caustic soda on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sodium hydroxide, also known as
Solid-Liquid Equilibrium (SLE) and Vapour-Liquid Equilibrium (VLE) of Aqueous NaOH
. Online report, accessed on 2017-04-29. When solutions with less than 18.4% NaOH are cooled, water
5th edition, John Wiley & Sons. Historically, sodium hydroxide was produced by treating sodium carbonate with calcium hydroxide in a metathesis reaction which takes advantage of the fact that sodium hydroxide is soluble, while calcium carbonate is not. This process was called causticizing. : This process was superseded by the
Clean green finish that sends a loved one down the drain
Times Online. Retrieved 2013-02-20.Thacker, H. Leon; Kastner, Justin (August 2004)
''Carcass Disposal: A Comprehensive Review. Chapter 6''
National Agricultural Biosecurity Center, Kansas State University, 2004. Retrieved 2010-03-08 and the only solids that remain are bone hulls, which can be crushed between one's fingertips.Roach, Mary (2004). ''Stiff: The Curious Lives of Human Cadavers'', New York: W.W. Norton & Company. . Sodium hydroxide is frequently used in the process of decomposing roadkill dumped in landfills by animal disposal contractors. Due to its availability and low cost, it has been used by criminals to dispose of corpses. Italian

 Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of
Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of
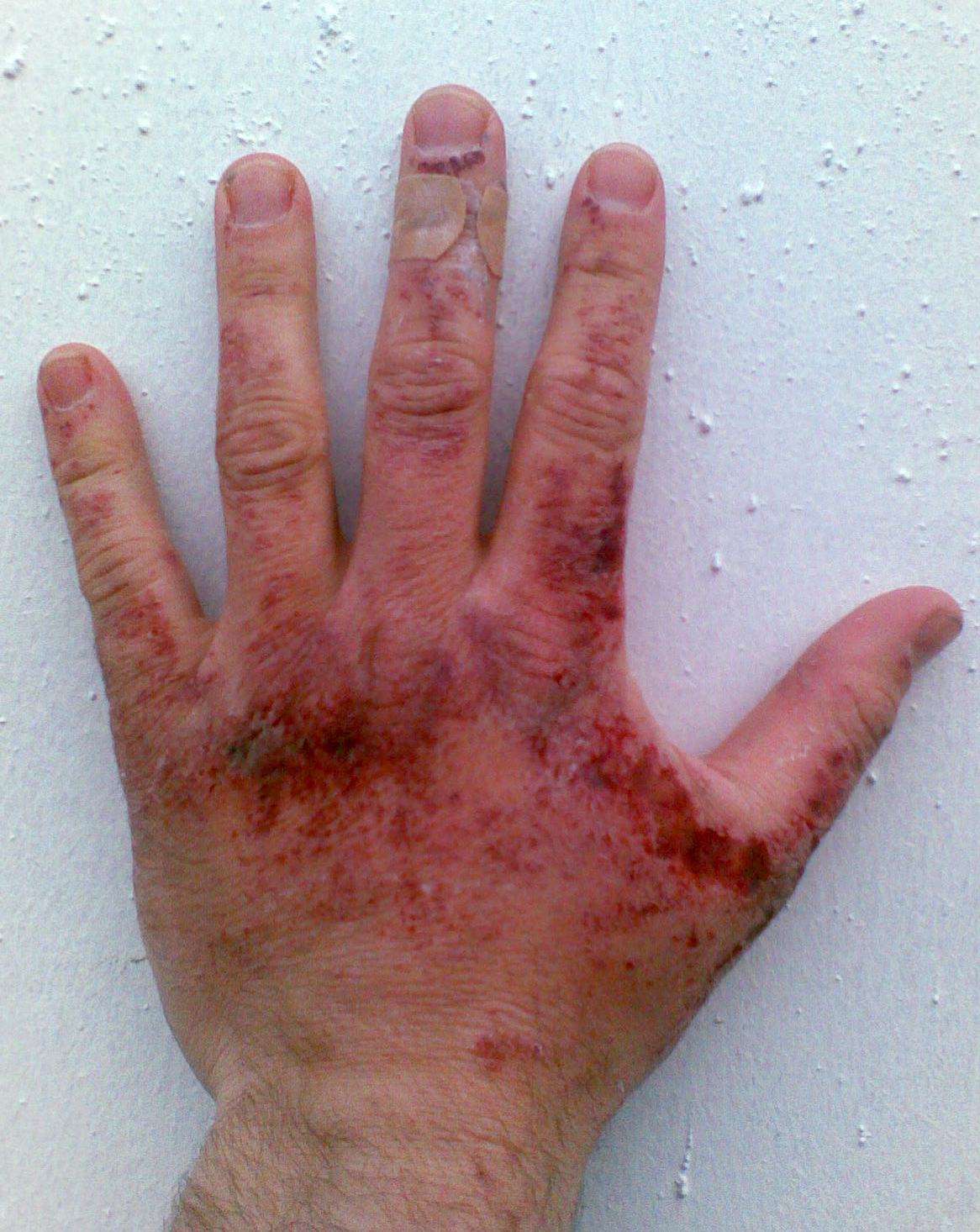 Like other
Like other
 Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within
Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within
/ref> A procedure for making sodium hydroxide appeared as part of a recipe for making soap in an Arab book of the late 13th century: (Inventions from the Various Industrial Arts), which was compiled by al-Muzaffar Yusuf ibn 'Umar ibn 'Ali ibn Rasul (d. 1295), a king of Yemen. The recipe called for passing water repeatedly through a mixture of '' alkali'' (Arabic: , where is ash from Glasswort, saltwort plants, which are rich in sodium; hence ''alkali'' was impure sodium carbonate) and quicklime (
International Chemical Safety Card 0360
*Euro Chlor-How is chlorine made
Chlorine OnlineCDC – Sodium Hydroxide – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic
*Data sheets
Technical charts (page 33—41)
for enthalpy, temperature and pressure
Sodium Hydroxide MSDS
Certified Lye MSDS
Hill Brothers MSDS
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20150508191719/http://www.inclusive-science-engineering.com/inorganic-chemical-caustic-soda-production-process-description-and-flowsheet/ Caustic soda production in continuous causticising plant by lime soda process] {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodium Hydroxide Chemical engineering Cleaning products Deliquescent substances Desiccants Household chemicals Hydroxides Inorganic compounds Photographic chemicals Sodium compounds E-number additives Food acidity regulators
lye
A lye is a metal hydroxide traditionally obtained by leaching wood ashes, or a strong alkali which is highly soluble in water producing caustic basic solutions. "Lye" most commonly refers to sodium hydroxide (NaOH), but historically has been u ...
and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
cations and hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. I ...
anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic
Caustic most commonly refers to:
* Causticity, a property of various corrosive substances
** Sodium hydroxide, sometimes called ''caustic soda''
** Potassium hydroxide, sometimes called ''caustic potash''
** Calcium oxide, sometimes called ''caus ...
base and alkali that decomposes protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s at ordinary ambient temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
s and may cause severe chemical burn
A chemical burn occurs when living tissue is exposed to a corrosive substance (such as a strong acid, base or oxidizer) or a cytotoxic agent (such as mustard gas, lewisite or arsine). Chemical burns follow standard burn classification and may c ...
s. It is highly soluble in water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
, and readily absorbs moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some commercial products. Moisture also refers to the amount of water vapo ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
from the air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound.
As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
and acidic hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students.
Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material
...
and paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distrib ...
, textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
s, drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
, soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
s and detergents, and as a drain cleaner
A drain cleaner is method for unblocking sewer pipes or clogged wastewater drains. The term may also refer to a mechanical device such as a plumber's snake, drain auger, toilet plunger, or similar device. Occasionally, the term is applied to a pl ...
. Worldwide production in 2004 was approximately 60 million tons, while demand was 51 million tons.
Properties
Physical properties
Pure sodium hydroxide is a colorless crystalline solid that melts at without decomposition, and with a boiling point of . It is highly soluble in water, with a lower solubility inpolar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
Polar may refer to:
* Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface of a rotating body or planet, at 90 degrees from the equator, based on the axis around which a body rotates
* Polar climate, the c ...
solvents such as ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
and methanol. NaOH is insoluble in ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be ...
and other non-polar solvents.
Similar to the hydration of sulfuric acid, dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
of solid sodium hydroxide in water is a highly exothermic reaction
In thermochemistry, an exothermic reaction is a "reaction for which the overall standard enthalpy change Δ''H''⚬ is negative." Exothermic reactions usually release heat. The term is often confused with exergonic reaction, which IUPAC defines ...
where a large amount of heat is liberated, posing a threat to safety through the possibility of splashing. The resulting solution is usually colorless and odorless. As with other alkaline solutions, it feels slippery with skin contact due to the process of saponification
Saponification is a process of converting esters into soaps and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali (for example, aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions). Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains. ...
that occurs between NaOH and natural skin oils.
Viscosity
Concentrated (50%) aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide have a characteristicviscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
, 78 m Pa·s, that is much greater than that of water (1.0 mPa·s) and near that of olive oil (85 mPa·s) at room temperature. The viscosity of aqueous NaOH, as with any liquid chemical, is inversely related to its service temperature, i.e., its viscosity decreases as temperature increases, and vice versa. The viscosity of sodium hydroxide solutions plays a direct role in its application as well as its storage.
Hydrates
Sodium hydroxide can form several hydrates , which result in a complexsolubility diagram
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
that was described in detail by S. U. Pickering in 1893. The known hydrates and the approximate ranges of temperature and concentration (mass percent of NaOH) of their saturated
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
** Saturated and unsaturated compounds
**Degree of unsaturation
** Saturated fat or fatty ac ...
water solutions are:
*Heptahydrate, : from −28 °C (18.8%) to −24 °C (22.2%).
*Pentahydrate, : from −24 °C (22.2%) to −17.7 (24.8%).
*Tetrahydrate, , α form: from −17.7 (24.8%) to +5.4 °C (32.5%).
*Tetrahydrate, , β form: metastable.
*Trihemihydrate, : from +5.4 °C (32.5%) to +15.38 °C (38.8%) and then to +5.0 °C (45.7%).
*Trihydrate, : metastable.
*Dihydrate, : from +5.0 °C (45.7%) to +12.3 °C (51%).
*Monohydrate, : from +12.3 °C (51%) to 65.10 °C (69%) then to 62.63 °C (73.1%).
Early reports refer to hydrates with ''n'' = 0.5 or ''n'' = 2/3, but later careful investigations failed to confirm their existence.
The only hydrates with stable melting points are (65.10 °C) and (15.38 °C). The other hydrates, except the metastable ones and (β) can be crystallized from solutions of the proper composition, as listed above. However, solutions of NaOH can be easily supercooled by many degrees, which allows the formation of hydrates (including the metastable ones) from solutions with different concentrations.
For example, when a solution of NaOH and water with 1:2 mole ratio (52.6% NaOH by mass) is cooled, the monohydrate normally starts to crystallize (at about 22 °C) before the dihydrate. However, the solution can easily be supercooled down to −15 °C, at which point it may quickly crystallize as the dihydrate. When heated, the solid dihydrate might melt directly into a solution at 13.35 °C; however, once the temperature exceeds 12.58 °C. it often decomposes into solid monohydrate and a liquid solution. Even the ''n'' = 3.5 hydrate is difficult to crystallize, because the solution supercools so much that other hydrates become more stable.
A hot water solution containing 73.1% (mass) of NaOH is a eutectic that solidifies at about 62.63 °C as an intimate mix of anhydrous and monohydrate crystals.
A second stable eutectic composition is 45.4% (mass) of NaOH, that solidifies at about 4.9 °C into a mixture of crystals of the dihydrate and of the 3.5-hydrate.
The third stable eutectic has 18.4% (mass) of NaOH. It solidifies at about −28.7 °C as a mixture of water ice and the heptahydrate .M. Conde Engineering:Solid-Liquid Equilibrium (SLE) and Vapour-Liquid Equilibrium (VLE) of Aqueous NaOH
. Online report, accessed on 2017-04-29. When solutions with less than 18.4% NaOH are cooled, water
ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaqu ...
crystallizes first, leaving the NaOH in solution.
The α form of the tetrahydrate has density 1.33 g/cm3. It melts congruously at 7.55 °C into a liquid with 35.7% NaOH and density 1.392 g/cm3, and therefore floats on it like ice on water. However, at about 4.9 °C it may instead melt incongruously into a mixture of solid and a liquid solution.
The β form of the tetrahydrate is metastable, and often transforms spontaneously to the α form when cooled below −20 °C. Once initiated, the exothermic transformation is complete in a few minutes, with a 6.5% increase in volume of the solid. The β form can be crystallized from supercooled solutions at −26 °C, and melts partially at −1.83 °C.
The "sodium hydroxide" of commerce is often the monohydrate (density 1.829 g/cm3). Physical data in technical literature may refer to this form, rather than the anhydrous compound.
Crystal structure
NaOH and its monohydrate form orthorhombic crystals with the space groups Cmcm ( oS8) and Pbca (oP24), respectively. The monohydrate cell dimensions are a = 1.1825, b = 0.6213, c = 0.6069 nm. The atoms are arranged in a hydrargillite-like layer structure, with each sodium atom surrounded by six oxygen atoms, three each from hydroxide ions and three from water molecules. The hydrogen atoms of the hydroxyls form strong bonds with oxygen atoms within each O layer. Adjacent O layers are held together by hydrogen bonds between water molecules.Chemical properties
Reaction with acids
Sodium hydroxide reacts with protic acids to produce water and the corresponding salts. For example, when sodium hydroxide reacts withhydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
, sodium chloride is formed:
:
In general, such neutralization reactions are represented by one simple net ionic equation:
:
This type of reaction with a strong acid releases heat, and hence is exothermic. Such acid–base reaction
An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their applica ...
s can also be used for titration
Titration (also known as titrimetry and volumetric analysis) is a common laboratory method of quantitative chemical analysis to determine the concentration of an identified analyte (a substance to be analyzed). A reagent, termed the ''titrant'' ...
s. However, sodium hydroxide is not used as a primary standard A primary standard in metrology is a standard that is sufficiently accurate such that it is not calibrated by or subordinate to other standards. Primary standards are defined via other quantities like length, mass and time. Primary standards are ...
because it is hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substan ...
and absorbs carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
from air.
Reaction with acidic oxides
Sodium hydroxide also reacts withacidic oxides
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or orga ...
, such as sulfur dioxide. Such reactions are often used to " scrub" harmful acidic gases (like and ) produced in the burning of coal and thus prevent their release into the atmosphere. For example,
:
Reaction with metals and oxides
Glass reacts slowly with aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions at ambient temperatures to form soluble silicates. Because of this, glass joints and stopcocks exposed to sodium hydroxide have a tendency to "freeze".Flask
Flask may refer to:
Container
* Hip flask, a small container used to carry a small amount of liquid
* Laboratory flask, laboratory glassware for holding larger volumes than simple test tubes
** Erlenmeyer flask, a common laboratory flask wit ...
s and glass-lined chemical reactor
A chemical reactor is an enclosed volume in which a chemical reaction takes place. In chemical engineering, it is generally understood to be a process vessel used to carry out a chemical reaction, which is one of the classic unit operations in chem ...
s are damaged by long exposure to hot sodium hydroxide, which also frosts the glass. Sodium hydroxide does not attack iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
at room temperatures, since iron does not have amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used.
One type of amphoteric species are amphipro ...
properties (i.e., it only dissolves in acid, not base).
Nevertheless, at high temperatures (e.g. above 500 °C), iron can react endothermic
In thermochemistry, an endothermic process () is any thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015).''Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. ...
ally with sodium hydroxide to form iron(III) oxide, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
metal, and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
gas. This is due to the lower enthalpy of formation
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant p ...
of iron(III) oxide (−824.2 kJ/mol) compared to sodium hydroxide (-500 kJ/mol) and positive entropy change of reaction, which imply spontaneity at high temperatures (, ) and non-spontaneity at low temperatures (, ). Consider the following reaction between molten sodium hydroxide and finely divided iron filings:
:
A few transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that ca ...
s, however, may react vigorously with sodium hydroxide under milder conditions.
In 1986, an aluminium road tanker in the UK was mistakenly used to transport 25% sodium hydroxide solution, causing pressurization of the contents and damage to the tanker. The pressurization was due to the hydrogen gas which is produced in the reaction between sodium hydroxide and aluminium:
:
Precipitant
Unlike sodium hydroxide, which is soluble, the hydroxides of most transition metals are insoluble, and therefore sodium hydroxide can be used toprecipitate
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the process of transforming a dissolved substance into an insoluble solid from a super-saturated solution. The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading ...
transition metal hydroxides. The following colours are observed:
*Copper - blue
*Iron(II) - green
*Iron(III) - yellow / brown
Zinc and lead salts dissolve in excess sodium hydroxide to give a clear solution of or .
Aluminium hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic an ...
is used as a gelatinous flocculant to filter out particulate matter in water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
. Aluminium hydroxide is prepared at the treatment plant from aluminium sulfate by reacting it with sodium hydroxide or bicarbonate.
:
:
Saponification
Sodium hydroxide can be used for the base-drivenhydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolys ...
of ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides a ...
s (as in saponification
Saponification is a process of converting esters into soaps and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali (for example, aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions). Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains. ...
), amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
s and alkyl halide
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely us ...
s. However, the limited solubility of sodium hydroxide in organic solvents means that the more soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubi ...
potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
(KOH) is often preferred. Touching a sodium hydroxide solution with bare hands, while not recommended, produces a slippery feeling. This happens because oils on the skin such as sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
are converted to soap.
Despite solubility in propylene glycol it is unlikely to replace water in saponification due to propylene glycol's primary reaction with fat before reaction between sodium hydroxide and fat.
Production
Sodium hydroxide is industrially produced as a 50% solution by variations of the electrolyticchloralkali process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodit ...
. Chlorine gas
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate betwee ...
is also produced in this process. Solid sodium hydroxide is obtained from this solution by the evaporation of water. Solid sodium hydroxide is most commonly sold as flakes, prill
A prill is a small aggregate or globule of a material, most often a dry sphere, formed from a melted liquid through spray crystallization. Prilled is a term used in mining and manufacturing to refer to a product that has been pelletized. ANFO e ...
s, and cast blocks.
In 2004, world production was estimated at 60 million dry tonnes of sodium hydroxide, and demand was estimated at 51 million tonnes. In 1998, total world production was around 45 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s. North America and Asia each contributed around 14 million tonnes, while Europe produced around 10 million tonnes. In the United States, the major producer of sodium hydroxide is Olin, which has annual production around 5.7 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s from sites at Freeport, Texas, and Plaquemine
Plaquemine is a city in and the parish seat of Iberville Parish, Louisiana, United States. It is part of the Baton Rouge metropolitan statistical area. At the 2010 United States census, the population was 7,119; the 2020 census determined i ...
, Louisiana, St Gabriel, Louisiana, McIntosh, Alabama, Charleston, Tennessee, Niagara Falls, New York, and Becancour, Canada. Other major US producers include Oxychem
Occidental Petroleum Corporation (often abbreviated Oxy in reference to its ticker symbol and logo) is an American company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration in the United States, and the Middle East as well as petrochemical manufacturing in the ...
, Westlake, Shintek and Formosa. All of these companies use the chloralkali process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodit ...
.''Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology''5th edition, John Wiley & Sons. Historically, sodium hydroxide was produced by treating sodium carbonate with calcium hydroxide in a metathesis reaction which takes advantage of the fact that sodium hydroxide is soluble, while calcium carbonate is not. This process was called causticizing. : This process was superseded by the
Solvay process
The Solvay process or ammonia-soda process is the major industrial process for the production of sodium carbonate (soda ash, Na2CO3). The ammonia-soda process was developed into its modern form by the Belgian chemist Ernest Solvay during the 1860s ...
in the late 19th century, which was in turn supplanted by the Leblanc process and then chloralkali process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodit ...
which is in use today.
Sodium hydroxide is also produced by combining pure sodium metal with water. The byproducts are hydrogen gas and heat, often resulting in a flame.
:
This reaction is commonly used for demonstrating the reactivity of alkali metals in academic environments; however, it is not commercially viable, as the isolation of sodium metal is typically performed by reduction or electrolysis of sodium compounds including sodium hydroxide.
Uses
Sodium hydroxide is a popular strong base used in industry. Sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of sodium salts and detergents, pH regulation, and organic synthesis. In bulk, it is most often handled as an aqueous solution, since solutions are cheaper and easier to handle. Sodium hydroxide is used in many scenarios where it is desirable to increase thealkalinity
Alkalinity (from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is the capacity of water to resist acidification. It should not be confused with basicity, which is an absolute measurement on the pH scale.
Alkalinity is the strength ...
of a mixture, or to neutralize acids.
For example, in the petroleum industry, sodium hydroxide is used as an additive in drilling mud to increase alkalinity
Alkalinity (from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is the capacity of water to resist acidification. It should not be confused with basicity, which is an absolute measurement on the pH scale.
Alkalinity is the strength ...
in bentonite
Bentonite () is an absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelling capacity than Ca-m ...
mud systems, to increase the mud viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
, and to neutralize any acid gas Acid gas is a particular typology of natural gas or any other gas mixture containing significant quantities of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), or similar acidic gases. A gas is determined to be acidic or not after it is mixed with w ...
(such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
) which may be encountered in the geological formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exp ...
as drilling progresses.
Another use is in Salt spray test
The salt spray test (or salt fog test) is a standardized and popular corrosion test method, used to check corrosion resistance of materials and surface coatings. Usually, the materials to be tested are metallic (although stone, ceramics, and poly ...
ing where pH needs to be regulated. Sodium hydroxide is used with hydrochloric acid to balance pH. The resultant salt, NaCl, is the corrosive agent used in the standard neutral pH salt spray test.
Poor quality crude oil can be treated with sodium hydroxide to remove sulfurous impurities in a process known as ''caustic washing''. As above, sodium hydroxide reacts with weak acids such as hydrogen sulfide and mercaptans to yield non-volatile sodium salts, which can be removed. The waste which is formed is toxic and difficult to deal with, and the process is banned in many countries because of this. In 2006, Trafigura
Trafigura Group Pte. Ltd. is a Singaporean-based Swiss multinational commodity trading company founded in 1993 that trades in base metals and energy. It is the world's largest private metals trader and second-largest oil trader having built or ...
used the process and then dumped the waste in Ivory Coast.
Other common uses of sodium hydroxide include:
*for making soaps and detergents. Sodium hydroxide is used for hard bar soap, while potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
is used for liquid soaps. Sodium hydroxide is used more often than potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
because it is cheaper and a smaller quantity is needed.
*as drain cleaners that contain sodium hydroxide convert fats and grease that can clog pipes into soap, which dissolves in water ''(see cleaning agent
Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances (usually liquids, powders, sprays, or granules) used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, bad smells, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removin ...
)''.
*for making artificial textile fibres (such as Rayon).
*in the manufacture of paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distrib ...
. Around 56% of sodium hydroxide produced is used by industry, 25% of which is used in the paper industry ''(see chemical pulping
Paper chemicals designate a group of chemicals that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing i ...
)''.
*in purifying bauxite ore from which aluminium metal is extracted. This is known as Bayer process ''(see dissolving amphoteric metals and compounds)''.
*in de-greasing metals, oil refining, and making dyes and bleaches.
*in water treatment plants for pH regulation.
*to treat bagels and pretzel dough, giving the distinctive shiny finish.
Chemical pulping
Sodium hydroxide is also widely used in pulping of wood for making paper or regenerated fibers. Along with sodium sulfide, sodium hydroxide is a key component of the white liquor solution used to separate lignin fromcellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
fiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorpora ...
s in the kraft process. It also plays a key role in several later stages of the process of bleaching the brown pulp resulting from the pulping process. These stages include oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
delignification, oxidative
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
extraction, and simple extraction, all of which require a strong alkaline environment with a pH > 10.5 at the end of the stages.
Tissue digestion
In a similar fashion, sodium hydroxide is used to digest tissues, as in a process that was used with farm animals at one time. This process involved placing a carcass into a sealed chamber, then adding a mixture of sodium hydroxide and water (which breaks the chemical bonds that keep the flesh intact). This eventually turns the body into a liquid with a dark brown color,Ayres, Chris (27 February 2010Clean green finish that sends a loved one down the drain
Times Online. Retrieved 2013-02-20.Thacker, H. Leon; Kastner, Justin (August 2004)
''Carcass Disposal: A Comprehensive Review. Chapter 6''
National Agricultural Biosecurity Center, Kansas State University, 2004. Retrieved 2010-03-08 and the only solids that remain are bone hulls, which can be crushed between one's fingertips.Roach, Mary (2004). ''Stiff: The Curious Lives of Human Cadavers'', New York: W.W. Norton & Company. . Sodium hydroxide is frequently used in the process of decomposing roadkill dumped in landfills by animal disposal contractors. Due to its availability and low cost, it has been used by criminals to dispose of corpses. Italian
serial killer
A serial killer is typically a person who murders three or more persons,A
*
*
*
* with the murders taking place over more than a month and including a significant period of time between them. While most authorities set a threshold of three ...
Leonarda Cianciulli
Leonarda Cianciulli (18 April 1894 – 15 October 1970) was an Italian serial killer. Better known as the Soap-Maker of Correggio (Italian: ''la Saponificatrice di Correggio''), she murdered three women in the town of Correggio, Reggio Emilia, in ...
used this chemical to turn dead bodies into soap. In Mexico, a man who worked for drug cartels admitted disposing of over 300 bodies with it.
Sodium hydroxide is a dangerous chemical due to its ability to hydrolyze protein. If a dilute solution is spilled on the skin, burns may result if the area is not washed thoroughly and for several minutes with running water. Splashes in the eye can be more serious and can lead to blindness.
Dissolving amphoteric metals and compounds
Strong bases attackaluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
. Sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium and water to release hydrogen gas. The aluminium takes the oxygen atom from sodium hydroxide, which in turn takes the oxygen atom from the water, and releases the two hydrogen atoms. The reaction thus produces hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
gas and sodium aluminate
Sodium aluminate is an inorganic chemical that is used as an effective source of aluminium hydroxide for many industrial and technical applications. Pure sodium aluminate (anhydrous) is a white crystalline solid having a formula variously given as ...
. In this reaction, sodium hydroxide acts as an agent to make the solution alkaline, which aluminium can dissolve in.
:
Sodium aluminate is an inorganic chemical that is used as an effective source of aluminium hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic an ...
for many industrial and technical applications. Pure sodium aluminate (anhydrous) is a white crystalline solid having a formula variously given as , , , or . Formation of sodium tetrahydroxoaluminate(III) or hydrated sodium aluminate is given by:
:
This reaction can be useful in etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types ...
, removing anodizing, or converting a polished surface to a satin-like finish, but without further passivation such as anodizing
Anodizing is an electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts.
The process is called ''anodizing'' because the part to be treated forms the anode electrode of an electr ...
or alodining
Chromate conversion coating or alodine coating is a type of conversion coating used to passivate steel, aluminium, zinc, cadmium, copper, silver, titanium, magnesium, and tin alloys. The coating serves as a corrosion inhibitor, as a primer ...
the surface may become degraded, either under normal use or in severe atmospheric conditions.
In the Bayer process, sodium hydroxide is used in the refining of alumina containing ores (bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO ...
) to produce alumina ( aluminium oxide) which is the raw material used to produce aluminium metal via the electrolytic
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon di ...
Hall-Héroult process. Since the alumina is amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used.
One type of amphoteric species are amphipro ...
, it dissolves in the sodium hydroxide, leaving impurities less soluble at high pH such as iron oxides
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. All are black magnetic solids. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of whi ...
behind in the form of a highly alkaline red mud
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary ...
.
Other amphoteric metals are zinc and lead which dissolve in concentrated sodium hydroxide solutions to give sodium zincate and sodium plumbate respectively.
Esterification and transesterification reagent
Sodium hydroxide is traditionally used in soap making ( cold process soap,saponification
Saponification is a process of converting esters into soaps and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali (for example, aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions). Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains. ...
). It was made in the nineteenth century for a hard surface rather than liquid product because it was easier to store and transport.
For the manufacture of biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil ...
, sodium hydroxide is used as a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
for the transesterification
In organic chemistry, transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction ca ...
of methanol and triglycerides. This only works with anhydrous sodium hydroxide, because combined with water the fat would turn into soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
, which would be tainted with methanol. NaOH is used more often than potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
because it is cheaper and a smaller quantity is needed. Due to production costs, NaOH, which is produced using common salt is cheaper than potassium hydroxide.
Food preparation
Food uses of sodium hydroxide include washing or chemical peeling of fruits andvegetables
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems ...
, chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civ ...
and cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
processing, caramel coloring
Caramel color or caramel coloring is a water-soluble food coloring. It is made by heat treatment of carbohydrates (sugars), in general in the presence of acids, alkalis, or salts, in a process called caramelization. It is more fully oxidized tha ...
production, poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quails, ...
scalding, soft drink processing, and thickening ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as ...
. Olives are often soaked in sodium hydroxide for softening; Pretzels and German lye rolls are glazed with a sodium hydroxide solution before baking to make them crisp. Owing to the difficulty in obtaining food grade sodium hydroxide in small quantities for home use, sodium carbonate is often used in place of sodium hydroxide. It is known as E number E524.
Specific foods processed with sodium hydroxide include:
*German pretzels are poached in a boiling sodium carbonate solution or cold sodium hydroxide solution before baking, which contributes to their unique crust.
*Lye-water is an essential ingredient in the crust of the traditional baked Chinese moon cakes.
*Most yellow coloured Chinese noodles
Chinese noodles vary widely according to the region of production, ingredients, shape or width, and manner of preparation. Noodles were invented in China, and are an essential ingredient and staple in Chinese cuisine. They are an important part ...
are made with lye
A lye is a metal hydroxide traditionally obtained by leaching wood ashes, or a strong alkali which is highly soluble in water producing caustic basic solutions. "Lye" most commonly refers to sodium hydroxide (NaOH), but historically has been u ...
-water but are commonly mistaken for containing egg.
*One variety of zongzi
''Zongzi'' (; ), ''rouzong'' () or simply ''zong'' (Cantonese Jyutping: ''zung2'') is a traditional Chinese rice dish made of glutinous rice stuffed with different fillings and wrapped in bamboo leaves (generally of the species ''Indocalamus t ...
uses lye water to impart a sweet flavor.
*Sodium hydroxide is also the chemical that causes gelling of egg whites in the production of Century eggs.
*Some methods of preparing olives involve subjecting them to a lye-based brine.
*The Filipino dessert ( fil, kakanin) called uses a small quantity of lye water to help give the rice flour batter a jelly like consistency. A similar process is also used in the kakanin known as or except that the mixture uses grated cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
instead of rice flour.
*The Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
dish known as lutefisk
''Lutefisk'' ( Norwegian, in Northern and parts of Central Norway, in Southern Norway; sv, lutfisk ; fi, lipeäkala ; literally " lye fish") is dried whitefish (normally cod, but ling and burbot are also used). It is made from aged sto ...
( no, lutfisk, lit=lye fish).
*Bagel
A bagel ( yi, בײגל, translit=beygl; pl, bajgiel; also spelled beigel) is a bread roll originating in the Jewish communities of Poland. It is traditionally shaped by hand into a roughly hand-sized ring from yeasted wheat dough that is first ...
s are often boiled in a lye solution before baking, contributing to their shiny crust.
* Hominy is dried maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
(corn) kernels reconstituted by soaking in lye
A lye is a metal hydroxide traditionally obtained by leaching wood ashes, or a strong alkali which is highly soluble in water producing caustic basic solutions. "Lye" most commonly refers to sodium hydroxide (NaOH), but historically has been u ...
-water. These expand considerably in size and may be further processed by frying to make corn nuts
Corn nuts, also known as toasted corn, are a snack food made of roasted or deep-fried corn kernels. It is referred to as ''cancha'' in Peru and ''chulpi'' in Ecuador.
Preparation
Corn nuts are prepared by soaking whole corn kernels in wa ...
or by drying and grinding to make grits
Grits are a type of porridge made from boiled cornmeal. Hominy grits are a type of grits made from hominy – corn that has been treated with an alkali in a process called nixtamalization, with the pericarp (ovary wall) removed. Grits are of ...
. Hominy is used to create Masa
''Masa'' (or ''masa de maíz'') (; ) is a maize dough that comes from ground nixtamalized corn. It is used for making corn tortillas, '' gorditas'', ''tamales'', '' pupusas'', and many other Latin American dishes. It is dried and powdered into ...
, a popular flour used in Mexican cuisine to make Corn tortillas
In North America, a corn tortilla or just tortilla (, ) is a type of thin, unleavened flatbread, made from hominy, that is the whole kernels of maize treated with alkali to improve their nutrition in a process called nixtamalization. A simple ...
and tamales
A tamale, in Spanish tamal, is a traditional Mesoamerican dish made of masa, a dough made from nixtamalized corn, which is steamed in a corn husk or banana leaf. The wrapping can either be discarded prior to eating or used as a plate. Tamale ...
. Nixtamal is similar, but uses calcium hydroxide instead of sodium hydroxide.
Cleaning agent
Sodium hydroxide is frequently used as an industrialcleaning agent
Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances (usually liquids, powders, sprays, or granules) used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, bad smells, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removin ...
where it is often called "caustic". It is added to water, heated, and then used to clean process equipment, storage tanks, etc. It can dissolve grease, oils
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
, fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
s and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
-based deposits. It is also used for cleaning waste discharge pipes under sinks and drains in domestic properties. Surfactants
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming ...
can be added to the sodium hydroxide solution in order to stabilize dissolved substances and thus prevent redeposition. A sodium hydroxide soak solution is used as a powerful degreaser on stainless steel and glass bakeware. It is also a common ingredient in oven cleaners.
A common use of sodium hydroxide is in the production of parts washer
A parts washer is a piece of equipment used to remove contaminants or debris, such as dirt, grime, carbon, oil, grease, metal chips, cutting fluids, mold release agents, ink, paint, and corrosion from workpieces. Parts washers are used in new ...
detergents. Parts washer detergents based on sodium hydroxide are some of the most aggressive parts washer cleaning chemicals. The sodium hydroxide-based detergents include surfactants, rust inhibitors and defoamers. A parts washer heats water and the detergent in a closed cabinet and then sprays the heated sodium hydroxide and hot water at pressure against dirty parts for degreasing applications. Sodium hydroxide used in this manner replaced many solvent-based systems in the early 1990s when trichloroethane Trichloroethane (CHCl) may refer to either of two isomeric chemical compounds:
* 1,1,1-Trichloroethane (methyl chloroform, CClCH)
* 1,1,2-Trichloroethane
1,1,2-Trichloroethane, or 1,1,2-TCA, is an organochloride solvent with the molecular formula ...
was outlawed by the Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force o ...
. Water and sodium hydroxide detergent-based parts washers are considered to be an environmental improvement over the solvent-based cleaning methods.

 Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of
Sodium hydroxide is used in the home as a type of drain opener
A drain cleaner is method for unblocking sewer pipes or clogged wastewater drains. The term may also refer to a mechanical device such as a plumber's snake, drain auger, toilet plunger, or similar device. Occasionally, the term is applied to a plu ...
to unblock clogged drains, usually in the form of a dry crystal or as a thick liquid gel. The alkali dissolves greases to produce water soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
products
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
. It also hydrolyzes
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
proteins, such as those found in hair, which may block water pipes. These reactions are sped by the heat generated when sodium hydroxide and the other chemical components of the cleaner dissolve in water. Such alkaline drain cleaners and their acidic versions are highly corrosive
A corrosive substance is one that will damage or destroy other substances with which it comes into contact by means of a chemical reaction.
Etymology
The word ''corrosive'' is derived from the Latin verb ''corrodere'', which means ''to gnaw'', ...
and should be handled with great caution.
Relaxer
Sodium hydroxide is used in somerelaxer
A relaxer is a type of lotion or cream generally used by people with tight curls or very curly hair which makes hair easier to hair straightening, straighten by chemically "relaxing" the natural curls. The active agent is usually a strong alkali, a ...
s to straighten hair
Hair straightening is a hair styling technique used since the 1890s involving the flattening and straightening of hair in order to give it a smooth, streamlined, and sleek appearance. It became very popular during the 1950s among black males and ...
. However, because of the high incidence and intensity of chemical burns, manufacturers of chemical relaxers use other alkaline chemicals in preparations available to consumers. Sodium hydroxide relaxers are still available, but they are used mostly by professionals.
Paint stripper
A solution of sodium hydroxide in water was traditionally used as the most common paint stripper on wooden objects. Its use has become less common, because it can damage the wood surface, raising the grain and staining the colour.Water treatment
Sodium hydroxide is sometimes used duringwater purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ...
to raise the pH of water supplies. Increased pH makes the water less corrosive to plumbing and reduces the amount of lead, copper and other toxic metals that can dissolve into drinking water.
Historical uses
Sodium hydroxide has been used for detection ofcarbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning typically occurs from breathing in carbon monoxide (CO) at excessive levels. Symptoms are often described as " flu-like" and commonly include headache, dizziness, weakness, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion. Large ...
, with blood samples of such patients turning to a vermilion
Vermilion (sometimes vermillion) is a color, color family, and pigment most often made, since antiquity until the 19th century, from the powdered mineral cinnabar (a form of mercury sulfide, which is toxic) and its corresponding color. It i ...
color upon the addition of a few drops of sodium hydroxide. Today, carbon monoxide poisoning can be detected by CO oximetry.
In cement mixes, mortars, concrete, grouts
Sodium hydroxide is used in some cement mix plasticisers. This helps homogenise cement mixes, preventing segregation of sands and cement, decreases the amount of water required in a mix and increases workability of the cement product, be it mortar, render or concrete.Experimental
Flavonoids
See:Sodium hydroxide test
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
Chemically, flavonoids ...
for flavonoids
Summer-winter heat storage
After decades of research,EMPA
The Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa, German acronym for ''Eidgenössische Materialprüfungs- und Forschungsanstalt'') is an interdisciplinary Swiss research institute for applied materials sciences and tech ...
researchers and others are experimenting with concentrated sodium hydroxide (NaOH) as the thermal storage or seasonal reservoir medium for power plants and domestic space-heating. If water is added to solid or concentrated sodium hydroxide (NaOH), heat is released. The dilution is exothermic – chemical energy is released in the form of heat. Conversely, by applying heat energy into a dilute sodium hydroxide solution the water will evaporate so that the solution becomes more concentrated and thus stores the supplied heat as latent chemical energy.
Neutron moderator
Seaborg Technologies
Seaborg Technologies is a private Danish startup. It is developing small molten salt reactors.
Founded in 2015 and based in Copenhagen, Denmark, Seaborg emerged as a small team of physicists, chemists, and engineers with educational roots at the ...
is working on a reactor design in which NaOH is used as a neutron moderator,
Safety
 Like other
Like other corrosive
A corrosive substance is one that will damage or destroy other substances with which it comes into contact by means of a chemical reaction.
Etymology
The word ''corrosive'' is derived from the Latin verb ''corrodere'', which means ''to gnaw'', ...
acids and alkalis, drops of sodium hydroxide solutions can readily decompose proteins and lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
in living tissues via amide hydrolysis and ester hydrolysis, which consequently cause chemical burn
A chemical burn occurs when living tissue is exposed to a corrosive substance (such as a strong acid, base or oxidizer) or a cytotoxic agent (such as mustard gas, lewisite or arsine). Chemical burns follow standard burn classification and may c ...
s and may induce permanent blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
upon contact with eyes. Solid alkali can also express its corrosive nature if there is water, such as water vapor. Thus, protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, ele ...
, like rubber gloves
A rubber glove is a glove made out of natural rubber or Synthetic rubber. The term ‘rubber’ refers to durable, waterproof and elastic material made from natural or synthetic latex. Rubber gloves can be unsupported (rubber only) or supported ( ...
, safety clothing
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, ele ...
and eye protection
Eye protection is protective gear for the eyes, and sometimes face, designed to reduce the risk of injury. Examples of risks requiring eye protection can include: impact from particles or debris, light or radiation, wind blast, heat, sea sp ...
, should always be used when handling this chemical or its solutions. The standard first aid measures for alkali spills on the skin is, as for other corrosives, irrigation with large quantities of water. Washing is continued for at least ten to fifteen minutes.
Moreover, dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
of sodium hydroxide is highly exothermic, and the resulting heat may cause heat burns or ignite flammables. It also produces heat when reacted with acids.
Sodium hydroxide is also mildly corrosive to glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching ...
, which can cause damage to glazing or cause ground glass joint
Ground glass joints are used in laboratories to quickly and easily fit leak-tight apparatus together from interchangeable commonly available parts. For example, a round bottom flask, Liebig condenser, and oil bubbler with ground glass joints may ...
s to bind. Sodium hydroxide is corrosive to several metals, like aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
which reacts with the alkali to produce flammable hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
gas on contact:
Storage
 Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within
Careful storage is needed when handling sodium hydroxide for use, especially bulk volumes. Following proper NaOH storage guidelines and maintaining worker/environment safety is always recommended given the chemical's burn hazard.
Sodium hydroxide is often stored in bottles for small-scale laboratory use, within intermediate bulk container
Intermediate bulk containers (also known as IBC tank, IBC tote, IBC, or pallet tank) are industrial-grade containers engineered for the mass handling, transport, and storage of liquids, semi-solids, pastes, or solids. The two main categories of I ...
s (medium volume containers) for cargo handling and transport, or within large stationary storage tanks with volumes up to 100,000 gallons for manufacturing or waste water plants with extensive NaOH use. Common materials that are compatible with sodium hydroxide and often utilized for NaOH storage include: polyethylene (HDPE
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, ...
, usual, XLPE
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, ins ...
, less common), carbon steel, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), stainless steel, and fiberglass reinforced plastic
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth ...
(FRP, with a resistant liner).
Sodium hydroxide must be stored in airtight containers to preserve its normality as it will absorb water from the atmosphere.
History
Sodium hydroxide was first prepared by soap makers.Thorpe, Thomas Edward, ed., ''A Dictionary of Applied Chemistry'' (London, England: Longmans, Green, and Co., 1913), vol. 5/ref> A procedure for making sodium hydroxide appeared as part of a recipe for making soap in an Arab book of the late 13th century: (Inventions from the Various Industrial Arts), which was compiled by al-Muzaffar Yusuf ibn 'Umar ibn 'Ali ibn Rasul (d. 1295), a king of Yemen. The recipe called for passing water repeatedly through a mixture of '' alkali'' (Arabic: , where is ash from Glasswort, saltwort plants, which are rich in sodium; hence ''alkali'' was impure sodium carbonate) and quicklime (
calcium oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ...
, CaO), whereby a solution of sodium hydroxide was obtained. European soap makers also followed this recipe. When in 1791 the French chemist and surgeon Nicolas Leblanc
Nicolas Leblanc (December 6, 1742 – January 16, 1806) was a French chemist and surgeon who discovered how to manufacture soda ash from common salt.
Earlier days
Leblanc was born in Ivoy le Pré, Cher, France on 6 December 1742. His fathe ...
(1742–1806) patented a process for mass-producing sodium carbonate, natural "soda ash" (impure sodium carbonate that was obtained from the ashes of plants that are rich in sodium) was replaced by this artificial version. However, by the 20th century, the electrolysis of sodium chloride had become the primary method for producing sodium hydroxide.O'Brien, Thomas F.; Bommaraju, Tilak V. and Hine, Fumio (2005) ''Handbook of Chlor-Alkali Technology'', vol. 1. Berlin, Germany: Springer. Chapter 2: History of the Chlor-Alkali Industry, p. 34.
See also
*Acid and base
In chemistry, pH (), historically denoting "potential of hydrogen" (or "power of hydrogen"), is a scale used to specify the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Acidic solutions (solutions with higher concentrations of ions) are ...
* HAZMAT Class 8 Corrosive Substances
*List of cleaning agents
Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances (usually liquids, powders, sprays, or granules) used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, bad smells, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing ...
References
Bibliography
*External links
International Chemical Safety Card 0360
*Euro Chlor-How is chlorine made
Chlorine Online
*Data sheets
Technical charts (page 33—41)
for enthalpy, temperature and pressure
Sodium Hydroxide MSDS
Certified Lye MSDS
Hill Brothers MSDS
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20150508191719/http://www.inclusive-science-engineering.com/inorganic-chemical-caustic-soda-production-process-description-and-flowsheet/ Caustic soda production in continuous causticising plant by lime soda process] {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodium Hydroxide Chemical engineering Cleaning products Deliquescent substances Desiccants Household chemicals Hydroxides Inorganic compounds Photographic chemicals Sodium compounds E-number additives Food acidity regulators