|
Electrosurgery
Electrosurgery is the application of a high-frequency (radio frequency) alternating polarity, electrical current to biological tissue as a means to cut, coagulate, desiccate, or fulgurate tissue.Hainer BL, "Fundamentals of electrosurgery", ''Journal of the American Board of Family Practice'', 4(6):419–26, 1991 Nov.–Dec. 400 V peak-to-peak) the vapor sheath is ionized, forming conductive plasma. Electric current continues to flow from the metal electrode through the ionized gas into the tissue. Rapid overheating of tissue results in its vaporization, fragmentation and ejection of fragments, allowing for tissue cutting. In applications of a continuous wave the heat diffusion typically leads to formation of a significant thermal damage zone at the edges of the lesion. Open circuit voltage in electrosurgical waveforms is typically in the range of 300–10,000 V peak-to-peak. Higher precision can be achieved with pulsed waveforms. Using bursts of several tens of microseconds i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyfrecator
A hyfrecator is a low-powered medical apparatus used in electrosurgery on conscious patients, usually in an office setting. It is used to destroy tissue directly, and to stop bleeding during minor surgery. It works by emitting low-power high-frequency high-voltage AC electrical pulses, via an electrode mounted on a handpiece, directly to the affected area of the body. A continuous electrical spark discharge may be drawn between probe and tissue, especially at the highest settings of power, although this is not necessary for the device to function. The amount of output power is adjustable, and the device is equipped with different tips, electrodes and forceps, depending on the electrosurgical requirement. Unlike other types of electrosurgery, the hyfrecator does not employ a dispersive electrode pad that is attached to the patient in an area not being treated, and that leads back to the apparatus (sometimes loosely but not quite correctly called a "ground pad"). It is designed to w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
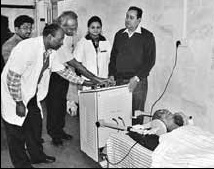
Diathermy
Diathermy is electrically induced heat or the use of high-frequency electromagnetic currents as a form of physical therapy and in surgical procedures. The earliest observations on the reactions of high-frequency electromagnetic currents upon the human organism were made by Jacques Arsene d'Arsonval. The field was pioneered in 1907 by German physician Karl Franz Nagelschmidt, who coined the term ''diathermy'' from the Greek words ''dia'' and θέρμη ''therma'', literally meaning "heating through" (adj., diather´mal, diather´mic). Diathermy is commonly used for muscle relaxation, and to induce deep heating in tissue for therapeutic purposes in medicine. It is used in physical therapy to deliver moderate heat directly to pathologic lesions in the deeper tissues of the body. Diathermy is produced by three techniques: ultrasound (''ultrasonic diathermy''), short-wave radio frequencies in the range 1–100 MHz (''shortwave diathermy'') or microwaves typically in the 915&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diathermy
Diathermy is electrically induced heat or the use of high-frequency electromagnetic currents as a form of physical therapy and in surgical procedures. The earliest observations on the reactions of high-frequency electromagnetic currents upon the human organism were made by Jacques Arsene d'Arsonval. The field was pioneered in 1907 by German physician Karl Franz Nagelschmidt, who coined the term ''diathermy'' from the Greek words ''dia'' and θέρμη ''therma'', literally meaning "heating through" (adj., diather´mal, diather´mic). Diathermy is commonly used for muscle relaxation, and to induce deep heating in tissue for therapeutic purposes in medicine. It is used in physical therapy to deliver moderate heat directly to pathologic lesions in the deeper tissues of the body. Diathermy is produced by three techniques: ultrasound (''ultrasonic diathermy''), short-wave radio frequencies in the range 1–100 MHz (''shortwave diathermy'') or microwaves typically in the 915&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocautery
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable. The practice was once widespread for treatment of wounds. Its utility before the advent of antibiotics was said to be effective at more than one level: *To prevent exsanguination *To close amputations Cautery was historically believed to prevent infection, but current research shows that cautery actually increases the risk for infection by causing more tissue damage and providing a more hospitable environment for bacterial growth. Actual cautery refers to the metal device, generally heated to a dull red glow, that a physician applies to produce blisters, to stop bleeding of a blood vessel, and for other similar purposes., page 16. The main f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies and the lower limit of infrared frequencies; these are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conductors can radiate into space as electromagnetic waves ( radio waves). This is the basis of radio technology. * RF current does not penetrate deeply into ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoma
A lipoma is a benign tumor made of fat tissue. They are generally soft to the touch, movable, and painless. They usually occur just under the skin, but occasionally may be deeper. Most are less than in size. Common locations include upper back, shoulders, and abdomen. It is possible to have a number of lipomas. The cause is generally unclear. Risk factors include family history, obesity, and lack of exercise. Diagnosis is typically based on a physical exam. Occasionally medical imaging or tissue biopsy is used to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment is typically by observation or surgical removal. Rarely, the condition may recur following removal, but this can generally be managed with repeat surgery. They are not generally associated with a future risk of cancer. Lipomas have a prevalence of roughly 2 out of every 100 people. Lipomas typically occur in adults between 40 and 60 years of age. Males are more often affected than females. They are the most common noncancerous so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauterization
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable. The practice was once widespread for treatment of wounds. Its utility before the advent of antibiotics was said to be effective at more than one level: *To prevent exsanguination *To close amputations Cautery was historically believed to prevent infection, but current research shows that cautery actually increases the risk for infection by causing more tissue damage and providing a more hospitable environment for bacterial growth. Actual cautery refers to the metal device, generally heated to a dull red glow, that a physician applies to produce blisters, to stop bleeding of a blood vessel, and for other similar purposes., page 16. The main f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroporation
Electroporation, or electropermeabilization, is a microbiology technique in which an electrical field is applied to cells in order to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, allowing chemicals, drugs, electrode arrays or DNA to be introduced into the cell (also called electrotransfer). In microbiology, the process of electroporation is often used to transform bacteria, yeast, or plant protoplasts by introducing new coding DNA. If bacteria and plasmids are mixed together, the plasmids can be transferred into the bacteria after electroporation, though depending on what is being transferred, cell-penetrating peptides or CellSqueeze could also be used. Electroporation works by passing thousands of volts (~8 kV/cm) across suspended cells in an electroporation cuvette. Afterwards, the cells have to be handled carefully until they have had a chance to divide, producing new cells that contain reproduced plasmids. This process is approximately ten times more effective in increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its graph as a function of time, independent of its time and magnitude scales and of any displacement in time.David Crecraft, David Gorham, ''Electronics'', 2nd ed., , CRC Press, 2002, p. 62 In electronics, the term is usually applied to periodically varying voltages, currents, or electromagnetic fields. In acoustics, it is usually applied to steady periodic sounds—variations of pressure in air or other media. In these cases, the waveform is an attribute that is independent of the frequency, amplitude, or phase shift of the signal. The term can also be used for non-periodic signals, like chirps and pulses. The waveform of an electrical signal can be visualized in an oscilloscope or any other device that can capture and plot its value at various times, with a suitable scales in the time and value axes. The electrocardiograph is a medical device to record the waveform of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sine Wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mathematics, as well as in physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Formulation Its most basic form as a function of time (''t'') is: y(t) = A\sin(2 \pi f t + \varphi) = A\sin(\omega t + \varphi) where: * ''A'', ''amplitude'', the peak deviation of the function from zero. * ''f'', '' ordinary frequency'', the ''number'' of oscillations (cycles) that occur each second of time. * ''ω'' = 2''f'', ''angular frequency'', the rate of change of the function argument in units of radians per second. * \varphi, '' phase'', specifies (in radians) where in its cycle the oscillation is at ''t'' = 0. When \varphi is non-zero, the entire waveform appears to be shifted in time by the amount ''φ''/''ω'' seconds. A negative value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge and relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. An archaic term is voltaic arc, as used in the phrase "voltaic arc lamp". Techniques for arc suppression can be used to reduce the duration or likelihood of arc formation. In the late 19th century, electric arc lighting was in wide use for public lighting. Some low-pressure electric arcs are used in many applications. For example, fluorescent tubes, mercury, sodium, and metal-halide lamps are used for lighting; xenon arc lamps have been used for movie projectors. Electric arcs can be utilized for manufacturing processes, such as electric arc welding, and electric arc furnace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. Industry Desiccation is widely employed in the oil and gas industry. These materials are obtained in a hydrated state, but the water content leads to corrosion or is incompatible with downstream processing. Removal of water is achieved by cryogenic condensation, absorption into glycols, and absorption onto desiccants such as silica gel. Laboratory A desiccator is a heavy glass or plastic container, now somewhat antiquated, used in practical chemistry for drying or keeping small amounts of materials very dry. The material is placed on a shelf, and a drying agent or ''desiccant'', such as dry silica gel or anhydrous sodium hydroxide, is placed below the shelf. Often some sort of humidity indicator is included in the desiccator to sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |