|
Drainage System (geomorphology)
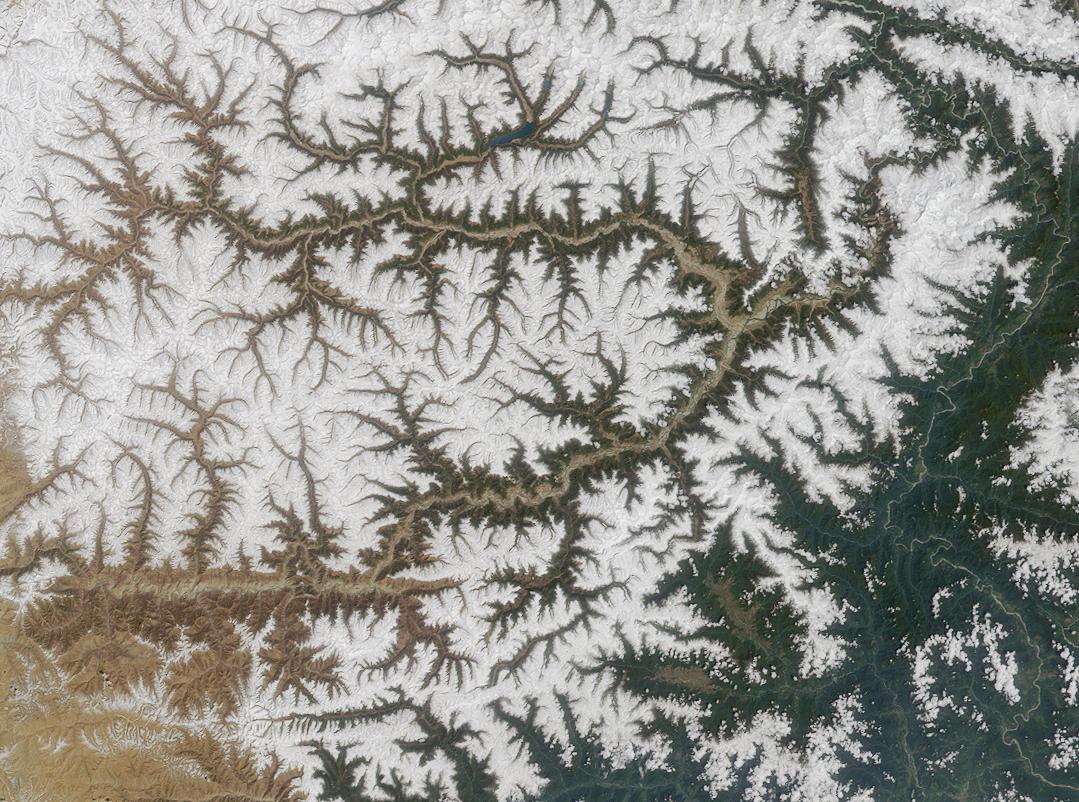
In geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as part of drainage basins (and sub-basins). This is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map, the more information is available. Drainage patterns Per the lie of channels, drainage systems can fall into one of several categories, known as drainage patterns. These depend on the topography and geology of the land. All forms of transitions can occur between parallel, dendritic, and trellis patterns. Accordant versus discordant drainage patterns A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarlung Tsangpo River Tibet , a river in Tibet and upper course of the Brahmaputra
{{Disambig ...
Yarlung can refer to: *Yarlung Kingdom, see also: Tibetan empire * Yarlung Dynasty, see also: List of emperors of Tibet *Yarlung Valley, formed by the Yarlung River and refers especially to the district where it joins with the Chongye River, and broadens out into a large plain about 2 km wide, before they flow north into the Yarlung Tsangpo River or Brahmaputra *Yarlung River, also called Yarlung Tsangpo River The Yarlung Tsangpo, also called Yarlung Zangbo () is the upper stream of the Brahmaputra River located in the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It is the longest river of Tibet and the fifth longest in China. The upper section is also called Dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antecedent Drainage Stream
An antecedent stream is a stream that maintains its original course and pattern despite the changes in underlying rock topography. A stream with a dendritic drainage pattern, for example, can be subject to slow tectonic uplift. However, as the uplift occurs, the stream erodes through the rising ridge to form a steep-walled gorge. The stream thus keeps its dendritic pattern even though it flows over a landscape that will normally produce a trellis drainage pattern.Grotzinger, J. & Jordan, T.H. 2006. Understanding Earth, 5th ed., Freeman, New York A superimposed stream is a stream that forms over horizontal beds that overlie folded and faulted rock with varying resistance. Having cut down through the horizontal beds, the stream retains its course and pattern as it proceeds to erode the underlying rocks despite their different character. The stream erodes a gorge in the resistant bed and continues its flow as before. Examples * Many Himalayan rivers are good examples of anteced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of , it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies. Name The original name for the island in the Arawaks' language was which meant "Land of the Hummingbird". Christopher Columbus renamed it ('The Island of the Trinity'), fulfilling a vow he had made before setting out on his third voyage. This has since been shortened to ''Trinidad''. History Caribs and Arawaks lived in Trinidad long before Christopher Columbus encountered the islands on his third voyage on 31 July 1498. The island remained Spanish until 1797, but it was largely settled by French colonists from the French Caribbean, especially Martinique.Besson, Gerard (2000-08-27). "Land of Beginnings – A historical digest", ''Newsda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west. Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the ''Appalachian Highlands'' physiographic division as consisting of 13 provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, St. Lawrence Valle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trellis (architecture)
A trellis (treillage) is an architectural structure, usually made from an open framework or lattice of interwoven or intersecting pieces of wood, bamboo or metal that is normally made to support and display climbing plants, especially shrubs.The Book of Garden Furniture C. Thonger, 1903 Types There are many types of trellis for different places and for different plants, from agricultural types, especially in , which are covered at , to garden uses for climbers such as |
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: �mjænmɑː, ˈbɜːmə So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as ɑːror of Burma as ɜːrməby some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. The final ''r'' in ''Myanmar'' was not intended for pronunciation and is there to ensure that the final a is pronounced with the broad ''ah'' () in "father". If the Burmese name my, မြန်မာ, label=none were spelled "Myanma" in English, this would be pronounced at the end by al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdare Mountains
The Aberdare Range (formerly the Sattima Range, Kikuyu: ''Nyandarua'') is a 160 km (100 mile) long mountain range of upland, north of Kenya's capital Nairobi with an average elevation of . It straddles across the counties of Nyandarua, Nyeri, Muranga, Kiambu and Laikipia. The mountain range is located in west central Kenya, northeast of Naivasha and Gilgil and lies just south of the Equator. The mountain range is called Nyandarua among the Agikuyu people in whose territory this forest and mountain range is located. The name Nyandarua comes from the Kikuyu word rwandarua meaning a drying hide, due to the distinctive fold of its silhouette. Topology The Aberdare Range forms a section of the eastern rim of the Great Rift Valley running roughly north to south. On the west, the range falls off steeply into the Kinangop Plateau and then into the Great Rift Valley. On the east, the range slopes more gently. Lake Naivasha and the distant Mau Escarpment can be seen from peaks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escarpment''. Some sources differentiate the two terms, with ''escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Drainage Pattern
Parallel is a geometric term of location which may refer to: Computing * Parallel algorithm * Parallel computing * Parallel metaheuristic * Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel * Parallel Sysplex, a cluster of IBM mainframes * Parallel communication * Parallel port * Parallel ATA * Parallel Computers, Inc., an American computer manufacturer of the 1980s Mathematics and science * Parallel circuits, as opposed to series * Parallel (geometry) *Parallel (operator), mathematical function used in electrical engineering * Parallel postulate * Parallel evolution * Parallel transport *Parallel manipulator Navigation * Parallel (latitude), an imaginary east–west line circling a globe * Parallel of declination, used in astronomy Music and entertainment * ''Parallel'' (manga) * ''Parallel'' (2018 film), a Canadian science fiction thriller film * Parallel (2023 film) an upcoming American science fiction thriller film * Parallel key, the minor (or majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-shaped Valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms that may be global in use or else applied only locally. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |