
br>Chapter 195(in Chinese) *Xin Tangshu ()
New Book of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the So ...
, chapter 217,part 1
an
part 2
(in Chinese). Translation in English her
(most of part 1 and beginning of part 2).
Die chinesische Inschrift auf dem uigurischen Denkmal in Kara Balgassun (1896)
{{Empires Historical Turkic states Turkic peoples of Asia Former countries in Chinese history Former monarchies of Asia 744 establishments States and territories established in the 740s 847 disestablishments Khanates States and territories disestablished in the 9th century Former empires