|
Lughnasadh
Lughnasadh or Lughnasa ( , ) is a Gaelic festival marking the beginning of the harvest season. Historically, it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. In Modern Irish it is called , in gd, Lùnastal, and in gv, Luanistyn. Traditionally it is held on 1 August, or about halfway between the summer solstice and autumn equinox. In recent centuries some of the celebrations have been shifted to the Sunday nearest this date. Lughnasadh is one of the four Gaelic seasonal festivals, along with Samhain, Imbolc and Beltane. It corresponds to other European harvest festivals such as the Welsh and the English Lammas. Lughnasadh is mentioned in some of the earliest Irish literature and has pagan origins. The festival itself is named after the god Lugh. It inspired great gatherings that included religious ceremonies, ritual athletic contests (most notably the Tailteann Games), feasting, matchmaking, and trading. Lughnasadh occurred during a very poor t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lammas
Lammas Day (Anglo-Saxon ''hlaf-mas'', "loaf-mass"), also known as Loaf Mass Day, is a Christian holiday celebrated in some English-speaking countries in the Northern Hemisphere on 1 August. The name originates from the word "loaf" in reference to bread and "Mass" in reference to the Eucharist. It is a festival in the liturgical calendar to mark the blessing of the First Fruits of harvest, with a loaf of bread being brought to the church for this purpose. On Loaf Mass Day, it is customary to bring to a Christian church a loaf made from the new crop, which began to be harvested at Lammastide, which falls at the halfway point between the summer solstice and autumn September equinox. Christians also have church processions to bakeries, where those working therein are blessed by Christian clergy. Lammas has coincided with the feast of St. Peter in Chains, commemorating St. Peter's miraculous deliverance from prison, but in the liturgical reform of 1969 the feast of St. Alphonsus L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugh
Lugh or Lug (; ga, label= Modern Irish, Lú ) is a figure in Irish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, a group of supernatural beings, Lugh is portrayed as a warrior, a king, a master craftsman and a savior.Olmsted, Garrett. ''The Gods of the Celts and the Indo-Europeans''. University of Innsbruck, 1994. p.117 He is associated with skill and mastery in multiple disciplines, including the arts.Monaghan, Patricia. ''The Encyclopedia of Celtic Mythology and Folklore''. Infobase Publishing, 2004. pp.296-297 Lugh also has associations with oaths, truth and the law, and therefore with rightful kingship.Koch, John T. ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia''. ABC-CLIO, 2006. p.1200 Lugh is linked with the harvest festival of Lughnasadh, which bears his name. His most common epithets are ''Lámfada'' ("long hand" or "long arm", possibly for his skill with a spear or his ability as a ruler) and ''Samildánach'' ("equally skilled in many arts"). In mythology, Lugh is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beltane
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking the start of summer in Ireland, May being ''Mí na Bealtaine''. Historically, it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. In Irish the name for the festival day is (), in Scottish Gaelic (), and in Manx Gaelic /. Beltane is one of the principal four Gaelic seasonal festivals—along with Samhain, Imbolc, and Lughnasadh—and is similar to the Welsh . Bealtaine is mentioned in the earliest Irish literature and is associated with important events in Irish mythology. Also known as ("first of summer"), it marked the beginning of summer and was when cattle were driven out to the summer pastures. Rituals were performed to protect cattle, people and crops, and to encourage growth. Special bonfires were kindled, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Polytheism
Ancient Celtic religion, commonly known as Celtic paganism, was the religion of the ancient Celtic peoples of Europe. Because the ancient Celts did not have writing, evidence about their religion is gleaned from archaeology, Greco-Roman accounts (some of it hostile and probably not well-informed), and literature from the early Christian period. Green, Miranda (2012). "Chapter 25: The Gods and the supernatural", ''The Celtic World''. Routledge. pp.465–485 Celtic paganism was one of a larger group of Iron Age polytheistic religions of Europe. It varied by region and over time, but underlying this were "broad structural similarities" Cunliffe, Barry (1997). ''The Ancient Celts''. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. p. 184. and "a basic religious homogeneity" among the Celtic peoples. The names of over two hundred Celtic deities have survived (see list of Celtic deities), although it is likely that many of these were alternative names, regional names or titles for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Máire MacNeill
Máire MacNeill (7 December 1904 – 15 May 1987) was an Irish journalist, folklorist and translator. She is best known for her magisterial study of the Irish harvest festival, ''The Festival of Lughnasa'' (1962, 1983). Biography She was born at Portmarnock, County Dublin, the second daughter of historian and political figure Eoin MacNeill and Agnes Moore. After the family moved into the city she attended Muckross Park school. She received her BA in Celtic Studies from University College Dublin in 1925. From 1927 to 1932, she worked as a journalist and then as sub-editor on the Cumann na nGaedheal newspaper, ''The Star''. She also assisted her father with his memoirs.Maureen Murphy: Máire MacNeill. Béaloideas 72, 2004 (Irish Folklore Commission) In 1935, Séamus Ó Duilearga invited her to work for the newly founded Irish Folklore Commission as office manager. She trained in folklore methods at Uppsala University, Sweden, before starting research on the Lughnasadh fest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
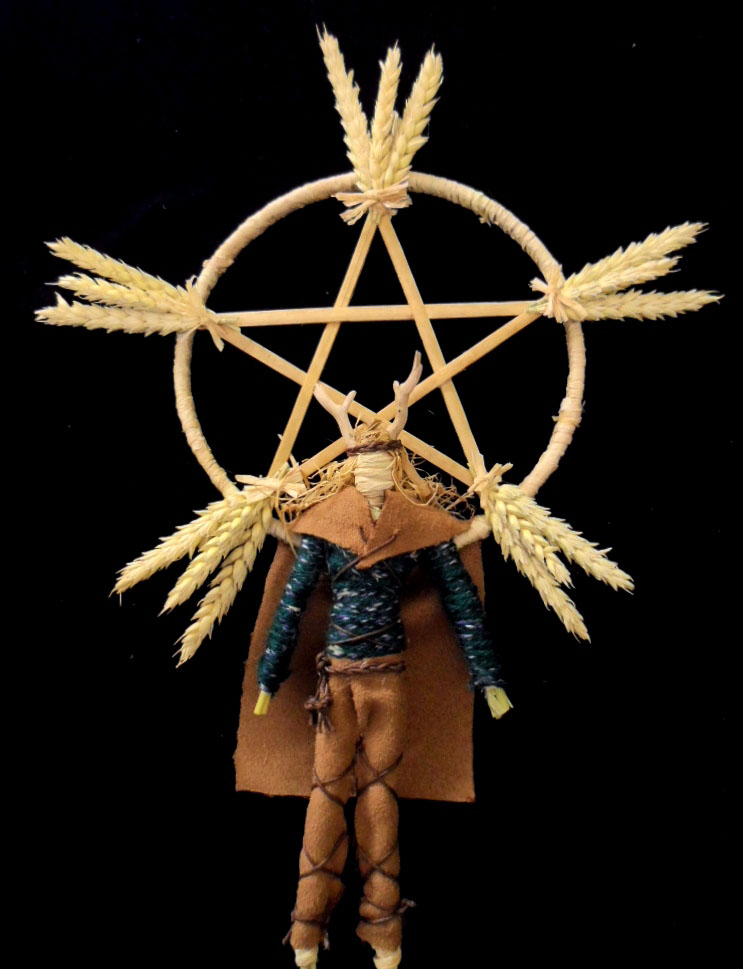
Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and was introduced to the public in 1954 by Gerald Gardner, a retired British civil servant. Wicca draws upon a diverse set of ancient pagan and 20th-century hermetic motifs for its theological structure and ritual practices. Wicca has no central authority figure. Its traditional core beliefs, principles, and practices were originally outlined in the 1940s and 1950s by Gardner and an early High Priestess, Doreen Valiente. The early practices were disseminated through published books and in secret written and oral teachings passed along to their initiates. There are many variations on the core structure, and the religion grows and evolves over time. It is divided into a number of diverse lineages, sects and denominations, referred to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imbolc
Imbolc or Imbolg (), also called Saint Brigid's Day ( ga, Lá Fhéile Bríde; gd, Là Fhèill Brìghde; gv, Laa'l Breeshey), is a Gaelic traditional festival. It marks the beginning of spring, and for Christians it is the feast day of Saint Brigid, Ireland's patroness saint. It is held on 1 February, which is about halfway between the winter solstice and the spring equinox.Danaher, Kevin (1972) ''The Year in Ireland: Irish Calendar Customs'' Dublin, Mercier. p. 38McNeill, F. Marian (1959, 1961) ''The Silver Bough'', Vol. 1–4. William MacLellan, Glasgow; Vol. 2, pp. 11–42 Historically, its traditions were widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. It is one of the four Gaelic seasonal festivals, along with: Bealtaine, Lughnasadh and Samhain. Imbolc is mentioned in early Irish literature, and there is evidence suggesting it was also an important date in ancient times. It is believed that Imbolc was originally a pagan festival associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crom Dubh
Crom Dubh (, ; meaning "black crooked ne; also ''Crum Dubh'', ''Dark Crom'') is a mythological and folkloric figure of Ireland, based on the god ''Crom Cruach'', mentioned in the 12th-century ''dinnseanchas'' of Magh Slécht. Folklore Conflict with Saint Patrick According to one legend, Cainnech of Aghaboe saw a number of demons flying past and when he inquired of their errand, one of them told him that Crom Dubh had died and they were after collecting his soul. Cainnech bid him on their return to tell him how they had fared. Some time later the demon returned limping badly. He told Cainnech that they were just about to seize Crom Dubh's soul when St Patrick appeared with a host of angels and saints and drove them off, Crom Dubh's good works having outweighed his sins. Another location associated with Crom Dubh is Downpatrick Head in County Mayo. According to Irish legend, St. Patrick came to the headland to confront Crom Dubh, who is variously identified as a pagan chie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year was into two parts, the summer half beginning at Bealtaine (May 1st) and the winter half at Samhain (November 1st) ... The festivals properly began at sunset on the day before the actual date, evincing the Celtic tendency to regard the night as preceding the day". marking the end of the harvest season and beginning of winter or " darker half" of the year. Celebrations begin on the evening of 31 October, since the Celtic day began and ended at sunset. This is about halfway between the autumnal equinox and winter solstice. It is one of the four Gaelic seasonal festivals along with Imbolc, Beltaine and Lughnasa. Historically it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland, Galicia and the Isle of Man (where it is spelled Sauin). A simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx and Scottish Gaelic. Gaelic language and culture originated in Ireland, extending to Dál Riata in western Scotland. In antiquity, the Gaels traded with the Roman Empire and also raided Roman Britain. In the Middle Ages, Gaelic culture became dominant throughout the rest of Scotland and the Isle of Man. There was also some Gaelic settlement in Wales, as well as cultural influence through Celtic Christianity. In the Viking Age, small numbers of Vikings raided and settled in Gaelic lands, becoming the Norse-Gaels. In the 9th century, Dál Riata and Pictland merged to form the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba. Meanwhile, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King often claiming lordship over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailteann Games (ancient)
The Tailteann Games, Tailtin Fair, Áenach Tailteann, Aonach Tailteann, Assembly of Talti, Fair of Taltiu or Festival of Taltii were funeral games associated with the semi-legendary history of Pre-Christian Ireland. There is a complex of ancient earthworks dating to the Iron Age in the area of Teltown where the festival was historically known to be celebrated off and on from medieval times into the modern era. History and archaeology The games were founded, according to the '' Book of Invasions'', by Lugh Lámhfhada, the Ollamh Érenn (master craftsman or doctor of the sciences), as a mourning ceremony for the death of his foster-mother Tailtiu. Lugh buried Tailtiu underneath a mound in an area that took her name and was later called Tailteann in County Meath. The event was held during the last fortnight of July and culminated with the celebration of Lughnasadh, or Lammas Eve (1 August). Modern folklore claims that the Tailteann Games started around 1600 BC, with some sources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
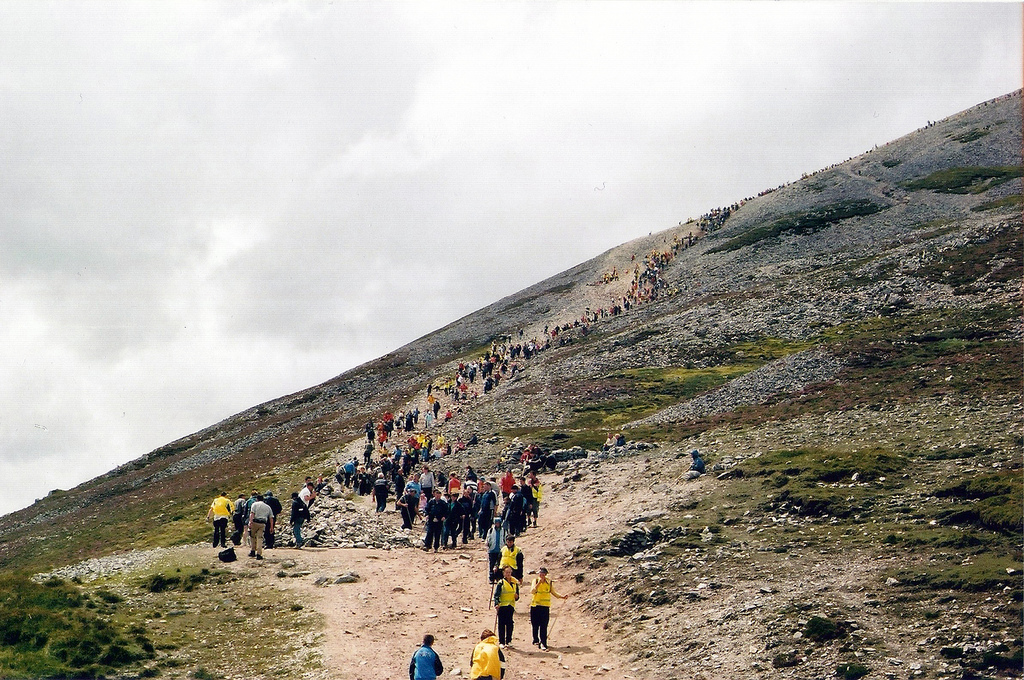
Reek Sunday
Reek Sunday ( ga, Domhnach na Cruaiche) or Garland Sunday is an annual day of pilgrimage in Ireland. On the last Sunday in July, thousands of pilgrims climb Ireland's holiest mountain, Croagh Patrick (764 metres) in County Mayo. It is held in honour of Saint Patrick who is said to have spent forty days fasting on the mountain in the 5th century. Masses are held at the summit, where there is a small chapel. Some climb the mountain barefoot, as an act of penance, and some carry out ' rounding rituals', which were formerly a key part of the pilgrimage. This involves praying while walking sunwise around features on the mountain: seven times around the cairn of Leacht Benáin ( Benan's grave), fifteen times around the circular perimeter of the summit, seven times around Leaba Phádraig (Patrick's bed), and then seven times around three ancient burial cairns known as Reilig Mhuire (Mary's cemetery). Until 1970, it was traditional for pilgrims to climb the mountain after sunset.Corlett, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |