|
Kapalika
The Kāpālika tradition was a Tantric, non-Puranic form of Shaivism which originated in Medieval India between the 7th and 8th century CE. The word is derived from the Sanskrit term '' kapāla'', meaning "skull", and ''kāpālika'' means the "skull-men". History The Kāpālikas were an extinct sect of Shaivite ascetics devoted to the Hindu god Shiva dating back to the 8th century CE, which traditionally carried a skull-topped trident (''khaṭvāṅga'') and an empty human skull as a begging bowl. Other attributes associated with Kāpālikas were that they revered the fierce Bhairava form of Shiva by emulating his behavior and characteristics, smeared their body with ashes from the cremation grounds, wore their hair long and matted, and engaged in transgressive rituals such as sexual intercourse with lower-class women, human sacrifices, consumption of meat and alcoholic beverages, and offerings involving orgiastic sexuality and sexual fluids. According to David Lore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantra
Tantra (; sa, तन्त्र, lit=loom, weave, warp) are the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards. The term ''tantra'', in the Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. Starting in the early centuries of the common era, newly revealed Tantras centering on Vishnu, Shiva or Shakti emerged. There are tantric lineages in all main forms of modern Hinduism, such as the Shaiva Siddhanta tradition, the Shakta sect of Sri-Vidya, the Kaula, and Kashmir Shaivism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matted Hair
Dreadlocks, also known as locs or dreads, are rope-like strands of hair formed by locking or braiding hair. Origins Some of the earliest depictions of dreadlocks date back as far as 1600–1500 BCE in the Minoan Civilization, one of Europe's earliest civilizations, centred in Crete (now part of Greece). Frescoes discovered on the Aegean island of Thera (modern Santorini, Greece) depict individuals with long braided hair or long dreadlocks. In ancient Egypt, examples of Egyptians wearing locked hairstyles and wigs have appeared on bas-reliefs, statuary and other artifacts. Mummified remains of Egyptians with locked wigs have also been recovered from archaeological sites. During the Bronze and Iron Ages, many peoples in the Near East, Anatolia, Caucasus, East Mediterranean and North Africa such as the Sumerians, Elamites and Ancient Egyptians were depicted in art with braided or plaited hair and beards. However, braids are not dreadlocks, and it is not always possible to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions ranging from devotional dualistic theism such as Shaiva Siddhanta to yoga-orientated monistic non-theism such as Kashmiri Shaivism.Ganesh Tagare (2002), The Pratyabhijñā Philosophy, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 16–19 It considers both the Vedas and the Agama texts as important sources of theology.Mariasusai Dhavamony (1999), Hindu Spirituality, Gregorian University and Biblical Press, , pages 31–34 with footnotesMark Dyczkowski (1989), The Canon of the Śaivāgama, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 43–44 Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Vedic religions and traditions derived from the southern Tamil Shaiva Siddhanta traditions and philosophies, which were assimilated in the non-Vedic Shiva-tradition. In the process of Sanskritisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
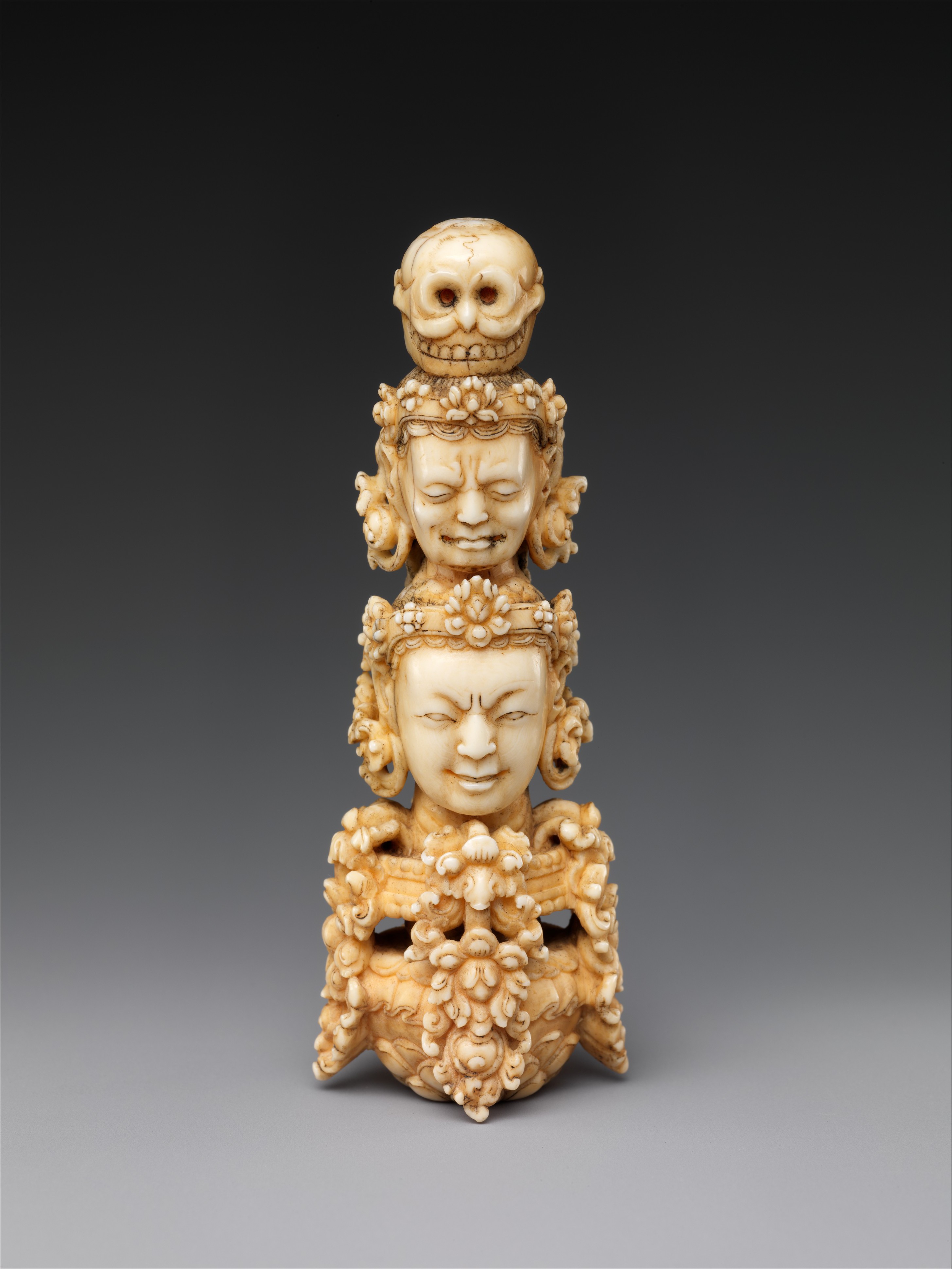
Kapala
A kapala (Sanskrit for "skull") is a skull cup used as a ritual implement (bowl) in both Hindu Tantra and Buddhist Tantra (Vajrayana). Especially in Tibet, they are often carved or elaborately mounted with precious metals and jewels. Etymology 'Kapala' () is a loan word into Tibetan from Sanskrit ''kapāla'' (Devanagari: कपाल) referring to the skull or forehead, usually of a human. By association, it refers to the ritual skullcup fashioned out of a human cranium. The Sanskrit word, in turn, was derived from Proto Indo-Aryan *kapā́las, and descended from Proto-Indo-European *káp-ōl- (cup, bowl), from *kap- (to seize, to hold). In Hinduism Kapalas are used mainly for esoteric purposes such as rituals. Among the rituals using kapalas are higher tantric meditation to achieve a transcendental state of mind within the shortest possible time; libation to gods and deities to win their favor. Hindu deities Hindu deities that may be depicted with the kapala include Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaṭvāṅga
A khaṭvāṅga ( sa, खट्वाङ्ग) is a long, studded club originally created as a weapon. It was adopted as a traditional religious symbol in Indian religions such as Tantric traditions like Shaivism and Vajrayana Buddhism. The khatvāṅga was adopted by some lineages of historical tantra though it preceded such traditions as of an original tribal shaman shaft. Hinduism In Hinduism, Shiva-Rudra carried the khatvāṅga as a staff weapon and are thus referred to as ''khatvāṅgī''s. Author Robert Beer says, "In Hinduism the khatvanga is an emblem or weapon of Shiva, and is variously described as a skull - topped club, a skull - mounted trident, or a trident - staff on which three skulls are impaled". Author A. V. Narasimha Murthy says, "In classical literature the weapon Khatvanga is mentioned in works like Mālatīmādhava of Bhavabhuti and Śiva Stutī of Narayana Panditacharya". Fabrication Originally, the khatvāṅga was made of bones, especially, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
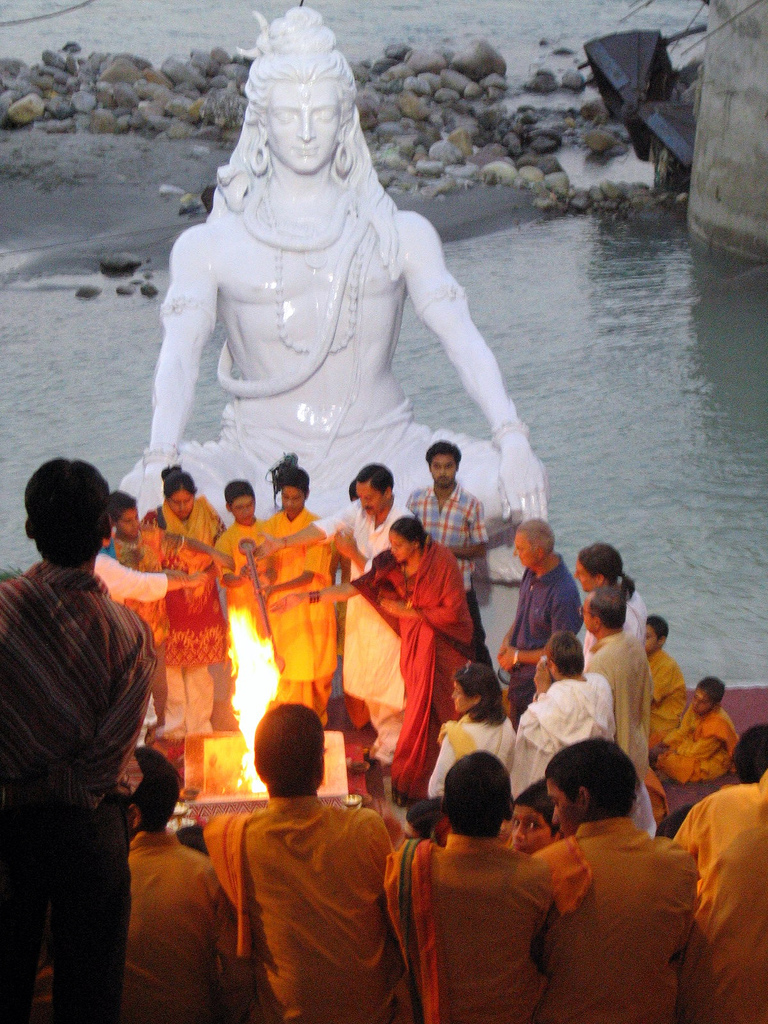
Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hinduism. Shiva is known as "The Destroyer" within the Trimurti, the Hindu trinity which also includes Brahma and Vishnu. In the Shaivite tradition, Shiva is the Supreme Lord who creates, protects and transforms the universe. In the goddess-oriented Shakta tradition, the Supreme Goddess (Devi) is regarded as the energy and creative power (Shakti) and the equal complementary partner of Shiva. Shiva is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. Shiva has many aspects, benevolent as well as fearsome. In benevolent aspects, he is depicted as an omniscient Yogi who lives an ascetic life on Mount Kailash as well as a householder with his wife Parvati and his three children, Ganesha, Kartikeya and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaula (Hinduism)
In the Hindu religious traditions of Shaktism and Shaivism, Kaula, also known as Kula, ("the Kula path") and ("the Kaula tradition"), is a Tantric tradition which is characterised by distinctive rituals and symbolism connected with the worship of Shakti and Shiva. It flourished in ancient India primarily in the 1st millennium CE. Kaula preserves some of the distinctive features of the '' Kāpālika'' tradition, from which it is derived. It is subdivided into four subcategories of texts based on the goddesses Kuleśvarī, Kubjikā, Kālī, and Tripurasundarī respectively. The Trika texts are closely related to the Kuleśvarī texts and can be considered as part of the Kulamārga. In later Hatha Yoga, the Kaula visualization of kundalini rising through a system of chakras is overlaid onto the earlier bindu-oriented system. ''Kaula'' and ''kula'' The translation of the term ''kula'' in English is considered difficult and has raised some problems for researchers. The basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremation Ground
Shmashana outside Indian village A ''śmaśāna'' (Devanagari: श्मशान) is a Hindu crematory ground, where dead bodies are brought to be burnt on a pyre. It is usually located near a river or body of water on the outskirts of a village or town; as they are usually located near river ghats they are also called ''smashan ghat''. The word has its origin from Sanskrit language: ''shma'' refers to ''shava'' ("corpse"), while ''shana'' refers to ''shanya'' ("bed"). The other Indian religions like Sikhism, Jainism and Buddhism also use ''śmaśāna'' for the last rites of the dead. Hinduism As per Hindu rites of Nepal and India, the dead body is brought to śmaśāna for ''Antim Sanskar'' (last rites). At the cremation ground, the chief mourner has to obtain the sacred fire from the Dom caste, who reside by the śmaśāna and light funeral pyres (''chita'') for a fee. Various Hindu scriptures also give details of how to select the site of śmaśāna: it should be on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of his journey to India in 629–645 CE, his efforts to bring over 657 Indian texts to China, and his translations of some of these texts.Li Rongxi (1996), ''The Great Tang Dynasty Record of the Western Regions'', Bukkyo Dendo Kyokai and Numata Center for Buddhist Translation and Research, Berkeley, , pp. xiii-xiv Xuanzang was born on 6 April 602 in Chenliu, what is now Kaifeng municipality in Henan province. As a boy, he took to reading religious books, and studying the ideas therein with his father. Like his elder brother, he became a student of Buddhist studies at Jingtu monastery. Xuanzang was ordained as a ''śrāmaṇera'' (novice monk) at the age of thirteen. Due to the political and social unrest caused by the fall of the Sui dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
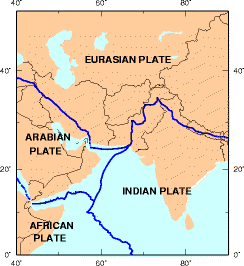
Geography Of Pakistan
The Geography of Pakistan ( ur, ) is a profound blend of landscapes varying from plains to deserts, forests, and plateaus ranging from the coastal areas of the Arabian Sea in the south to the mountains of the Karakoram, Hindukush, Himalayas ranges in the north. Pakistan geologically overlaps both with the Indian and the Eurasian tectonic plates where its Sindh and Punjab provinces lie on the north-western corner of the Indian plate while Balochistan and most of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa lie within the Eurasian plate which mainly comprises the Iranian Plateau. Pakistan is bordered by India to the east, Afghanistan to the northwest and Iran to the west while China borders the country in the northeast. The nation is geopolitically situated within some of the most controversial regional boundaries which share disputes and have many-a-times escalated military tensions between the nations, e.g., that of Kashmir with India and the Durand Line with Afghanistan. Its western borders inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chickens, sheep, rabbits, pigs, and cattle. This eventually led to their use in meat production on an industrial scale in slaughterhouses. Meat is mainly composed of water, protein, and fat. It is edible raw but is normally eaten after it has been cooked and seasoned or processed in a variety of ways. Unprocessed meat will spoil or rot within hours or days as a result of infection with, and decomposition by, bacteria and fungi. Meat is important to the food industry, economies, and cultures around the world. There are nonetheless people who choose to not eat meat (vegetarians) or any animal products (vegans), for reasons such as taste preferences, ethics, environmental concerns, health concerns or religious dietary rules. Terminology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification of religions: Geographical", ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2007. Retrieved 15 July 2010 are also classified as Eastern religions. Although Indian religions are connected through the history of India, they constitute a wide range of religious communities, and are not confined to the Indian subcontinent. Evidence attesting to prehistoric religion in the Indian subcontinent derives from scattered Mesolithic rock paintings. The Harappan people of the Indus Valley civilisation, which lasted from 3300 to 1300 BCE (mature period 2600–1900 BCE), had an early urbanized culture which predates the Vedic religion. The documented history of Indian religions begins with the historical Vedic religion, the religious practices of the early Indo-Iran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |