Historical European martial arts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are
Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are
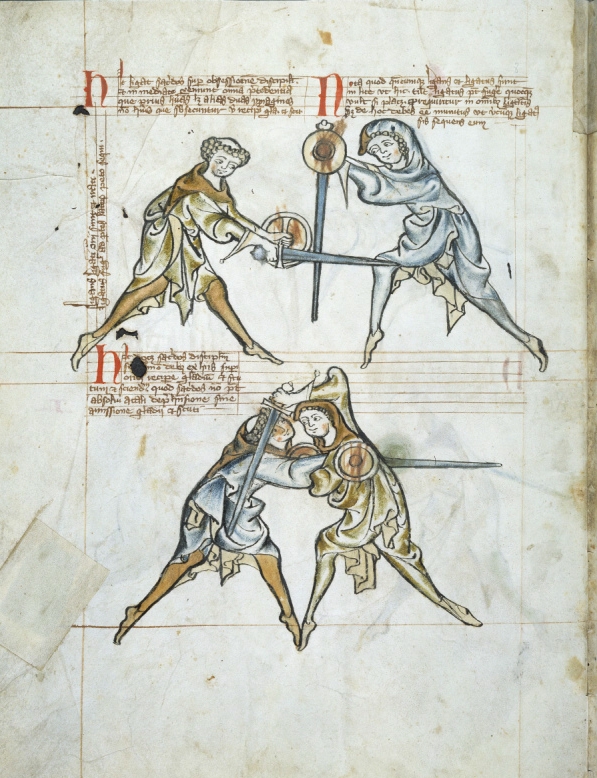 The first book about the fighting arts, ''Epitoma rei militaris'' '','' was written into
The first book about the fighting arts, ''Epitoma rei militaris'' '','' was written into
 Normally, several modes of combat were taught alongside one another, typically unarmed
Normally, several modes of combat were taught alongside one another, typically unarmed
 During the
During the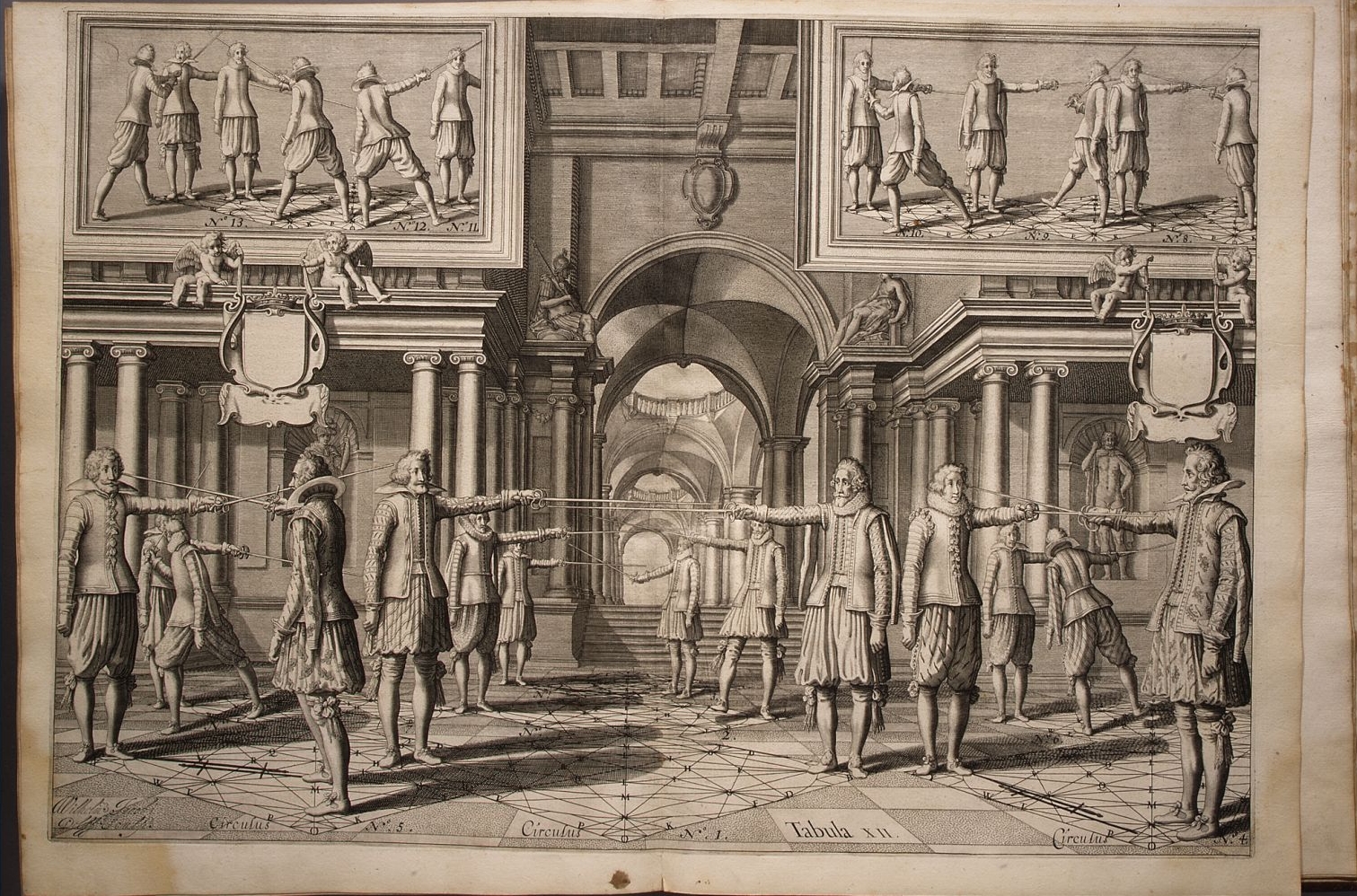  In Italy, 17th century swordsmanship is dominated by Salvator Fabris, whose ''De lo schermo overo scienza d'arme'' of 1606 exerted great influence not only in Italy but also in Germany, where it all but extinguished the native German traditions of fencing. Fabris was followed by Italian masters such as Nicoletto Giganti (1606), Ridolfo Capo Ferro (1610), Francesco Alfieri (1640), Francesco Antonio Marcelli (1686) and Bondi' di Mazo (1696).
The
In Italy, 17th century swordsmanship is dominated by Salvator Fabris, whose ''De lo schermo overo scienza d'arme'' of 1606 exerted great influence not only in Italy but also in Germany, where it all but extinguished the native German traditions of fencing. Fabris was followed by Italian masters such as Nicoletto Giganti (1606), Ridolfo Capo Ferro (1610), Francesco Alfieri (1640), Francesco Antonio Marcelli (1686) and Bondi' di Mazo (1696).
The
 In the 18th century Late Baroque /
In the 18th century Late Baroque /
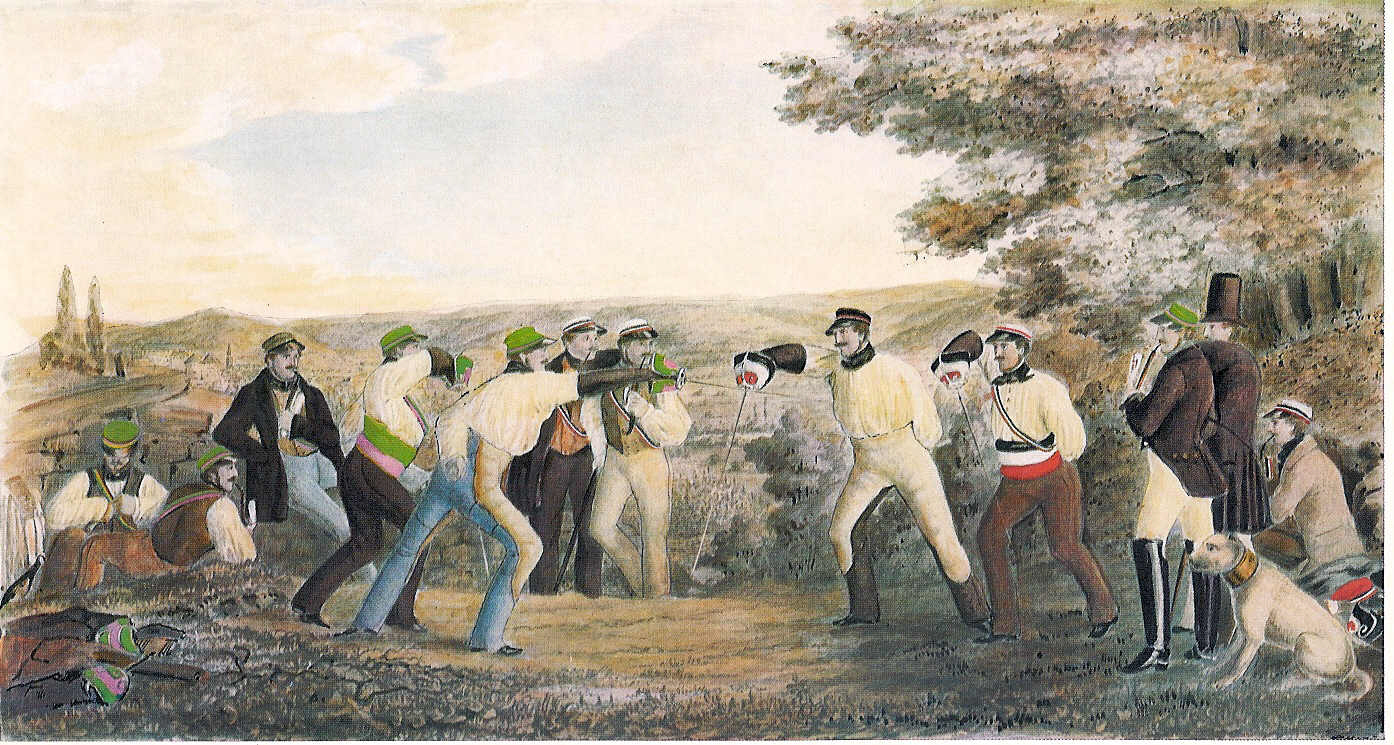
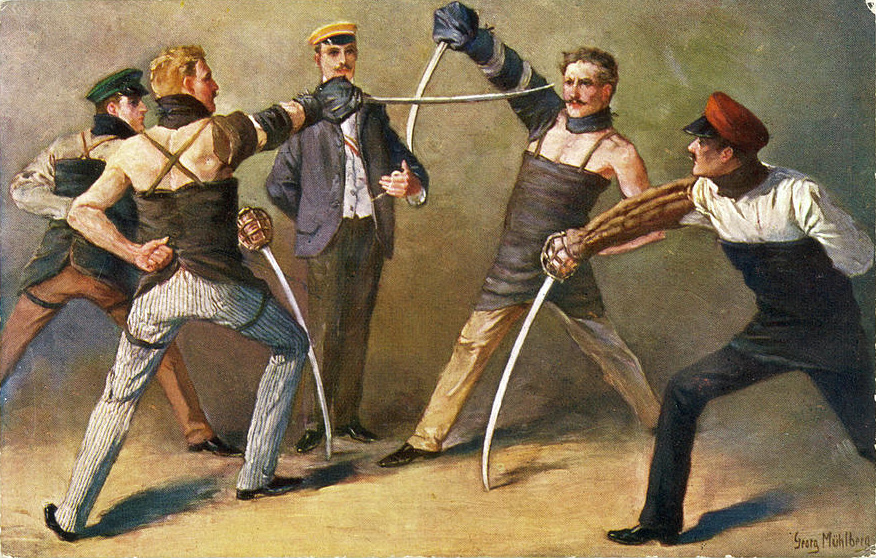
 In the course of the 19th century, Western martial arts became divided into modern
In the course of the 19th century, Western martial arts became divided into modern
 Attempts at reconstructing the discontinued traditions of European systems of combat began in the late 19th century, with a revival of interest in the
Attempts at reconstructing the discontinued traditions of European systems of combat began in the late 19th century, with a revival of interest in the
Western Martial arts Workshop
(WMAW) in the United States. In 2000, The Association for Renaissance Martial Arts (ARMA), then known as the "Historical Armed Combat Association" (HACA), hosted the Inaugural Swordplay Symposium International conference bringing together many of the then leading researchers from the US, Europe and Australia. Since 2003 ARMA has held the ARMA International Gathering every two to three years. The Fiore-oriented Schola Saint George has hosted a Medieval Swordsmanship Symposium annually in the United States since 2001. The annual Australian Historical Swordplay Convention, primarily a teaching event was hosted and attended by diverse Australian groups from 1999 to 2006. It was held in Brisbane in 1999 and 2006, Sydney in 2000 and 2004, Canberra in 2001 and 2005, the Gold Coast in 2003 and Melbourne in 2004. Since 2009, Swordplay, a tournament event has been run each year in Brisbane. Since 2002, Royal Arts Fencing Academy and the Rose & Gold foundation have hosted Ascalon Sword Festival, one of the largest HEMA tournaments in the United States. The event covers Olympic fencing, as well as the HEMA disciplines of longsword, rapier and dagger, military saber, and Harnisfechten. It was originally part of the larger Arnold Sports Festival as the Arnold Fencing Classic. FightCamp has been running since 2004 and it is organized by London-based
Acta Periodica Duellatorum
, a peer-reviewed journal of historical European martial arts research
Meyer Freifechter Guild
International Fencing Guild with a mission to educate people on the efficacy and art of Medieval & Renaissance martial arts.
by Joseph R. Svinth
Historical European Martial Arts: Studies & Sources.
On-line historical and literary magazine for Russian speaking and partly for English speaking readers.
HROARR
an online repository of articles and other resources on historical European martial arts and sports
Wiktenauer
the world's largest library of historical European martial arts treatises, currently complete up to the late 1500s
AEMMA - Academy of European Medieval Martial Arts
Official website of HEMA ITALIA - Societas Artis Gladii - Information Point of Italian Martial Arts
Academy of Medieval Fencing and Culture - HEMA in Russia
Fencing club "NoName" - HEMA in Russia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Historical European Martial Arts
 Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are
Historical European martial arts (HEMA) are martial arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; and the preser ...
of European origin, particularly using arts formerly practised, but having since died out or evolved into very different forms.
While there is limited surviving documentation of the martial arts of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
(such as Greek wrestling or gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
ial combat), surviving dedicated technical treatises or martial arts manuals date to the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
and the early modern period. For this reason, the focus of HEMA is ''de facto'' on the period of the half-millennium of ca. 1300 to 1800, with a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
and an Italian school flowering in the Late Middle Ages and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
(14th to 16th centuries), followed by Spanish, Portuguese, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, and Scottish schools of fencing in the modern period (17th and 18th centuries). Arts of the 19th century such as classical fencing, and even early hybrid styles such as Bartitsu
Bartitsu is an eclectic martial art and self-defence method originally developed in England in 1898–1902, combining elements of boxing, jujitsu, cane fighting and French kickboxing (savate). In 1903, it was immortalised (as "baritsu") by Sir Ar ...
, may also be included in the term HEMA in a wider sense, as may traditional or folkloristic styles attested in the 19th and early 20th centuries, including forms of folk wrestling
A folk wrestling style is any traditional style of wrestling, which may or may not be codified as a modern sport. Most cultures have developed regional forms of grappling.
Europe
Britain
Traditionally wrestling has two main centres in Great ...
and traditional stick-fighting methods.
The term Western martial arts (WMA) is sometimes used in the United States and in a wider sense including modern and traditional disciplines. During the Late Middle Ages, the longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximatel ...
had a position of honour among these disciplines, and sometimes historical European swordsmanship (HES) is used to refer to swordsmanship techniques specifically.
Modern reconstructions of some of these arts arose from the 1890s and have been practiced systematically since the 1990s.
History of European martial arts
Ancient history
 The first book about the fighting arts, ''Epitoma rei militaris'' '','' was written into
The first book about the fighting arts, ''Epitoma rei militaris'' '','' was written into Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
by a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
writer, Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also r ...
, who lived in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
between the fourth and fifth centuries. There are no other known martial arts manuals predating the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
(except for fragmentary instructions on Greek wrestling, see Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 466), although medieval literature (e.g., sagas of Icelanders
The sagas of Icelanders ( is, Íslendingasögur, ), also known as family sagas, are one genre of Icelandic sagas. They are prose narratives mostly based on historical events that mostly took place in Iceland in the ninth, tenth, and early el ...
, Eastern Roman Acritic songs, the '' Digenes Akritas'' and Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; german: Mittelhochdeutsch (Mhd.)) is the term for the form of German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German and into Early New High German. Hig ...
epics) record specific martial deeds and military knowledge; in addition, historical artwork depicts combat and weaponry (e.g., the Bayeux Tapestry, the ''Synopsis of Histories'' by John Skylitzes, the Morgan Bible). Some researchers have attempted to reconstruct older fighting methods such as Pankration
Pankration (; el, παγκράτιον) was a sporting event introduced into the Greek Olympic Games in 648 BC, which was an empty-hand submission sport with few rules. The athletes used boxing and wrestling techniques but also others, suc ...
, Eastern Roman hoplomachia, Viking swordsmanship and gladiatorial combat by reference to these sources and practical experimentation.
The Royal Armouries Ms. I.33
Royal Armouries Ms. I.33 is the earliest known surviving European ''fechtbuch'' (combat manual), and one of the oldest surviving martial arts manuals dealing with armed combat worldwide. I.33 is also known as the Walpurgis manuscript, after a fig ...
(also known as the "Walpurgis" or "Tower Fechtbuch"), dated to ca. 1300, is the oldest surviving Fechtbuch, teaching sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
and buckler combat.
Post-classical history
The central figure of late medieval martial arts, at least in Germany, is Johannes Liechtenauer. Though no manuscript written by him is known to have survived, his teachings were first recorded in the late fourteenth-centuryNürnberger Handschrift GNM 3227a
Codex 3227a of the in Nuremberg (also known as ''Hs. 3227a'', ''GNM 3227a'', ) is a manuscript of 169 folia, dated to the close of the 14th century. Its text is written in Latin and German. The German portions have been identified as in East ...
. From the 15th century into the 17th, numerous ''Fechtbücher'' (German "fencing-books") were produced, of which some several hundred are extant; a great many of these describe methods descended from Liechtenauer's. Liechtenauer's ''Zettel'' (recital) remains one of the most famous - if cryptic - pieces of European martial arts scholarship to this day, with several translations and interpretations of the poem being put into practice by fencers and scholars around the world.
 Normally, several modes of combat were taught alongside one another, typically unarmed
Normally, several modes of combat were taught alongside one another, typically unarmed grappling
Grappling, in hand-to-hand combat, describes sports that consist of gripping or seizing the opponent. Grappling is used at close range to gain a physical advantage over an opponent, either by imposing a position or causing injury. Grappling ...
(''Kampfringen
''Ringen'' is the German language term for grappling (wrestling).
In the context of the German school of historical European martial arts during the Late Middle Ages and the German Renaissance, ''Ringen'' refers to unarmed combat in general, inc ...
'' or ''abrazare''), dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a thrusting or stabbing weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or popular-use def ...
(''Degen'' or ''daga'', often of the rondel dagger), long knife
A knife ( : knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evid ...
( Messer) or Dusack
A dusack (also ''dusägge'' and variants, from Czech ''tesák'' "cleaver; hunting sword", lit. "fang") is a single-edged sword of the cutlass or sabre type, in use as a side arm in Germany and the Habsburg monarchy during the 16th to 17th cent ...
, half- or quarterstaff, pole weapon
A polearm or pole weapon is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, thereby extending the user's effective range and striking power. Polearms are predominantl ...
s, longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximatel ...
(''Langesschwert'', ''spada longa'', ''spadone''), and combat in plate armour
Plate armour is a historical type of personal body armour made from bronze, iron, or steel plates, culminating in the iconic suit of armour entirely encasing the wearer. Full plate steel armour developed in Europe during the Late Middle Ages, ...
(''Harnischfechten'' or ''armazare''), both on foot and on horseback. Some ''Fechtbücher'' have sections on dueling shields (''Stechschild''), special weapons used only in trial by combat
Trial by combat (also wager of battle, trial by battle or judicial duel) was a method of Germanic law to settle accusations in the absence of witnesses or a confession in which two parties in dispute fought in single combat; the winner of the ...
.
Important 15th-century German fencing masters include Sigmund Ringeck, Peter von Danzig (see Cod. 44 A 8), Hans Talhoffer and Paulus Kal, all of whom taught the teachings of Liechtenauer. From the late 15th century, there were "brotherhoods" of fencers (''Fechtbruderschaften''), most notably the Brotherhood of St. Mark
The Brotherhood of Saint Mark (german: Marxbrüder, Marx brothers) was the name of the most important organization of German swordsmen in the 16th century.
History
The brotherhood originated in the 15th century, but it is not known when exac ...
(attested 1474) and the Federfechter
The ''Freifechter'' or ''Federfechter'' (''Freifechter von der Feder zum Greifenfels'') were a fencing guild founded around 1570 in Prague. They were known, from early in their existence, to be skilled, rivalling the Marx brothers who for the best ...
.
An early Burgundian French treatise is '' Le jeu de la hache'' ("The Play of the Axe") of ca. 1400.
The earliest master to write in the Italian language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 8 ...
was Fiore dei Liberi, commissioned by the Marquis di Ferrara
Ferrara (, ; egl, Fràra ) is a city and ''comune'' in Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy, capital of the Province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream ...
. Between 1407 and 1410, he documented comprehensive fighting techniques in a treatise entitled ''Flos Duellatorum
The Flos Duellatorum is the name given to one of the manuscript versions of Fiore dei Liberi's illuminated manuscript fight book, written in 1410 (dated to 1409 in the old reckoning). There are five other surviving recensions, under the title F ...
'' covering grappling, dagger, arming sword, longsword, pole-weapons, armoured combat and mounted combat. The Italian school is continued by Filippo Vadi (1482–1487) and Pietro Monte (1492, Latin with Italian and Spanish terms).
Three early (before George Silver) natively English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
swordplay texts exist, all very obscure and of uncertain date; they are generally thought to belong to the latter half of the 15th century.
Early modern period
Renaissance
In the 16th century, compendia of older ''Fechtbücher'' techniques were produced, some of them printed, notably by Paulus Hector Mair (in the 1540s) and by Joachim Meyer (in the 1570s). The extent of Mair's writing is unmatched by any other German master, and is considered invaluable by contemporary scholars. In the 16th century, German fencing had developed sportive tendencies. The treatises of Paulus Hector Mair and Joachim Meyer derived from the teachings of the earlier centuries within the Liechtenauer tradition, but with new and distinctive characteristics. The printed ''fechtbuch'' ofJacob Sutor
Jacob Sutor (also spelled "Jakob Sutor") was a German fencing master who published a fighting manual in 1612, called the ''Neues Künstliches Fechtbuch''. The book was mostly an updated version (or outright plagiarism) of Joachim Meyer's work.
S ...
(1612) is one of the last in the German tradition.
In Italy, the 16th century is a period of big change. It opens with the two treatises of Bolognese masters Antonio Manciolino and Achille Marozzo, who describe a variation of the eclectic knightly arts of the previous century. From sword and buckler to sword and dagger, sword alone to two-handed sword, from polearms to wrestling (though absent in Manciolino), early 16th-century Italian fencing reflects the versatility that a martial artist of the time was supposed to achieve.
Towards the mid-century, however, polearms and companion weapons beside the dagger and the cape gradually begin to fade out of treatises. In 1553, Camillo Agrippa
Camillo Agrippa (died 1 January 1600) was a noted fencer, architect, engineer and mathematician of the Renaissance. He is considered to be one of the greatest fencing theorists of all time.
Biography
Though born in Milan, Agrippa lived and wor ...
is the first to define the prima, seconda, terza and quarta guards (or hand-positions), which would remain the mainstay of Italian fencing into the next century and beyond. From the late 16th century, Italian rapier fencing attained considerable popularity all over Europe, notably with the treatise by Salvator Fabris (1606).
* Antonio Manciolino (1531, Italian)
* Achille Marozzo (1536, Italian)
* Angelo Viggiani (1551, Italian)
* Camillo Agrippa
Camillo Agrippa (died 1 January 1600) was a noted fencer, architect, engineer and mathematician of the Renaissance. He is considered to be one of the greatest fencing theorists of all time.
Biography
Though born in Milan, Agrippa lived and wor ...
(1553, Italian)
* Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza (1569, Spanish)
* Giacomo di Grassi Giacomo is an Italian name. It is the Italian version of the Hebrew name Jacob.
People
* Giacomo (name), including a list of people with the name
Other uses
* Giacomo (horse)
Giacomo (foaled February 16, 2002 in Kentucky) is a champion American ...
(1570, Italian)
* Giovanni Dall'Agocchie
Giovanni Dall'Agocchie was an Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian langu ...
(1572, Italian)
* Henry de Sainct-Didier (1573, French)
* Angelo Viggiani (1575, Italian)
* Frederico Ghisliero (1587, Italian)
* Vincentio Saviolo
Fencing master Vincentio Saviolo (d. 1598/9), though Italian born and raised, authored one of the first books on fencing to be available in the English language.
Saviolo was born in Padua. He arrived in London at an unknown date and is first ...
(1595, Italian)
* Girolamo Cavalcabo Girolamo Cavalcabo (known in France as 'Hieronyme' or 'Hieronymus') was a Bolognese fencing master, teaching in Rome and later Paris in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries.
Egerton Castle suggests that his father was Zacharia Cavalc ...
(1597, Italian)
* George Silver (1599 (English)
Baroque style
 During the
During the Baroque period
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires includin ...
, wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat s ...
fell from favour among the upper classes, being now seen as unrefined and rustic. The fencing styles practice also needed to conform with the new ideals of elegance and harmony.
This ideology was taken to great lengths in Spain in particular, where ''La Verdadera Destreza
is the conventional term for the Spain, Spanish tradition of Historical fencing, fencing of the early modern period. The word literally translates to 'wiktionary:dexterity, dexterity' or 'skill, ability', and thus to 'the true skill' or 'the t ...
'' "the true art (of swordsmanship)" was now based on Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
and scientific principles, contrasting with the traditional "vulgar" approach to fencing inherited from the medieval period. Significant masters of Destreza included Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza ("the father of Destreza", d. 1600) and Luis Pacheco de Narváez (1600, 1632). Girard Thibault (1630) was a Dutch master influenced by these ideals.
The French school of fencing also moves away from its Italian roots, developing its own terminology, rules and systems of teaching. French masters of the Baroque period include Le Perche du Coudray (1635, 1676, teacher of Cyrano de Bergerac), Besnard (1653, teacher of Descartes), François Dancie (1623) and Philibert de la Touche (1670).
 In Italy, 17th century swordsmanship is dominated by Salvator Fabris, whose ''De lo schermo overo scienza d'arme'' of 1606 exerted great influence not only in Italy but also in Germany, where it all but extinguished the native German traditions of fencing. Fabris was followed by Italian masters such as Nicoletto Giganti (1606), Ridolfo Capo Ferro (1610), Francesco Alfieri (1640), Francesco Antonio Marcelli (1686) and Bondi' di Mazo (1696).
The
In Italy, 17th century swordsmanship is dominated by Salvator Fabris, whose ''De lo schermo overo scienza d'arme'' of 1606 exerted great influence not only in Italy but also in Germany, where it all but extinguished the native German traditions of fencing. Fabris was followed by Italian masters such as Nicoletto Giganti (1606), Ridolfo Capo Ferro (1610), Francesco Alfieri (1640), Francesco Antonio Marcelli (1686) and Bondi' di Mazo (1696).
The Elizabethan
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia (a female personific ...
and Jacobean eras produce English fencing writers, such as the Gentleman George Silver (1599) and the professional fencing master Joseph Swetnam
Joseph Swetnam (died 1621) was an English pamphleteer and fencing master. He is best known for a misogynistic pamphlet and an early English fencing treatise. Three defensive responses as pamphlets were made by Rachel Speght, Ester Sowernam and C ...
(1617). The English verb ''to fence'' is first attested in Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
's '' Merry Wives of Windsor'' (1597).
The French school of fencing originates in the 16th century, based on the Italian school, and develops into its classic form in the Baroque period.
Rococo style
 In the 18th century Late Baroque /
In the 18th century Late Baroque / Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
period, the French style of fencing with the small sword
The small sword or smallsword (also court sword, Gaelic: or claybeg, French: or dress sword) is a light one-handed sword designed for thrusting which evolved out of the longer and heavier rapier of the late Renaissance. The height of the small ...
and later with the foil (''fleuret''), in origin a training weapon for small sword fencing.
By the year 1715, the rapier had been largely replaced by the lighter small sword
The small sword or smallsword (also court sword, Gaelic: or claybeg, French: or dress sword) is a light one-handed sword designed for thrusting which evolved out of the longer and heavier rapier of the late Renaissance. The height of the small ...
throughout most of Europe, although treatments of the former continued to be included by authors such as Donald McBane (1728), P. J. F. Girard (1736) and Domenico Angelo (1763).
In this time, bare-knuckle boxing emerged as a popular sport in England and Ireland. The foremost pioneers of the sport of boxing were Englishmen James Figg and Jack Broughton.
In the course of the 18th century, the French school became the western European standard to the extent that Angelo, an Italian-born master teaching in England, published his ''L'Ecole des Armes'' in French in 1763. It was extremely successful and became a standard fencing manual over the following 50 years, throughout the Napoleonic period. Angelo's text was so influential that it was chosen to be included under the heading of "Éscrime" in the ''Encyclopédie
''Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''Encyclopédie'', was a general encyclopedia publis ...
'' of Diderot.
Late modern period
Development into modern sports

 In the course of the 19th century, Western martial arts became divided into modern
In the course of the 19th century, Western martial arts became divided into modern sports
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, ...
on one hand and applications that retain military significance on the other. In the latter category are the methods of close-quarter combat with the bayonet
A bayonet (from French ) is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped weapon designed to fit on the end of the muzzle of a rifle, musket or similar firearm, allowing it to be used as a spear-like weapon.Brayley, Martin, ''Bayonets: An Illustr ...
besides use of the sabre
A sabre (French: �sabʁ or saber in American English) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as t ...
and the lance by cavalrists and of the cutlass
A cutlass is a short, broad sabre or slashing sword, with a straight or slightly curved blade sharpened on the cutting edge, and a hilt often featuring a solid cupped or basket-shaped guard. It was a common naval weapon during the early Age of ...
by naval forces. The English longbow
The English longbow was a powerful medieval type of bow, about long. While it is debated whether it originated in England or in Wales from the Welsh bow, by the 14th century the longbow was being used by both the English and the Welsh as a ...
is another European weapon that is still used in the sport of archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In ...
.
Apart from the many styles of fencing, European combat sports of the 19th century include Boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, Savate in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and regional forms of wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat s ...
such as Cumberland and Westmorland Wrestling, Lancashire Wrestling, and Cornish Wrestling
Cornish wrestling ( kw, Omdowl Kernewek) is a form of wrestling that has been established in Cornwall for many centuries and possibly longer. It is similar to the Breton Gouren wrestling style. It is colloquially known as "wrasslin’"Philli ...
.
Fencing in the 19th century transformed into a pure sport. While duel
A duel is an arranged engagement in combat between two people, with matched weapons, in accordance with agreed-upon rules.
During the 17th and 18th centuries (and earlier), duels were mostly single combats fought with swords (the rapier and ...
s remained common among members of the aristocratic and officer classes, they became increasingly frowned upon in society during the course of the century, and such duels as were fought to the death were increasingly fought with pistols, not bladed weapons.
Stick fighting
Styles of stick fighting include walking-stick fighting (including Irish bata or shillelagh, Frenchla canne
Canne de combat is a French combat sport. As weapon, it uses a ''canne'' or cane (a kind of walking-stick) designed for fighting. ''Canne de combat'' was standardized in the 1970s for sporting competition by Maurice Sarry. The ''canne'' is very ...
and English singlestick) and Bartitsu
Bartitsu is an eclectic martial art and self-defence method originally developed in England in 1898–1902, combining elements of boxing, jujitsu, cane fighting and French kickboxing (savate). In 1903, it was immortalised (as "baritsu") by Sir Ar ...
(an early hybrid of Eastern and Western schools popularized at the turn of the 20th century).
Some existing forms of European stick fighting can be traced to direct teacher-student lineages from the 19th century. Notable examples include the methods of Scottish and British Armed Services singlestick, la canne
Canne de combat is a French combat sport. As weapon, it uses a ''canne'' or cane (a kind of walking-stick) designed for fighting. ''Canne de combat'' was standardized in the 1970s for sporting competition by Maurice Sarry. The ''canne'' is very ...
and Bâton français, Portuguese Jogo do Pau, Italian Paranza or Bastone Siciliano and some styles of Canarian Juego del Palo.
In the 19th century and early 20th century, the greatstick (pau/bâton/bastone) was employed by some Portuguese, French and Italian military academies as a method of exercise, recreation and as preparation for bayonet training.
A third category might be traditional "folk styles", mostly folk wrestling
A folk wrestling style is any traditional style of wrestling, which may or may not be codified as a modern sport. Most cultures have developed regional forms of grappling.
Europe
Britain
Traditionally wrestling has two main centres in Great ...
. Greco-Roman wrestling
Greco-Roman (American English), Graeco-Roman (British English), classic wrestling ( Euro English) or French wrestling (in Russia until 1948) is a style of wrestling that is practiced worldwide. Greco-Roman wrestling was included in the first mo ...
was a discipline at the first modern Olympic Games in 1896. Inclusion of Freestyle wrestling
Freestyle wrestling is a style of wrestling originated from Great Britain and the United States. Along with Greco-Roman, it is one of the two styles of wrestling contested in the Olympic Games. American high school and men's college wrestlin ...
followed in 1904.
19th Century Revival
 Attempts at reconstructing the discontinued traditions of European systems of combat began in the late 19th century, with a revival of interest in the
Attempts at reconstructing the discontinued traditions of European systems of combat began in the late 19th century, with a revival of interest in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. The movement was led in England by the soldier, writer, antiquarian and swordsman, Alfred Hutton.
Hutton learned fencing at the school founded by Domenico Angelo. In 1862, he organized in his regiment stationed in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
the Cameron Fencing Club, for which he prepared his first work, a 12-page booklet entitled ''Swordsmanship''.
After returning from India in 1865, Hutton focused on the study and revival of older fencing systems and schools. He began tutoring groups of students in the art of 'ancient swordplay' at a club attached to the London Rifle Brigade School of Arms in the 1880s. In 1889, Hutton published his most influential work ''Cold Steel: A Practical Treatise on the Sabre'', which presented the historical method of military sabre use on foot, combining the 18th century English backsword with modern Italian duelling sabre
A sabre (French: �sabʁ or saber in American English) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as t ...
.
Hutton's pioneering advocacy and practice of historical fencing included reconstructions of the fencing systems of several historical masters including George Silver and Achille Marozzo. He delivered numerous practical demonstrations with his colleague Egerton Castle of these systems during the 1890s, both in order to benefit various military charities and to encourage patronage of the contemporary methods of competitive fencing. Exhibitions were held at the Bath Club and a fund-raising event was arranged at Guy's Hospital
Guy's Hospital is an NHS hospital in the borough of Southwark in central London. It is part of Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and one of the institutions that comprise the King's Health Partners, an academic health science centre.
...
.
Among his many acolytes were Egerton Castle, Captain Carl Thimm, Colonel Cyril Matthey, Captain Percy Rolt, Captain Ernest George Stenson Cooke, Captain Frank Herbert Whittow, Esme Beringer, Sir Frederick and Walter Herries Pollock. Despite this revival and the interest that it received in late Victorian England, the practice died out soon after the death of Hutton in 1910. Interest in the physical application of historical fencing techniques remained largely dormant during the first half of the 20th century due to a number of factors.
Similar work, although more academic than practical in nature, occurred in other European countries. In Germany, Karl Wassmannsdorf conducted research on the German school and Gustav Hergsell reprinted three of Hans Talhoffer's manuals. In France there was the work of the Academie D'Armes circa 1880–1914. Italy's Jacopo Gelli and Francesco Novati
Francesco Novati (Cremona, 1859 - Sanremo, 1915) was an Italian historian and philologist.
Novati taught in the University of Palermo and Genoa, and in 1890 he became a professor of history and comparative literature at the Regia Accademia Scient ...
published a facsimile of the "Flos Duellatorum" of Fiore dei Liberi, and Giuseppe Cerri's book on the Bastone drew inspiration from the two-handed sword of Achille Marozzo. Baron Leguina's bibliography of Spanish swordsmanship is still a standard reference today.
20th Century
Starting in 1966, the Society for Creative Anachronism, an amateurmedieval reenactment
Medieval reenactment is a form of historical reenactment that focuses on re-enacting European history in the period from the fall of Rome to about the end of the 15th century. The second half of this period is often called the Middle Ages. This m ...
organization, renewed public interest in the practice of historic fighting arts, and has hosted numerous tournaments in which participants compete in simulated medieval and renaissance fighting styles using padded weapons. Dividing their focus between Heavy Armored Fighting, to simulate early medieval warfare, and adapted sport Rapier fencing, to reenact later renaissance styles, the SCA regularly holds large re-creation scenarios throughout the world. Their styles have been criticized by other groups as lacking historical authenticity, although a number of members of the group regularly engage in scholarship.
A number of researchers, principally academics with access to some of the sources, continued exploring the field of historical European martial arts from a largely academic perspective. In 1972, James Jackson published a book called ''Three Elizabethan Manuals of Fence''. This work reprinted the works of George Silver, Giacomo di Grassi Giacomo is an Italian name. It is the Italian version of the Hebrew name Jacob.
People
* Giacomo (name), including a list of people with the name
Other uses
* Giacomo (horse)
Giacomo (foaled February 16, 2002 in Kentucky) is a champion American ...
, and Vincentio Saviolo
Fencing master Vincentio Saviolo (d. 1598/9), though Italian born and raised, authored one of the first books on fencing to be available in the English language.
Saviolo was born in Padua. He arrived in London at an unknown date and is first ...
. In 1965, Martin Wierschin published a bibliography of German fencing manuals, along with a transcription of Codex Ringeck and a glossary of terms. In turn, this led to the publication of Hans-Peter Hils' seminal work on Johannes Liechtenauer in 1985.
During the mid-20th century, a small number of professional fight directors for theatre, film and television - notably including Arthur Wise. William Hobbs and John Waller, all of them British - studied historical combat treatises as inspiration for their fight choreography.
In the 1980s and 1990s, Patri J. Pugliese began making photocopies of historical treatises available to interested parties, greatly spurring on research. 1994 saw the rise of the Hammerterz Forum, a publication devoted entirely to the history of swordsmanship. During the late 1990s, translations and interpretations of historical sources began appearing in print as well as online.
The modern HEMA community
Since the 1990s, there have emerged flourishing Historical European Martial Arts communities in Europe, North America, Australia and the widerEnglish-speaking world
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the '' Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest languag ...
. These groups are engaged in attempting to reconstruct Historical European Martial Arts using various training methods. Although the focus generally is on the martial arts of Medieval and Renaissance masters, nineteenth and early twentieth century martial arts teachers are also studied and their systems are reconstructed, including Edward William Barton-Wright, the founder of Bartitsu
Bartitsu is an eclectic martial art and self-defence method originally developed in England in 1898–1902, combining elements of boxing, jujitsu, cane fighting and French kickboxing (savate). In 1903, it was immortalised (as "baritsu") by Sir Ar ...
; combat savate and stick fighting master Pierre Vigny
Pierre Vigny was a French Master-at-arms (born in Taninges, Haute-Savoie in 1866) who was active during the late 19th century and early 20th century. He specialised in French savate and in the art of stick fighting known as canne de combat, which ...
; London-based boxer and fencer Rowland George Allanson-Winn; French journalist and self-defence enthusiast Jean Joseph-Renaud; and British quarterstaff expert Thomas McCarthy.
Research and publications
Research into the rapier style of the innovative Roman, Neapolitan and Sicilian School of Fencing in Italy's 16th and 17th century was pioneered by M° Francesco Lodà, PhD, founder of Accademia Romana d'Armi in Rome, Italy. While research focused on the Marcelli family of fencing masters and their pupils in Rome and abroad (e.g. Mattei, Villardita, Marescalchi, De Greszy, Terracusa), through publication of papers and books on rapier fencing, attention was also paid to the influences of 16th century's masters active in Rome, such as Agrippa, Cavalcabò, Paternoster, or of the early 17th like D'Alessandri. Within Accademia Romana d'Armi historical research has continuously been carried out also on Fiore de' Liberi's longsword system, publishing the first Italian analysis and transcription of MS. Par. Lat. 11269, Radaelli's military saber and MS. I.33 sword and buckler, and more recently on Liechtenauer's tradition of fencing. Research into Italian sword forms and their influence on the French styles of the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries has been undertaken by Rob Runacres ofEngland
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
's Renaissance Sword Club.
Italian traditions are mainly investigated in Italy by Sala d'Arme Achille Marozzo, where you can find studies dedicated to the Bolognese tradition, to the Italian medieval tradition by Luca Cesari and Marco Rubboli, and to the Florentine tradition by Alessandro Battistini. Central and Southern Italian traditions are also investigated by Accademia Romana d'Armi, through the studies of Francesco Lodà on Spetioli (Marche) and Pagano (Neaples). Italian rapier instructors Tom Leoni (US) and Piermarco Terminiello (UK) have published annotated English translations of some of the most important rapier treatises of the 17th century, making this fencing style available to a worldwide audience. Leoni has also authored English translations of all of Fiore de' Liberi's Italian-language manuscripts, as well as Manciolino's ''Opera Nova'' and the third book of Viggiani's ''Lo Schermo''. Ken Mondschein, one of the few professional academics working in this field, translated Camillo Agrippa
Camillo Agrippa (died 1 January 1600) was a noted fencer, architect, engineer and mathematician of the Renaissance. He is considered to be one of the greatest fencing theorists of all time.
Biography
Though born in Milan, Agrippa lived and wor ...
's treatise of 1553 as well as the Paris manuscript of Fiore dei Liberi and written several academic articles.
The martial traditions of the Netherlands are researched by Reinier van Noort, who additionally focuses on German and French martial sources of the 17th century.
The ongoing study of the Germanic Langes Messer is most notably represented by the work of Jens Peter Kleinau Martin Enzi. Dierk Hagedorn has also published significant translations.
Leading researchers on Manuscript I.33's style of fence include Roland Warzecha, at the head of the Dimicator fencing school in Germany as well as Herbert Schmidt of Ars Gladii.
Other fencing traditions are represented in the scholarship of Stephen Hand and Paul Wagner of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
's Stoccata School of Defence, focusing on a range of systems, ranging from the works of George Silver and the techniques depicted in the Royal Armouries' Manuscript I.33 to the surviving evidence for how large shields were used, rapier according to Saviolo and Swetnam and Scottish Highland broadsword.
Christian Henry Tobler is one of the earliest researchers on the German school of swordsmanship.
Early publications also included books by Terry Brown, John Clements, David M. Cvet (self-published in 2001). In 2003 Stephen Hand edited a collection of scholarly papers titled SPADA, followed by a second volume in 2005. Since the mid 2000s the rate of publication of HEMA related texts has greatly increased. A list of current publications is included below.
Events
Since 1998, Sala d'Arme Achille Marozzo has organized an annual championship in Italy. Due to the excessive number of participants, in 2011 this competitive event was split in two separate events: military weapons (in autumn) and civil weapons (in spring), extending the organization in a larger coalition of Italian HEMA clubs. Civilian weapons include single sword, sword and cape, sword and dagger, and sword and Brocchiero (Buckler). The military weapons are the two-handed sword, spear, shield and spear, sword and targe, and sword and rotella. The civil weapons championship is one of the largest HEMA tournaments in the world. Since 1999 a number of HEMA groups have held thWestern Martial arts Workshop
(WMAW) in the United States. In 2000, The Association for Renaissance Martial Arts (ARMA), then known as the "Historical Armed Combat Association" (HACA), hosted the Inaugural Swordplay Symposium International conference bringing together many of the then leading researchers from the US, Europe and Australia. Since 2003 ARMA has held the ARMA International Gathering every two to three years. The Fiore-oriented Schola Saint George has hosted a Medieval Swordsmanship Symposium annually in the United States since 2001. The annual Australian Historical Swordplay Convention, primarily a teaching event was hosted and attended by diverse Australian groups from 1999 to 2006. It was held in Brisbane in 1999 and 2006, Sydney in 2000 and 2004, Canberra in 2001 and 2005, the Gold Coast in 2003 and Melbourne in 2004. Since 2009, Swordplay, a tournament event has been run each year in Brisbane. Since 2002, Royal Arts Fencing Academy and the Rose & Gold foundation have hosted Ascalon Sword Festival, one of the largest HEMA tournaments in the United States. The event covers Olympic fencing, as well as the HEMA disciplines of longsword, rapier and dagger, military saber, and Harnisfechten. It was originally part of the larger Arnold Sports Festival as the Arnold Fencing Classic. FightCamp has been running since 2004 and it is organized by London-based
Schola Gladiatoria
''Schola Gladiatoria'' (SG) is a historical European martial arts (HEMA) group based in Ealing, west London, Great Britain, founded in 2001 and led by Matt Easton (nom de guerre "Captain Context"). It provides organized instruction in the serious ...
.
Since 2006 a Swedish annual event called Swordfish has been taking place every year in Gothenburg
Gothenburg (; abbreviated Gbg; sv, Göteborg ) is the second-largest city in Sweden, fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and capital of the Västra Götaland County. It is situated by the Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has ...
, hosted by the Gothenburg Historical Fencing School (GHFS). It is currently one of the biggest HEMA tournaments in the world and is generally considered to be the "world cup of HEMA".
Since 2006 a Canadian event called Nordschlag has been taking place annually in Edmonton, Alberta
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anch ...
, hosted by The Academy of European Swordsmanship (The AES). It is Canada's first interprovincial tournament, and currently largest Canadian tournament, and has participants from all over Western Canada. The event also includes a full day workshop that features international and local instructors.
Since 2010, The annual Pacific Northwest HEMA Gathering has been hosted by multiple schools and clubs in the Pacific Northwest. The tournament includes longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximatel ...
, singlestick, glima, and one rotating weapon which is changed every year. The location of the event changes every year, and has been located at Fort Casey
Fort Casey State Park is located on Whidbey Island, in Island County, Washington state. It is a Washington state park and a historic district within the U.S. Ebey's Landing National Historical Reserve.
Admiralty Inlet was considered so strat ...
and Pacific Lutheran University.
Since 2011, a biannual event called the Vancouver International Swordplay Symposium, has been held in Vancouver, Canada. Hosted by Academie Duello, this event has brought instructors, authors and researchers from around the world for workshops, lectures and seminars.
Since 2013 an annual event, Fechtschule Edinburgh, an event focusing on 16th century Fencing has been hosted in Edinburgh, UK, by the Stork's Beak: School of Historical Swordplay. This Event has attracted many practitioners from around the world.
Since 2014, the Purpleheart Armoury Open has been held in Houston, TX. Formerly Fechtshule America, the Purpleheart Armoury Open is one of the largest and fastest growing HEMA competitions in North America.
In 2015 Australia's Stoccata School of Defence hosted a revival of the World Broadsword Championship in Sydney, Australia. This event, held throughout the late 19th century in England, the United States and Australia was last won by Parker in Sydney in 1891. Parker was never challenged. The 2015 event was won by Paul Wagner of Sydney, also the current holder of the Glorianna Cup, the broadsword championship of Britain. Lewis Hand of Hobart, Australia won the junior title. In the tradition of the 19th century title, the championship is held in the home town of the current Champion. As such the next championship will be held in Sydney in early 2017.
Jousting tournaments
A tournament is a competition involving at least three competitors, all participating in a sport or game. More specifically, the term may be used in either of two overlapping senses:
# One or more competitions held at a single venue and concentr ...
have become more common, with Jousters travelling Internationally to compete. These include a number organised by an expert in the Joust, Arne Koets, including The Grand Tournament of Sankt Wendel and The Grand Tournament at Schaffhausen
Another type of event that is becoming more common is the sparring camp/fight camp. These events are often more casual than tournaments, with events and competitions not typical of more formal tournaments, and an emphasis on classes and sparring.
Umbrella groups
In 2001, the Historical European Martial Arts Coalition (HEMAC) was created to act as an umbrella organization for groups inEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, with 4 sets of goals:
;Martial: reconstruct historical martial arts from primary sources; refine interpretations into viable, effective martial arts; test martial skills in a variety of competitive environments
;Research: locate, transcribe, translate primary sources; have a better understanding of the socio-historical context of the arts
;Outreach: promote and publicise HEMA; dispel misconceptions & stereotypes; educate the general public
;Community: establish a network of individuals and groups devoted to HEMA; foster close friendships and a sense of community among members; organise at least one annual HEMAC event. Since 2002, HEMAC has organized the annual ''International Historical European Martial arts Gathering'' in Dijon
Dijon (, , ) (dated)
* it, Digione
* la, Diviō or
* lmo, Digion is the prefecture of the Côte-d'Or department and of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in northeastern France. the commune had a population of 156,920.
The earlie ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
In 2003, the Australian Historical Swordplay Federation became the umbrella organization for groups in Australia.
In 2010, several dozen HEMA schools and clubs from around the world united under the umbrella of the HEMA Alliance, a US-based martial arts federation dedicated to developing and sharing the Historical European Martial Arts and assisting HEMA schools and instructors with such things as instructor certification, insurance, and equipment development.
In 2012, Ruth García Navarro and Mariana López Rodríguez started Esfinges, an umbrella affinity group for women in or interested in HEMA. The goal of Esfinges is to encourage more participation of underrepresented genders in HEMA, and to support those already practicing the discipline.
See also
* Arne Koets * Historical European Martial Arts in Australia * Combat reenactment * English Longsword School *Fencing
Fencing is a group of three related combat sports. The three disciplines in modern fencing are the foil, the épée, and the sabre (also ''saber''); winning points are made through the weapon's contact with an opponent. A fourth discipline, ...
* French school of fencing
* German school of swordsmanship
* Italian school of swordsmanship
* Laurentius Guild
* Martial arts manual
* Spanish school of swordsmanship
* Renaissance Sword Club
*Schola Gladiatoria
''Schola Gladiatoria'' (SG) is a historical European martial arts (HEMA) group based in Ealing, west London, Great Britain, founded in 2001 and led by Matt Easton (nom de guerre "Captain Context"). It provides organized instruction in the serious ...
* Swordsmanship
* Waster
*History of physical training and fitness
Physical training has been present in human societies throughout history. Usually, it was performed for the purposes of preparing for physical competition or display, improving physical, emotional and mental health, and looking attractive. It ...
References
Further reading
*Angelo, Domenico, The School of Fencing: With a General Explanation of the Principal Attitudes and Positions Peculiar to the Art, eds. Jared Kirby, Greenhill Books, 2005. * Anglo, Sydney. ''The Martial Arts of Renaissance Europe''. Yale University Press, 2000. * Blanes, Jerome. ''Nicolaes Petter, the Biography''. Lulu.com, 2014. * Brown, Terry. ''English Martial Arts''. Anglo-Saxon Books, 1997. * Butera, Matteo, Francesco Lanza, Jherek Swanger, and Reinier van Noort. ''The Spada Maestra of Bondì di Mazo''. Van Noort, Reinier, 2016. * Clements, John. ''Medieval Swordsmanship: Illustrated Methods and Techniques''. Paladin Press, 1998. * Clements, John. ''Renaissance Swordsmanship: The Illustrated Book of Rapiers and Cut-and-Thrust Swords and Their Use''. Paladin Press, 1997. *Clements, John et al. ''Masters of Medieval and Renaissance Martial Arts: Rediscovering The Western Combat Heritage''. Paladin Press, 2008. * Forgeng, Jeffrey L. ''The Art of Combat: A German Martial Arts Treatise of 1570''. Frontline Books, 2014. . * Gaugler, William. ''The History of Fencing: Foundations of Modern European Fencing''. Laureate Press, 1997. * Hand, Stephen. ''SPADA: An Anthology of Swordsmanship in Memory of Ewart Oakeshott''. Chivalry Bookshelf, 2003. * Hand, Stephen. ''SPADA 2: Anthology of Swordsmanship''. Chivalry Bookshelf, 2005. * Hand, Stephen. ''English Swordsmanship: The True Fight of George Silver, Vol. 1: Single Sword''. Chivalry Bookshelf,2006. * Heim, Hans and Alex Kiermayer. ''The Longsword of Johannes Liechtenauer'', Part I (DVD). Agilitas TV, 2005. * Kirby, Jared (ed.), ''Italian Rapier Combat'' - Ridolfo Capo Ferro, Greenhill Books, London, 2004. * Kirby, Jared (ed.), ''A Gentleman's Guide to Duelling: Of Honour and Honourable Quarrels.'' Frontline Books, 2014. * Knight, David James and Brian Hunt. ''Polearms of Paulus Hector Mair''. Paladin Press, 2008. * Leoni, Tommaso. ''The Art of Dueling''. The Chivalry Bookshelf, 2005. * Leoni, Tom. ''Venetian Rapier''. Freelance Academy Press, 2010. * Leoni, Tom. ''The Complete Renaissance Swordsman''. Freelance Academy Press, 2010. * Lindholm, David and Peter Svärd. ''Sigmund Ringeck's Knightly Art of the Longsword''. Paladin Press, 2003. * Lindholm, David and Peter Svärd. ''Knightly Arts of Combat - Sigmund Ringeck's Sword and Buckler Fighting, Wrestling, and Fighting in Armor''. Paladin Press, 2006. * Lindholm, David. ''Fighting with the Quarterstaff''. The Chivalry Bookshelf, 2006. * Mele, Gregory, ed. ''In the Service of Mars: Proceedings from the Western Martial Arts Workshop 1999–2009, Volume I''. Freelance Academy Press, 2010. * Price, Brian R., ed. ''Teaching & Interpreting Historical Swordsmanship''. The Chivalry Bookshelf, 2005. * Runacres, Rob. ''Treatise or Instruction for Fencing'', Lulu.com (2015), * Runacres, Rob and Thibault Ghesquiere. ''The Sword of Combat or The Use of Fighting With Weapons''. Lulu.com, 2014. * Runacres, Rob. Book of Lessons. Fallen Rook, 2017. * Schmidt, Herbert, Sword Fighting - An Introduction to handling a Long Sword, Schiffer Books, * Thompson, Christopher. ''Lannaireachd: Gaelic Swordsmanship''. BookSurge Publishing, 2001. * Tobler, Christian Henry. ''Secrets of German Medieval Swordsmanship''. The Chilvarly Bookshelf, 2001. * Tobler, Christian Henry. ''Fighting with the German Longsword''. The Chivalry Bookshelf, 2004. * Vail, Jason. ''Medieval and Renaissance Dagger Combat''. Paladin Press, 2006. * Van Noort, Reinier. ''Lessons on the thrust''. Fallen Rook Publishing, 2014, * Van Noort, Reinier. ''Of the Single Rapier''. Fallen Rook Publishing, 2015, * Van Noort, Reinier. ''Swordplay: an anonymous illustrated Dutch treatise for fencing with rapier, sword and polearms from 1595''. Freelance Academy Press, 2015, * Van Noort, Reinier and Antoine Coudre. ''True Principles of the Single Sword''. Fallen Rook Publishing, 2016, * Wagner, Paul. ''Master Of Defence: The Works of George Silver''. Paladin Press, 2008. * Wagner, Paul and Stephen Hand. ''Medieval Sword and Shield: The Combat System of Royal Armouries MS. I.33.'' Chivalry Bookshelf, 2004. * Windsor, Guy. ''The Swordsman's Companion: A Modern Training Manual for Medieval Longsword''. The Chivalry Bookshelf, 2004. * Zabinski, Grzegorz and Bartlomiej Walczak. ''The Codex Wallerstein: A Medieval Fighting Book from the Fifteenth Century on the Longsword, Falchion, Dagger, and Wrestling''. Paladin Press, 2002.External links
Acta Periodica Duellatorum
, a peer-reviewed journal of historical European martial arts research
Meyer Freifechter Guild
International Fencing Guild with a mission to educate people on the efficacy and art of Medieval & Renaissance martial arts.
by Joseph R. Svinth
Historical European Martial Arts: Studies & Sources.
On-line historical and literary magazine for Russian speaking and partly for English speaking readers.
HROARR
an online repository of articles and other resources on historical European martial arts and sports
Wiktenauer
the world's largest library of historical European martial arts treatises, currently complete up to the late 1500s
AEMMA - Academy of European Medieval Martial Arts
Official website of HEMA ITALIA - Societas Artis Gladii - Information Point of Italian Martial Arts
Academy of Medieval Fencing and Culture - HEMA in Russia
Fencing club "NoName" - HEMA in Russia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Historical European Martial Arts