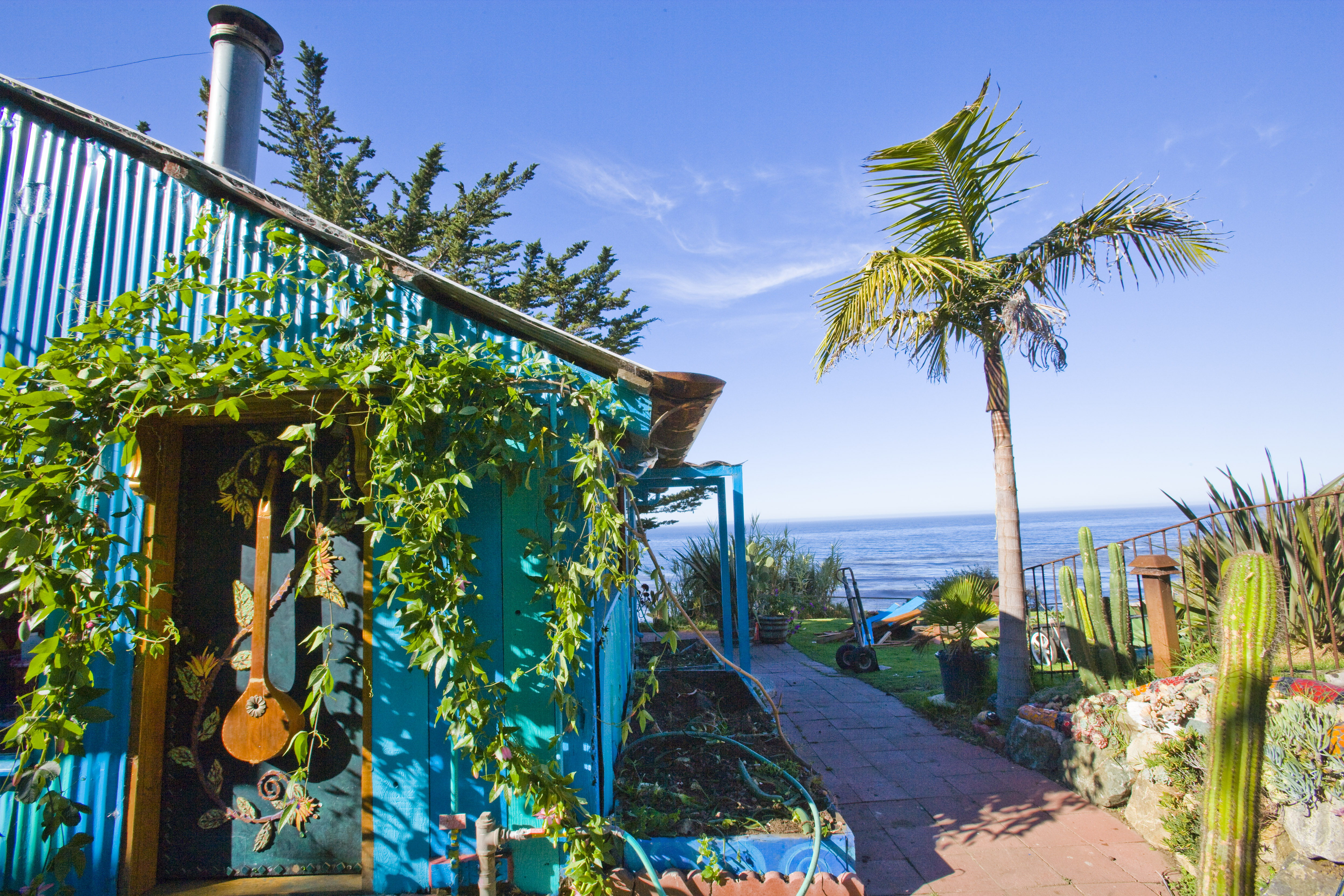


The Esalen Institute, commonly called Esalen, is a non-profit American
retreat center and
intentional community in
Big Sur,
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, which focuses on
humanistic alternative education.
The institute played a key role in the
Human Potential Movement beginning in the 1960s. Its innovative use of encounter groups, a focus on the mind-body connection, and their ongoing experimentation in personal awareness introduced many ideas that later became mainstream.
Esalen was founded by
Michael Murphy and
Dick Price
Richard Price (October 12, 1930 – November 25, 1985) was co-founder of the Esalen Institute in 1962 and a veteran of the Beat Generation. He ran Esalen in Big Sur for many years, sometimes virtually single-handed."Dick's life in the late 1960s ...
in 1962. Their intention was to support alternative methods for exploring human consciousness, what
Aldous Huxley
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher. He wrote nearly 50 books, both novels and non-fiction works, as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxle ...
described as "human potentialities". Over the next few years, Esalen became the center of practices and beliefs that make up the
New Age movement
New Age is a range of spiritual or religious practices and beliefs which rapidly grew in Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise definition difficult. Although many scholars consid ...
, from
Eastern religions/
philosophy, to
alternative medicine and
mind-body interventions, from
transpersonal The transpersonal is a term used by different schools of philosophy and psychology in order to describe experiences and worldviews that extend beyond the personal level of the psyche, and beyond mundane worldly events.
Definition and context
The ...
to Gestalt Practice.
[
Price ran the institute until he died in a hiking accident in 1985. In 2012, the board hired professional executives to help raise money and keep the institute profitable. Until 2016, Esalen offered over 500 workshops yearly in areas including personal growth, ]meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm ...
, massage
Massage is the manipulation of the body's soft tissues. Massage techniques are commonly applied with hands, fingers, elbows, knees, forearms, feet or a device. The purpose of massage is generally for the treatment of body stress or pain. In E ...
, Gestalt Practice, yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consci ...
, psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between ...
, ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
, spirituality, and organic food
Organic food, ecological food or biological food are food and drinks produced by methods complying with the standards of organic farming. Standards vary worldwide, but organic farming features practices that cycle resources, promote ecological ...
. In 2016, about 15,000 people attended its workshops.[
In February 2017, the institute was cut off when Highway 1 was closed by a mud slide on either side of the hot springs. It closed its doors, evacuated guests via helicopter, and was forced to lay off 90% of its staff through at least July, when they reopened with limited workshop offerings. It also decided to revamp its offerings to include topics more relevant to a younger generation.][
As of July 2017, due to the limited access resulting from the road closures, the hot springs are only open to Esalen guests.][
]
Early history
The grounds of the Esalen Institute were first home to a Native American tribe known as the Esselen, from whom the institute adopted its name. Carbon dating tests of artifacts found on Esalen's property have indicated a human presence as early as 2600 BCE.
The location was homesteaded by Thomas Slate on September 9, 1882, when he filed a land patent under the Homestead Act
The Homestead Acts were several laws in the United States by which an applicant could acquire ownership of government land or the public domain, typically called a homestead. In all, more than of public land, or nearly 10 percent of t ...
of 1862. The settlement became known as Slates Hot Springs
Slates Hot Springs (also known as Big Sur Hot Springs, Slate's Hot Springs, Slate's Springs, and Slate's Hot Sulphur Springs) is the site of a hot spring in the Big Sur region of Monterey County, California. It is located north-northwest of Lope ...
. It was the first tourist-oriented business in Big Sur, frequented by people seeking relief from physical ailments. In 1910, the land was purchased by Henry Murphy,
Founding
Stanford grads meet
Michael Murphy and Dick Price
Richard Price (October 12, 1930 – November 25, 1985) was co-founder of the Esalen Institute in 1962 and a veteran of the Beat Generation. He ran Esalen in Big Sur for many years, sometimes virtually single-handed."Dick's life in the late 1960s ...
both attended Stanford University in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Both had developed an interest in human psychology and earned degrees in the subject in 1952.Aldous Huxley
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher. He wrote nearly 50 books, both novels and non-fiction works, as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxle ...
give in 1960 titled "Human Potentialities". After graduating from Stanford, Price attended Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ...
to continue studying psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between ...
. Murphy, meanwhile, traveled to Sri Aurobindo's ashram in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
where he resided for several months before returning to San Francisco.
Price's parents involuntarily committed him to a mental hospital for a year, ending on November 26, 1957. He hated the experience and thought he would like to create an environment where people could explore new ideas and thoughts without judgment and influence from the outside world. In May 1960, Price returned to San Francisco and lived at the East-West House with Taoist teacher Gia-Fu Feng. That year he met fellow Stanford University graduate Michael Murphy at Haridas Chaudhuri
Haridas Chaudhuri (May 1913 – 1975) was an Indian integral philosopher. He was a correspondent with Sri Aurobindo and the founder of the California Institute of Integral Studies (CIIS).
Early life and career
He was born in May 1913 in Shya ...
’s Cultural Integration Fellowship where Murphy was in residence. They met at the suggestion of Frederic Spiegelberg, a Stanford professor of comparative religion and Indic studies, with whom both had studied.
By then they had both dropped out of their graduate programs (Price at Harvard and Murphy at Stanford), and had served time in the military.Gestalt
Gestalt may refer to:
Psychology
* Gestalt psychology, a school of psychology
* Gestalt therapy, a form of psychotherapy
* Bender Visual-Motor Gestalt Test, an assessment of development disorders
* Gestalt Practice, a practice of self-exploration ...
Awareness process that is still taught and followed by many today.
Lease property
Price and Murphy wanted to create a venue where non-traditional workshops and lecturers could present their ideas free of the dogma associated with traditional education. The two began drawing up plans for a forum that would be open to ways of thinking beyond the constraints of mainstream academia while avoiding the dogma so often seen in groups organized around a single idea promoted by a charismatic leader. They envisioned offering a wide range of philosophies, religious disciplines and psychological techniques.
In 1961, they went to look at property owned by the Murphy family at Slates Hot Springs
Slates Hot Springs (also known as Big Sur Hot Springs, Slate's Hot Springs, Slate's Springs, and Slate's Hot Sulphur Springs) is the site of a hot spring in the Big Sur region of Monterey County, California. It is located north-northwest of Lope ...
in Big Sur. It included a run-down hotel occupied in part by members of a Pentecostal church.[ The property was patrolled by gun-toting Hunter S. Thompson. Gay men from San Francisco filled the baths on the weekends.][
Henry Murphy's widow and Michael's grandmother Vinnie "Bunnie" MacDonald Murphy, who owned the property, lived away in Salinas. She had previously refused to lease the property to anyone, even turning down an earlier request from Michael. She was afraid her grandson was going to "give the hotel to the Hindus," Murphy later said. Not long after, Thompson attempted to visit the baths with friends and got into a fistfight after antagonizing some of the gay men present. The men almost tossed him over the cliff. Murphy's father, a lawyer, finally persuaded his mother to allow her grandson to take over][ and she agreed to lease the property to them in 1962.]Sears
Sears, Roebuck and Co. ( ), commonly known as Sears, is an American chain of department stores founded in 1892 by Richard Warren Sears and Alvah Curtis Roebuck and reincorporated in 1906 by Richard Sears and Julius Rosenwald, with what began a ...
. They incorporated their business as a non-profit named Esalen Institute in 1963.
Develop counterculture workshops
Murphy and Price were assisted by Spiegelberg, Watts, Huxley and his wife Laura, as well as by Gerald Heard
Henry FitzGerald Heard (6 October 1889 – 14 August 1971), commonly called Gerald Heard, was a British-born American historian, science writer, public lecturer, educator, and philosopher. He wrote many articles and over 35 books.
Heard was a g ...
and Gregory Bateson. They modeled the concept of Esalen partially upon Trabuco College
Trabuco College was an American retreat center founded by Gerald Heard and Aldous Huxley early in the Human Potential Movement near the community of Trabuco Canyon, California. Although it only operated from 1942 to 1949, it is cited as an inspirat ...
, founded by Heard as a quasi-monastic experiment in the mountains east of Irvine, California, and later donated to the Vedanta Society. Their intent was to provide "a forum to bring together a wide variety of approaches to enhancement of the human potential... including experiential sessions involving encounter groups, sensory awakening, gestalt awareness training, related disciplines." They stated that they did not want to be viewed as a "cult" or a new church but that it was to be a center where people could explore the concepts that Price and Murphy were passionate about. The philosophy of Esalen lies in the idea that "the cosmos, the universe itself, the whole evolutionary unfoldment is what a lot of philosophers call slumbering spirit. The divine is incarnate in the world and is present in us and is trying to manifest," according to Murphy.
Fritz Perls residency
In 1964, Fritz Perls began what became a five-year long residency at Esalen, leaving a lasting influence. Perls offered many Gestalt therapy
Gestalt therapy is a form of psychotherapy that emphasizes personal responsibility and focuses on the individual's experience in the present moment, the therapist–client relationship, the environmental and social contexts of a person's life ...
seminars at the institute until he left in July 1969. Jim Simkin and Perls led Gestalt training courses at Esalen. Simkin started a Gestalt training center on property next door that was later incorporated into Esalen's main campus.
When Perls left Esalen he considered it to be "in crisis again". He saw young people without any training leading encounter groups. And he feared that charlatans would take the lead.
However, Grogan claims that Perls’ practice at Esalen had been ethically "questionable", and according to Kripal, Perls insulted Abraham Maslow.
Gestalt Practice developed
Dick Price became one of Perls' closest students. Price managed the institute and developed his own form he called Gestalt Practice, which he taught at Esalen until his death in a hiking accident in 1985.[''The Only Way Out Is In: The Life Of Richard Price'' Barclay James Erickson, in ] Michael Murphy lived in the San Francisco Bay Area and wrote non-fiction books about Esalen-related topics, as well as several novels.
Leads counterculture movement
Esalen gained popularity quickly and started to regularly publish catalogs full of programs. The facility was large enough to run multiple programs simultaneously, so Esalen created numerous resident teacher positions. Murphy recruited Will Schutz, the well-known encounter group leader, to take up permanent residence at Esalen. All this combined to firmly position Esalen in the nexus of the counterculture of the 1960s.
The institute gained increased attention in 1966 when several magazines wrote about it. George Leonard published an article in ''Look'' magazine about the California scene which mentioned Esalen and included a picture of Murphy. ''Time'' magazine published an article about Esalen in September 1967. ''The New York Times Magazine
''The New York Times Magazine'' is an American Sunday magazine supplement included with the Sunday edition of ''The New York Times''. It features articles longer than those typically in the newspaper and has attracted many notable contributors. ...
'' published an article by Leo E. Litwak in late December. ''Life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
'' also published an article about the resort. These articles increased the media and the public's awareness of the institute in the U.S. and abroad. Esalen responded by holding large-scale conferences in Midwestern
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
and East Coast cities, as well as in Europe. Esalen opened a satellite center in San Francisco that offered extensive programming until it closed in the mid-1970s for financial reasons.
Programs and management
 The institute continues to offer workshops about humanistic psychology, physical wellness, and spiritual awareness. The institute has also added workshops on
The institute continues to offer workshops about humanistic psychology, physical wellness, and spiritual awareness. The institute has also added workshops on permaculture
Permaculture is an approach to land management and settlement design that adopts arrangements observed in flourishing natural ecosystems. It includes a set of design principles derived using whole-systems thinking. It applies these principle ...
and ecological sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livin ...
. Other workshops cover a wide range of subjects including arts, health, Gestalt
Gestalt may refer to:
Psychology
* Gestalt psychology, a school of psychology
* Gestalt therapy, a form of psychotherapy
* Bender Visual-Motor Gestalt Test, an assessment of development disorders
* Gestalt Practice, a practice of self-exploration ...
, integral thought, martial arts, massage, dance, mythology, philosophical inquiry, somatics, spiritual and religious studies, ecopsychology
Ecopsychology is an interdisciplinary and transdisciplinarity field that focuses on the synthesis of ecology and psychology and the promotion of sustainability. It is distinguished from conventional psychology as it focuses on studying the emotion ...
, wilderness experience, yoga, tai chi
Tai chi (), short for Tai chi ch'üan ( zh, s=太极拳, t=太極拳, first=t, p=Tàijíquán, labels=no), sometimes called " shadowboxing", is an internal Chinese martial art practiced for defense training, health benefits and meditation. ...
, mindfulness practice, and meditation. The institute was closed for the first half of 2017 and forced to drastically reduce staff. They also decided to revamp their offerings upon reopening to include topics more relevant to a younger generation.[
]
Center for Theory and Research
In 1998, Esalen launched the Center for Theory and Research to initiate new areas of practice and action which foster social change and realization of the human potential. It is the research and development arm of Esalen Institute. , Michael Cornwall, who previously worked in the institutes' Schizophrenia Research Project at Agnews State Hospital, was conducting workshops titled the ''Alternative Views and Approaches to Psychosis Initiative'' at Esalen. He was inviting leaders in the field of psychosis treatment to attend the workshops.
Management changes
Esalen has been making changes to respond to internal and external factors. Dick Price was the key leader of the institute until his sudden death in a hiking accident in late 1985 brought about many changes in personnel and programming.[ Nancy Lunney became the director of programming, and Dick Price's son David Price served as general manager of Esalen beginning in the mid-1990s.
The baths were destroyed in 1998 by severe weather and were rebuilt at great expense, but this caused severe institutional stress. Afterward, Andy Nusbaum developed an economic plan to stabilize Esalen's finances.
In 2011, the institute commissioned the company Beyond the Leading Edge to conduct a Leadership Culture Survey to assess the quality of its leadership culture. The results were negative. The survey measured how well the leadership "builds quality relationships, fosters teamwork, collaborates, develops people, involves people in decision making and planning, and demonstrates a high level of interpersonal skill." In the "relating dimension" the survey returned a score of 18%, compared to a desired 88%. It also produced strongly dissonant scores in measures of community welfare, relating with ]interpersonal intelligence
The theory of multiple intelligences proposes the differentiation of human intelligence into specific modalities of intelligence, rather than defining intelligence as a single, general ability. The theory has been criticized by mainstream psych ...
, clearly communicating vision, and building a sense of personal worth within the community. It ranked management as overly compliant and lacking authenticity. However, the survey found that Esalen closely matched its overall goal for customer focus.
Early leaders and programs
 In the few years after its founding, many of the seminars like "The Value of Psychotic Experience" attempted to challenge the status quo. There were even Esalen programs that questioned the movement of which Esalen itself was a part—for instance, "Spiritual and Therapeutic Tyranny: The Willingness To Submit". There were also a series of encounter groups focused on racial prejudice.
Early leaders included many well-known individuals, including Ansel Adams, Gia-fu Feng, Buckminster Fuller,
In the few years after its founding, many of the seminars like "The Value of Psychotic Experience" attempted to challenge the status quo. There were even Esalen programs that questioned the movement of which Esalen itself was a part—for instance, "Spiritual and Therapeutic Tyranny: The Willingness To Submit". There were also a series of encounter groups focused on racial prejudice.
Early leaders included many well-known individuals, including Ansel Adams, Gia-fu Feng, Buckminster Fuller, Timothy Leary
Timothy Francis Leary (October 22, 1920 – May 31, 1996) was an American psychologist and author known for his strong advocacy of psychedelic drugs. Evaluations of Leary are polarized, ranging from bold oracle to publicity hound. He was "a her ...
,
Robert Nadeau, Linus Pauling, Carl Rogers
Carl Ransom Rogers (January 8, 1902 – February 4, 1987) was an American psychologist and among the founders of the humanistic approach (and client-centered approach) in psychology. Rogers is widely considered one of the founding fathers of ps ...
, Virginia Satir, B.F. Skinner, and Arnold Toynbee. Rather than merely lecturing, many leaders experimented with what Huxley called the non-verbal humanities: the education of the body, the senses, and the emotions. Their intention was to help individuals develop awareness of their present flow of experience, to express this fully and accurately, and to listen to feedback. These "experiential" workshops were particularly well attended and were influential in shaping Esalen's future course.

Staff residency
Because of Esalen's isolated location, its operational staff members have lived on site from the beginning and for many years collectively contributed to the character of the institute.Gestalt
Gestalt may refer to:
Psychology
* Gestalt psychology, a school of psychology
* Gestalt therapy, a form of psychotherapy
* Bender Visual-Motor Gestalt Test, an assessment of development disorders
* Gestalt Practice, a practice of self-exploration ...
that pervades all aspects of daily life, including meeting structures, workplace practices, and individual language styles. There is a preschool on site called the Gazebo, serving the children of staff, some program participants, and affiliated local residents.
Scholars in residence
Esalen has sponsored long-term resident scholars, including notable individuals such as Gregory Bateson, Joseph Campbell, Stanislav Grof, Sam Keen
Sam Keen (born 1931) is an American author, professor, and philosopher who is best known for his exploration of questions regarding love, life, wonder, religion, and being a male in contemporary society. He co-produced ''Faces of the Enemy'', an a ...
, George Leonard, Fritz Perls, Ida Rolf, Virginia Satir, William Schutz
William Schutz (December 19, 1925 – November 9, 2002) was an American psychologist. , and
Alan Watts
Alan Wilson Watts (6 January 1915 – 16 November 1973) was an English writer, speaker and self-styled "philosophical entertainer", known for interpreting and popularising Japanese, Chinese and Indian traditions of Buddhist, Taoist, and Hindu ...
.
Esalen Massage and Bodywork Association
Bodywork has always been a significant part of the Esalen experience. In the late 1990s, the "EMBA" was organized as a semi-autonomous Esalen association for the regulation of Esalen massage practitioners.
Past initiatives and projects
Esalen Institute has sponsored many research initiatives, educational projects, and invitational conferences. The Big Sur facility has been used for these events, as well as other locations, including international sites.
Arts events
 In 1964, Joan Baez led a workshop entitled "The New Folk Music" which included a free performance. This was the first of seven "Big Sur Folk Festivals" featuring many of the era's music legends. The 1969 concert included musicians who had just come from the Woodstock Festival. This event was featured in a documentary movie, '' Celebration at Big Sur'', which was released in 1971.
John Cage and Robert Rauschenberg performed together at Esalen. Robert Bly,
In 1964, Joan Baez led a workshop entitled "The New Folk Music" which included a free performance. This was the first of seven "Big Sur Folk Festivals" featuring many of the era's music legends. The 1969 concert included musicians who had just come from the Woodstock Festival. This event was featured in a documentary movie, '' Celebration at Big Sur'', which was released in 1971.
John Cage and Robert Rauschenberg performed together at Esalen. Robert Bly, Lawrence Ferlinghetti
Lawrence Monsanto Ferlinghetti (March 24, 1919 – February 22, 2021) was an American poet, painter, social activist, and co-founder of City Lights Booksellers & Publishers. The author of poetry, translations, fiction, theatre, art criticism, an ...
, Allen Ginsberg, Michael McClure, Kenneth Rexroth (who led one of the first workshops), Gary Snyder and others held poetry readings and workshops.
In 1994, president and CEO Sharon Thom created an artist-in-residence program to provide artists with a two-week retreat in which to focus upon works in progress. These artists interacted with the staff, offered informal gatherings, and staged performances on the newly created dance platform. Located next to the Art Barn, the dance platform was used by Esalen teachers for dance and martial arts. The platform was later covered by a dome and renamed the Leonard Pavilion after deceased Esalen past president and board member, George Leonard.
In 1995 and 1996, Esalen hosted two arts festivals which gathered together artists, poets, musicians, photographers and performers, including artist Margot McLean, psychotherapist James Hillman, guitarist Michael Hedges
Michael Alden Hedges (December 31, 1953 – December 2, 1997) was an American acoustic guitarist and songwriter.
Early years
The son of Thayne Alden Hedges and Ruth Evelyn Hedges Ipsen, Michael Hedges was born in Sacramento, California. His l ...
and Joan Baez. All staff members were allowed to attend every class and performance that did not interfere with their schedules. Arts festivals have since become a popular yearly event at Esalen.
Schizophrenia Research Project
Encouraged by Dick Price
Richard Price (October 12, 1930 – November 25, 1985) was co-founder of the Esalen Institute in 1962 and a veteran of the Beat Generation. He ran Esalen in Big Sur for many years, sometimes virtually single-handed."Dick's life in the late 1960s ...
, the Schizophrenia Research Project was conducted over a three-year period at Agnews State Hospital in San Jose, California
San Jose, officially San José (; ; ), is a major city in the U.S. state of California that is the cultural, financial, and political center of Silicon Valley and largest city in Northern California by both population and area. With a 2020 popu ...
, involving 80 young males diagnosed with schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social wit ...
. Funded in part by Esalen Institute, this program was co-sponsored by the California Department of Mental Hygiene (reorganized: CMHSA) and the National Institute of Mental Health
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) is one of 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The NIH, in turn, is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and is the prima ...
. It explored the thesis that the health of certain patients would permanently improve if their psychotic
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior t ...
process was not interrupted by administration of antipsychotic pharmaceutical drug
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field an ...
s. Julian Silverman was chief of research for the project. He also served as Esalen's general manager in the 1970s. The Agnews double blind
In a blind or blinded experiment, information which may influence the participants of the experiment is withheld until after the experiment is complete. Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental biases that arise from a participants' expec ...
study was the largest first-episode psychosis research project ever conducted in the United States. It demonstrated that the young men given a placebo had a 75 percent lower re-hospitalization rate and much better outcomes than the men who received anti-psychotic medication. These results were used as justification for medication-free programs in the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
. Esalen has recently begun to revive some of this interest in schizophrenia and psychosis, and hosted the R.D. Laing Symposium and workshops on compassionately responding to psychosis.
Publishing
Starting in 1969, in association with Viking Press, the institute published a series of 17 books about Esalen-related topics, including the first edition of Michael Murphy's novel, '' Golf in the Kingdom'' (1971). Some of these books remain in print. In the mid-1980s, Esalen entered into a joint publishing arrangement with Lindisfarne Press to publish a small library of Russian philosophical and theological books.
Soviet–American Exchange Program
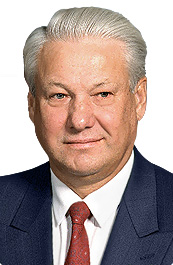 In 1979, Esalen began the Soviet–American Exchange Program (later renamed: Track Two, an institute for citizen diplomacy). This initiative came at a time when Cold War tensions were at their peak. The program was credited with substantial success in fostering peaceful private exchanges between citizens of the "super powers". In the 1980s, Michael Murphy and his wife Dulce were instrumental in organizing the program with Soviet citizen Joseph Goldin, in order to provide a vehicle for citizen-to-citizen relations between Russians and Americans. In 1982, Esalen and Goldin pioneered the first U.S.–Soviet Space Bridge, allowing Soviet and American citizens to speak directly with one another via satellite communication. In 1988, Esalen brought Abel Aganbegyan, one of Mikhail Gorbachev's chief economic advisors, to the United States. In 1989, Esalen brought
In 1979, Esalen began the Soviet–American Exchange Program (later renamed: Track Two, an institute for citizen diplomacy). This initiative came at a time when Cold War tensions were at their peak. The program was credited with substantial success in fostering peaceful private exchanges between citizens of the "super powers". In the 1980s, Michael Murphy and his wife Dulce were instrumental in organizing the program with Soviet citizen Joseph Goldin, in order to provide a vehicle for citizen-to-citizen relations between Russians and Americans. In 1982, Esalen and Goldin pioneered the first U.S.–Soviet Space Bridge, allowing Soviet and American citizens to speak directly with one another via satellite communication. In 1988, Esalen brought Abel Aganbegyan, one of Mikhail Gorbachev's chief economic advisors, to the United States. In 1989, Esalen brought Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
on his first trip to the United States, although Yeltsin did not visit the Esalen facility in Big Sur. Esalen arranged meetings for Yeltsin with then President George H. W. Bush as well as many other leaders in business and government. Two former presidents of the exchange program included Jim Garrison and Jim Hickman. After Gorbachev stepped down, and effectively dissolved the Soviet Union, Garrison helped establish The State of the World Forum, with Gorbachev as its convening chairman. These successes led to other Esalen citizen diplomacy programs, including exchanges with China, an initiative to further understanding among Jews, Christians and Muslims, as well as further work on Russian-American relations.
Prices and finances
2017 closure
On February 12, 2017, a number of mud and land slides closed Highway 1 in several locations to the south and north of the hot springs and caused Esalen to partially shut down. On February 18, 2017, shifting earth damaged a pier supporting the Pfeiffer Canyon Bridge north of Esalen and forced CalTrans to close Highway 1.[ A landslide at Mud Creek south of the hot springs severely restricted vehicle access to the resort, and Esalen temporarily closed its doors. Then, on May 20, 2017, a new slide at Mud Creek closed Highway 1 for at least a year.
On June 20, Esalen announced that it would lay off 45 staff members through at least July, leaving only about 10 percent of its staff.]
Attendance and costs
In 2012, 600 Esalen workshops were attended by more than 12,000 people. Topics ranged from sustainable business practices to hypnosis to "The Holy Fool: Crazy Wisdom From Van Gogh to Tina Fey and The Big Lebowski."
Revenue and expenses
In 2013, the institute reported revenue of $18,513,254, $13,066,407 from programs, and after expenses of $13,515,552 a net income of $4,997,702. In that year it paid CEO Patricia McEntee $152,077 In 2014, it reported total revenue of $15,934,586, expenses totalling $14,472,201, and net income of $1,462,385. McEntee was paid $157,839.
The company spent nearly $10 million for renovations from 2014 to 2016, including $7.4 million to renovate the main lodge and add a cafe and bar. It also spent $1.8 million on a six-room guesthouse. There is only limited internet cellular service available, but Esalen is planning to make some of its workshops available to online participants.[
]
Lease terms
The annual cost of its 87-year lease for the 27-acre site[ from the Vinnie A. Murphy Trust—which extends through 2049—was $344,704 in 2014. McEntee told the '' Monterey County Weekly'' that the cost of the lease is highly discounted, and that the terms of the lease allow the trust to re-assess the lease terms in 2017. This could potentially increase the institute's rent to market value.
]
Past teachers
Past guest teachers include:
In popular culture
Cultural influence
Esalen has been cited as having played a key role in the cultural transformations of the 1960s. In its beginnings as a "laboratory for new thought", it was seen by some as the headquarters of the human potential movement.The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Eco ...
'' wrote, "For many others in America and around the world, Esalen stands more vaguely for that metaphorical point where ‘East meets West’ and is transformed into something uniquely and mystically American or New Agey. And for a great many others yet, Esalen is simply that notorious bagno-bordello where people had sex and got high throughout the 1960s and 1970s before coming home talking psychobabble and dangling crystals."Christopher Lasch
Robert Christopher Lasch (June 1, 1932 – February 14, 1994) was an American historian, moralist and social critic who was a history professor at the University of Rochester. He sought to use history to demonstrate what he saw as the pervasiven ...
claimed that humanistic techniques encourage narcissistic, spiritual materialistic or self-obsessive thoughts and behaviors. In 1990 a graffiti artist spray painted "Jive shit for rich white folk" on the entrance to Esalen,Michel Houellebecq
Michel Houellebecq (; born Michel Thomas, 26 February 1956 or 1958) is a French author, known for his novels, poems and essays, as well as an occasional actor, filmmaker and singer.
His first book was a biographical essay on the horror writer ...
's ''Atomised
''Atomised'', also known as ''The Elementary Particles'' (french: Les Particules élémentaires), is a novel by the French author Michel Houellebecq, published in France in 1998. It tells the story of two half-brothers, Michel and Bruno, and ...
'' traces the New Age movement's influence on the novel's protagonists to older generations' chance meetings at Esalen.
Popular media
Films
In the comedy-drama ''Bob & Carol & Ted & Alice
''Bob & Carol & Ted & Alice'' is a 1969 American comedy-drama film directed by Paul Mazursky, written by Mazursky and Larry Tucker, who also produced the film, and starring Natalie Wood, Robert Culp, Elliott Gould, and Dyan Cannon. The origi ...
'' (1969), sophisticated Los Angeles residents Bob (played by Robert Culp
Robert Martin Culp (August 16, 1930 – March 24, 2010) was an American actor widely known for his work in television. Culp earned an international reputation for his role as Kelly Robinson on ''I Spy'' (1965–1968), the espionage television se ...
) and Carol Sanders (Natalie Wood
Natalie Wood ( Zacharenko; July 20, 1938 – November 29, 1981) was an American actress who began her career in film as a child and successfully transitioned to young adult roles.
Wood started acting at age four and was given a co-starring r ...
) spend a weekend of emotional honesty at an Esalen-style retreat, after which they return to their life determined to embrace free love and complete openness.
In the film '' What About Bob?'' (1991), Bill Murray
William James Murray (born September 21, 1950) is an American actor and comedian. He is known for his deadpan delivery. He rose to fame on ''The National Lampoon Radio Hour'' (1973–1974) before becoming a national presence on '' Saturday Nig ...
's character mentions that he hasn't felt this good since Esalen, upon his arrival at his psychiatrist's vacation home.
Literature
In Edward St Aubyn's comic novel ''On the Edge'' (1998), Esalen features prominently.
In Thomas Pynchon
Thomas Ruggles Pynchon Jr. ( , ; born May 8, 1937) is an American novelist noted for his dense and complex novels. His fiction and non-fiction writings encompass a vast array of subject matter, genres and themes, including history, music, scie ...
's novel ''Inherent Vice
''Inherent Vice'' is a novel by American author Thomas Pynchon, originally published in August 2009. A darkly comic detective novel set in 1970s California, the plot follows sleuth Larry "Doc" Sportello whose ex-girlfriend asks him to investiga ...
'' (2009) and Paul Thomas Anderson's eponymous 2014 film adaptation, the Chryskylodon Institute is modeled after Esalen.Mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite- sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. ''Fertilization'' is the fusion of two gametes. ''Copulation'' is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reprod ...
'' (1992), Esalen is referred to as a "twit factory."
Television
The BBC television series, '' The Century of the Self'' (2002), is critical of the Human Potentials Movement and includes video segments recorded at Esalen.
The ''Mad Men
''Mad Men'' is an American period drama television series created by Matthew Weiner and produced by Lionsgate Television. It ran on the cable network AMC from July 19, 2007, to May 17, 2015, lasting for seven seasons and 92 episodes. Its f ...
'' show finale, "Person to Person" (airdate May 17, 2015), features Don and Stephanie staying at an Esalen-like coastline retreat in the year 1970.
Music
On July 10, 1968 The Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the most influential band of all time and were integral to the developmen ...
guitarist George Harrison was given sitar lessons at Esalen by Ravi Shankar for the movie Raga (film).[Archived a]
Ghostarchive
and th
Wayback Machine
References
Notes
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Esalen Institute website
Notes on Gestalt Practice
*
from ''Esalen: America and the Religion of No Religion'' by Jeff Kripal
{{Authority control
1962 establishments in California
Gestalt therapy
Hot springs of California
Human Potential Movement
Buildings and structures in Monterey County, California
Personal development
Tourist attractions in Monterey County, California
Big Sur
New Age organizations

 The Esalen Institute, commonly called Esalen, is a non-profit American retreat center and intentional community in Big Sur,
The Esalen Institute, commonly called Esalen, is a non-profit American retreat center and intentional community in Big Sur, 
 The institute continues to offer workshops about humanistic psychology, physical wellness, and spiritual awareness. The institute has also added workshops on
The institute continues to offer workshops about humanistic psychology, physical wellness, and spiritual awareness. The institute has also added workshops on 
 In 1964, Joan Baez led a workshop entitled "The New Folk Music" which included a free performance. This was the first of seven "Big Sur Folk Festivals" featuring many of the era's music legends. The 1969 concert included musicians who had just come from the Woodstock Festival. This event was featured in a documentary movie, '' Celebration at Big Sur'', which was released in 1971.
John Cage and Robert Rauschenberg performed together at Esalen. Robert Bly,
In 1964, Joan Baez led a workshop entitled "The New Folk Music" which included a free performance. This was the first of seven "Big Sur Folk Festivals" featuring many of the era's music legends. The 1969 concert included musicians who had just come from the Woodstock Festival. This event was featured in a documentary movie, '' Celebration at Big Sur'', which was released in 1971.
John Cage and Robert Rauschenberg performed together at Esalen. Robert Bly, 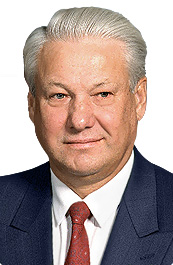 In 1979, Esalen began the Soviet–American Exchange Program (later renamed: Track Two, an institute for citizen diplomacy). This initiative came at a time when Cold War tensions were at their peak. The program was credited with substantial success in fostering peaceful private exchanges between citizens of the "super powers". In the 1980s, Michael Murphy and his wife Dulce were instrumental in organizing the program with Soviet citizen Joseph Goldin, in order to provide a vehicle for citizen-to-citizen relations between Russians and Americans. In 1982, Esalen and Goldin pioneered the first U.S.–Soviet Space Bridge, allowing Soviet and American citizens to speak directly with one another via satellite communication. In 1988, Esalen brought Abel Aganbegyan, one of Mikhail Gorbachev's chief economic advisors, to the United States. In 1989, Esalen brought
In 1979, Esalen began the Soviet–American Exchange Program (later renamed: Track Two, an institute for citizen diplomacy). This initiative came at a time when Cold War tensions were at their peak. The program was credited with substantial success in fostering peaceful private exchanges between citizens of the "super powers". In the 1980s, Michael Murphy and his wife Dulce were instrumental in organizing the program with Soviet citizen Joseph Goldin, in order to provide a vehicle for citizen-to-citizen relations between Russians and Americans. In 1982, Esalen and Goldin pioneered the first U.S.–Soviet Space Bridge, allowing Soviet and American citizens to speak directly with one another via satellite communication. In 1988, Esalen brought Abel Aganbegyan, one of Mikhail Gorbachev's chief economic advisors, to the United States. In 1989, Esalen brought