American science fiction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a
 Some scholars assert that science fiction had its beginnings in
Some scholars assert that science fiction had its beginnings in
Quoted by Amazon.com
. Retrieved 2011-07-16. In 1968, Philip K. Dick's ''
in ''New York Review of Science Fiction'', October 1998 (Number 122) 1992's ''
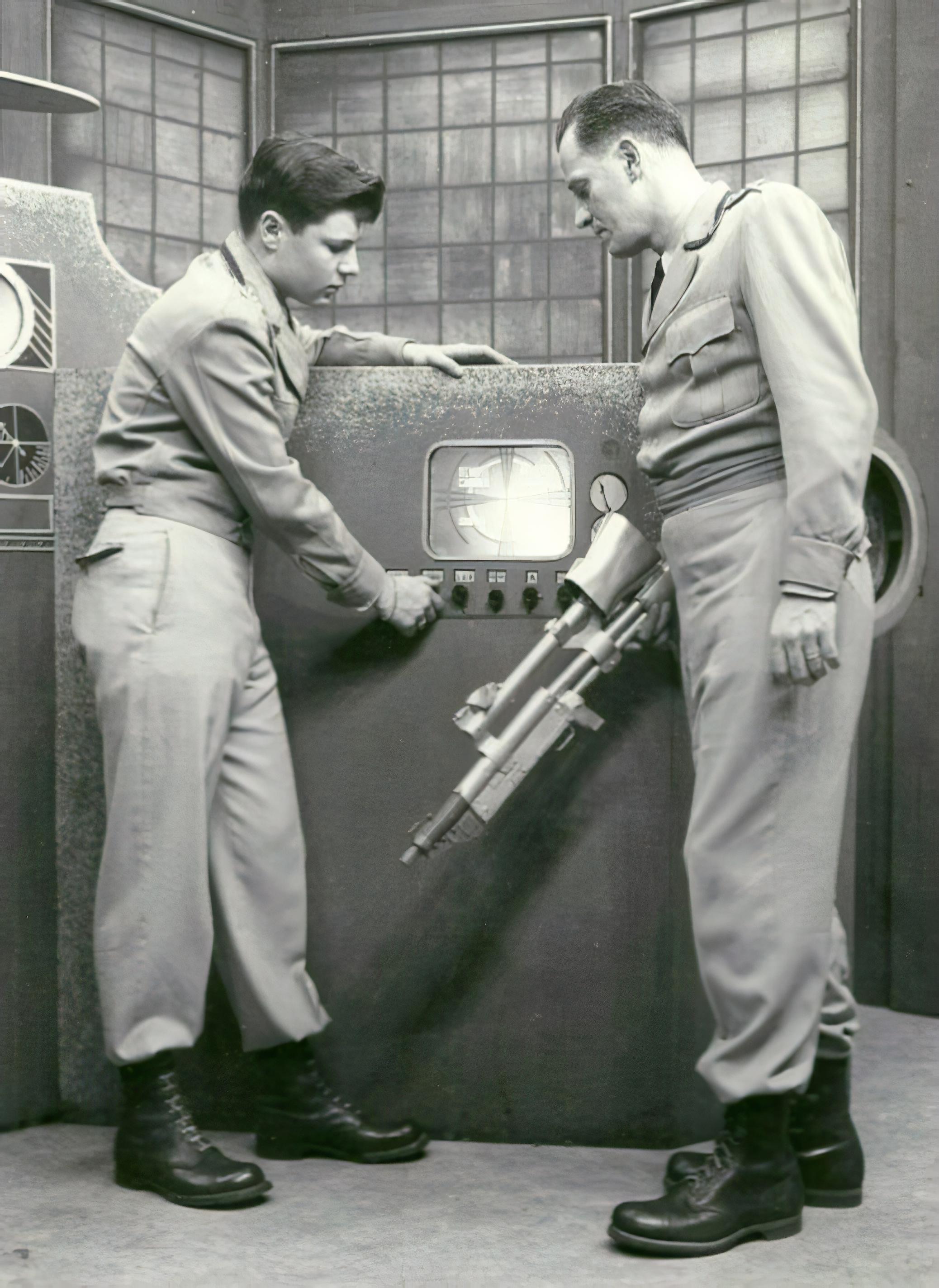 Science fiction and
Science fiction and
''Star Trek'' Pitch
, first draft. Accessed at ''LeeThomson.myzen.co.uk''. '' Star Trek: The Next Generation'' (1987–1994) led to six additional live action ''
 Science fiction has sometimes been used as a means of
Science fiction has sometimes been used as a means of
 Science fiction is often said to inspire a "
Science fiction is often said to inspire a "
 Respected authors have written science fiction.
Respected authors have written science fiction.
 Convention (meeting), Conventions (in fandom, often shortened as "cons," such as "comic-con") are held in City, cities around the world, catering to a local, regional, national, or international membership. Interest (emotion), General-interest conventions cover all aspects of science fiction, while others focus on a particular interest like media fandom, filking, and so on. Most science fiction conventions are organized by volunteering, volunteers in Non-profit organization, non-profit groups, though most media-oriented events are organized by Advertising, commercial promoters.
Convention (meeting), Conventions (in fandom, often shortened as "cons," such as "comic-con") are held in City, cities around the world, catering to a local, regional, national, or international membership. Interest (emotion), General-interest conventions cover all aspects of science fiction, while others focus on a particular interest like media fandom, filking, and so on. Most science fiction conventions are organized by volunteering, volunteers in Non-profit organization, non-profit groups, though most media-oriented events are organized by Advertising, commercial promoters.
 Science fiction elements can include, among others:
*Temporal settings in the future, or in alternate history, alternative histories.
*Space travel in science fiction, Space travel, settings in outer space, on other worlds, in Hollow Earth, subterranean earth, or in Parallel universe (fiction)#Science fiction, parallel universes.
* Aspects of biology in fiction such as Extraterrestrial life, aliens, Mutant (fictional), mutants, and enhanced humans.
* Predicted or speculative technology such as Brain–computer interface, brain-computer interface, Biological engineering, bio-engineering, Superintelligence, superintelligent
Science fiction elements can include, among others:
*Temporal settings in the future, or in alternate history, alternative histories.
*Space travel in science fiction, Space travel, settings in outer space, on other worlds, in Hollow Earth, subterranean earth, or in Parallel universe (fiction)#Science fiction, parallel universes.
* Aspects of biology in fiction such as Extraterrestrial life, aliens, Mutant (fictional), mutants, and enhanced humans.
* Predicted or speculative technology such as Brain–computer interface, brain-computer interface, Biological engineering, bio-engineering, Superintelligence, superintelligent
Science Fiction Bookshelf
at Project Gutenberg
Science fiction fanzines (current and historical) online
SFWA "Suggested Reading" list
Science fiction at standardebooks.org
Science Fiction Research Association
A selection of articles written by Mike Ashley, Iain Sinclair and others, exploring 19th-century visions of the future.
from the British Library's Discovering Literature website.
Merril Collection of Science Fiction, Speculation and Fantasy
at Toronto Public Library
Science Fiction Studies' Chronological Bibliography of Science Fiction History, Theory, and Criticism
Best 50 sci-fi novels of all time
(Esquire (magazine), Esquire; 21 March 2022) {{Authority control Science fiction, Speculative fiction, Speculative fiction
genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other f ...
of speculative fiction
Speculative fiction is a term that has been used with a variety of (sometimes contradictory) meanings. The broadest interpretation is as a category of fiction encompassing genres with elements that do not exist in reality, recorded history, nat ...
which typically deals with imaginative
Imagination is the production or simulation of novel objects, sensations, and ideas in the mind without any immediate input of the senses. Stefan Szczelkun characterises it as the forming of experiences in one's mind, which can be re-creation ...
and futuristic concepts such as advanced science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
and technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
, space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by uncrewed robo ...
, time travel
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a ...
, parallel universes, extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life, colloquially referred to as alien life, is life that may occur outside Earth and which did not originate on Earth. No extraterrestrial life has yet been conclusively detected, although efforts are underway. Such life might ...
, sentient artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech ...
, cybernetics
Cybernetics is a wide-ranging field concerned with circular causality, such as feedback, in regulatory and purposive systems. Cybernetics is named after an example of circular causal feedback, that of steering a ship, where the helmsperson ma ...
, certain forms of immortality
Immortality is the concept of eternal life. Some modern species may possess biological immortality.
Some scientists, futurists, and philosophers have theorized about the immortality of the human body, with some suggesting that human immorta ...
(like mind uploading
Mind uploading is a speculative process of whole brain emulation in which a brain scan is used to completely emulate the mental state of the individual in a digital computer. The computer would then run a simulation of the brain's information pr ...
), and the singularity. Science fiction predicted several existing inventions, such as the atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
, robots "\n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visi ...
, and borazon
Borazon is a brand name of a cubic form of boron nitride (cBN). Its color ranges from black to brown and gold, depending on the chemical bond. It is one of the hardest known materials, along with various forms of diamond and kinds of boron nitride ...
, whose names entirely match their fictional predecessors. In addition, science fiction might serve as an outlet to facilitate future scientific and technological innovations.
Science fiction can trace its roots to ancient mythology. It is also related to fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
, horror, and superhero
A superhero or superheroine is a stock character that typically possesses ''superpowers'', abilities beyond those of ordinary people, and fits the role of the hero, typically using his or her powers to help the world become a better place, ...
fiction and contains many subgenres
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other fo ...
. Its exact definition has long been disputed among author
An author is the writer of a book, article, play, mostly written work. A broader definition of the word "author" states:
"''An author is "the person who originated or gave existence to anything" and whose authorship determines responsibility f ...
s, critic
A critic is a person who communicates an assessment and an opinion of various forms of creative works such as art, literature, music, cinema, theater, fashion, architecture, and food. Critics may also take as their subject social or gover ...
s, scholar
A scholar is a person who pursues academic and intellectual activities, particularly academics who apply their intellectualism into expertise in an area of study. A scholar can also be an academic, who works as a professor, teacher, or researche ...
s, and readers.
Science fiction, in literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
, film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
, television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
, and other media, has become popular and influential over much of the world. It has been called the "literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
of idea
In common usage and in philosophy, ideas are the results of thought. Also in philosophy, ideas can also be mental representational images of some object. Many philosophers have considered ideas to be a fundamental ontological category of bei ...
s", and often explores the potential consequences of scientific, social, and technological innovations. It is also often said to inspire a "sense of wonder
A sense of wonder (sometimes jokingly written sensawunda) is an intellectual and emotional state frequently invoked in discussions of science and biology, higher consciousness, science fiction, and philosophy.
__TOC__
Definitions
This entry f ...
". Besides providing entertainment
Entertainment is a form of activity that holds the attention and interest of an audience or gives pleasure and delight. It can be an idea or a task, but is more likely to be one of the activities or events that have developed over thousa ...
, it can also criticize present-day society and explore alternatives.
Definitions
American science fiction author and editorLester del Rey
Lester del Rey (June 2, 1915 – May 10, 1993) was an American science fiction author and editor. He was the author of many books in the juvenile Winston Science Fiction series, and the editor at Del Rey Books, the fantasy and scienc ...
wrote, "Even the devoted aficionado or fan—has a hard time trying to explain what science fiction is," and the lack of a "full satisfactory definition" is because "there are no easily delineated limits to science fiction." According to Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (192 ...
, "Science fiction can be defined as that branch of literature which deals with the reaction of human beings to changes in science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
and technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
."Asimov, "How Easy to See the Future!", ''Natural History'', 1975 Robert A. Heinlein wrote that "A handy short definition of almost all science fiction might read: realistic speculation about possible future events, based solidly on adequate knowledge of the real world, past and present, and on a thorough understanding of the nature and significance of the scientific method
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientifi ...
."
Science fiction tries to blend fiction and reality seamlessly so that the viewer can be immersed in the imaginative world. This includes characters, settings, and tools and perhaps most critically, the scientific plausibility and accuracy of technology and technological concepts. Sometimes, science fiction forecasts real life innovations and discoveries. In the 2020 series '' Away'' astronauts use a real-life Mars rover called InSight to listen intently for a landing on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
. Two years later in 2022 scientists used InSight to listen for the landing of a real spacecraft.
In the Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
franchise, dinosaurs are created from ancient DNA and 18 years later, real life scientists found dinosaur DNA in ancient fossils.
Part of the reason that it is so difficult to pin down an agreed definition of science fiction is because there is a tendency among science fiction enthusiasts to act as their own arbiter in deciding what exactly constitutes science fiction. Damon Knight
Damon Francis Knight (September 19, 1922 – April 15, 2002) was an American science fiction author, editor, and critic. He is the author of " To Serve Man", a 1950 short story adapted for ''The Twilight Zone''.Stanyard, ''Dimensions Behind t ...
summed up the difficulty, saying "science fiction is what we point to when we say it." Ultimately, it may be more useful to talk around science fiction as the intersection of other, more concrete, genres and subgenres.
Alternative terms
Forrest J Ackerman
Forrest James Ackerman (November 24, 1916 – December 4, 2008) was an American magazine editor; science fiction writer and literary agent; a founder of science fiction fandom; a leading expert on science fiction, horror, and fantasy films; a pr ...
has been credited with first using the term "sci-fi" (analogous to the then-trendy " hi-fi") in about 1954; the first known use in print was a description of ''Donovan's Brain
''Donovan's Brain'' is a 1942 science fiction novel by American writer Curt Siodmak.
The novel was an instant success and has been adapted to film three times. Since then the book has become something of a cult classic, with fans including Ste ...
'' by movie critic Jesse Zunser in January 1954. As science fiction entered popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
, writers and fans active in the field came to associate the term with low-budget, low-tech "B-movies
A B movie or B film is a low-budget commercial motion picture. In its original usage, during the Golden Age of Hollywood, the term more precisely identified films intended for distribution as the less-publicized bottom half of a double feature ...
," and with low-quality pulp science fiction. By the 1970s, critics within the field, such as Damon Knight
Damon Francis Knight (September 19, 1922 – April 15, 2002) was an American science fiction author, editor, and critic. He is the author of " To Serve Man", a 1950 short story adapted for ''The Twilight Zone''.Stanyard, ''Dimensions Behind t ...
and Terry Carr
Terry Gene Carr (February 19, 1937 – April 7, 1987) was an American science fiction fan, author, editor, and writing instructor.
Background and discovery of fandom
Carr was born in Grants Pass, Oregon. He attended the City College of San ...
, were using "sci fi" to distinguish hack-work from serious science fiction. Peter Nicholls writes that "SF" (or "sf") is "the preferred abbreviation within the community of sf writers and readers." Robert Heinlein
Robert Anson Heinlein (; July 7, 1907 – May 8, 1988) was an American science fiction author, aeronautical engineer, and naval officer. Sometimes called the "dean of science fiction writers", he was among the first to emphasize scientific accu ...
found even "science fiction" insufficient for certain types of works in this genre, and suggested the term speculative fiction
Speculative fiction is a term that has been used with a variety of (sometimes contradictory) meanings. The broadest interpretation is as a category of fiction encompassing genres with elements that do not exist in reality, recorded history, nat ...
to be used instead for those that are more "serious" or "thoughtful."
History
 Some scholars assert that science fiction had its beginnings in
Some scholars assert that science fiction had its beginnings in ancient times
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
, when the line between myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
and fact
A fact is a datum about one or more aspects of a circumstance, which, if accepted as true and proven true, allows a logical conclusion to be reached on a true–false evaluation. Standard reference works are often used to check facts. Scie ...
was blurred. Written in the 2nd century CE by the satirist
This is an incomplete list of writers, cartoonists and others known for involvement in satire – humorous social criticism. They are grouped by era and listed by year of birth. Included is a list of modern satires.
Under Contemporary, 1930-196 ...
Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 – after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridiculed supersti ...
, ''A True Story
''A True Story'' ( grc, Ἀληθῆ διηγήματα, ''Alēthē diēgēmata''; or ), also translated as True History, is a long novella or short novel written in the second century AD by the Greek author Lucian of Samosata. The novel is a sa ...
'' contains many themes and tropes characteristic of modern science fiction, including travel to other worlds, extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life, colloquially referred to as alien life, is life that may occur outside Earth and which did not originate on Earth. No extraterrestrial life has yet been conclusively detected, although efforts are underway. Such life might ...
forms, interplanetary warfare, and artificial life
Artificial life (often abbreviated ALife or A-Life) is a field of study wherein researchers examine systems related to natural life, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulations with computer models, robotics, and biochemistry ...
. Some consider it the first science-fiction novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself ...
. Some of the stories from ''The Arabian Nights
''One Thousand and One Nights'' ( ar, أَلْفُ لَيْلَةٍ وَلَيْلَةٌ, italic=yes, ) is a collection of Middle Eastern folk tales compiled in Arabic during the Islamic Golden Age. It is often known in English as the ''Arabian ...
'', along with the 10th-century ''The Tale of the Bamboo Cutter
is a (fictional prose narrative) containing elements of Japanese folklore. Written by an unknown author in the late 9th or early 10th century during the Heian period, it is considered the oldest surviving work in the form.
The story detail ...
'' and Ibn al-Nafis's 13th-century ''Theologus Autodidactus
''Theologus Autodidactus'' ("The Self-taught Theologian"), originally titled ''The Treatise of Kāmil on the Prophet's Biography'' ( ar, الرسالة الكاملية في السيرة النبوية), also known as ''Risālat Fādil ibn Nātiq'' ...
,'' also contain elements of science fiction.
Written during the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transforme ...
and the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
's '' Somnium'' (1634), Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both ...
's '' New Atlantis'' (1627), Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 – 27 November 1680) was a German Jesuit scholar and polymath who published around 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine. Kircher has been compared to fe ...
's ''Itinerarium extaticum'' (1656), Cyrano de Bergerac
Savinien de Cyrano de Bergerac ( , ; 6 March 1619 – 28 July 1655) was a French novelist, playwright, epistolarian, and duelist.
A bold and innovative author, his work was part of the libertine literature of the first half of the 17th cen ...
's ''Comical History of the States and Empires of the Moon
''The Other World: Comical History of the States and Empires of the Moon'' (french: L’Autre monde ou les états et empires de la Lune) was the first of three satirical novels written by Cyrano de Bergerac. It was published posthumously in 1657 ...
'' (1657) and ''The States and Empires of the Sun
Savinien de Cyrano de Bergerac ( , ; 6 March 1619 – 28 July 1655) was a French novelist, playwright, epistolarian, and duelist.
A bold and innovative author, his work was part of the libertine literature of the first half of the 17th cen ...
'' (1662), Margaret Cavendish's "The Blazing World
''The Description of a New World, Called The Blazing-World'', better known as ''The Blazing World'', is a 1666 work of prose fiction by the English writer Margaret Cavendish, the Duchess of Newcastle. Feminist critic Dale Spender calls it a ...
" (1666), Jonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish satirist, author, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whigs, then for the Tories), poet, and Anglican cleric who became Dean of St Patrick's Cathedral, Du ...
's ''Gulliver's Travels
''Gulliver's Travels'', or ''Travels into Several Remote Nations of the World. In Four Parts. By Lemuel Gulliver, First a Surgeon, and then a Captain of Several Ships'' is a 1726 prose satire by the Anglo-Irish writer and clergyman Jonathan ...
'' (1726), Ludvig Holberg
Ludvig Holberg, Baron of Holberg (3 December 1684 – 28 January 1754) was a writer, essayist, philosopher, historian and playwright born in Bergen, Norway, during the time of the Dano-Norwegian dual monarchy. He was influenced by Humanism, ...
's '' Nicolai Klimii Iter Subterraneum'' (1741) and Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his '' nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—e ...
's ''Micromégas
''Le Micromégas'' is a 1752 novella by the French philosopher and satirist Voltaire. Along with his story "Plato's Dream", it is an early example in the literary genre of science fiction and has its place in the development of the history of ...
'' (1752) are regarded as some of the first true science-fantasy
Science fantasy is a hybrid genre within speculative fiction that simultaneously draws upon or combines tropes and elements from both science fiction and fantasy. In a conventional science fiction story, the world is presented as being scient ...
works. Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (192 ...
and Carl Sagan
Carl Edward Sagan (; ; November 9, 1934December 20, 1996) was an American astronomer, planetary scientist, cosmologist, astrophysicist, astrobiologist, author, and science communicator. His best known scientific contribution is research on ex ...
considered '' Somnium'' the first science-fiction story; it depicts a journey to the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
and how the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
's motion is seen from there.
Following the 17th-century development of the novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself ...
as a literary form, Mary Shelley's ''Frankenstein
''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' is an 1818 novel written by English author Mary Shelley. ''Frankenstein'' tells the story of Victor Frankenstein, a young scientist who creates a sapient creature in an unorthodox scientific ...
'' (1818) and ''The Last Man
''The Last Man'' is an apocalyptic, dystopian science fiction novel by Mary Shelley, first published in 1826. The narrative concerns Europe in the late 21st century, ravaged by a mysterious plague pandemic that rapidly sweeps across the ent ...
'' (1826) helped define the form of the science-fiction novel. Brian Aldiss
Brian Wilson Aldiss (; 18 August 1925 – 19 August 2017) was an English writer, artist, and anthology editor, best known for science fiction novels and short stories. His byline reads either Brian W. Aldiss or simply Brian Aldiss, except for o ...
has argued that ''Frankenstein'' was the first work of science fiction. Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wid ...
wrote several stories considered to be science fiction, including " The Unparalleled Adventure of One Hans Pfaall" (1835) which featured a trip to the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
. Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the '' Voyages extra ...
was noted for his attention to detail and scientific accuracy, especially in ''Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea
''Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas'' (french: Vingt mille lieues sous les mers) is a classic science fiction adventure novel by French writer Jules Verne.
The novel was originally serialized from March 1869 through June 1870 in Pierre- ...
'' (1870). In 1887, the novel '' El anacronópete'' by Spanish author Enrique Gaspar y Rimbau
Enrique Lucio Eugenio Gaspar y Rimbau (2 March 1842 in Madrid – 7 September 1902 in Oloron) was a Spanish diplomat and writer, who wrote many plays (''zarzuelas''), and one of the first novels involving time travel with a time machine, El ...
introduced the first time machine. A rather unknown early French/Belgian science fiction writer was J.-H. Rosny aîné (1856–1940).
Many critics consider H. G. Wells one of science fiction's most important authors, or even "the Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
of science fiction." His notable science-fiction works include ''The Time Machine
''The Time Machine'' is a science fiction novella by H. G. Wells, published in 1895. The work is generally credited with the popularization of the concept of time travel by using a vehicle or device to travel purposely and selectively for ...
'' (1895), '' The Island of Doctor Moreau'' (1896), ''The Invisible Man
''The Invisible Man'' is a science fiction novel by H. G. Wells. Originally serialized in '' Pearson's Weekly'' in 1897, it was published as a novel the same year. The Invisible Man to whom the title refers is Griffin, a scientist who has devo ...
'' (1897), and ''The War of the Worlds
''The War of the Worlds'' is a science fiction novel by English author H. G. Wells, first serialised in 1897 by ''Pearson's Magazine'' in the UK and by ''Cosmopolitan (magazine), Cosmopolitan'' magazine in the US. The novel's first appear ...
'' (1898). His science fiction imagined alien invasion
The alien invasion or space invasion is a common feature in science fiction stories and film, in which extraterrestrial lifeforms invade the Earth either to exterminate and supplant human life, enslave it under an intense state, harvest people ...
, biological engineering
Biological engineering or
bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically-viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number o ...
, invisibility
Invisibility is the state of an object that cannot be seen. An object in this state is said to be ''invisible'' (literally, "not visible"). The phenomenon is studied by physics and perceptual psychology.
Since objects can be seen by light i ...
, and time travel
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a ...
. In his non-fiction
Nonfiction, or non-fiction, is any document or media content that attempts, in good faith, to provide information (and sometimes opinions) grounded only in facts and real life, rather than in imagination. Nonfiction is often associated with b ...
futurologist works he predicted the advent of airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad ...
s, military tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engin ...
s, nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
s, satellite television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna com ...
, space travel, and something resembling the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web ...
.
Edgar Rice Burroughs
Edgar Rice Burroughs (September 1, 1875 – March 19, 1950) was an American author, best known for his prolific output in the adventure, science fiction, and fantasy genres. Best-known for creating the characters Tarzan and John Carter, ...
' ''A Princess of Mars
''A Princess of Mars'' is a science fantasy novel by American writer Edgar Rice Burroughs, the first of his Barsoom series. It was first serialized in the pulp magazine ''All-Story Magazine'' from February–July, 1912. Full of swordplay and dari ...
'', published in 1912, was the first of his three-decade
A decade () is a period of ten years. Decades may describe any ten-year period, such as those of a person's life, or refer to specific groupings of calendar years.
Usage
Any period of ten years is a "decade". For example, the statement that "du ...
-long planetary romance
Planetary romance is a subgenre of science fiction in which the bulk of the action consists of adventures on one or more exotic alien planets, characterized by distinctive physical and cultural backgrounds. Some planetary romances take place ag ...
series of Barsoom novels which were set on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
and featured John Carter as the hero
A hero (feminine: heroine) is a real person or a main fictional character who, in the face of danger, combats adversity through feats of ingenuity, courage, or strength. Like other formerly gender-specific terms (like ''actor''), ''her ...
. In 1926, Hugo Gernsback
Hugo Gernsback (; born Hugo Gernsbacher, August 16, 1884 – August 19, 1967) was a Luxembourgish–American editor and magazine publisher, whose publications including the first science fiction magazine. His contributions to the genre as pub ...
published the first American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
science-fiction magazine, ''Amazing Stories
''Amazing Stories'' is an American science fiction magazine launched in April 1926 by Hugo Gernsback's Experimenter Publishing. It was the first magazine devoted solely to science fiction. Science fiction stories had made regular appearances ...
''. In its first issue he wrote:
In 1928, E. E. "Doc" Smith's first published work, ''The Skylark of Space
''The Skylark of Space'' is a science fiction novel by American writer Edward E. "Doc" Smith, written between 1915 and 1921 while Smith was working on his doctorate. Though the original idea for the novel was Smith's, he co-wrote the first part o ...
,'' written in collaboration with Lee Hawkins Garby, appeared in ''Amazing Stories
''Amazing Stories'' is an American science fiction magazine launched in April 1926 by Hugo Gernsback's Experimenter Publishing. It was the first magazine devoted solely to science fiction. Science fiction stories had made regular appearances ...
''. It is often called the first great space opera
Space opera is a subgenre of science fiction that emphasizes space warfare, with use of melodramatic, risk-taking space adventures, relationships, and chivalric romance. Set mainly or entirely in outer space, it features technological and soc ...
. The same year, Philip Francis Nowlan's original Buck Rogers
Buck Rogers is a science fiction adventure hero and feature comic strip created by Philip Francis Nowlan first appearing in daily US newspapers on January 7, 1929, and subsequently appearing in Sunday newspapers, international newspapers, books ...
story, ''Armageddon 2419
''Armageddon 2419 A.D.'' is a science fiction novella by Philip Francis Nowlan that first appeared in the August 1928 issue of the pulp magazine ''Amazing Stories''. A sequel called '' The Airlords of Han'' was published in the March 1929 issue ...
'', also appeared in ''Amazing Stories''. This was followed by a Buck Rogers comic strip
A comic strip is a Comics, sequence of drawings, often cartoons, arranged in interrelated panels to display brief humor or form a narrative, often Serial (literature), serialized, with text in Speech balloon, balloons and Glossary of comics ter ...
, the first serious science-fiction comic
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel u ...
.
In 1937, John W. Campbell
John Wood Campbell Jr. (June 8, 1910 – July 11, 1971) was an American science fiction writer and editor. He was editor of ''Astounding Science Fiction'' (later called ''Analog Science Fiction and Fact'') from late 1937 until his death ...
became editor
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written, photographic, visual, audible, or cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing process can involve correction, condensation, or ...
of ''Astounding Science Fiction
''Analog Science Fiction and Fact'' is an American science fiction magazine published under various titles since 1930. Originally titled ''Astounding Stories of Super-Science'', the first issue was dated January 1930, published by William C ...
'', an event which is sometimes considered the beginning of the Golden Age of Science Fiction
The first Golden Age of Science Fiction, often recognized in the United States as the period from 1938 to 1946, was an era during which the science fiction genre gained wide public attention and many classic science fiction stories were published. ...
, which is characterized by stories celebrating scientific achievement and progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension w ...
. In 1942, Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (192 ...
started his Foundation series
The ''Foundation'' series is a science fiction book series written by American author Isaac Asimov. First published as a series of short stories in 1942–50, and subsequently in three collections in 1951–53, for thirty years the series was ...
, which chronicles the rise and fall of galactic empires and introduced psychohistory. The series was later awarded a one-time Hugo Award
The Hugo Award is an annual literary award for the best science fiction or fantasy works and achievements of the previous year, given at the World Science Fiction Convention and chosen by its members. The Hugo is widely considered the premier ...
for "Best All-Time Series." The "Golden Age" is often said to have ended in 1946, but sometimes the late 1940s and the 1950s are included.
Theodore Sturgeon's '' More Than Human'' (1953) explored possible future human evolution
Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of '' Homo sapiens'' as a distinct species of the hominid family, which includes the great apes. This process involved the gradual developmen ...
. In 1957, '' Andromeda: A Space-Age Tale'' by the Russian writer and paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
Ivan Yefremov
Ivan Antonovich (real patronymic Antipovich) Yefremov ( ru , Ива́н Анто́нович (Анти́пович) Ефре́мов; April 23, 1908 – October 5, 1972; last name sometimes transliterated as Efremov) was a Soviet paleonto ...
presented a view of a future interstellar communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
civilization and is considered one of the most important Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
science fiction novels. In 1959, Robert A. Heinlein's ''Starship Troopers
''Starship Troopers'' is a military science fiction novel by American writer Robert A. Heinlein. Written in a few weeks in reaction to the US suspending nuclear tests, the story was first published as a two-part serial in ''The Magazine of F ...
'' marked a departure from his earlier juvenile stories and novels. It is one of the first and most influential examples of military science fiction
Military science fiction is a subgenre of science fiction that features the use of science fiction technology, mainly weapons, for military purposes and usually principal characters who are members of a military organization involved in military a ...
, and introduced the concept of powered armor
A powered exoskeleton, also known as power armor, powered armor, powered suit, cybernetic suit, cybernetic armor, exosuit, hardsuit, exoframe or augmented mobility, is a mobile machine that is wearable over all or part of the human body, prov ...
exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
s. The German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
space opera
Space opera is a subgenre of science fiction that emphasizes space warfare, with use of melodramatic, risk-taking space adventures, relationships, and chivalric romance. Set mainly or entirely in outer space, it features technological and soc ...
series '' Perry Rhodan'', written by various authors, started in 1961 with an account of the first Moon landing
A Moon landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon. This includes both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was the Soviet Union's Luna 2, on 13 September 1959.
The United S ...
and has since expanded in space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consi ...
to multiple universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
s, and in time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and event (philosophy), events that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various me ...
by billions of years. It has become the most popular science fiction book series
A book series is a sequence of books having certain characteristics in common that are formally identified together as a group. Book series can be organized in different ways, such as written by the same author, or marketed as a group by their pub ...
of all time.
In the 1960s and 1970s, New Wave science fiction
The New Wave was a science fiction (SF) style of the 1960s and 1970s, characterized by a great degree of experimentation with the form and content of stories, greater imitation of the styles of trendy non-science fiction literature, and an emphasis ...
was known for its embrace of a high degree of experimentation, both in form and in content, and a highbrow
Used colloquially as a noun or adjective, "highbrow" is synonymous with intellectual; as an adjective, it also means elite, and generally carries a connotation of high culture. The term, first recorded in 1875, draws its metonymy from the pseudo ...
and self-consciously "literary
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to includ ...
" or "artistic
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wh ...
" sensibility
Sensibility refers to an acute perception of or responsiveness toward something, such as the emotions of another. This concept emerged in eighteenth-century Britain, and was closely associated with studies of sense perception as the means thr ...
. In 1961, '' Solaris'' by Stanisław Lem
Stanisław Herman Lem (; 12 September 1921 – 27 March 2006) was a Polish writer of science fiction and essays on various subjects, including philosophy, futurology, and literary criticism. Many of his science fiction stories are of satirical ...
was published in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. The novel dealt with the theme of human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
limitations as its characters attempted to study a seemingly intelligent ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
on a newly discovered planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
. 1965's ''Dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, f ...
'' by Frank Herbert
Franklin Patrick Herbert Jr. (October 8, 1920February 11, 1986) was an American science fiction author best known for the 1965 novel ''Dune'' and its five sequels. Though he became famous for his novels, he also wrote short stories and worked as ...
featured a much more complex and detailed imagined future society than had previous science fiction.
In 1967 Anne McCaffrey
Anne Inez McCaffrey (1 April 1926 – 21 November 2011) was an American-Irish writer known for the ''Dragonriders of Pern'' science fiction series. She was the first woman to win a Hugo Award for fiction (Best Novella, ''Weyr Search'', 19 ...
began her ''Dragonriders of Pern
''Dragonriders of Pern'' is a science fantasy series written primarily by American author Anne McCaffrey, who initiated it in 1967. Beginning in 2003, her middle child Todd McCaffrey has written Pern novels, both solo and jointly with Anne. T ...
'' science fantasy
Science fantasy is a hybrid genre within speculative fiction that simultaneously draws upon or combines tropes and elements from both science fiction and fantasy. In a conventional science fiction story, the world is presented as being scient ...
series. Two of the novellas included in the first novel, ''Dragonflight
''Dragonflight'' is a science fiction novel by the American-Irish author Anne McCaffrey. It is the first book in the ''Dragonriders of Pern'' series. First published by Ballantine Books in July 1968, it was a fix-up of two novellas which betwe ...
'', made McCaffrey the first woman to win a Hugo or Nebula Award
The Nebula Awards annually recognize the best works of science fiction or fantasy published in the United States. The awards are organized and awarded by the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America (SFWA), a nonprofit association of prof ...
.''Publishers Weekly'' review of Robin Roberts, ''Anne McCaffrey: A Life with Dragons'' (2007)Quoted by Amazon.com
. Retrieved 2011-07-16. In 1968, Philip K. Dick's ''
Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?
''Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?'' (retroactively retitled ''Blade Runner: Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?'' in some later printings) is a dystopian science fiction novel by American writer Philip K. Dick, first published in 1968. Th ...
,'' was published. It is the literary source of the ''Blade Runner
''Blade Runner'' is a 1982 science fiction film directed by Ridley Scott, and written by Hampton Fancher and David Peoples. Starring Harrison Ford, Rutger Hauer, Sean Young, and Edward James Olmos, it is an adaptation of Philip K. Dick's ...
'' movie franchise
A media franchise, also known as a multimedia franchise, is a collection of related media in which several derivative works have been produced from an original creative work of fiction, such as a film, a work of literature, a television program ...
.Sammon, Paul M. (1996). Future Noir: the Making of Blade Runner. London: Orion Media. p. 49. . 1969's ''The Left Hand of Darkness
''The Left Hand of Darkness'' is a science fiction novel by U.S. writer Ursula K. Le Guin. Published in 1969, it became immensely popular, and established Le Guin's status as a major author of science fiction. The novel is set in the fictional ...
'' by Ursula K. Le Guin
Ursula Kroeber Le Guin (; October 21, 1929 – January 22, 2018) was an American author best known for her works of speculative fiction, including science fiction works set in her Hainish universe, and the '' Earthsea'' fantasy series. She was ...
was set on a planet in which the inhabitants have no fixed gender
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most culture ...
. It is one of the most influential examples of social science fiction
Social science fiction is a subgenre of science fiction, usually (but not necessarily) soft science fiction, concerned less with technology/space opera and more with speculation about society. In other words, it "absorbs and discusses anthropol ...
, feminist science fiction, and anthropological science fiction
The anthropologist Leon E. Stover says of science fiction's relationship to anthropology: "Anthropological science fiction enjoys the philosophical luxury of providing answers to the question "What is man?" while anthropology the science is still ...
.
In 1979, ''Science Fiction World
''Science Fiction World (Sci-Fi World; SFW)'' (, Kehuan Shijie), began in 1979, is a monthly science fiction magazine published in the People's Republic of China, headquartered in Chengdu, Sichuan. It dominates the Chinese science fiction magazi ...
'' began publication in the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. It dominates the Chinese science fiction magazine
A science fiction magazine is a publication that offers primarily science fiction, either in a hard-copy periodical format or on the Internet.
Science fiction magazines traditionally featured speculative fiction in short story, novelette, nove ...
market, at one time claiming a circulation of 300,000 copies per issue and an estimated 3–5 readers per copy (giving it a total estimated readership of at least 1 million), making it the world's most popular science fiction periodical
A periodical literature (also called a periodical publication or simply a periodical) is a published work that appears in a new edition on a regular schedule. The most familiar example is a newspaper, but a magazine or a journal are also example ...
. In 1984, William Gibson's first novel, ''Neuromancer
''Neuromancer'' is a 1984 science fiction novel by American-Canadian writer William Gibson. Considered one of the earliest and best-known works in the cyberpunk genre, it is the only novel to win the Nebula Award, the Philip K. Dick Award, and ...
,'' helped popularize cyberpunk
Cyberpunk is a subgenre of science fiction in a dystopian futuristic setting that tends to focus on a "combination of lowlife and high tech", featuring futuristic technological and scientific achievements, such as artificial intelligence and ...
and the word "cyberspace
Cyberspace is a concept describing a widespread interconnected digital technology. "The expression dates back from the first decade of the diffusion of the internet. It refers to the online world as a world 'apart', as distinct from everyday re ...
," a term he originally coined in his 1982 short story
A short story is a piece of prose fiction that typically can be read in one sitting and focuses on a self-contained incident or series of linked incidents, with the intent of evoking a single effect or mood. The short story is one of the oldest ...
''Burning Chrome
"Burning Chrome" is a science fiction short story by Canadian-American writer William Gibson, first published in '' Omni'' in July 1982. Gibson first read the story at a science fiction convention in Denver, Colorado in the autumn of 1981, to an a ...
''. In 1986, '' Shards of Honor'' by Lois McMaster Bujold
Lois McMaster Bujold ( ; born November 2, 1949) is an American speculative fiction writer. She is an acclaimed writer, having won the Hugo Award for best novel four times, matching Robert A. Heinlein's record (not counting his Retro Hugos). Her n ...
began her Vorkosigan Saga.Loud Achievements: Lois McMaster Bujold's Science Fictionin ''New York Review of Science Fiction'', October 1998 (Number 122) 1992's ''
Snow Crash
''Snow Crash'' is a science fiction novel by the American writer Neal Stephenson, published in 1992. Like many of Stephenson's novels, it covers history, linguistics, anthropology, archaeology, religion, computer science, politics, cryptography ...
'' by Neal Stephenson
Neal Town Stephenson (born October 31, 1959) is an American writer known for his works of speculative fiction. His novels have been categorized as science fiction, historical fiction, cyberpunk, postcyberpunk, and baroque.
Stephenson's work e ...
predicted immense social upheaval due to the information revolution
The term information revolution describes current economic, social and technological trends beyond the Industrial Revolution.
Many competing terms have been proposed that focus on different aspects of this societal development.
The British polymat ...
.
In 2007, Liu Cixin
Liu Cixin (, pronounced ; born 23 June 1963) is a Chinese science fiction writer. He is a nine-time winner of China's Galaxy Award and has also received the 2015 Hugo Award for his novel '' The Three-Body Problem'' as well as the 2017 Lo ...
's novel, '' The Three-Body Problem'', was published in China. It was translated into English by Ken Liu
Ken Liu (born 1976) is an American author of science fiction and fantasy. His epic fantasy series ''The Dandelion Dynasty'', which he describes as silkpunk, is published by Simon & Schuster. Liu has won Hugo and Nebula Awards for his short fi ...
and published by Tor Books
Tor Books is the primary imprint of Tor Publishing Group (previously Tom Doherty Associates), a publishing company based in New York City. It primarily publishes science fiction and fantasy titles, and is the largest publisher of Chinese scienc ...
in 2014, and won the 2015 Hugo Award for Best Novel
The Hugo Award for Best Novel is one of the Hugo Awards given each year for science fiction or fantasy stories published in, or translated to, English during the previous calendar year. The novel award is available for works of fiction of 40,000 ...
, making Liu the first Asian writer to win the award.
Emerging themes in late 20th and early 21st century science fiction include environmental issues
Environmental issues are effects of human activity on the biophysical environment, most often of which are harmful effects that cause environmental degradation. Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment on t ...
, the implications of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
and the expanding information universe, questions about biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
, nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal ...
, and post-scarcity societies
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societ ...
. Recent trends and subgenres
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other fo ...
include steampunk
Steampunk is a subgenre of science fiction that incorporates retrofuturistic technology and aesthetics inspired by 19th-century industrial steam-powered machinery. Steampunk works are often set in an alternative history of the Victorian ...
, biopunk
Biopunk (a portmanteau of "biotechnology" or "biology" and "punk") is a subgenre of science fiction that focuses on biotechnology. It is derived from cyberpunk, but focuses on the implications of biotechnology rather than mechanical cyberware ...
, and mundane science fiction
Mundane science fiction (MSF) is a niche literary movement within science fiction that developed in the early 2000s, with principles codified by the "Mundane Manifesto"Geoff Ryman ''et al''. (2004), "The Mundane Manifesto". The manifesto was or ...
.
Film
The first, or at least one of the first, recorded science fictionfilm
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
is 1902's ''A Trip to the Moon
''A Trip to the Moon'' (french: Le Voyage dans la Lune) is a 1902 French adventure short film directed by Georges Méliès. Inspired by a wide variety of sources, including Jules Verne's 1865 novel '' From the Earth to the Moon'' and its 187 ...
'', directed by French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
filmmaker
Filmmaking (film production) is the process by which a motion picture is produced. Filmmaking involves a number of complex and discrete stages, starting with an initial story, idea, or commission. It then continues through screenwriting, castin ...
Georges Méliès
Marie-Georges-Jean Méliès (; ; 8 December 1861 – 21 January 1938) was a French illusionist, actor, and film director. He led many technical and narrative developments in the earliest days of cinema.
Méliès was well known for the use of ...
. It was profoundly influential on later filmmakers
Filmmaking (film production) is the process by which a motion picture is produced. Filmmaking involves a number of complex and discrete stages, starting with an initial story, idea, or commission. It then continues through screenwriting, casti ...
, bringing a different kind of creativity
Creativity is a phenomenon whereby something new and valuable is formed. The created item may be intangible (such as an idea, a scientific theory, a musical composition, or a joke) or a physical object (such as an invention, a printed lit ...
and fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
to the cinematic medium
Medium may refer to:
Science and technology
Aviation
* Medium bomber, a class of war plane
* Tecma Medium, a French hang glider design
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to store and deliver information or data
* Medium ...
. In addition, Méliès's innovative editing
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written, photographic, visual, audible, or cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing process can involve correction, condensation, or ...
and special effect
Special effects (often abbreviated as SFX, F/X or simply FX) are illusions or visual tricks used in the theatre, film, television, video game, amusement park and simulator industries to simulate the imagined events in a story or virtual ...
s techniques were widely imitated and became important elements of the medium.
1927's ''Metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big c ...
'', directed by Fritz Lang
Friedrich Christian Anton Lang (; December 5, 1890 – August 2, 1976), known as Fritz Lang, was an Austrian film director, screenwriter, and producer who worked in Germany and later the United States.Obituary '' Variety'', August 4, 1976, p. ...
, is the first feature-length
A feature film or feature-length film is a narrative film (motion picture or "movie") with a running time long enough to be considered the principal or sole presentation in a commercial entertainment program. The term ''feature film'' originall ...
science fiction film. Though not well received in its time, it is now considered a great and influential film. In 1954, ''Godzilla
is a fictional monster, or '' kaiju'', originating from a series of Japanese films. The character first appeared in the 1954 film '' Godzilla'' and became a worldwide pop culture icon, appearing in various media, including 32 films produ ...
'', directed by Ishirō Honda
was a Japanese filmmaker who directed 44 feature films in a career spanning 59 years. The most internationally successful Japanese filmmaker prior to Hayao Miyazaki, his films have had a significant influence on the film industry.
Honda enter ...
, began the kaiju
is a Japanese media genre that focuses on stories involving giant monsters. The word ''kaiju'' can also refer to the giant monsters themselves, which are usually depicted attacking major cities and battling either the military or other monster ...
subgenre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other for ...
of science fiction film, which feature large creatures of any form, usually attacking a major city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
or engaging other monster
A monster is a type of fictional creature found in horror, fantasy, science fiction, folklore, mythology and religion. Monsters are very often depicted as dangerous and aggressive with a strange, grotesque appearance that causes terror and fe ...
s in battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and for ...
.
1968's '' 2001: A Space Odyssey'', directed by Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick (; July 26, 1928 – March 7, 1999) was an American film director, producer, screenwriter, and photographer. Widely considered one of the greatest filmmakers of all time, his films, almost all of which are adaptations of nove ...
and based on the work of Arthur C. Clarke
Sir Arthur Charles Clarke (16 December 191719 March 2008) was an English science-fiction writer, science writer, futurist, inventor, undersea explorer, and television series host.
He co-wrote the screenplay for the 1968 film '' 2001: A Spac ...
, rose above the mostly B-movie
A B movie or B film is a low-budget commercial motion picture. In its original usage, during the Golden Age of Hollywood, the term more precisely identified films intended for distribution as the less-publicized bottom half of a double feat ...
offerings up to that time both in scope and quality, and greatly influenced later science fiction films. That same year, ''Planet of the Apes
''Planet of the Apes'' is an American science fiction media franchise consisting of films, books, television series, comics, and other media about a world in which humans and intelligent apes clash for control. The franchise is based on Frenc ...
'' (the original), directed by Franklin J. Schaffner and based on the 1963 French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself ...
'' La Planète des Singes'' by Pierre Boulle
Pierre François Marie Louis Boulle (20 February 1912 – 30 January 1994) was a French novelist best known for two works, '' The Bridge over the River Kwai'' (1952) and ''Planet of the Apes'' (1963), that were both made into award-winning films. ...
, was released to popular and critical acclaim, due in large part to its vivid depiction of a post-apocalyptic world
Apocalyptic and post-apocalyptic fiction is a subgenre of speculative fiction in which the Earth's (or another planet's) civilization is collapsing or has collapsed. The apocalypse event may be climatic, such as runaway climate change; astr ...
in which intelligent apes dominate human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s.
In 1977, George Lucas
George Walton Lucas Jr. (born May 14, 1944) is an American filmmaker. Lucas is best known for creating the '' Star Wars'' and '' Indiana Jones'' franchises and founding Lucasfilm, LucasArts, Industrial Light & Magic and THX. He served as c ...
began the ''Star Wars'' film series with the film now identified as "'' Star Wars: Episode IV – A New Hope.''" The series, often called a space opera
Space opera is a subgenre of science fiction that emphasizes space warfare, with use of melodramatic, risk-taking space adventures, relationships, and chivalric romance. Set mainly or entirely in outer space, it features technological and soc ...
, went on to become a worldwide popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
phenomenon
A phenomenon ( : phenomena) is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfrie ...
, and the second-highest-grossing film series of all time.
Since the 1980s, science fiction film
Science fiction (or sci-fi) is a film genre that uses speculative, fictional science-based depictions of phenomena that are not fully accepted by mainstream science, such as extraterrestrial lifeforms, spacecraft, robots, cyborgs, interstel ...
s, along with fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
, horror, and superhero
A superhero or superheroine is a stock character that typically possesses ''superpowers'', abilities beyond those of ordinary people, and fits the role of the hero, typically using his or her powers to help the world become a better place, ...
films, have dominated Hollywood's big-budget productions. Science fiction films often " cross-over" with other genres, including animation
Animation is a method by which still figures are manipulated to appear as moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most ani ...
''(WALL-E
''WALL-E'' (stylized with an interpunct as ''WALL·E'') is a 2008 American computer-animated science fiction film produced by Pixar Animation Studios and released by Walt Disney Pictures. It was directed and co-written by Andrew Stanton, pro ...
'' – 2008, '' Big Hero 6'' – 2014), gangster
A gangster is a criminal who is a member of a gang. Most gangs are considered to be part of organized crime. Gangsters are also called mobsters, a term derived from '' mob'' and the suffix '' -ster''. Gangs provide a level of organization and ...
('' Sky Racket'' – 1937), Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
('' Serenity'' – 2005), comedy
Comedy is a genre of fiction that consists of discourses or works intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter, especially in theatre, film, stand-up comedy, television, radio, books, or any other entertainment medium. The term o ...
(''Spaceballs
''Spaceballs'' is a 1987 American space opera parody film co-written, produced and directed by Mel Brooks. It is primarily a parody of the original ''Star Wars'' trilogy, but also parodies other sci-fi films and popular franchises including ...
'' −1987, ''Galaxy Quest
''Galaxy Quest'' is a 1999 American science fiction comedy film directed by Dean Parisot and written by David Howard and Robert Gordon. A parody of and homage to science-fiction films and series, especially ''Star Trek'' and its fandom, the f ...
'' – 1999), war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
('' Enemy Mine'' – 1985), action
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
(''Edge of Tomorrow
''Edge of Tomorrow'' (also known as ''Live Die Repeat: Edge of Tomorrow'') is a 2014 American science fiction action film starring Tom Cruise and Emily Blunt with Bill Paxton and Brendan Gleeson in supporting roles. Directed by Doug Liman wi ...
'' – 2014, ''The Matrix
''The Matrix'' is a 1999 science fiction action film written and directed by the Wachowskis. It is the first installment in ''The Matrix'' film series, starring Keanu Reeves, Laurence Fishburne, Carrie-Anne Moss, Hugo Weaving, and Joe Pantolia ...
'' – 1999), adventure
An adventure is an exciting experience or undertaking that is typically bold, sometimes risky. Adventures may be activities with danger such as traveling, exploring, skydiving, mountain climbing, scuba diving, river rafting, or other extreme ...
(''Jupiter Ascending
''Jupiter Ascending'' is a 2015 space opera film written, directed and co-produced by the Wachowskis. Starring Channing Tatum and Mila Kunis with Sean Bean, Eddie Redmayne and Douglas Booth in supporting roles, the film is centered on Jupiter J ...
'' – 2015, '' Interstellar'' – 2014), sports
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, ...
('' Rollerball'' – 1975), mystery ('' Minority Report'' – 2002), thriller
Thriller may refer to:
* Thriller (genre), a broad genre of literature, film and television
** Thriller film, a film genre under the general thriller genre
Comics
* ''Thriller'' (DC Comics), a comic book series published 1983–84 by DC Comics i ...
('' Ex Machina'' – 2014), horror (''Alien
Alien primarily refers to:
* Alien (law), a person in a country who is not a national of that country
** Enemy alien, the above in times of war
* Extraterrestrial life, life which does not originate from Earth
** Specifically, intelligent extrater ...
'' – 1979), film noir
Film noir (; ) is a cinematic term used primarily to describe stylish Hollywood crime dramas, particularly those that emphasize cynical attitudes and motivations. The 1940s and 1950s are generally regarded as the "classic period" of American '' ...
(''Blade Runner
''Blade Runner'' is a 1982 science fiction film directed by Ridley Scott, and written by Hampton Fancher and David Peoples. Starring Harrison Ford, Rutger Hauer, Sean Young, and Edward James Olmos, it is an adaptation of Philip K. Dick's ...
'' – 1982), superhero
A superhero or superheroine is a stock character that typically possesses ''superpowers'', abilities beyond those of ordinary people, and fits the role of the hero, typically using his or her powers to help the world become a better place, ...
(''Marvel Cinematic Universe
The Marvel Cinematic Universe (MCU) is an American media franchise and shared universe centered on a series of superhero films produced by Marvel Studios. The films are based on characters that appear in American comic books published ...
'' – 2008–), drama
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance: a play, opera, mime, ballet, etc., performed in a theatre, or on radio or television.Elam (1980, 98). Considered as a genre of poetry in general, the dramatic mode has b ...
(''Melancholia
Melancholia or melancholy (from el, µέλαινα χολή ',Burton, Bk. I, p. 147 meaning black bile) is a concept found throughout ancient, medieval and premodern medicine in Europe that describes a condition characterized by markedly d ...
'' – 2011, ''Predestination
Predestination, in theology, is the doctrine that all events have been willed by God, usually with reference to the eventual fate of the individual soul. Explanations of predestination often seek to address the paradox of free will, whereby ...
'' – 2014), and romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
(''Her
Her is the objective and possessive form of the English-language feminine pronoun she.
Her, HER or H.E.R. may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Music
* H.E.R. (born 1997), American singer
** ''H.E.R.'' (album), 2017
* HIM (Finnish ...
'' – 2013).Science Fiction Film: A Critical Introduction, Keith M. Johnston, Berg, 9 May 2013, pages 24–25. Some of the examples are given by this book.
Television
television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
have consistently been in a close relationship. Television or television-like technologies
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ...
frequently appeared in science fiction long before television itself became widely available in the late 1940s and early 1950s.
Science Fiction TV, J. P. Telotte, Routledge, 26 March 2014, pages 112, 179
The first known science fiction television program was a thirty-five-minute adapted excerpt of the play '' RUR'', written by the Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
playwright
A playwright or dramatist is a person who writes plays.
Etymology
The word "play" is from Middle English pleye, from Old English plæġ, pleġa, plæġa ("play, exercise; sport, game; drama, applause"). The word "wright" is an archaic English ...
Karel Čapek
Karel Čapek (; 9 January 1890 – 25 December 1938) was a Czech writer, playwright and critic. He has become best known for his science fiction, including his novel '' War with the Newts'' (1936) and play '' R.U.R.'' (''Rossum's Universal ...
, broadcast
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio or video content to a dispersed audience via any electronic mass communications medium, but typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a one-to-many model. Broadcasting began wi ...
live
Live may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Live!'' (2007 film), 2007 American film
* ''Live'' (2014 film), a 2014 Japanese film
*'' ''Live'' (Apocalyptica DVD)
Music
* Live (band), American alternative rock band
* List of album ...
from the BBC's Alexandra Palace
Alexandra Palace is a Grade II listed entertainment and sports venue in London, situated between Wood Green and Muswell Hill in the London Borough of Haringey. It is built on the site of Tottenham Wood and the later Tottenham Wood Farm. Origi ...
studios on 11 February 1938. The first popular science fiction program on American television
Television is one of the major mass media outlets in the United States. , household ownership of television sets in the country is 96.7%, with approximately 114,200,000 American households owning at least one television set as of August 2013. ...
was the children's
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person young ...
adventure serial ''Captain Video and His Video Rangers
''Captain Video and His Video Rangers'' is an American science fiction television series that aired on the DuMont Television Network and was the first series of its genre on American television.
The series aired between June 27, 1949, and Apri ...
'', which ran from June 1949 to April 1955.
''The Twilight Zone
''The Twilight Zone'' is an American media franchise based on the anthology television series created by Rod Serling. The episodes are in various genres, including fantasy, science fiction, absurdism, dystopian fiction, suspense, horror, sup ...
'' (the original series), produced and narrated by Rod Serling
Rodman Edward Serling (December 25, 1924 – June 28, 1975) was an American screenwriter, playwright, television producer, and narrator/on-screen host, best known for his live television dramas of the 1950s and his anthology television series ...
, who also wrote or co-wrote most of the episodes, ran from 1959 to 1964. It featured fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
, suspense
Suspense is a state of mental uncertainty, anxiety, being Decision-making, undecided, or being Doubt, doubtful. In a Drama, dramatic work, suspense is the anticipation of the wikt:outcome, outcome of a plot (narrative), plot or of the solution t ...
, and horror as well as science fiction, with each episode being a complete story. Critic
A critic is a person who communicates an assessment and an opinion of various forms of creative works such as art, literature, music, cinema, theater, fashion, architecture, and food. Critics may also take as their subject social or gover ...
s have ranked it as one of the best TV programs of any genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other f ...
.
The animated
Animation is a method by which still figures are manipulated to appear as moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most ani ...
series ''The Jetsons
''The Jetsons'' is an American animated sitcom produced by Hanna-Barbera Productions. It originally aired in prime time from September 23, 1962, to March 17, 1963, on ABC, then later aired in reruns via syndication, with new episodes produced ...
'', while intended as comedy
Comedy is a genre of fiction that consists of discourses or works intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter, especially in theatre, film, stand-up comedy, television, radio, books, or any other entertainment medium. The term o ...
and only running for one season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and ...
(1962–1963), predicted many inventions now in common use: flat-screen television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
s, newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, spor ...
s on a computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
-like screen, computer virus
A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a comput ...
es, video chat
Videotelephony, also known as videoconferencing and video teleconferencing, is the two-way or multipoint reception and transmission of audio and video signals by people in different locations for real time communication.McGraw-Hill Concise Ency ...
, tanning bed
Indoor tanning involves using a device that emits ultraviolet radiation to produce a cosmetic tan. Typically found in tanning salons, gyms, spas, hotels, and sporting facilities, and less often in private residences, the most common device is a ...
s, home treadmill
A treadmill is a device generally used for walking, running, or climbing while staying in the same place. Treadmills were introduced before the development of powered machines to harness the power of animals or humans to do work, often a type o ...
s, and more. In 1963, the time travel-themed ''Doctor Who
''Doctor Who'' is a British science fiction television series broadcast by the BBC since 1963. The series depicts the adventures of a Time Lord called the Doctor, an extraterrestrial being who appears to be human. The Doctor explores the ...
'' premiered on BBC Television. The original series ran until 1989 and was revived in 2005. It has been extremely popular
Popularity or social status is the quality of being well liked, admired or well known to a particular group.
Popular may also refer to:
In sociology
* Popular culture
* Popular fiction
* Popular music
* Popular science
* Populace, the total ...
worldwide and has greatly influenced later TV science fiction. Other programs in the 1960s included '' The Outer Limits'' (1963–1965), ''Lost in Space
''Lost in Space'' is an American science fiction television series, created and produced by Irwin Allen, which originally aired between 1965 and 1968 on CBS. The series was inspired by the 1812 novel ''The Swiss Family Robinson.'' The series fo ...
'' (1965–1968), and ''The Prisoner
''The Prisoner'' is a 1967 British television series about an unnamed British intelligence agent who is abducted and imprisoned in a mysterious coastal village, where his captors designate him as Number Six and try to find out why he abruptl ...
'' (1967).
''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' (the original series), created by Gene Roddenberry
Eugene Wesley Roddenberry Sr. (August 19, 1921 – October 24, 1991) was an American television screenwriter, producer, and creator of '' Star Trek: The Original Series'', its sequel spin-off series '' Star Trek: The Animated Series,'' and '' ...
, premiered in 1966 on NBC Television and ran for three seasons. It combined elements of space opera
Space opera is a subgenre of science fiction that emphasizes space warfare, with use of melodramatic, risk-taking space adventures, relationships, and chivalric romance. Set mainly or entirely in outer space, it features technological and soc ...
and Space Western. Only mildly successful at first, the series gained popularity
In sociology, popularity is how much a person, idea, place, item or other concept is either liked or accorded status by other people. Liking can be due to reciprocal liking, interpersonal attraction, and similar factors. Social status can be ...
through syndication
Syndication may refer to:
* Broadcast syndication, where individual stations buy programs outside the network system
* Print syndication, where individual newspapers or magazines license news articles, columns, or comic strips
* Web syndication, ...
and extraordinary fan interest. It became a very popular and influential franchise with many films
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
, television shows
A television show – or simply TV show – is any content produced for viewing on a television set which can be broadcast via over-the-air, satellite, or cable, excluding breaking news, advertisements, or trailers that are typically placed betw ...
, novels
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself ...
, and other works and products.Roddenberry, Gene (11 March 1964)''Star Trek'' Pitch
, first draft. Accessed at ''LeeThomson.myzen.co.uk''. '' Star Trek: The Next Generation'' (1987–1994) led to six additional live action ''
Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' shows (''Deep Space 9
''Star Trek: Deep Space Nine'' (abbreviated as ''DS9'') is an American science fiction television series created by Rick Berman and Michael Piller. The fourth series in the ''Star Trek'' media franchise, it originally aired in syndication fro ...
'' (1993–1999), ''Voyager
Voyager may refer to:
Computing and communications
* LG Voyager, a mobile phone model manufactured by LG Electronics
* NCR Voyager, a computer platform produced by NCR Corporation
* Voyager (computer worm), a computer worm affecting Oracle ...
'' (1995–2001)'','' ''Enterprise
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to:
Business and economics
Brands and enterprises
* Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company
* Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company
* Enterprise ...
'' (2001–2005), ''Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discove ...
'' (2017–present), '' Picard'' (2020–present), and Strange ''New'' Worlds (2022–present)) with more in some form of development.
The miniseries
A miniseries or mini-series is a television series that tells a story in a predetermined, limited number of episodes. "Limited series" is another more recent US term which is sometimes used interchangeably. , the popularity of miniseries format ...
''V'' premiered in 1983 on NBC. It depicted an attempted takeover of Earth by reptilian aliens. ''Red Dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. ...
'', a comic science fiction
Science fiction comedy (sci-fi comedy) or comic science fiction is a subgenre of science fiction or science fantasy that exploits the science-fiction (SF) genre's conventions for comedy, comedic effect. Comic science fiction often mocks or satirize ...
series aired on BBC Two
BBC Two is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network owned and operated by the BBC. It covers a wide range of subject matter, with a remit "to broadcast programmes of depth and substance" in contrast to the more mainstream a ...
between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave Dave may refer to:
Film, television, and theater
* ''Dave'' (film), a 1993 film starring Kevin Kline and Sigourney Weaver
* ''Dave'' (musical), a 2018 stage musical adaptation of the film
* Dave (TV channel), a digital television channel in the ...
since 2009. ''The X-Files
''The X-Files'' is an American science fiction on television, science fiction drama (film and television), drama television series created by Chris Carter (screenwriter), Chris Carter. The series revolves around Federal Bureau of Investigation ...
'', which featured UFO
An unidentified flying object (UFO), more recently renamed by US officials as a UAP (unidentified aerial phenomenon), is any perceived aerial phenomenon that cannot be immediately identified or explained. On investigation, most UFOs are ide ...
s and conspiracy theories
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a conspiracy by sinister and powerful groups, often political in motivation, when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
*
*
*
* The term has a nega ...
, was created by Chris Carter and broadcast by Fox Broadcasting Company
The Fox Broadcasting Company, commonly known simply as Fox and stylized in all caps as FOX, is an American commercial broadcast television network owned by Fox Corporation and headquartered in New York City, with master control operations ...
from 1993 to 2002, and again from 2016 to 2018. ''Stargate
''Stargate'' (often stylized in all caps) is a military science fiction media franchise based on the film directed by Roland Emmerich, which he co-wrote with producer Dean Devlin. The franchise is based on the idea of an alien Einstein–Rosen ...
'', a film about ancient astronauts
Ancient astronauts (or ancient aliens) refers to a pseudoscientific hypothesis which holds that intelligent extraterrestrial beings visited Earth and made contact with humans in antiquity and prehistoric times. Proponents suggest that thi ...
and interstellar teleportation
Teleportation is the hypothetical transfer of matter or energy from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them. It is a common subject in science fiction literature and in other popular culture. Teleportation is oft ...
, was released in 1994. ''Stargate SG-1
''Stargate SG-1'' (often stylized in all caps, or abbreviated ''SG-1'') is a military science fiction adventure television series within Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer's ''Stargate'' franchise. The show, created by Brad Wright and Jonathan Glassner, ...
'' premiered in 1997 and ran for 10 seasons (1997–2007). Spin-off series included ''Stargate Infinity
''Stargate Infinity'' (often abbreviated as ''SGI'' or just ''Infinity'') (French: ''Stargate: Le Dessin Animé'') is a 2002-2003 animated science fiction television series co-produced by Les Studios Tex S.A.R.L. and DIC Entertainment Corporation ...
'' (2002–2003), ''Stargate Atlantis
''Stargate Atlantis'' (usually stylized in all caps and often abbreviated ''SGA'') is an adventure and military science fiction television series and part of MGM's ''Stargate'' franchise. The show was created by Brad Wright and Robert C. Coop ...
'' (2004–2009), and ''Stargate Universe
''Stargate Universe'' (often abbreviated as ''SGU'') is a military science fiction television series and part of MGM's ''Stargate'' franchise. It follows the adventures of a present-day, multinational exploration team traveling on the Ancient ...
'' (2009–2011). Other 1990s series included ''Quantum Leap
''Quantum Leap'' is an American science fiction television series, created by Donald P. Bellisario, that premiered on NBC and aired for five seasons, from March 26, 1989, to May 5, 1993. The series stars Scott Bakula as Dr. Sam Beckett, a phys ...
'' (1989–1993) and ''Babylon 5
''Babylon 5'' is an American space opera television series created by writer and producer J. Michael Straczynski, under the Babylonian Productions label, in association with Straczynski's Synthetic Worlds Ltd. and Warner Bros. Domestic Tele ...
'' (1994–1999).
SyFy
Syfy (formerly Sci-Fi Channel, later shortened to Sci Fi; stylized as SYFY) is an American basic cable channel owned by the NBCUniversal Television and Streaming division of Comcast's NBCUniversal through NBCUniversal Cable Entertainment. La ...
, launched in 1992 as The Sci-Fi Channel, specializes in science fiction, supernatural horror
Horror is a genre of fiction which is intended to frighten, scare, or disgust. Horror is often divided into the sub-genres of psychological horror and supernatural horror, which is in the realm of speculative fiction. Literary historian J ...
, and fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction involving magical elements, typically set in a fictional universe and sometimes inspired by mythology and folklore. Its roots are in oral traditions, which then became fantasy literature and d ...
.
The space-Western series Firefly
The Lampyridae are a family of elateroid beetles with more than 2,000 described species, many of which are light-emitting. They are soft-bodied beetles commonly called fireflies, lightning bugs, or glowworms for their conspicuous production ...
premiered in 2002 on Fox. It is set in the year 2517, after the arrival of humans in a new star system, and follows the adventures of the renegade crew of '' Serenity'', a "''Firefly''-class" spaceship.''Orphan Black
''Orphan Black'' is a Canadian science-fiction thriller television series created by screenwriter Graeme Manson and director John Fawcett and starring Tatiana Maslany. The series focuses on Sarah Manning, one of several genetically identical ...
'' began its 5-season run in 2013, about a woman who assumes the identity of one of her several genetically identical human clones. In late 2015 SyFy
Syfy (formerly Sci-Fi Channel, later shortened to Sci Fi; stylized as SYFY) is an American basic cable channel owned by the NBCUniversal Television and Streaming division of Comcast's NBCUniversal through NBCUniversal Cable Entertainment. La ...
premiered ''The Expanse
Expanse or The Expanse may refer to:
Media and entertainment
''The Expanse'' franchise
* ''The Expanse'' (novel series), a series of science fiction novels by James S. A. Corey
* ''The Expanse'' (TV series), a television adaptation of the ...
'' to great critical acclaim, an American TV series about Humanity's colonization of the Solar System. Its later seasons would then be aired through Amazon Prime Video
Amazon Prime Video, also known simply as Prime Video, is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming and rental service of Amazon offered as a standalone service or as part of Amazon's Prime subscription. The service pr ...
.
Social influence
Science fiction's rapid rise in popularity during the first half of the 20th century was closely tied to the popular respect paid to science at that time, as well as the rapid pace oftechnological innovation
Technological innovation is an extended concept of innovation. While innovation is a rather well-defined concept, it has a broad meaning to many people, and especially numerous understanding in the academic and business world.
Innovation refers ...
and new invention
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
s.Astounding Wonder: Imagining Science and Science Fiction in Interwar America, John Cheng, University of Pennsylvania Press, 19 March 2012 pages 1–12. Science fiction has often predicted scientific and technological progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension w ...
. Some works predict that new inventions and progress will tend to improve life and society, for instance the stories of Arthur C. Clarke
Sir Arthur Charles Clarke (16 December 191719 March 2008) was an English science-fiction writer, science writer, futurist, inventor, undersea explorer, and television series host.
He co-wrote the screenplay for the 1968 film '' 2001: A Spac ...
and ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
''. Others, such as H.G. Wells's ''The Time Machine
''The Time Machine'' is a science fiction novella by H. G. Wells, published in 1895. The work is generally credited with the popularization of the concept of time travel by using a vehicle or device to travel purposely and selectively for ...
'' and Aldous Huxley's ''Brave New World
''Brave New World'' is a dystopian novel by English author Aldous Huxley, written in 1931 and published in 1932. Largely set in a futuristic World State, whose citizens are environmentally engineered into an intelligence-based social hiera ...
'', warn about possible negative consequences.The Greenwood Encyclopedia of Science Fiction and Fantasy: Themes, Works, and Wonders, Volume 2, Gary Westfahl, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005
In 2001 the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
conducted a survey on "Public
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociology, sociological concept of the ''Öf ...
Attitudes and Public Understanding: Science Fiction and Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
." It found that people who read or prefer science fiction may think about or relate to science differently than other people. They also tend to support the space program
A space program is an organized effort by a government or a company with a goal related to outer space.
Lists of space programs include:
* List of government space agencies
* List of private spaceflight companies
* List of human spaceflight prog ...
and the idea of contacting extraterrestrial civilizations
''Extraterrestrial Civilizations'' is a 1979 book by Isaac Asimov, in which the author estimates the probability of there being intelligent extraterrestrial civilizations within the Milky Way galaxy. This estimation is approached by progressively ...
. Carl Sagan
Carl Edward Sagan (; ; November 9, 1934December 20, 1996) was an American astronomer, planetary scientist, cosmologist, astrophysicist, astrobiologist, author, and science communicator. His best known scientific contribution is research on ex ...
wrote: "Many scientists deeply involved in the exploration of the solar system
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
(myself among them) were first turned in that direction by science fiction."
Brian Aldiss
Brian Wilson Aldiss (; 18 August 1925 – 19 August 2017) was an English writer, artist, and anthology editor, best known for science fiction novels and short stories. His byline reads either Brian W. Aldiss or simply Brian Aldiss, except for o ...
described science fiction as "cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.T ...
wallpaper
Wallpaper is a material used in interior decoration to decorate the interior walls of domestic and public buildings. It is usually sold in rolls and is applied onto a wall using wallpaper paste. Wallpapers can come plain as "lining paper" (so ...
." Evidence for this widespread influence can be found in trends for writers to employ science fiction as a tool for advocacy and generating cultural insights, as well as for educators when teaching across a range of academic disciplines not limited to the natural sciences. Scholar and science fiction critic George Edgar Slusser
George Edgar Slusser (July 14, 1939 – November 4, 2014) was an American scholar, professor and writer. Slusser was a well-known science fiction critic. A professor emeritus of comparative literature at University of California, Riverside, he ...
said that science fiction "is the one real international literary form we have today, and as such has branched out to visual media, interactive media
Interactive media normally refers to products and services on digital computer-based systems which respond to the user's actions by presenting content such as text, moving image, animation, video and audio. Since its early conception, various f ...
and on to whatever new media the world will invent in the 21st century. Crossover issues between the science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
s and the humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at t ...
are crucial for the century
A century is a period of 100 years. Centuries are numbered ordinally in English and many other languages. The word ''century'' comes from the Latin ''centum'', meaning ''one hundred''. ''Century'' is sometimes abbreviated as c.
A centennial or ...
to come."
As protest literature
social protest
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration or remonstrance) is a public expression of objection, disapproval or dissent towards an idea or action, typically a political one.
Protests can be thought of as acts of coopera ...
. George Orwell's ''Nineteen Eighty-Four
''Nineteen Eighty-Four'' (also stylised as ''1984'') is a dystopian social science fiction novel and cautionary tale written by the English writer George Orwell. It was published on 8 June 1949 by Secker & Warburg as Orwell's ninth and fina ...
'' (1949) is an important work of dystopian science fiction. It is often invoked in protests against governments and leaders who are seen as totalitarian
Totalitarianism is a form of government and a political system that prohibits all opposition parties, outlaws individual and group opposition to the state and its claims, and exercises an extremely high if not complete degree of control and reg ...
. James Cameron's 2009 film ''Avatar
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appear ...
'' was intended as a protest against imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic powe ...
, and specifically the European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short t ...
.
Robots "\n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visi ...
, artificial humans, human clones
Clone or Clones or Cloning or Cloned or The Clone may refer to:
Places
* Clones, County Fermanagh
* Clones, County Monaghan, a town in Ireland
Biology
* Clone (B-cell), a lymphocyte clone, the massive presence of which may indicate a pathologi ...
, intelligent computers
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
, and their possible conflicts with human society have all been major themes of science fiction since, at least, the publication of Shelly's ''Frankenstein
''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' is an 1818 novel written by English author Mary Shelley. ''Frankenstein'' tells the story of Victor Frankenstein, a young scientist who creates a sapient creature in an unorthodox scientific ...
''. Some critics have seen this as reflecting authors’ concerns over the social alienation
Social alienation is a person's feeling of disconnection from a group whether friends, family, or wider society to which the individual has an affinity. Such alienation has been described as "a condition in social relationships reflected by (1) ...
seen in modern society.Androids, Humanoids, and Other Science Fiction Monsters: Science and Soul in Science Fiction Films, Per Schelde, NYU Press, 1994, pages 1–10
Feminist science fiction poses questions about social issues such as how society constructs gender role
A gender role, also known as a sex role, is a social role encompassing a range of behaviors and attitudes that are generally considered acceptable, appropriate, or desirable for a person based on that person's sex. Gender roles are usually cen ...
s, the role reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
plays in defining gender
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most culture ...
, and the inequitable political or personal power of one gender over others. Some works have illustrated these themes using utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book '' Utopia'', describing a fictional island soc ...
s to explore a society in which gender differences or gender power imbalances do not exist, or dystopia
A dystopia (from Ancient Greek δυσ- "bad, hard" and τόπος "place"; alternatively cacotopiaCacotopia (from κακός ''kakos'' "bad") was the term used by Jeremy Bentham in his 1818 Plan of Parliamentary Reform (Works, vol. 3, p. 493). ...
s to explore worlds in which gender inequalities
Gender inequality is the social phenomenon in which men and women are not treated equally. The treatment may arise from distinctions regarding biology, psychology, or cultural norms prevalent in the society. Some of these distinctions are empi ...
are intensified, thus asserting a need for feminist work to continue.
Climate fiction
Climate fiction (sometimes shortened as cli-fi) is literature that deals with climate change.Glass, Rodge (31 May 2013).Global Warning: The Rise of 'Cli-fi' retrieved 3 March 2016 Generally speculative in nature but scientifically-grounded, wor ...
, or "cli-fi," deals with issues concerning climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
and global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. University
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
courses
Course may refer to:
Directions or navigation
* Course (navigation), the path of travel
* Course (orienteering), a series of control points visited by orienteers during a competition, marked with red/white flags in the terrain, and corresponding ...
on literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
and environmental issue
Environmental issues are effects of human activity on the biophysical environment, most often of which are harmful effects that cause environmental degradation. Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment o ...
s may include climate change fiction in their syllabi, and it is often discussed by other media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
outside of science fiction fandom
Science fiction fandom or SF fandom is a community or fandom of people interested in science fiction in contact with one another based upon that interest. SF fandom has a life of its own, but not much in the way of formal organization (although ...
.
Libertarian science fiction
Libertarian science fiction is a subgenre of science fiction that focuses on the politics and social order implied by right-libertarian philosophies with an emphasis on individualism and private ownership of the means of production—and in so ...
focuses on the politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
and social order
The term social order can be used in two senses: In the first sense, it refers to a particular system of social structures and institutions. Examples are the ancient, the feudal, and the capitalist social order. In the second sense, social order ...
implied by right libertarian
Right-libertarianism,Rothbard, Murray (1 March 1971)"The Left and Right Within Libertarianism" ''WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action''. 7 (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.Goodway, David (2006). '' Anarchist Seeds Beneath the ...
philosophies with an emphasis on individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and to value independence and self-reli ...
and private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and personal property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or ...
, and in some cases anti-statism
Anti-statism is any approach to social, economic or political philosophy that rejects statism. An anti-statist is one who opposes intervention by the state into personal, social and economic affairs. In anarchism, this is characterized by a comp ...
.
Science fiction comedy
Science fiction comedy (sci-fi comedy) or comic science fiction is a subgenre of science fiction or science fantasy that exploits the science-fiction (SF) genre's conventions for comedic effect. Comic science fiction often mocks or satirizes stand ...
often satirizes and criticizes present-day society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Soc ...
, and sometimes makes fun of the conventions and cliché
A cliché ( or ) is an element of an artistic work, saying, or idea that has become overused to the point of losing its original meaning or effect, even to the point of being weird or irritating, especially when at some earlier time it was consi ...
s of more serious science fiction.The Animal Fable in Science Fiction and Fantasy, Bruce Shaw, McFarland, 2010, page 19
The potential for Science Fiction as a genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other f ...
is not just limited to being a literary sandbox for exploring otherworldly narratives but can act as a vehicle to analyze and recognize a society's past, present, and potential future social relationships
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
with the Other
In Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology, the terms the Other and the Constitutive Other identify the other human being, in their differences from the Self, as being a cumulative, constituting factor in the self-image of a person; as acknow ...
. More specifically, Science Fiction offers a medium and representation of Alterity
Alterity is a philosophical and anthropological term meaning "otherness", that is, the "other of two" (Latin ''alter''). It is also increasingly being used in media to express something other than "sameness", or something outside of tradition or co ...
and differences in social identity
Identity is the qualities, beliefs, personality traits, appearance, and/or expressions that characterize a person or group.Compare ''Collins Dictionary of Sociology'', quoted in
In sociology, emphasis is placed on collective identity, in which ...
.
Sense of wonder
 Science fiction is often said to inspire a "
Science fiction is often said to inspire a "sense of wonder
A sense of wonder (sometimes jokingly written sensawunda) is an intellectual and emotional state frequently invoked in discussions of science and biology, higher consciousness, science fiction, and philosophy.
__TOC__
Definitions
This entry f ...
." Science fiction editor and critic David Hartwell
David Geddes Hartwell (July 10, 1941 – January 20, 2016) was an American critic, publisher, and editor of thousands of science fiction and fantasy novels. He was best known for work with Signet, Pocket, and Tor Books publishers. He was also ...
wrote: "Science fiction’s appeal lies in combination of the rational, the believable, with the miraculous. It is an appeal to the sense of wonder." Carl Sagan said: "One of the great benefits of science fiction is that it can convey bits and pieces, hints, and phrases, of knowledge unknown or inaccessible to the reader . . . works you ponder over as the water is running out of the bathtub or as you walk through the woods in an early winter snowfall."
In 1967, Isaac Asimov commented on the changes then occurring in the science fiction community: "And because today’s real life so resembles day-before-yesterday’s fantasy, the old-time fans are restless. Deep within, whether they admit it or not, is a feeling of disappointment and even outrage that the outer world has invaded their private domain. They feel the loss of a 'sense of wonder' because what was once truly confined to 'wonder' has now become prosaic and mundane."
Science fiction studies
The study of science fiction, orscience fiction studies
''Science Fiction Studies'' (''SFS'') is an academic journal founded in 1973 by R. D. Mullen. The journal is published three times per year at DePauw University. As the name implies, the journal publishes articles and book reviews on science fic ...
, is the critical
Critical or Critically may refer to:
*Critical, or critical but stable, medical states
**Critical, or intensive care medicine
* Critical juncture, a discontinuous change studied in the social sciences.
*Critical Software, a company specializing ...
assessment, interpretation
Interpretation may refer to:
Culture
* Aesthetic interpretation, an explanation of the meaning of a work of art
* Allegorical interpretation, an approach that assumes a text should not be interpreted literally
* Dramatic Interpretation, an event ...
, and discussion of science fiction literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
, film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
, TV shows
A television show – or simply TV show – is any content produced for viewing on a television set which can be broadcast via over-the-air, satellite, or cable, excluding breaking news, advertisements, or trailers that are typically placed bet ...
, new media
New media describes communication technologies that enable or enhance interaction between users as well as interaction between users and content. In the middle of the 1990s, the phrase "new media" became widely used as part of a sales pitch for ...
, fandom
A fandom is a subculture composed of fans characterized by a feeling of empathy and camaraderie with others who share a common interest. Fans typically are interested in even minor details of the objects of their fandom and spend a significant ...
, and fan fiction
Fan fiction or fanfiction (also abbreviated to fan fic, fanfic, fic or FF) is fictional writing written in an amateur capacity by fans, unauthorized by, but based on an existing work of fiction. The author uses copyrighted characters, setti ...
. Science fiction scholar
A scholar is a person who pursues academic and intellectual activities, particularly academics who apply their intellectualism into expertise in an area of study. A scholar can also be an academic, who works as a professor, teacher, or researche ...
s study science fiction to better understand it and its relationship to science, technology, politics, other genres, and culture-at-large. Science fiction studies began around the turn of the 20th century, but it was not until later that science fiction studies solidified as a discipline with the publication of the academic journals ''Extrapolation
In mathematics, extrapolation is a type of estimation, beyond the original observation range, of the value of a variable on the basis of its relationship with another variable. It is similar to interpolation, which produces estimates between know ...
'' (1959), '' Foundation: The International Review of Science Fiction'' (1972), and ''Science Fiction Studies
''Science Fiction Studies'' (''SFS'') is an academic journal founded in 1973 by R. D. Mullen. The journal is published three times per year at DePauw University. As the name implies, the journal publishes articles and book reviews on science fic ...
'' (1973), and the establishment of the oldest organizations devoted to the study
Study or studies may refer to:
General
* Education
** Higher education
* Clinical trial
* Experiment
* Observational study
* Research
* Study skills, abilities and approaches applied to learning
Other
* Study (art), a drawing or series of ...
of science fiction in 1970, the Science Fiction Research Association The Science Fiction Research Association (SFRA), founded in 1970, is the oldest, non-profit professional organization committed to encouraging, facilitating, and rewarding the study of science fiction and fantasy literature, film, and other media. ...
and the Science Fiction Foundation
The Science Fiction Foundation is a Registered Charity established 1970 in England by George Hay and others. Its purpose is to "promote science fiction and bring together those who read, write, study, teach, research or archive science fiction ...
. The field has grown considerably since the 1970s with the establishment of more journals, organization
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived f ...
s, and conference
A conference is a meeting of two or more experts to discuss and exchange opinions or new information about a particular topic.
Conferences can be used as a form of group decision-making, although discussion, not always decisions, are the main p ...
s, as well as science fiction degree-granting programs such as those offered by the University of Liverpool
, mottoeng = These days of peace foster learning
, established = 1881 – University College Liverpool1884 – affiliated to the federal Victoria Universityhttp://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukla/2004/4 University of Manchester Act 200 ...
and the University of Kansas
The University of Kansas (KU) is a public research university with its main campus in Lawrence, Kansas, United States, and several satellite campuses, research and educational centers, medical centers, and classes across the state of Kansas. T ...
.
Classification
Science fiction has historically been sub-divided betweenhard science fiction
Hard science fiction is a category of science fiction characterized by concern for scientific accuracy and logic. The term was first used in print in 1957 by P. Schuyler Miller in a review of John W. Campbell's ''Islands of Space'' in the Novemb ...
and soft science fiction, with the division centering on the feasibility of the science central to the story. However, this distinction has come under increasing scrutiny in the 21st century. Some author
An author is the writer of a book, article, play, mostly written work. A broader definition of the word "author" states:
"''An author is "the person who originated or gave existence to anything" and whose authorship determines responsibility f ...
s, such as Tade Thompson
Tade Thompson is a British-born Nigerian psychiatrist best known for his science fiction novels.
Life and career
Thompson was born in London to Yoruba parents. His family left the United Kingdom for Nigeria in 1976, when Thompson was seven. He ...
and Jeff VanderMeer
Jeff VanderMeer (born July 7, 1968) is an American author, editor, and literary critic. Initially associated with the New Weird literary genre, VanderMeer crossed over into mainstream success with his bestselling Southern Reach Trilogy. The t ...
, have pointed out that stories that focus explicitly on physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, and engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
tend to be considered "hard" science fiction, while stories that focus on botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
, mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans, including as a source for tinder, traditional medicine, food, and entheogen ...
, zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, an ...
, and the social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of s ...
s tend to be categorized as "soft," regardless of the relative rigor of the science.
Max Gladstone
Max Gladstone (born May 28, 1984) is an American fantasy author. He is best known for his 2012 debut novel ''Three Parts Dead'', which is part of ''The Craft Sequence'', his urban fantasy serial ''Bookburners'', and for co-writing ''This Is How You ...
defined "hard" science fiction as stories "where the math
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
works," but pointed out that this ends up with stories that often seem "weirdly dated," as scientific paradigm
In science and philosophy, a paradigm () is a distinct set of concepts or thought patterns, including theories, research methods, postulates, and standards for what constitute legitimate contributions to a field.
Etymology
''Paradigm'' comes f ...
s shift over time. Michael Swanwick
Michael Swanwick (born 18 November 1950) is an American fantasy and science fiction author who began publishing in the early 1980s.
Writing career
Swanwick's fiction writing began with short stories, starting in 1980 when he published "Ginungagap ...
dismissed the traditional definition of "hard" SF altogether, instead saying that it was defined by characters striving to solve problems "in the right way–with determination, a touch of stoicism
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy founded by Zeno of Citium in Athens in the early 3rd century BCE. It is a philosophy of personal virtue ethics informed by its system of logic and its views on the natural world, asserting tha ...
, and the consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
that the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
is not on his or her side."
Ursula K. Le Guin
Ursula Kroeber Le Guin (; October 21, 1929 – January 22, 2018) was an American author best known for her works of speculative fiction, including science fiction works set in her Hainish universe, and the '' Earthsea'' fantasy series. She was ...
also criticized the more traditional view on the difference between "hard" and "soft" SF: "The 'hard' science fiction writers dismiss everything except, well, physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, and maybe chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
. Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
, sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation an ...
, anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
—that's not science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
to them, that's soft stuff. They're not that interested in what human beings
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, an ...
do, really. But I am. I draw on the social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of s ...
s a great deal."
As serious literature
 Respected authors have written science fiction.
Respected authors have written science fiction. Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley (; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel '' Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an early example of science fiction. She also ...
wrote a number of science fiction novels including '' Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), and is considered a major writer of the Romantic Age
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
. Aldous Huxley's ''Brave New World
''Brave New World'' is a dystopian novel by English author Aldous Huxley, written in 1931 and published in 1932. Largely set in a futuristic World State, whose citizens are environmentally engineered into an intelligence-based social hiera ...
'' (1932) is often listed as one of England's most important novels, both for its criticism of modern culture and its prediction of future trends including reproductive technology
Reproductive technology encompasses all current and anticipated uses of technology in human and animal reproduction, including assisted reproductive technology, contraception and others. It is also termed Assisted Reproductive Technology, where it ...
and social engineering. Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut Jr. (November 11, 1922 – April 11, 2007) was an American writer known for his satirical and darkly humorous novels. In a career spanning over 50 years, he published fourteen novels, three short-story collections, five plays, and ...
was a highly respected American author whose works contain science fiction premises or themes. Other science fiction authors whose works are widely considered to be "serious" literature include Ray Bradbury
Ray Douglas Bradbury (; August 22, 1920June 5, 2012) was an American author and screenwriter. One of the most celebrated 20th-century American writers, he worked in a variety of modes, including fantasy, science fiction, horror, mystery, and ...
(including, especially, ''Fahrenheit 451
''Fahrenheit 451'' is a 1953 dystopian novel by American writer Ray Bradbury. Often regarded as one of his best works, ''Fahrenheit 451'' presents an American society where books have been personified and outlawed and "firemen" burn any that ar ...
'' (1953) and ''The Martian Chronicles
''The Martian Chronicles'' is a science fiction fix-up novel, published in 1950, by American writer Ray Bradbury that chronicles the exploration and settlement of Mars, the home of indigenous Martians, by Americans leaving a troubled Earth th ...
'' (1951)), Arthur C. Clarke
Sir Arthur Charles Clarke (16 December 191719 March 2008) was an English science-fiction writer, science writer, futurist, inventor, undersea explorer, and television series host.
He co-wrote the screenplay for the 1968 film '' 2001: A Spac ...
(especially for ''Childhood's End''), and Paul Myron Anthony Linebarger, writing under the name Cordwainer Smith. In his book "The Western Canon", literary critic Harold Bloom includes ''Brave New World'', ''Solaris'', ''Cat's Cradle'' (1963) by Vonnegut, and ''The Left Hand of Darkness'' as culturally and aesthetically significant works of western literature.
David Barnett (writer), David Barnett has pointed out that there are books such as ''The Road'' (2006) by Cormac McCarthy, ''Cloud Atlas (novel), Cloud Atlas'' (2004) by David Mitchell (author), David Mitchell, ''The Gone-Away World'' (2008) by Nick Harkaway, ''The Stone Gods (novel), The Stone Gods'' (2007) by Jeanette Winterson, and ''Oryx and Crake'' (2003) by Margaret Atwood, which use recognizable science fiction Trope (literature), tropes, but whose authors and publishers do not Marketing, market them as science fiction. Doris Lessing, who was later awarded the Nobel Prize in literature, wrote a series of five SF novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself ...
s, ''Canopus in Argos, Canopus in Argos: Archives'' (1979–1983), which depict the efforts of more advanced species and civilizations to influence those less advanced, including humans on Earth.
In her much reprinted 1976 essay "Science Fiction and Mrs Brown," Ursula K. Le Guin
Ursula Kroeber Le Guin (; October 21, 1929 – January 22, 2018) was an American author best known for her works of speculative fiction, including science fiction works set in her Hainish universe, and the '' Earthsea'' fantasy series. She was ...
was asked: "Can a science fiction writer write a novel?" She answered: "I believe that all novels ... deal with Character (arts), character, and that it is to express character–not to preach doctrines [or] sing songs... that the form of the novel, so clumsy, verbose, and undramatic, so rich, elastic, and alive, has been evolved. ... The great novelists have brought us to see whatever they wish us to see through some character. Otherwise, they would not be novelists, but poets, historians, or pamphleteers." Orson Scott Card, best known for his 1985 science fiction novel ''Ender's Game'', has postulated that in science fiction the message and intellectual significance of the work are contained within the story itself and, therefore, does not need stylistic gimmicks or literary games.
Jonathan Lethem, in a 1998 essay in the ''Village Voice'' entitled "Close Encounters: The Squandered Promise of Science Fiction," suggested that the point in 1973 when Thomas Pynchon's ''Gravity's Rainbow'' was nominated for the Nebula Award
The Nebula Awards annually recognize the best works of science fiction or fantasy published in the United States. The awards are organized and awarded by the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America (SFWA), a nonprofit association of prof ...
and was passed over in favor of Clarke's ''Rendezvous with Rama'', stands as "a hidden tombstone marking the death of the hope that SF was about to merge with the mainstream." In the same year science fiction author and physicist Gregory Benford wrote: "SF is perhaps the defining genre of the twentieth century, although its conquering Army, armies are still camped outside the Roman Empire, Rome of the literary citadels."
Community
Authors
Science fiction is being written, and has been written, by Cultural diversity, diverse authors from around the world. According to 2013 statistics by the science fiction Publishing, publisherTor Books
Tor Books is the primary imprint of Tor Publishing Group (previously Tom Doherty Associates), a publishing company based in New York City. It primarily publishes science fiction and fantasy titles, and is the largest publisher of Chinese scienc ...
, men outnumber women by 78% to 22% among submissions to the publisher. 2015 Hugo Awards controversy, A controversy about voting slates in the 2015 Hugo Award
The Hugo Award is an annual literary award for the best science fiction or fantasy works and achievements of the previous year, given at the World Science Fiction Convention and chosen by its members. The Hugo is widely considered the premier ...
s highlighted tensions in the science fiction community between a trend of increasingly diverse works and authors being honored by awards, and reaction by groups of authors and fans who preferred what they considered more "traditional" science fiction.
Awards
Among the most respected and well-known awards for science fiction are theHugo Award
The Hugo Award is an annual literary award for the best science fiction or fantasy works and achievements of the previous year, given at the World Science Fiction Convention and chosen by its members. The Hugo is widely considered the premier ...
for literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
, presented by the World Science Fiction Society at Worldcon, and voted on by fans; the Nebula Award
The Nebula Awards annually recognize the best works of science fiction or fantasy published in the United States. The awards are organized and awarded by the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America (SFWA), a nonprofit association of prof ...
for literature, presented by the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America, and voted on by the community of authors; the John W. Campbell Memorial Award for Best Science Fiction Novel, presented by a jury of writers; and the Theodore Sturgeon Award, Theodore Sturgeon Memorial Award for Short story, short fiction, presented by a jury. One notable award for science fiction films and TV programs is the Saturn Award, which is presented annually by Academy of Science Fiction, Fantasy and Horror Films, The Academy of Science Fiction, Fantasy, and Horror Films.
There are other national awards, like Canada's Prix Aurora Awards, regional awards, like the Endeavour Award presented at OryCon, Orycon for works from the Pacific Northwest, U.S. Pacific Northwest, and special interest or subgenre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other for ...
awards such as the Chesley Award for art, presented by the Association of Science Fiction & Fantasy Artists, or the World Fantasy Award for fantasy. Magazines may organize reader polls, notably the Locus Award.
Conventions
 Convention (meeting), Conventions (in fandom, often shortened as "cons," such as "comic-con") are held in City, cities around the world, catering to a local, regional, national, or international membership. Interest (emotion), General-interest conventions cover all aspects of science fiction, while others focus on a particular interest like media fandom, filking, and so on. Most science fiction conventions are organized by volunteering, volunteers in Non-profit organization, non-profit groups, though most media-oriented events are organized by Advertising, commercial promoters.
Convention (meeting), Conventions (in fandom, often shortened as "cons," such as "comic-con") are held in City, cities around the world, catering to a local, regional, national, or international membership. Interest (emotion), General-interest conventions cover all aspects of science fiction, while others focus on a particular interest like media fandom, filking, and so on. Most science fiction conventions are organized by volunteering, volunteers in Non-profit organization, non-profit groups, though most media-oriented events are organized by Advertising, commercial promoters.
Fandom and fanzines
Science fiction fandom emerged from the Comic book letter column, letters column in ''Amazing Stories
''Amazing Stories'' is an American science fiction magazine launched in April 1926 by Hugo Gernsback's Experimenter Publishing. It was the first magazine devoted solely to science fiction. Science fiction stories had made regular appearances ...
'' magazine. Soon fans began writing Letter (message), letters to each other, and then grouping their comments together in informal publications that became known as fanzines. Once they were in regular contact, fans wanted to meet each other, and they organized local clubs. In the 1930s, the first science fiction conventions gathered fans from a wider area.
The earliest organized online fandom
A fandom is a subculture composed of fans characterized by a feeling of empathy and camaraderie with others who share a common interest. Fans typically are interested in even minor details of the objects of their fandom and spend a significant ...
was the SF Lovers Community, originally a mailing list in the late 1970s with a text File archiver, archive file that was updated regularly. In the 1980s, Usenet groups greatly expanded the circle of fans Online and offline, online. In the 1990s, the development of the World-Wide Web exploded the community of online fandom by orders of magnitude, with thousands and then millions of websites devoted to science fiction and related genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other f ...
s for all media.
The first Science-fiction fanzine, science fiction fanzine, ''The Comet (fanzine), The Comet'', was published in 1930 by the Science Correspondence Club in Chicago, Illinois. One of the best known fanzines today is ''Ansible (magazine), Ansible'', Editing, edited by David Langford, winner of numerous Hugo Award, Hugo awards. Other notable fanzines to win one or more Hugo awards include ''File 770'', ''Mimosa (magazine), Mimosa'', and ''Plokta''. Artists working for fanzines have frequently risen to prominence in the field, including Brad W. Foster, Teddy Harvia, and Joe Mayhew; the Hugo Award, Hugos include a category for Hugo Award for Best Fan Artist, Best Fan Artists.
Elements
 Science fiction elements can include, among others:
*Temporal settings in the future, or in alternate history, alternative histories.
*Space travel in science fiction, Space travel, settings in outer space, on other worlds, in Hollow Earth, subterranean earth, or in Parallel universe (fiction)#Science fiction, parallel universes.
* Aspects of biology in fiction such as Extraterrestrial life, aliens, Mutant (fictional), mutants, and enhanced humans.
* Predicted or speculative technology such as Brain–computer interface, brain-computer interface, Biological engineering, bio-engineering, Superintelligence, superintelligent
Science fiction elements can include, among others:
*Temporal settings in the future, or in alternate history, alternative histories.
*Space travel in science fiction, Space travel, settings in outer space, on other worlds, in Hollow Earth, subterranean earth, or in Parallel universe (fiction)#Science fiction, parallel universes.
* Aspects of biology in fiction such as Extraterrestrial life, aliens, Mutant (fictional), mutants, and enhanced humans.
* Predicted or speculative technology such as Brain–computer interface, brain-computer interface, Biological engineering, bio-engineering, Superintelligence, superintelligent computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
s, robots "\n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visi ...
, and Raygun, ray guns and other Weapons in science fiction, advanced weapons.
* Undiscovered scientific possibilities such as teleportation
Teleportation is the hypothetical transfer of matter or energy from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them. It is a common subject in science fiction literature and in other popular culture. Teleportation is oft ...
, time travel
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a ...
, and faster-than-light travel or Ansible, communication.
* New and different political and social systems and situations, including Utopian, dystopia
A dystopia (from Ancient Greek δυσ- "bad, hard" and τόπος "place"; alternatively cacotopiaCacotopia (from κακός ''kakos'' "bad") was the term used by Jeremy Bentham in his 1818 Plan of Parliamentary Reform (Works, vol. 3, p. 493). ...
n, post-apocalyptic, or post-scarcity.
* Future history and Speculative evolution, evolution of humans on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
or on other planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
s.Ashley, M. (April 1989). The Immortal Professor, Astro Adventures No.7, p.6.
* Paranormal abilities such as Mind control in popular culture, mind control, telepathy, and telekinesis.
International examples
Subgenres
Related genres
See also
* Outline of science fiction * History of science fiction * Timeline of science fiction * Fantastic art * Fictional worlds * Futures studies * List of comic science fiction * List of religious ideas in science fiction * List of science fiction and fantasy artists * List of science fiction authors * List of science fiction films * List of science fiction novels * List of science fiction television programs * List of science fiction themes * List of science fiction universes * Planets in science fiction * Political ideas in science fiction * Retrofuturism * Robots in science fiction * Science fiction comics * Science fiction libraries and museums * Science in science fiction * Time travel in fiction * TranshumanismCitations
General and cited sources
* Brian Aldiss, Aldiss, Brian. ''Billion Year Spree: The True History of Science Fiction'', 1973. * Aldiss, Brian, and David Wingrove, Wingrove, David. ''Trillion Year Spree: The History of Science Fiction'', revised and updated edition, 1986. * Kingsley Amis, Amis, Kingsley. ''New Maps of Hell: A Survey of Science Fiction'', 1958. * Barron, Neil, ed. ''Anatomy of Wonder: A Critical Guide to Science Fiction'' (5th ed.). Westport, Conn.: Libraries Unlimited, 2004. . * Damien Broderick, Broderick, Damien. ''Reading by Starlight: Postmodern Science Fiction.'' London: Routledge, 1995. Print. * John Clute, Clute, John ''Science Fiction: The Illustrated Encyclopedia''. London: Dorling Kindersley, 1995. . * John Clute, Clute, John and Peter Nicholls, eds., ''The Encyclopedia of Science Fiction''. St Albans, Herts, UK: Granada Publishing, 1979. . * John Clute, Clute, John and Peter Nicholls, eds., ''The Encyclopedia of Science Fiction''. New York: St Martin's Press, 1995. . * Thomas M. Disch, Disch, Thomas M. ''The Dreams Our Stuff Is Made Of''. New York: The Free Press, 1998. . * Fredric Jameson, Jameson, Fredric. ''Archaeologies of the Future: This Desire Called Utopia and Other Science Fictions.'' London and New York: Verso, 2005. * Andrew Milner, Milner, Andrew. ''Locating Science Fiction''. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 2012. * Masood Ashraf Raja, Raja, Masood Ashraf, Jason W. Ellis and Swaralipi Nandi. eds., ''The Postnational Fantasy: Essays on Postcolonialism, Cosmopolitics and Science Fiction''. McFarland 2011. . * Reginald, Robert. ''Science Fiction and Fantasy Literature, 1975–1991''. Detroit, MI/Washington, D.C./London: Gale Research, 1992. . * Roy, Pinaki. "Science Fiction: ''Some Reflections''". ''Shodh Sanchar Bulletin'', 10.39 (July–September 2020): 138–42. * * Darko Suvin, Suvin, Darko. ''Metamorphoses of Science Fiction: on the Poetics and History of a Literary Genre.'' New Haven : Yale University Press, 1979. * Weldes, Jutta, ed. ''To Seek Out New Worlds: Exploring Links between Science Fiction and World Politics''. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2003. . * Westfahl, Gary, ed. ''The Greenwood Encyclopedia of Science Fiction and Fantasy: Themes, Works, and Wonders'' (three volumes). Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press, 2005. * Wolfe, Gary K. ''Critical Terms for Science Fiction and Fantasy: A Glossary and Guide to Scholarship''. New York: Greenwood Press, 1986. .External links
Science Fiction Bookshelf
at Project Gutenberg
Science fiction fanzines (current and historical) online
SFWA "Suggested Reading" list
Science fiction at standardebooks.org
Science Fiction Research Association
A selection of articles written by Mike Ashley, Iain Sinclair and others, exploring 19th-century visions of the future.
from the British Library's Discovering Literature website.
Merril Collection of Science Fiction, Speculation and Fantasy
at Toronto Public Library
Science Fiction Studies' Chronological Bibliography of Science Fiction History, Theory, and Criticism
Best 50 sci-fi novels of all time
(Esquire (magazine), Esquire; 21 March 2022) {{Authority control Science fiction, Speculative fiction, Speculative fiction