marine biology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Marine biology is the scientific study of the
 Marine biology can be contrasted with
Marine biology can be contrasted with

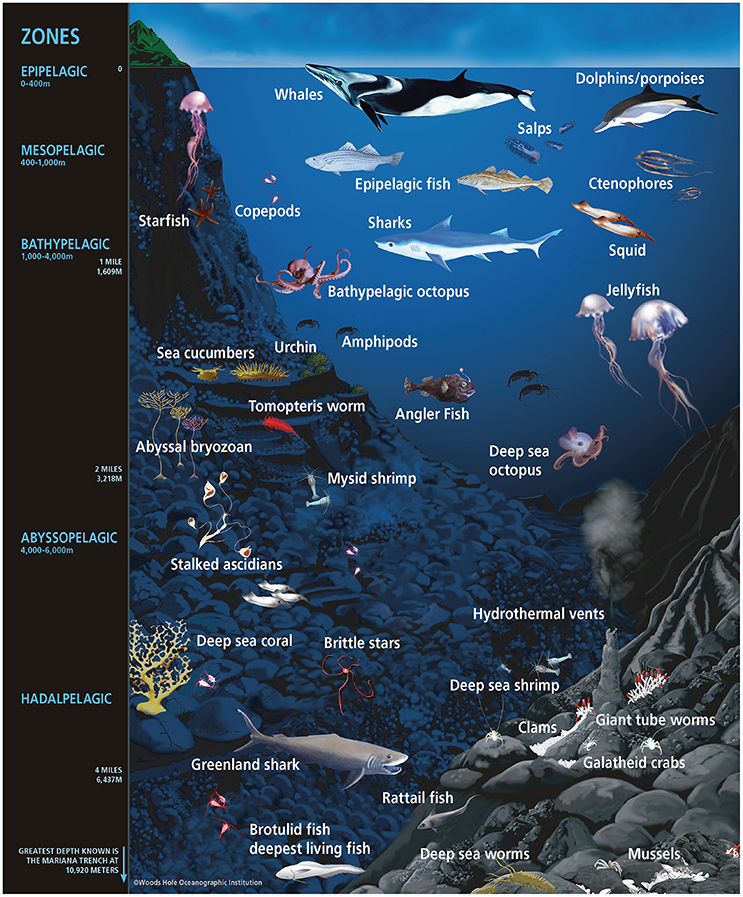
 The deepest recorded
The deepest recorded
, ''Rolex Deep Sea Special'', January 2006. In general, the deep sea is considered to start at the aphotic zone, the point where sunlight loses its power of transference through the water. Many life forms that live at these depths have the ability to create their own light known as bio-luminescence. Marine life also flourishes around seamounts that rise from the depths, where fish and other sea life congregate to spawn and feed. Hydrothermal vents along the
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
. Accessed 7 August 2007. Some
 The study of marine biology dates to
The study of marine biology dates to  The observations made in the first studies of marine biology fueled the
The observations made in the first studies of marine biology fueled the
''Introduction to the Biology of Marine Life''
Jones & Bartlett Publishers. . * Mladenov, Philip V., Marine Biology: A Very Short Introduction, 2nd edn (Oxford, 2020; online edn, Very Short Introductions online, Feb. 2020), http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/actrade/9780198841715.001.0001, accessed 21 Jun. 2020.
Smithsonian Ocean Portal
Marine Conservation Society
Marine Ecology – an evolutionary perspective
Free special issue: Marine Biology in Time and Space
Creatures of the deep ocean
– ''National Geographic'' documentary, 2010.
Exploris
– From the University of Washington Library
Marine Training Portal
– Portal grouping training initiatives in the field of Marine Biology {{DEFAULTSORT:Marine Biology Biological oceanography Fisheries science >
biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
of marine life
Marine life, sea life or ocean life is the collective ecological communities that encompass all aquatic animals, aquatic plant, plants, algae, marine fungi, fungi, marine protists, protists, single-celled marine microorganisms, microorganisms ...
, organisms that inhabit the sea
A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order section ...
. Given that in biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
many phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
, families and genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
.
A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. The exact size of this "large proportion" is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world, covering approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension (physics), tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. Ge ...
between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trench
Oceanic trenches are prominent, long, narrow topography, topographic depression (geology), depressions of the seabed, ocean floor. They are typically wide and below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor, but can be thousands of kilometers ...
es, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean.
Specific habitats include estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
, coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s, kelp forest
Kelp forests are underwater areas with a high density of kelp, which covers a large part of the world's coastlines. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on E ...
s, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the sur ...
) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
and zooplankton to huge cetaceans
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...
(whales) in length. Marine ecology is the study of how marine organisms interact with each other and the environment.
Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for happiness, enjoyment, amusement, ...
and tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.
Many species are economically important to humans, including both finfish and shellfish. It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycl ...
) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.
Biological oceanography
 Marine biology can be contrasted with
Marine biology can be contrasted with biological oceanography
Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics, chemistry, and geology of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography may also be referred to as ocean ecology, in which the root word of ecology ...
. Marine life
Marine life, sea life or ocean life is the collective ecological communities that encompass all aquatic animals, aquatic plant, plants, algae, marine fungi, fungi, marine protists, protists, single-celled marine microorganisms, microorganisms ...
is a field of study both in marine biology and in biological oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology.
It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of to ...
. Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, and geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth ...
of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography mostly focuses on the microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s within the ocean; looking at how they are affected by their environment and how that affects larger marine creatures and their ecosystem.Lalli, Carol M., and Timothy R. Parsons. "Introduction." Biological Oceanography: An Introduction. First Edition ed. Tarrytown, New York: Pergamon, 1993. 7–21. Print.
Biological oceanography is similar to marine biology, but it studies ocean life from a different perspective. Biological oceanography takes a bottom up approach in terms of the food web, while marine biology studies the ocean from a top down perspective. Biological oceanography mainly focuses on the ecosystem of the ocean with an emphasis on plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
: their diversity (morphology, nutritional sources, motility, and metabolism); their productivity and how that plays a role in the global carbon cycle; and their distribution (predation and life cycle). Biological oceanography also investigates the role of microbes in food webs, and how humans impact the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s in the oceans.
Marine habitats
Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from theshoreline
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
to the edge of the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an islan ...
. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the sur ...
and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean and affected by ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s, while demersal habitats are near or on the bottom. Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp and sea grasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.
Intertidal and near shore

Intertidal zone
The intertidal zone or foreshore is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide; in other words, it is the part of the littoral zone within the tidal range. This area can include several types of habitats with various ...
s, the areas that are close to the shore, are constantly being exposed and covered by the ocean's tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
. A huge array of life can be found within this zone. Shore habitats span from the upper intertidal zones to the area where land vegetation takes prominence. It can be underwater anywhere from daily to very infrequently. Many species here are scavengers, living off of sea life that is washed up on the shore. Many land animals also make much use of the shore and intertidal habitats. A subgroup of organisms in this habitat bores and grinds exposed rock through the process of bioerosion.
Estuaries
Estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
are also near shore and influenced by the tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
. An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between freshwater river environments and saltwater maritime environments. They are subject both to marine influences—such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water—and to riverine influences—such as flows of fresh water and sediment. The shifting flows of both sea water and fresh water provide high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.
Reefs

Reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral, or similar relatively stable material lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic component, abiotic (non-living) processes such as deposition (geol ...
s comprise some of the densest and most diverse habitats in the world. The best-known types of reefs are tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s which exist in most tropical waters; however, reefs can also exist in cold water. Reefs are built up by coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
s and other calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
-depositing animals, usually on top of a rocky outcrop on the ocean floor. Reefs can also grow on other surfaces, which has made it possible to create artificial reef
An artificial reef (AR) is a human-created freshwater or marine benthic structure.
Typically built in areas with a generally featureless bottom to promote Marine biology#Reefs, marine life, it may be intended to control #Erosion prevention, erosio ...
s. Coral reefs also support a huge community of life, including the corals themselves, their symbiotic zooxanthellae, tropical fish and many other organisms.
Much attention in marine biology is focused on coral reefs and the El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit
* Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things''
* El, fami ...
weather phenomenon. In 1998, coral reefs experienced the most severe mass bleaching events on record, when vast expanses of reefs across the world died because sea surface temperatures rose well above normal. Some reefs are recovering, but scientists say that between 50% and 70% of the world's coral reefs are now endangered and predict that global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
could exacerbate this trend.

Open ocean
The open ocean is relatively unproductive because of a lack of nutrients, yet because it is so vast, in total it produces the most primary productivity. The open ocean is separated into different zones, and the different zones each have different ecologies. Zones which vary according to their depth include theepipelagic
The photic zone (or euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone) is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological ...
, mesopelagic
The mesopelagic zone (Greek language, Greek μέσον, middle), also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light ...
, bathypelagic, abyssopelagic, and hadopelagic zones. Zones which vary by the amount of light they receive include the photic and aphotic zones. Much of the aphotic zone's energy is supplied by the open ocean in the form of detritus
In biology, detritus ( or ) is organic matter made up of the decomposition, decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decomposition, decompose (Reminera ...
.
Deep sea and trenches
 The deepest recorded
The deepest recorded oceanic trench
Oceanic trenches are prominent, long, narrow topography, topographic depression (geology), depressions of the seabed, ocean floor. They are typically wide and below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor, but can be thousands of kilometers ...
measured to date is the Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deep sea, deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maxi ...
, near the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, in the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
at . At such depths, water pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and ev ...
is extreme and there is no sunlight, but some life still exists. A white flatfish
A flatfish is a member of the Ray-finned fish, ray-finned demersal fish Order (biology), suborder Pleuronectoidei, also called the Heterosomata. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through or around ...
, a shrimp and a jellyfish were seen by the crew of the bathyscaphe
A bathyscaphe () is a free-diving, self-propelled deep-sea submersible, consisting of a crew cabin similar to a '' Bathysphere'', but suspended below a float rather than from a surface cable, as in the classic ''Bathysphere'' design.
The floa ...
''Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
'' when it dove to the bottom in 1960, which led to scientific debate surrounding the likelihood of bony fish surviving in such deep waters. General scientific consensus has discredited the possible viewing of a flatfish at such depths.Polmar, Norman; Mathers, Lee J. (January 2020). "The First Deepest Dive". ''U.S. Naval Institute Proceedings''. 146/1/1, 403.Seven Miles Down: The Story of The Bathyscaph Trieste., ''Rolex Deep Sea Special'', January 2006. In general, the deep sea is considered to start at the aphotic zone, the point where sunlight loses its power of transference through the water. Many life forms that live at these depths have the ability to create their own light known as bio-luminescence. Marine life also flourishes around seamounts that rise from the depths, where fish and other sea life congregate to spawn and feed. Hydrothermal vents along the
mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
spreading centers act as oases, as do their opposites, cold seeps
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where seepage of fluids rich in hydrogen sulfide, methane, and other hydrocarbons occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature o ...
. Such places support unique biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
s and many new microbe
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
s and other lifeforms have been discovered at these locations. There is still much more to learn about the deeper parts of the ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
.
Marine life
In biology, many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land. Marine biology classifies species based on their environment rather than their taxonomy. For this reason, marine biology encompasses not only organisms that live only in a marine environment, but also other organisms whose lives revolve around the sea.Microscopic life
As inhabitants of the largest environment on Earth, microbial marine systems drive changes in every global system. Microbes are responsible for virtually allphotosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
that occurs in the ocean, as well as the cycling of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
and other nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
and trace elements.
Microscopic life undersea is incredibly diverse and still poorly understood. For example, the role of virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es in marine ecosystems is barely being explored even in the beginning of the 21st century.
The role of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
is better understood due to their critical position as the most numerous primary producers on Earth. Phytoplankton are categorized into cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
(also called blue-green algae/bacteria), various types of algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
(red, green, brown, and yellow-green), diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's B ...
s, dinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also commo ...
s, euglenoids, coccolithophorids, cryptomonads, chrysophytes, chlorophyte
Chlorophyta is a division (botany), division of green algae informally called chlorophytes.
Description
Chlorophytes are eukaryotic organisms composed of cells with a variety of coverings or walls, and usually a single green chloroplast in ea ...
s, prasinophytes, and silicoflagellates.
Zooplankton tend to be somewhat larger, and not all are microscopic. Many Protozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
are zooplankton, including dinoflagellates, zooflagellates, foraminifera
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are unicellular organism, single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class (biology), class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell bio ...
ns, and radiolarians. Some of these (such as dinoflagellates) are also phytoplankton; the distinction between plants and animals often breaks down in very small organisms. Other zooplankton include cnidarian
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
s, ctenophores, chaetognaths, mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, urochordates, and annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s such as polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s. Many larger animals begin their life as zooplankton before they become large enough to take their familiar forms. Two examples are fish larvae and sea stars (also called starfish
Starfish or sea stars are Star polygon, star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class (biology), class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to brittle star, ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to ...
).
Plants and algae
Microscopic algae and plants provide important habitats for life, sometimes acting as hiding places for larval forms of larger fish and foraging places for invertebrates. Algal life is widespread and very diverse under the ocean. Microscopic photosynthetic algae contribute a larger proportion of the world's photosynthetic output than all the terrestrial forests combined. Most of the niche occupied by sub plants on land is actually occupied by macroscopicalgae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
in the ocean, such as '' Sargassum'' and kelp
Kelps are large brown algae or seaweeds that make up the order (biology), order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genus, genera. Despite its appearance and use of photosynthesis in chloroplasts, kelp is technically not a plant but a str ...
, which are commonly known as seaweeds that create kelp forest
Kelp forests are underwater areas with a high density of kelp, which covers a large part of the world's coastlines. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on E ...
s.
Plants that survive in the sea are often found in shallow waters, such as the seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine (ocean), marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four Family (biology), families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and ...
es (examples of which are eelgrass, '' Zostera'', and turtle grass, '' Thalassia''). These plants have adapted to the high salinity of the ocean environment. The intertidal zone
The intertidal zone or foreshore is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide; in other words, it is the part of the littoral zone within the tidal range. This area can include several types of habitats with various ...
is also a good place to find plant life in the sea, where mangroves or cordgrass or beach grass might grow.
Invertebrates
As on land,invertebrates
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum ...
, or animals that lack a backbone, make up a huge portion of all life in the sea. Invertebrate sea life includes Cnidaria
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
such as jellyfish
Jellyfish, also known as sea jellies or simply jellies, are the #Life cycle, medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, which is a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animal ...
and sea anemone
Sea anemones ( ) are a group of predation, predatory marine invertebrates constituting the order (biology), order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the ''Anemone'', a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemone ...
s; Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; : ctenophore ) is a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are ...
; sea worms including the phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
Platyhelminthes, Nemertea
Nemertea is a phylum of animals also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms, consisting of about 1300 known species. Most ribbon worms are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. ...
, Annelida
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to variou ...
, Sipuncula, Echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of ocean, marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, but e ...
, Chaetognatha, and Phoronida; Mollusca
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
including shellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
, squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ...
, octopus
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like oth ...
; Arthropoda
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated ( metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. ...
including Chelicerata
The subphylum Chelicerata (from Neo-Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. Chelicerates include the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, tic ...
and Crustacea
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
; Porifera
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile ...
; Bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary Colony (biology), colonies. Typically about long, they have a spe ...
; Echinodermata
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larvae, ...
including starfish
Starfish or sea stars are Star polygon, star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class (biology), class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to brittle star, ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to ...
; and Urochordata including sea squirts or tunicates.
Fungi
Over 10,000 species offungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
are known from marine environments. These are parasitic on marine algae or animals, or are saprobes on algae, corals, protozoan cysts, sea grasses, wood and other substrata, and can also be found in sea foam. Spores of many species have special appendages which facilitate attachment to the substratum. A very diverse range of unusual secondary metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s is produced by marine fungi.
Vertebrates
Fish
A reported 33,400 species of fish, including bony andcartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
, had been described by 2016, more than all other vertebrates combined. About 60% of fish species live in saltwater.
Reptiles
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s which inhabit or frequent the sea include sea turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerh ...
s, sea snake
Sea snakes, or coral reef snakes, are Elapidae, elapid snakes that inhabit Marine (ocean), marine environments for most or all of their lives. They belong to two subfamilies, Hydrophiinae and Sea krait, Laticaudinae. Hydrophiinae also includes ...
s, terrapins, the marine iguana, and the saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It ha ...
. Most extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
marine reptiles, except for some sea snakes, are oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
and need to return to land to lay their eggs. Thus most species, excluding sea turtles, spend most of their lives on or near land rather than in the ocean. Despite their marine adaptations, most sea snakes prefer shallow waters nearby land, around islands, especially waters that are somewhat sheltered, as well as near estuaries.Stidworthy J. 1974. Snakes of the World. Grosset & Dunlap Inc. 160 pp. . tp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/009/y0870e/y0870e65.pdf Sea snakesaFood and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
. Accessed 7 August 2007. Some
extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
marine reptiles, such as ichthyosaurs, evolved to be viviparous and had no requirement to return to land.
Birds
Birds adapted to living in the marine environment are often calledseabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
s. Examples include albatross
Albatrosses, of the biological family Diomedeidae, are large seabirds related to the procellariids, storm petrels, and diving petrels in the order Procellariiformes (the tubenoses). They range widely in the Southern Ocean and the North Paci ...
, penguin
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae () of the order Sphenisciformes (). They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere. Only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is equatorial, with a sm ...
s, gannets, and auk
Auks or alcids are birds of the family Alcidae in the order Charadriiformes. The alcid family includes the Uria, murres, guillemots, Aethia, auklets, puffins, and Brachyramphus, murrelets. The family contains 25 extant or recently extinct speci ...
s. Although they spend most of their lives in the ocean, species such as gull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the subfamily Larinae. They are most closely related to terns and skimmers, distantly related to auks, and even more distantly related to waders. Until the 21st century, most gulls were placed ...
s can often be found thousands of miles inland.
Mammals
There are five main types of marine mammals:cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively c ...
ns ( toothed whales and baleen whale
Baleen whales (), also known as whalebone whales, are marine mammals of the order (biology), parvorder Mysticeti in the infraorder Cetacea (whales, dolphins and porpoises), which use baleen plates (or "whalebone") in their mouths to sieve plankt ...
s); sirenians such as manatee
Manatees (, family (biology), family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivory, herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing t ...
s; pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant families Odobenidae (whose onl ...
s including seals and the walrus; sea otters; and the
polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can Hybrid (biology), interbreed. The polar bear is the largest extant species of bear ...
. All are air-breathing, meaning that while some such as the sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the Genus (biology), genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the s ...
can dive for prolonged periods, all must return to the surface to breathe.
Subfields
Themarine ecosystem
Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in Saline water, waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 7 ...
is large, and thus there are many sub-fields of marine biology. Most involve studying specializations of particular animal groups, such as phycology, invertebrate zoology and ichthyology. Other subfields study the physical effects of continual immersion in sea water and the ocean in general, adaptation to a salty environment, and the effects of changing various oceanic properties on marine life. A subfield of marine biology studies the relationships between oceans and ocean life, and global warming and environmental issues (such as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
displacement). Recent marine biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists ...
has focused largely on marine biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is loosely defined as a molecule produced by a living organism and essential to one or more typically biological processes. Biomolecules include large macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids ...
s, especially protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, that may have uses in medicine or engineering. Marine environments are the home to many exotic biological materials that may inspire biomimetic materials.
Through constant monitoring of the ocean, there have been discoveries of marine life which could be used to create remedies for certain diseases such as cancer and leukemia. In addition, Ziconotide, an approved drug used to treat pain, was created from a snail which resides in the ocean.
Related fields
Marine biology is a branch ofbiology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
. It is closely linked to oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology.
It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of to ...
, especially biological oceanography
Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics, chemistry, and geology of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography may also be referred to as ocean ecology, in which the root word of ecology ...
, and may be regarded as a sub-field of marine science. It also encompasses many ideas from ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
. Fisheries science and marine conservation can be considered partial offshoots of marine biology (as well as environmental studies
Environmental studies (EVS or EVST) is a multidisciplinary academic field which systematically studies human behavior, human interaction with the Natural environment, environment. Environmental studies connects principles from the physical sci ...
). Marine chemistry, physical oceanography and atmospheric science
Atmospheric science is the study of the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Clima ...
s are also closely related to this field.
Distribution factors
An active research topic in marine biology is to discover and map the life cycles of various species and where they spend their time. Technologies that aid in this discovery include pop-up satellite archival tags, acoustic tags, and a variety of other data loggers. Marine biologists study how theocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s, tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s and many other oceanic factors affect ocean life forms, including their growth, distribution and well-being. This has only recently become technically feasible with advances in GPS and newer underwater visual devices.
Most ocean life breeds in specific places, nests in others, spends time as juveniles in still others, and in maturity in yet others. Scientists know little about where many species spend different parts of their life cycles especially in the infant and juvenile years. For example, it is still largely unknown where juvenile sea turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerh ...
s and some shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s in the first year of their life travel. Recent advances in underwater tracking devices are illuminating what we know about marine organisms that live at great ocean depths. The information that pop-up satellite archival tags gives aids in fishing closures for certain times of the year and the development of marine protected areas. This data is important to both scientists and fishermen because they are discovering that, by restricting commercial fishing in one small area, they can have a large impact in maintaining a healthy fish population in a much larger area.
History
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
(384–322 BC), who made many observations of life in the sea around Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of , with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, eighth largest ...
, laying the foundation for many future discoveries. In 1768, Samuel Gottlieb Gmelin (1744–1774) published the ''Historia Fucorum'', the first work dedicated to marine algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
and the first book on marine biology to use the new binomial nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, altho ...
of Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
. It included elaborate illustrations of seaweed and marine algae on folded leaves. The British naturalist Edward Forbes (1815–1854) is generally regarded as the founder of the science of marine biology. The pace of oceanographic and marine biology studies quickly accelerated during the course of the 19th century.
 The observations made in the first studies of marine biology fueled the
The observations made in the first studies of marine biology fueled the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
and exploration that followed. During this time, a vast amount of knowledge was gained about the life that exists in the oceans of the world. Many voyages contributed significantly to this pool of knowledge. Among the most significant were the voyages of where Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
came up with his theories of evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
and on the formation of coral reefs
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
...
. Another important expedition was undertaken by HMS ''Challenger'', where findings were made of unexpectedly high species diversity among fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
stimulating much theorizing by population ecologists on how such varieties of life could be maintained in what was thought to be such a hostile environment. This era was important for the history of marine biology but naturalists were still limited in their studies because they lacked technology that would allow them to adequately examine species that lived in deep parts of the oceans.
The creation of marine laboratories was important because it allowed marine biologists to conduct research and process their specimens from expeditions. The oldest marine laboratory in the world, Station biologique de Roscoff, was established in Concarneau, France founded by the College of France in 1859. In the United States, the Scripps Institution of Oceanography dates back to 1903, while the prominent Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute was founded in 1930. The development of technology such as sound navigation and ranging, scuba diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub ...
gear, submersible
A submersible is an underwater vehicle which needs to be transported and supported by a larger ship, watercraft or dock, platform. This distinguishes submersibles from submarines, which are self-supporting and capable of prolonged independent ope ...
s and remotely operated vehicles allowed marine biologists to discover and explore life in deep oceans that was once thought to not exist. Public interest in the subject continued to develop in the post-war years with the publication of Rachel Carson's sea trilogy (1941–1955).
In 1960, the bathyscaphe
A bathyscaphe () is a free-diving, self-propelled deep-sea submersible, consisting of a crew cabin similar to a '' Bathysphere'', but suspended below a float rather than from a surface cable, as in the classic ''Bathysphere'' design.
The floa ...
Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
descended the furthest point man had yet traveled, bottoming Challenger's Deep at 35,797 feet. The vessel was captained by Jacques Piccard and Don Walsh, whose discoveries while at the bottom of the ocean bolstered scientific discussion and interest about life in the hadal zone.
See also
* Acoustic ecology *Aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
* Bathymetry
* Biological oceanography
Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics, chemistry, and geology of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography may also be referred to as ocean ecology, in which the root word of ecology ...
* Effects of climate change on oceans
There are many effects of climate change on oceans. One of the most important is an increase in ocean temperatures. More frequent marine heatwaves are linked to this. The rising temperature contributes to a Sea level rise, rise in sea levels due ...
* Freshwater biology
* Marine habitat concrete
* Modular ocean model
* Oceanic basin
In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, most of the ocean basins are large Structural basin, geologic basins that are below sea level.
Most commonly the ocea ...
* Oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
* Phycology
Lists
* Glossary of ecology * Index of biology articles * Large marine ecosystem * List of ecologists * List of marine biologists * List of marine ecoregions (WWF) * Outline of biology * Outline of ecologyReferences
Further references
* Morrissey J and Sumich J (2011''Introduction to the Biology of Marine Life''
Jones & Bartlett Publishers. . * Mladenov, Philip V., Marine Biology: A Very Short Introduction, 2nd edn (Oxford, 2020; online edn, Very Short Introductions online, Feb. 2020), http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/actrade/9780198841715.001.0001, accessed 21 Jun. 2020.
External links
Smithsonian Ocean Portal
Marine Conservation Society
Marine Ecology – an evolutionary perspective
Free special issue: Marine Biology in Time and Space
Creatures of the deep ocean
– ''National Geographic'' documentary, 2010.
Exploris
– From the University of Washington Library
Marine Training Portal
– Portal grouping training initiatives in the field of Marine Biology {{DEFAULTSORT:Marine Biology Biological oceanography Fisheries science >