apocalypticist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Apocalypticism is the
Apocalypticism is the
 There is no current consensus among historians about widespread apocalypticism in the
There is no current consensus among historians about widespread apocalypticism in the
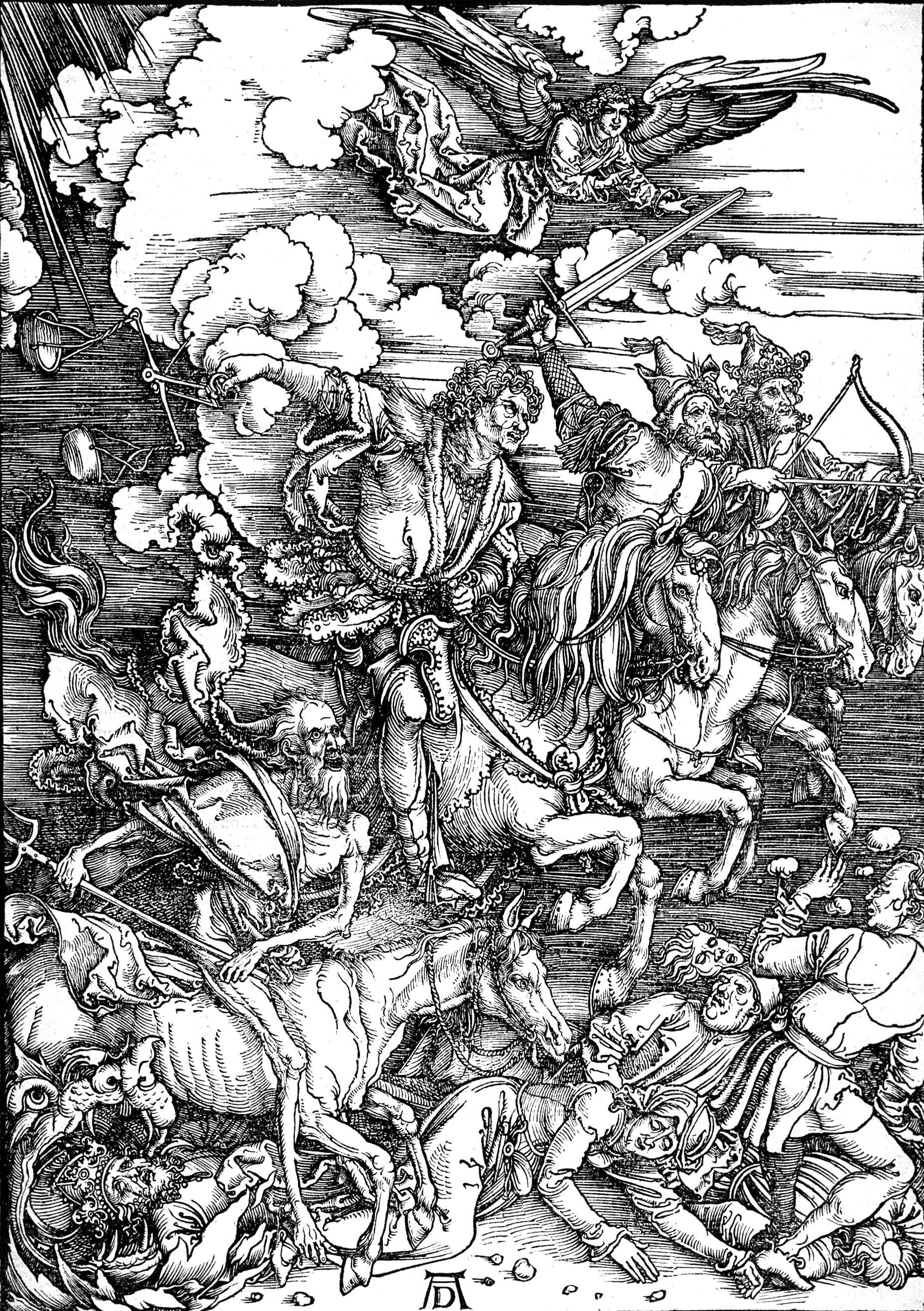
 The Great Disappointment in the
The Great Disappointment in the
KJV Church members believe that there will be increasingly severe wars, earthquakes, hurricanes, and other man-made and natural disasters prior to the Second Coming.
July 15, 1894, p. 1677
: "We see no reason for changing the figures—nor could we change them if we would. They are, we believe, God's dates, not ours. But bear in mind that the end of 1914 is not the date for the beginning, but for the end of the time of trouble." 1918September 1, 1916 ''The Watchtower'', page
264-265
and 1925''Millions Now Living Will Never Die'', 1920, page 97, "Based upon the argument heretofore set forth, then, that the old order of things, the old world, is ending and is therefore passing away, and that the new order is coming in, and that 1925 shall mark the resurrection of the faithful worthies of old and the beginning of reconstruction, it is reasonable to conclude that millions of people now on the earth will be still on the earth in 1925. Then, based upon the promises set forth in the divine Word, we must reach the positive and indisputable conclusion that millions now living will never die." made in the Watch Tower Society's publications between 1879 and 1924. Claims about the significance of those years, including the presence of Jesus Christ, the beginning of the " last days", the destruction of worldly governments and the earthly resurrection of Jewish patriarchs, were successively abandoned. In 1922 the society's principal journal, '' Watch Tower'', described its chronology as "no stronger than its weakest link", but also claimed the chronological relationships to be "of divine origin and divinely corroborated...in a class by itself, absolutely and unqualifiedly correct" and "indisputable facts", while repudiation of Russell's teachings was described as "equivalent to a repudiation of the Lord". The Watch Tower Society has stated that its early leaders promoted "incomplete, even inaccurate concepts". The Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses says that, unlike
– ''Globe and Mail''. May 23, 2011. Retrieved May 23, 2011. However, on October 16, Camping admitted to an interviewer that he did not know when the end would come. In March 2012, Camping "humbly acknowledged" in a letter to Family Radio listeners that he had been mistaken, that the attempt to predict a date was "sinful", and that critics had been right in pointing to the scriptural text "of that day and hour knoweth no man". He added that he was searching the Bible "even more fervently ..not to find dates, but to be more faithful in our understanding."

Apocalypticism
" In James Crossley and Alastair Lockhart (eds.) ''Critical Dictionary of Apocalyptic and Millenarian Movements''. * Cohn, Norman (1993). ''Cosmos, Chaos and the World to Come: The Ancient Roots of Apocalyptic Faith.'' New Haven: Yale University Press. * Fuller, Robert C. (1995). ''Naming the Antichrist: The History of an American Obsession.'' New York: Oxford University Press. * Hall, John R. (2009). ''Apocalypse: From Antiquity to the Empire of Modernity'', Cambridge, UK: Polity. ( band ) * Heard, Alex and Klebnikov, Peter, December 27, 1998,
Apocalypse Now. No, Really. Now!
, ''The New York Times Magazine'' * * Landes, Richard. (2011). ''Heaven on Earth: The Varieties of the Millennial Experience.'' New York, N.Y.: Oxford University Press. (hard cover) * Mason, Carol. (2002). ''Killing for Life: The Apocalyptic Narrative of Pro-life Politics.'' Ithaca, N.Y.: Cornell University Press. (hard cover) (paperback) * O'Leary, Stephen. (1994). ''Arguing the Apocalypse: A Theory of Millennial Rhetoric.'' New York: Oxford University Press. * Palmer, James T. (2014) "The Apocalypse in the Early Middle Ages" Cambridge, Cambridge University press * * Quinby, Lee. (1994). ''Anti-Apocalypse: Exercises in Genealogical Criticism.'' Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. (hard bound) (paperback) * Robbins, Thomas, and Susan J. Palmer, eds. 1997. ''Millennium, Messiahs, and Mayhem: Contemporary Apocalyptic Movements.'' New York: Routledge. (hard bound) (paperback) * Staker, Susan, ed. (1993). ''Waiting for World's End: The Diaries of Wilford Woodruff''. Salt Lake City, Utah: Signature Books. * Stewart, Kathleen and Susan Harding. 1999. "Bad Endings: American Apocalypsis." ''Annual Review of Anthropology'', 28, pp. 285–310. * Stone, Jon R., ed. (2000). ''Expecting Armageddon: Essential Readings in Failed Prophecy.'' New York: Routledge. (paperback) * Strozier, Charles B. (1994). ''Apocalypse: On the Psychology of Fundamentalism in America.'' Boston: Beacon Press. * Strozier, Charles B, and Michael Flynn, eds. (1997). ''The Year 2000: Essays on the End.'' New York: New York University Press. (hard bound) (paperback) * Thompson, Damian. (1996). ''The End of Time: Faith and Fear in the Shadow of the Millennium.'' London:
The Millenarian World of Early Mormonism
'' Urbana: University of Illinois Press. * Wessinger, Catherine, ed.. (2000). ''Millennialism, Persecution, and Violence: Historical Cases.'' Religion and Politics Series, Michael Barkun, (ed.). Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press. (hard bound) (paperback) * * Zuquete, Jose Pedro. "Apocalyptic Movements. "Encyclopædia Britannica
Encyclopædia Britannica Online Academic Edition
Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. 31 Dec. 2012 {{Authority control Eschatology Religious terminology
 Apocalypticism is the
Apocalypticism is the religious belief
Faith, derived from Latin ''fides'' and Old French ''feid'', is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or In the context of religion, one can define faith as "belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion".
Religious people often ...
that the end of the world is imminent, even within one's own lifetime. This belief is usually accompanied by the idea that civilization will soon come to a tumultuous end due to some sort of catastrophic global event. Apocalypticism is one aspect of eschatology
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age, human history, or of the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic and non-Abrahamic), which teach that nega ...
in certain religions—the part of theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing th ...
concerned with the final events of world history, or the ultimate destiny of humanity (societal collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of socioeconomic complexity, the downfall of government, and the rise of violence. Possible cause ...
, human extinction
Human extinction, also known as omnicide, is the hypothetical end of the human species due to either natural causes such as population decline from sub-replacement fertility, an asteroid impact, or large-scale volcanism, or to anthropogenic ...
, etc.).
The religious versions of these views and movements often focus on cryptic revelations about a sudden, dramatic, and cataclysmic intervention of God in history; the judgment of humanity; the salvation of the faithful elect; and the eventual rule of the elect with God in a renewed heaven and earth. Arising initially in Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
, apocalypticism was developed more fully in Judaic
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the M ...
, Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
, and Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ma ...
eschatological speculation.
Apocalypticism is often conjoined with the belief that esoteric knowledge
Western esotericism, also known as esotericism, esoterism, and sometimes the Western mystery tradition, is a term scholars use to categorise a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas ...
will likely be revealed in a major confrontation between good and evil forces, destined to change the course of history.Paul O. Ingram, Frederick John Streng
Frederick John Streng (September 30, 1933 – June 21, 1993) was a noted scholar in Buddhist-Christian studies, author, editor, leader of religious organizations, and Professor of the History of Religions, Southern Methodist University in Texas fr ...
. ''Buddhist-Christian Dialogue: Mutual Renewal and Transformation''. University of Hawaii Press, 1986. pp. 148–149. Apocalypse
Apocalypse () is a literary genre in which a supernatural being reveals cosmic mysteries or the future to a human intermediary. The means of mediation include dreams, visions and heavenly journeys, and they typically feature symbolic imager ...
s can be viewed as good, evil, ambiguous or neutral, depending on the particular religion or belief system
A belief is an attitude that something is the case, or that some proposition is true. In epistemology, philosophers use the term "belief" to refer to attitudes about the world which can be either true or false. To believe something is to take ...
promoting them. However, it is not exclusively a religious idea and there are end times or transitional scenarios based in modern science
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal.
Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesop ...
, technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
, political discourse
Discourse analysis (DA), or discourse studies, is an approach to the analysis of written, vocal, or sign language use, or any significant semiotic event.
The objects of discourse Analysis (discourse, writing, conversation, communicative event) ...
, and conspiracy theories
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a conspiracy by sinister and powerful groups, often political in motivation, when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
*
*
*
* The term has a nega ...
.
Abrahamic religions
Christianity
Beginning with the Christian theologians Johannes Weiss andAlbert Schweitzer
Ludwig Philipp Albert Schweitzer (; 14 January 1875 – 4 September 1965) was an Alsatian-German/French polymath. He was a theologian, organist, musicologist, writer, humanitarian, philosopher, and physician. A Lutheran minister, Schweit ...
, most scholars have believed that Jesus' apocalyptic teachings were the central message Jesus intended to impart.Bart D. Ehrman
Bart Denton Ehrman (born 1955) is an American New Testament scholar focusing on textual criticism of the New Testament, the historical Jesus, and the origins and development of early Christianity. He has written and edited 30 books, includin ...
's Jesus: Apocalyptic Prophet Simultaneously, these scholars tend to see Jesus' prediction as mistakenSanders, E. P. The Historical Figure of Jesus. Penguin, 1993. Chapter 13, The Coming of the Kingdom. although some view it from the perspective of the conditional nature of judgement prophecy. The major focus for Jesus' apocalyptic sayings in the Gospels is the Olivet Discourse in Mark 13 where "Jesus speaks as if Peter, James, and John will personally experience the parousia
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
."John-Christian Eurell. "The Delay of the Parousia and the Changed Function of Eschatological Language". Journal of Early Christian History 2020. In the Gospel of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew), or simply Matthew. It is most commonly abbreviated as "Matt." is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells how Israel's Messiah, Jesus, comes to his people and form ...
, the major locus for Jesus' apocalyptic sayings is in Matthew 24:36-51. In addition, many scholars point to Jesus' association with John the Baptist as confirmation for his apocalyptic intentions. In the New Testament narrative, John's preparation for the end through baptismal forgiveness of sins is comparable to the sentiments of other apocalyptic movements of the late Second Temple Period
The Second Temple period in Jewish history lasted approximately 600 years (516 BCE - 70 CE), during which the Second Temple existed. It started with the return to Zion and the construction of the Second Temple, while it ended with the First Je ...
. As attested to in the synoptic gospels, Jesus is deliberate in beginning his teaching with John the Baptist, a reflection on the nature of his apocalyptic ministry. In the Pauline epistles
The Pauline epistles, also known as Epistles of Paul or Letters of Paul, are the thirteen books of the New Testament attributed to Paul the Apostle, although the authorship of some is in dispute. Among these epistles are some of the earliest ex ...
(1 Thess. 4:13-18) Paul states he expects to be alive when the end comes, and this passage is often cited (although the interpretation is disputed). In contrast, other passages in the Pauline epistles are seen as describing the nearness of the ''parousia'' whether or not Paul himself will live to see it. However, these statements find tensions with other New Testament passages, conflicting with texts which form the basis for later Christian apocalyptic theology. This includes a passage from the apocalyptic discourse of Matthew 24, where Jesus states "only the Father" knows of the hour of the coming of the Son of Man. While later Christians favor Matthew 24 over Mark 13, modern critical scholars recognize this contradiction as evidence of shifting Christian belief. This is a shift that suggests the apocalyptic moment will occur at a later date, not in the lifetime of Jesus' followers.
While the notion of an apocalyptic Jesus remains the view of most experts, it has not gone unchallenged. The Jesus Seminar
The Jesus Seminar was a group of about 50 critical biblical scholars and 100 laymen founded in 1985 by Robert Funk that originated under the auspices of the Westar Institute.''Making Sense of the New Testament'' by Craig Blomberg (Mar 1, 2004) ...
has rejected the historicity of Jesus' apocalyptic expectations, arguing that the evidence for it in the Gospels is largely tied to Jesus' Son of Man sayings which they do not consider historical. They further attribute the apocalyptic expectations of the early church as emerging from their belief in the resurrection of Jesus, where resurrection was tied to eschatological expectations in Jewish theology. Some argued earlier traditions in the Q Source
The Q source (also called Q document(s), Q Gospel, or Q; from german: Quelle, meaning "source") is a hypothetical written collection of primarily Jesus' sayings (λόγια : ). Q is part of the common material found in the Gospels of Matthew ...
and Gospel of Thomas
The Gospel of Thomas (also known as the Coptic Gospel of Thomas) is an extra-canonical sayings gospel. It was discovered near Nag Hammadi, Egypt, in December 1945 among a group of books known as the Nag Hammadi library. Scholars speculate ...
showed that apocalyptic eschatalogy was not present in earlier layers of the Jesus tradition. The approach by the Jesus Seminar is not short of many critics. Another well-known but different perspective has been that of R.T. France
Richard Thomas France (1938–2012), known as R. T. France or Dick France, was a New Testament scholar and Anglican cleric. He was Principal of Wycliffe Hall, Oxford, from 1989 to 1995. He also worked for the London School of Theology. ...
and N.T. Wright, who argue that the apocalyptic sayings in the Gospels are historical but largely amount to Jewish idiom using language of cosmic destruction to describe political upheavals, namely concerning itself with the destruction of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and the Temple around 70.
Various Christian eschatological systems have developed, providing different frameworks for understanding the timing and nature of apocalyptic predictions. Some like dispensational premillennialism
Dispensationalism is a system that was formalized in its entirety by John Nelson Darby. Dispensationalism maintains that history is divided into multiple ages or "dispensations" in which God acts with humanity in different ways. Dispensationali ...
tend more toward an apocalyptic vision, while others like postmillennialism
In Christian eschatology (end-times theology), postmillennialism, or postmillenarianism, is an interpretation of chapter 20 of the Book of Revelation which sees Christ's second coming as occurring ''after'' (Latin ''post-'') the "Millennium", ...
and amillennialism
Amillennialism or amillenarism is a chillegoristic eschatological position in Christianity which holds that there will be no millennial reign of the righteous on Earth. This view contrasts with both postmillennial and, especially, with premi ...
, while teaching that the end of the world could come at any moment, tend to focus on the present life and contend that one should not attempt to predict when the end should come, though there have been exceptions such as postmillennialist Jonathan Edwards, who estimated that the end times would occur around the year 2000.
Year 1000
 There is no current consensus among historians about widespread apocalypticism in the
There is no current consensus among historians about widespread apocalypticism in the year 1000
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the h ...
. Richard Landes, Johannes Fried, and others think there were widespread expectations, both hopes and fears, The notion of a widespread expectation of the year 1000 first appeared during the Renaissance. Historians denounced it as a myth around 1900.
There are a many recorded instances of both fascination with the advent of the year 1000, and examples of apocalyptic excitement leading up to the year 1000, the most explicit and revealing examples provided by Rodulfus Glaber Rodulfus, or Raoul Glaber (which means "the Smooth" or "the Bald") (985–1047), was an 11th-century Benedictine chronicler.
Life
Glaber was born in 985 in Burgundy. At the behest of his uncle, a monk at Saint-Léger-de-Champeaux, Glaber was se ...
.
Specifically in Western Europe, during the year 1000, Christian philosophers held many debates on when Jesus was actually born and the debates continue to today. This caused confusion between the common people on whether or not the apocalypse would occur at a certain time. Because both literate and illiterate people commonly accepted this idea of the apocalypse, they could only accept what they heard from religious leaders on when the disastrous event would occur. Religious leader, Abbo of Fleury
Abbo or Abbon of Fleury ( la, Abbo Floriacensis; – 13 November 1004), also known as Saint Abbo or Abbon, was a monk and abbot of Fleury Abbey in present-day Saint-Benoît-sur-Loire near Orléans, France.
Life
Abbo was born near Orléans ...
believed that Jesus was born 21 years after year 1 which was commonly accepted by close circles of his followers. Abbot Heriger of Lobbes
Herigerus ( – 31 October 1007) was a Benedictine monk, often known as Heriger of Lobbes for serving as abbot of the abbey of Lobbes between 990 and 1007. Remembered for his writings as theologian and historian, Herigerus was a teacher to numero ...
, argued that the birth of Jesus occurred not during the year 1 but rather during the 42nd year of the common era. Eventually many scholars came to accept that the apocalypse would occur sometime between 979-1042. Under the influence of the Sibylline Oracles and figures such as Otto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was Holy Roman Emperor from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of the Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was crowned as King of ...
and Abbot Adso of Montier-en-Der many felt that the apocalypse would soon occur.
Some historians, such as Richard Landes, think there were extensive apocalyptic expectations at the approach the year 1000 and again at the approach of 1000 anno passionis (1033). Alessandro Barbero
Alessandro Barbero (born April 30, 1959) is an Italian historian, novelist and essayist.
Barbero was born in Turin. He attended the University of Turin, where he studied literature and Medieval history. He won the 1996 Strega Prize, Italy's m ...
, on the other hand, claims that the fear of the 1000 is a myth and there was no widespread apocalyptic sentiment. As evidence, he cites that on 31 December 999 Pope Sylvester II granted certain privileges and guarantees to the Abbey of Fulda
The Abbey of Fulda (German ''Kloster Fulda'', Latin ''Abbatia Fuldensis''), from 1221 the Princely Abbey of Fulda (''Fürstabtei Fulda'') and from 1752 the Prince-Bishopric of Fulda (''Fürstbistum Fulda''), was a Benedictine abbey and ecclesiastic ...
, without any indication that neither the pope nor the abbot believed that the world was soon to end. Similarly, Barbero points out a document from 3 October 999 in which Otto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was Holy Roman Emperor from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of the Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was crowned as King of ...
grants future concessions to Farfa Abbey
Farfa Abbey ( it, Abbazia di Farfa) is a territorial abbey in northern Lazio, central Italy. In the Middle Ages it was one of the richest and most famous abbeys in Italy. It belongs to the Benedictine Order and is located about from Rome, ...
. Another document in 999 shows two brothers taking a 29-year loan on lands of the abbey of San Marciano in Tortona, suggesting that even common people did not believe the world was ending. On the other hand, the fact that Otto III visited the tomb of Charlemagne, the emperor of the year 6000 (Annus Mundi) on Pentecost of the year 1000 suggests that even the man who appointed Sylvester pope, had his own views on the matter.
Fifth Monarchy Men
The Fifth Monarchists or Fifth Monarchy Men were an extremePuritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
sect active from 1649 to 1660 during the Interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
, following the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
s of the 17th century. They took their name from a prophecy in the Book of Daniel
The Book of Daniel is a 2nd-century BC biblical apocalypse with a 6th century BC setting. Ostensibly "an account of the activities and visions of Daniel, a noble Jew exiled at Babylon", it combines a prophecy of history with an eschatology (a ...
that four ancient monarchies (Babylonian, Persian, Macedonian, and Roman) would precede the kingdom of Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
. They also referred to the year 1666 and its relationship to the biblical Number of the Beast
The number of the beast ( grc-koi, Ἀριθμὸς τοῦ θηρίου, ) is associated with the Beast of Revelation in chapter 13, verse 18 of the Book of Revelation. In most manuscripts of the New Testament and in English translations of t ...
indicating the end of earthly rule by carnal human beings. They were one of a number of nonconformist dissenting groups that emerged around this time.
Isaac Newton and the end of the world in 2060
In late February and early March 2003, a large amount of media attention circulated around the globe regarding largely unknown and unpublished documents, evidently written by Isaac Newton, indicating that he believed the world would end no earlier than 2060. The story garnered vast amounts of public interest and found its way onto the front page of several widely distributed newspapers, including the UK's ''The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was f ...
'', Canada's ''National Post
The ''National Post'' is a Canadian English-language broadsheet newspaper available in several cities in central and western Canada. The paper is the flagship publication of Postmedia Network and is published Mondays through Saturdays, with ...
'', Israel's ''Maariv
''Maariv'' or ''Maʿariv'' (, ), also known as ''Arvit'' (, ), is a Jewish prayer service held in the evening or night. It consists primarily of the evening ''Shema'' and '' Amidah''.
The service will often begin with two verses from Psalms ...
'' and '' Yediot Aharonot'', and was also featured in an article in the scientific journal ''Canadian Journal of History
The ''Canadian Journal of History/Annales canadiennes d'histoire'' is a triannual peer-reviewed academic journal covering all areas of history. It was established in 1966 at the University of Saskatchewan and was acquired by University of Toronto P ...
''.
The two documents detailing this prediction are currently housed within the Jewish National and University Library in Jerusalem. Both were believed to be written toward the end of Newton's life, circa 1705, a time frame most notably established by the use of the full title of ''Sir'' Isaac Newton within portions of the documents.
These documents do not appear to have been written with the intention of publication and Newton expressed a strong personal dislike for individuals who provided specific dates for the Apocalypse
Apocalypse () is a literary genre in which a supernatural being reveals cosmic mysteries or the future to a human intermediary. The means of mediation include dreams, visions and heavenly journeys, and they typically feature symbolic imager ...
purely for sensational value. Furthermore, he at no time provides a specific date for the end of the world in either of these documents. See Isaac Newton's religious views
Isaac Newton (4 January 1643 – 31 March 1727) was considered an insightful and erudite theologian by his Protestant contemporaries. NGLISH & LATINIslamic theology
Schools of Islamic theology are various Islamic schools and branches in different schools of thought regarding '' ʿaqīdah'' (creed). The main schools of Islamic Theology include the Qadariyah, Falasifa, Jahmiyya, Murji'ah, Muʿtazila, Batin ...
this concept is often referred to as The Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
of Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
and the establishment of The Kingdom of God
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms Kingdom of God and Kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" ...
on Earth. In a separate manuscript, Isaac Newton paraphrases Revelation 21 and 22 and relates the post 2060 events by writing:
Millerism and The Great Disappointment
 The Great Disappointment in the
The Great Disappointment in the Millerite movement
The Millerites were the followers of the teachings of William Miller, who in 1831 first shared publicly his belief that the Second Advent of Jesus Christ would occur in roughly the year 1843–1844. Coming during the Second Great Awakening, hi ...
was the reaction that followed Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul c ...
preacher William Miller's proclamations that Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
would return to the Earth by 1844, what he called the Advent
Advent is a Christian season of preparation for the Nativity of Christ at Christmas. It is the beginning of the liturgical year in Western Christianity.
The name was adopted from Latin "coming; arrival", translating Greek '' parousia''. ...
. His study of the Daniel 8
Daniel 8 is the eighth chapter of the Book of Daniel. It tells of Daniel's vision of a two-horned ram destroyed by a one-horned goat, followed by the history of the "little horn", which is Daniel's code-word for the Greek king Antiochus IV Epiph ...
prophecy during the Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Protestant religious revival during the early 19th century in the United States. The Second Great Awakening, which spread religion through revivals and emotional preaching, sparked a number of reform movements. R ...
led him to the conclusion that Daniel's "cleansing of the sanctuary" was cleansing of the world from sin when Christ would come, and he and many others prepared, but October 22, 1844 came and they were disappointed.
These events paved the way for the Adventists
Adventism is a branch of Protestant Christianity that believes in the imminent Second Coming (or the "Second Advent") of Jesus Christ. It originated in the 1830s in the United States during the Second Great Awakening when Baptist preacher Wil ...
who formed the Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and ...
. They contended that what had happened on October 22 was not Jesus' return, as Miller had thought, but the start of Jesus' final work of atonement, the cleansing in the heavenly sanctuary
In Seventh-day Adventist theology, the heavenly sanctuary teaching asserts that many aspects of the Hebrew tabernacle or sanctuary are representative of heavenly realities. In particular, Jesus is regarded as the High Priest who provides cleansin ...
, leading up to the Second Coming of Christ
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
.
Seventh-day Adventism
The ideological descendants of the Millerites are the Seventh-day Adventists. They are aProtestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
Christian denomination
A Christian denomination is a distinct Religion, religious body within Christianity that comprises all Church (congregation), church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadersh ...
which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday
Saturday is the day of the week between Friday and Sunday. No later than the 2nd century, the Romans named Saturday ("Saturn's Day") for the planet Saturn, which controlled the first hour of that day, according to Vettius Valens. The da ...
, the seventh day of the week
In many languages, the names given to the seven days of the week are derived from the names of the classical planets in Hellenistic astronomy, which were in turn named after contemporary deities, a system introduced by the Sumerians and lat ...
in both the Jewish calendar
The Hebrew calendar ( he, הַלּוּחַ הָעִבְרִי, translit=HaLuah HaIvri), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel ...
, and calendars in use in the Christian world (such as the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years d ...
), as the Sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, commanded by God to be kept as a holy day of rest, as ...
, and its emphasis on the imminent Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
(advent) of Jesus Christ. The denomination grew out of the Millerite movement
The Millerites were the followers of the teachings of William Miller, who in 1831 first shared publicly his belief that the Second Advent of Jesus Christ would occur in roughly the year 1843–1844. Coming during the Second Great Awakening, hi ...
in the United States during the mid-19th century and it was formally established in 1863. Among its founders was Ellen G. White
Ellen Gould White (née Harmon; November 26, 1827 – July 16, 1915) was an American woman author and co-founder of the Seventh-day Adventist Church. Along with other Adventist leaders such as Joseph Bates and her husband James White, she wa ...
, whose extensive writings are still held in high regard by the adherents of the Seventh-day Adventist Church.
Mormonism
Like many 19th-century AmericanRestorationist
Restorationism (or Restitutionism or Christian primitivism) is the belief that Christianity has been or should be restored along the lines of what is known about the apostolic early church, which restorationists see as the search for a purer a ...
Christian denominations
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
, the Mormon tradition teaches that adherents are living shortly before the Second Coming of Christ. The term "latter days" is used in the official names of several Mormon churches, including the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
. LDS president Wilford Woodruff
Wilford Woodruff Sr. (March 1, 1807September 2, 1898) was an American religious leader who served as the fourth president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) from 1889 until his death. He ended the public practice of ...
preached multiple times that many then-living adherents "would not taste death" before witnessing the return of Christ. According to LDS Church teachings, the true gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
will be taught in all parts of the world prior to the Second Coming.Matthew 24:14KJV Church members believe that there will be increasingly severe wars, earthquakes, hurricanes, and other man-made and natural disasters prior to the Second Coming.
Jehovah's Witnesses
Theeschatology of Jehovah's Witnesses
The eschatology of Jehovah's Witnesses is central to their religious beliefs. They believe that Jesus Christ has been ruling in heaven as king since 1914, a date they believe was prophesied in Scripture, and that after that time a period of cle ...
is central to their faith and religious beliefs. They believe that Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
has been ruling in heaven as king since 1914 (a date they believe was prophesied in Scripture), and that after that time a period of cleansing occurred, resulting in God's selection of the Bible Students associated with Charles Taze Russell
Charles Taze Russell (February 16, 1852 – October 31, 1916), or Pastor Russell, was an American Christian restorationist minister from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and founder of what is now known as the Bible Student movement. He was an ...
to be his people in 1919. They also believe the destruction of those who reject their message and thus willfully refuse to obey God will shortly take place at Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
, ensuring that the beginning of the new earthly society will be composed of willing subjects of that kingdom.
The group's doctrines surrounding 1914 are the legacy of a series of emphatic claims regarding the years 1799,''The Watchtower'', March 1, 1922, page 73, "The indisputable facts, therefore, show that the 'time of the end' began in 1799; that the Lord's second presence began in 1874." 1874, 1878, 1914,''The Watchtower''July 15, 1894, p. 1677
: "We see no reason for changing the figures—nor could we change them if we would. They are, we believe, God's dates, not ours. But bear in mind that the end of 1914 is not the date for the beginning, but for the end of the time of trouble." 1918September 1, 1916 ''The Watchtower'', page
264-265
and 1925''Millions Now Living Will Never Die'', 1920, page 97, "Based upon the argument heretofore set forth, then, that the old order of things, the old world, is ending and is therefore passing away, and that the new order is coming in, and that 1925 shall mark the resurrection of the faithful worthies of old and the beginning of reconstruction, it is reasonable to conclude that millions of people now on the earth will be still on the earth in 1925. Then, based upon the promises set forth in the divine Word, we must reach the positive and indisputable conclusion that millions now living will never die." made in the Watch Tower Society's publications between 1879 and 1924. Claims about the significance of those years, including the presence of Jesus Christ, the beginning of the " last days", the destruction of worldly governments and the earthly resurrection of Jewish patriarchs, were successively abandoned. In 1922 the society's principal journal, '' Watch Tower'', described its chronology as "no stronger than its weakest link", but also claimed the chronological relationships to be "of divine origin and divinely corroborated...in a class by itself, absolutely and unqualifiedly correct" and "indisputable facts", while repudiation of Russell's teachings was described as "equivalent to a repudiation of the Lord". The Watch Tower Society has stated that its early leaders promoted "incomplete, even inaccurate concepts". The Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses says that, unlike
Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
, its interpretations of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
are not inspired or infallible. Witness publications say that Bible prophecies can be fully understood only after their fulfillment, citing examples of biblical figures who did not understand the meaning of prophecies they received. Watch Tower publications often cite Proverbs 4:18, "The path of the righteous ones is like the bright light that is getting lighter and lighter until the day is firmly established" ( NWT) to support their view that there would be an increase in knowledge during "the time of the end", as mentioned in Daniel 12:4. Jehovah's Witnesses state that this increase in knowledge needs adjustments. Watch Tower publications also say that unfulfilled expectations are partly due to eagerness for God's Kingdom
The concept of the kingship of God appears in all Abrahamic religions, where in some cases the terms Kingdom of God and Kingdom of Heaven are also used. The notion of God's kingship goes back to the Hebrew Bible, which refers to "his kingdom" ...
and that they do not call their core beliefs into question.
Christadelphians
For Christadelphians,Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
marks the "great climax of history when the nations would be gathered together "into a place called in the Hebrew tongue Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
", and the judgment on them would herald the setting up of the Kingdom of God." After this Christadelphians believe that Jesus will return to the earth in person to set up the Kingdom of God in fulfilment of the promises made to Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
and David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
. This includes the belief that the coming Kingdom will be the restoration of God's first Kingdom of Israel, which was under David and Solomon. For Christadelphians, this is the focal point of the gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
taught by Jesus and the apostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...
.
Realized eschatology
Realized eschatology is a Christian eschatological theory popularized byJ.A.T. Robinson
John Arthur Thomas Robinson (16 May 1919 – 5 December 1983) was an English New Testament scholar, author and the Anglican Bishop of Woolwich. He was a lecturer at Trinity College, Cambridge, and later Dean of Trinity College until his death in ...
, Joachim Jeremias
Joachim Jeremias (20 September 1900 – 6 September 1979) was a German Lutheran theologian, scholar of Near Eastern Studies and university professor for New Testament studies. He was abbot of Bursfelde, 1968–1971.
He was born in Dresden and sp ...
, Ethelbert Stauffer Ethelbert Stauffer (May 8, 1902 in Friedelsheim – August 1, 1979 in Erlangen) was a German Protestant theologian and numismatist.
Life
Stauffer was the son of a Mennonite preacher born and raised in Worms. After attending the local grammar school ...
(1902–1979), and
C. H. Dodd (1884–1973), that holds that the eschatological passages in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
do not refer to the future, but instead refer to the ministry of Jesus
The ministry of Jesus, in the canonical gospels, begins with his baptism in the countryside of Roman Judea and Transjordan, near the River Jordan by John the Baptist, and ends in Jerusalem, following the Last Supper with his disciples.''Ch ...
and his lasting legacy. Eschatology
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age, human history, or of the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic and non-Abrahamic), which teach that nega ...
is therefore not the end of the world but its rebirth instituted by Jesus and continued by his disciples, a historical (rather than transhistorical
Transhistoricity is the quality of holding throughout human history, not merely within the frame of reference of a particular form of society at a particular stage of historical development. An entity or concept that has transhistoricity is said to ...
) phenomenon. Those holding this view generally dismiss end times
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age, human history, or of the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic and non-Abrahamic), which teach that nega ...
theories, believing them to be irrelevant; they hold that what Jesus said and did, and told his disciples to do likewise, are of greater significance than any messianic expectations.
Harold Camping
American Christian radio hostHarold Camping
Harold Egbert Camping (July 19, 1921December 15, 2013) was an American Christian radio broadcaster and evangelist. Beginning in 1958, he served as president of Family Radio, a California-based radio station group that, at its peak, broadcast t ...
stated that the Rapture
The rapture is an Christian eschatology, eschatological position held by some Christians, particularly those of American evangelicalism, consisting of an Eschatology, end-time event when all Christian believers who are alive, along with resurre ...
and Judgment Day
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
would take place on May 21, 2011, and that the end of the world would take place five months later on October 21, 2011, based on adding the 153 fish of John 20 to May 21. The Rapture, as indicated in 1 Thessalonians 4:17 (''harpagēsometha'' = we shall be raptured / taken up, "rapture" derivable from the Latin translation ''rapiemur'') is the taking up of believers to a meeting in the air with the Lord Jesus, but for Camping the rapture was also associated with the End of the World.
Camping, who was then president of the Family Radio
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
Christian network, claimed the Bible as his source and said May 21 would be the date of the Rapture and the day of judgment "beyond the shadow of a doubt". Camping suggested that it would occur at 6 pm local time, with the Rapture sweeping the globe time zone by time zone, while some of his supporters claimed that around 200 million people (approximately 3% of the world's population) would be 'raptured'. Camping had previously claimed that the Rapture would occur in September 1994.
The vast majority of Christian groups, including most Protestant and Catholic believers, did not accept Camping's predictions; some explicitly rejected them, citing Bible passages including the words of Jesus stating "about that day or hour no one knows" (Matthew 24:36). An interview with a group of church leaders noted that all of them had scheduled church services as usual for Sunday, May 22.
Following the failure of the prediction, media attention shifted to the response from Camping and his followers. On May 23, Camping stated that May 21 had been a "spiritual" day of judgment, and that the physical Rapture would occur on October 21, 2011, simultaneously with the destruction of the universe by God.Radio host says Rapture actually coming in October– ''Globe and Mail''. May 23, 2011. Retrieved May 23, 2011. However, on October 16, Camping admitted to an interviewer that he did not know when the end would come. In March 2012, Camping "humbly acknowledged" in a letter to Family Radio listeners that he had been mistaken, that the attempt to predict a date was "sinful", and that critics had been right in pointing to the scriptural text "of that day and hour knoweth no man". He added that he was searching the Bible "even more fervently ..not to find dates, but to be more faithful in our understanding."
David Meade
David Meade is the pen name of an American end-timesconspiracy theorist
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a conspiracy by sinister and powerful groups, often political in motivation, when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
*
*
*
* The term has a nega ...
and book author who has yet to disclose his real name. Meade, who describes himself as a "Christian numerologist", claims to have attended the University of Louisville
The University of Louisville (UofL) is a public research university in Louisville, Kentucky. It is part of the Kentucky state university system. When founded in 1798, it was the first city-owned public university in the United States and one ...
, where he "studied astronomy, among other subjects", but, because his real name is unknown, ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large n ...
'' reported that the university could not confirm whether he had ever been a student there. He is also a writer, researcher and investigator who has written and self-published at least 13 books. He made appearances and interviews on ''Coast to Coast AM
''Coast to Coast AM'' is an American late-night radio talk show that deals with a variety of topics. Most frequently the topics relate to either the paranormal or conspiracy theories. It was hosted by creator Art Bell from its inception in 1 ...
'', ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large n ...
'', ''Glenn Beck Program
''Glenn'' (previously titled ''The Glenn Beck Program'') is a news talk and political opinion show on TheBlaze hosted by Glenn Beck. It is produced and recorded at TheBlaze studios in Dallas, TX. The show originally ran on CNN Headline News fr ...
'', YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
with pastor Paul Begley, and the ''Daily Express
The ''Daily Express'' is a national daily United Kingdom middle-market newspaper printed in tabloid format. Published in London, it is the flagship of Express Newspapers, owned by publisher Reach plc. It was first published as a broadsheet ...
''. He is best known for making numerous predictions, which have passed, regarding the end times, including that a hidden planet named Nibiru (sometimes known as Planet X) would destroy the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
.
Meade predicted that planet Nibiru would collide with Earth on September 23, 2017, destroying it. After his prediction failed, he revised the apocalypse to October, where he stated that the seven-year tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation ( grc, θλῖψις μεγάλη, thlîpsis megálē) is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the Eschatology, time of the end.
At Book of Revelation, ...
would possibly start followed by a millennium
A millennium (plural millennia or millenniums) is a period of one thousand years, sometimes called a kiloannus, kiloannum (ka), or kiloyear (ky). Normally, the word is used specifically for periods of a thousand years that begin at the starting ...
of peace. In 2018, Meade again made several predictions for that year, for instance, that North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
becoming a superpower in March 2018 and that Nibiru would destroy the Earth in spring. Meade announced that the apocalypse would begin in March 2018, but he did not predict the exact date. After March 2018 passed, he moved the apocalypse to April 23, 2018, in which he also predicted the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
, and Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
*Virgo (astrology), the sixth astrological sign of the zodiac
* Virgo (constellation), a constellation
*Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo
*Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy
* Virgo Su ...
will signal the rapture, and that Nibiru would destroy the Earth that day. However, before that date he said that reports that he predicted the end on 23 April were "fake news", but that the rapture—but not the end of the world—would take place on an unspecified date between May and December 2018.
Branch Davidians
The Branch Davidians (also known as The Branch) are a religious group that originated in 1955 from aschism
A schism ( , , or, less commonly, ) is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization, movement, or religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a split in what had previously been a single religious body, suc ...
among the Shepherd's Rod/Davidians. The Branch group was initially led by Benjamin Roden
Benjamin Lloyd Roden (January 5, 1902 – October 22, 1978) was an American religious leader and the prime organizer of the Branch Davidian Seventh-day Adventist Association.
Early life
Benjamin Roden was born on January 5, 1902 in Bea ...
. Branch Davidians are most associated with the Waco siege
The Waco siege, also known as the Waco massacre, was the law enforcement siege of the compound that belonged to the religious sect Branch Davidians. It was carried out by the U.S. federal government, Texas state law enforcement, and the U.S. ...
of 1993, which involved David Koresh. There is documented evidence (FBI negotiation transcripts between Kathryn Shroeder and Steve Schneider with interjections from Koresh himself) that David Koresh and his followers did not call themselves Branch Davidians. In addition, David Koresh, through forgery, stole the identity of the Branch Davidian Seventh-day Adventists for the purpose of obtaining the Mount Carmel Center property. The doctrinal beliefs of the Branch Davidians differ on teachings such as the Holy Spirit
In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is the divine force, quality, and influence of God over the Universe or over his creatures. In Nicene Christianity, the Holy Spirit or Holy Ghost is the third person of the Trinity. In Islam, the Holy Spirit acts as ...
and his nature, and the feast days and their requirements. Both groups have disputed the relevance of the other's spiritual authority based on the proceedings following Victor Houteff
Victor Tasho Houteff ( Bulgarian; Виктор Ташо Хутев ; March 2, 1885 – February 5, 1955) was the founder of the Davidian Seventh-day Adventist organization, known as The Shepherd's Rod.
Early life
Houteff was born in Raicovo, Eas ...
's death. From its inception in 1930, the Davidians/Shepherd's Rod group believed themselves to be living in a time when Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of ...
prophecies of a final divine judgment were coming to pass as a prelude to Christ's Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
.
In the late 1980s, Koresh and his followers abandoned many Branch Davidian teachings. Koresh became the group's self-proclaimed final prophet. "Koreshians" were the majority resulting from the schism among the Branch Davidians, but some of the Branch Davidians did not join Koresh's group and instead gathered around George Roden
George Buchanan Roden (January 17, 1938 – December 8, 1998) was an American leader of the Branch Davidian sect, a Seventh-day Adventist splinter group. In 1987, he was evicted from the Mount Carmel Center near Waco, Texas, by his rival David Kor ...
or became independent. Following a series of violent shootouts between Roden's and Koresh's group, the Mount Carmel compound was eventually taken over by the "Koreshians". In 1993, the ATF and Texas Army National Guard
The Texas Army National Guard is a component of the United States Army, the United States National Guard and the Texas Military Forces (along with the Texas Air National Guard and the Texas State Guard).
Texas Army National Guard units are tra ...
raided one of the properties belonging to a new religious movement
A new religious movement (NRM), also known as alternative spirituality or a new religion, is a religious or Spirituality, spiritual group that has modern origins and is peripheral to its society's dominant religious culture. NRMs can be novel in ...
centered around David Koresh that evolved from the Branch Davidians for suspected weapons violations. It is unknown who shot first, but the ATF surrounded and tried to invade the home of the Branch Davidians. This raid resulted in a two-hour firefight in which four ATF agents were killed; this was followed by a standoff with government agents that lasted for 51 days. The siege ended in a fire that engulfed the Mount Carmel compound which led to the deaths of 76 Branch Davidians inside.
Islam
Islamic eschatology
Islamic eschatology ( ar, علم آخر الزمان في الإسلام, ) is a field of study in Islam concerning future events that would happen in the end times. It is primarily based on hypothesis and speculations based on sources from ...
is the aspect of Islamic theology
Schools of Islamic theology are various Islamic schools and branches in different schools of thought regarding '' ʿaqīdah'' (creed). The main schools of Islamic Theology include the Qadariyah, Falasifa, Jahmiyya, Murji'ah, Muʿtazila, Batin ...
concerning ideas of life after death, matters of the soul, and the "Day of Judgement," known as ''Yawm al-Qiyāmah'' ( ar, يوم القيامة, , "the Day of Resurrection") or '' Yawm ad-Dīn'' (, , "the Day of Judgment"). The Day of Judgement is characterized by the annihilation of all life, which will then be followed by the resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead (Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died w ...
and judgment by God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
. It is not specified when al-Qiyamah will happen, but according to prophecy
In religion, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a ''prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain divine will or law, or p ...
elaborated by hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approva ...
-literature, there are major and minor signs that will foretell its coming. Multiple verses in the Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
mention the Last Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
.
The main subject of Surat al-Qiyama is the resurrection. The Great Tribulation
In Christian eschatology, the Great Tribulation ( grc, θλῖψις μεγάλη, thlîpsis megálē) is a period mentioned by Jesus in the Olivet Discourse as a sign that would occur in the time of the end.
At Revelation 7:14, "the Great Tri ...
is described in the hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approva ...
and commentaries of the ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
, including al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali ( – 19 December 1111; ), full name (), and known in Persian-speaking countries as Imam Muhammad-i Ghazali (Persian: امام محمد غزالی) or in Medieval Europe by the Latinized as Algazelus or Algazel, was a Persian poly ...
, Ibn Kathir
Abū al-Fiḍā’ ‘Imād ad-Dīn Ismā‘īl ibn ‘Umar ibn Kathīr al-Qurashī al-Damishqī (Arabic: إسماعيل بن عمر بن كثير القرشي الدمشقي أبو الفداء عماد; – 1373), known as Ibn Kathīr (, was ...
, Ibn Majah
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Yazīd Ibn Mājah al-Rabʿī al-Qazwīnī ( ar, ابو عبد الله محمد بن يزيد بن ماجه الربعي القزويني; (b. 209/824, d. 273/887) commonly known as Ibn Mājah, was a medieval sch ...
, Muhammad al-Bukhari
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monoth ...
, and Ibn Khuzaymah
Abu Bakr Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Khuzaymah ( ar , أبو بكر محمد بن إسحاق بن خزيمة, 837 CE/223 AH – 923 CE/311 AH) was a prominent Muslims, Muslim Hadith studies#Muhaddith: scholar of hadith, Muhaddith and Shafi'i school, ...
. The Day of Judgment is also known as the Day of Reckoning, the Last Day, and the Hour (''al-sā'ah'').
Unlike the Quran, the hadith contains several events, happening before the Day of Judgment, which are described as several ''minor signs'' and twelve ''major signs''. During this period, terrible corruption and chaos would rule the earth, caused by the Masih ad-Dajjal
Al-Masih ad-Dajjal (), otherwise referred to simply as the Dajjal, is an evil figure in Islamic eschatology similar to the Antichrist in Christianity, who will pretend to be the promised Messiah, appearing before the Day of Judgment accordin ...
(the Antichrist in Islam), then Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
will appear, defeating the Dajjal and establish a period of peace, liberating the world from cruelty. These events will be followed by a time of serenity when people live according to religious values.
Similarly to other Abrahamic religions
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
, Islam teaches that there will be a resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead (Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died w ...
that will be followed by a final tribulation and eternal division of the righteous and wicked. Islamic apocalyptic literature describing Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
is often known as '' fitna'', '' Al-Malhama Al-Kubra'' (The Great Massacre) or ''ghaybah'' in Shī'a Islam. The righteous are rewarded with the pleasures of Jannah
In Islam, Jannah ( ar, جَنّة, janna, pl. ''jannāt'',lit. "paradise, garden", is the final abode of the righteous. According to one count, the word appears 147 times in the Quran. Belief in the afterlife is one of the six articles of f ...
(Paradise), while the unrighteous are punished in Jahannam
In Islam, the place of punishment for unbelievers and other evildoers in the afterlife, or hell, is an "integral part of Islamic theology", Thomassen, "Islamic Hell", Numen, 56, 2009: p.401 and has "occupied an important place in the Muslim imagi ...
(Hell).
Judaism
Moses of Crete Moses of Crete was a Jewish Messiah claimant and apocalyptic prophet in the 5th century A.D.
After the failed Bar Kokba war, there was an end to Messianic movements for several centuries. However, the hope of a coming messiah nonetheless continue ...
, a rabbi in the 5th century, claimed to be the Jewish Messiah and promised to lead the people, like the ancient Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu ( Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pr ...
, through a parted sea back to Palestine. His followers left their possessions and waited for the promised day, when, at his command, many cast themselves into the sea, some finding death, others being rescued by sailors.
Ancient Norse religion

Ragnarök
In Norse mythology, (; non, wikt:ragnarǫk, Ragnarǫk) is a series of events, including a great battle, foretelling the death of numerous great figures (including the Æsir, gods Odin, Thor, Týr, Freyr, Heimdallr, and Loki), natural disast ...
is an important eschatological event in the Ancient Norse religion
Old Norse religion, also known as Norse paganism, is the most common name for a branch of Germanic religion which developed during the Proto-Norse period, when the North Germanic peoples separated into a distinct branch of the Germanic people ...
and its mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narra ...
, and has been the subject of scholarly discourse and theory in the history of Germanic studies
Germanic philology is the philological study of the Germanic languages, particularly from a comparative or historical perspective.
The beginnings of research into the Germanic languages began in the 16th century, with the discovery of literary te ...
and is attested primarily in the ''Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic med ...
'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources and the ''Prose Edda
The ''Prose Edda'', also known as the ''Younger Edda'', ''Snorri's Edda'' ( is, Snorra Edda) or, historically, simply as ''Edda'', is an Old Norse textbook written in Iceland during the early 13th century. The work is often assumed to have been ...
'', composed in the 13th century by the Icelandic scholar, lawspeaker
A lawspeaker or lawman ( Swedish: ''lagman'', Old Swedish: ''laghmaþer'' or ''laghman'', Danish: ''lovsigemand'', Norwegian: ''lagmann'', Icelandic: , Faroese: '' løgmaður'', Finnish: ''laamanni'', kl, inatsitinuk) is a unique Scandina ...
, and historian Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
. In the ''Prose Edda'' and in a single poem in the ''Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic med ...
'', the event is referred to as ''Ragnarök'' or ''Ragnarøkkr'' (), a usage popularised by 19th-century composer Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
with the title of the last of his ''Der Ring des Nibelungen
(''The Ring of the Nibelung''), WWV 86, is a cycle of four German-language epic music dramas composed by Richard Wagner. The works are based loosely on characters from Germanic heroic legend, namely Norse legendary sagas and the '' Nibe ...
'' operas, ''Götterdämmerung
' (; ''Twilight of the Gods''), WWV 86D, is the last in Richard Wagner's cycle of four music dramas titled (''The Ring of the Nibelung'', or ''The Ring Cycle'' or ''The Ring'' for short). It received its premiere at the on 17 August 1876, as ...
'' (1876), which is "Twilight of the Gods" in German. There are various theories and interpretations of Ragnarök.
Cyclic time and ''Hoddmímis holt''
Rudolf Simek
Rudolf Simek (born 21 February 1954) is an Austrian philologist and religious studies scholar who is Professor and Chair of Ancient German and Nordic Studies at the University of Bonn. Simek specializes in Germanic studies, and is the author o ...
theorizes that the survival of Líf and Lífþrasir at the end of Ragnarök is "a case of reduplication of the anthropogeny, understandable from the cyclic nature of the Eddic eschatology
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age, human history, or of the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic and non-Abrahamic), which teach that nega ...
". Simek says that Hoddmímis holt "should not be understood literally as a wood or even a forest in which the two keep themselves hidden, but rather as an alternative name for the world-tree Yggdrasill. Thus, the creation of mankind from tree trunks ( Askr, Embla) is repeated after the Ragnarök as well". Simek says that in Germanic regions, the concept of mankind originating from trees is ancient, and additionally points out legendary parallels in a Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
n legend of a shepherd
A shepherd or sheepherder is a person who tends, herds, feeds, or guards flocks of sheep. ''Shepherd'' derives from Old English ''sceaphierde (''sceap'' 'sheep' + ''hierde'' ' herder'). ''Shepherding is one of the world's oldest occupations, ...
who lives inside a tree, whose descendants repopulate the land after life there has been wiped out by plague (citing a retelling by F. R. Schröder). In addition, Simek points to an Old Norse parallel in the figure of Örvar-Oddr
Örvar-Oddr ( non, Ǫrvar-Oddr , "Arrow-Odd" or "Arrow's Point") is a legendary hero about whom an anonymous Icelander wrote a ''fornaldarsaga'' in the latter part of the 13th century. ''Örvar-Odds saga'', the Saga of Örvar-Odd, became very popul ...
, "who is rejuvenated after living as a tree-man (''Ǫrvar-Odds saga'' 24–27)".
''Muspille'', ''Heliand'', and Christianity
Theories have been proposed about the relation between Ragnarök and the 9th centuryOld High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old Hig ...
epic poem
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants.
...
''Muspilli
''Muspilli'' is an Old High German poem known in incomplete form (103 lines) from a ninth-century Bavarian manuscript. Its subject is the fate of the soul immediately after death and at the Last Judgment. Many aspects of the interpretation of the ...
'' about the Christian Last Judgment, where the word ''Muspille'' appears, and the 9th century Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). I ...
epic poem '' Heliand'' about the life of Christ, where various other forms of the word appear. In both sources, the word is used to signify the end of the world through fire. Old Norse forms of the term also appear throughout accounts of Ragnarök, where the world is also consumed in flames, and, though various theories exist about the meaning and origins of the term, its etymology has not been solved.
Proto-Indo-European basis
Parallels have been pointed out between the Ragnarök ofNorse religion
Old Norse religion, also known as Norse paganism, is the most common name for a branch of Germanic religion which developed during the Proto-Norse period, when the North Germanic peoples separated into a distinct branch of the Germanic people ...
and the beliefs of other related Proto-Indo-European peoples. Subsequently, theories have been put forth that Ragnarök represents a later evolution of a Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
belief along with other cultures descending from the Proto-Indo-Europeans. These parallels include comparisons of a cosmic winter motif between the Norse Fimbulwinter
In Norse mythology, (commonly rendered in English as Fimbulwinter), is the immediate prelude to the events of Ragnarök. It means 'great winter'.
Summary
is the harsh winter that precedes the end of the world and puts an end to all life o ...
, the Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
''Bundahishn
''Bundahishn'' (Avestan: , "Primal Creation") is the name traditionally given to an encyclopedic collection of Zoroastrian cosmogony and cosmology written in Book Pahlavi. The original name of the work is not known.
Although the ''Bundahishn'' ...
'' and Yima. Víðarr's stride has been compared to the Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute th ...
god Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
in that both have a "cosmic stride" with a special shoe used to tear apart a beastly wolf. Larger patterns have also been drawn between "final battle" events in Indo-European cultures, including the occurrence of a blind or semi-blind figure in "final battle" themes, and figures appearing suddenly with surprising skills.
Volcanic eruptions
Hilda Ellis Davidson
Hilda Roderick Ellis Davidson (born Hilda Roderick Ellis; 1 October 1914 – 12 January 2006) was an English folklorist. She was a scholar at the University of Cambridge and The Folklore Society, and specialized in the study of Celtic and G ...
theorizes that the events in ''Völuspá'' occurring after the death of the gods (the sun turning black, steam rising, flames touching the heavens, etc.) may be inspired by the volcanic eruptions on Iceland. Records of eruptions on Iceland bear strong similarities to the sequence of events described in ''Völuspá'', especially the eruption at Laki that occurred in 1783. Bertha Phillpotts
Dame Bertha Surtees Phillpotts (25 October 1877 – 20 January 1932) was an English scholar in Scandinavian languages, literature, history, archaeology and anthropology.
Biography
Phillpotts was born in Bedford on 25 October 1877. Her fa ...
theorizes that the figure of Surtr was inspired by Icelandic eruptions, and that he was a volcano demon. Surtr's name occurs in some Icelandic place names, among them the lava tube
A lava tube, or pyroduct, is a natural conduit formed by flowing lava from a volcanic vent that moves beneath the hardened surface of a lava flow. If lava in the tube empties, it will leave a cave.
Formation
A lava tube is a type of lava ...
Surtshellir
Surtshellir () is a lava cave located in western Iceland, around 60 km from the settlement of Borgarnes. Approximately a mile in length, it is one of the longest such caves in the country. It was the first known lava tube in the world, at l ...
, a number of dark caverns in the volcanic central region of Iceland.
''Bergbúa þáttr''
Parallels have been pointed out between a poem spoken by ajötunn
A (also jotun; in the normalised scholarly spelling of Old Norse, ; ; plural / ) or, in Old English, (plural ) is a type of supernatural being in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, they are often contrasted with gods ( Æsir and Vani ...
found in the 13th century þáttr
The ''þættir'' (Old Norse singular ''þáttr'', literally meaning a "strand" of rope or yarn)O'Donoghue (2004:226). are short stories written mostly in Iceland during the 13th and 14th centuries.
The majority of ''þættir'' occur in two compend ...
'' Bergbúa þáttr'' ("the tale of the mountain dweller"). In the tale, Thórd and his servant get lost while traveling to church in winter, and so take shelter for the night within a cave. Inside the cave they hear noises, witness a pair of immense burning eyes, and then the being with burning eyes recites a poem of 12 stanzas. The poem the being recites contains references to Norse mythology (including a mention of Thor) and also prophecies (including that "mountains will tumble, the earth will move, men will be scoured by hot water and burned by fire"). Surtr's fire receives a mention in stanza 10. John Lindow
John Frederick Lindow (born July 23, 1946) is an American philologist who is Professor Emeritus of Old Norse and Folklore at University of California, Berkeley. He is a well known authority on Old Norse religion and literature.
Biography
John ...
says that the poem may describe "a mix of the destruction of the race of giants and of humans, as in Ragnarök" but that "many of the predictions of disruption on earth could also fit the volcanic activity that is so common in Iceland."
Modern influences
In late 2013 and early 2014, English-language media outlets widely reported that Ragnarök was foretold to occur on 22 February 2014. Apparently patterned after the2012 phenomenon
The 2012 phenomenon was a range of eschatological beliefs that cataclysmic or transformative events would occur on or around 21 December 2012. This date was regarded as the end-date of a 5,126-year-long cycle in the Mesoamerican Long Count cal ...
, the claim was at times attributed to a "Viking Calendar". No such calendar is known to have existed, and the source was a "prediction" made to media outlets by the Jorvik Viking Centre
The Jorvik Viking Centre is a museum and visitor attraction in York, England, containing lifelike mannequins and life-size dioramas depicting Viking life in the city. Visitors are taken through the dioramas in small carriages equipped with sp ...
in York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
, England, intended to draw attention to an event that the institution was to hold on that date. The Jorvik Viking Centre was criticized for misleading the public to promote the event. In a 2014 article on the claims, philologist Joseph S. Hopkins perceives the media response as an example of a broad revival of interest in the Viking Age and ancient Germanic topics.
Far-right accelerationism
In spite of its original philosophical and theoretical interests, since the late 2010s international networks ofneo-fascists
Neo-fascism is a post-World War II far-right ideology that includes significant elements of fascism. Neo-fascism usually includes ultranationalism, racial supremacy, populism, authoritarianism, nativism, xenophobia, and anti-immigration sent ...
, neo-Nazis
Neo-Nazism comprises the post–World War II militant, social, and political movements that seek to revive and reinstate Nazi ideology. Neo-Nazis employ their ideology to promote hatred and racial supremacy (often white supremacy), attack ...
, White nationalists
White nationalism is a type of racial nationalism or pan-nationalism which espouses the belief that white people are a raceHeidi Beirich and Kevin Hicks. "Chapter 7: White nationalism in America". In Perry, Barbara. ''Hate Crimes''. Greenwoo ...
, and White supremacists
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White s ...
have increasingly appropriated the term "accelerationism
Accelerationism is a range of Marxist and reactionary ideas in critical and social theory that call for the drastic intensification of capitalist growth, technological change and other social processes in order to destabilize existing systems ...
" to refer to right-wing extremist
Far-right politics, also referred to as the extreme right or right-wing extremism, are political beliefs and actions further to the right of the left–right political spectrum than the standard political right, particularly in terms of bein ...
goals and reactionary
In political science, a reactionary or a reactionist is a person who holds political views that favor a return to the '' status quo ante'', the previous political state of society, which that person believes possessed positive characteristics abs ...
ideals, and have been known to refer to an "acceleration" of racial conflict through violent means such as assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
s, murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification or valid excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the ...
s, terrorist attacks, and societal collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of socioeconomic complexity, the downfall of government, and the rise of violence. Possible cause ...
, in order to achieve the building of a White ethnostate
A White ethnostate is a proposed type of state in which residence or citizenship would be limited to whites, and non-whites, such as Blacks, Asians, Jews, Middle Easterners and North Africans and Hispanics would be excluded from citizenship. Wit ...
. Far-right accelerationism has been widely considered as detrimental to public safety. The inspiration for this distinct variation of "accelerationism" is occasionally cited as American Nazi Party
The American Nazi Party (ANP) is an American far-right and neo-Nazi political party founded by George Lincoln Rockwell and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. The organization was originally named the World Union of Free Enterprise Nation ...
and National Socialist Liberation Front member James Mason
James Neville Mason (; 15 May 190927 July 1984) was an English actor. He achieved considerable success in British cinema before becoming a star in Hollywood. He was the top box-office attraction in the UK in 1944 and 1945; his British films inc ...
's newsletter ''Siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
'', where he argued for sabotage
Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening a polity, effort, or organization through subversion, obstruction, disruption, or destruction. One who engages in sabotage is a ''saboteur''. Saboteurs typically try to conceal their identitie ...
, mass killings, and assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
s of high-profile targets to destabilize and destroy the current society, seen as a system upholding a Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and multicultural
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for " ethnic pluralism", with the two terms often used interchang ...
New World Order. His works were republished and popularized by the Iron March forum and Atomwaffen Division
The Atomwaffen Division (''Atomwaffen'' meaning " nuclear weapons" in German), also known as the National Socialist Resistance Front, is an international far right-wing extremist and neo-Nazi terrorist network. Formed in 2013 and based in t ...
, right-wing extremist organizations strongly connected to various terrorist attacks, murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification or valid excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the ...
s, and assault
An assault is the act of committing physical harm or unwanted physical contact upon a person or, in some specific legal definitions, a threat or attempt to commit such an action. It is both a crime and a tort and, therefore, may result in cr ...
s. According to the Southern Poverty Law Center
The Southern Poverty Law Center (SPLC) is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit legal advocacy organization specializing in civil rights and public interest litigation. Based in Montgomery, Alabama, it is known for its legal cases against white ...
(SPLC), which tracks hate groups and files class action lawsuit
A class action, also known as a class-action lawsuit, class suit, or representative action, is a type of lawsuit where one of the parties is a group of people who are represented collectively by a member or members of that group. The class actio ...
s against discriminatory organizations and entities, "on the case of white supremacists, the accelerationist set sees modern society as irredeemable and believe it should be pushed to collapse so a fascist society built on ethnonationalism can take its place. What defines white supremacist accelerationists is their belief that violence is the only way to pursue their political goals."
Brenton Harrison Tarrant
On 15 March 2019, two consecutive mass shootings occurred in a terrorist attack on two mosques in Christchurch, New Zealand. The attacks, carried out by a lone gunman who entered both mosques during Friday prayer, began at the Al Noor Mosque ...
, the perpetrator of the Christchurch mosque shootings
On 15 March 2019, two consecutive mass shootings occurred in a terrorist attack on two mosques in Christchurch, New Zealand. The attacks, carried out by a lone gunman who entered both mosques during Friday prayer, began at the Al Noor Mosque ...
that killed 51 people and injured 49 others, had embraced right-wing accelerationism in a section of his manifesto titled "Destabilization and Accelerationism: tactics". It also influenced John Timothy Earnest
The Poway synagogue shooting occurred on April 27, 2019, at Chabad of Poway synagogue in Poway, California, United States, a city approximately north of San Diego, on the last day of the Jewish Passover holiday, which fell on a Shabbat. Armed w ...
, the man accused of causing the Escondido mosque fire
The Escondido mosque fire was a terrorist arson attack perpetrated against the Islamic Center of Escondido, California, in March 2019.
Police found graffiti on the mosque's driveway that referenced the Christchurch mosque shootings in New Zeala ...
at Dar-ul-Arqam Mosque in Escondido, California
Escondido is a city in San Diego County, California, United States. Located in the North County region, it was incorporated in 1888, and is one of the oldest cities in San Diego County. It has a population of 151,038 as of the 2020 census.
Ety ...
; and committing the Poway synagogue shooting which resulted in one dead and three injured, and influenced Patrick Crusius
On August 3, 2019, a mass shooting occurred at a Walmart store in El Paso, Texas, United States. In the terrorist attack, a far-right individual killed 23 people and injured 23 others. The Federal Bureau of Investigation is investigating the sh ...
, the man accused of committing the El Paso Walmart shooting that killed 23 people and injured 23 others.
Although these right-wing extremist variants and their connected strings of terrorist attacks and murders are regarded as certainly uninformed by critical theory
A critical theory is any approach to social philosophy that focuses on society and culture to reveal, critique and challenge power structures. With roots in sociology and literary criticism, it argues that social problems stem more from s ...
, which was a prime source of inspiration for Land's original ideas that led to accelerationism, Land became interested in the Atomwaffen
The Atomwaffen Division (''Atomwaffen'' meaning "nuclear weapons" in German), also known as the National Socialist Resistance Front, is an international far right-wing extremist and neo-Nazi terrorist network. Formed in 2013 and based in the ...
-affiliated theistic Satanist
Theistic Satanism, otherwise referred to as religious Satanism, spiritual Satanism, or traditional Satanism, is an umbrella term for religious groups that consider Satan, the Devil, or Lucifer to objectively exist as a deity, supernatural entit ...
organization Order of Nine Angles
The Order of Nine Angles (ONA or O9A) is a Satanic and left-hand path occultist group which is based in the United Kingdom, and associated groups are based in other parts of the world. Claiming to have been established in the 1960s, it rose to ...
(ONA), that adheres to the ideology of neo-Nazi terrorist accelerationism, describing the ONA's works as "highly-recommended" in a blog post. Since the 2010s, the political ideology and religious worldview of the Order of Nine Angles, founded by the British neo-Nazi leader David Myatt
David Wulstan Myatt (born 1950) Additionally gone by the pseudonym Abdul al-Qari, is a British author, religious leader, far-right and Islamist militant, most notable for allegedly being the political and religious leader of the theistic Satani ...
in 1974, have increasingly influenced militant
The English word ''militant'' is both an adjective and a noun, and it is generally used to mean vigorously active, combative and/or aggressive, especially in support of a cause, as in "militant reformers". It comes from the 15th century Latin ...
neo-fascist
Neo-fascism is a post-World War II far-right ideology that includes significant elements of fascism. Neo-fascism usually includes ultranationalism, racial supremacy, populism, authoritarianism, nativism, xenophobia, and anti-immigration ...
and neo-Nazi
Neo-Nazism comprises the post–World War II militant, social, and political movements that seek to revive and reinstate Nazi ideology. Neo-Nazis employ their ideology to promote hatred and racial supremacy (often white supremacy), attack ...
insurgent
An insurgency is a violent, armed rebellion against authority waged by small, lightly armed bands who practice guerrilla warfare from primarily rural base areas. The key descriptive feature of insurgency is its asymmetric nature: small irre ...
groups associated with right-wing extremist
Far-right politics, also referred to as the extreme right or right-wing extremism, are political beliefs and actions further to the right of the left–right political spectrum than the standard political right, particularly in terms of bein ...
and White supremacist
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White s ...
international networks, most notably the Iron March forum.
Mayan calendar and the year 2012
The2012 phenomenon
The 2012 phenomenon was a range of eschatological beliefs that cataclysmic or transformative events would occur on or around 21 December 2012. This date was regarded as the end-date of a 5,126-year-long cycle in the Mesoamerican Long Count cal ...
was a range of eschatological
Eschatology (; ) concerns expectations of the end of the present age, human history, or of the world itself. The end of the world or end times is predicted by several world religions (both Abrahamic and non-Abrahamic), which teach that nega ...
belief
A belief is an attitude that something is the case, or that some proposition is true. In epistemology, philosophers use the term "belief" to refer to attitudes about the world which can be either true or false. To believe something is to tak ...
s that cataclysmic or otherwise transformative events would occur on or around 21 December 2012. This date was regarded as the end-date of a 5,126-year-long cycle in the Mesoamerican Long Count calendar
The Mesoamerican Long Count calendar is a non-repeating, vigesimal (base 20) and octodecimal (base 18) calendar used by several pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya. For this reason, it is often known as the May ...
, and as such, festivities to commemorate the date took place on 21 December 2012 in the countries that were part of the Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, ...
(Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
, Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, and El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south ...
), with main events at Chichén Itzá in Mexico, and Tikal
Tikal () (''Tik’al'' in modern Mayan orthography) is the ruin of an ancient city, which was likely to have been called Yax Mutal, found in a rainforest in Guatemala. It is one of the largest archeological sites and urban centers of the pre- ...
in Guatemala.
Various astronomical alignments and numerological formulae were proposed as pertaining to this date. A New Age
New Age is a range of spiritual or religious practices and beliefs which rapidly grew in Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise definition difficult. Although many scholars consi ...
interpretation held that the date marked the start of a period during which Earth and its inhabitants would undergo a positive physical or spiritual transformation
Spiritual transformation involves a fundamental change in a person's sacred or spiritual life.
Psychologists examine spiritual transformation within the context of an individual's ''meaning system'',
Israela Silberman (2005)Religion as a meanin ...
, and that 21 December 2012 would mark the beginning of a new era. Others suggested that the date marked the end of the world or a similar catastrophe. Scenarios suggested for the end of the world included the arrival of the next solar maximum
Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year solar cycle. During solar maximum, large numbers of sunspots appear, and the solar irradiance output grows by about 0.07%. On average, the solar cycle tak ...
, an interaction between Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
and the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy, or Earth's collision with a mythical planet called Nibiru.
Scholars from various disciplines quickly dismissed predictions of concomitant cataclysmic events as they arose. Professional Mayanist
A Mayanist ( es, mayista) is a scholar specialising in research and study of the Mesoamerican pre-Columbian Maya civilisation. This discipline should not be confused with Mayanism, a collection of New Age beliefs about the ancient Maya.
May ...
scholars stated that no extant classic Maya accounts forecast impending doom, and that the idea that the Long Count calendar ends in 2012 misrepresented Maya history
The history of Maya civilization is divided into three principal periods: the Preclassic, Classic and Postclassic periods; these were preceded by the Archaic Period, which saw the first settled villages and early developments in agriculture. Modern ...
and culture, Milbrath 1999, p. 4David Stuart, ''The Order of Days: The Maya World and the Truth about 2012'', Harmony Books, 2011 while astronomers rejected the various proposed doomsday scenarios as pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
, easily refuted by elementary astronomical observations.
UFO religions
UFO religions sometimes feature an anticipated end-time scenario in which extraterrestrial beings will bring about a radical change on Earth and/or "lift" the religious believers to a higher plane of existence. One such religious group's failed expectations of such an event,the Seekers
The Seekers were an Australian folk music, folk-influenced pop music, pop quartet, originally formed in Melbourne in 1962. They were the first Australian pop music group to achieve major chart and sales success in the United Kingdom and the Un ...
, served as the basis for the classic social psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people or by social norms. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the ...
research on cognitive dissonance
In the field of psychology, cognitive dissonance is the perception of contradictory information, and the mental toll of it. Relevant items of information include a person's actions, feelings, ideas, beliefs, values, and things in the environmen ...
conducted by the American psychologists Leon Festinger
Leon Festinger (8 May 1919 – 11 February 1989) was an American social psychologist who originated the theory of cognitive dissonance and social comparison theory. The rejection of the previously dominant behaviorist view of social psycholog ...
, Henry Riecken Henry William Riecken (November 11, 1917 – December 27, 2012) was an American psychologist.
Riecken was born on November 11, 1917, and was raised in Brooklyn. He obtained a bachelor's degree from Harvard University in 1939, and completed a mast ...
, and Stanley Schachter and published in their book '' When Prophecy Fails: A Social and Psychological Study of a Modern Group That Predicted the Destruction of the World'' (1956). Some adherents of UFO religions believe that the arrival or rediscovery of alien civilizations, technologies, and spirituality will enable human beings to overcome current ecological, spiritual, political, and social problems. Issues such as hatred, war, bigotry, poverty, and so on are said to be resolvable through the use of superior alien technology and spiritual abilities. Such belief systems are also described as millenarian
Millenarianism or millenarism (from Latin , "containing a thousand") is the belief by a religious, social, or political group or movement in a coming fundamental transformation of society, after which "all things will be changed". Millenarian ...
in their outlook.
Zoroastrianism
The Zoroastrian eschatological ideas are only alluded to in the surviving texts of theAvesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the lit ...
, and are known of in detail only from the texts of Zoroastrian tradition, in particular in the ca. 9th century ''Bundahishn
''Bundahishn'' (Avestan: , "Primal Creation") is the name traditionally given to an encyclopedic collection of Zoroastrian cosmogony and cosmology written in Book Pahlavi. The original name of the work is not known.
Although the ''Bundahishn'' ...
''. The accompanying story, as it appears in the ''Bundahishn'' (''GBd'' 30.1ff), runs as follows:. At the end of the "third time" (the first being the age of creation, the second of mixture, and the third of separation), there will be a great battle between the forces of good (the ''yazata''s) and those of evil (the ''daeva''s) in which the good will triumph. On earth, the Saoshyant
Saoshyanet (Avestan: 𐬯𐬀𐬊𐬳𐬌𐬌𐬀𐬧𐬝 saoš́iiaṇt̰) is the Avestan language expression that literally means "one who brings benefit", and which is used in several different ways in Zoroastrian scripture and tradition. In par ...
will bring about a resurrection of the dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead (Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died w ...
in the bodies they had before they died. This is followed by a last judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
through ordeal. The ''yazata''s Airyaman and Atar
Atar, Atash, or Azar ( ae, 𐬁𐬙𐬀𐬭, translit=ātar) is the Zoroastrian concept of holy fire, sometimes described in abstract terms as "burning and unburning fire" or "visible and invisible fire" (Mirza, 1987:389). It is considered to ...
will melt the metal in the hills and mountains, and the molten metal will then flow across the earth like a river. All mankind—both the living and the resurrected dead—will be required to wade through that river, but for the righteous (''ashavan
Ashavan (Avestan: 𐬀𐬴𐬀𐬬𐬀𐬥 ''ašavan'') is a Zoroastrian theological term. It literally means "possessing/mastering '' aša''" and has been interpreted as "possessing/mastering truth" or "possessing/mastering righteousness", but ha ...
'') it will seem to be a river of warm milk, while the wicked will be burned. The river will then flow down to hell, where it will annihilate Angra Mainyu
Angra Mainyu (; Avestan: 𐬀𐬢𐬭𐬀⸱𐬨𐬀𐬌𐬥𐬌𐬌𐬎 ''Aŋra Mainiiu'') is the Avestan-language name of Zoroastrianism's hypostasis of the "destructive/evil spirit" and the main adversary in Zoroastrianism either of th ...
and the last vestiges of wickedness in the universe..
The narrative continues with a projection of Ahura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna'' ...
and the six Amesha Spenta
In Zoroastrianism, the Amesha Spenta ( ae, , Aməša Spəṇta—literally "Immortal (which is) holy/bounteous/furthering") are a class of seven divine entities emanating from Ahura Mazda, the highest divinity of the religion. Later Middle Persia ...
s solemnizing a final act of worship (''yasna''), and the preparation of ''parahaoma'' from "white haoma
''Haoma'' (; Avestan: 𐬵𐬀𐬊𐬨𐬀) is a divine plant in Zoroastrianism and in later Persian culture and mythology. ''Haoma'' has its origins in Indo-Iranian religion and is the cognate of Vedic ''soma''.
Etymology
Both Avestan ''haoma'' ...
". The righteous will partake of the ''parahaoma'', which will confer immortality upon them. Thereafter, humankind will become like the Amesha Spentas, living without food, without hunger or thirst, and without weapons (or possibility of bodily injury). The material substance of the bodies will be so light as to cast no shadow. All humanity will speak a single language and belong to a single nation without borders. All will share a single purpose and goal, joining with the divine for a perpetual exaltation of God's glory.
Although ''frashokereti'' is a restoration of the time of creation, there is no return to the uniqueness of the primordial plant, animal and human; while in the beginning there was one plant, one animal and one human, the variety that had since issued would remain forever. Similarly, the host of divinities brought into existence by Mazda continue to have distinct existences, "and there is no prophecy of their re-absorption into the Godhead."
See also
* ''1975 in Prophecy!
Herbert W. Armstrong (July 31, 1892 – January 16, 1986) was an American evangelist who founded the Worldwide Church of God (WCG). An early pioneer of radio and television evangelism, Armstrong preached what he claimed was the comprehensive ...
''
* Antichrist
In Christian eschatology, the Antichrist refers to people prophesied by the Bible to oppose Jesus Christ and substitute themselves in Christ's place before the Second Coming. The term Antichrist (including one plural form)1 John ; . 2 John . ...
* Apocalypse of Pseudo-Methodius
* Apocalyptic literature
Apocalyptic literature is a genre of prophetical writing that developed in post- Exilic Jewish culture and was popular among millennialist early Christians. ''Apocalypse'' ( grc, , }) is a Greek word meaning " revelation", "an unveiling or u ...
* Center for Millennial Studies
* Disaster risk reduction
Disaster risk reduction (DRR) sometimes called disaster risk management (DRM) is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing and reducing the risks of disaster. It aims to reduce socio-economic vulnerabilities to disaster as well as dealing w ...
* Dispensationalism
Dispensationalism is a system that was formalized in its entirety by John Nelson Darby. Dispensationalism maintains that history is divided into multiple ages or "dispensations" in which God acts with humanity in different ways. Dispensationali ...
* Doomsday cult
A doomsday cult is a cult, that believes in apocalypticism and millenarianism, including both those that predict disaster and those that attempt to destroy the entire universe. Sociologist John Lofland coined the term ''doomsday cult'' in his ...
* Essenes
The Essenes (; Hebrew: , ''Isiyim''; Greek: Ἐσσηνοί, Ἐσσαῖοι, or Ὀσσαῖοι, ''Essenoi, Essaioi, Ossaioi'') were a mystic Jewish sect during the Second Temple period that flourished from the 2nd century BCE to the 1st ce ...
* Global catastrophic risk
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical future event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanen ...
* List of dates predicted for apocalyptic events
Predictions of apocalyptic events that would result in the extinction of humanity, a collapse of civilization, or the destruction of the planet have been made since at least the beginning of the Common Era. Most predictions are related to Ab ...
* Tim LaHaye
Timothy Francis LaHaye (April 27, 1926 – July 25, 2016) was an American Baptist evangelical Christian minister who wrote more than 85 books, both fiction and non-fiction, including the ''Left Behind'' series of apocalyptic fiction, which h ...
* Hal Lindsey
Harold Lee Lindsey (born November 23, 1929) – known as Hal Lindsey – is a best-selling American evangelical writer. He is a Christian Zionist, a dispensationalist and a television host. He wrote a series of popular apocalyptic books – beg ...
* Millenarianism
Millenarianism or millenarism (from Latin , "containing a thousand") is the belief by a religious, social, or political group or movement in a coming fundamental transformation of society, after which "all things will be changed". Millenarian ...
* Millennialism
Millennialism (from millennium, Latin for "a thousand years") or chiliasm (from the Greek equivalent) is a belief advanced by some religious denominations that a Golden Age or Paradise will occur on Earth prior to the final judgment and futu ...
* Order of the Solar Temple
* Peoples Temple
The Peoples Temple of the Disciples of Christ, originally Peoples Temple Full Gospel Church and commonly shortened to Peoples Temple, was an American new religious organization which existed between 1954 and 1978. Founded in Indianapolis, Ind ...
* Premillennialism
Premillennialism, in Christian eschatology, is the belief that Jesus will physically return to the Earth (the Second Coming) before the Millennium, a literal thousand-year golden age of peace. Premillennialism is based upon a literal interpretat ...
* James Redfield
James Redfield is an American author, lecturer, screenwriter, and film producer. He is notable for his 1993 novel ''The Celestine Prophecy''.
Biography
Redfield grew up in a rural area near Birmingham, Alabama. He studied Eastern philosophie ...
* Singularitarianism
Singularitarianism is a movement defined by the belief that a technological singularity—the creation of superintelligence—will likely happen in the medium future, and that deliberate action ought to be taken to ensure that the singularity bene ...
* Chuck Smith (pastor)
Charles Ward "Chuck" Smith (June 25, 1927 – October 3, 2013) was an American pastor who founded the Calvary Chapel movement. Beginning with the 25-person Costa Mesa congregation in 1965, Smith's influence now extends to "more than 1, ...
* The Brethren (Jim Roberts group)
The Brethren is one of several informal names for a nameless religious movement created by Jimmie T. "Jim" Roberts. Other names include The Travellers, The Road Ministry, Body of Christ, and the Brothers and Sisters. The movement's members shu ...
* Ultimate fate of the Universe
The ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology, whose theoretical restrictions allow possible scenarios for the evolution and ultimate fate of the universe to be described and evaluated. Based on available observational e ...
* Unfulfilled Christian religious predictions
This article lists unfulfilled Christian religious predictions that failed to come about in the specified time frame, listed by religious group.
Adventism, Millerism
Adventism has its roots in the teachings of a Baptist preacher by the name of ...
* Jack Van Impe
Jack Leo Van Impe ( ; February 9, 1931 – January 18, 2020) was an American televangelist known for his half-hour weekly television series ''Jack Van Impe Presents'', an eschatological commentary on the news of the week through an interpre ...
* ''When Prophecy Fails
''When Prophecy Fails: A Social and Psychological Study of a Modern Group That Predicted the Destruction of the World'' is a classic work of social psychology by Leon Festinger, Henry Riecken, and Stanley Schachter, published in 1956, detailing a ...
''
References
Further reading
* Allison, Dale C. (1999) ''Jesus of Nazareth: Millenarian Prophet'' (Augsburg Fortress) * Aukerman, Dale. (1993). ''Reckoning with Apocalypse.'' New York: Crossroad. * Boyer, Paul S. (1992). ''When Time Shall Be No More: Prophecy Belief in Modern American Culture.'' Cambridge, Massachusetts: Belknap/Harvard University Press. * Brasher, Brenda E. (2000). "From Revelation to The X-Files: An Autopsy of Millennialism in American Popular Culture", ''Semeia
''Semeia'' was a journal published by the Society of Biblical Literature, "devoted to the exploration of new and emergent areas and methods of biblical criticism."
Semeia Studies
After 2002, the journal Semeia was replaced by the book series S ...
'' 82:281–295.
* CenSAMM. (2021).Apocalypticism
" In James Crossley and Alastair Lockhart (eds.) ''Critical Dictionary of Apocalyptic and Millenarian Movements''. * Cohn, Norman (1993). ''Cosmos, Chaos and the World to Come: The Ancient Roots of Apocalyptic Faith.'' New Haven: Yale University Press. * Fuller, Robert C. (1995). ''Naming the Antichrist: The History of an American Obsession.'' New York: Oxford University Press. * Hall, John R. (2009). ''Apocalypse: From Antiquity to the Empire of Modernity'', Cambridge, UK: Polity. ( band ) * Heard, Alex and Klebnikov, Peter, December 27, 1998,
Apocalypse Now. No, Really. Now!
, ''The New York Times Magazine'' * * Landes, Richard. (2011). ''Heaven on Earth: The Varieties of the Millennial Experience.'' New York, N.Y.: Oxford University Press. (hard cover) * Mason, Carol. (2002). ''Killing for Life: The Apocalyptic Narrative of Pro-life Politics.'' Ithaca, N.Y.: Cornell University Press. (hard cover) (paperback) * O'Leary, Stephen. (1994). ''Arguing the Apocalypse: A Theory of Millennial Rhetoric.'' New York: Oxford University Press. * Palmer, James T. (2014) "The Apocalypse in the Early Middle Ages" Cambridge, Cambridge University press * * Quinby, Lee. (1994). ''Anti-Apocalypse: Exercises in Genealogical Criticism.'' Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. (hard bound) (paperback) * Robbins, Thomas, and Susan J. Palmer, eds. 1997. ''Millennium, Messiahs, and Mayhem: Contemporary Apocalyptic Movements.'' New York: Routledge. (hard bound) (paperback) * Staker, Susan, ed. (1993). ''Waiting for World's End: The Diaries of Wilford Woodruff''. Salt Lake City, Utah: Signature Books. * Stewart, Kathleen and Susan Harding. 1999. "Bad Endings: American Apocalypsis." ''Annual Review of Anthropology'', 28, pp. 285–310. * Stone, Jon R., ed. (2000). ''Expecting Armageddon: Essential Readings in Failed Prophecy.'' New York: Routledge. (paperback) * Strozier, Charles B. (1994). ''Apocalypse: On the Psychology of Fundamentalism in America.'' Boston: Beacon Press. * Strozier, Charles B, and Michael Flynn, eds. (1997). ''The Year 2000: Essays on the End.'' New York: New York University Press. (hard bound) (paperback) * Thompson, Damian. (1996). ''The End of Time: Faith and Fear in the Shadow of the Millennium.'' London:
Sinclair-Stevenson
Sinclair-Stevenson Ltd is a British publisher founded in 1989 by Christopher Sinclair-Stevenson.
Christopher Sinclair-Stevenson became an editor at Hamish Hamilton
Hamish Hamilton Limited was a British book publishing house, founded in 1931 ...
.
* Thompson, Damian. (1997). ''The End of Time: Faith and Fear in the Shadow of the Millennium.'' Hanover, N.H.: University Press of New England.
* Underwood, Grant. (1999) 993 The Millenarian World of Early Mormonism
'' Urbana: University of Illinois Press. * Wessinger, Catherine, ed.. (2000). ''Millennialism, Persecution, and Violence: Historical Cases.'' Religion and Politics Series, Michael Barkun, (ed.). Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press. (hard bound) (paperback) * * Zuquete, Jose Pedro. "Apocalyptic Movements. "Encyclopædia Britannica
Encyclopædia Britannica Online Academic Edition
Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. 31 Dec. 2012 {{Authority control Eschatology Religious terminology