|
Lignin
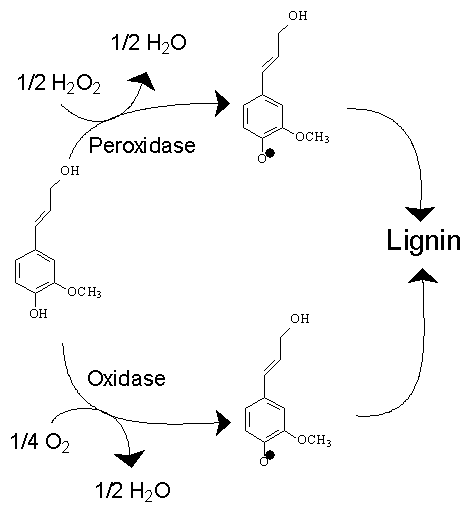
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance “lignine”, which is derived from the Latin word ''lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose. Lignin constitutes 30% of non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor of plants and red algae als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin Structure
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and Bark (botany), bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenols, phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle, A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be Precipitation (chemistry), precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance “lignine”, which is derived from the Latin word ''wikt:lignum, lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose. Lignin constitutes 30% of non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Ligni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or it is defined more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree it performs a support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients between the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, or woodchips or fiber. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bark (botany)
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner bark, which in older stems is living tissue, includes the innermost layer of the periderm. The outer bark on older stems includes the dead tissue on the surface of the stems, along with parts of the outermost periderm and all the tissues on the outer side of the periderm. The outer bark on trees which lies external to the living periderm is also called the rhytidome. Products derived from bark include bark shingle siding and wall coverings, spices and other flavorings, tanbark for tannin, resin, latex, medicines, poisons, various hallucinogenic chemicals and cork. Bark has been used to make cloth, canoes, and ropes and used as a surface for paintings and map making. A number of pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolignols General
Monolignols, also called lignols, are the source materials for biosynthesis of both lignans and lignin and consist mainly of paracoumaryl alcohol (H), coniferyl alcohol (G) and sinapyl alcohol (S). These monolignols differ in their degree of methoxilation of the aromatic ring. The monolignols are derived from the amino acid phenylalanine via the phenylpropanoid pathway involving various enzymes. Phenylalanine is first converted to paracoumaryl alcohol (H), which is subsequently elaborated to coniferyl alcohol (G) and sinapyl alcohol (S). This reaction happens in the cytosol, while the polymerization of the monolignols occurs in the apoplast to which the monolignols have to be transported to though the cell membrane. The monolignols have been found as monolignol-4-O-β-d- glucosides, which might be their major way of storage. Another theory for this conversion is that is improving the transportation of the monolignols. The polymerization consists of oxidative coupling reactions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolignol
Monolignols, also called lignols, are the source materials for biosynthesis of both lignans and lignin and consist mainly of paracoumaryl alcohol (H), coniferyl alcohol (G) and sinapyl alcohol (S). These monolignols differ in their degree of methoxilation of the aromatic ring. The monolignols are derived from the amino acid phenylalanine via the phenylpropanoid pathway involving various enzymes. Phenylalanine is first converted to paracoumaryl alcohol (H), which is subsequently elaborated to coniferyl alcohol (G) and sinapyl alcohol (S). This reaction happens in the cytosol, while the polymerization of the monolignols occurs in the apoplast to which the monolignols have to be transported to though the cell membrane. The monolignols have been found as monolignol-4-O-β-d- glucosides, which might be their major way of storage. Another theory for this conversion is that is improving the transportation of the monolignols. The polymerization consists of oxidative coupling reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%. Cellulose is mainly used to produce paperboard and paper. Smaller quantities are converted into a wide variety of derivative products such as cellophane and rayon. Conversion of cellulose from energy crops into biofuels such as cellulosic ethanol is under development as a renewable fuel source. Cellulose for industrial use is mainly obtained from wood pulp and cotton. Some animals, particularly ruminants and termites, can digest cellulose wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria). A major function is to act as pressure vessels, preventing over-expansion of the cell when water enters. The composition of cell walls varies between taxonomic group and species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. Often, other polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae possess cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides such as carrageenan and agar that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemicellulose
A hemicellulose (also known as polyose) is one of a number of heteropolymers (matrix polysaccharides), such as arabinoxylans, present along with cellulose in almost all terrestrial plant cell walls.Scheller HV, Ulvskov Hemicelluloses.// Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:263-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112315. Cellulose is crystalline, strong, and resistant to hydrolysis. Hemicelluloses are branched, shorter in length than cellulose, and also show a propensity to crystallize. They can be hydrolyzed by dilute acid or base as well as a myriad of hemicellulase enzymes. Composition Diverse kinds of hemicelluloses are known. Important examples include xylan, glucuronoxylan, arabinoxylan, glucomannan, and xyloglucan. Hemicelluloses are polysaccharides often associated with cellulose, but with distinct compositions and structures. Whereas cellulose is derived exclusively from glucose, hemicelluloses are composed of diverse sugars, and can include the five-carbon sugars xy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coniferyl Alcohol
Coniferyl alcohol is an organic compound with the formula HO(CH3O)C6H3CH=CHCH2OH. A colourless or white solid, it is one of the monolignols, produced via the phenylpropanoid biochemical pathway. When copolymerized with related aromatic compounds, coniferyl alcohol forms lignin or lignans. Coniferin is a glucoside of coniferyl alcohol. Coniferyl alcohol is an intermediate in biosynthesis of eugenol and of stilbenoids and coumarin. Gum benzoin contains significant amount of coniferyl alcohol and its esters. It is found in both gymnosperm and angiosperm plants. Sinapyl alcohol and paracoumaryl alcohol, the other two lignin monomers, are found in angiosperm plants and grasses. Occurrence Coniferyl alcohol is produced from coniferyl aldehyde by the action of dehydrogenase enzymes. It is a queen retinue pheromone (QRP), a type of honey bee pheromone found in the mandibular glands. In '' Forsythia intermedia'' a dirigent protein was found to direct the stereoselective biosy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinapyl Alcohol
Sinapyl alcohol is an organic compound structurally related to cinnamic acid. It is biosynthetized via the phenylpropanoid biochemical pathway, its immediate precursor being sinapaldehyde. This phytochemical is one of the monolignols, which are precursor to lignin or lignans. It is also a biosynthetic precursor to various stilbenoids and coumarins. See also *Sinapinic acid *Syringol *Syringaldehyde *Syringic acid *Acetosyringone *Sinapine *Canolol *Phenolic content in wine The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Sinapyl Alcohol Monolignols Ethers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calliarthron
''Calliarthron'' is a genus containing two species of thalloid intertidal alga. Specimens can reach around 30 cm in size. The thalli take a crustose form. The organisms lack secondary pit connections. ''Calliarthron'' reproduces by means of conceptacles; it produces tetraspores, dispores and carpospores. The genus has lignin and contains secondary cell walls, traits which are normally associated with the vascular plants. It is similar to the genus ''Bossiella''. ''Calliarthron'' is calcified, but also has uncalcified joints that allow it to flex in response to the waves to which it is subjected. These joints start out calcified, and decalcify as they grow older. After decalcifying they grow much longer, then fatten themselves up in the same way as xylem formation, resulting in secondary walls. Species The 2 species currently recognised are:Paul W. Gabrielson, Kathy Ann Miller, and Patrick T. Martone (2011) Morphometric and molecular analyses confirm two distinct specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |