nephridia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an

 A metanephridium (''meta'' = "after") is a type of excretory
A metanephridium (''meta'' = "after") is a type of excretory
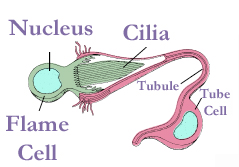 A protonephridium (''proto'' = "first") is found in the phyla Platyhelminthes,
A protonephridium (''proto'' = "first") is found in the phyla Platyhelminthes,
invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the ...
wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia come in two basic categories: metanephridia and protonephridia. All nephridia- and kidney- having animals belong to the clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
Nephrozoa
Nephrozoa is a proposed major clade of bilaterian animals. Under this hypothesis, Xenacoelomorpha forms the earliest diverging branch of Bilateria, with all other bilaterians placed in Nephrozoa. It contrasts with the Xenambulacraria hypothesis, ...
.
Metanephridia
gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also funct ...
found in many types of invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s such as annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s, arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s and mollusca
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
. (In mollusca, it is known as the Bojanus organ.)
A metanephridium typically consists of the nephrostome (a ciliated funnel) opening into the body cavity
A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.
The two largest human body cavities are the ventral body cavity, a ...
, connected to a duct which may be variously glandularized, folded or expanded (vesiculate) and which typically opens to the organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
's exterior. These ciliated tubules pump water carrying surplus ions, metabolic waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds ...
, toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived ...
s from food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
, and useless hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s out of the organism by directing them down funnel-shaped bodies called nephrostomes. This waste is passed out of the organism at the nephridiopore. The primary urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
produced by filtration of blood (or a similarly functioning fluid) is modified into secondary urine through selective reabsorption by the cells lining the metanephridium.
Saccate metanephridia
The saccate metanephridia are excretory glands which function similarly to the metanephridia. They are found in thearthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s: coxal glands of arachnids, antennal (or green) glands and maxillary glands of crustaceans, etc.
The saccate metanephridia filter the fluid of the hemocoel
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a organ system, system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of ...
, as opposed to the metanephridia which filter coelomic fluid. In a saccate metanephridium, there is a ciliated funnel covered with a membrane that helps to filter the hemocoel of heavy particles (such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s and carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s) before the fluid even enters the funnel. Inside the funnel, the fluid is further processed through selective reabsorption, and eventually excreted from the nephridiopore.
In Crustacea
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
, the saccate metanephridia are associated with the antennae and form the antennal gland. In freshwater crustacea
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
, the saccate metanephridia are especially large due to their role in osmoregulation; crustacea must remove large amounts of water from the tissues, as the cells are hypertonic to the surrounding water.
Protonephridia
 A protonephridium (''proto'' = "first") is found in the phyla Platyhelminthes,
A protonephridium (''proto'' = "first") is found in the phyla Platyhelminthes, Nemertea
Nemertea is a phylum of animals also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms, consisting of about 1300 known species. Most ribbon worms are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. ...
, Rotifera and Chordata
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphies) th ...
( lancelets). They have the same anatomy as the metanephridia but with the internal ciliated funnel blocked by terminal cells: either a ''flame cell
A flame cell is a specialized excretory cell found in simple invertebrates, including flatworms ( Platyhelminthes), rotifers and nemerteans; these are the simplest animals to have a dedicated excretory system. Flame cells function like a kidney ...
'' (if ciliated) or a '' solenocyte'' (if flagellated). Thus their tubules lack internal openings, while retaining their opening to the organism's exterior. They function in osmoregulation (ionoregulation).
Each terminal cell has one or more cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
and their beating inside the protonephridial tube creates an outward going current and hence a partial pressurization in the blind of the tube. Because of this, pressurization drives waste fluids from the inside of the animal, and they are pulled through small perforations in the terminal cells and into the protonephridium. The perforations in the terminal cell are large enough for small molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s to pass, but larger protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s are retained within the animal. From the bottom of the protonephridium the solutes are led through the tube, formed by the canal cells, and exits the animal from a small opening formed by the nephridiopore.
Selective reabsorption of useful molecules by the canal cells occurs as the solutes pass down the tubule. Protonephridia are generally found in basal organisms such as flatworm
Platyhelminthes (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") is a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), ...
s. Protonephridia likely first arose as a way to cope with a hypotonic environment by removing excess water from the organism ( osmoregulation). Their use as excretory and ionoregulatory structures likely arose secondarily.
These are excretory systems in phyla Platyhelminthes and are also called blind tubules. These tubules bear a tuft of cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
or flagellum. An organ of excretion in flatworms: a hollow cup-shaped cell containing a bunch of cilia or flagellum, whose movement draws in waste products and wafts them to the outside through a connecting tubule.
External links
*http://www.biology.ualberta.ca/courses.hp/zool250/animations/Excretion.swf * Baeumler N., Haszprunar G. & Ruthensteiner B. (2012). "Development of the excretory system in a polyplacophoran mollusc: stages in metanephridial system development". '' Frontiers in Zoology'' 9: 23. . {{Gastropod anatomy Annelid anatomy Arthropod anatomy Mollusc anatomy Platyhelminth anatomy