Manitoba Köppen.svg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg , map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada , Label_map = yes , coordinates = , capital =
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg , map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada , Label_map = yes , coordinates = , capital =
Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
, largest_city = Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
, largest_metro = Winnipeg Region
, official_lang = English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, government_type = Parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
, Viceroy = Anita Neville
Anita Ruth Neville (born July 22, 1942) is a Canadian politician, who has served as the 26th lieutenant governor of Manitoba since 2022. She was elected to the House of Commons of Canada as a Liberal in the general election of 2000. She was ...
, ViceroyType = Lieutenant Governor
, Premier = Heather Stefanson
Heather Dorothy Stefanson (born May 11, 1970) is a Canadian politician who has served as the 24th premier of Manitoba since November 2, 2021. She is the leader of the Progressive Conservative Party of Manitoba and sits as a member of the Legi ...
, Legislature = Legislative Assembly of Manitoba
, area_rank = 8th
, area_total_km2 = 649950
, area_land_km2 = 548360
, area_water_km2 = 101593
, PercentWater = 15.6
, population_demonym = Manitoban
, population_rank = 5th
, population_total = 1342153
, population_as_of = 2021
File:2021 collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: the James Webb Space Telescope was launched in 2021; Protesters in Yangon, Myanmar following the coup d'état; A civil demonstration against the October 2021 coup in Sudan; Crowd shortly after t ...
, population_est = 1420228
, pop_est_as_of = Q4 2022
, pop_est_ref =
, DensityRank = 8th
, Density_km2 = 2.3
, GDP_year = 2015
, GDP_total = C$65.862 billion
, GDP_rank = 6th
, GDP_per_capita = C$50,820
, GDP_per_capita_rank = 9th
, AdmittanceOrder = 5th, with Northwest Territories
, AdmittanceDate = 15 July 1870
, HouseSeats = 14
, SenateSeats = 6
, timezone1 = Central
, utc_offset1 = −06:00
, timezone1_DST = Central DST
, utc_offset1_DST = −05:00
, PostalAbbreviation =
, PostalCodePrefix =
Manitoba ( ) is a province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on th ...
at the longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's fifth-most populous province, with a population of 1,342,153 as of 2021, of widely varied landscape, from arctic tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
and the Hudson Bay coastline in the north
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
to dense boreal forest
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruc ...
, large freshwater lakes, and prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
grassland in the central and southern regions.
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
have inhabited what is now Manitoba for thousands of years. In the early 17th century, British and French fur traders
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mo ...
began arriving in the area and establishing settlements. The Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, ...
secured control of the region in 1673 and created a territory named Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land t ...
, which was placed under the administration of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
. Rupert's Land, which included all of present-day Manitoba, grew and evolved from 1673 until 1869 with significant settlements of Indigenous and Métis people
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives ...
in the Red River Colony
The Red River Colony (or Selkirk Settlement), also known as Assinboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hudson's Bay ...
. In 1869, negotiations with the Government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown ...
for the creation of the province of Manitoba commenced. During the negotiations, several factors led to an armed uprising of the Métis people against the Government of Canada, a conflict known as the Red River Rebellion
The Red River Rebellion (french: Rébellion de la rivière Rouge), also known as the Red River Resistance, Red River uprising, or First Riel Rebellion, was the sequence of events that led up to the 1869 establishment of a provisional government by ...
. The resolution of the conflict and further negotiations led to Manitoba becoming the fifth province to join Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominion ...
, when the Parliament of Canada passed the ''Manitoba Act
The ''Manitoba Act, 1870'' (french: link=no, Loi de 1870 sur le Manitoba)Originally entitled (until renamed in 1982) ''An Act to amend and continue the Act 32 and 33 Victoria, chapter 3; and to establish and provide for the Government of the Pro ...
'' on July 15, 1870.
Manitoba's capital and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
is Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
, the seventh most populous municipality in Canada. Winnipeg is the seat of government, home to the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba
The Legislative Assembly of Manitoba (french: Assemblée législative du Manitoba) is the deliberative assembly of the Manitoba Legislature in the Canadian province of Manitoba. Fifty-seven members are elected to this assembly at provincial gen ...
and the Provincial Court
The provincial and territorial courts in Canada are local trial "inferior" or "lower" courts of limited jurisdiction established in each of the provinces and territories of Canada. These courts typically hear criminal, civil (or “ small claims” ...
. Four of the province's five universities, all four of its professional sports teams, and most of its cultural activities (including Festival du Voyageur
The Festival du Voyageur is an annual 10-day winter festival that takes place in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The event is held during each February in Winnipeg's French quarter, Saint-Boniface, and is western Canada's largest winter festival. It ...
and Folklorama) are located in Winnipeg. The city has train and bus stations and an international airport; a Canadian Forces base, CFB Winnipeg, operates from the airport and is the regional headquarters of the North American Aerospace Defense Command
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection ...
.
Toponymy
The name ''Manitoba'' possibly derives from either Cree ''manitou-wapow'' orOjibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
''manidoobaa'', both meaning "straits of Manitou
Manitou (), akin to the Iroquois '' orenda'', is the spiritual and fundamental life force among Algonquian groups in the Native American theology. It is omnipresent and manifests everywhere: organisms, the environment, events, etc. ''Aasha ...
, the Great Spirit." Alternatively, it may be from the Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
"minnetoba," meaning "Lake of the Prairie" (the lake was known to French explorers as ''Lac des Prairies''). The name was chosen by Thomas Spence for the new republic he proposed for the area south of the lake. Métis leader Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its first ...
preferred the name over the proposed alternative of "Assiniboia." It was accepted in Ottawa under the ''Manitoba Act
The ''Manitoba Act, 1870'' (french: link=no, Loi de 1870 sur le Manitoba)Originally entitled (until renamed in 1982) ''An Act to amend and continue the Act 32 and 33 Victoria, chapter 3; and to establish and provide for the Government of the Pro ...
'' of 1870.
History
Indigenous societies and European settlement
Modern-day Manitoba was inhabited by theFirst Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
people shortly after the last ice age glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s retreated in the southwest about 10,000 years ago; the first exposed land was the Turtle Mountain area. The Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
, Cree, Dene
The Dene people () are an indigenous group of First Nations who inhabit the northern boreal and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages. ''Dene'' is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term "Dene" ha ...
, Sioux, Mandan
The Mandan are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains who have lived for centuries primarily in what is now North Dakota. They are enrolled in the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation. About half of the Mandan still re ...
, and Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
peoples founded settlements, and other tribes entered the area to trade. In Northern Manitoba, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
was mined to make arrowhead
An arrowhead or point is the usually sharpened and hardened tip of an arrow, which contributes a majority of the projectile mass and is responsible for impacting and penetrating a target, as well as to fulfill some special purposes such as sign ...
s. The first farming in Manitoba was along the Red River, where corn and other seed crops were planted before contact with Europeans.
In 1611, Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
was one of the first Europeans to sail into what is now known as Hudson Bay, where he was abandoned by his crew. Thomas Button travelled this area in 1612 in an unsuccessful attempt to find and rescue Hudson. When the British ship '' Nonsuch'' sailed into Hudson Bay in 1668–1669, she became the first trading vessel to reach the area; that voyage led to the formation of the Hudson's Bay Company, to which the British government gave absolute control of the entire Hudson Bay watershed. This watershed was named Rupert's Land, after Prince Rupert, who helped to subsidize the Hudson's Bay Company. York Factory
York Factory was a settlement and Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) factory (trading post) located on the southwestern shore of Hudson Bay in northeastern Manitoba, Canada, at the mouth of the Hayes River, approximately south-southeast of Churchill. ...
was founded in 1684 after the original fort of the Hudson's Bay Company, Fort Nelson (built in 1682), was destroyed by rival French traders.
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (17 November 1685 – 5 December 1749) was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader, and explorer. In the 1730s, he and his four sons explored the area west of Lake Superior and ...
, visited the Red River Valley in the 1730s to help open the area for French exploration and trade. As French explorers entered the area, a Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
-based company, the North West Company, began trading with the local Indigenous people. Both the North West Company and the Hudson's Bay Company built fur-trading forts; the two companies competed in southern Manitoba, occasionally resulting in violence, until they merged in 1821 (the Hudson's Bay Company Archives
Archives of Manitoba (), formerly the Provincial Archives of Manitoba () until 2003,
 Rupert's Land was ceded to Canada by the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869 and incorporated into the Northwest Territories; a lack of attention to Métis concerns caused Métis leader Louis Riel to establish a local provisional government which formed into the Convention of Forty and the subsequent elected
Rupert's Land was ceded to Canada by the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869 and incorporated into the Northwest Territories; a lack of attention to Métis concerns caused Métis leader Louis Riel to establish a local provisional government which formed into the Convention of Forty and the subsequent elected
 By 1911,
By 1911,  Winnipeg was inundated during the
Winnipeg was inundated during the
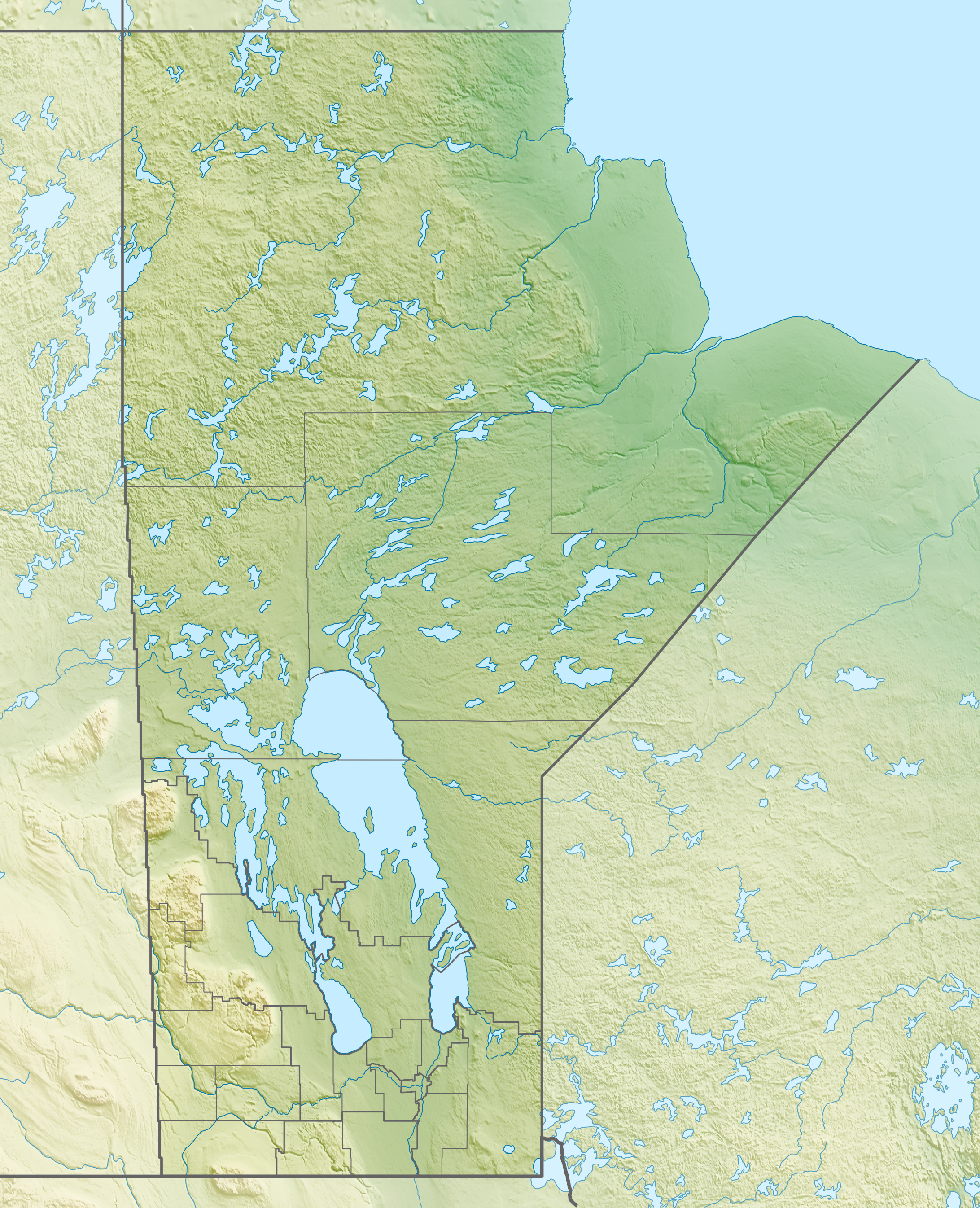 Manitoba is bordered by the provinces of
Manitoba is bordered by the provinces of
 Manitoba has an extreme continental climate. Temperatures and precipitation generally decrease from south to north and increase from east to west. Manitoba is far from the moderating influences of mountain ranges or large bodies of water. Because of the generally flat landscape, it is exposed to cold Arctic high-pressure air masses from the northwest during January and February. In the summer, air masses sometimes come out of the
Manitoba has an extreme continental climate. Temperatures and precipitation generally decrease from south to north and increase from east to west. Manitoba is far from the moderating influences of mountain ranges or large bodies of water. Because of the generally flat landscape, it is exposed to cold Arctic high-pressure air masses from the northwest during January and February. In the summer, air masses sometimes come out of the  The province's northern sections (including the city of
The province's northern sections (including the city of
 Manitoba natural communities may be grouped within five ecozones:
Manitoba natural communities may be grouped within five ecozones:
 Manitoba's early economy depended on mobility and living off the land. Indigenous Nations (Cree, Ojibwa, Dene, Sioux and Assiniboine) followed herds of bison and congregated to trade among themselves at key meeting places throughout the province. After the arrival of the first European traders in the 17th century, the economy centred on the trade of beaver pelts and other furs. Diversification of the economy came when Lord Selkirk brought the first agricultural settlers in 1811, though the triumph of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) over its competitors ensured the primacy of the fur trade over widespread agricultural colonization.
HBC control of Rupert's Land ended in 1868; when Manitoba became a province in 1870, all land became the property of the federal government, with homesteads granted to settlers for farming. Transcontinental railways were constructed to simplify trade. Manitoba's economy depended mainly on farming, which persisted until drought and the Great Depression led to further diversification.
Manitoba's early economy depended on mobility and living off the land. Indigenous Nations (Cree, Ojibwa, Dene, Sioux and Assiniboine) followed herds of bison and congregated to trade among themselves at key meeting places throughout the province. After the arrival of the first European traders in the 17th century, the economy centred on the trade of beaver pelts and other furs. Diversification of the economy came when Lord Selkirk brought the first agricultural settlers in 1811, though the triumph of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) over its competitors ensured the primacy of the fur trade over widespread agricultural colonization.
HBC control of Rupert's Land ended in 1868; when Manitoba became a province in 1870, all land became the property of the federal government, with homesteads granted to settlers for farming. Transcontinental railways were constructed to simplify trade. Manitoba's economy depended mainly on farming, which persisted until drought and the Great Depression led to further diversification.
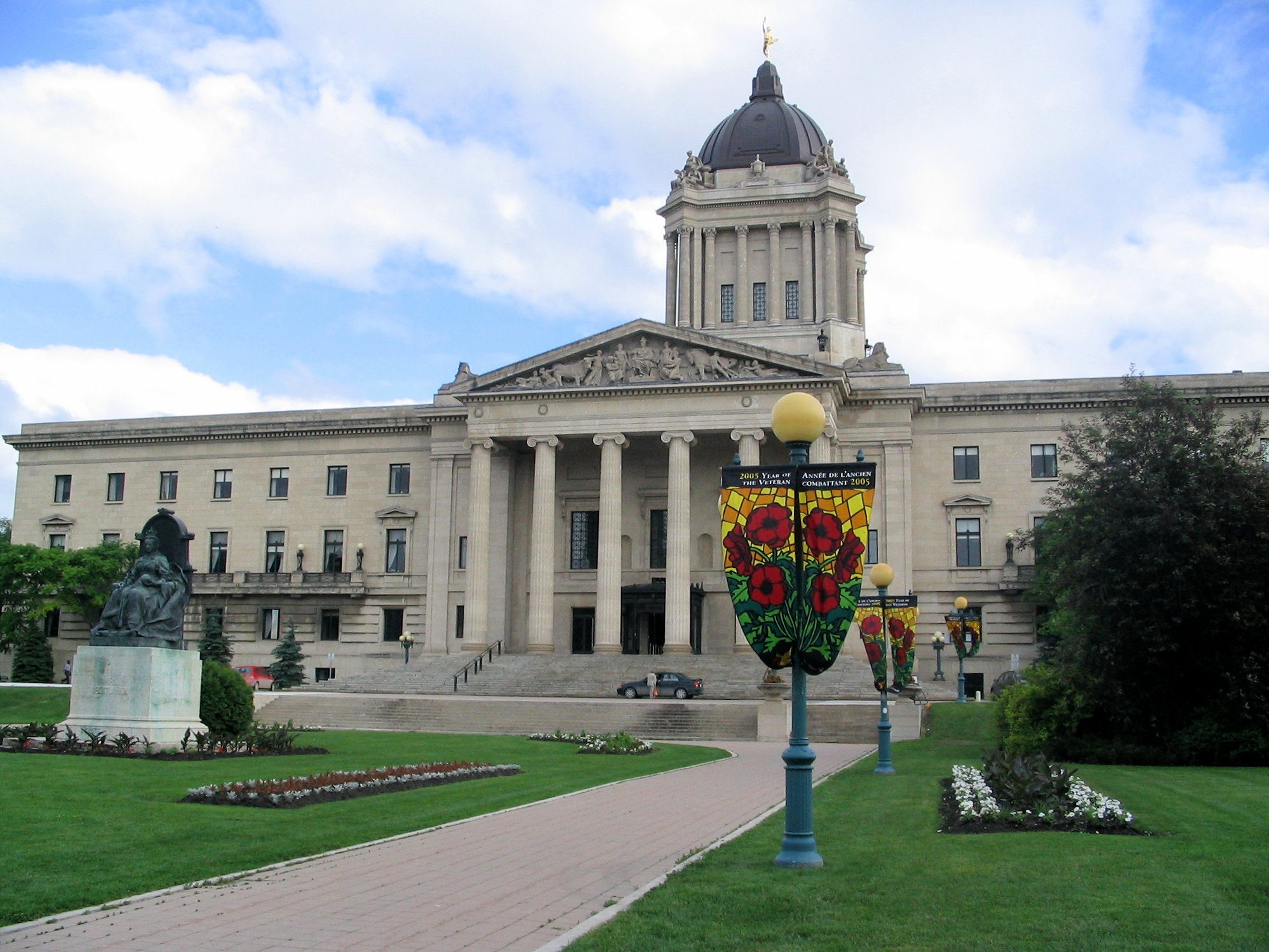 After the control of Rupert's Land was passed from Great Britain to the Government of Canada in 1869, Manitoba attained full-fledged rights and responsibilities of self-government as the first Canadian province carved out of the Northwest Territories. The
After the control of Rupert's Land was passed from Great Britain to the Government of Canada in 1869, Manitoba attained full-fledged rights and responsibilities of self-government as the first Canadian province carved out of the Northwest Territories. The
 Manitoba has two Class I railroad, Class I railways: Canadian National Railway (CN) and Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). Winnipeg is centrally located on the main lines of both carriers, and both maintain large inter-modal terminals in the city. Via Rail offers transcontinental and Northern Manitoba passenger service from Union Station (Winnipeg), Winnipeg's Union Station. Numerous small regional and short-line railways also run trains within Manitoba: the Hudson Bay Railway (1997), Hudson Bay Railway, the Southern Manitoba Railway, Burlington Northern Santa Fe Manitoba, Greater Winnipeg Water District Railway, and Central Manitoba Railway.
Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport, Manitoba's largest List of airports in Manitoba, airport, is one of only a few 24-hour unrestricted airports in Canada and is part of the National Airports System. A new, larger terminal opened in October 2011. It is the seventh List of the busiest airports in Canada, busiest airport in Canada by passenger traffic, serving 4,484,343 passengers in 2018, and the 11th busiest airport by aircraft movements. The airport handles approximately of cargo annually, making it the third largest cargo airport in the country. Winnipeg is a major sorting facility for both FedEx and Purolator Courier, Purolator, and receives daily trans-border service from United Parcel Service, UPS.
The Port of Churchill is the only Arctic deep-water port in Canada. It is nautically closer to ports in Northern Europe and Russia than any other port in Canada. It has four deep-sea berths for the loading and unloading of grain, general cargo and tanker vessels. The port is served by the Hudson Bay Railway. The port and railway came under complete community and Indigenous ownership in 2021, after AGT Food and Ingredients and Fairfax Financial transferred their shares in Arctic Gateway to OneNorth – a consortium of community and Indigenous partners which owned the other fifty percent of Arctic Gateway's shares.
Manitoba has two Class I railroad, Class I railways: Canadian National Railway (CN) and Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). Winnipeg is centrally located on the main lines of both carriers, and both maintain large inter-modal terminals in the city. Via Rail offers transcontinental and Northern Manitoba passenger service from Union Station (Winnipeg), Winnipeg's Union Station. Numerous small regional and short-line railways also run trains within Manitoba: the Hudson Bay Railway (1997), Hudson Bay Railway, the Southern Manitoba Railway, Burlington Northern Santa Fe Manitoba, Greater Winnipeg Water District Railway, and Central Manitoba Railway.
Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport, Manitoba's largest List of airports in Manitoba, airport, is one of only a few 24-hour unrestricted airports in Canada and is part of the National Airports System. A new, larger terminal opened in October 2011. It is the seventh List of the busiest airports in Canada, busiest airport in Canada by passenger traffic, serving 4,484,343 passengers in 2018, and the 11th busiest airport by aircraft movements. The airport handles approximately of cargo annually, making it the third largest cargo airport in the country. Winnipeg is a major sorting facility for both FedEx and Purolator Courier, Purolator, and receives daily trans-border service from United Parcel Service, UPS.
The Port of Churchill is the only Arctic deep-water port in Canada. It is nautically closer to ports in Northern Europe and Russia than any other port in Canada. It has four deep-sea berths for the loading and unloading of grain, general cargo and tanker vessels. The port is served by the Hudson Bay Railway. The port and railway came under complete community and Indigenous ownership in 2021, after AGT Food and Ingredients and Fairfax Financial transferred their shares in Arctic Gateway to OneNorth – a consortium of community and Indigenous partners which owned the other fifty percent of Arctic Gateway's shares.
 The Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport (Manitoba), Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport is responsible for promoting and, to some extent, financing Manitoban culture. Manitoba is the birthplace of the Red River Jig, a combination of Indigenous pow-wows and European Reel (dance), reels popular among early settlers. Manitoba's traditional music has strong roots in Métis and First Nations culture, in particular the old-time music, old-time fiddle, fiddling of the Métis. Manitoba's cultural scene also incorporates classical European traditions. The Winnipeg-based Royal Winnipeg Ballet (RWB), is Canada's oldest ballet and North America's longest continuously operating ballet company; it was granted its royal title in 1953 under Queen Elizabeth II. The Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra (WSO) performs classical music and new compositions at the Centennial Concert Hall. Manitoba Opera, founded in 1969, also performs out of the Centennial Concert Hall.
The Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport (Manitoba), Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport is responsible for promoting and, to some extent, financing Manitoban culture. Manitoba is the birthplace of the Red River Jig, a combination of Indigenous pow-wows and European Reel (dance), reels popular among early settlers. Manitoba's traditional music has strong roots in Métis and First Nations culture, in particular the old-time music, old-time fiddle, fiddling of the Métis. Manitoba's cultural scene also incorporates classical European traditions. The Winnipeg-based Royal Winnipeg Ballet (RWB), is Canada's oldest ballet and North America's longest continuously operating ballet company; it was granted its royal title in 1953 under Queen Elizabeth II. The Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra (WSO) performs classical music and new compositions at the Centennial Concert Hall. Manitoba Opera, founded in 1969, also performs out of the Centennial Concert Hall.
 Le Cercle Molière (founded 1925) is the oldest French-language theatre in Canada, and Royal Manitoba Theatre Centre (founded 1958) is Canada's oldest English-language regional theatre. Manitoba Theatre for Young People was the first English-language theatre to win the Canadian Institute of the Arts for Young Audiences Award, and offers plays for children and teenagers as well as a theatre school. The Winnipeg Art Gallery (WAG), Manitoba's largest art gallery and the sixth largest in the country, hosts an art school for children; the WAG's permanent collection comprises over twenty thousand works, with a particular emphasis on Manitoban and Canadian art.
The 1960s pop group The Guess Who was formed in Manitoba, and later became the first Canadian band to have a No. 1 hit in the United States; Guess Who guitarist Randy Bachman later created Bachman–Turner Overdrive (BTO) with fellow Winnipeg-based musician Fred Turner (musician), Fred Turner. Fellow rocker Neil Young, grew up in Manitoba, and later played in Buffalo Springfield, and Crosby, Stills, Nash & Young. Folk rock band Crash Test Dummies formed in the late 1980s in Winnipeg and were the 1992 Juno Awards Group of the Year.
Several prominent Canadian films were produced in Manitoba, such as ''The Stone Angel (film), The Stone Angel'', based on the Margaret Laurence book of the The Stone Angel, same title, ''The Saddest Music in the World'', ''Foodland (film), Foodland'', ''For Angela'', and ''My Winnipeg''. Major films shot in Manitoba include ''The Assassination of Jesse James by the Coward Robert Ford'' and ''Capote (film), Capote'', both of which received Academy Award nominations. ''Falcon Beach'', an internationally broadcast television drama, was filmed at Winnipeg Beach, Manitoba.
Manitoba has a strong literary tradition. Bertram Brooker won the first-ever Governor General's Awards, Governor General's Award for Fiction in 1936. Cartoonist Lynn Johnston, author of the comic strip ''For Better or For Worse'', was a finalist for a 1994 Pulitzer Prize and inducted into the Canadian Cartoonist Hall of Fame. Margaret Laurence's ''The Stone Angel'' and ''A Jest of God'' were set in Manawaka, a fictional town representing Neepawa, Manitoba, Neepawa; the latter title won the Governor General's Award in 1966. Carol Shields won both the Governor General's Award and the Pulitzer Prize for ''The Stone Diaries''. Gabrielle Roy, a Franco-Manitoban writer, won the Governor General's Award three times. A quote from her writings is featured on the Canadian $20 bill. Joan Thomas was nominated for the Governor General's Award twice and won in 2019 for ''Five Wives''. The province has also been home to many of the key figures in Mennonite literature, including Governor General Award-winning Miriam Toews, Giller winner David Bergen, Armin Wiebe and many others. Sandra Birdsell, whose fiction focusses on her Métis people (Canada), Métis and Mennonite heritage, was thrice nominated for the Governor General's Literary Award for English Language Fiction, and also for the Scotiabank Giller Prize in 2001.
Le Cercle Molière (founded 1925) is the oldest French-language theatre in Canada, and Royal Manitoba Theatre Centre (founded 1958) is Canada's oldest English-language regional theatre. Manitoba Theatre for Young People was the first English-language theatre to win the Canadian Institute of the Arts for Young Audiences Award, and offers plays for children and teenagers as well as a theatre school. The Winnipeg Art Gallery (WAG), Manitoba's largest art gallery and the sixth largest in the country, hosts an art school for children; the WAG's permanent collection comprises over twenty thousand works, with a particular emphasis on Manitoban and Canadian art.
The 1960s pop group The Guess Who was formed in Manitoba, and later became the first Canadian band to have a No. 1 hit in the United States; Guess Who guitarist Randy Bachman later created Bachman–Turner Overdrive (BTO) with fellow Winnipeg-based musician Fred Turner (musician), Fred Turner. Fellow rocker Neil Young, grew up in Manitoba, and later played in Buffalo Springfield, and Crosby, Stills, Nash & Young. Folk rock band Crash Test Dummies formed in the late 1980s in Winnipeg and were the 1992 Juno Awards Group of the Year.
Several prominent Canadian films were produced in Manitoba, such as ''The Stone Angel (film), The Stone Angel'', based on the Margaret Laurence book of the The Stone Angel, same title, ''The Saddest Music in the World'', ''Foodland (film), Foodland'', ''For Angela'', and ''My Winnipeg''. Major films shot in Manitoba include ''The Assassination of Jesse James by the Coward Robert Ford'' and ''Capote (film), Capote'', both of which received Academy Award nominations. ''Falcon Beach'', an internationally broadcast television drama, was filmed at Winnipeg Beach, Manitoba.
Manitoba has a strong literary tradition. Bertram Brooker won the first-ever Governor General's Awards, Governor General's Award for Fiction in 1936. Cartoonist Lynn Johnston, author of the comic strip ''For Better or For Worse'', was a finalist for a 1994 Pulitzer Prize and inducted into the Canadian Cartoonist Hall of Fame. Margaret Laurence's ''The Stone Angel'' and ''A Jest of God'' were set in Manawaka, a fictional town representing Neepawa, Manitoba, Neepawa; the latter title won the Governor General's Award in 1966. Carol Shields won both the Governor General's Award and the Pulitzer Prize for ''The Stone Diaries''. Gabrielle Roy, a Franco-Manitoban writer, won the Governor General's Award three times. A quote from her writings is featured on the Canadian $20 bill. Joan Thomas was nominated for the Governor General's Award twice and won in 2019 for ''Five Wives''. The province has also been home to many of the key figures in Mennonite literature, including Governor General Award-winning Miriam Toews, Giller winner David Bergen, Armin Wiebe and many others. Sandra Birdsell, whose fiction focusses on her Métis people (Canada), Métis and Mennonite heritage, was thrice nominated for the Governor General's Literary Award for English Language Fiction, and also for the Scotiabank Giller Prize in 2001.

 Festivals take place throughout the province, with the largest centred in Winnipeg. The Winnipeg Folk Festival has an annual attendance of over 70,000. The
Festivals take place throughout the province, with the largest centred in Winnipeg. The Winnipeg Folk Festival has an annual attendance of over 70,000. The

Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
secured the territory in 1763 after their victory over France in the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
, better known as the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
in North America; lasting from 1754 to 1763. The founding of the first agricultural community and settlements in 1812 by Lord Selkirk, north of the area which is now downtown Winnipeg, led to conflict between British colonists and the Métis. Twenty colonists, including the governor, and one Métis were killed in the Battle of Seven Oaks in 1816.
Confederation
 Rupert's Land was ceded to Canada by the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869 and incorporated into the Northwest Territories; a lack of attention to Métis concerns caused Métis leader Louis Riel to establish a local provisional government which formed into the Convention of Forty and the subsequent elected
Rupert's Land was ceded to Canada by the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869 and incorporated into the Northwest Territories; a lack of attention to Métis concerns caused Métis leader Louis Riel to establish a local provisional government which formed into the Convention of Forty and the subsequent elected Legislative Assembly of Assiniboia
The Legislative Assembly of Assiniboia (french: Assemblée législative d'Assiniboine) was a short-lived legislature established to pass laws for the North-Western Territory and Rupert's Land under the provisional government led by Louis Riel from ...
on 9 March 1870. This assembly subsequently sent three delegates to Ottawa to negotiate with the Canadian government. This resulted in the ''Manitoba Act'' and that province's entry into the Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominion ...
. Prime Minister Sir John A. Macdonald introduced the ''Manitoba Act'' in the House of Commons of Canada, the bill was given Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
and Manitoba was brought into Canada as a province in 1870. Louis Riel was pursued by British army officer Garnet Wolseley
Field Marshal Garnet Joseph Wolseley, 1st Viscount Wolseley, (4 June 183325 March 1913), was an Anglo-Irish officer in the British Army. He became one of the most influential and admired British generals after a series of successes in Canada, W ...
because of the rebellion, and Riel fled into exile. The Canadian government blocked the Métis' attempts to obtain land promised to them as part of Manitoba's entry into confederation. Facing racism from the new flood of white settlers from Ontario, large numbers of Métis moved to what would become Saskatchewan and Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
.
Numbered Treaties
The Numbered Treaties (or Post-Confederation Treaties) are a series of eleven treaties signed between the First Nations, one of three groups of Indigenous peoples in Canada, and the reigning monarch of Canada (Victoria, Edward VII or George V) ...
were signed in the late 19th century with the chiefs of First Nations that lived in the area. They made specific promises of land for every family. As a result, a reserve system was established under the jurisdiction of the federal government. The prescribed amount of land promised to the native peoples was not always given; this led Indigenous groups to assert rights to the land through land claims
A land claim is defined as "the pursuit of recognized territorial ownership by a group or individual". The phrase is usually only used with respect to disputed or unresolved land claims. Some types of land claims include aboriginal land claims, A ...
, many of which are still ongoing.
The original province of Manitoba was a square one-eighteenth of its current size, and was known colloquially as the "postage stamp province". Its borders were expanded in 1881, taking land from the Northwest Territories and the District of Keewatin, but Ontario claimed a large portion of the land; the disputed portion was awarded to Ontario in 1889. Manitoba grew to its current size in 1912, absorbing land from the Northwest Territories to reach 60°N, uniform with the northern reach of its western neighbours Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
.
The Manitoba Schools Question
The Manitoba Schools Question () was a political crisis in the Canadian province of Manitoba that occurred late in the 19th century, attacking publicly-funded separate schools for Roman Catholics and Protestants. The crisis was precipitated by a se ...
showed the deep divergence of cultural values in the territory. The Catholic Franco-Manitobans had been guaranteed a state-supported separate school system in the original constitution of Manitoba, but a grassroots political movement among English Protestants from 1888 to 1890 demanded the end of French schools. In 1890, the Manitoba legislature passed a law removing funding for French Catholic schools. The French Catholic minority asked the federal government for support; however, the Orange Order and other anti-Catholic forces mobilized nationwide to oppose them. The federal Conservatives
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
proposed remedial legislation to override Manitoba, but they were blocked by the Liberals, led by Wilfrid Laurier
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier, ( ; ; November 20, 1841 – February 17, 1919) was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadian prime minis ...
. Once elected Prime Minister in 1896, Laurier implemented a compromise stating Catholics in Manitoba could have their own religious instruction for 30 minutes at the end of the day if there were enough students to warrant it, implemented on a school-by-school basis.
Contemporary era
 By 1911,
By 1911, Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
was the third largest city in Canada, and remained so until overtaken by Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
in the 1920s. A boomtown, it grew quickly around the start of the 20th century, with outside investors and immigrants contributing to its success. The drop in growth in the second half of the decade was a result of the opening of the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
in 1914, which reduced reliance on transcontinental railways for trade, as well as a decrease in immigration due to the outbreak of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Over 18,000 Manitoba residents enlisted in the first year of the war; by the end of the war, 14 Manitobans had received the Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
.
During the First World War, Nellie McClung
Nellie Letitia McClung (; 20 October 18731 September 1951) was a Canadian author, politician, and social activist, who is regarded as one of Canada's most prominent suffragists. She began her career in writing with the 1908 book ''Sowing Seeds ...
started the campaign for women's votes. On January 28, 1916, the vote for women was legalized. Manitoba was the first province to allow women to vote in provincial elections. This was two years before Canada as a country granted women the right to vote.
After the First World War ended, severe discontent among farmers (over wheat prices) and union members (over wage rates) resulted in an upsurge of radicalism, coupled with a polarization over the rise of Bolshevism
Bolshevism (from Bolshevik) is a revolutionary socialist current of Soviet Marxist–Leninist political thought and political regime associated with the formation of a rigidly centralized, cohesive and disciplined party of social revolution, ...
in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
. The most dramatic result was the Winnipeg general strike of 1919. It began on 15 May and collapsed on 25 June 1919; as the workers gradually returned to their jobs, the Central Strike Committee decided to end the movement. Government efforts to violently crush the strike, including a Royal North-West Mounted Police
The North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) was a Canadian para-military police force, established in 1873, to maintain order in the new Canadian North-West Territories (NWT) following the 1870 transfer of Rupert’s Land and North-Western Territor ...
charge into a crowd of protesters that resulted in multiple casualties and one death, had led to the arrest of the movement's leaders. In the aftermath, eight leaders went on trial, and most were convicted on charges of seditious conspiracy
Seditious conspiracy is a crime in various jurisdictions of conspiring against the authority or legitimacy of the state. As a form of sedition, it has been described as a serious but lesser counterpart to treason, targeting activities that undermi ...
, illegal combinations, and seditious libel; four were deported under the '' Canadian Immigration Act''.
The Great Depression (1929–c. 1939) hit especially hard in Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West or the Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada� ...
, including Manitoba. The collapse of the world market combined with a steep drop in agricultural production due to drought led to economic diversification, moving away from a reliance on wheat production. The Manitoba Co-operative Commonwealth Federation
The Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (Manitoba) (CCF), known informally as the Manitoba CCF, was a provincial branch of the national Canadian party by the same name. The national CCF was the dominant social-democratic party in Canada from th ...
, forerunner to the New Democratic Party of Manitoba
The New Democratic Party of Manitoba (french: Nouveau Parti démocratique du Manitoba) is a social-democratic political party in Manitoba, Canada. It is the provincial wing of the federal New Democratic Party, and is a successor to the Manitoba ...
(NDP), was founded in 1932.
Canada entered the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
in 1939. Winnipeg was one of the major commands for the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan to train fighter pilots, and there were air training schools throughout Manitoba. Several Manitoba-based regiments were deployed overseas, including Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry. In an effort to raise money for the war effort, the Victory Loan campaign organized "If Day
If Day (french: "Si un jour", "If one day") was a simulated Nazi German invasion and occupation of the Canadian city of Winnipeg, Manitoba, and surrounding areas on 19 February 1942, during the Second World War. It was organized as a war bond pr ...
" in 1942. The event featured a simulated Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
invasion and occupation of Manitoba, and eventually raised over C$65 million.
1950 Red River Flood
The 1950 Red River flood was a devastating flood that took place along the Red River in The Dakotas and Manitoba from April 15 to June 12, 1950. Damage was particularly severe in the city of Winnipeg and its environs, which were inundated on M ...
and had to be partially evacuated. In that year, the Red River reached its highest level since 1861 and flooded most of the Red River Valley. The damage caused by the flood led then-Premier Duff Roblin to advocate for the construction of the Red River Floodway
The Red River Floodway (french: Canal de dérivation de la rivière Rouge) is an artificial flood control waterway in Western Canada. It is a long channel which, during flood periods, takes part of the Red River's flow around the city of Winn ...
; it was completed in 1968 after six years of excavation. Permanent dikes were erected in eight towns south of Winnipeg, and clay dikes and diversion dams were built in the Winnipeg area. In 1997, the " Flood of the Century" caused over in damages in Manitoba, but the floodway prevented Winnipeg from flooding.
In 1990, Prime Minister Brian Mulroney attempted to pass the Meech Lake Accord
The Meech Lake Accord (french: Accord du lac Meech) was a series of proposed amendments to the Constitution of Canada negotiated in 1987 by Prime Minister Brian Mulroney and all 10 Canadian provincial premiers. It was intended to persuade the gov ...
, a series of constitutional amendments to persuade Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
to endorse the ''Canada Act 1982
The Canada Act 1982 (1982 c. 11; french: Loi de 1982 sur le Canada) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and one of the enactments which make up the Constitution of Canada. It was enacted at the request of the Senate and House ...
''. Unanimous support in the legislature was needed to bypass public consultation. Cree politician Elijah Harper
Elijah Harper (March 3, 1949 – May 17, 2013) was a Canadian Oji-Cree politician who served as a member of the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba (MLA) from 1981 to 1992 and a member of Parliament (MP) from 1993 to 1997. Harper was elected chie ...
opposed because he did not believe First Nations had been adequately involved in the Accord's process, and thus the Accord failed.
Glen Murray, elected in Winnipeg in 1998, became the first openly gay
''Gay'' is a term that primarily refers to a homosexual person or the trait of being homosexual. The term originally meant 'carefree', 'cheerful', or 'bright and showy'.
While scant usage referring to male homosexuality dates to the late 1 ...
mayor of a large North American city. The province was impacted by major flooding in 2009 and 2011. In 2004, Manitoba became the first province in Canada to ban indoor smoking in public places. In 2013, Manitoba was the second province to introduce accessibility legislation, protecting the rights of persons with disabilities.
Geography
 Manitoba is bordered by the provinces of
Manitoba is bordered by the provinces of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
to the east and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dak ...
to the west, the territory of Nunavut to the north, and the US states
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sov ...
of North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, So ...
and Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
to the south. Manitoba is at the centre of the Hudson Bay drainage basin, with a high volume of the water draining into Lake Winnipeg and then north down the Nelson River
The Nelson River is a river of north-central North America, in the Canadian province of Manitoba. The river drains Lake Winnipeg and runs before it ends in Hudson Bay. Its full length (including the Saskatchewan River and Bow River) is , i ...
into Hudson Bay. This basin's rivers reach far west to the mountains, far south into the United States, and east into Ontario. Major watercourses include the Red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
, Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
, Nelson, Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
, Hayes, Whiteshell
Whiteshells (also known as Cowrie shells or Sacred ''Miigis'' Shells) were used by aboriginal peoples around the world, but the words "whiteshell" and "''Miigis'' Shell" specifically refers to shells used by Ojibway peoples in their Midewiwin cerem ...
and Churchill rivers. Most of Manitoba's inhabited south has developed in the prehistoric bed of Glacial Lake Agassiz. This region, particularly the Red River Valley, is flat and fertile; receding glaciers left hilly and rocky areas throughout the province.
The province has a saltwater coastline bordering Hudson Bay and more than 110,000 lakes, covering approximately 15.6 percent or of its surface area. Manitoba's major lakes are Lake Manitoba, Lake Winnipegosis
Lake Winnipegosis is a large (5,370 km2) lake in central North America, in Manitoba, Canada, some 300 km northwest of Winnipeg. It is Canada's eleventh-largest lake. An alternate spelling, once common but now rare, is Lake Winipigoos or ...
, and Lake Winnipeg
Lake Winnipeg (french: Lac Winnipeg, oj, ᐑᓂᐸᑲᒥᐠᓴᑯ˙ᑯᐣ, italics=no, Weenipagamiksaguygun) is a very large, relatively shallow lake in North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Its southern end is about north of t ...
, the tenth-largest freshwater lake in the world. A total of of traditional First Nations lands and boreal forest
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruc ...
on Lake Winnipeg's east side were officially designated as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
known as Pimachiowin Aki
Pimachiowin Aki ( ) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the boreal forest that covers parts of Manitoba and Ontario. The site is more than in area, and includes ancestral lands of four First Nations including Poplar River First Nation, L ...
in 2018.
Baldy Mountain
There are a number of peaks named Baldy:
Canada
*Baldy Mountain (Manitoba), ,
*Big Baldy Mountain (Vancouver Island, British Columbia)
Big Baldy Mountain is a mountain on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, located west of Gold River ...
is the province's highest point at above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
, and the Hudson Bay coast is the lowest at sea level. Riding Mountain, the Pembina Hills, Sandilands Provincial Forest
The Sandilands Provincial Forest is a forest located within the southeastern area of Manitoba, Canada, and consists of thousands of acres of sand hills, forest, wetlands, and mostly unpopulated crown lands. Sandilands Provincial Forest covers ...
, and the Canadian Shield are also upland regions. Much of the province's sparsely inhabited north and east lie on the irregular granite Canadian Shield, including Whiteshell
Whiteshells (also known as Cowrie shells or Sacred ''Miigis'' Shells) were used by aboriginal peoples around the world, but the words "whiteshell" and "''Miigis'' Shell" specifically refers to shells used by Ojibway peoples in their Midewiwin cerem ...
, Atikaki, and Nopiming Provincial Park
Nopiming Provincial Park is a natural provincial park in Manitoba, Canada, located on the southeast side of the province, along the boundary with Ontario.
The area was designated a provincial park by the Government of Manitoba in 1976. The park ...
s.
Extensive agriculture is found only in the province's southern areas, although there is grain farming in the Carrot Valley Region (near The Pas
The Pas ( ; french: Le Pas) is a town in Manitoba, Canada, located at the confluence of the Pasquia River and the Saskatchewan River and surrounded by the unorganized Northern Region of the province. It is approximately northwest of the provinc ...
). Around 11 percent of Canada's farmland is in Manitoba.
Climate
Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
, as warm humid air is drawn northward from the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
. Temperatures exceed numerous times each summer, and the combination of heat and humidity can bring the humidex value to the mid-40s. Carman, Manitoba, recorded the second-highest humidex ever in Canada in 2007, with 53.0. According to Environment Canada, Manitoba ranked first for clearest skies year round and ranked second for clearest skies in the summer and for the sunniest province in the winter and spring.
Southern Manitoba
Southern Manitoba is the southernmost area of the Canadian province of Manitoba. Southern Manitoba encompasses the Winnipeg Metropolitan Region, Westman Region, Central Plains Region, Eastman Region, and Pembina Valley Region, as well as the M ...
(including the city of Winnipeg), falls into the humid continental climate zone (Köppen Dfb). This area is cold and windy in the winter and often has blizzards because of the open landscape. Summers are warm with a moderate length. This region is the most humid area in the prairie provinces, with moderate precipitation. Southwestern Manitoba, though under the same climate classification as the rest of Southern Manitoba, is closer to the semi-arid interior of Palliser's Triangle
Palliser's Triangle, or the Palliser Triangle, is a semi-arid steppe occupying a substantial portion of the Western Canadian Prairie Provinces, Saskatchewan, Alberta and Manitoba, within the Great Plains region. While initially determined to be un ...
. The area is drier and more prone to drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s than other parts of southern Manitoba. This area is cold and windy in the winter and has frequent blizzards due to the openness of the Canadian Prairie landscape. Summers are generally warm to hot, with low to moderate humidity.
Southern parts of the province, just north of Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley is a loosely defined area of the central United States where tornadoes are most frequent. The term was first used in 1952 as the title of a research project to study severe weather in areas of Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Kansas, ...
, experience tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, altho ...
es, with 16 confirmed touchdowns in 2016. In 2007, on 22 and 23 June, numerous tornadoes touched down, the largest an F5 tornado that devastated parts of Elie
Elie and Earlsferry is a coastal town and former royal burgh in Fife, and parish, Scotland, situated within the East Neuk beside Chapel Ness on the north coast of the Firth of Forth, eight miles east of Leven. The burgh comprised the linked v ...
(the strongest recorded tornado in Canada).
Thompson
Thompson may refer to:
People
* Thompson (surname)
* Thompson M. Scoon (1888–1953), New York politician
Places Australia
*Thompson Beach, South Australia, a locality
Bulgaria
* Thompson, Bulgaria, a village in Sofia Province
Canada
* ...
) fall in the subarctic climate zone (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfc''). This region features long and extremely cold winters and brief, warm summers with little precipitation. Overnight temperatures as low as occur on several days each winter.
Flora and fauna
 Manitoba natural communities may be grouped within five ecozones:
Manitoba natural communities may be grouped within five ecozones: boreal plains
The Boreal Plains Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a terrestrial ecozone in the western Canadian provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan and Alberta. It also has minor extensions into northeastern British C ...
, prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
, taiga shield
The Taiga Shield Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is an ecozone which stretches across Canada's subarctic region. Some regions exhibit exposed Precambrian bedrock of the Canadian Shield, the oldest of the ...
, boreal shield
The Boreal Shield Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is the largest ecozone in Canada. Covering 1.8 million square kilometres it covers almost 20% of Canada's landmass, stretching from northern Saskatchew ...
and Hudson plains
The Southern Hudson Bay taiga is a terrestrial ecoregion, as classified by the World Wildlife Fund, which extends along the southern coast of Hudson Bay and resides within the larger taiga biome. The region is nearly coterminous with the Hudso ...
. Three of these—taiga shield, boreal shield and Hudson plain—contain part of the Boreal forest of Canada
Boreal may refer to:
Climatology and geography
*Boreal (age), the first climatic phase of the Blytt-Sernander sequence of northern Europe, during the Holocene epoch
*Boreal climate, a climate characterized by long winters and short, cool to mild ...
which covers the province's eastern, southeastern, and northern reaches.
Forests make up about , or 48 percent, of the province's land area. The forests consist of pines (Jack Pine
Jack pine (''Pinus banksiana'') is an eastern North American pine. Its native range in Canada is east of the Rocky Mountains from the Mackenzie River in the Northwest Territories to Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, and the north-central and ...
, Red Pine
''Pinus resinosa'', known as red pine (also Norway pine in Minnesota), is a pine native to North America.
Description
Red pine is a coniferous evergreen tree characterized by tall, straight growth. It usually ranges from in height and in trun ...
, Eastern White Pine), spruces (White Spruce White spruce is a common name for several species of spruce ('' Picea'') and may refer to:
* ''Picea glauca'', native to most of Canada and Alaska with limited populations in the northeastern United States
* '' Picea engelmannii'', native to the ...
, Black Spruce), Balsam Fir
''Abies balsamea'' or balsam fir is a North American fir, native to most of eastern and central Canada (Newfoundland west to central Alberta) and the northeastern United States (Minnesota east to Maine, and south in the Appalachian Mountains to ...
, Tamarack (larch), poplars ( Trembling Aspen, Balsam Poplar
''Populus balsamifera'', commonly called balsam poplar, bam, bamtree, eastern balsam-poplar, hackmatack, tacamahac poplar, tacamahaca, is a tree species in the balsam poplar species group in the poplar genus, ''Populus.'' The genus name ''Populu ...
), birches (White Birch
''Betula papyrifera'' (paper birch, also known as (American) white birch and canoe birch) is a short-lived species of birch native to northern North America. Paper birch is named for the tree's thin white bark, which often peels in paper like ...
, Swamp Birch) and small pockets of Eastern White Cedar.
Two sections of the province are not dominated by forest. The province's northeast corner bordering Hudson Bay is above the treeline
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snowp ...
and is considered tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
. The tallgrass prairie
The tallgrass prairie is an ecosystem native to central North America. Historically, natural and anthropogenic fire, as well as grazing by large mammals (primarily bison) provided periodic disturbances to these ecosystems, limiting the encroachm ...
once dominated the south central and southeastern parts including the Red River Valley. Mixed grass prairie is found in the southwestern region. Agriculture has replaced much of the natural prairie but prairie still can be found in parks and protected areas; some are notable for the presence of the endangered western prairie fringed orchid.
Manitoba is especially noted for its northern polar bear population; Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
is commonly referred to as the "Polar Bear Capital". Other large animals, including moose, white-tailed deer, American black bear, black bears, cougars, lynx, and gray wolf, wolves, are common throughout the province, especially in the provincial and national List of protected areas of Manitoba, parks. There is a large population of garter snake, red sided garter snakes near Narcisse, Manitoba, Narcisse; the dens there are home to the world's largest concentration of snakes.
Manitoba's bird diversity is enhanced by its position on two major migration routes, with 392 confirmed identified species; 287 of these nesting within the province. These include the great grey owl, the province's official bird, and the endangered peregrine falcon.
Manitoba's lakes host 18 species of game fish, particularly species of trout, Pike (fish), pike, and goldeye, as well as many smaller fish.
Demography
At the 2021 census, Manitoba had a population of 1,342,153, more than half of which is in Winnipeg. Although initial colonization of the province revolved mostly around homesteading, the last century has seen a shift towards urbanization; Manitoba is the only Canadian province with over fifty-five percent of its population in a single city. The largest ethnic group in Manitoba is English Canadian, English (16.1%), followed by Scottish Canadian, Scottish (14.5%), Canadians of German ethnicity, German (13.6%), Ukrainian Canadian, Ukrainian (12.6%), Irish Canadian, Irish (11.0%), French Canadian, French (9.3%), Filipino Canadians, Filipino (7.0%), Métis people (Canada), Métis (6.8%), Polish Canadians, Polish (6.0%),First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
(4.5%), Mennonite (3.9%), Russians in Canada, Russian (3.7%), Canadians of Dutch descent, Dutch (3.3%), Indian Canadian, Indian (3.0%), and Icelandic Canadians, Icelandic (2.4%). Indigenous peoples (including Métis) are Manitoba's fastest-growing ethnic group, representing 13.6 percent of Manitoba's population as of 2001 (some reserves refused to allow census-takers to enumerate their populations or were otherwise incompletely counted). Rural Municipality of Gimli, Gimli, Manitoba is home to the largest Icelanders, Icelandic community outside of Iceland.
As of the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 Canadian Census, the ten most spoken languages in the province included English (1,288,950 or 98.6%), French (111,790 or 8.55%), Tagalog (73,440 or 5.62%), Punjabi (42,820 or 3.28%), German (41,980 or 3.21%), Hindi (26,980 or 2.06%), Spanish (23,435 or 1.79%), Mandarin (16,765 or 1.28%), Cree (16,115 or 1.23%), and Plautdietsch (15,055 or 1.15%). The question on knowledge of languages allows for multiple responses.
Most Manitobans belong to a Christian denomination: on the 2021 census, 54.2% reported being Christian, followed by 2.7% Sikh, 2.0% Muslim, 1.4% Hindu, 0.9% Jewish, and 0.8% Native American religion, Indigenous spirituality. 36.7% reported no religious affiliation. The largest Christian denominations by number of adherents were the Roman Catholicism in Canada, Roman Catholic Church with 21.2%; the United Church of Canada with 5.8%; and the Anglican Church of Canada with 3.3%.
Economy
Manitoba has a moderately strong economy based largely on natural resources. Its Gross Domestic Product was C$50.834 billion in 2008. The province's economy grew 2.4 percent in 2008, the third consecutive year of growth. The average individual income in Manitoba in 2006 was C$25,100 (compared to a national average of C$26,500), ranking fifth-highest among the provinces. As of October 2009, Manitoba's unemployment rate was 5.8 percent. Manitoba's economy relies heavily on agriculture, tourism, electricity, oil, mining, and forestry. Agriculture is vital and is found mostly in the southern half of the province, although grain farming occurs as far north as The Pas. The most common agricultural activity is cattle husbandry, followed by assorted grains and oilseed. Manitoba is the nation's largest producer of sunflower seed and dry beans, and one of the leading sources of potatoes. Portage la Prairie is a major potato processing centre. Richardson International, one of the largest oat mills in the world, also has a plant in the List of rural municipalities in Manitoba, municipality. Manitoba's largest employers are government and government-funded institutions, including crown corporations and services like List of hospitals in Manitoba, hospitals and List of universities in Manitoba, universities. Major private-sector employers are The Great-West Life Assurance Company, Cargill Ltd., and Richardson International. Manitoba also has large manufacturing and tourism sectors. Churchill's Arctic wildlife is a major tourist attraction; the town is a world capital for polar bear and beluga whale watchers. Manitoba is the only province with an Arctic deep-water seaport, at Churchill. In January 2018, the Canadian Federation of Independent Business claimed Manitoba was the most improved province for tackling red tape.Economic history
 Manitoba's early economy depended on mobility and living off the land. Indigenous Nations (Cree, Ojibwa, Dene, Sioux and Assiniboine) followed herds of bison and congregated to trade among themselves at key meeting places throughout the province. After the arrival of the first European traders in the 17th century, the economy centred on the trade of beaver pelts and other furs. Diversification of the economy came when Lord Selkirk brought the first agricultural settlers in 1811, though the triumph of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) over its competitors ensured the primacy of the fur trade over widespread agricultural colonization.
HBC control of Rupert's Land ended in 1868; when Manitoba became a province in 1870, all land became the property of the federal government, with homesteads granted to settlers for farming. Transcontinental railways were constructed to simplify trade. Manitoba's economy depended mainly on farming, which persisted until drought and the Great Depression led to further diversification.
Manitoba's early economy depended on mobility and living off the land. Indigenous Nations (Cree, Ojibwa, Dene, Sioux and Assiniboine) followed herds of bison and congregated to trade among themselves at key meeting places throughout the province. After the arrival of the first European traders in the 17th century, the economy centred on the trade of beaver pelts and other furs. Diversification of the economy came when Lord Selkirk brought the first agricultural settlers in 1811, though the triumph of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) over its competitors ensured the primacy of the fur trade over widespread agricultural colonization.
HBC control of Rupert's Land ended in 1868; when Manitoba became a province in 1870, all land became the property of the federal government, with homesteads granted to settlers for farming. Transcontinental railways were constructed to simplify trade. Manitoba's economy depended mainly on farming, which persisted until drought and the Great Depression led to further diversification.
Military bases
CFB Winnipeg is a Canadian Forces base, Canadian Forces Base at the Winnipeg International Airport. The base is home to flight operations support divisions and several training schools, as well as the 1 Canadian Air Division and Canadian North American Aerospace Defense Command, NORAD Region Headquarters. 17 Wing of the Canadian Forces is based at CFB Winnipeg; the Wing has three squadrons and six schools. It supports 113 units from Thunder Bay to the Saskatchewan/Alberta border, and from the 49th parallel north to the Northern Canada, high Arctic. 17 Wing acts as a deployed operating base for CF-18 Hornet fighter–bombers assigned to the Canadian NORAD Region. The two 17 Wing squadrons based in the city are: the 402 ("City of Winnipeg" Squadron), which flies the Canadian designed and produced de Havilland Canada Bombardier Dash 8, CT-142 Dash 8 navigation trainer in support of the 1 Canadian Forces Flight Training School's Air Combat Systems Officer and Airborne Electronic Sensor Operator training programs (which trains all Canadian Air Combat Systems Officer); and the 435 ("Chinthe" Transport and Rescue Squadron), which flies the Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed C-130 Hercules tanker/transport in airlift search and rescue roles, and is the only Air Force squadron equipped and trained to conduct Aerial refueling, air-to-air refuelling of fighter aircraft. CFB Shilo, Canadian Forces Base Shilo (CFB Shilo) is an Operations and Training base of the Canadian Forces east of Brandon. During the 1990s, Canadian Forces Base Shilo was designated as an Area Support Unit, acting as a local base of operations for Southwest Manitoba in times of military and civil emergency. CFB Shilo is the home of the Royal Canadian Horse Artillery, 1st Regiment, Royal Canadian Horse Artillery, both battalions of the 1 Canadian Mechanized Brigade Group, and the Royal Regiment of Canadian Artillery, Royal Canadian Artillery. The Second Battalion of Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry (2 PPCLI), which was originally stationed in Winnipeg (first at Fort Osborne, then in Kapyong Barracks), has operated out of CFB Shilo since 2004. CFB Shilo hosts a training unit, 3rd Canadian Division Training Centre. It serves as a base for support units of Land Force Western Area, 3rd Canadian Division, also including 3 CDSG Signals Squadron, Shared Services Unit (West), 11 CF Health Services Centre, 1 Dental Unit, 1 Military Police Regiment, and an Integrated Personnel Support Centre. The base houses 1,700 soldiers.Government and politics
 After the control of Rupert's Land was passed from Great Britain to the Government of Canada in 1869, Manitoba attained full-fledged rights and responsibilities of self-government as the first Canadian province carved out of the Northwest Territories. The
After the control of Rupert's Land was passed from Great Britain to the Government of Canada in 1869, Manitoba attained full-fledged rights and responsibilities of self-government as the first Canadian province carved out of the Northwest Territories. The Legislative Assembly of Manitoba
The Legislative Assembly of Manitoba (french: Assemblée législative du Manitoba) is the deliberative assembly of the Manitoba Legislature in the Canadian province of Manitoba. Fifty-seven members are elected to this assembly at provincial gen ...
was established on 14 July 1870. Political parties first emerged between 1878 and 1883, with a two-party system (Manitoba Liberal Party, Liberals and Progressive Conservative Party of Manitoba, Conservatives). The Progressive Party of Manitoba, United Farmers of Manitoba appeared in 1922, and later merged with the Liberals in 1932. Other parties, including the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF), appeared during the Great Depression; in the 1950s, Manitoban politics became a three-party system, and the Liberals gradually declined in power. The CCF became the New Democratic Party of Manitoba (NDP), which came to power in 1969. Since then, the Progressive Conservatives and the NDP have been the dominant parties.
Like all Canadian provinces, Manitoba is governed by a unicameralism, unicameral legislative assembly. The executive (government), executive branch is formed by the governing party; the party leader is the premier of Manitoba, the head of the executive branch. The head of state, King Charles III, is represented by the Lieutenant Governor of Manitoba, who is appointed by the Governor General of Canada on advice of the Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Minister. The head of state is primarily a ceremonial role, although the List of lieutenant governors of Manitoba, Lieutenant Governor has the official responsibility of ensuring Manitoba has a duly constituted government.
The Legislative Assembly consists of the 57 Members elected to represent the people of Manitoba. The List of premiers of Manitoba, premier of Manitoba is Heather Stefanson
Heather Dorothy Stefanson (born May 11, 1970) is a Canadian politician who has served as the 24th premier of Manitoba since November 2, 2021. She is the leader of the Progressive Conservative Party of Manitoba and sits as a member of the Legi ...
of the PC Party, after Brian Pallister's resignation. The province is represented in federal politics by 14 Members of Parliament and six Senate of Canada, Senators.
Manitoba's judiciary consists of the Manitoba Court of Appeal, Court of Appeal, the Court of King's Bench of Manitoba, Court of King's Bench, and the Provincial Court
The provincial and territorial courts in Canada are local trial "inferior" or "lower" courts of limited jurisdiction established in each of the provinces and territories of Canada. These courts typically hear criminal, civil (or “ small claims” ...
. The Provincial Court is primarily for criminal law; 95 per cent of criminal cases in Manitoba are heard here. The Court of King's Bench is the highest trial court in the province. It has four jurisdictions: family law (child and family services cases), civil law (common law), civil law, criminal law (for indictable offences), and appeals. The Court of Appeal hears appeals from both benches; its decisions can only be appealed to the Supreme Court of Canada.
Official languages
Both English and French are official languages of the legislature of Manitoba, legislature and Provincial Court of Manitoba, courts of Manitoba, according to section 23 of the ''Manitoba Act, 1870'' (part of the Constitution of Canada). In April 1890, the Manitoba legislature attempted to abolish the official status of French and ceased to publish bilingual legislation. However, in 1985, the Supreme Court of Canada ruled in the Reference re Manitoba Language Rights that section 23 still applied, and that legislation published only in English was invalid (unilingual legislation was declared valid for a temporary period to allow time for translation). Although French is an official language for the purposes of the legislature, legislation, and the courts, the ''Manitoba Act'' does not require it to be an official language for the purpose of the executive branch (except when performing legislative or judicial functions). Hence, Manitoba's government is not completely bilingual. The Manitoba French Language Services Policy of 1999 is intended to provide a comparable level of provincial government services in both official languages. According to the 2006 Census, 82.8 percent of Manitoba's population spoke only English, 3.2 percent spoke only French, 15.1 percent spoke both, and 0.9 percent spoke neither. In 2010, the provincial government of Manitoba passed the ''Aboriginal Languages Recognition Act'', which gives official recognition to seven indigenous languages: Cree, Dakota language, Dakota, Dene language, Dene, Inuktitut, Michif, Ojibway language, Ojibway and Oji-Cree language, Oji-Cree.Transportation
 Manitoba has two Class I railroad, Class I railways: Canadian National Railway (CN) and Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). Winnipeg is centrally located on the main lines of both carriers, and both maintain large inter-modal terminals in the city. Via Rail offers transcontinental and Northern Manitoba passenger service from Union Station (Winnipeg), Winnipeg's Union Station. Numerous small regional and short-line railways also run trains within Manitoba: the Hudson Bay Railway (1997), Hudson Bay Railway, the Southern Manitoba Railway, Burlington Northern Santa Fe Manitoba, Greater Winnipeg Water District Railway, and Central Manitoba Railway.
Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport, Manitoba's largest List of airports in Manitoba, airport, is one of only a few 24-hour unrestricted airports in Canada and is part of the National Airports System. A new, larger terminal opened in October 2011. It is the seventh List of the busiest airports in Canada, busiest airport in Canada by passenger traffic, serving 4,484,343 passengers in 2018, and the 11th busiest airport by aircraft movements. The airport handles approximately of cargo annually, making it the third largest cargo airport in the country. Winnipeg is a major sorting facility for both FedEx and Purolator Courier, Purolator, and receives daily trans-border service from United Parcel Service, UPS.
The Port of Churchill is the only Arctic deep-water port in Canada. It is nautically closer to ports in Northern Europe and Russia than any other port in Canada. It has four deep-sea berths for the loading and unloading of grain, general cargo and tanker vessels. The port is served by the Hudson Bay Railway. The port and railway came under complete community and Indigenous ownership in 2021, after AGT Food and Ingredients and Fairfax Financial transferred their shares in Arctic Gateway to OneNorth – a consortium of community and Indigenous partners which owned the other fifty percent of Arctic Gateway's shares.
Manitoba has two Class I railroad, Class I railways: Canadian National Railway (CN) and Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). Winnipeg is centrally located on the main lines of both carriers, and both maintain large inter-modal terminals in the city. Via Rail offers transcontinental and Northern Manitoba passenger service from Union Station (Winnipeg), Winnipeg's Union Station. Numerous small regional and short-line railways also run trains within Manitoba: the Hudson Bay Railway (1997), Hudson Bay Railway, the Southern Manitoba Railway, Burlington Northern Santa Fe Manitoba, Greater Winnipeg Water District Railway, and Central Manitoba Railway.
Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport, Manitoba's largest List of airports in Manitoba, airport, is one of only a few 24-hour unrestricted airports in Canada and is part of the National Airports System. A new, larger terminal opened in October 2011. It is the seventh List of the busiest airports in Canada, busiest airport in Canada by passenger traffic, serving 4,484,343 passengers in 2018, and the 11th busiest airport by aircraft movements. The airport handles approximately of cargo annually, making it the third largest cargo airport in the country. Winnipeg is a major sorting facility for both FedEx and Purolator Courier, Purolator, and receives daily trans-border service from United Parcel Service, UPS.
The Port of Churchill is the only Arctic deep-water port in Canada. It is nautically closer to ports in Northern Europe and Russia than any other port in Canada. It has four deep-sea berths for the loading and unloading of grain, general cargo and tanker vessels. The port is served by the Hudson Bay Railway. The port and railway came under complete community and Indigenous ownership in 2021, after AGT Food and Ingredients and Fairfax Financial transferred their shares in Arctic Gateway to OneNorth – a consortium of community and Indigenous partners which owned the other fifty percent of Arctic Gateway's shares.
Education
Public schools follow a provincially mandated curriculum in either French or English. There are sixty-five funded independent schools in Manitoba, including three boarding schools. These schools must follow the Manitoban curriculum and meet other provincial requirements. There are forty-four non-funded independent schools, which are not required to meet those standards. Public schools in Manitoba fall under the regulation of one of thirty-seven List of school districts in Manitoba, school divisions within Minister of Education, Citizenship and Youth (Manitoba), the provincial education system (except for the Manitoba Band Operated Schools, which are administered by the federal government). In 2021, the provincial government announced a plan to merge all English-language school divisions into 15 regional catchment areas, overseen by a provincial education authority. There are five universities in Manitoba, regulated by the Minister of Advanced Education and Literacy (Manitoba), Ministry of Advanced Education and Literacy. Four of these universities are in Winnipeg: the University of Manitoba, the largest and most comprehensive; the University of Winnipeg, a liberal arts college, liberal arts school primarily focused on undergrad studies downtown; Université de Saint-Boniface, the province's only French-language university; and the Canadian Mennonite University, a religious-based institution. The Université de Saint-Boniface, established in 1818 and now affiliated with the University of Manitoba, is the oldest university in Western Canada. Brandon University, formed in 1899 and in Brandon, is the province's only university not in Winnipeg. Manitoba has fifty-four public library systems. Of these, Winnipeg Public Library has the largest collections, at 1.1 million items as of 2020.Culture
Arts
 The Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport (Manitoba), Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport is responsible for promoting and, to some extent, financing Manitoban culture. Manitoba is the birthplace of the Red River Jig, a combination of Indigenous pow-wows and European Reel (dance), reels popular among early settlers. Manitoba's traditional music has strong roots in Métis and First Nations culture, in particular the old-time music, old-time fiddle, fiddling of the Métis. Manitoba's cultural scene also incorporates classical European traditions. The Winnipeg-based Royal Winnipeg Ballet (RWB), is Canada's oldest ballet and North America's longest continuously operating ballet company; it was granted its royal title in 1953 under Queen Elizabeth II. The Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra (WSO) performs classical music and new compositions at the Centennial Concert Hall. Manitoba Opera, founded in 1969, also performs out of the Centennial Concert Hall.
The Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport (Manitoba), Minister of Culture, Heritage, Tourism and Sport is responsible for promoting and, to some extent, financing Manitoban culture. Manitoba is the birthplace of the Red River Jig, a combination of Indigenous pow-wows and European Reel (dance), reels popular among early settlers. Manitoba's traditional music has strong roots in Métis and First Nations culture, in particular the old-time music, old-time fiddle, fiddling of the Métis. Manitoba's cultural scene also incorporates classical European traditions. The Winnipeg-based Royal Winnipeg Ballet (RWB), is Canada's oldest ballet and North America's longest continuously operating ballet company; it was granted its royal title in 1953 under Queen Elizabeth II. The Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra (WSO) performs classical music and new compositions at the Centennial Concert Hall. Manitoba Opera, founded in 1969, also performs out of the Centennial Concert Hall.
 Le Cercle Molière (founded 1925) is the oldest French-language theatre in Canada, and Royal Manitoba Theatre Centre (founded 1958) is Canada's oldest English-language regional theatre. Manitoba Theatre for Young People was the first English-language theatre to win the Canadian Institute of the Arts for Young Audiences Award, and offers plays for children and teenagers as well as a theatre school. The Winnipeg Art Gallery (WAG), Manitoba's largest art gallery and the sixth largest in the country, hosts an art school for children; the WAG's permanent collection comprises over twenty thousand works, with a particular emphasis on Manitoban and Canadian art.
The 1960s pop group The Guess Who was formed in Manitoba, and later became the first Canadian band to have a No. 1 hit in the United States; Guess Who guitarist Randy Bachman later created Bachman–Turner Overdrive (BTO) with fellow Winnipeg-based musician Fred Turner (musician), Fred Turner. Fellow rocker Neil Young, grew up in Manitoba, and later played in Buffalo Springfield, and Crosby, Stills, Nash & Young. Folk rock band Crash Test Dummies formed in the late 1980s in Winnipeg and were the 1992 Juno Awards Group of the Year.
Several prominent Canadian films were produced in Manitoba, such as ''The Stone Angel (film), The Stone Angel'', based on the Margaret Laurence book of the The Stone Angel, same title, ''The Saddest Music in the World'', ''Foodland (film), Foodland'', ''For Angela'', and ''My Winnipeg''. Major films shot in Manitoba include ''The Assassination of Jesse James by the Coward Robert Ford'' and ''Capote (film), Capote'', both of which received Academy Award nominations. ''Falcon Beach'', an internationally broadcast television drama, was filmed at Winnipeg Beach, Manitoba.
Manitoba has a strong literary tradition. Bertram Brooker won the first-ever Governor General's Awards, Governor General's Award for Fiction in 1936. Cartoonist Lynn Johnston, author of the comic strip ''For Better or For Worse'', was a finalist for a 1994 Pulitzer Prize and inducted into the Canadian Cartoonist Hall of Fame. Margaret Laurence's ''The Stone Angel'' and ''A Jest of God'' were set in Manawaka, a fictional town representing Neepawa, Manitoba, Neepawa; the latter title won the Governor General's Award in 1966. Carol Shields won both the Governor General's Award and the Pulitzer Prize for ''The Stone Diaries''. Gabrielle Roy, a Franco-Manitoban writer, won the Governor General's Award three times. A quote from her writings is featured on the Canadian $20 bill. Joan Thomas was nominated for the Governor General's Award twice and won in 2019 for ''Five Wives''. The province has also been home to many of the key figures in Mennonite literature, including Governor General Award-winning Miriam Toews, Giller winner David Bergen, Armin Wiebe and many others. Sandra Birdsell, whose fiction focusses on her Métis people (Canada), Métis and Mennonite heritage, was thrice nominated for the Governor General's Literary Award for English Language Fiction, and also for the Scotiabank Giller Prize in 2001.
Le Cercle Molière (founded 1925) is the oldest French-language theatre in Canada, and Royal Manitoba Theatre Centre (founded 1958) is Canada's oldest English-language regional theatre. Manitoba Theatre for Young People was the first English-language theatre to win the Canadian Institute of the Arts for Young Audiences Award, and offers plays for children and teenagers as well as a theatre school. The Winnipeg Art Gallery (WAG), Manitoba's largest art gallery and the sixth largest in the country, hosts an art school for children; the WAG's permanent collection comprises over twenty thousand works, with a particular emphasis on Manitoban and Canadian art.
The 1960s pop group The Guess Who was formed in Manitoba, and later became the first Canadian band to have a No. 1 hit in the United States; Guess Who guitarist Randy Bachman later created Bachman–Turner Overdrive (BTO) with fellow Winnipeg-based musician Fred Turner (musician), Fred Turner. Fellow rocker Neil Young, grew up in Manitoba, and later played in Buffalo Springfield, and Crosby, Stills, Nash & Young. Folk rock band Crash Test Dummies formed in the late 1980s in Winnipeg and were the 1992 Juno Awards Group of the Year.
Several prominent Canadian films were produced in Manitoba, such as ''The Stone Angel (film), The Stone Angel'', based on the Margaret Laurence book of the The Stone Angel, same title, ''The Saddest Music in the World'', ''Foodland (film), Foodland'', ''For Angela'', and ''My Winnipeg''. Major films shot in Manitoba include ''The Assassination of Jesse James by the Coward Robert Ford'' and ''Capote (film), Capote'', both of which received Academy Award nominations. ''Falcon Beach'', an internationally broadcast television drama, was filmed at Winnipeg Beach, Manitoba.
Manitoba has a strong literary tradition. Bertram Brooker won the first-ever Governor General's Awards, Governor General's Award for Fiction in 1936. Cartoonist Lynn Johnston, author of the comic strip ''For Better or For Worse'', was a finalist for a 1994 Pulitzer Prize and inducted into the Canadian Cartoonist Hall of Fame. Margaret Laurence's ''The Stone Angel'' and ''A Jest of God'' were set in Manawaka, a fictional town representing Neepawa, Manitoba, Neepawa; the latter title won the Governor General's Award in 1966. Carol Shields won both the Governor General's Award and the Pulitzer Prize for ''The Stone Diaries''. Gabrielle Roy, a Franco-Manitoban writer, won the Governor General's Award three times. A quote from her writings is featured on the Canadian $20 bill. Joan Thomas was nominated for the Governor General's Award twice and won in 2019 for ''Five Wives''. The province has also been home to many of the key figures in Mennonite literature, including Governor General Award-winning Miriam Toews, Giller winner David Bergen, Armin Wiebe and many others. Sandra Birdsell, whose fiction focusses on her Métis people (Canada), Métis and Mennonite heritage, was thrice nominated for the Governor General's Literary Award for English Language Fiction, and also for the Scotiabank Giller Prize in 2001.
Festivals
 Festivals take place throughout the province, with the largest centred in Winnipeg. The Winnipeg Folk Festival has an annual attendance of over 70,000. The
Festivals take place throughout the province, with the largest centred in Winnipeg. The Winnipeg Folk Festival has an annual attendance of over 70,000. The Festival du Voyageur
The Festival du Voyageur is an annual 10-day winter festival that takes place in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The event is held during each February in Winnipeg's French quarter, Saint-Boniface, and is western Canada's largest winter festival. It ...
is an annual ten-day event held in Winnipeg's French Quarter, and is Western Canada's largest winter festival. It celebrates Canada's fur-trading past and French-Canadian heritage and culture. Folklorama, a multicultural festival run by the Folk Arts Council, receives around 400,000 pavilion visits each year, of which about thirty percent are from non-Winnipeg residents. The Winnipeg Fringe Theatre Festival is an annual Fringe theatre, alternative theatre festival, the second-largest festival of its kind in North America (after the Edmonton International Fringe Festival).
Museums
Manitoban museums document different aspects of the province's heritage. The Manitoba Museum is the largest museum in Manitoba and focuses on Manitoban history from prehistory to the 1920s. The full-size replica of the Nonsuch is the museum's showcase piece. The Manitoba Children's Museum at The Forks, Winnipeg, The Forks presents exhibits for children. There are two museums dedicated to the native flora and fauna of Manitoba: the Living Prairie Museum, a tall grass prairie preserve featuring 160 species of grasses and wildflowers, and FortWhyte Alive, a park encompassing prairie, lake, forest and wetland habitats, home to a large herd of bison. The Canadian Fossil Discovery Centre houses the largest collection of marine reptile fossils in Canada. Other museums feature the history of Western Canada Aviation Museum, aviation, Marine Museum of Manitoba, marine transport, and Winnipeg Railway Museum, railways in the area. The Canadian Museum for Human Rights is the first Canadian national museum outside of the National Capital Region (Canada), National Capital Region.Media
Winnipeg has two daily newspapers: the ''Winnipeg Free Press'', a broadsheet with the highest circulation numbers in Manitoba, as well as the ''Winnipeg Sun'', a smaller Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid-style paper. There are several ethnic weekly newspapers, including the weekly French-language ''La Liberté (Canada), La Liberté'', and regional and national magazines based in the city. Brandon has two newspapers: the daily ''Brandon Sun'' and the weekly ''Wheat City Journal''. Many small towns have local newspapers. There are five English-language television stations and one French-language station based in Winnipeg. The Global Television Network (owned by Canwest) is headquartered in the city. Winnipeg is home to twenty-one AM and FM radio stations, two of which are French-language stations. Brandon's five local radio stations are provided by Astral Media and Westman Communications Group. In addition to the Brandon and Winnipeg stations, radio service is provided in rural areas and smaller towns by Golden West Broadcasting, Corus Entertainment, and local broadcasters. CBC Radio broadcasts local and national programming throughout the province. Native Communications is devoted to indigenous programming and broadcasts to many of the isolated native communities as well as to larger cities.
Sports
Manitoba has five professional sports teams: the Winnipeg Blue Bombers (Canadian Football League), the Winnipeg Jets (National Hockey League) and Manitoba Moose (American Hockey League), the Winnipeg Goldeyes (American Association of Independent Professional Baseball, American Association), and Valour FC (Canadian Premier League). The province was previously home to another team called the Winnipeg Jets (1972–96), Winnipeg Jets, which played in the World Hockey Association and National Hockey League from 1972 until 1996, when financial troubles prompted a sale and move of the team, renamed the Phoenix Coyotes. A second incarnation of the Winnipeg Jets returned, after True North Sports & Entertainment bought the Atlanta Thrashers and moved the team to Winnipeg in time for the 2011 hockey season. Manitoba has two Canadian Hockey League, major junior-level ice hockey teams, the Western Hockey League's Brandon Wheat Kings and Winnipeg Ice, and one junior football team, the Winnipeg Rifles of the Canadian Junior Football League. The province is represented in university athletics by the university of Manitoba Bisons, the university of Winnipeg Wesmen, and the Brandon University Brandon Bobcats, Bobcats. All three teams compete in the Canada West Universities Athletic Association, a regional division of U Sports. Curling is an important winter sport in the province with Manitoba producing more Tim Hortons Brier#Top 3 finishes table, men's national champions than any other province, while additionally in the Scotties Tournament of Hearts#Top 3 finishes table, top 3 women's national champions, as well as multiple world champions in the sport. The province also hosts the world's largest curling tournament in the MCA Bonspiel. Although not as prominent as ice hockey and curling, long track speed skating also features as a notable and top winter sport in Manitoba. The province has produced some of the world's best female speed skaters including Susan Auch and the country's top Olympic Games, Olympic medal earners Cindy Klassen and Clara Hughes.See also
*Outline of ManitobaNotes
References
Further reading
* * *External links
* * {{Authority control Manitoba, Provinces and territories of Canada 1870 establishments in Canada Canadian Prairies States and territories established in 1870