phyllosphere on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Rain and wind also cause temporal variation to the phyllosphere microbiome. The phyllosphere includes the total aerial (above-ground) surface of a plant, and as such includes the surface of the stem, flowers and fruit, but most particularly the leaf surfaces. Compared with the rhizosphere and the Divergent definitions of “core microbiome” have arisen across scientific literature with researchers variably identifying “core taxa” as those persistent across distinct host microhabitats and even different species. Given the functional divergence of microorganisms across different host species and microhabitats, defining core taxa ''sensu stricto'' as those persistent across broad geographic distances within tissue- and species-specific host microbiomes, represents the most biologically and ecologically appropriate application of this conceptual framework. Tissue- and species-specific core microbiomes across host populations separated by broad geographical distances have not been widely reported for the phyllosphere using the stringent definition established by Ruinen.
Divergent definitions of “core microbiome” have arisen across scientific literature with researchers variably identifying “core taxa” as those persistent across distinct host microhabitats and even different species. Given the functional divergence of microorganisms across different host species and microhabitats, defining core taxa ''sensu stricto'' as those persistent across broad geographic distances within tissue- and species-specific host microbiomes, represents the most biologically and ecologically appropriate application of this conceptual framework. Tissue- and species-specific core microbiomes across host populations separated by broad geographical distances have not been widely reported for the phyllosphere using the stringent definition established by Ruinen.
 Microorganisms have been studied in the mānuka rhizosphere and endosphere. Earlier studies primarily focussed on fungi, and a 2016 study provided the first investigation of endophytic bacterial communities from three geographically and environmentally distinct mānuka populations using fingerprinting techniques and revealed tissue-specific core endomicrobiomes. A 2020 study identified a habitat-specific and relatively abundant core microbiome in the mānuka phyllosphere, which was persistent across all samples. In contrast, non-core phyllosphere microorganisms exhibited significant variation across individual host trees and populations that was strongly driven by environmental and spatial factors. The results demonstrated the existence of a dominant and ubiquitous core microbiome in the phyllosphere of mānuka.
Microorganisms have been studied in the mānuka rhizosphere and endosphere. Earlier studies primarily focussed on fungi, and a 2016 study provided the first investigation of endophytic bacterial communities from three geographically and environmentally distinct mānuka populations using fingerprinting techniques and revealed tissue-specific core endomicrobiomes. A 2020 study identified a habitat-specific and relatively abundant core microbiome in the mānuka phyllosphere, which was persistent across all samples. In contrast, non-core phyllosphere microorganisms exhibited significant variation across individual host trees and populations that was strongly driven by environmental and spatial factors. The results demonstrated the existence of a dominant and ubiquitous core microbiome in the phyllosphere of mānuka.
 In
In microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, ...
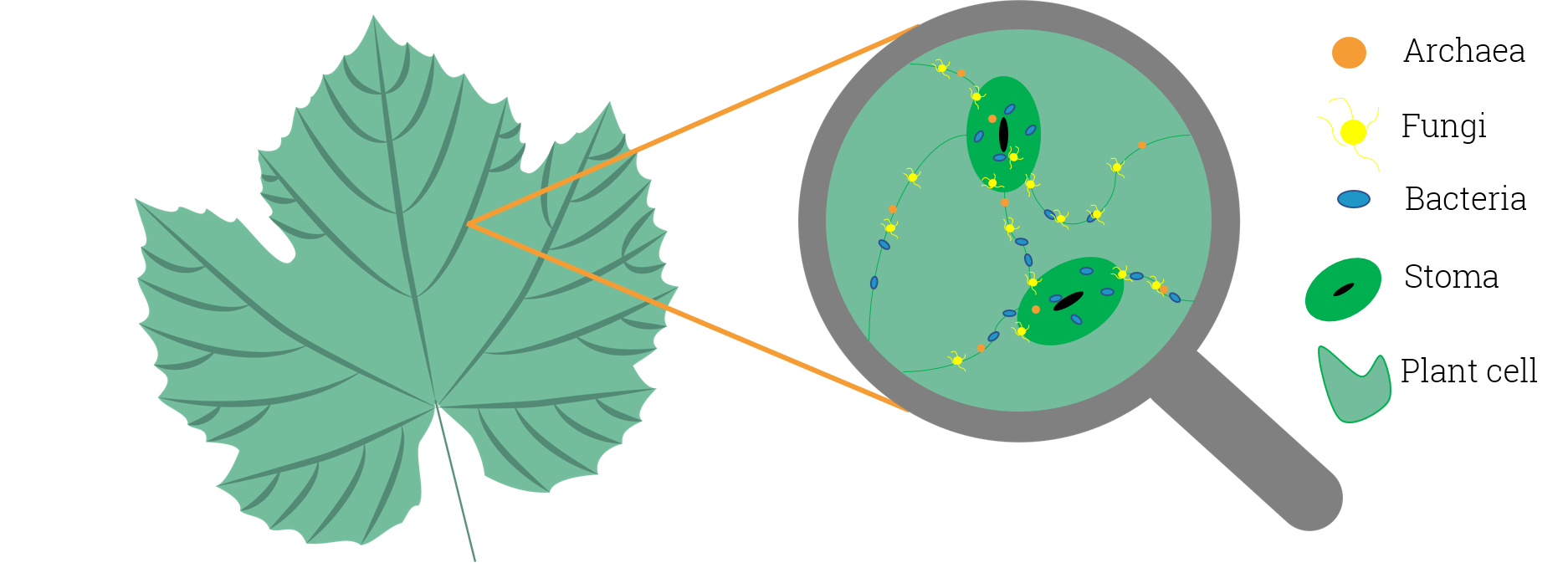
, the phyllosphere is the total above-ground surface of a plant when viewed as a habitat for microorganisms
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
. The phyllosphere can be further subdivided into the caulosphere (stems), phylloplane (leaves), anthosphere (flowers), and carposphere (fruits). The below-ground microbial habitats (i.e. the thin-volume of soil surrounding root or subterranean stem surfaces) are referred to as the rhizosphere and laimosphere
The laimosphere is the microbiologically enriched zone of soil that surrounds below-ground portions of plant stems; the laimosphere is analogous to the rhizosphere and spermosphere. The combining form laim- from (Greek: λαιμός, "throat") d ...
.
Most plants host diverse communities of microorganisms including bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
, archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaeba ...
, and protists
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
. Some are beneficial to the plant, others function as plant pathogen
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomy ...
s and may damage the host plant or even kill it.
The phyllosphere microbiome
The leaf surface, or phyllosphere, harbours amicrobiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
comprising diverse communities of bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaeba ...
, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
and virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es. Microbial colonizers are subjected to diurnal and seasonal fluctuations of heat, moisture, and radiation. In addition, these environmental elements affect plant physiology (such as photosynthesis, respiration, water uptake etc.) and indirectly influence microbiome composition.Dastogeer, K.M., Tumpa, F.H., Sultana, A., Akter, M.A. and Chakraborty, A. (2020) "Plant microbiome–an account of the factors that shape community composition and diversity". ''Current Plant Biology'': 100161. . Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Rain and wind also cause temporal variation to the phyllosphere microbiome. The phyllosphere includes the total aerial (above-ground) surface of a plant, and as such includes the surface of the stem, flowers and fruit, but most particularly the leaf surfaces. Compared with the rhizosphere and the
endosphere
Some microorganisms, such as endophytes, penetrate and occupy the plant internal tissues, forming the endospheric microbiome. The arbuscular mycorrhizal and other endophytic fungi are the dominant colonizers of the endosphere. Bacteria, and to so ...
the phyllosphere is nutrient poor and its environment more dynamic.
Interactions between plants and their associated microorganisms in many of these microbiomes can play pivotal roles in host plant health, function, and evolution. Interactions between the host plant and phyllosphere bacteria have the potential to drive various aspects of host plant physiology. However, as of 2020 knowledge of these bacterial associations in the phyllosphere remains relatively modest, and there is a need to advance fundamental knowledge of phyllosphere microbiome dynamics.
The assembly of the phyllosphere microbiome, which can be strictly defined as epiphytic bacterial communities on the leaf surface, can be shaped by the microbial communities Microbial population biology is the application of the principles of population biology to microorganisms.
Distinguishing from other biological disciplines
Microbial population biology, in practice, is the application of population ecology and popu ...
present in the surrounding environment (i.e., stochastic
Stochastic (, ) refers to the property of being well described by a random probability distribution. Although stochasticity and randomness are distinct in that the former refers to a modeling approach and the latter refers to phenomena themselv ...
colonisation) and the host plant (i.e., biotic selection). However, although the leaf surface is generally considered a discrete microbial habitat, there is no consensus on the dominant driver of community assembly across phyllosphere microbiomes. For example, host-specific bacterial communities have been reported in the phyllosphere of co-occurring plant species, suggesting a dominant role of host selection.
Conversely, microbiomes of the surrounding environment have also been reported to be the primary determinant of phyllosphere community composition. As a result, the processes that drive phyllosphere community assembly are not well understood but unlikely to be universal across plant species. However, the existing evidence does indicate that phyllosphere microbiomes exhibiting host-specific associations are more likely to interact with the host than those primarily recruited from the surrounding environment.
Overall, there remains high species richness in phyllosphere communities. Fungal communities are highly variable in the phyllosphere of temperate regions and are more diverse than in tropical regions. There can be up to 107 microbes per square centimetre present on the leaf surfaces of plants, and the bacterial population of the phyllosphere on a global scale is estimated to be 1026 cells. The population size of the fungal phyllosphere is likely to be smaller.
Phyllosphere microbes from different plants appear to be somewhat similar at high levels of taxa, but at the lower levels taxa there remain significant differences. This indicates microorganisms may need finely tuned metabolic adjustment to survive in phyllosphere environment. Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. Th ...
seems to be the dominant colonizers, with Bacteroidota
The phylum Bacteroidota (synonym Bacteroidetes) is composed of three large classes of Gram-negative, nonsporeforming, anaerobic or aerobic, and rod-shaped bacteria that are widely distributed in the environment, including in soil, sediments, and ...
and Actinomycetota also predominant in phyllospheres. Although there are similarities between the rhizosphere and soil microbial communities, very little similarity has been found between phyllosphere communities and microorganisms floating in open air (aeroplankton
Aeroplankton (or aerial plankton) are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by wind. Most of the living things that make up aeroplankton are very small to microscopic in size, and many can be difficult to identify because of ...
).
The search for a core microbiome in host-associated microbial communities is a useful first step in trying to understand the interactions that may be occurring between a host and its microbiome. The prevailing core microbiome concept is built on the notion that the persistence of a taxon across the spatiotemporal boundaries of an ecological niche is directly reflective of its functional importance within the niche it occupies; it therefore provides a framework for identifying functionally critical microorganisms that consistently associate with a host species.
 Divergent definitions of “core microbiome” have arisen across scientific literature with researchers variably identifying “core taxa” as those persistent across distinct host microhabitats and even different species. Given the functional divergence of microorganisms across different host species and microhabitats, defining core taxa ''sensu stricto'' as those persistent across broad geographic distances within tissue- and species-specific host microbiomes, represents the most biologically and ecologically appropriate application of this conceptual framework. Tissue- and species-specific core microbiomes across host populations separated by broad geographical distances have not been widely reported for the phyllosphere using the stringent definition established by Ruinen.
Divergent definitions of “core microbiome” have arisen across scientific literature with researchers variably identifying “core taxa” as those persistent across distinct host microhabitats and even different species. Given the functional divergence of microorganisms across different host species and microhabitats, defining core taxa ''sensu stricto'' as those persistent across broad geographic distances within tissue- and species-specific host microbiomes, represents the most biologically and ecologically appropriate application of this conceptual framework. Tissue- and species-specific core microbiomes across host populations separated by broad geographical distances have not been widely reported for the phyllosphere using the stringent definition established by Ruinen.
Example: The mānuka phyllosphere
The flowering tea tree commonly known asmānuka
''Leptospermum scoparium'', commonly called mānuka, () mānuka myrtle, New Zealand teatree, broom tea-tree, or just tea tree, is a species of flowering plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae, native to New Zealand (including the Chatham Islands ...
is indigenous to New Zealand. Mānuka honey
Mānuka honey () is a monofloral honey produced from the nectar of the mānuka tree, ''Leptospermum scoparium''. The mānuka tree is indigenous to New Zealand and some parts of coastal Australia, but is today produced globally. Used as a sugar s ...
, produced from the nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualist ...
of mānuka flowers, is known for its non-peroxide antibacterial properties. These non-peroxide antibacterial properties have been principally linked to the accumulation of the three-carbon sugar dihydroxyacetone (DHA) in the nectar of the mānuka flower, which undergoes a chemical conversion to methylglyoxal
Methylglyoxal (MGO) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CHO. It is a reduced derivative of pyruvic acid. It is a reactive compound that is implicated in the biology of diabetes. Methylglyoxal is produced industrially by degradation ...
(MGO) in mature honey. However, the concentration of DHA in the nectar of mānuka flowers is notoriously variable, and the antimicrobial efficacy of mānuka honey consequently varies from region to region and from year to year. Despite extensive research efforts, no reliable correlation has been identified between DHA production and climatic, edaphic
Edaphology (from Greek , ''edaphos'', "ground",, '' -logia'') is concerned with the influence of soils on living beings, particularly plants.
It is one of two main divisions of soil science, the other being pedology. Edaphology includes the stu ...
, or host genetic factors.
 Microorganisms have been studied in the mānuka rhizosphere and endosphere. Earlier studies primarily focussed on fungi, and a 2016 study provided the first investigation of endophytic bacterial communities from three geographically and environmentally distinct mānuka populations using fingerprinting techniques and revealed tissue-specific core endomicrobiomes. A 2020 study identified a habitat-specific and relatively abundant core microbiome in the mānuka phyllosphere, which was persistent across all samples. In contrast, non-core phyllosphere microorganisms exhibited significant variation across individual host trees and populations that was strongly driven by environmental and spatial factors. The results demonstrated the existence of a dominant and ubiquitous core microbiome in the phyllosphere of mānuka.
Microorganisms have been studied in the mānuka rhizosphere and endosphere. Earlier studies primarily focussed on fungi, and a 2016 study provided the first investigation of endophytic bacterial communities from three geographically and environmentally distinct mānuka populations using fingerprinting techniques and revealed tissue-specific core endomicrobiomes. A 2020 study identified a habitat-specific and relatively abundant core microbiome in the mānuka phyllosphere, which was persistent across all samples. In contrast, non-core phyllosphere microorganisms exhibited significant variation across individual host trees and populations that was strongly driven by environmental and spatial factors. The results demonstrated the existence of a dominant and ubiquitous core microbiome in the phyllosphere of mānuka.
See also
*Epiphytes
An epiphyte is an organism that grows on the surface of a plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphytes grow are called phoroph ...
* Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found ...
References
{{reflist, refs= {{cite journal, last=Last, first=F.T., title=Seasonal incidence of Sporobolomyces on cereal leaves, journal=Trans Br Mycol Soc, year=1955, volume=38, issue=3, pages=221–239, doi=10.1016/s0007-1536(55)80069-1 Microbiology terms Botany Microbiomes