monetarism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Monetarism is a school of thought in
Monetarism is a school of thought in
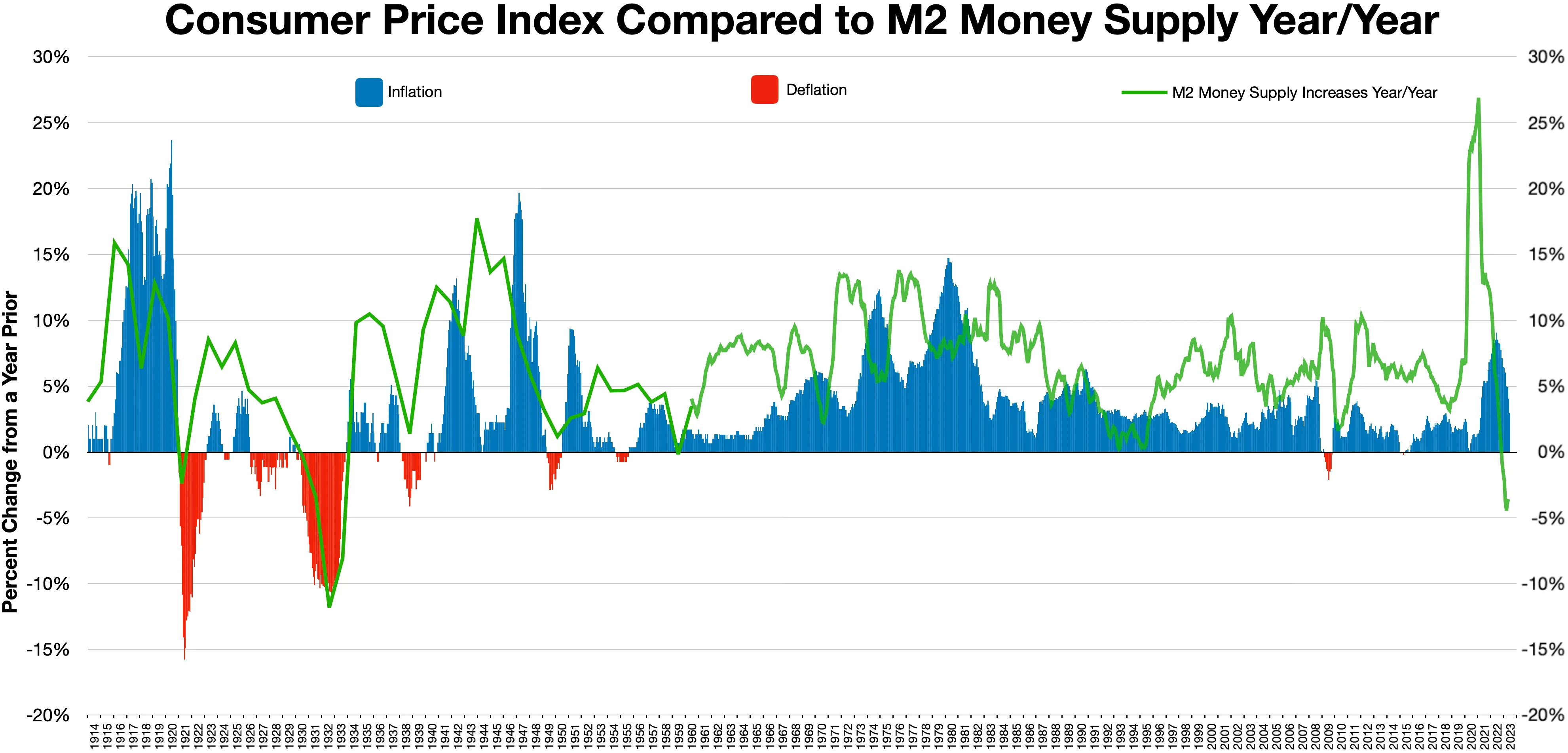
 Monetarists argued that central banks sometimes caused major unexpected fluctuations in the money supply. Friedman asserted that actively trying to stabilize demand through monetary policy changes can have negative unintended consequences. In part he based this view on the historical analysis of monetary policy, '' A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960'', which he coauthored with Anna Schwartz in 1963. The book attributed inflation to excess money supply generated by a central bank. It attributed deflationary spirals to the reverse effect of a failure of a central bank to support the money supply during a
Monetarists argued that central banks sometimes caused major unexpected fluctuations in the money supply. Friedman asserted that actively trying to stabilize demand through monetary policy changes can have negative unintended consequences. In part he based this view on the historical analysis of monetary policy, '' A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960'', which he coauthored with Anna Schwartz in 1963. The book attributed inflation to excess money supply generated by a central bank. It attributed deflationary spirals to the reverse effect of a failure of a central bank to support the money supply during a
PDF
(30 sec. load: press +) an
HTML.
* _____, 1969. "Monetary and Fiscal Actions: A Test of Their Relative Importance in Economic Stabilisation — Reply", Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis ''Review'' (April), pp. 12–16
PDF
(15 sec. load; press +) an
HTML.
* Brunner, Karl, and Allan H. Meltzer, 1993. ''Money and the Economy: Issues in Monetary Analysis'', Cambridge
Description
and chapter previews, pp
ix
x.
* Cagan, Phillip, 1965. ''Determinants and Effects of Changes in the Stock of Money, 1875–1960''. NBER. Foreword by Milton Friedman, pp. xiii–xxviii
Table of Contents.
* Friedman, Milton, ed. 1956. ''Studies in the Quantity Theory of Money'', Chicago. Chapter 1 is previewed at Friedman, 2005, ch. 2 link. * _____, 1960. ''A Program for Monetary Stability''. Fordham University Press. * _____, 1968. "The Role of Monetary Policy", ''American Economic Review'', 58(1), pp
1–17
(press +). * _____, 9692005. ''The Optimum Quantity of Money''
Description
an
table of contents
with previews of 3 chapters. * Friedman, Milton, and David Meiselman, 1963. "The Relative Stability of Monetary Velocity and the Investment Multiplier in the United States, 1897–1958", in ''Stabilization Policies'', pp. 165–268. Prentice-Hall/Commission on Money and Credit, 1963. * Friedman, Milton, and Anna Jacobson Schwartz, 1963a. "Money and Business Cycles", ''Review of Economics and Statistics'', 45(1), Part 2, Supplement, p
p. 32
€“64. Reprinted in Schwartz, 1987, ''Money in Historical Perspective'', ch. 2. * _____. 1963b. ''A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960''. Princeton. Page-searchable links to chapters o
1929-41
an
1948–60
* Johnson, Harry G., 1971. "The Keynesian Revolutions and the Monetarist Counter-Revolution", ''American Economic Review'', 61(2), p
p. 1
€“14. Reprinted in John Cunningham Wood and Ronald N. Woods, ed., 1990, ''Milton Friedman: Critical Assessments'', v. 2, p
p. 72–
88. Routledge, * Laidler, David E.W., 1993. ''The Demand for Money: Theories, Evidence, and Problems'', 4th ed
Description.
* Schwartz, Anna J., 1987. ''Money in Historical Perspective'', University of Chicago Press
Description
and Chapter-preview links, pp
viiviii.
* Warburton, Clark, 1966. ''Depression, Inflation, and Monetary Policy; Selected Papers, 1945–1953'' Johns Hopkins Press
Amazon Summary
in Anna J. Schwartz, ''Money in Historical Perspective'', 1987.
at The New School's Economics Department's History of Economic Thought website. *
Monetarism
from the Economics A–Z of
 Monetarism is a school of thought in
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics
Monetary economics is the branch of economics that studies the different theories of money: it provides a framework for analyzing money and considers its functions (as medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account), and it considers how m ...
that emphasizes the role of policy-makers in controlling the amount of money in circulation. It gained prominence in the 1970s, but was mostly abandoned as a direct guidance to monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
during the following decade because of the rise of inflation targeting through movements of the official interest rate.
The monetarist theory states that variations in the money supply have major influences on national output in the short run and on price levels over longer periods. Monetarists assert that the objectives of monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply rather than by engaging in discretionary monetary policy. Phillip Cagan, 1987. "Monetarism", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 3, Reprinted in John Eatwell et al. (1989), ''Money: The New Palgrave'', pp. 195–205, 492–97. Monetarism is commonly associated with neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
.
Monetarism is mainly associated with the work of Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and ...
, who was an influential opponent of Keynesian economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomics, macroeconomic theories and Economic model, models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongl ...
, criticising Keynes's theory of fighting economic downturns using fiscal policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variab ...
(e.g. government spending
Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or ...
). Friedman and Anna Schwartz wrote an influential book, '' A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960'', and argued that inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
is "always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon".
Although opposed to the existence of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of ...
, Friedman advocated, given its existence, a central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
policy aimed at keeping the growth of the money supply at a rate commensurate with the growth in productivity and demand for goods. Money growth targeting was mostly abandoned by the central banks who tried it, however. Contrary to monetarist thinking, the relation between money growth and inflation proved to be far from tight. Instead, starting in the early 1990s, most major central banks turned to direct inflation targeting, relying on steering short-run interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
s as their main policy instrument. Afterwards, monetarism was subsumed into the new neoclassical synthesis which appeared in macroeconomics around 2000.
Description
Monetarism is an economic theory that focuses on themacroeconomic
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output/ GDP ...
effects of the supply of money and central banking
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
. Formulated by Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and ...
, it argues that excessive expansion of the money supply is inherently inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
ary, and that monetary authorities should focus solely on maintaining price stability.
Monetarist theory draws its roots from the quantity theory of money, a centuries-old economic theory which had been put forward by various economists, among them Irving Fisher and Alfred Marshall
Alfred Marshall (26 July 1842 – 13 July 1924) was an English economist and one of the most influential economists of his time. His book ''Principles of Economics (Marshall), Principles of Economics'' (1890) was the dominant economic textboo ...
, before Friedman restated it in 1956.
Monetary history of the United States
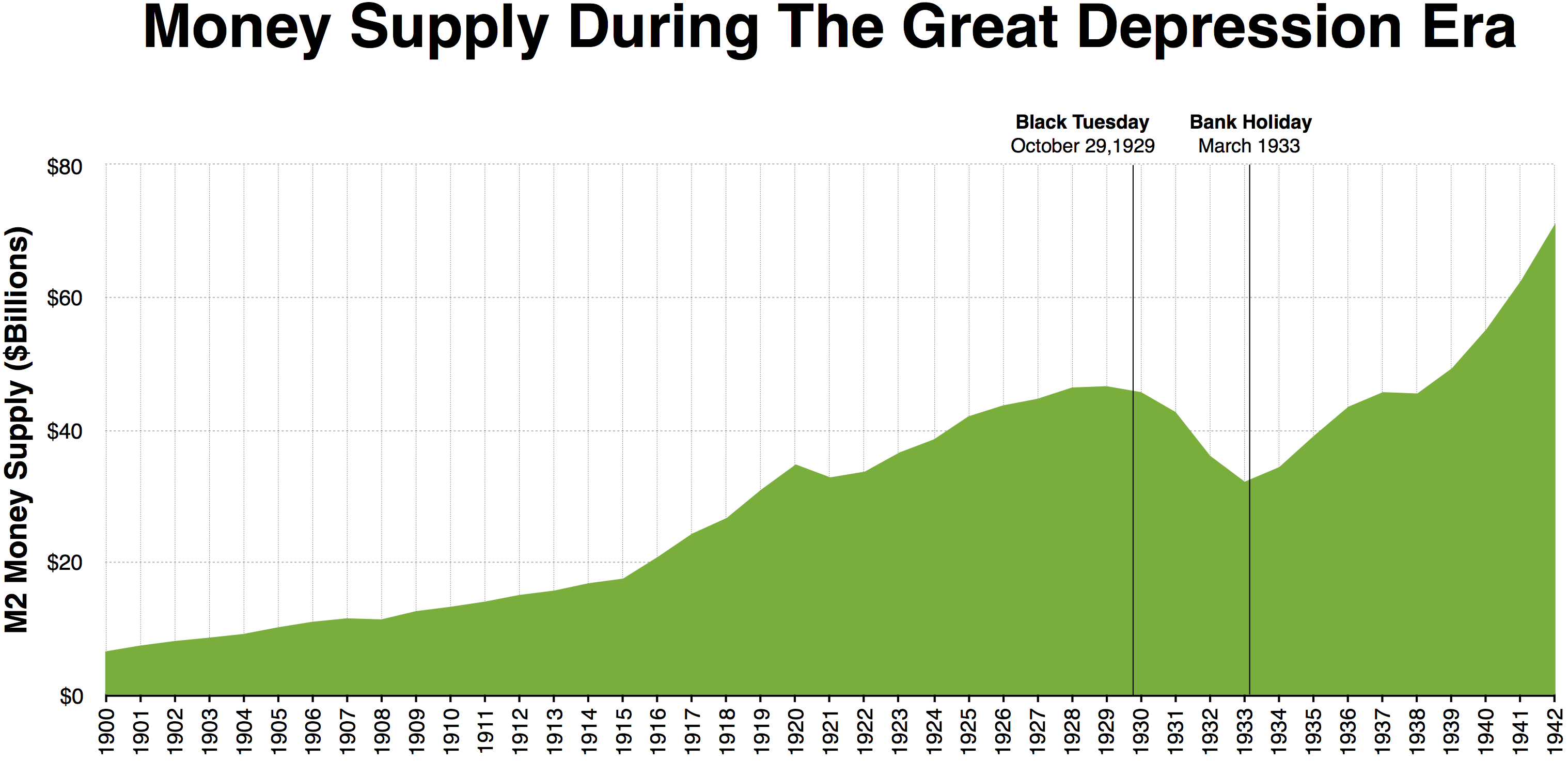
 Monetarists argued that central banks sometimes caused major unexpected fluctuations in the money supply. Friedman asserted that actively trying to stabilize demand through monetary policy changes can have negative unintended consequences. In part he based this view on the historical analysis of monetary policy, '' A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960'', which he coauthored with Anna Schwartz in 1963. The book attributed inflation to excess money supply generated by a central bank. It attributed deflationary spirals to the reverse effect of a failure of a central bank to support the money supply during a
Monetarists argued that central banks sometimes caused major unexpected fluctuations in the money supply. Friedman asserted that actively trying to stabilize demand through monetary policy changes can have negative unintended consequences. In part he based this view on the historical analysis of monetary policy, '' A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960'', which he coauthored with Anna Schwartz in 1963. The book attributed inflation to excess money supply generated by a central bank. It attributed deflationary spirals to the reverse effect of a failure of a central bank to support the money supply during a liquidity
Liquidity is a concept in economics involving the convertibility of assets and obligations. It can include:
* Market liquidity
In business, economics or investment, market liquidity is a market's feature whereby an individual or firm can quic ...
crunch. In particular, the authors argued that the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
of the 1930s was caused by a massive contraction of the money supply (they deemed it "the Great Contraction"), and not by the lack of investment that Keynes had argued. They also maintained that post-war inflation was caused by an over-expansion of the money supply. They made famous the assertion of monetarism that "inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon."
Fixed monetary rule
Friedman proposed a fixed ''monetary rule'', called Friedman's k-percent rule, where the money supply would be automatically increased by a fixed percentage per year. The rate should equal the growth rate of real GDP, leaving the price level unchanged. For instance, if the economy is expected to grow at 2 percent in a given year, the Fed should allow the money supply to increase by 2 percent. Because discretionary monetary policy would be as likely to destabilise as to stabilise the economy, Friedman advocated that the Fed be bound to fixed rules in conducting its policy.Opposition to the gold standard
Most monetarists oppose thegold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
. Friedman viewed a pure gold standard as impractical. For example, whereas one of the benefits of the gold standard is that the intrinsic limitations to the growth of the money supply by the use of gold would prevent inflation, if the growth of population or increase in trade outpaces the money supply, there would be no way to counteract deflation and reduced liquidity (and any attendant recession) except for the mining of more gold. But he also admitted that if a government was willing to surrender control over its monetary policy and not to interfere with economic activities, a gold-based economy would be possible.
Rise
Clark Warburton is credited with making the first solid empirical case for the monetarist interpretation of business fluctuations in a series of papers from 1945.p. 493 Withinmainstream economics
Mainstream economics is the body of knowledge, theories, and models of economics, as taught by universities worldwide, that are generally accepted by economists as a basis for discussion. Also known as orthodox economics, it can be contrasted to ...
, the rise of monetarism started with Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and ...
's 1956 restatement of the quantity theory of money. Friedman argued that the demand for money could be described as depending on a small number of economic variables.
Thus, according to Friedman, when the money supply expanded, people would not simply wish to hold the extra money in idle money balances; i.e., if they were in equilibrium before the increase, they were already holding money balances to suit their requirements, and thus after the increase they would have money balances surplus to their requirements. These excess money balances would therefore be spent and hence aggregate demand
In economics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is often called effective demand, though at other times this term is distinguished. This is the ...
would rise. Similarly, if the money supply were reduced people would want to replenish their holdings of money by reducing their spending. In this, Friedman challenged a simplification attributed to Keynes suggesting that "money does not matter." Thus the word 'monetarist' was coined.
The popularity of monetarism picked up in political circles when the prevailing view of neo-Keynesian economics
The neoclassical synthesis (NCS), or neoclassical–Keynesian synthesisMankiw, N. Gregory. "The Macroeconomist as Scientist and Engineer". ''The Journal of Economic Perspectives''. Vol. 20, No. 4 (Fall, 2006), p. 35. is an academic movement and ...
seemed unable to explain the contradictory problems of rising unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
and inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
in response to the Nixon shock in 1971 and the oil shocks of 1973. On one hand, higher unemployment seemed to call for reflation, but on the other hand rising inflation seemed to call for disinflation. The social-democratic post-war consensus that had prevailed in first world countries was thus called into question by the rising neoliberal
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pej ...
political forces.
Monetarism in the US and the UK
In 1979, United States PresidentJimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (October 1, 1924December 29, 2024) was an American politician and humanitarian who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
appointed as Federal Reserve Chief Paul Volcker, who made fighting inflation his primary objective, and who restricted the money supply (in accordance with the Friedman rule) to tame inflation in the economy. The result was a major rise in interest rates, not only in the United States; but worldwide. The "Volcker shock" continued from 1979 to the summer of 1982, decreasing inflation and increasing unemployment.
In May 1979, Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013), was a British stateswoman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of th ...
, Leader of the Conservative Party in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, won the general election
A general election is an electoral process to choose most or all members of a governing body at the same time. They are distinct from By-election, by-elections, which fill individual seats that have become vacant between general elections. Gener ...
, defeating the sitting Labour Government led by James Callaghan
Leonard James Callaghan, Baron Callaghan of Cardiff ( ; 27 March 191226 March 2005) was a British statesman and Labour Party (UK), Labour Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1976 to 1979 and Leader of the L ...
. By that time, the UK had endured several years of severe inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
, which was rarely below the 10% mark and stood at 10.3% by the time of the election. Thatcher implemented monetarism as the weapon in her battle against inflation, and succeeded at reducing it to 4.6% by 1983. However, unemployment in the United Kingdom increased from 5.7% in 1979 to 12.2% in 1983, reaching 13.0% in 1982; starting with the first quarter of 1980, the UK economy contracted in terms of real gross domestic product for six straight quarters.
Decline
Monetarist ascendancy was brief, however. The period when major central banks focused on targeting the growth of money supply, reflecting monetarist theory, lasted only for a few years, in the US from 1979 to 1982. The money supply is useful as a policy target only if the relationship between money and nominal GDP, and therefore inflation, is stable and predictable. This implies that the velocity of money must be predictable. In the 1970s velocity had seemed to increase at a fairly constant rate, but in the 1980s and 1990s velocity became highly unstable, experiencing unpredictable periods of increases and declines. Consequently, the stable correlation between the money supply and nominal GDP broke down, and the usefulness of the monetarist approach came into question. Many economists who had been convinced by monetarism in the 1970s abandoned the approach after this experience. The changing velocity originated in shifts in the demand for money and created serious problems for the central banks. This provoked a thorough rethinking of monetary policy. In the early 1990s central banks started focusing on targeting inflation directly using the short-runinterest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
as their central policy variable, abandoning earlier emphasis on money growth. The new strategy proved successful, and today most major central banks follow a flexible inflation targeting.
Measurement Issues on the Stability of Money Demand
While monetarism's influence on policy diminished in the 1980s, subsequent research suggests that the apparent instability in money demand functions may have stemmed from measurement issues rather than a fundamental breakdown in the money-income relationship. Barnett and others argued that simple-sum monetary aggregates, which weight all monetary components equally regardless of their liquidity characteristics, introduce significant measurement error that obscures stable underlying relationships. Studies using theoretically-grounded Divisia monetary aggregates, which weight monetary components based on their "monetary services" or liquidity properties, have found considerably more stable money demand relationships. For instance, Belongia and Ireland demonstrated that money demand equations using Divisia measures remain stable even through periods of financial innovation and policy regime changes that destabilized traditional simple-sum specifications. This finding has important implications for monetary policy frameworks. The breakdown in simple-sum money demand relationships was a key factor in central banks abandoning monetary targeting in favor of interest rate rules. However, research using Divisia aggregates suggests that money could still serve as a useful policy indicator or intermediate target if properly measured. The stability of Divisia money demand functions has been demonstrated across different time periods and countries. For example, Hendrickson found that replacing simple-sum with Divisia measures resolves apparent instabilities in U.S. money demand, while similar results have been documented for other economies. Chen and Valcarcel argued that the properly measured monetary quantities and their holding costs maintain a stable, long-term cointegration. These findings suggest that the historical shift away from monetary aggregates in policy frameworks may have been premature and based on flawed measurement rather than a true breakdown in the relationship between money and economic activity. While most central banks continue to focus primarily on interest rates, the stability of properly-measured money demand functions indicates that monetary aggregates could potentially play a more prominent role in policy frameworks.Legacy
Even though monetarism failed in practical policy, and the close attention to money growth which was at the heart of monetarist analysis is rejected by most economists today, some aspects of monetarism have found their way into modern mainstream economic thinking. Among them are the belief that controlling inflation should be a primary responsibility of the central bank. It is also widely recognized that monetary policy, as well as fiscal policy, can affect output in the short run. In this way, important monetarist thoughts have been subsumed into the new neoclassical synthesis or consensus view of macroeconomics that emerged in the 2000s.Notable proponents
* Karl Brunner * Phillip D. Cagan * Tim Congdon *Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and ...
* Alan Greenspan
* Steve Hanke
* David Laidler
* Allan H. Meltzer
* Anna Schwartz
* Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013), was a British stateswoman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of th ...
* Paul Volcker
* Clark Warburton
See also
*Chicago school of economics
The Chicago school of economics is a Neoclassical economics, neoclassical Schools of economic thought, school of economic thought associated with the work of the faculty at the University of Chicago, some of whom have constructed and populari ...
* Demurrage currency
* Fiscalism (usually contrasted to monetarism)
* Market monetarism
* Modern Monetary Theory
* Money creation - process in which private banks (primarily) or Central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
s ( quantitative easing) create money
References
Further reading
* Andersen, Leonall C., and Jerry L. Jordan, 1968. "Monetary and Fiscal Actions: A Test of Their Relative Importance in Economic Stabilisation", Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis ''Review'' (November), pp. 11–24(30 sec. load: press +) an
HTML.
* _____, 1969. "Monetary and Fiscal Actions: A Test of Their Relative Importance in Economic Stabilisation — Reply", Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis ''Review'' (April), pp. 12–16
(15 sec. load; press +) an
HTML.
* Brunner, Karl, and Allan H. Meltzer, 1993. ''Money and the Economy: Issues in Monetary Analysis'', Cambridge
Description
and chapter previews, pp
ix
x.
* Cagan, Phillip, 1965. ''Determinants and Effects of Changes in the Stock of Money, 1875–1960''. NBER. Foreword by Milton Friedman, pp. xiii–xxviii
Table of Contents.
* Friedman, Milton, ed. 1956. ''Studies in the Quantity Theory of Money'', Chicago. Chapter 1 is previewed at Friedman, 2005, ch. 2 link. * _____, 1960. ''A Program for Monetary Stability''. Fordham University Press. * _____, 1968. "The Role of Monetary Policy", ''American Economic Review'', 58(1), pp
1–17
(press +). * _____, 9692005. ''The Optimum Quantity of Money''
Description
an
table of contents
with previews of 3 chapters. * Friedman, Milton, and David Meiselman, 1963. "The Relative Stability of Monetary Velocity and the Investment Multiplier in the United States, 1897–1958", in ''Stabilization Policies'', pp. 165–268. Prentice-Hall/Commission on Money and Credit, 1963. * Friedman, Milton, and Anna Jacobson Schwartz, 1963a. "Money and Business Cycles", ''Review of Economics and Statistics'', 45(1), Part 2, Supplement, p
p. 32
€“64. Reprinted in Schwartz, 1987, ''Money in Historical Perspective'', ch. 2. * _____. 1963b. ''A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960''. Princeton. Page-searchable links to chapters o
1929-41
an
1948–60
* Johnson, Harry G., 1971. "The Keynesian Revolutions and the Monetarist Counter-Revolution", ''American Economic Review'', 61(2), p
p. 1
€“14. Reprinted in John Cunningham Wood and Ronald N. Woods, ed., 1990, ''Milton Friedman: Critical Assessments'', v. 2, p
p. 72
88. Routledge, * Laidler, David E.W., 1993. ''The Demand for Money: Theories, Evidence, and Problems'', 4th ed
Description.
* Schwartz, Anna J., 1987. ''Money in Historical Perspective'', University of Chicago Press
Description
and Chapter-preview links, pp
vii
* Warburton, Clark, 1966. ''Depression, Inflation, and Monetary Policy; Selected Papers, 1945–1953'' Johns Hopkins Press
Amazon Summary
in Anna J. Schwartz, ''Money in Historical Perspective'', 1987.
External links
at The New School's Economics Department's History of Economic Thought website. *
Monetarism
from the Economics A–Z of
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British newspaper published weekly in printed magazine format and daily on Electronic publishing, digital platforms. It publishes stories on topics that include economics, business, geopolitics, technology and culture. M ...
{{Authority control
Monetary economics
Milton Friedman
20th century in economic history
21st century in economic history
Schools of economic thought