carpal tunnel syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a
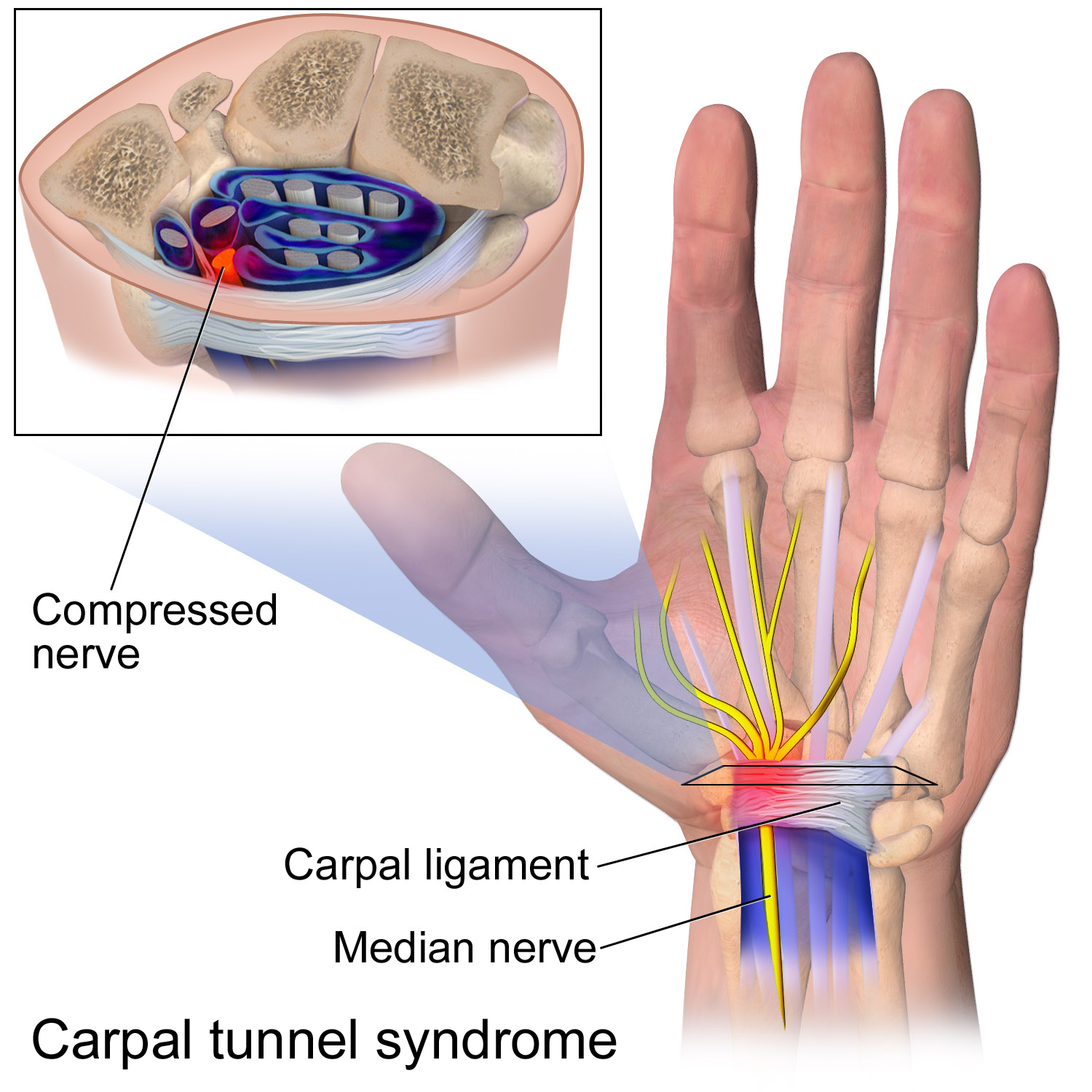 The carpal tunnel is an anatomical compartment located at the base of the palm. Nine flexor tendons and the median nerve pass through the carpal tunnel that is surrounded on three sides by the carpal bones that form an arch. The median nerve provides feeling or sensation to the thumb, index finger, long finger, and half of the ring finger. At the level of the wrist, the median nerve supplies the muscles at the base of the thumb that allow it to abduct, move away from the other four fingers, as well as move out of the plane of the palm. The carpal tunnel is located at the middle third of the base of the palm, bounded by the bony prominence of the scaphoid tubercle and trapezium at the base of the thumb, and the
The carpal tunnel is an anatomical compartment located at the base of the palm. Nine flexor tendons and the median nerve pass through the carpal tunnel that is surrounded on three sides by the carpal bones that form an arch. The median nerve provides feeling or sensation to the thumb, index finger, long finger, and half of the ring finger. At the level of the wrist, the median nerve supplies the muscles at the base of the thumb that allow it to abduct, move away from the other four fingers, as well as move out of the plane of the palm. The carpal tunnel is located at the middle third of the base of the palm, bounded by the bony prominence of the scaphoid tubercle and trapezium at the base of the thumb, and the
 The carpal tunnel is formed by the carpal bones and the transverse carpal ligament. The median nerve passes through this space along with the flexor
The carpal tunnel is formed by the carpal bones and the transverse carpal ligament. The median nerve passes through this space along with the flexor

 Wrist braces (
Wrist braces (
 The natural history of untreated CTS seems to be gradual worsening of the neuropathy. It is difficult to prove that this is always the case, but the supportive evidence is compelling.
Atrophy of the thenar muscles, weakness of palmar abduction, and loss of sensibility (constant numbness as opposed to intermittent paresthesia) are signs of advanced neuropathy. Advanced neuropathy is often permanent. The nerve will try to recover after surgery for more than 2 years, but the recovery may be incomplete.
Paresthesia may increase after release of advanced carpal tunnel syndrome, and people may feel worse than they did prior to surgery for many months.
Troublesome recovery seems related to symptoms of anxiety or depression, and unhelpful thoughts about symptoms (such as worst-case or catastrophic thinking) as well as advanced neuropathy with potentially permanent neuropathy.
Recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome after successful surgery is rare. Caution is warranted in considering additional surgery for people dissatisfied with the result of carpal tunnel release as perceived recurrence may more often be due to renewed awareness of persistent symptoms rather than worsening pathology.
The natural history of untreated CTS seems to be gradual worsening of the neuropathy. It is difficult to prove that this is always the case, but the supportive evidence is compelling.
Atrophy of the thenar muscles, weakness of palmar abduction, and loss of sensibility (constant numbness as opposed to intermittent paresthesia) are signs of advanced neuropathy. Advanced neuropathy is often permanent. The nerve will try to recover after surgery for more than 2 years, but the recovery may be incomplete.
Paresthesia may increase after release of advanced carpal tunnel syndrome, and people may feel worse than they did prior to surgery for many months.
Troublesome recovery seems related to symptoms of anxiety or depression, and unhelpful thoughts about symptoms (such as worst-case or catastrophic thinking) as well as advanced neuropathy with potentially permanent neuropathy.
Recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome after successful surgery is rare. Caution is warranted in considering additional surgery for people dissatisfied with the result of carpal tunnel release as perceived recurrence may more often be due to renewed awareness of persistent symptoms rather than worsening pathology.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Fact Sheet (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke)
NHS website carpal-tunnel.net provides a free to use, validated, online self diagnosis questionnaire for CTS
* {{Authority control Mononeuropathies of upper limb Physical ergonomics Syndromes affecting the nervous system Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate
nerve compression syndrome
Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by chronic, direct pressure on a peripheral nerve. It is known colloquially as a ''trapped nerve'', though this may also refer to ...
associated with the collected signs and symptoms of compression of the median nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has cont ...
at the carpal tunnel
In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is a flattened body cavity on the flexor ( palmar/volar) side of the wrist, bounded by the carpal bones and flexor retinaculum. It forms the passageway that transmits the median nerve and the ...
in the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
. Carpal tunnel syndrome usually has no known cause, but there are environmental and medical risk factors associated with the condition.> CTS can affect both wrists.
Other conditions can cause CTS such as wrist fracture or rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
. After fracture, the resulting swelling, bleeding, and deformity compress the median nerve. With rheumatoid arthritis, the enlarged synovial lining of the tendons causes compression.
The main symptoms are numbness
Hypoesthesia or numbness is a common side effect of various medical conditions that manifests as a reduced sense of touch or sensation, or a partial loss of sensitivity to Sensory receptor, sensory stimuli. In everyday speech this is generally r ...
and tingling of the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the thumb side of the ring finger, as well as pain in the hand and fingers.
Symptoms are typically most troublesome at night. Many people sleep with their wrists bent, and the ensuing symptoms may lead to awakening. Untreated, and over years to decades, CTS causes loss of sensibility, weakness, and shrinkage (atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
) of the thenar muscles
The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The w ...
at the base of the thumb.
Work-related factors such as vibration, wrist extension or flexion, hand force, and repetitive strain are risk factors for CTS. Other risk factors include being female, obesity, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease, and genetics.
Diagnosis can be made with a high probability based on characteristic symptoms and signs. It can also be measured with electrodiagnostic tests.
People wake less often at night if they wear a wrist splint. Injection of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s may or may not alleviate symptoms better than simulated (placebo
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
) injections. There is no evidence that corticosteroid injection sustainably alters the natural history of the disease, which seems to be a gradual progression of neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
.
Surgery to cut the transverse carpal ligament
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.
Structur ...
is the only known disease modifying treatment.
Anatomy
 The carpal tunnel is an anatomical compartment located at the base of the palm. Nine flexor tendons and the median nerve pass through the carpal tunnel that is surrounded on three sides by the carpal bones that form an arch. The median nerve provides feeling or sensation to the thumb, index finger, long finger, and half of the ring finger. At the level of the wrist, the median nerve supplies the muscles at the base of the thumb that allow it to abduct, move away from the other four fingers, as well as move out of the plane of the palm. The carpal tunnel is located at the middle third of the base of the palm, bounded by the bony prominence of the scaphoid tubercle and trapezium at the base of the thumb, and the
The carpal tunnel is an anatomical compartment located at the base of the palm. Nine flexor tendons and the median nerve pass through the carpal tunnel that is surrounded on three sides by the carpal bones that form an arch. The median nerve provides feeling or sensation to the thumb, index finger, long finger, and half of the ring finger. At the level of the wrist, the median nerve supplies the muscles at the base of the thumb that allow it to abduct, move away from the other four fingers, as well as move out of the plane of the palm. The carpal tunnel is located at the middle third of the base of the palm, bounded by the bony prominence of the scaphoid tubercle and trapezium at the base of the thumb, and the hamate
The hamate bone (from Latin language, Latin wiktionary:hamatus, hamatus, "hooked"), or unciform bone (from Latin language, Latin ''wikt:uncus, uncus'', "hook"), Latin os hamatum and occasionally abbreviated as just hamatum, is a bone in the huma ...
hook that can be palpated along the axis of the ring finger. From the anatomical position, the carpal tunnel is bordered on the anterior surface by the transverse carpal ligament, also known as the flexor retinaculum. The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that attaches to the pisiform and the hamulus of the hamate. The proximal boundary is the distal wrist skin crease, and the distal boundary is approximated by a line known as Kaplan's cardinal line. This line uses surface landmarks, and is drawn between the apex of the skin fold between the thumb and index finger to the palpated hamate hook.
Pathophysiology
tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue that connects skeletal muscle, muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tensi ...
s. Increased compartmental pressure for any reason can squeeze the median nerve. Theoretically, increased pressure can interfere with normal intraneural blood flow, eventually causing a cascade of physiological changes in the nerve itself. There is a dose-respondent curve such that greater and longer periods of pressure are associated with greater nerve dysfunction. The symptoms and signs of carpal tunnel syndrome causes are hypertrophy of the synovial tissue surrounding the flexor tendons such as with rheumatoid arthritis.
Prolonged pressure can lead to a cascade of physiological changes in neural tissue. First, the blood-nerve barrier breaks down (increased permeability of perineureum and endothelial cells of endoneural blood vessels). If the pressure continues, the nerves will start the process of demyelination under the area of compression. This will result in abnormal nerve conduction even when the pressure is relieved leading to persistent sensory symptoms until remyelination can occur. If the compression continues and is severe enough, axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ...
s may be injured and Wallerian degeneration will occur. At this point there may be weakness and muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakne ...
, depending on the extent of axon damage.
The critical pressure above which the microcirculatory environment of a nerve becomes compromised depends on diastolic/systolic blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
. Higher blood pressure will require higher external pressure on the nerve to disrupt its microvascular environment. The critical pressure necessary to disrupt the blood supply of a nerve is approximately 30 mm Hg below diastolic blood pressure or 45mm Hg below mean arterial pressure
In medicine, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) is an average calculated blood pressure in an individual during a single cardiac cycle. Although methods of estimating MAP vary, a common calculation is to take one-third of the pulse pressure (the d ...
. For normohypertensive (normal blood pressure) adults, the average values for systolic blood pressure is 116mm Hg diastolic blood pressure is 69mm Hg. Using this data, the average person would become symptomatic with approximately 39mm Hg of pressure in the wrist (69 - 30 = 39 and 69 + (116 - 69)/3 - 45 ~ 40). Carpal tunnel syndrome patients tend to have elevated carpal tunnel pressures (12-31mm Hg) compared to controls (2.5 - 13mm Hg). Applying pressure to the carpal tunnel of normal subjects in a lab can produce mild neurophysiological changes at 30mm Hg with a rapid, complete sensory block at 60mm Hg. Carpal tunnel pressure may be affected by wrist movement/position, with flexion and extension capable of raising the tunnel pressure as high as 111mm Hg. Many of the activities associated with carpal tunnel symptoms such as driving, holding a phone, etc. involve flexing the wrist and it is likely due to an increase in carpal tunnel pressure during these activities.
Nerve compression can result in various stages of nerve injury. The majority of carpal tunnel syndrome patients have a degree I nerve injury
Nerve injury is an injury to a nerve. There is no single classification system that can describe all the many variations of nerve injuries. In 1941, Herbert Seddon introduced a classification of nerve injuries based on three main types of nerve ...
(Sunderland classification), also called neuropraxia. This is characterized by a conduction block, segmental demyelination, and intact axons. With no further compression, the nerves will remyelinate and fully recover. Severe carpal tunnel syndrome patients may have degree II/III injuries (Sunderland classification), or axonotmesis
Axonotmesis is an injury to the peripheral nerve of one of the extremities of the body. The axons and their myelin sheath are damaged in this kind of injury, but the endoneurium, perineurium and epineurium remain intact. Motor and sensory function ...
, where the axon is injured partially or fully. With axon injury there would be muscle weakness or atrophy, and with no further compression the nerves may only partially recover.
While there is evidence that chronic compression is a major cause of carpal tunnel syndrome, it may not be the only cause. Several alternative, potentially speculative, theories exist which describe alternative forms of nerve entrapment. One is the theory of nerve scarring (specifically adherence between the mesoneurium and epineureum) preventing the nerve from gliding during wrist/finger movements, causing repetitive traction injuries. Another is the double crush syndrome, where compression may interfere with axonal transport, and two separate points of compression (e.g. neck and wrist), neither enough to cause local demyelination, may together impair normal nerve function.
Epidemiology
Carpal tunnel syndrome is estimated to affect one out of ten people during their lifetime and is the most commonnerve compression syndrome
Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by chronic, direct pressure on a peripheral nerve. It is known colloquially as a ''trapped nerve'', though this may also refer to ...
. There is notable variation in such estimates based on how one defines the problem, in particular whether one studies people presenting with symptoms vs. measurable median neuropathy whether or not people are seeking care. Idiopathic neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
accounts for about 90% of all nerve compression syndromes. The best data regarding CTS comes from population-based studies, which demonstrate no relationship to gender, and increasing prevalence (accumulation) with age.
Symptoms
The characteristic symptom of CTS is numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the thumb, index, middle, and radial half of the ring finger. These areas process sensation through the median nerve. Numbness or tingling is usually worse with sleep. People tend to sleep with their wrists flexed, which increases pressure on the nerve. Ache and discomfort may be reported in theforearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, techn ...
or even the upper arm
The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the should ...
. Symptoms that are not characteristic of CTS include pain in the wrists or hands, loss of grip strength, minor loss of sleep, and loss of manual dexterity.
As the median neuropathy gets worse, there is loss of sensibility in the thumb, index, middle, and thumb side of the ring finger. As the neuropathy progresses, there may be first weakness, then to atrophy of the muscles of thenar eminence
The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The w ...
(the flexor pollicis brevis
The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
Origin and insertion
The muscle's superficial head arises from the distal edge of the ...
, opponens pollicis, and abductor pollicis brevis
The abductor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that functions as an abductor of the thumb.
Structure
The abductor pollicis brevis is a flat, thin muscle located just under the skin. It is a thenar muscle, and therefore contributes to th ...
). The sensibility of the palm remains normal because the superficial sensory branch of the median nerve branches proximal to the transverse carpal ligament
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.
Structur ...
(TCL) and travels superficial to it.
Median nerve symptoms may arise from nerve compression at the level of the thoracic outlet or the area where the median nerve passes between the two heads of the pronator teres in the forearm, although this is debated.
Signs
Severe CTS is associated with measurable loss of sensibility. Diminished threshold sensibility (the ability to distinguish different amounts of pressure) can be measured using Semmes-Weinstein monofilament testing. Diminished discriminant sensibility can be measured by testing two-point discrimination: the number of millimeters two points of contact need to be separated before you can distinguish them. A person with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome will not have any sensory loss over thethenar eminence
The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The w ...
(bulge of muscles in the palm of hand and at the base of the thumb). This is because the palmar branch of the median nerve, which innervates that area of the palm, separates from the median nerve and passes over the carpal tunnel.
Severe CTS is also associated with weakness and atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
of the muscles at the base of the thumb. The ability to palmarly abduct the thumb may be lost. CTS can be detected on examination using one of several maneuvers to provoke paresthesia (a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the median nerve distribution). These so-called provocative signs include:
* Phalen's maneuver. Performed by fully flexing the wrist, then holding this position and awaiting symptoms. A positive test is one that results in paresthesia in the median nerve distribution within sixty seconds.
* Tinel's sign is performed by lightly tapping the median nerve just proximal to flexor retinaculum to elicit paresthesia.
* Durkan's test, ''carpal compression test'', or applying firm pressure to the palm over the nerve for up to 30 seconds to elicit paresthesia.
* Hand elevation test The hand elevation test is performed by lifting both hands above the head. Paresthesia in the median nerve distribution within 2 minutes is considered positive.
Diagnostic performance characteristics such as sensitivity and specificity are reported, but difficult to interpret because of the lack of a consensus reference standard for CTS.
Causes
Most presentations of CTS have no known disease cause (idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin.
For some medical conditions, one or more causes are somewhat understood, but in a certain percentage of people with the condition, the cause ...
).
The association of other factors with CTS is a source of notable debate. It is important to distinguish factors that provoke symptoms, and factors that are associated with seeking care, from factors that make the neuropathy worse.
Genetic factors are believed to be the most-important determinants of who develops carpal tunnel syndrome. In other words, one's wrist structure seems programmed at birth to develop CTS later in life. A genome-wide association study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA s ...
(GWAS) of carpal tunnel syndrome identified 50 genomic loci significantly associated with the disease, including several loci previously known to be associated with human height.
Some other factors that contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome are conditions such as diabetes, alcoholism, vitamin deficiency or toxicity as well as exposure to toxins. Conditions such as these don't necessarily increase the interstitial pressure of the carpal tunnel. One case-control study noted that individuals classified as obese ( BMI >29) are 2.5 times more likely than slender individuals (BMI <20) to be diagnosed with CTS. It is not clear whether this association is due to an alteration of pathophysiology, a variation in symptoms, or a variation in care-seeking.
Discrete pathophysiology and CTS
Hereditary neuropathy with susceptibility to pressure palsies is a genetic condition that appears to increase the probability of developing CTS. Heterozygous mutations in the gene SH3TC2, associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth, may confer susceptibility toneuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
, including CTS.
Association between common benign tumors such as lipomas, ganglion
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there are ...
, and vascular malformation should be handled with care. Such tumors are very common and are more likely to cause pressure on the median nerve. Similarly, the association between transthyretin amyloidosis-associated polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy () is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy) in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hands and feet and may prog ...
and carpal tunnel syndrome is under investigation. Prior carpal tunnel release is often noted in individuals who later present with transthyretin
Transthyretin (TTR or TBPA) is a transport protein in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid that transports the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and retinol to the liver. This is how transthyretin gained its name: ''transports thyroxine and retinol' ...
amyloid-associated cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. A ...
. There is consideration that bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome could be a reason to consider amyloidosis, timely diagnosis of which could improve heart health. Amyloidosis is rare, even among people with carpal tunnel syndrome (0.55% incidence within 10 years of carpal tunnel release). In the absence of other factors associated with a notable probability of amyloidosis, it is not clear that biopsy at the time of carpal tunnel release has a suitable balance between potential harms and potential benefits.
Other specific pathophysiologies that can cause CTS via pressure include:
* Rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases that cause inflammation of the flexor tendons.
* With severe untreated hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
, generalized myxedema causes deposition of mucopolysaccharides within both the perineurium of the median nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has cont ...
, as well as the tendons passing through the carpal tunnel. Association of CTS with lesser degrees of hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
is questioned.
* Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
may bring out symptoms in genetically predisposed individuals, which may be caused by the temporary changes in hormones and fluid increase pressure in the carpal tunnel. High progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
levels and water retention may increase the size of the synovium.
* Bleeding and swelling from a fracture or dislocation. This is referred to as acute carpal tunnel syndrome.
* Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There ...
causes excessive secretion of growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in ...
s. This causes the soft tissues and bones around the carpal tunnel to grow and compress the median nerve.
Other considerations
* Double crush syndrome is a debated hypothesis that nerve compression or irritation of nerve branches contributing to the median nerve in the neck, or anywhere above the wrist, increases sensitivity of the nerve to compression in the wrist. There is little evidence to support this theory and some concern that it may be used to justify more surgery.CTS and activity
Work-related factors that increase risk of CTS include vibration (5.4odds ratio
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of event A taking place in the presence of B, and the odds of A in the absence of B ...
), hand force (4.2), and repetition (2.3). Exposure to wrist extension or flexion at work increases the risk of CTS by 2.0 times. , a systematic review of studies looking at the relationship between CTS and computer use has found current studies to be inconclusive and contradictory, due to poor study methods and confounding variables not being accounted for.
The international debate regarding the relationship between CTS and repetitive hand use (at work in particular) is ongoing. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
(OSHA) has adopted rules and regulations regarding so-called "cumulative trauma disorders" based concerns regarding potential harm from exposure to repetitive tasks, force, posture, and vibration.
A review of available scientific data by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occ ...
(NIOSH) indicated that job tasks that involve highly repetitive manual acts or specific wrist postures were associated with symptoms of CTS, but there was not a clear distinction of paresthesia (appropriate) from pain (inappropriate) and causation was not established. The distinction from work-related arm pains that are not carpal tunnel syndrome was unclear. It is proposed that repetitive use of the arm can affect the biomechanics
Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to Organ (anatomy), organs, Cell (biology), cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechani ...
of the upper limb or cause damage to tissues. It is proposed that postural and spinal assessment along with ergonomic assessments should be considered, based on observation that addressing these factors has been found to improve comfort in some studies although experimental data are lacking and the perceived benefits may not be specific to those interventions. A 2010 survey by NIOSH showed that two-thirds of the 5million carpal tunnel diagnosed in the US that year were related to work. Women are more likely to be diagnosed with work-related carpal tunnel syndrome than men. Many if not most patients described in published series of carpal tunnel release are older and often not working.
Normal pressure of the carpal tunnel has been defined as a range of . Wrist flexion increases the pressure eight-fold and extension increases it ten-fold. There is speculation that repetitive flexion and extension in the wrist can cause thickening of the synovial tissue that lines the tendons within the carpal tunnel.
Associated conditions
A variety of patient factors can lead to CTS, including heredity, size of the carpal tunnel, associated local and systematic diseases, and certain habits. Non-traumatic causes generally happen over a period of time, and are not triggered by one certain event. Many of these factors are manifestations of physiologic aging.Diagnosis
There is no consensus reference standard for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. A combination of characteristic symptoms (how it feels) and signs (what the clinician finds on exam) are associated with a high probability of CTS withoutelectrophysiological
Electrophysiology (from ee the Electron#Etymology, etymology of "electron" ; and ) is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cell (biology), cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change ...
testing.
Electrodiagnostic testing including electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
, and nerve conduction studies can objectively measure and verify median neuropathy.
Ultrasound can image and measure the cross sectional diameter of the median nerve, which has some correlation with CTS. The role of ultrasound in diagnosis—just as for electrodiagnostic testing—is a matter of debate. EDX cannot fully exclude the diagnosis of CTS due to the lack of sensitivity.
The role of confirmatory electrodiagnostic testing is debated. The goal of electrodiagnostic testing is to compare the speed of conduction in the median nerve with conduction in other nerves supplying the hand. When the median nerve is compressed, it will conduct more slowly than normal and more slowly than other nerves. Nerve compression results in damage to the myelin sheath and manifests as delayed latencies and slowed conduction velocities. Electrodiagnosis rests upon demonstrating impaired median nerve conduction across the carpal tunnel in context of normal conduction elsewhere.
It is often stated that normal electrodiagnostic studies do not preclude the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. The rationale for this is that a threshold of neuropathy must be reached before study results become abnormal and also that threshold values for abnormality vary. Others contend that idiopathic median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel with normal electrodiagnostic tests would represent very, very mild neuropathy that would be best managed as a normal median nerve. Even more important, notable symptoms with mild disease is strongly associated with unhelpful thoughts and symptoms of worry and despair. Notable CTS should remind clinicians to always consider the whole person, including their mindset and circumstances, in strategies to help people get and stay healthy.
A joint report published by the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM), the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (AAPM&R), and the American Academy of Neurology defines practice parameters, standards, and guidelines for EDX studies of CTS based on an extensive critical literature review. This joint review concluded median and sensory nerve conduction studies are valid and reproducible in a clinical laboratory setting and a clinical diagnosis of CTS can be made with a sensitivity greater than 85% and specificity greater than 95%. The AANEM has issued evidence-based practice guidelines for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome, both by electrodiagnostic studies and by neuromuscular ultrasound.
Imaging
The role ofMRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
or ultrasound imaging
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, join ...
in the diagnosis of CTS is unclear. Their routine use is not recommended. Morphological MRI has high sensitivity but low specificity for CTS. High signal intensity may suggest accumulation of axonal transportation, myelin sheath degeneration or oedema. However, more recent quantitative MRI techniques which derive repeatable, reliable and objective biomarkers from nerves and skeletal muscle may have utility, including diffusion-weighted (typically diffusion tensor) MRI which has demonstrable normal values and aberrations in carpal tunnel syndrome.
Differential diagnosis
Cervical radiculopathy can also cause paresthesia abnormal sensibility in the hands and wrist. The distribution usually follows the nerve root, and the paresthesia may be provoked by neck movement. Electromyography and imaging of the cervical spine can help to differentiate cervical radiculopathy from carpal tunnel syndrome if the diagnosis is unclear. Carpal tunnel syndrome is sometimes applied as a label to anyone with pain, numbness, swelling, or burning in the radial side of the hands or wrists. When pain is the primary symptom, carpal tunnel syndrome is unlikely to be the source of the symptoms. When the symptoms and signs point to atrophy and muscle weakness more than numbness, consider neurodegenerative disorders such asAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
or Charcot-Marie Tooth.
Prevention
There is little or no data to support the concept that activity adjustment prevents carpal tunnel syndrome. The evidence for using awrist rest
A wrist rest ( palm rest, wrist support, or palm support) is a device used to support the wrists while using a computer keyboard or mouse. Wrist rests have common usage in the workplace.
Design
Wrist rests can be made from memory foam, gel, ...
at a computer keyboard is debated. There is also little research supporting that ergonomics
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of Psychology, psychological and Physiology, physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goa ...
is related to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Given that biological factors such as genetic predisposition and anthropometric features are more strongly associated with carpal tunnel syndrome than occupational/environmental factors such as hand use, CTS might not be prevented by activity modifications.
Some claim that worksite modifications such as switching from a QWERTY
QWERTY ( ) is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six Computer keyboard keys#Types, keys on the top letter row of the keyboard: . The QWERTY design is based on a layout included in the Sh ...
computer keyboard layout to Dvorak is helpful, but meta-analyses
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
of the available studies note limited supported evidence.
Treatment
There are more than 50 types of treatments for CTS with varied levels of evidence and recommendation across healthcare guidelines, with evidence most strongly supporting surgery, steroids, splinting for wrist positioning, and physical or occupational therapy interventions. When selecting treatment, it is important to consider the severity and chronicity of the CTS pathophysiology and to distinguish treatments that can alter the natural history of the pathophysiology (disease-modifying treatments) and treatments that only alleviate symptoms (palliative treatments). The strongest evidence for disease-modifying treatment in chronic or severe CTS cases is carpal tunnel surgery to change the shape of the carpal tunnel. The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons recommends proceeding conservatively with a course of nonsurgical therapies tried before release surgery is considered. A different treatment should be tried if the current treatment fails to resolve the symptoms within 2 to 7 weeks. Early surgery with carpal tunnel release is indicated where there is evidence of median nerve denervation or a person elects to proceed directly to surgical treatment. Recommendations may differ when carpal tunnel syndrome is found in association with the following conditions:diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
, coexistent cervical radiculopathy, hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
, polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy () is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy) in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hands and feet and may prog ...
, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, and carpal tunnel syndrome in the workplace. CTS related to another pathophysiology is addressed by treating that pathology. For instance, disease-modifying medications for rheumatoid arthritis or surgery for traumatic acute carpal tunnel syndrome.
There is insufficient evidence to recommend gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropath ...
, non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs), yoga
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as pra ...
, acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
, low level laser therapy, magnet therapy, vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and is an essential nutrient for humans. The term essential nutrient refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active f ...
or other supplements.
Splint immobilization

splints
Splints is an ailment of the horse or pony, characterized by a hard, bony swelling, usually on the inside of a front leg, lying between the splint and cannon bone or on the splint bone itself. It may be "hot," meaning that it occurred recently an ...
) alleviate symptoms by keeping the wrist straight, which avoids the increased pressure in the carpal tunnel associated with wrist flexion or extension. They are used primarily to help people sleep.
Many health professionals suggest that, for the best results, one should wear braces at night. When possible, braces can be worn during the activity primarily causing stress on the wrists. The brace should not generally be used during the day as wrist activity is needed to keep the wrist from becoming stiff and to prevent muscles from weakening.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
injections may provide temporary alleviation of symptoms although they are not clearly better than placebo. This form of treatment is thought to reduce discomfort in those with CTS due to its ability to decrease median nerve swelling. The use of ultrasound while performing the injection is more expensive but leads to faster resolution of CTS symptoms. The injections are done under local anesthesia. This treatment is not appropriate for extended periods, however. In general, local steroid injections are only used until more definitive treatment options can be used. Corticosteroid injections do not appear to slow disease progression.
Surgery
Release of the transverse carpal ligament is undertaken in carpal tunnel surgery. The purpose of cutting the transverse carpal ligament is to relieve pressure on the median nerve, and this is a type ofnerve decompression
A nerve decompression is a neurosurgical procedure to relieve chronic, direct pressure on a nerve to treat nerve entrapment, a pain syndrome characterized by severe chronic pain and muscle weakness. In this way a nerve decompression targets the ...
surgery. It is recommended when there is constant (not just intermittent) numbness, muscle weakness, or atrophy, and when night-splinting or other palliative interventions no longer alleviate intermittent symptoms. The surgery may be done with local or regional anesthesia with or without sedation, or under general anesthesia. In general, milder cases can be controlled without surgery for months to years, but severe cases are unrelenting symptomatically and are likely to result in surgical treatment.
Physical and occupational therapy
There are many different techniques used in manual therapy for patients with CTS. Some examples are manual and instrumental soft tissue mobilizations, massage therapy, bone mobilizations or manipulations, and neurodynamic techniques, focused on skeletal system or soft tissue. In cases of epineural tethering in the upper extremity, manual therapy can reduce this dysfunction and can have a positive impact on the gliding of the nerves through the carpal tunnel while moving the elbow, fingers, or wrist. Manual therapy included the incorporation of specified neurodynamic techniques, functional massage, and carpal bone mobilizations. People who receive physical therapy not only report a decrease in symptoms of pain, but also have increased functional ability of their wrists and hands. Self-myofascial ligament stretching has been suggested as an effective technique, although a meta-analysis claimed this kind of therapy does not show significant improvement in symptoms or function. However, if stretching is received from a physical therapist, it can be more beneficial rather than if it is done by the patient themself. Tendon and nerve gliding exercises appear to be useful in carpal tunnel syndrome.Alternative medicine
A 2018 Cochrane review on acupuncture and related interventions for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome concluded that, "Acupuncture and laser acupuncture may have little or no effect in the short term on symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) in comparison with placebo or sham acupuncture." It was also noted that all studies had an unclear or high overall risk of bias and that all evidence was of low or very low quality.Prognosis
 The natural history of untreated CTS seems to be gradual worsening of the neuropathy. It is difficult to prove that this is always the case, but the supportive evidence is compelling.
Atrophy of the thenar muscles, weakness of palmar abduction, and loss of sensibility (constant numbness as opposed to intermittent paresthesia) are signs of advanced neuropathy. Advanced neuropathy is often permanent. The nerve will try to recover after surgery for more than 2 years, but the recovery may be incomplete.
Paresthesia may increase after release of advanced carpal tunnel syndrome, and people may feel worse than they did prior to surgery for many months.
Troublesome recovery seems related to symptoms of anxiety or depression, and unhelpful thoughts about symptoms (such as worst-case or catastrophic thinking) as well as advanced neuropathy with potentially permanent neuropathy.
Recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome after successful surgery is rare. Caution is warranted in considering additional surgery for people dissatisfied with the result of carpal tunnel release as perceived recurrence may more often be due to renewed awareness of persistent symptoms rather than worsening pathology.
The natural history of untreated CTS seems to be gradual worsening of the neuropathy. It is difficult to prove that this is always the case, but the supportive evidence is compelling.
Atrophy of the thenar muscles, weakness of palmar abduction, and loss of sensibility (constant numbness as opposed to intermittent paresthesia) are signs of advanced neuropathy. Advanced neuropathy is often permanent. The nerve will try to recover after surgery for more than 2 years, but the recovery may be incomplete.
Paresthesia may increase after release of advanced carpal tunnel syndrome, and people may feel worse than they did prior to surgery for many months.
Troublesome recovery seems related to symptoms of anxiety or depression, and unhelpful thoughts about symptoms (such as worst-case or catastrophic thinking) as well as advanced neuropathy with potentially permanent neuropathy.
Recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome after successful surgery is rare. Caution is warranted in considering additional surgery for people dissatisfied with the result of carpal tunnel release as perceived recurrence may more often be due to renewed awareness of persistent symptoms rather than worsening pathology.
History
CTS was first described around 1850, but infrequently diagnosed until findings publicized by neurologist W. Russell Brain in 1947. People were often diagnosed with acroparesthesia. Clinicians would often ascribe it to "poor circulation" and not pursue it further. Sir James Paget described median nerve compression at the carpal tunnel in two patients after trauma in 1854.Paget J (1854) Lectures on surgical pathology. Lindsay & Blakinston, Philadelphia The first was due to an injury where a cord had been wrapped around a man's wrist. The second was related to a distal radial fracture. For the first case Paget performed an amputation of the hand. For the second case Paget recommended a wrist splint. The first to notice the association between the carpal ligament pathology and median nerve compression appear to have been Pierre Marie and Charles Foix in 1913. They described the results of a postmortem of an 80-year-old man with bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. They suggested that division of the carpal ligament would be curative in such cases. Putman had previously described a series of 37 patients and suggested a vasomotor origin. The association between the thenar muscle atrophy and compression was noted in 1914. The name "carpal tunnel syndrome" appears to have been coined by Moersch in 1938. Physician George S. Phalen of theCleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic is an American Nonprofit organization, nonprofit Academic health science center, academic Medical centers in the United States, medical center based in Cleveland, Ohio. Owned and operated by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, an O ...
drew attention to the pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
of compression as the reason for CTS after working with a group of patients in the 1950s and 1960s.
Treatment
In 1933 Sir James Learmonth outlined a method ofnerve decompression
A nerve decompression is a neurosurgical procedure to relieve chronic, direct pressure on a nerve to treat nerve entrapment, a pain syndrome characterized by severe chronic pain and muscle weakness. In this way a nerve decompression targets the ...
of the nerve at the wrist. This procedure appears to have been pioneered by the Canadian surgeons Herbert Galloway and Andrew MacKinnon in 1924 in Winnipeg but was not published. Endoscopic release was described in 1988.
See also
* Cheiralgia paresthetica * Cubital tunnel syndrome * Radial tunnel syndrome * Tarsal tunnel syndrome * Ulnar tunnel syndromeReferences
External links
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Fact Sheet (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke)
NHS website carpal-tunnel.net provides a free to use, validated, online self diagnosis questionnaire for CTS
* {{Authority control Mononeuropathies of upper limb Physical ergonomics Syndromes affecting the nervous system Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate