Diskit Monastery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Diskit Monastery also known as Deskit Gompa or Diskit Gompa is the oldest and largest
Diskit Monastery also known as Deskit Gompa or Diskit Gompa is the oldest and largest
 The Diskit monastery was founded by Changzem Tserab Zangpo in the 14th century. The history of the Nubra Valley and the monastery could thus be traced from the 14th century onwards. Ladakh was then ruled by King Grags-pa-‘bum-lde (1400–1440) and his brother, who unsuccessfully attempted to usurp Nubra Valley, which was under a local ruler named Nyig-ma-grags-pa. The local ruler assisted a Gelugpa order advocate to build the monastery at Diskit and deify the idol of
The Diskit monastery was founded by Changzem Tserab Zangpo in the 14th century. The history of the Nubra Valley and the monastery could thus be traced from the 14th century onwards. Ladakh was then ruled by King Grags-pa-‘bum-lde (1400–1440) and his brother, who unsuccessfully attempted to usurp Nubra Valley, which was under a local ruler named Nyig-ma-grags-pa. The local ruler assisted a Gelugpa order advocate to build the monastery at Diskit and deify the idol of
 The Diskit monastery is situated on the hill, just above the flood plains of the
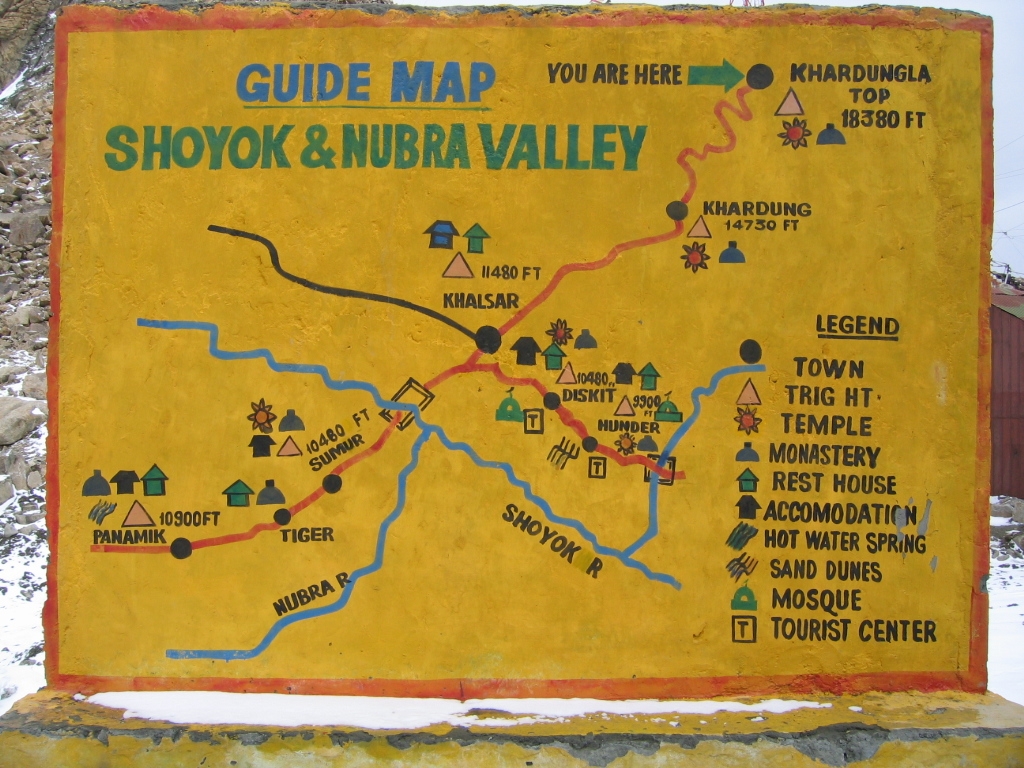
The Diskit monastery is situated on the hill, just above the flood plains of the  The approach road to the monastery is from the Diskit village through a rugged and dusty road that crosses a stream in the middle of the village. The village is approachable from Leh by road via the Khardung pass. The traffic on this road may be disrupted between October and May due to snow fall and landslides. This road is often -and incorrectly -claimed to be the highest motorable road in the world. The road from Leh passes through South Pullu (an army camp), then to
The approach road to the monastery is from the Diskit village through a rugged and dusty road that crosses a stream in the middle of the village. The village is approachable from Leh by road via the Khardung pass. The traffic on this road may be disrupted between October and May due to snow fall and landslides. This road is often -and incorrectly -claimed to be the highest motorable road in the world. The road from Leh passes through South Pullu (an army camp), then to
 Diskit Monastery has been built at the edge of the approach road. This road links with Parthapur and Those. Approach to the monastery is through a flight of steps made of stones, which lead to the prayer hall of the monastery. A statue of
Diskit Monastery has been built at the edge of the approach road. This road links with Parthapur and Those. Approach to the monastery is through a flight of steps made of stones, which lead to the prayer hall of the monastery. A statue of
Diskit monastery
and is said to be one of the oldest temples in the Nubra Valley where a large idol of
 Desmochhey or Dosmoche, also known as "Festival of the Scapegoat" is the popular prayer festival that is celebrated at Diskit Monastery,
Desmochhey or Dosmoche, also known as "Festival of the Scapegoat" is the popular prayer festival that is celebrated at Diskit Monastery,
File:Diskit gompa nubra1.jpg, Diskit Monastery
File:Nubra disket 03.jpg, Diskit monastery perched against the hills
File:Diskit Monastery, Diskit.jpg, Diskit Monastery broad view
File:Diskit Gompa. Nubra. 2010.jpg, Diskit Gompa. Nubra. 2010
Traverse Nubra valley with the lens of 22 years old
{{Authority control Buddhist monasteries in Ladakh Gelug monasteries and temples
 Diskit Monastery also known as Deskit Gompa or Diskit Gompa is the oldest and largest
Diskit Monastery also known as Deskit Gompa or Diskit Gompa is the oldest and largest Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
monastery (gompa
A Gompa or Gönpa ( "remote place", Sanskrit ''araṇya''), also known as ling (), is a Buddhist ecclesiastical fortification of learning, lineage and sādhanā that may be understood as a conflation of a fortification, a vihara and a universit ...
) in Diskit, in the Nubra Valley
Nubra, also called Dumra, is a historical region of Ladakh, India that is currently administered as a subdivision and a tehsil in the Leh district. Its inhabited areas form a tri-armed valley cut by the Nubra and Shyok rivers. Its Tibetan name ...
in the Leh district
Leh district is a district in the union territory of Ladakh, India. With an area of 45,110 ''km'2'', it is the second largest district in the country smaller only to Kutch. It is bounded on the north by Gilgit-Baltistan's Kharmang and Gh ...
of Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu a ...
, India.
It belongs to the Gelugpa
240px, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Bodhgaya (India).
The Gelug (, also Geluk; "virtuous")Kay, David N. (2007). ''Tibetan and Zen Buddhism in Britain: Transplantati ...
(Yellow Hat) sect of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
. It was founded by Changzem Tserab Zangpo, a disciple of Tsong Khapa
Tsongkhapa ('','' meaning: "the man from Tsongkha" or "the Man from Onion Valley", c. 1357–1419) was an influential Tibetan Buddhist monk, philosopher and tantric yogi, whose activities led to the formation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Bud ...
, founder of Gelugpa, in the 14th century. It is a sub-gompa of the Thikse gompa.
Lachung Temple and Hundur Monastery are also located nearby, the latter is below the main road near a bridge.
The monastery has statue of Cho Rinpoche (Crowned Buddha) in the prayer hall, a huge drum and several images of fierce guardian deities. An elevated cupola of the monastery depicts a fresco of the Tashilhunpo Monastery
Tashi Lhunpo Monastery (), founded in 1447 by the 1st Dalai Lama, is the traditional
monastic seat of the Panchen Lama, and an historically and culturally important monastery in Shigatse, the second-largest city in Tibet.
The monastery was ...
of Tibet.
The monastery administration runs a school, with support from a non-government organization known as the "Tibet Support Group", which has computer facilities and teaches science subjects, in English, to Tibetan children of the region.
A popular festival known as ''Dosmoche'' or the "Festival of the Scapegoat" is held in the precincts of the monastery in February during the winter season, which is largely attended by people from villages of the Nubra Valley
Nubra, also called Dumra, is a historical region of Ladakh, India that is currently administered as a subdivision and a tehsil in the Leh district. Its inhabited areas form a tri-armed valley cut by the Nubra and Shyok rivers. Its Tibetan name ...
since the other regions in Leh
Leh () ( lbj, ) is the joint capital and largest city of Ladakh, a union territory of India. Leh, located in the Leh district, was also the historical capital of the Kingdom of Ladakh, the seat of which was in the Leh Palace, the former ...
are inaccessible during this period due to heavy snow fall.
History
 The Diskit monastery was founded by Changzem Tserab Zangpo in the 14th century. The history of the Nubra Valley and the monastery could thus be traced from the 14th century onwards. Ladakh was then ruled by King Grags-pa-‘bum-lde (1400–1440) and his brother, who unsuccessfully attempted to usurp Nubra Valley, which was under a local ruler named Nyig-ma-grags-pa. The local ruler assisted a Gelugpa order advocate to build the monastery at Diskit and deify the idol of
The Diskit monastery was founded by Changzem Tserab Zangpo in the 14th century. The history of the Nubra Valley and the monastery could thus be traced from the 14th century onwards. Ladakh was then ruled by King Grags-pa-‘bum-lde (1400–1440) and his brother, who unsuccessfully attempted to usurp Nubra Valley, which was under a local ruler named Nyig-ma-grags-pa. The local ruler assisted a Gelugpa order advocate to build the monastery at Diskit and deify the idol of Tsong Khapa
Tsongkhapa ('','' meaning: "the man from Tsongkha" or "the Man from Onion Valley", c. 1357–1419) was an influential Tibetan Buddhist monk, philosopher and tantric yogi, whose activities led to the formation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Bud ...
, the founder of the Gelugpa sect, in the monastery. During the rule of King Blogros-chog-idan (1440–1470) who had even controlled western Tibet, Panchen Lha-btsun - a resident of Nubra Valley by birth - studied in Tibet and later became a regent to the founder of Tashilhunpo Monastery
Tashi Lhunpo Monastery (), founded in 1447 by the 1st Dalai Lama, is the traditional
monastic seat of the Panchen Lama, and an historically and culturally important monastery in Shigatse, the second-largest city in Tibet.
The monastery was ...
and finally during his last stage of life returned to Nubra. His remains have been preserved in Charasa. In 1500, Ladakh was ruled by Bkra-shis-rnam-rgyal, who fought the invader Mirza Haider of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, in Nubra and close to Leh, finally defeated the latter and thus bringing Nubra under Ladakh King’s rule. Even then, the local chieftains still yielded power in Diskit and Hundar. Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
Muslims started settling in Nubra after this war. Bkra-shis-rnam-rgyal’ son, Tshedbang-rnam-rgyal ruled Ladakh from 1530 and expanded his kingdom. At that time, Nubra people prevailed on him and preventing him from invading Hor in Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
, as trade with Yarkand
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous ...
was considered crucial to Nubra. During the reign of Jams-dbang-rnam-rgyal, historical records indicate that a regular tribute payment was made by the Nubra people to the king. The King Bde-‘Idanrnam-rgyal (1620–45) successfully defeated Baltistan
Baltistan ( ur, ; bft, སྦལ་ཏི་སྟཱན, script=Tibt), also known as Baltiyul or Little Tibet ( bft, སྦལ་ཏི་ཡུལ་།, script=Tibt), is a mountainous region in the Pakistani-administered territory of Gil ...
and the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. Rgyal kings were very religious and built mani
Mani may refer to:
Geography
* Maní, Casanare, a town and municipality in Casanare Department, Colombia
* Mani, Chad, a town and sub-prefecture in Chad
* Mani, Evros, a village in northeastern Greece
* Mani, Karnataka, a village in Dakshina ...
walls throughout their kingdom. Monks were specially engaged to recite hymns of ''Mani-tung chur'' in Nubra Valley and in other surrounding areas. In mid eighteenth century, Tshe-dbang-rnam-rgyal gave away the control of Diskit monastery to the Rinpoche
Rinpoche, also spelled Rimboche and Rinboku (), is an honorific term used in the Tibetan language. It literally means "precious one", and may refer to a person, place, or thing—like the words "gem" or "jewel" ( Sanskrit: ''Ratna'').
The word co ...
of Thikse Monastery
Thikse Gompa or Thikse Monastery (also transliterated from Ladakhi as Tiksey, Thiksey or Thiksay) is a gompa (Tibetan-style monastery) affiliated with the Gelug sect of Tibetan Buddhism. It is located on top of a hill in Thiksey approximately e ...
and this arrangement has been perpetuated to this day. Since then, Diskit is considered a sub-gompa of Thikse.
Geography
 The Diskit monastery is situated on the hill, just above the flood plains of the
The Diskit monastery is situated on the hill, just above the flood plains of the Shyok River
The Shyok River is a tributary of the Indus River that flows through northern Ladakh and enters Gilgit–Baltistan, spanning some .
The Shyok River originates at the Rimo Glacier, one of the tongues of Siachen Glacier. Its alignment is ver ...
, on its right bank in the Diskit village () in Nubra Valley. Nubra River
The Nubra River is a river in the Nubra Valley of Ladakh in India. It is a tributary of the Shyok River (a part of the Indus River system) and originates from the Siachen Glacier, the second-longest non-polar glacier in the world. In earlier Ti ...
is a tributary of the Shyok River, which flows parallel to the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
on the northern side of the Ladakh Range
The Ladakh Range is a mountain range in central Ladakh in India with its northern tip extending into Baltistan in Pakistan. It lies between the Indus and Shyok river valleys, stretching to 230 miles (370 km). Leh, the capital city of Lada ...
. Since the valley is at lower elevation, it has a mild climate. This climatic condition has created lush vegetation in the valley and the valley is, therefore, called the "Orchard of Ladakh". The valley was part of the caravan route between Tibet and China. It has various trekking sites, along the countryside. The valley is also the natural home of the double-humped Bactrian camel
The Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''), also known as the Mongolian camel or domestic Bactrian camel, is a large even-toed ungulate native to the steppes of Central Asia. It has two humps on its back, in contrast to the single-humped dro ...
. It is located trans Leh, beyond the snow-clad Khardung La
Khardung La () or Khardung Pass is a mountain pass in the Leh district of the Indian union territory of Ladakh.
The pass is on the Ladakh Range, north of Leh, and connects the Indus river valley and the Shyok river valley. It also forms the ...
pass. Since the snow clad mountains become unpassable many times during winter, Diskit village and the monastery in the valley have become the congregation centre for people of the region of the valley. Diskit is the headquarters of the Nubra Valley and thus has lot of government offices with basic facilities. It is also connected by road with Leh.
 The approach road to the monastery is from the Diskit village through a rugged and dusty road that crosses a stream in the middle of the village. The village is approachable from Leh by road via the Khardung pass. The traffic on this road may be disrupted between October and May due to snow fall and landslides. This road is often -and incorrectly -claimed to be the highest motorable road in the world. The road from Leh passes through South Pullu (an army camp), then to
The approach road to the monastery is from the Diskit village through a rugged and dusty road that crosses a stream in the middle of the village. The village is approachable from Leh by road via the Khardung pass. The traffic on this road may be disrupted between October and May due to snow fall and landslides. This road is often -and incorrectly -claimed to be the highest motorable road in the world. The road from Leh passes through South Pullu (an army camp), then to Khardung La
Khardung La () or Khardung Pass is a mountain pass in the Leh district of the Indian union territory of Ladakh.
The pass is on the Ladakh Range, north of Leh, and connects the Indus river valley and the Shyok river valley. It also forms the ...
(), goes down to the North Pullu (foreign visitors have to register their entry to Nubru Valley), moves down to the Khardung village, slopes down to the Khalsar village in the valley floor and then bifurcates into two branches. The left branch from Khalsar village leads to the Diskit and Hunder villages, while the right branch road leads to Sumur and Panamik
Panamic or Panamik is a village in the Leh district of Ladakh in India.
It is located in the Nubra tehsil. Hot sulphur springs are found in the village.
Panamik is a contraction of སྤང་ན་ཆུ་མིག་ 'Spang na Chumik', ...
villages. Leh to Diskit is by road which is maintained by the Indian Army
The Indian Army is the Land warfare, land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Arm ...
'.
Structures
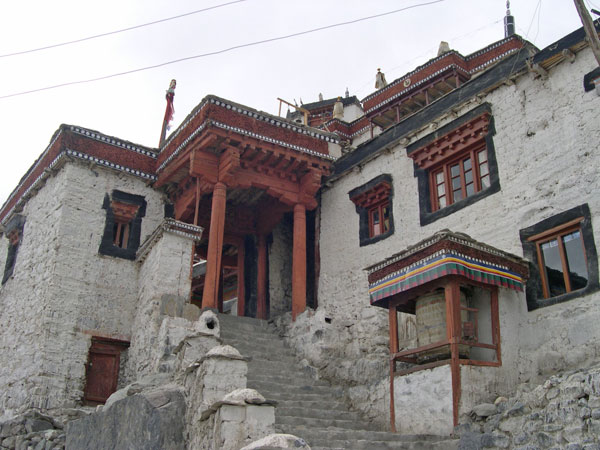
 Diskit Monastery has been built at the edge of the approach road. This road links with Parthapur and Those. Approach to the monastery is through a flight of steps made of stones, which lead to the prayer hall of the monastery. A statue of
Diskit Monastery has been built at the edge of the approach road. This road links with Parthapur and Those. Approach to the monastery is through a flight of steps made of stones, which lead to the prayer hall of the monastery. A statue of Maitreya Buddha
Maitreya ( Sanskrit: ) or Metteyya (Pali: ), also Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha, is regarded as the future Buddha of this world in Buddhist eschatology. As the 5th and final Buddha of the current kalpa, Maitreya's teachings will be aimed a ...
is enshrined in the hall. There is a huge drum located within the hall. In the chamber on the second floor, there are many images of fierce guardian deities.
Diskit Monastery also has an elevated cupola, with a fresco depicting the Tashilhunpo Monastery
Tashi Lhunpo Monastery (), founded in 1447 by the 1st Dalai Lama, is the traditional
monastic seat of the Panchen Lama, and an historically and culturally important monastery in Shigatse, the second-largest city in Tibet.
The monastery was ...
of Tibet. It also has a number of shrines and Mongolian and Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken diale ...
texts in the storehouse. Diskit Monastery is connected to Mongol mythology
The Mongol mythology is the traditional religion of the Mongols.
Creation
There are many Mongol creation myths. In the most ancient one, the creation of the world is attributed to a Buddhist deity Lama. At the start of time, there was only wat ...
in that the monastery is believed to be the place where an evil anti-Buddhist Mongol demon once lived and was killed near the monastery grounds but is said to have been resurrected several times. Today, the wrinkled head and hand of the demon are believed to lie inside a temple in the monastery. The ''Lonely Planet
Lonely Planet is a travel guide book publisher. Founded in Australia in 1973, the company has printed over 150 million books.
History Early years
Lonely Planet was founded by married couple Maureen and Tony Wheeler. In 1972, they embark ...
'' India guide describes that the gompa roof offers "glorious" views of the Nubra Valley.
Recent extensions to the monastery building are in good shape but the Dukhang ("main prayer hall") and Zimcchungh are not in good condition. Paintings have been covered with soot and images are kept in total disorder. The older part of the monastery is said to be in certain degree of decay, as cracks have been observed, and they remain untended.
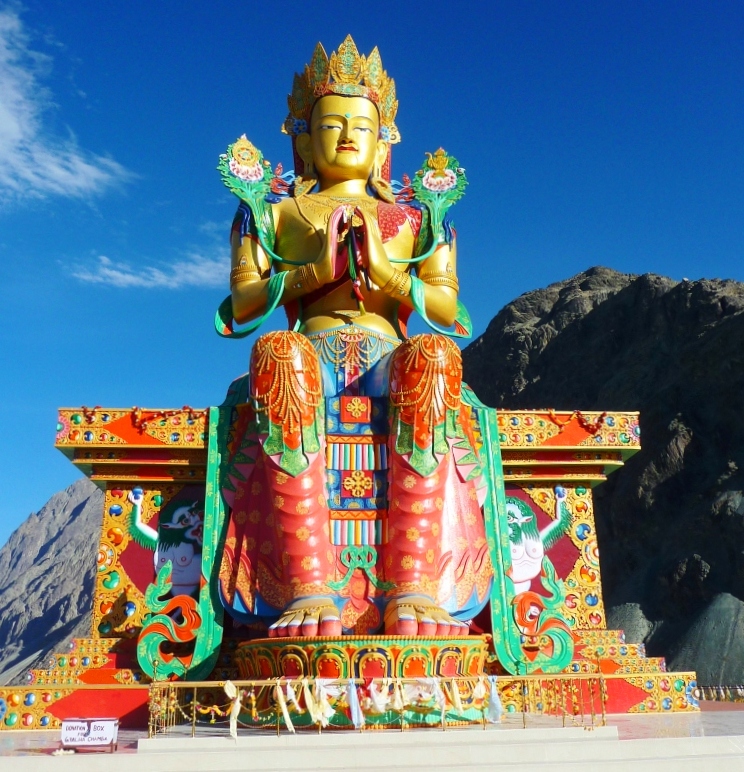
Large statue of Jampa (Maitreya) Buddha
The ''photong'' or official residence of the Chief Lama of Nubra is located at the foot hill where there is also a very large statue of Jampa (Maitreya) Buddha. This impressive 32 metre (106 foot) statue on top of a hill below the monastery, faces down the ''Shyok River'' towards Pakistan and, according to Mr.Tsering Norphel, chairman of the committee which organised it, most of the money came from local donations. The Head of the Gelugpa, Ganden Thipa (the reincarnation ofTsongkhapa
Tsongkhapa ('','' meaning: "the man from Tsongkha" or "the Man from Onion Valley", c. 1357–1419) was an influential Tibetan Buddhist monk, philosopher and tantric yogi, whose activities led to the formation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Budd ...
), and Abbott of ''Rizu Monastery'', gave 8 kg of gold for its decoration. It is the first time a Ladakhi monk has been the head of the Gelugpa sect.
The statue's construction was started in April 2006 and it was consecrated by the Dalai Lama on 25 July 2010. Mr. Nophel says the statue was built with three main functions in mind - protection of Diskit Village, prevention of further war with Pakistan, and to promote world peace.
Lachung temple
Lachung temple is close but above thDiskit monastery
and is said to be one of the oldest temples in the Nubra Valley where a large idol of
Tsong Khapa
Tsongkhapa ('','' meaning: "the man from Tsongkha" or "the Man from Onion Valley", c. 1357–1419) was an influential Tibetan Buddhist monk, philosopher and tantric yogi, whose activities led to the formation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Bud ...
is deified and a Gelugpa yellow hat crowns the image.
School
The monastery, which houses about 100 monks, runs a school in its precincts. This school teaches Tibetan children. The school has been upgraded recently to enable teaching of scientific subjects with support from the Lungta, a 'Tibet Support Group' (a non governmental organization) that has created computer facilities in the school. Lungta has trained the monks of the monastery in computer skills and in the English language so that they could in turn teach the children of the school. Further additions to the school library in the form of dictionaries, encyclopaedias and English teaching materials are being provided.Festival
 Desmochhey or Dosmoche, also known as "Festival of the Scapegoat" is the popular prayer festival that is celebrated at Diskit Monastery,
Desmochhey or Dosmoche, also known as "Festival of the Scapegoat" is the popular prayer festival that is celebrated at Diskit Monastery, Likir Monastery
Likir Monastery or Likir Gompa (Klud-kyil) is a Buddhist monastery in Ladakh, Northern India. It is located at 3700m elevation, approximately in the west of Leh. It is picturesquely situated on a little hill in the valley, in Likir village ne ...
and Leh Palace
Leh Palace also known as Lachen Palkar Palace is a former royal palace overlooking the city of Leh in Ladakh, India. It was constructed circa 1600 by Sengge Namgyal. The palace was abandoned when Dogra forces took control of Ladakh in the mid ...
in Leh
Leh () ( lbj, ) is the joint capital and largest city of Ladakh, a union territory of India. Leh, located in the Leh district, was also the historical capital of the Kingdom of Ladakh, the seat of which was in the Leh Palace, the former ...
. Since the festival is celebrated in February during the winter season, when snowbound Khardong peak is not passable to attend similar festivities at Likir monastery in Leh, large crowds from villages in the Nubra Valley assemble at Diskit to witness the mask dance. The mask dance also known as Cham dance is performed by the Lama
Lama (; "chief") is a title for a teacher of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. The name is similar to the Sanskrit term ''guru'', meaning "heavy one", endowed with qualities the student will eventually embody. The Tibetan word "lama" means "hig ...
s of the Monastery to dramatically express the superiority of good over evil forces. The dances are believed to avoid ill-fortune in the new year (Tibetan new year is celebrated in December/January). On this occasion, images made of dough are thrown out to deter any disaster occurring and to usher peace and prosperity to the people. The cloths covering the heads of deity statues are removed in this period.
Gallery
Footnotes
Literature
*Rizvi, Janet. 1996. ''Ladakh: Crossroads of High Asia''. Second Edition. Oxford India Paperbacks. 3rd Impression 2001. .Traverse Nubra valley with the lens of 22 years old
{{Authority control Buddhist monasteries in Ladakh Gelug monasteries and temples