|
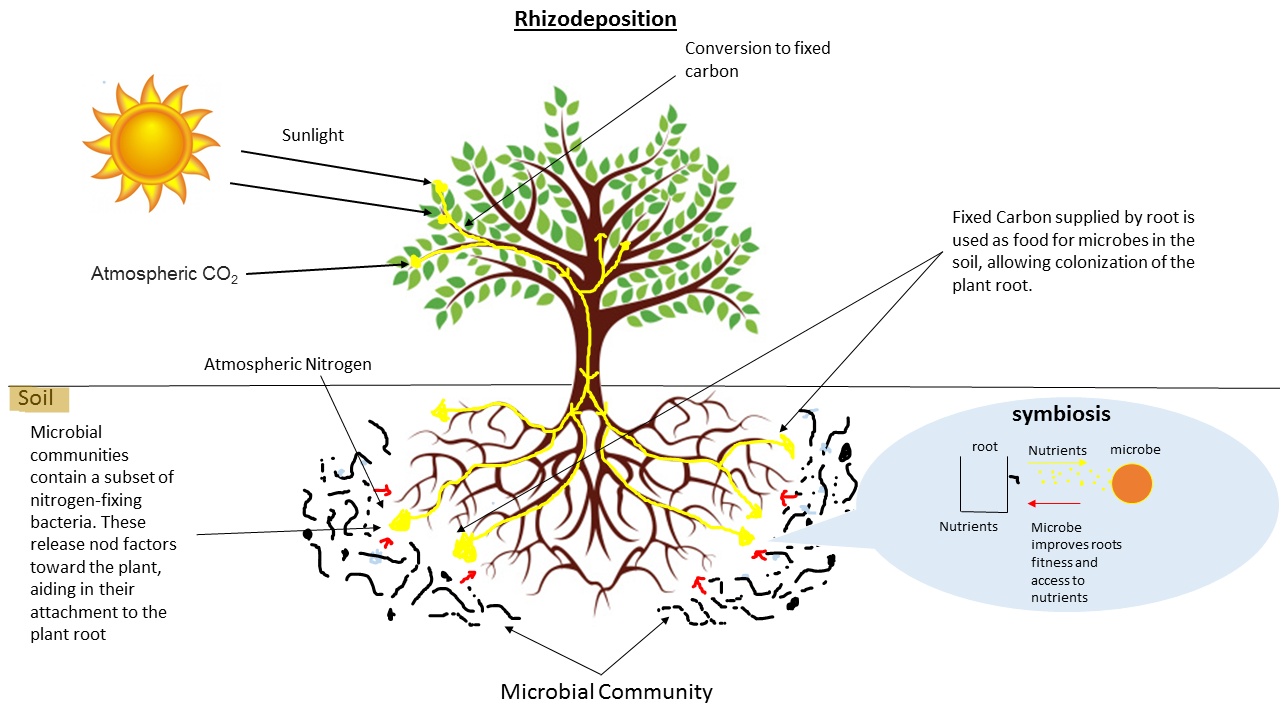
Rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or Substrate (biology), substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Pore space in soil, Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microorganisms that feed on sloughed-off plant cells, termed ''rhizodeposition'', and the proteins and sugars released by roots, termed Root mucilage, root exudates. This symbiosis leads to more complex interactions, influencing plant growth and competition for resources. Much of the nutrient cycle, nutrient cycling and disease suppression by antibiotics required by plants occurs immediately adjacent to roots due to root exudates and metabolism, metabolic products of symbiotic and Plant pathology, pathogenic communities of microorganisms. The rhizosphere also provides space to produce Allelopathy, allelochemicals to control neighbours and relatives. The ''rhizoplane'' refers to the root surface including it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Exudate
Plant root exudates are fluids emitted through the roots of plants. These secretions influence the rhizosphere around the roots to inhibit harmful microbes and promote the growth of self and kin plants. Plant root systems can grow to be complex due to a variety of species and microorganisms existing in a common soil. Plants have adapted to respond to the soil conditions and presence of microorganism, microbes through various mechanisms, one of which is the secretion of root exudates. This secretion allows plants to largely influence the rhizosphere as well as the organisms that exist within it. The contents of exudates and the amount of substance released is reliant on multiple factors, including the root system architecture, presence of harmful microbes, and metal toxicity. The species of the plant as well as its developmental stage can also influence the chemical mixture that is released through exudates. The contents may include ions, compounds of carbon, carbon-based compounds, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Microbiome
The root microbiome (also called rhizosphere microbiome) is the dynamic community of microorganisms associated with plant roots. Because they are rich in a variety of carbon compounds, plant roots provide unique environments for a diverse assemblage of soil microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and archaea. The microbial communities inside the root and in the rhizosphere are distinct from each other, and from the microbial communities of bulk soil, although there is some overlap in species composition. Different microorganisms, both beneficial and harmful, affect the development and physiology of plants. Beneficial microorganisms include bacteria that fix nitrogen, various microbes that promote plant growth, mycorrhizal fungi, mycoparasitic fungi, protozoa, and certain biocontrol microorganisms. Pathogenic microorganisms can also include certain bacteria, fungi, and nematodes that can colonize the rhizosphere. Pathogens are able to compete with protective microbes and break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Soil
Bulk soil is soil outside the rhizosphere that is not penetrated by plant roots. The bulk soil is like an ecosystem, it is made up of many things such as: nutrients, ions, soil particles, and root exudates. There are many different interactions that occur between all the members of the bulk soil. Natural organic compounds are much lower in bulk soil than in the rhizosphere. Furthermore, bulk soil inhabitants are generally smaller than identical species in the rhizosphere. The main two aspects of bulk soil are its chemistry and microbial community composition. Chemistry of bulk soil Soil is made up of layers called soil horizons, these make up a vertical soil profile. There are five master horizons O, A, E, B, and C. The O horizon contains organic matter, A is considered the topsoil, E is present or absent depending on the type of soil and conditions, B is the subsoil, and C is unconsolidated rock. There are many chemical interactions and properties that are in all the soil. Chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Mucilage
Root mucilage is made of plant-specific polysaccharides or long chains of sugar molecules. This polysaccharide secretion of root exudate forms a gelatinous substance that sticks to the caps of roots. Root mucilage is known to play a role in forming relationships with soil-dwelling life forms. Just how this root mucilage is secreted is debated, but there is growing evidence that mucilage derives from ruptured cells. As roots penetrate through the soil, many of the cells surrounding the caps of roots are continually shed and replaced. These ruptured or lysed cells release their component parts, which include the polysaccharides that form root mucilage. These polysaccharides come from the Golgi apparatus and plant cell wall, which are rich in plant-specific polysaccharides. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell wall that acts as a barrier surrounding the cell providing strength, which supports plants just like a skeleton. This cell wall is used to produce everyday products suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorenz Hiltner
Lorenz Hiltner (November 30, 1862 – June 6, 1923), born in Neumarkt in the Kingdom of Bavaria and passed away in Munich, was a German agronomist and microbiologist, known for developing the concept of the rhizosphere and for pioneering the development of the field of microbial ecology. Personal life Lorenz Hiltner was born on November 30, 1862, in Neumarkt. After completing his primary and secondary education in Neumarkt, he received a scholarship to study natural sciences in Nuremberg with a specialization in zoology and botany. In 1882, he was awarded a scholarship that allowed him to study for a short period at the Institute of Zoology at the University of Naples. He passed away unexpectedly from a sudden illness on June 6, 1923, in his office in Munich. His eldest son, Erhard Hiltner (born 1893), continued his research, notably publishing in 1929 a second edition of his book ''Pflanzenschutz nach Monaten geordnet'' (Plant Protection Organized by Months). Scientific work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in Jain literature authored in 6th-century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Microorganisms are extremely diverse, representing most unicellular organisms in all three domains of life: two of the three domains, Archaea and Bacteria, only contain microorganisms. The third domain, Eukaryota, includes all multicellular o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pore Space In Soil
The pore space of soil contains the liquid and gas phases of soil, i.e., everything but the solid phase that contains mainly minerals of varying sizes as well as organic compounds. In order to understand porosity better a series of equations have been used to express the quantitative interactions between the three phases of soil. Macropores or fractures play a major role in infiltration rates in many soils as well as preferential flow patterns, hydraulic conductivity and evapotranspiration. Cracks are also very influential in gas exchange, influencing respiration within soils. Modeling cracks therefore helps understand how these processes work and what the effects of changes in soil cracking such as compaction, can have on these processes. The pore space of soil may contain the habitat of plants (rhizosphere) and microorganisms. Background Dry bulk density : \rho_ = \frac The dry bulk density of a soil greatly depends on the mineral assemblage making up the soil and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Acid
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are relatively stronger acids. Alcohols, with –OH, can act as acids but they are usually very weak. The relative stability of the conjugate base of the acid determines its acidity. Other groups can also confer acidity, usually weakly: the thiol group –SH, the enol group, and the phenol group. In biological systems, organic compounds containing these groups are generally referred to as organic acids. A few common examples include: * Lactic acid * Acetic acid * Formic acid * Citric acid * Oxalic acid * Uric acid * Malic acid * Tartaric acid * Butyric acid * Folic acid Characteristics In general, organic acids are weak acids and do not dissociate completely in water, whereas the strong mineral acids do. Lower molecular mass organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |