currency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to
 At around the same time in the medieval Islamic world, a vigorous monetary economy was created during the 7th–12th centuries on the basis of the expanding levels of circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar). Innovations introduced by Muslim economists, traders and merchants include the earliest uses of credit, cheques, promissory notes, savings accounts, transaction accounts, loaning, trusts, exchange rates, the transfer of credit and debt, and banking institutions for loans and deposits.
In Europe, paper currency was first introduced on a regular basis in
At around the same time in the medieval Islamic world, a vigorous monetary economy was created during the 7th–12th centuries on the basis of the expanding levels of circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar). Innovations introduced by Muslim economists, traders and merchants include the earliest uses of credit, cheques, promissory notes, savings accounts, transaction accounts, loaning, trusts, exchange rates, the transfer of credit and debt, and banking institutions for loans and deposits.
In Europe, paper currency was first introduced on a regular basis in
 The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. (See Fiat currency.)
The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. (See Fiat currency.)
government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
agencies.
Other definitions of the term ''currency'' appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote, coin, and money. This article uses the definition which focuses on the currency systems of countries.
One can classify currencies into three monetary systems: fiat money
Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tende ...
, commodity money, and representative money, depending on what guarantees a currency's value (the economy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
at large vs. the government's precious metal reserves). Some currencies function as legal tender in certain jurisdictions, or for specific purposes, such as payment to a government ( taxes), or government agencies (fees, fines). Others simply get traded for their economic value.
The concept of a digital currency has arisen in recent years. Whether government-backed digital notes and coins (such as the digital renminbi in China, for example) will be successfully developed and implemented remains unknown. Digital currencies that are not issued by a government monetary authority, such as cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, are different because their value is market-dependent and has no safety net. Various countries have expressed concern about the opportunities that cryptocurrencies create for illegal activities such as scams, ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that Encryption, encrypts the victim's personal data until a ransom is paid. Difficult-to-trace Digital currency, digital currencies such as paysafecard or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency, cryptocurrencies are com ...
( extortion), money laundering and terrorism. In 2014, the United States IRS advised that virtual currency is treated as property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, re ...
for federal income-tax purposes, and it provides examples of how long-standing tax principles applicable to transactions involving property apply to virtual currency.
History
Early currency
Originally, currency was a form of receipt, representing grain stored in temple granaries in Sumer in ancientMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
. In this first stage of currency, metals were used as symbols to represent value stored in the form of commodities. This formed the basis of trade in the Fertile Crescent for over 1500 years. However, the collapse of the Near Eastern trading system pointed to a flaw: in an era where there was no place that was safe to store value, the value of a circulating medium could only be as sound as the forces that defended that store. A trade could only reach as far as the credibility of that military. By the late Bronze Age, however, a series of treaties had established safe passage for merchants around the Eastern Mediterranean, spreading from Minoan Crete and Mycenae in the northwest to Elam and Bahrain in the southeast. It is not known what was used as a currency for these exchanges, but it is thought that oxhide-shaped ingots of copper, produced in Cyprus, may have functioned as a currency.
It is thought that the increase in piracy and raiding associated with the Bronze Age collapse, possibly produced by the Peoples of the Sea, brought the trading system of oxhide ingots to an end. It was only the recovery of Phoenician trade in the 10th and 9th centuries BC that led to a return to prosperity, and the appearance of real coinage, possibly first in Anatolia with Croesus of Lydia and subsequently with the Greeks and Persians. In Africa, many forms of value store have been used, including beads, ingots, ivory, various forms of weapons, livestock, the manilla currency, shell money, and ochre and other earth oxides. The manilla rings of West Africa were one of the currencies used from the 15th century onwards to sell slaves. African currency is still notable for its variety, and in many places, various forms of barter still apply.
Coinage
The prevalence of metal coins possibly led to the metal itself being the store of value: first copper, then bothsilver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
and gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, and at one point also bronze. Today other non-precious metals are used for coins. Metals were mined, weighed, and stamped into coins. This was to assure the individual accepting the coin that he was getting a certain known weight of precious metal. Coins could be counterfeited, but the existence of standard coins also created a new unit of account, which helped lead to banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
. Archimedes' principle provided the next link: coins could now be easily tested for their fine weight of the metal, and thus the value of a coin could be determined, even if it had been shaved, debased or otherwise tampered with (see Numismatics).
Most major economies using coinage had several tiers of coins of different values, made of copper, silver, and gold. Gold coins were the most valuable and were used for large purchases, payment of the military, and backing of state activities. Units of account were often defined as the value of a particular type of gold coin. Silver coins were used for midsized transactions, and sometimes also defined a unit of account, while coins of copper or silver, or some mixture of them (see debasement), might be used for everyday transactions. This system had been used in ancient India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
since the time of the Mahajanapadas. The exact ratios between the values of the three metals varied greatly between different eras and places; for example, the opening of silver mines in the Harz mountains of central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
made silver relatively less valuable, as did the flood of New World silver after the Spanish conquests. However, the rarity of gold consistently made it more valuable than silver, and likewise silver was consistently worth more than copper.
Paper money
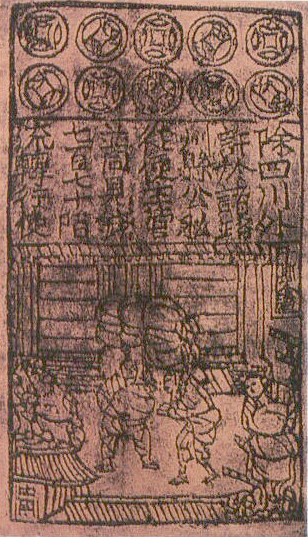
In premodern China, the need for lending and for a medium of exchange that was less physically cumbersome than large numbers of copper coins led to the introduction of paper money, i.e. banknotes. Their introduction was a gradual process that lasted from the lateTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
(618–907) into the Song dynasty (960–1279). It began as a means for merchants to exchange heavy coinage for receipt
A receipt (also known as a packing list, packing slip, packaging slip, (delivery) docket, shipping list, delivery list, bill of the parcel, Manifest (transportation), manifest, or customer receipt) is a document acknowledging that something h ...
s of deposit issued as promissory notes by wholesalers' shops. These notes were valid for temporary use in a small regional territory. In the 10th century, the Song dynasty government began to circulate these notes amongst the traders in its monopolized salt industry. The Song government granted several shops the right to issue banknotes, and in the early 12th century the government finally took over these shops to produce state-issued currency. Yet the banknotes issued were still only locally and temporarily valid: it was not until the mid 13th century that a standard and uniform government issue of paper money became an acceptable nationwide currency. The already widespread methods of woodblock printing and then Bi Sheng's movable type
Movable type (US English; moveable type in British English) is the system and technology of printing and typography that uses movable Sort (typesetting), components to reproduce the elements of a document (usually individual alphanumeric charac ...
printing by the 11th century were the impetus for the mass production of paper money in premodern China.
 At around the same time in the medieval Islamic world, a vigorous monetary economy was created during the 7th–12th centuries on the basis of the expanding levels of circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar). Innovations introduced by Muslim economists, traders and merchants include the earliest uses of credit, cheques, promissory notes, savings accounts, transaction accounts, loaning, trusts, exchange rates, the transfer of credit and debt, and banking institutions for loans and deposits.
In Europe, paper currency was first introduced on a regular basis in
At around the same time in the medieval Islamic world, a vigorous monetary economy was created during the 7th–12th centuries on the basis of the expanding levels of circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar). Innovations introduced by Muslim economists, traders and merchants include the earliest uses of credit, cheques, promissory notes, savings accounts, transaction accounts, loaning, trusts, exchange rates, the transfer of credit and debt, and banking institutions for loans and deposits.
In Europe, paper currency was first introduced on a regular basis in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
in 1661 (although Washington Irving records an earlier emergency use of it, by the Spanish in a siege during the Conquest of Granada). As Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
was rich in copper, many copper coins were in circulation, but its relatively low value necessitated extraordinarily big coins, often weighing several kilograms.
The advantages of paper currency were numerous: it reduced the need to transport gold and silver, which was risky; it facilitated loans of gold or silver at interest, since the underlying specie (money in the form of gold or silver coins rather than notes) never left the possession of the lender until someone else redeemed the note; and it allowed a division of currency into credit- and specie-backed forms. It enabled the sale of investment in joint-stock companies and the redemption of those shares in a paper.
But there were also disadvantages. First, since a note has no intrinsic value, there was nothing to stop issuing authorities from printing more notes than they had specie to back them with. Second, because this increased the money supply, it increased inflationary pressures, a fact observed by David Hume in the 18th century. Thus paper money would often lead to an inflationary bubble, which could collapse if people began demanding hard money, causing the demand for paper notes to fall to zero. The printing of paper money was also associated with wars, and financing of wars, and therefore regarded as part of maintaining a standing army. For these reasons, paper currency was held in suspicion and hostility in Europe and America. It was also addictive since the speculative profits of trade and capital creation were quite large. Major nations established mints to print money and mint coins, and branches of their treasury to collect taxes and hold gold and silver stock.
At that time, both silver and gold were considered a legal tender and accepted by governments for taxes. However, the instability in the exchange rate between the two grew over the course of the 19th century, with the increases both in the supply of these metals, particularly silver, and in trade. The parallel use of both metals is called bimetallism, and the attempt to create a bimetallic standard where both gold and silver backed currency remained in circulation occupied the efforts of inflationists. Governments at this point could use currency as an instrument of policy, printing paper currency such as the United States greenback, to pay for military expenditures. They could also set the terms at which they would redeem notes for specie, by limiting the amount of purchase, or the minimum amount that could be redeemed.
By 1900, most of the industrializing nations were on some form of gold standard, with paper notes and silver coins constituting the circulating medium. Private bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
s and governments across the world followed Gresham's law: keeping the gold and silver they received but paying out in notes. This did not happen all around the world at the same time, but occurred sporadically, generally in times of war or financial crisis, beginning in the early 20th century and continuing across the world until the late 20th century, when the regime of floating fiat currencies came into force. One of the last countries to break away from the gold standard was the United States in 1971, an action which was known as the Nixon shock. No country has an enforceable gold standard or silver standard currency system.
Banknote era
A banknote or a bill is a type of currency and it is commonly used as legal tender in many jurisdictions. Together with coins, banknotes make up the cash form of a currency. Banknotes were initially mostly paper, but Australia'sCommonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency that is responsible for scientific research and its commercial and industrial applications.
CSIRO works with leading organisations arou ...
developed a polymer currency in the 1980s; it went into circulation on the nation's bicentenary in 1988. Polymer banknotes had already been introduced in the Isle of Man in 1983. polymer currency is used in over 20 countries (over 40 if counting commemorative issues), and dramatically increases the life span of banknotes and reduces counterfeiting.
Modern currencies
 The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. (See Fiat currency.)
The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. (See Fiat currency.)
Currency codes and currency symbols
In 1978 the International Organization for Standardization published a system of three-digit alphabetic codes ( ISO 4217) to denote currencies. These codes are based on two initial letters allocated to a specific country and a final letter denoting a specific monetary unit of account. Many currencies use a currency symbol. These are not subject to international standards and are not unique: the dollar sign in particular has many uses.List of major world payment currencies
The following table are estimates of the 20 most frequently used currencies in world payments in April 2025 by SWIFT.Control and production
Commonly a central bank has the exclusive power to issue all forms of currency, including coins and banknotes (fiat money
Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tende ...
), and to restrain the circulation alternative currencies for its own area of circulation (a country or group of countries); it regulates the production of currency by banks ( credit) through monetary policy.
An exchange rate is a price at which two currencies can be exchanged against each other. This is used for trade between the two currency zones. Exchange rates can be classified as either floating or fixed. In the former, day-to-day movements in exchange rates are determined by the market; in the latter, governments intervene in the market to buy or sell their currency to balance supply and demand at a static exchange rate.
In cases where a country has control of its own currency, that control is exercised either by a central bank or by a Ministry of Finance. The institution that has control of monetary policy is referred to as the monetary authority. Monetary authorities have varying degrees of autonomy from the governments that create them. A monetary authority is created and supported by its sponsoring government, so independence can be reduced by the legislative or executive authority that creates it.
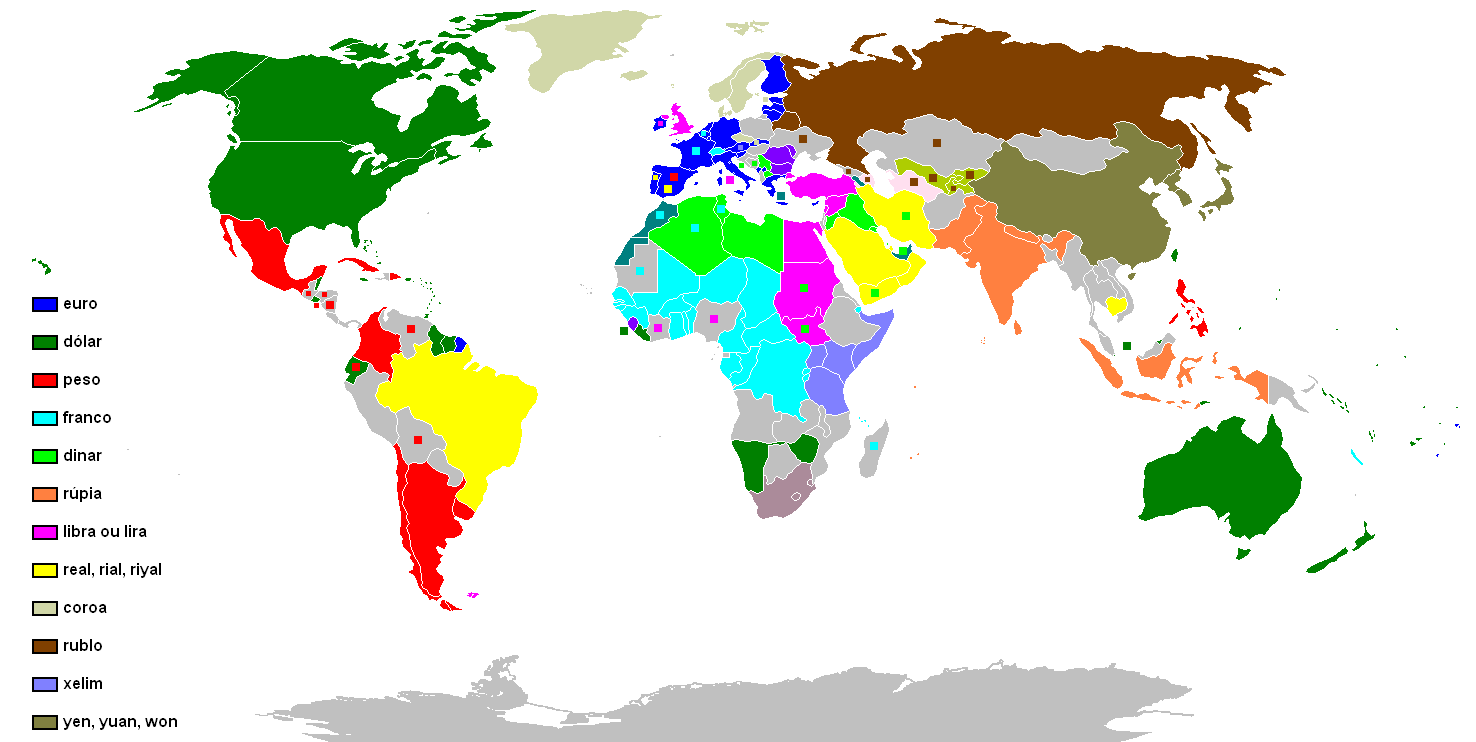
Several countries can use the same name for their own separate currencies (for example, a ''dollar'' in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
). By contrast, several countries can also use the same currency (for example, the euro or the CFA franc), or one country can declare the currency of another country to be legal tender. For example, Panama and El Salvador have declared US currency to be legal tender, and from 1791 to 1857, Spanish dollars were legal tender in the United States. At various times countries have either re-stamped foreign coins or used currency boards, issuing one note of currency for each note of a foreign government held, as Ecuador currently does.
Each currency typically has a main currency unit (the dollar, for example, or the euro) and a fractional unit, often defined as of the main unit: 100 cents = 1 dollar, 100 centimes = 1 franc, 100 pence = 1 pound, although units of or occasionally also occur. Some currencies do not have any smaller units at all, such as the Icelandic króna and the Japanese yen.
Mauritania and Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
are the only remaining countries that have theoretical fractional units not based on the decimal system; instead, the Mauritanian ouguiya is in theory divided into 5 khoums, while the Malagasy ariary is theoretically divided into 5 iraimbilanja. In these countries, words like ''dollar'' or ''pound'' "were simply names for given weights of gold". Due to inflation khoums and iraimbilanja have in practice fallen into disuse. (See non-decimal currencies for other historic currencies with non-decimal divisions.)
Currency convertibility
Subject to variation around the world, local currency can be converted to another currency or vice versa with or without central bank/government intervention. Such conversions take place in the foreign exchange market. Based on the above restrictions or free and readily conversion features, currencies are classified as: ; Fully convertible: When there are no restrictions or limitations on the amount of currency that can be traded on the international market, and the government does not artificially impose a fixed value or minimum value on the currency in international trade. The US dollar is one of the main fully convertible currencies. ; Partially convertible: Central banks control international investments flowing into and out of a country. While most domestic transactions are handled without any special requirements, there are significant restrictions on international investing, and special approval is often required in order to convert into other currencies. The Indian rupee and the renminbi are examples of partially convertible currencies. ; Nonconvertible: A government neither participates in the international currency market nor allows the conversion of its currency by individuals or companies. These currencies are also known as ''blocked'', e.g. the North Korean won and the Cuban peso. According to the three aspects of trade in goods and services, capital flows and national policies, the supply-demand relationship of different currencies determines the exchange ratio between currencies. Trade in goods and services Through cost transfer, goods and services circulating in the country (such as hotels, tourism, catering, advertising, household services) will indirectly affect the trade cost of goods and services and the price of export trade. Therefore, services and goods involved in international trade are not the only reason affecting the exchange rate. The large number of international tourists and overseas students has resulted in the flow of services and goods at home and abroad. It also represents that the competitiveness of global goods and services directly affects the change of international exchange rates. Capital flows National currencies will be traded on international markets for investment purposes. Investment opportunities in each country attract other countries into investment programs, so that these foreign currencies become the reserves of the central banks of each country. The exchange rate mechanism, in which currencies are quoted continuously between countries, is based on foreign exchange markets in which currencies are invested by individuals and traded or speculated by central banks and investment institutions. In addition, changes in interest rates, capital market fluctuations and changes in investment opportunities will affect the global capital inflows and outflows of countries around the world, and exchange rates will fluctuate accordingly. National policies The country's foreign trade, monetary and fiscal policies affect the exchange rate fluctuations. Foreign trade includes policies such as tariffs and import standards for commodity exports. The impact of monetary policy on the total amount and yield of money directly determines the changes in the international exchange rate. Fiscal policies, such as transfer payments, taxation ratios, and other factors, dominate the profitability of capital and economic development, and the ratio of national debt issuance to deficit determines the repayment capacity and credit rating of the country. Such policies determine the mechanism of linking domestic and foreign currencies and therefore have a significant impact on the generation of exchange rates. Currency convertibility is closely linked to economic development and finance. There are strict conditions for countries to achieve currency convertibility, which is a good way for countries to improve their economies. The currencies of some countries or regions in the world are freely convertible, such as the US dollar, Australian dollar and Japanese yen. The requirements for currency convertibility can be roughly divided into four parts: ; Sound microeconomic agency With a freely convertible currency, domestic firms will have to compete fiercely with their foreign counterparts. The development of competition among them will affect the implementation effect of currency convertibility. In addition, microeconomics is a prerequisite for macroeconomic conditions. ; The macroeconomic situation and policies are stable Since currency convertibility is the cross-border flow of goods and capital, it will have an impact on the macro economy. This requires that the national economy be in a normal and orderly state, that is, there is no serious inflation and economic overheating. In addition, the government should use macro policies to make mature adjustments to deal with the impact of currency exchange on the economy. ; A reasonable and open economy The maintainability of international balance of payments is the main performance of reasonable economic structure. Currency convertibility not only causes difficulties in the sustainability of international balance of payments but also affects the government's direct control over international economic transactions. To eliminate the foreign exchange shortage, the government needs adequate international reserves. ; Appropriate exchange rate regime and level The level of exchange rate is an important factor in maintaining exchange rate stability, both before and after currency convertibility. The exchange rate of freely convertible currency is too high or too low, which can easily trigger speculation and undermine the stability of macroeconomic and financial markets. Therefore, to maintain the level of exchange rate, a proper exchange rate regime is crucial.Alternative currencies
Distinct from centrally controlled government-issued currencies, private decentralized trust-reduced networks support alternative trading instruments (such as Bitcoin and Ethereum's ether) that describe themselves as currencies and that are classified as cryptocurrency. With few exceptions, these instruments are not asset backed. The U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission has declared Bitcoin (and, by extension, similar products) to be a commodity under the Commodity Exchange Act. Historically, pseudo-currencies have also included company scrip, a form of wages that could only be exchanged in company stores owned by the employers. Modern token money, such as the tokens operated by local exchange trading systems (LETS), is a form of barter rather than being a true currency. The pseudo-currency may be Internet-based and digital: for instance, Bitcoin is not tied to any specific country. Possession and sale of alternative forms of currencies is often outlawed by governments in order to preserve the legitimacy of the constitutional currency for the benefit of all citizens. For example, ArticleI, section8, clause5 of the United States Constitution delegates to Congress the power to coin money and to regulate the value thereof. This power was delegated to Congress in order to establish and preserve a uniform standard of value and to insure a singular monetary system for all purchases and debts in the United States, public and private. Along with the power to coin money, the United States Congress has the concurrent power to restrain the circulation of money which is not issued under its own authority in order to protect and preserve the constitutional currency. It is a violation of federal law for individuals, or organizations to create private coin or currency systems to compete with the official coinage and currency of the United States.Local currency
In economics, a local currency is a currency not backed by a national government and intended to trade only in a small area. Advocates such as Jane Jacobs argue that this enables an economically depressed region to pull itself up, by giving the people living there a medium of exchange that they can use to exchange services and locally produced goods (in a broader sense, this is the original purpose of all money). Opponents of this concept argue that local currency creates a barrier that can interfere witheconomies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in ...
and comparative advantage and that in some cases they can serve as a means of tax evasion.
Local currencies can also come into being when there is economic turmoil involving the national currency. An example of this is the Argentinian economic crisis of 2002 in which IOUs issued by local governments quickly took on some of the characteristics of local currencies.
One of the best examples of a local currency is the original LETS currency, founded on Vancouver Island in the early 1980s. In 1982, the Canadian Central Bank's lending rates ran up to 14% which drove chartered bank lending rates as high as 19%. The resulting currency and credit scarcity left island residents with few options other than to create a local currency.
See also
Related concepts * Counterfeit money * Currency band * Currency transaction tax * Debasement * Exchange rate * Fiscal localism * Foreign currency exchange * Foreign exchange reserves * Functional currency * History of banking * History of money * Mutilated currency * Optimum currency area * Slang terms for money * Demurrage currency * Virtual currency * World currency Accounting units * Currency pair * Currency symbol * Currency strength * European Currency Unit * Fictional currency * Franc Poincaré * Local currencies * Petrocurrency * Special drawing rights Lists * ISO 4217 * List of alternative names for currency * List of currencies * List of circulating currencies * List of proposed currencies * List of historical currencies * List of international trade topics * List of motifs on banknotesNotes
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Foreign exchange market