gastritis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gastritis is the
 Acute erosive gastritis typically involves discrete foci of surface necrosis due to damage to mucosal defenses. NSAIDs inhibit
Acute erosive gastritis typically involves discrete foci of surface necrosis due to damage to mucosal defenses. NSAIDs inhibit
 Often, a diagnosis can be made based on patients' description of their symptoms. Other methods which may be used to verify gastritis include:
* Blood tests:
** Blood cell count
** Presence of ''H. pylori''
**
Often, a diagnosis can be made based on patients' description of their symptoms. Other methods which may be used to verify gastritis include:
* Blood tests:
** Blood cell count
** Presence of ''H. pylori''
**
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Other possible symptoms include nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, bloating, loss of appetite and heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation felt behind the breastbone. It is a symptom that is commonly linked to acid reflux and is often triggered by food, particularly fatty, sugary, spicy, chocolate, citrus, onion-based and tomato-based products. Ly ...
. Complications may include stomach bleeding, stomach ulcers, and stomach tumors. When due to autoimmune problems, low red blood cells due to not enough vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino a ...
may occur, a condition known as pernicious anemia.
Common causes include infection with '' Helicobacter pylori'' and use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs). When caused by ''H. pylori'' this is now termed ''Helicobacter pylori'' induced gastritis, and included as a listed disease in ICD11. Less common causes include alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, severe illness, autoimmune problems, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
and Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
. Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
, a type of X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
known as an upper gastrointestinal series, blood tests, and stool tests may help with diagnosis. Other conditions with similar symptoms include inflammation of the pancreas, gallbladder problems, and peptic ulcer disease.
Prevention is by avoiding things that cause the disease. Treatment includes medications such as antacid
An antacid is a substance which neutralization (chemistry), neutralizes gastric acid, stomach acidity and is used to relieve heartburn, indigestion, or an upset stomach. Some antacids have been used in the treatment of constipation and diarrhe ...
s, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of gastric acid, stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase, H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. The body ...
. During an acute attack drinking viscous lidocaine may help. If gastritis is due to NSAIDs these may be stopped. If ''H. pylori'' is present it may be treated with a combination of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s such as amoxicillin and clarithromycin. For those with pernicious anemia, vitamin B12 supplements are recommended either by mouth or by injection. People are usually advised to avoid foods that bother them.
Gastritis is believed to affect about half of people worldwide. In 2013 there were approximately 90 million new cases of the condition. As people get older the disease becomes more common. It, along with a similar condition in the first part of the intestines known as duodenitis, resulted in 50,000 deaths in 2015. ''H. pylori'' was first discovered in 1981 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren.
Signs and symptoms
Many people with gastritis experience no symptoms at all. However, upper central abdominal pain is the most common symptom; the pain may be dull, vague, burning, aching, gnawing, sore, or sharp. Pain is usually located in the upper central portion of theabdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, but it may occur anywhere from the upper left portion of the abdomen around to the back.
Other signs and symptoms may include the following:
* Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
* Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
(may be clear, green or yellow, blood-streaked or completely bloody depending on the severity of the stomach inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
)
* Belching (does not usually relieve stomach pain if present)
* Bloating
Abdominal bloating (or simply bloating) is a short-term disease that affects the gastrointestinal tract. Bloating is generally characterized by an excess buildup of gas, air or fluids in the stomach. A person may have feelings of tightness, pressu ...
* Early satiety
* Loss of appetite
Causes
There are two categories of gastritis depending on the cause of the disease. There is erosive gastritis, for which the common causes are stress,alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
, some drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
s, such as aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and Crohn's disease. And, there is non-erosive gastritis, for which the most common cause is a '' Helicobacter pylori'' infection.
''Helicobacter pylori''
'' Helicobacter pylori'' colonizes the stomachs of more than half of the world's population, and the infection continues to play a key role in the pathogenesis of a number of gastroduodenal diseases. Colonization of the gastric mucosa with ''Helicobacter pylori'' results in the development of chronic gastritis in infected individuals and, in a subset of patients, chronic gastritis progresses to complications (e.g., ulcer disease, stomach cancers, and some distinct extragastric disorders). Gastritis caused by ''H. pylori'' infection is termed ''Helicobacter pylori'' induced gastritis, and listed as a disease in ICD11. More than 80% of individuals infected with the bacterium areasymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
and it has been postulated that it may play an important role in the natural stomach ecology.
Critical illness
Gastritis may also develop after major surgery or traumatic injury (" Cushing ulcer"), burns (" Curling ulcer"), or severe infections. Gastritis may also occur in those who have had weight loss surgery resulting in the banding or reconstruction of the digestive tract.Diet
Evidence does not support a role for specific foods, including spicy foods and coffee, in the development of peptic ulcers. People are usually advised to avoid foods that bother them. There is little specific advice on diet published by authoritative sources. TheNational Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ...
of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
advises avoiding spicy, acidic or fried foods which may irritate the stomach.
Pathophysiology
Acute
 Acute erosive gastritis typically involves discrete foci of surface necrosis due to damage to mucosal defenses. NSAIDs inhibit
Acute erosive gastritis typically involves discrete foci of surface necrosis due to damage to mucosal defenses. NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase-1
Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1), also known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (Human Genome Organisation, HUGO PTGS1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTGS1'' gene. In humans it is one of Cyclooxygenase-3, three cyclooxygenases.
...
, or COX-1, an enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of eicosanoids in the stomach, which increases the possibility of peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is when the inner part of the stomach's gastric mucosa (lining of the stomach), the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus, gets damaged. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while ...
s forming. Also, NSAIDs, such as aspirin, reduce a substance that protects the stomach called prostaglandin. These drugs used in a short period are not typically dangerous. However, regular use can lead to gastritis. Additionally, severe physiologic stress from sepsis, hypoxia, trauma, or surgery is also a common etiology for acute erosive gastritis, resulting in " stress ulcers". This form of gastritis can occur in more than 5% of hospitalized patients.
Also, alcohol consumption does not cause chronic gastritis. It does, however, erode the mucosal lining of the stomach; low doses of alcohol stimulate hydrochloric acid secretion. High doses of alcohol do not stimulate secretion of acid.
Chronic
Chronic gastritis refers to a wide range of problems of the gastric issues. The immune system makes proteins and antibodies that fight infections in the body to maintain a homeostatic condition. In some disorders the body targets the stomach as if it were a foreign protein or pathogen; it makes antibodies against, severely damages, and may even destroy the stomach or its lining. In some cases bile, normally used to aid digestion in the small intestine, will enter through the pyloric valve of the stomach if it has been removed during surgery or does not work properly, also leading to gastritis. Gastritis may also be caused by other medical conditions, includingHIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
, Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
, certain connective tissue disorders, and liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
or kidney failure. Since 1992, chronic gastritis lesions are classified according to the Sydney system.
Metaplasia
Mucous gland metaplasia, the reversible replacement of differentiated cells, occurs in the setting of severe damage of the gastric glands, which then waste away ( atrophic gastritis) and are progressively replaced by mucous glands. Gastric ulcers may develop; it is unclear if they are the causes or the consequences. Intestinal metaplasia typically begins in response to chronic mucosal injury in the antrum and may extend to the body. Gastric mucosa cells change to resemble intestinal mucosa and may even assume absorptive characteristics. Intestinal metaplasia is classified histologically as complete or incomplete. With complete metaplasia, gastric mucosa is completely transformed into small-bowel mucosa, both histologically and functionally, with the ability to absorb nutrients and secrete peptides. In incomplete metaplasia, the epithelium assumes a histologic appearance closer to that of the large intestine and frequently exhibits dysplasia.Diagnosis
 Often, a diagnosis can be made based on patients' description of their symptoms. Other methods which may be used to verify gastritis include:
* Blood tests:
** Blood cell count
** Presence of ''H. pylori''
**
Often, a diagnosis can be made based on patients' description of their symptoms. Other methods which may be used to verify gastritis include:
* Blood tests:
** Blood cell count
** Presence of ''H. pylori''
** Liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
, gallbladder, or pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
functions
* Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, m ...
* Stool sample, to look for blood in the stool
* X-rays
* Endoscopy, to check for stomach lining inflammation and mucous erosion
* Stomach biopsy, to test for gastritis and other conditions
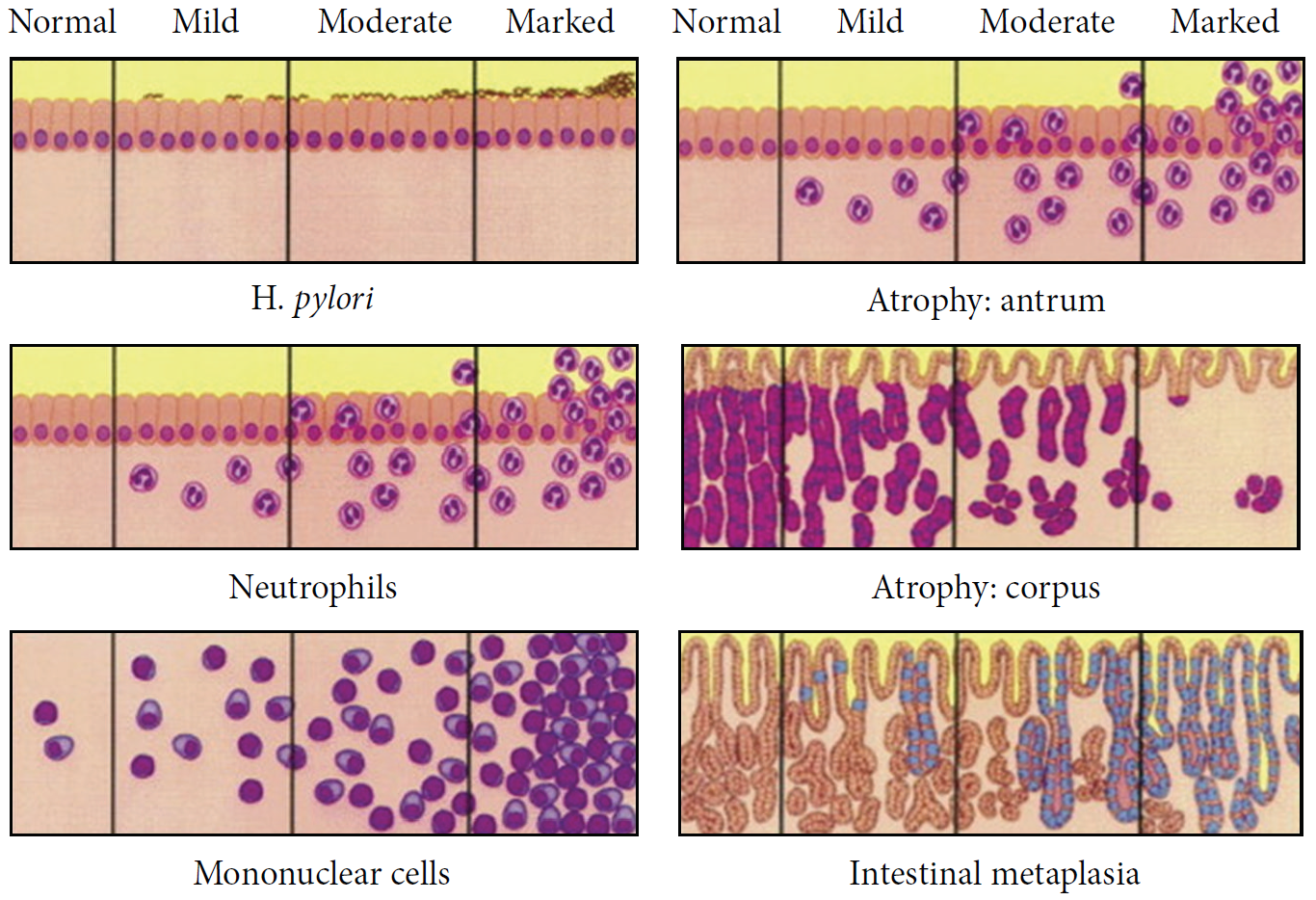
The OLGA staging frame of chronic gastritis on histopathology. Atrophy is scored as the percentage of atrophic glands and scored on a four-tiered scale. No atrophy (0%) = score 0; mild atrophy (1–30%) = score 1; moderate atrophy (31–60%) = score 2; severe atrophy (>60%) = score 3. These scores (0–3) are used in the OLGA staging assessment in each 10 compartment:
Treatment
Antacid
An antacid is a substance which neutralization (chemistry), neutralizes gastric acid, stomach acidity and is used to relieve heartburn, indigestion, or an upset stomach. Some antacids have been used in the treatment of constipation and diarrhe ...
s are a common treatment for mild to medium gastritis. When antacids do not provide enough relief, medications such as H2 blockers and proton-pump inhibitors that help reduce the amount of acid are often prescribed.
Cytoprotective agents are designed to help protect the tissues that line the stomach and small intestine. They include the medications sucralfate and misoprostol. If NSAIDs are being taken regularly, one of these medications to protect the stomach may also be taken. Another cytoprotective agent is bismuth subsalicylate.
Several regimens are used to treat ''H. pylori'' infection. Most use a combination of two antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
and a proton pump inhibitor. Sometimes bismuth is added to the regimen.
History
In 1,000 A.D,Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
first gave the description of stomach cancer. In 1728, German physician Georg Ernst Stahl first coined the term "gastritis". Italian anatomical pathologist Giovanni Battista Morgagni
Giovanni Battista Morgagni (25 February 1682 – 6 December 1771) was an Italian anatomy, anatomist, generally regarded as the father of modern anatomical pathology, who taught thousands of medical students from many countries during his 56 year ...
further described the characteristics of gastric inflammation. He described the characteristics of erosive or ulcerative gastritis and erosive gastritis. Between 1808 and 1831, French physician François-Joseph-Victor Broussais gathered information from the autopsies of dead French soldiers. He described chronic gastritis as "Gastritide" and erroneously believed that gastritis was the cause of ascites, typhoid fever, and meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasion ...
. In 1854, Charles Handfield Jones and Wilson Fox described the microscopic changes of stomach inner lining in gastritis which existed in diffuse and segmental forms. In 1855, Baron Carl von Rokitansky first described hypertrophic gastritis. In 1859, British physician, William Brinton first described about acute, subacute, and chronic gastritis. In 1870, Samuel Fenwick noted that pernicious anemia causes glandular atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
in gastritis. German surgeon Georg Ernst Konjetzny noticed that both gastric ulcer and gastric cancer are the results of gastric inflammation. Shields Warren and Willam A. Meissner described the intestinal metaplasia of the stomach as a feature of chronic gastritis.
See also
*Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
* Esophagitis
References
Further reading
*External links
{{Authority control Inflammations Conditions diagnosed by stool test Stomach disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate