|
Satiety
Satiety ( /səˈtaɪ.ə.ti/ ''sə-TYE-ə-tee'') is a state or condition of fullness gratified beyond the point of satisfaction, the opposite of hunger. Following satiation (meal termination), satiety is a feeling of fullness lasting until the next meal. When food is present in the GI tract after a meal, satiety signals overrule hunger signals, but satiety slowly fades as hunger increases. The satiety center in animals is located in ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. Mechanism Satiety is signaled through the vagus nerve as well as circulating hormones. During intake of a meal, the stomach must stretch to accommodate this increased volume. This gastric accommodation activates stretch receptors in the proximal (upper) portion of the stomach. These receptors then signal through afferent vagus nerve fibers to the hypothalamus, increasing satiety. Signalling factors In addition, as the food moves into the duodenum, duodenal cells release multiple substances that affect di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satiety Value
Satiety value is the degree at which food gives a human the feeling of satiety per calorie. The concept of the Satiety Value and Satiety Index was developed by Australians, Australian researcher and doctor, Susanna Holt. Highest satiety value is expected when the food that remains in the stomach for a longer period produces greatest functional activity of the organ. Limiting the food intake after reaching the satiety value helps reduce obesity problems. Foods with the most satiation per calorie are often: * high in certain Proteinase inhibitors in plants, proteinase inhibitors that suppress appetite - e.g. potatoes * high in protein leverage hypothesis, protein (which takes longer to digest than other energy sources) - e.g. meat * low in glycemic index (in which the carbohydrates take longer to digest) - e.g. oats * high in dietary fibre, fibre (which takes longer to digest than low fibre foods) - e.g. fruit * low in calories - e.g. vegetables * solid (which takes longer to digest t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventromedial Nucleus
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN, VMH or ventromedial hypothalamus) is a nucleus of the hypothalamus. In 2007, Kurrasch ''et al''. found that the ventromedial hypothalamus is a distinct morphological nucleus involved in terminating hunger, fear, thermoregulation, and sexual activity. This nuclear region is involved in the recognition of the feeling of fullness. Structure It has four subdivisions: * Anterior (VMHa) * Dorsomedial (VMHdm) * Ventrolateral (VMHvl) * Central (VMHc) These subdivisions differ anatomically, neurochemically, and behaviorally. Function The ventromedial nucleus (VMN) is most commonly associated with satiety. Early studies showed that VMN lesions caused over-eating and obesity in rats. However, the interpretation of these experiments was summarily discredited when Gold's research demonstrated that precision lesioning of the VMN did not result in hyperphagia. Nevertheless, numerous studies have shown that the immediacy of hyperphagia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the Basal (anatomy), basal part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is about the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus has the function of regulating certain metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls thermoregulation, body temperature, hunger (physiology), hunger, important aspects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunger (physiology)
Hunger is a sensation that motivates the consumption of food. The sensation of hunger typically manifests after only a few hours without eating and is generally considered to be unpleasant. Satiety occurs between 5 and 20 minutes after eating. There are several theories about how the feeling of hunger arises. The desire to eat food, or appetite, is another sensation experienced with regard to eating. The term ''hunger'' is also the most commonly used in social science and policy discussions to describe the condition of people who suffer from a chronic lack of sufficient food and constantly or frequently experience the sensation of hunger, and can lead to malnutrition. A healthy, well-nourished individual can survive for weeks without food intake (see fasting), with claims ranging from three to ten weeks. Satiety is the opposite of hunger; it is the sensation of feeling full. Hunger pangs The physical sensation of hunger is related to the contractions of the muscles of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin (CCK or CCK-PZ; from Greek ''chole'', "bile"; ''cysto'', "sac"; ''kinin'', "move"; hence, ''move the bile-sac (gallbladder)'') is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin, formerly called pancreozymin, is synthesized and secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum, the first segment of the small intestine. Its presence causes the release of pancreatic juice from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder. History Evidence that the small intestine controls the release of bile was uncovered as early as 1856, when French physiologist Claude Bernard showed that when dilute acetic acid was applied to the orifice of the bile duct, the duct released bile into the duodenum. In 1903, the French physiologist showed that this reflex was not mediated by the nervous system. In 1904, the French physiologist Charles Fleig showed that the discharge of bile was mediated by a substance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagon-like Peptide-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30- or 31-amino-acid-long peptide hormone deriving from tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon peptide. It is produced and secreted by intestinal enteroendocrine L-cells and certain neurons within the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem upon food consumption. The initial product GLP-1 (1–37) is susceptible to amidation and proteolytic cleavage, which gives rise to the two truncated and equipotent biologically active forms, GLP-1 (7–36) amide and GLP-1 (7–37). Active GLP-1 protein secondary structure includes two α-helices from amino acid position 13–20 and 24–35 separated by a linker region. Alongside glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), GLP-1 is an incretin; thus, it has the ability to decrease blood sugar levels in a glucose-dependent manner by enhancing the secretion of insulin. Beside the insulinotropic effects, GLP-1 has been associated with numerous regulatory and prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghrelin
Ghrelin (; or lenomorelin, INN) is a hormone primarily produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and stimulating the secretion of gastric acid. Ghrelin activates cells in the anterior pituitary gland and hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, including neuropeptide Y neurons that initiate appetite. Ghrelin stimulates brain structures having a specific receptor – the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1A ( GHSR-1A). Ghrelin also participates in regulation of reward cognition, learning and memory, the sleep-wake cycle, taste sensation, reward behavior, and glucose metabolism. History and name Ghrelin was discovered after the ghrelin receptor (called growth hormone secretag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
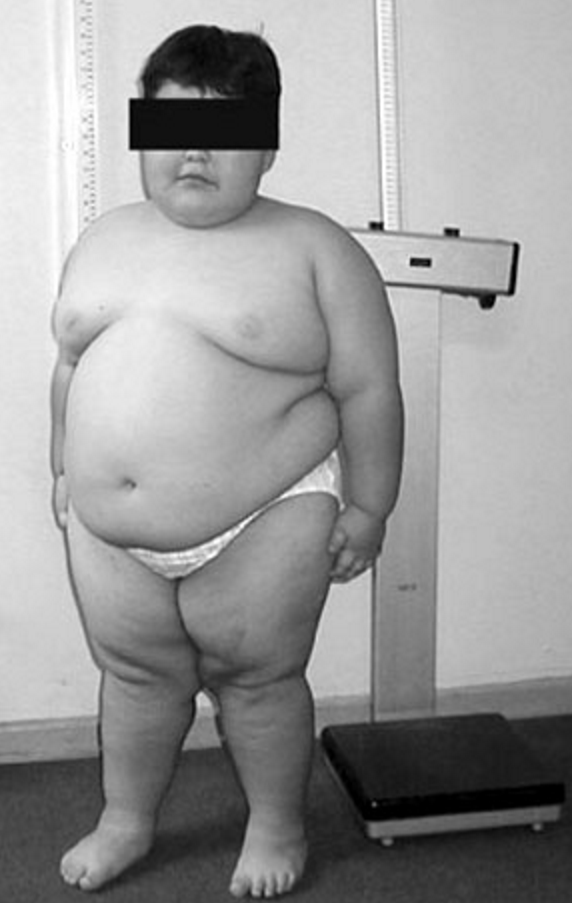
Prader–Willi Syndrome
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a rare genetic disorder caused by a loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15. In newborns, symptoms include hypotonia, weak muscles, poor feeding, and slow development. Beginning in childhood, those affected become constantly hungry, which often leads to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mild to moderate intellectual impairment and Behavioural problems, behavioral problems are also typical of the disorder. Often, affected individuals have a narrow forehead, small hands and feet, short height, and light skin and hair. Most are Infertility, unable to have children. About 74% of cases occur when part of the father's chromosome 15 is deleted. In another 25% of cases, the affected person has Uniparental disomy, two copies of the maternal chromosome 15 from the mother and lacks the paternal copy. As parts of the chromosome from the mother are turned off through Genomic imprinting, imprinting, they end up with no working copies of certain genes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronunciation Respelling Key
A pronunciation respelling for English is a notation used to convey the pronunciation of words in the English language, which do not have a phonemic orthography (i.e. the spelling does not reliably indicate pronunciation). There are two basic types of pronunciation respelling: * " Phonemic" systems, as commonly found in American dictionaries, consistently use one symbol per English phoneme. These systems are conceptually equivalent to the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) commonly used in bilingual dictionaries and scholarly writings but tend to use symbols based on English rather than Romance-language spelling conventions (e.g. ''ē'' for IPA ) and avoid non-alphabetic symbols (e.g. ''sh'' for IPA ). * On the other hand, "non-phonemic" or "newspaper" systems, commonly used in newspapers and other non-technical writings, avoid diacritics and literally "respell" words making use of well-known English words and spelling conventions, even though the resulting system may n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GI Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afferent Nerve Fiber
Afferent nerve fibers are axons (nerve fibers) of sensory neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Many afferent projections ''arrive'' at a particular brain region. In the peripheral nervous system, afferent nerve fibers are part of the sensory nervous system and arise from outside of the central nervous system. Sensory and mixed nerves contain afferent fibers. Structure Afferent neurons are pseudounipolar neurons that have a single process leaving the cell body dividing into two branches: the long one towards the sensory organ, and the short one toward the central nervous system (e.g. spinal cord). These cells do have sensory afferent dendrites, similar to those typically inherent in neurons. They have a smooth and rounded cell body located in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. Just outside the spinal cord, thousands of afferent neuronal cell bodies are aggregated in a swelling in the dorsal root known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |