E161j on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Astaxanthin is a keto-
Food-Info.net. Retrieved on April 25, 2013. The European Food Safety Authority has set an

 Astaxanthin is present in most red-coloured aquatic organisms. The content varies from species to species, but also from individual to individual as it is highly dependent on diet and living conditions. Astaxanthin, and other chemically related asta-carotenoids, has also been found in a number of
Astaxanthin is present in most red-coloured aquatic organisms. The content varies from species to species, but also from individual to individual as it is highly dependent on diet and living conditions. Astaxanthin, and other chemically related asta-carotenoids, has also been found in a number of
carotenoid
Carotenoids (), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic compound, organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and Fungus, fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpki ...
within a group of chemical compounds known as terpenes. Astaxanthin is a metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
of zeaxanthin and canthaxanthin
Canthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It ...
, containing both hydroxyl and ketone functional groups. It is a lipid-soluble pigment with red coloring properties, which result from the extended chain of conjugated (alternating double and single) double bonds at the center of the compound.
Astaxanthin is produced naturally in the freshwater microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist indiv ...
'' Haematococcus pluvialis'' and the yeast fungus ''Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous'' (also known as ''Phaffia rhodozyma''). When the algae are stressed by lack of nutrients, increased salinity, or excessive sunshine, they create astaxanthin. Animals who feed on the algae, such as salmon, red trout, red sea bream
The Sparidae are a family of fish in the order Perciformes, commonly called sea breams and porgies. The sheepshead, scup, and red seabream are species in this family. Most sparids are deep-bodied compressed fish with a small mouth separated by a ...
, flamingos, and crustaceans (shrimp, krill, crab, lobster, and crayfish), subsequently reflect the red-orange astaxanthin pigmentation.
Astaxanthin is used as a dietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
for human, animal, and aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
consumption. Astaxanthin from algae, synthetic and bacterial sources is generally recognized as safe in the United States. The US Food and Drug Administration has approved astaxanthin as a food coloring (or color additive) for specific uses in animal and fish foods. See Note 1. The European Commission considers it as a food dye with E number
E numbers ("E" stands for "Europe") are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly ...
E161j.E-numbers : E100- E200 Food ColoursFood-Info.net. Retrieved on April 25, 2013. The European Food Safety Authority has set an
Acceptable Daily Intake
Acceptable daily intake or ADI is a measure of the amount of a specific substance (originally applied for a food additive, later also for a residue of a veterinary drug or pesticide) in food or drinking water that can be ingested (orally) daily ove ...
of 0.2 mg per kg body weight, as of 2019. As a food color
Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used in both commercial foo ...
additive, astaxanthin and astaxanthin dimethyldisuccinate are restricted for use in Salmonid
Salmonidae is a family of ray-finned fish that constitutes the only currently extant family in the order Salmoniformes . It includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), chars, freshwater whitefis ...
fish feed only.
Natural sources

 Astaxanthin is present in most red-coloured aquatic organisms. The content varies from species to species, but also from individual to individual as it is highly dependent on diet and living conditions. Astaxanthin, and other chemically related asta-carotenoids, has also been found in a number of
Astaxanthin is present in most red-coloured aquatic organisms. The content varies from species to species, but also from individual to individual as it is highly dependent on diet and living conditions. Astaxanthin, and other chemically related asta-carotenoids, has also been found in a number of lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Euphausia pacifica'' (Pacific krill)
* '' Euphausia superba'' (Antarctic krill)
* '' Haematococcus pluvialis'' (algae)
* ''
U. S. Patent 6,022,701
Phaffia yeast ''Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous'' exhibits 100% free, non-esterified astaxanthin, which is considered advantageous because it is readily absorbable and need not be hydrolysed in the digestive tract of the fish. In contrast to synthetic and bacteria sources of astaxanthin, yeast sources of astaxanthin consist mainly of the (3''R'', 3R'')-form, an important astaxanthin source in nature. Finally, the geometrical isomer, all-''E'', is higher in yeast sources of astaxanthin, as compared to synthetic sources. In shellfish, astaxanthin is almost exclusively concentrated in the shells, with only low amounts in the flesh itself, and most of it only becomes visible during cooking as the pigment separates from the denatured proteins that otherwise bind it. Astaxanthin is extracted from '' Euphausia superba'' (Antarctic krill) and from shrimp processing waste. 12,000 pounds of wet shrimp shells can yield a 6–8 gallon astaxanthin/triglyceride oil mixture.
 Astaxanthin biosynthesis starts with three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and one molecule of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) that are combined by IPP isomerase and converted to geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) by GGPP synthase. Two molecules of GGPP are then coupled by phytoene synthase to form phytoene. Next, phytoene desaturase creates four double bonds in the phytoene molecule to form lycopene. After desaturation, lycopene cyclase first forms γ-carotene by converting one of the ψ acyclic ends of the lycopene as a β-ring, then subsequently converts the other to form β-carotene. From β-carotene, hydrolases (blue) are responsible for the inclusion of two 3-hydroxy groups, and ketolases (green) for the addition of two 4-keto groups, forming multiple intermediate molecules until the final molecule, astaxanthin, is obtained.
Astaxanthin biosynthesis starts with three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and one molecule of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) that are combined by IPP isomerase and converted to geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) by GGPP synthase. Two molecules of GGPP are then coupled by phytoene synthase to form phytoene. Next, phytoene desaturase creates four double bonds in the phytoene molecule to form lycopene. After desaturation, lycopene cyclase first forms γ-carotene by converting one of the ψ acyclic ends of the lycopene as a β-ring, then subsequently converts the other to form β-carotene. From β-carotene, hydrolases (blue) are responsible for the inclusion of two 3-hydroxy groups, and ketolases (green) for the addition of two 4-keto groups, forming multiple intermediate molecules until the final molecule, astaxanthin, is obtained.
Astaxanthin extract: Parry Nutraceuticals
acnfp.gov.uk
Pandalus borealis
''Pandalus borealis'' is a species of caridean shrimp found in cold parts of the northern Atlantic and northern Pacific Oceans, although the latter population now often is regarded as a separate species, ''P. eous''. The Food and Agriculture Orga ...
'' (Arctic shrimp)
* ''Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous'', formerly ''Phaffia rhodozyma'' (yeast)
Astaxanthin concentrations in nature are approximately:
Algae are the primary natural source of astaxanthin in the aquatic food chain. The microalgae '' Haematococcus pluvialis'' seems to accumulate the highest levels of astaxanthin in nature and is currently, the primary industrial source for natural astaxanthin production where more than 40 g of astaxanthin can be obtained from one kg of dry biomass. '' Haematococcus pluvialis'' has the productional advantage of the population doubling every week, which means scaling up is not an issue. Specifically, the microalgae are grown in two phases. First, in the green phase, the cells are given an abundance of nutrients to promote proliferation of the cells. In the subsequent red phase, the cells are deprived of nutrients and subjected to intense sunlight to induce encystment (carotogenesis), during which the cells produce high levels of astaxanthin as a protective mechanism against the environmental stress. The cells, with their high concentrations of astaxanthin, are then harvested.Boussiba; Sammy, V.; Avigad, C.; et al. (2000) Procedure for large-scale production of astaxanthin from haematococcusU. S. Patent 6,022,701
Phaffia yeast ''Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous'' exhibits 100% free, non-esterified astaxanthin, which is considered advantageous because it is readily absorbable and need not be hydrolysed in the digestive tract of the fish. In contrast to synthetic and bacteria sources of astaxanthin, yeast sources of astaxanthin consist mainly of the (3''R'', 3R'')-form, an important astaxanthin source in nature. Finally, the geometrical isomer, all-''E'', is higher in yeast sources of astaxanthin, as compared to synthetic sources. In shellfish, astaxanthin is almost exclusively concentrated in the shells, with only low amounts in the flesh itself, and most of it only becomes visible during cooking as the pigment separates from the denatured proteins that otherwise bind it. Astaxanthin is extracted from '' Euphausia superba'' (Antarctic krill) and from shrimp processing waste. 12,000 pounds of wet shrimp shells can yield a 6–8 gallon astaxanthin/triglyceride oil mixture.
Biosynthesis
 Astaxanthin biosynthesis starts with three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and one molecule of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) that are combined by IPP isomerase and converted to geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) by GGPP synthase. Two molecules of GGPP are then coupled by phytoene synthase to form phytoene. Next, phytoene desaturase creates four double bonds in the phytoene molecule to form lycopene. After desaturation, lycopene cyclase first forms γ-carotene by converting one of the ψ acyclic ends of the lycopene as a β-ring, then subsequently converts the other to form β-carotene. From β-carotene, hydrolases (blue) are responsible for the inclusion of two 3-hydroxy groups, and ketolases (green) for the addition of two 4-keto groups, forming multiple intermediate molecules until the final molecule, astaxanthin, is obtained.
Astaxanthin biosynthesis starts with three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and one molecule of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) that are combined by IPP isomerase and converted to geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) by GGPP synthase. Two molecules of GGPP are then coupled by phytoene synthase to form phytoene. Next, phytoene desaturase creates four double bonds in the phytoene molecule to form lycopene. After desaturation, lycopene cyclase first forms γ-carotene by converting one of the ψ acyclic ends of the lycopene as a β-ring, then subsequently converts the other to form β-carotene. From β-carotene, hydrolases (blue) are responsible for the inclusion of two 3-hydroxy groups, and ketolases (green) for the addition of two 4-keto groups, forming multiple intermediate molecules until the final molecule, astaxanthin, is obtained.
Synthetic sources
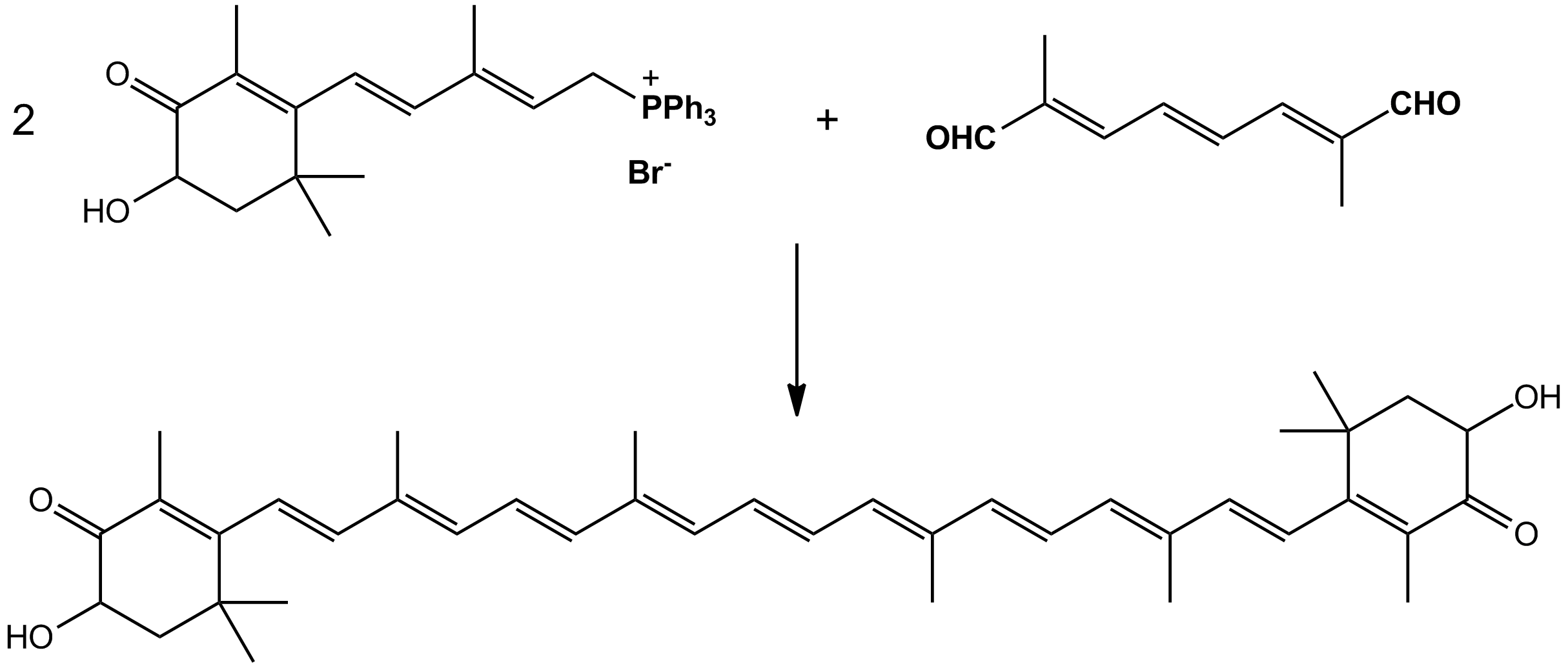
The structure of astaxanthin by synthesis was described in 1975. Nearly all commercially available astaxanthin for aquaculture is produced synthetically, with an annual turnover of over $200 million and a selling price of roughly $5000–6000 per kilo as of July 2012. The market grew to over $500 million by 2016 and is expected to continue to grow with theaquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
industry.
An efficient synthesis from isophorone, ''cis''-3-methyl-2-penten-4-yn-1-ol and a symmetrical C10-dialdehyde has been discovered and is used in industrial production. It combines these chemicals together with an ethynylation and then a Wittig reaction. Two equivalents of the proper ylide An ylide or ylid () is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms h ...
combined with the proper dialdehyde in a solvent of methanol, ethanol, or a mixture of the two, yields astaxanthin in up to 88% yields.

Metabolic engineering
The cost of astaxanthin extraction, high market price, and lack of efficient fermentation production systems, combined with the intricacies of chemical synthesis, discourage its commercial development. The metabolic engineering of bacteria ('' Escherichia coli'') enables efficient astaxanthin production from beta-carotene via either zeaxanthin orcanthaxanthin
Canthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It ...
.
Structure
Stereoisomers
In addition to structural isomeric configurations, astaxanthin also contains two chiral centers at the 3- and 3-positions, resulting in three unique stereoisomers (3R,3R and 3R,3'S meso and 3S,3'S). While all three stereoisomers are present in nature, relative distribution varies considerably from one organism to another. Synthetic astaxanthin contains a mixture of all three stereoisomers, in approximately 1:2:1 proportions.Esterification
Astaxanthin exists in two predominant forms, non-esterified (yeast, synthetic) oresterified
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fa ...
(algal) with various length fatty acid moieties whose composition is influenced by the source organism as well as growth conditions. The astaxanthin fed to salmon to enhance flesh coloration is in the non-esterified form
The predominance of evidence supports a de-esterification of fatty acids from the astaxanthin molecule in the intestine prior to or concomitant with absorption resulting in the circulation and tissue deposition of non-esterified astaxanthin. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) published a scientific opinion on a similar xanthophyll carotenoid, lutein, stating that "following passage through the gastrointestinal tract and/or uptake lutein esters are hydrolyzed to form free lutein again". While it can be assumed that non-esterified astaxanthin would be more bioavailable than esterified astaxanthin due to the extra enzymatic steps in the intestine needed to hydrolyse the fatty acid components, several studies suggest that bioavailability is more dependent on formulation than configuration.
Uses
Astaxanthin is used as adietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
and feed supplement as food colorant
Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used in both commercial food ...
for salmon, crabs, shrimp, chickens and egg production.
For seafood and animals
The primary use of synthetic astaxanthin today is as an animal feed additive to impart coloration, including farm-raised salmon and chicken egg yolks. Synthetic carotenoid pigments colored yellow, red or orange represent about 15–25% of the cost of production of commercial salmon feed. In the 21st century, most commercial astaxanthin for aquaculture is produced synthetically. Class action lawsuits were filed against some major grocery store chains for not clearly labeling the astaxanthin-treated salmon as "color added". The chains followed up quickly by labeling all such salmon as "color added". Litigation persisted with the suit for damages, but a Seattle judge dismissed the case, ruling that enforcement of the applicable food laws was up to government and not individuals.Dietary supplement
The primary human application for astaxanthin is as adietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
, and it remains under preliminary research. In 2020, the European Food Safety Authority reported that an intake of 8 mg astaxanthin per day from food supplements is safe for adults.
Role in the food chain
Lobsters, shrimp, and some crabs turn red when cooked because the astaxanthin, which was bound to the protein in the shell, becomes free as the protein denatures and unwinds. The freed pigment is thus available to absorb light and produce the red color.Regulations
In April 2009, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved astaxanthin as an additive for fish feed only as a component of a stabilized color additive mixture. Color additive mixtures for fish feed made with astaxanthin may contain only those diluents that are suitable. The color additives astaxanthin, ultramarine blue,canthaxanthin
Canthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It ...
, synthetic iron oxide
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. All are black magnetic solids. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of whic ...
, dried algae meal, '' Tagetes'' meal and extract, and corn endosperm oil are approved for specific uses in animal foods. ''Haematococcus'' algae meal (21 CFR 73.185) and ''Phaffia'' yeast (21 CFR 73.355) for use in fish feed to color salmonoids were added in 2000.
In the European Union, astaxanthin-containing food supplements derived from sources that have no history of use as a source of food in Europe, fall under the remit of the Novel Food legislation, EC (No.) 258/97. Since 1997, there have been five novel food applications concerning products that contain astaxanthin extracted from these novel sources. In each case, these applications have been simplified or substantial equivalence applications, because astaxanthin is recognised as a food component in the EU diet.acnfp.gov.uk
References
{{Carotenoids Articles containing video clips Carotenoids Cyclohexenes Food colorings Secondary alcohols Tetraterpenes