|
Reflation
Reflation is used to describe a return of prices to a previous rate of inflation. One usage describes an act of stimulating the economy by increasing the money supply or by reducing taxes, seeking to bring the economy (specifically the price level) back ''up'' to the long-term trend, following a dip in the business cycle. It is the opposite of disinflation, which seeks to return the economy back ''down'' to the long-term trend. Overview In this perspective, reflation, is contrasted with inflation (narrowly speaking) ''above'' the some long-term trend line, while reflation is a recovery of the price level when it has fallen ''below'' the trend line. For example, if inflation had been running at a 3% rate, but for one year it falls to 0%, the following year would need 6% inflation (actually 6.09% due to compounding) to catch back up to the long-term trend. This higher than normal inflation is considered reflation, since it is a return to trend, not exceeding the long-term trend. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
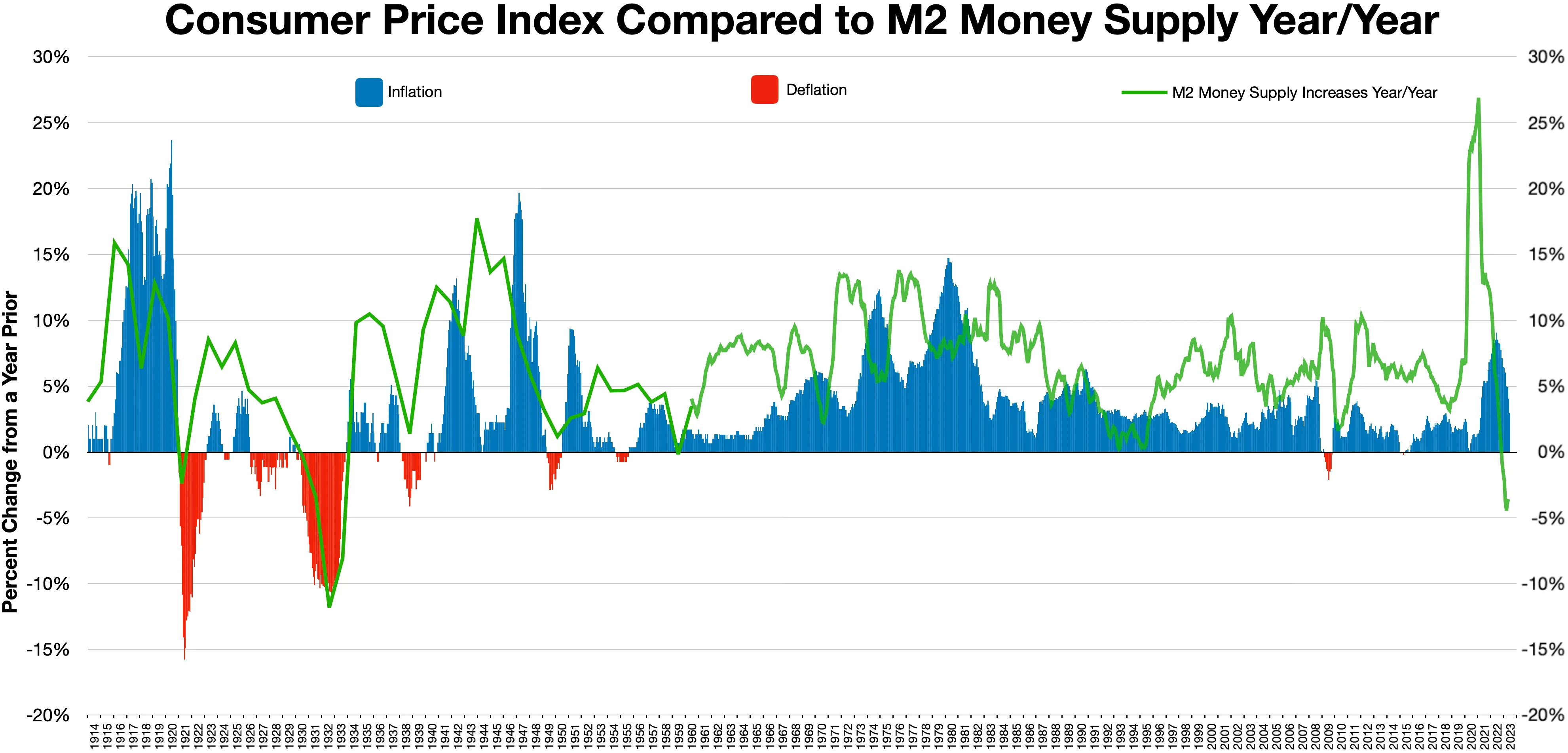
Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of CPI inflation is deflation, a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. Changes in inflation are widely attributed to fluctuations in Real versus nominal value (economics), real demand for goods and services (also known as demand shocks, including changes in fiscal policy, fiscal or monetary policy), changes in available supplies such as during energy crisis, energy crises (also known as supply shocks), or changes in inflation expectations, which may be self-fulfilling. Moderat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
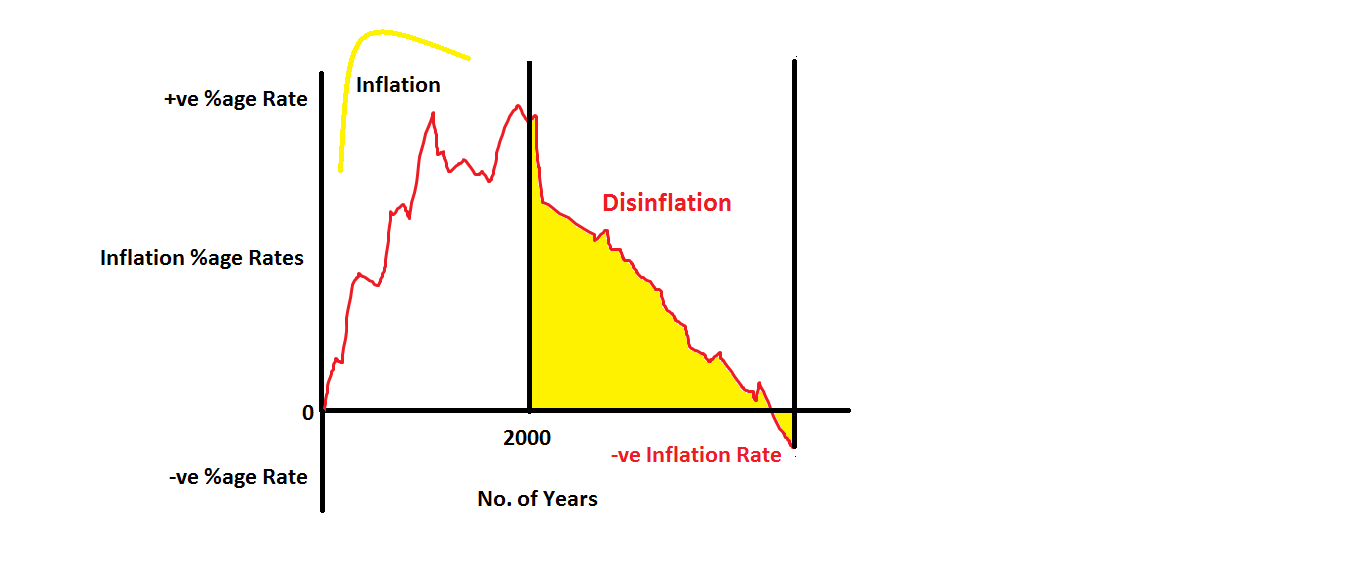
Disinflation
Disinflation is a decrease in the rate of inflation – a slowdown in the rate of increase of the general price level of goods and services in a nation's gross domestic product over time. It is the opposite of reflation. If the inflation rate is not very high to start with, disinflation can lead to deflation – decreases in the general price level of goods and services. For example if the annual inflation rate one month is 5% and it is 4% the following month, prices disinflated by 1% but are still increasing at a 4% annual rate. If the current rate is 1% and it is the -2% the following month, prices disinflated by 3% and are decreasing at a 2% annual rate. See also *Hyperinflation * Stagflation * Devaluation * Chronic inflation *Deflation In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
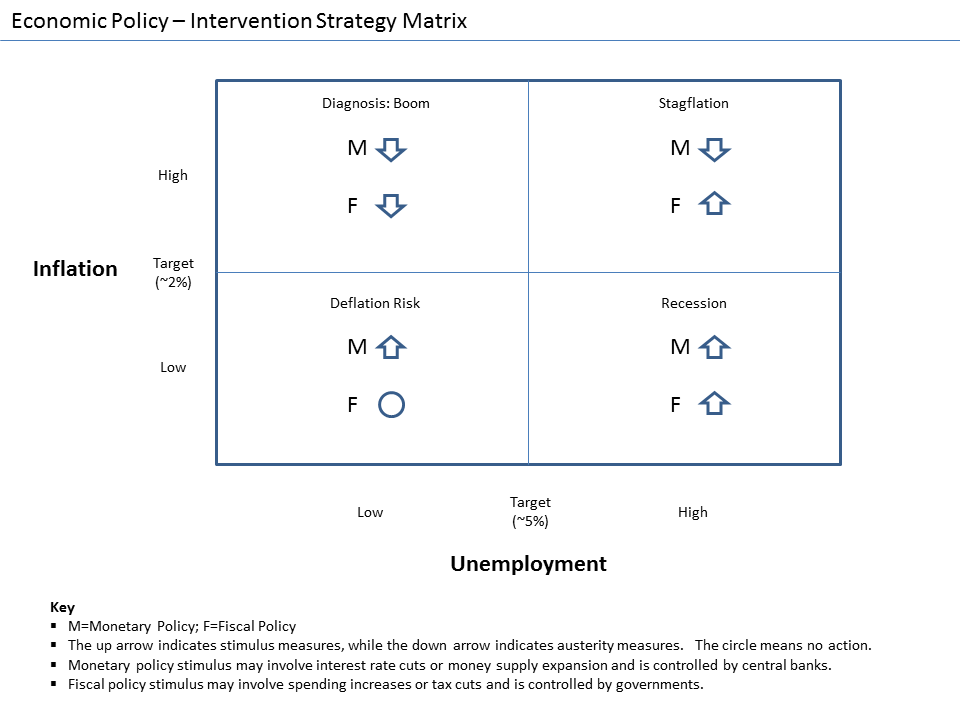
Economic Stimulus
In economics, stimulus refers to attempts to use monetary policy or fiscal policy (or stabilization policy in general) to stimulate the economy. Stimulus can also refer to monetary policies such as lowering interest rates and quantitative easing. A stimulus is sometimes colloquially referred to as "priming the pump" or "pump priming". Concept During a recession, production and employment are far below their sustainable potential due to lack of demand. It is hoped that increasing demand will stimulate growth and that any adverse side effects from stimulus will be mild. Fiscal stimulus refers to increasing government consumption or transfers or lowering taxes, increasing the rate of growth of public debt. Supporters of Keynesian economics assume the stimulus will cause sufficient economic growth to fill that gap partially or completely via the multiplier effect. Monetary stimulus refers to lowering interest rates, quantitative easing, or other ways of increasing the amou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the length of time over which it is lent, deposited, or borrowed. The annual interest rate is the rate over a period of one year. Other interest rates apply over different periods, such as a month or a day, but they are usually annualized. The interest rate has been characterized as "an index of the preference . . . for a dollar of present ncomeover a dollar of future income". The borrower wants, or needs, to have money sooner, and is willing to pay a fee—the interest rate—for that privilege. Influencing factors Interest rates vary according to: * the government's directives to the central bank to accomplish the government's goals * the currency of the principal sum lent or borrowed * the term to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in San Bruno, California, it is the second-most-visited website in the world, after Google Search. In January 2024, YouTube had more than 2.7billion monthly active users, who collectively watched more than one billion hours of videos every day. , videos were being uploaded to the platform at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute, and , there were approximately 14.8billion videos in total. On November 13, 2006, YouTube was purchased by Google for $1.65 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ). Google expanded YouTube's business model of generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by and for YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflationism
Inflationism is a heterodox economic, fiscal, or monetary policy, that predicts that a substantial level of inflation is harmless, desirable or even advantageous. Similarly, inflationist economists advocate for an inflationist policy. Mainstream economics holds that inflation is a necessary evil, and advocates a low, stable level of inflation, and thus is largely opposed to inflationist policies – some inflation is necessary, but inflation beyond a low level is not desirable. However, deflation is often seen as a worse or equal danger, particularly within Keynesian economics, as well as Monetarist economics and in the theory of debt deflation. Inflationism is not accepted within the economics community, and is often conflated with Modern Monetary Theory, which uses similar arguments, especially in relation to chartalism. Political debate In political debate, inflationism is opposed to hard currency, which believes that the real value of currency should be maintained. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Bubble
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of resources. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Employment
Full employment is an economic situation in which there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. Full employment does not entail the disappearance of all unemployment, as other kinds of unemployment, namely structural and frictional, may remain. Full employment does not entail 100% employment-to-population ratio. For instance, workers who are "between jobs" for short periods of time as they search for better employment are not counted against full employment, as such unemployment is frictional rather than cyclical. An economy with full employment might also have unemployment or underemployment where part-time workers cannot find jobs appropriate to their skill level, as such unemployment is considered structural rather than cyclical. Full employment marks the point past which expansionary fiscal and/or monetary policy cannot reduce unemployment any further without causing inflation. Some economists define full employment somewhat differently, as the unemployment rate at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company headquartered at 1585 Broadway in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. With offices in 42 countries and more than 80,000 employees, the firm's clients include corporations, governments, institutions, and individuals. Morgan Stanley ranked No. 61 in the 2023 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue and in the same year ranked #30 in Forbes Global 2000. The original Morgan Stanley, formed by J.P. Morgan & Co. partners Henry Sturgis Morgan (a grandson of J.P. Morgan), Harold Stanley, and others, came into existence on September 16, 1935, in response to the Glass–Steagall Act, which required the splitting of American commercial and investment banking businesses. In its first year, the company operated with a 24% market share (US$1.1 billion) in public offerings and private placements. The current Morgan Stanley is the result of the merger of the origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from '' disinflation'', a slowdown in the inflation rate; i.e., when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral . Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supply is hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Policy
''Economic Policy'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Oxford University Press, Oxford Academic on behalf of the Centre for Economic Policy Research, the Center for Economic Studies (University of Munich), and the Paris School of Economics. The journal was established in 1985 and covers international economic policy topics such as macroeconomics, microeconomics, the labour market, trade, exchange rate, taxation, economic growth, government spending, and Human migration, migration. The journal had an impact factor of 2.844 in 2016, ranking it 33/347 in the category "Economics". References External links * {{Official website, https://academic.oup.com/economicpolicy Wiley-Blackwell academic journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1985 Quarterly journals Economics journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of resources. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |