|
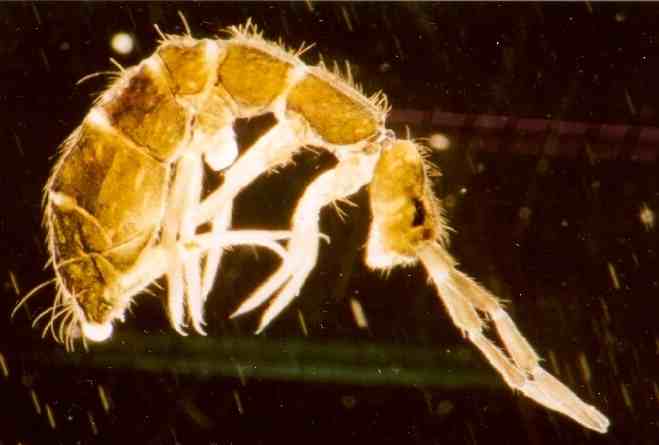
Springtail
Springtails (class Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern Hexapoda, hexapods that are no longer considered insects. Although the three lineages are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal Arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to insects, which have external mouthparts. Springtails are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from Ancient Greek 'glue' and 'peg'; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Early DNA sequence studies suggested that Collembola represent a separate Lineage (evolution), evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchesella Cincta
''Orchesella cincta'' is a species of springtail present in North America and Europe. They average in length, which is extremely large as most springtails don’t grow past 1 millimetre. The specific name ''cincta'' means "belted" and refers to the distinctive colouration of the third abdominal segment. Description Springtails are small, wingless relatives of insects and typically have six abdominal segments, a tubular appendage projecting ventrally from the first abdominal segment, and a forked, tail-like appendage, the Furcula (springtail), furcula, folded under the last abdominal segment, with which the animal can flip itself into the air. Members of the genus ''Orchesella'' have six antennal segments. ''Orchesella cincta'' reaches about in length and has a distinctively pigmented third abdominal segment and a dark third antennal segment. In contrast, the posterior part of the second abdominal segment and the distal part of the second antennal segments are white. The fifth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') or hexapods comprises the largest clade of arthropods and includes most of the extant arthropod species. It includes the crown group class Insecta (true insects), as well as the much smaller clade Entognatha, which includes three classes of wingless arthropods that were once considered insects: Collembola (springtails), Protura (coneheads) and Diplura (two-pronged bristletails). The insects and springtails are very abundant and are some of the most important pollinators, basal consumers, scavengers/ detritivores and micropredators in terrestrial environments. Hexapods are named for their most distinctive feature: a three-part body plan with a consolidated thorax and three pairs of legs. Most other arthropods have more than three pairs of legs. Most recent studies have recovered Hexapoda as a subgroup of Pancrustacea. Morphology Hexapods have bodies ranging in length from 0.5 mm to over 300 mm which are divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furcula (Collembola)
The furcula, or furca is a forked, tail-like appendage. It is present in most species of springtails, and in them it is attached ventrally to the fourth abdominal segment. The organ most often is present in species of ''Collembola'' that lives in the upper soil layers where it is used for jumping to avoid predators. While at rest, it is retracted under the abdomen and held there by a structure variously called the retinaculum or hamula, which in turn is located beneath the third abdominal segment. When the furcula escapes from retinaculum, it swings downwards and hits the substrate, propelling the springtail into the air. The animal does not use this mechanism for ordinary locomotion, but only for escaping from predators or severe stress. One reason not to use the furcula for general locomotion other than to escape threats, is that its action is very unpredictable; when the furcula is released, the springtail is sent tumbling through the air on a practically arbitrary traject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neelipleona
Neelipleona is a name given to some hexapods of the subclass Collembola (springtails). While their taxonomic rank remains broadly settled as family Neelidae, Neelipleona has been described at order or suborder rank. Eyes are absent. Taxonomic rank Many authors consider the "Neelipleona" Symphypleona of the superfamily Sminthuroidea, family Neelidae.See references in Haaramo (2008) However, in other accounts, Neelipleona are either a distinct order from the three less controversial Springtail orders (Entomobryomorpha, Poduromorpha and Symphypleona) or a distinct suborder Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized ... of Symphypleona, or placed in the Entomobryomorpha. References Footnotes Collembola {{springtail-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutonura Monticola - Flickr - Philippe Garcelon
''Deutonura'' is a genus of springtails in the family Neanuridae. There are at least 40 described species in ''Deutonura''. Species These 44 species belong to the genus ''Deutonura'': * '' Deutonura albella'' (Stach, 1920) * '' Deutonura anophthalma'' (Massoud & Thibaud, 1968) * '' Deutonura arbeai'' Lucianez & Simon, 1995 * '' Deutonura atlantica'' Deharveng, 1982 * '' Deutonura balsainensis'' Simon Benito, 1978 * '' Deutonura benzi'' Traser, Thibaud & Najt, 1993 * '' Deutonura betica'' Deharveng, 1979 * '' Deutonura caerulescens'' Deharveng, 1982 * '' Deutonura caprai'' Dallai, 1983 * '' Deutonura carinthiaca'' Deharveng, 1982 * '' Deutonura centralis'' (da Gama, 1964) * '' Deutonura coiffaiti'' Deharveng, 1979 * '' Deutonura conjuncta'' (Stach, 1926) * '' Deutonura corsica'' (Denis, 1947) * '' Deutonura czarnohorensis'' Deharveng, 1982 * '' Deutonura decolorata'' (da Gama & Gisin, 1964) * '' Deutonura deficiens'' Deharveng, 1979 * '' Deutonura deharvengi'' Arbea & Jordana, 1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury
John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury (30 April 1834 – 28 May 1913), known as Sir John Lubbock, 4th Baronet, from 1865 until 1900, was an English banker, Liberal Party (UK), Liberal politician, philanthropist, scientist and polymath. Lubbock worked in his family company as a banker but made significant contributions in archaeology, ethnography, and several branches of biology. He coined the terms "Paleolithic, Palaeolithic" and "Neolithic" to denote the Old and New Stone Ages, respectively. He helped establish archaeology as a scientific discipline, and was influential in debates concerning evolutionary theory. He introduced the first law for the protection of the UK's archaeological and architectural heritage. He promoted the establishment of public libraries and was also a founding member of the X Club. Early life John Lubbock was born in 1834, the son of Sir John Lubbock, 3rd Baronet, a London banker, and his wife Harriet. He was brought up in the family home of High Elms Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collophore
A collophore is a tube-like structure on the ventral side of the first abdominal segment of the body of springtails (collembolans). It used to be believed that it served to stabilise the animal when it jumped by sticking to the surface on which it moved. However, the current scientific consensus is that it plays a role in osmoregulation, water intake, and excretion Excretion is elimination of metabolic waste, which is an essential process in all organisms. In vertebrates, this is primarily carried out by the lungs, Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substa .... References Springtail anatomy {{arthropod-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poduromorpha
The order (biology), order Poduromorpha is one of the three main groups of springtails (Collembola), tiny Hexapoda, hexapods related to insects. This group was formerly treated as a Taxonomic rank, superfamily Poduroidea. They can be best distinguished from the other springtail groups by their body shape. The Symphypleona are very round animals, almost spherical and the abdominal segments are not visible. Both Entomobryomorpha and Poduromorpha are long springtails with six visible abdominal segments. While Entomobryomorpha have the first thorax segment reduced, Poduromorpha retain all three. The Poduromorpha also tend to have short legs and a plump body, but more oval in shape than the Symphypleona. Their name means 'foot tail formed', deriving from their short, flat, Furcula (springtail), furcula. __TOC__ Systematics The Poduromorpha were, as Poduroidea, united with the Entomobryomorpha (then called Entomobryoidea) in a group called "Arthropleona", but this has more recently t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistics
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to Taxonomy (biology), biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived (phylogenetics), derived characteristics (synapomorphies) that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose Phenotypic trait, character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms ''worms'' or ''fishes'' were used within a ''strict'' cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used Paraphyly, paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a 'E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segment (biology)
Segmentation in biology is the division of some animal and plant body plans into a linear series of repetitive segments that may or may not be interconnected to each other. This article focuses on the segmentation of animal body plans, specifically using the examples of the taxa Arthropoda, Chordata, and Annelida. These three groups form segments by using a "growth zone" to direct and define the segments. While all three have a generally segmented body plan and use a growth zone, they use different mechanisms for generating this patterning. Even within these groups, different organisms have different mechanisms for segmenting the body. Segmentation of the body plan is important for allowing free movement and development of certain body parts. It also allows for regeneration in specific individuals. Definition Segmentation is a difficult process to satisfactorily define. Many taxa (for example the molluscs) have some form of serial repetition in their units but are not conventiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |