Cellular neuroscience on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cellular neuroscience is a branch of
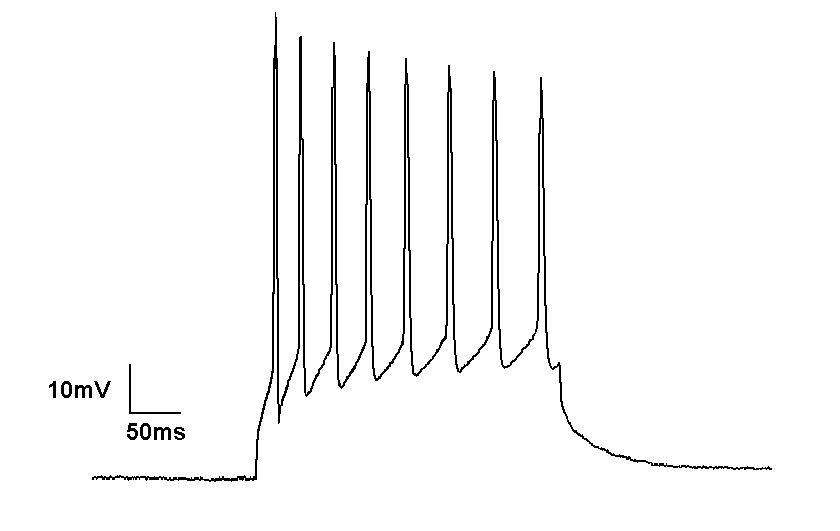 The Hodgkin–Huxley model of an
The Hodgkin–Huxley model of an
 Neurons communicate with one another via
Neurons communicate with one another via
neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, ...
concerned with the study of neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s at a cellular level. This includes morphology and physiological properties of single neurons. Several techniques such as intracellular recording, patch-clamp, and voltage-clamp technique, pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
, confocal imaging, molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
, two photon laser scanning microscopy and Ca2+ imaging have been used to study activity at the cellular level. Cellular neuroscience examines the various types of neurons, the functions of different neurons, the influence of neurons upon each other, and how neurons work together.
Neurons and glial cells
Neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
are cells that are specialized to receive, propagate, and transmit electrochemical impulses. In the human brain alone, there are over eighty billion neurons. Neurons are diverse with respect to morphology and function. Thus, not all neurons correspond to the stereotypical motor neuron with dendrites and myelinated axons that conduct action potentials. Some neurons such as photoreceptor cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation ...
s, for example, do not have myelinated axons that conduct action potentials. Other unipolar neurons found in invertebrates do not even have distinguishing processes such as dendrites. Moreover, the distinctions based on function between neurons and other cells such as cardiac and muscle cells are not helpful. Thus, the fundamental difference between a neuron and a nonneuronal cell is a matter of degree.
Another major class of cells found in the nervous system are glial cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up ...
. These cells are only recently beginning to receive attention from neurobiologists for being involved not just in nourishment and support of neurons, but also in modulating synapses. For example, Schwann cells
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include Satellite glial cell, satellite ...
, which are a type of glial cell found in the peripheral nervous system, modulate synaptic connections between presynaptic terminals of motor neuron endplates and muscle fibers at neuromuscular junctions.
Neuronal function
One prominent characteristic of many neurons is excitability. Neurons generate electrical impulses or changes in voltage of two types: graded potentials and action potentials. Graded potentials occur when the membrane potential depolarizes and hyperpolarizes in a graded fashion relative to the amount of stimulus that is applied to the neuron. An action potential on the other hand is an all-or-none electrical impulse. Despite being slower than graded potentials, action potentials have the advantage of traveling long distances in axons with little or no decrement. Much of the current knowledge of action potentials comes from squid axon experiments by Sir Alan Lloyd Hodgkin and Sir Andrew Huxley.Action potential
action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
in the squid giant axon
The squid giant axon is the very large (up to 1.5 mm in diameter; typically around 0.5 mm) axon that controls part of the water jet propulsion system in squid. It was first described by L. W. Williams in 1909, but this discovery was fo ...
has been the basis for much of the current understanding of the ionic bases of action potentials. Briefly, the model states that the generation of an action potential is determined by two ions: Na+ and K+. An action potential can be divided into several sequential phases: threshold, rising phase, falling phase, undershoot phase, and recovery. Following several local graded depolarizations of the membrane potential, the threshold of excitation is reached, voltage-gated sodium channels are activated, which leads to an influx of Na+ ions. As Na+ ions enter the cell, the membrane potential is further depolarized, and more voltage-gated sodium channels are activated. Such a process is also known as a positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
loop. As the rising phase reaches its peak, voltage-gated Na+ channels are inactivated whereas voltage-gated K+ channels are activated, resulting in a net outward movement of K+ ions, which re-polarizes the membrane potential towards the resting membrane potential. Repolarization of the membrane potential continues, resulting in an undershoot phase or absolute refractory period. The undershoot phase occurs because, unlike voltage-gated sodium channels, voltage-gated potassium channels inactivate much more slowly. Nevertheless, as more voltage-gated K+ channels become inactivated, the membrane potential recovers to its normal resting steady state.
Structure and formation of synapses
synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending o ...
. Synapses are specialized junctions between two cells in close apposition to one another. In a synapse, the neuron that sends the signal is the presynaptic neuron and the target cell receives that signal is the postsynaptic neuron or cell. Synapses can be either electrical or chemical. Electrical synapses are characterized by the formation of gap junctions that allow ions and other organic compound to instantaneously pass from one cell to another. Chemical synapses are characterized by the presynaptic release of neurotransmitters that diffuse across a synaptic cleft to bind with postsynaptic receptors. A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that is synthesized within neurons themselves and released by these same neurons to communicate
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmit ...
with their postsynaptic target cells. A receptor is a transmembrane protein molecule that a neurotransmitter or drug binds. Chemical synapses are slower than electrical synapses.
Neurotransmitter transporters, receptors, and signaling mechanisms
After neurotransmitters are synthesized, they are packaged and stored in vesicles. These vesicles are pooled together in terminal boutons of the presynaptic neuron. When there is a change in voltage in the terminal bouton, voltage-gated calcium channels embedded in the membranes of these boutons become activated. These allow Ca2+ ions to diffuse through these channels and bind with synaptic vesicles within the terminal boutons. Once bounded with Ca2+, the vesicles dock and fuse with the presynaptic membrane, and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft by a process known asexocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis ...
. The neurotransmitters then diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to postsynaptic receptors embedded on the postsynaptic membrane of another neuron. There are two families of receptors: ionotropic and metabotropic receptors. Ionotropic receptors are a combination of a receptor and an ion channel. When ionotropic receptors are activated, certain ion species such as Na+ enter the postsynaptic neuron, which depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane. If more of the same type of postsynaptic receptors are activated, then more Na+ will enter the postsynaptic membrane and depolarize cell. Metabotropic receptors on the other hand activate second messenger cascade systems that result in the opening of ion channel located some place else on the same postsynaptic membrane. Although slower than ionotropic receptors that function as on-and-off switches, metabotropic receptors have the advantage of changing the cell's responsiveness to ions and other metabolites, examples being gamma amino-butyric acid (inhibitory transmitter), glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ...
(excitatory transmitter), dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
, norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
, epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, melanin
Melanin (; ) is a family of biomolecules organized as oligomers or polymers, which among other functions provide the pigments of many organisms. Melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.
There are ...
, serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
, melatonin
Melatonin, an indoleamine, is a natural compound produced by various organisms, including bacteria and eukaryotes. Its discovery in 1958 by Aaron B. Lerner and colleagues stemmed from the isolation of a substance from the pineal gland of cow ...
, endorphins, dynorphins, nociceptin, and substance P.
Postsynaptic depolarizations can either transmit excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters. Those that release excitatory vesicles are referred to as excitatory postsynaptic potential
In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential, caused by the ...
( EPSP). Alternatively, inhibitory vesicles stimulate postsynaptic receptors such as to allow Cl− ions to enter the cell or K+ ions to leave the cell, which results in an inhibitory postsynaptic potential ( IPSP). If the EPSP is dominant, the threshold of excitation in the postsynaptic neuron may be reached, resulting in the generation of an action potential in the neuron(s) in turn postsynaptic to it, propagating the signal.
Synaptic plasticity
Synaptic plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to Chemical synapse#Synaptic strength, strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memory, memories are postulated to be represent ...
is the process whereby strengths of synaptic connections are altered. For example, long-term changes in synaptic connection may result in more postsynaptic receptors being embedded in the postsynaptic membrane, resulting in the strengthening of the synapse. Synaptic plasticity is also found to be the neural mechanism that underlies learning and memory. The basic properties, activity and regulation of membrane currents, synaptic transmission and synaptic plasticity, neurotransmission, neuroregensis, synaptogenesis and ion channels of cells are a few other fields studied by cellular neuroscientists.
Tissue, cellular and subcellular anatomy are studied to provide insight into mental retardation at the Mental Retardation Research Center MRRC Cellular Neuroscience Core. Journals such as ''Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience'' and '' Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience'' are published regarding cellular neuroscientific topics.
See also
*Action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
* Calcium concentration microdomains
*Cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
*Cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biol ...
*Chemical synapse
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous syste ...
*Dendrite
A dendrite (from Ancient Greek language, Greek δένδρον ''déndron'', "tree") or dendron is a branched cytoplasmic process that extends from a nerve cell that propagates the neurotransmission, electrochemical stimulation received from oth ...
*Hair cells
Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes. Through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment. ...
*IKK2
IKK-β also known as inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IKBKB'' (inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase beta) gene.
Function
IKK-β is an enzy ...
*Neuroendocrinology
Neuroendocrinology is the branch of biology (specifically of physiology) which studies the interaction between the nervous system and the endocrine system; i.e. how the brain regulates the hormonal activity in the body. The nervous and endocrine ...
* Neuropharmacology
* Pyramidal cells
* Soliton model
* Synaptotropic hypothesis
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cellular Neuroscience