Van Diemen's Land on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of
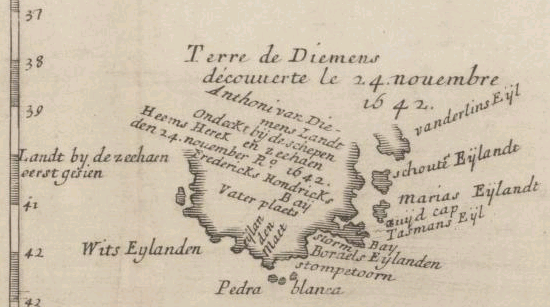 In 1642, Abel Tasman discovered the western side of the island and named it on behalf of the Dutch. He sailed around the south to the east, landing at Blackman Bay and assumed it was part of the Australian mainland.
Between 1772 and 1798, recorded European visits were only to the southeastern portion of the island and it was not known to be an island until
In 1642, Abel Tasman discovered the western side of the island and named it on behalf of the Dutch. He sailed around the south to the east, landing at Blackman Bay and assumed it was part of the Australian mainland.
Between 1772 and 1798, recorded European visits were only to the southeastern portion of the island and it was not known to be an island until
 *
*
, ''Index of Significant Tasmanian Women'', Department of Premier and Cabinet, Government of Tasmania. * Australian winner of the Nobel Prize for Literature Patrick White's novel '' A Fringe of Leaves'' places much of the novel's beginnings in Van Diemen's Land. * Van Diemen's Land is the setting of
Constitution Act 1855, establishing an elected parliament in the colony
{{Authority control Former penal colonies Colonial history of Tasmania States and territories established in 1825 1825 establishments in Australia States and territories disestablished in 1856 1856 disestablishments in Oceania
Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
during the European exploration and colonisation of Australia in the 19th century. The Aboriginal-inhabited island was first visited by the Dutch ship captained by Abel Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman (; 160310 October 1659) was a Dutch sea explorer, seafarer and exploration, explorer, best known for his voyages of 1642 and 1644 in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He was the first European to reach New ...
in 1642, working under the sponsorship of Anthony van Diemen, the Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies. The British retained the name when they established a settlement in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies
A penal colony or exile colony is a Human settlement, settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colony, colonial territory. Although the te ...
became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being escape-proof.
The name was changed to Tasmania on 1st January 1856 to disassociate the island from its convict past and to honour its discoverer, Abel Tasman. The old name had become a byword for horror in England because of the severity of its convict settlements such as Macquarie Harbour
Macquarie Harbour is a shallow fjord in the West Coast region of Tasmania, Australia. It is approximately , and has an average depth of , with deeper places up to . It is navigable by shallow-draft vessels. The main channel is kept clear by th ...
and Port Arthur. When the island became a self-governing colony in 1855, one of the first acts of the new legislature was to change its name.
With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
, South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
, Victoria, and Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. The last penal settlement in Tasmania was closed in 1877.
Toponym
The island was named in honour of Anthony van Diemen,Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies
The governor-general of the Dutch East Indies (, ) represented Dutch rule in the Dutch East Indies between 1610 and Dutch recognition of the independence of Indonesia in 1949. Occupied by Japanese forces between 1942 and 1945, followed by the ...
who had sent the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman (; 160310 October 1659) was a Dutch sea explorer, seafarer and exploration, explorer, best known for his voyages of 1642 and 1644 in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He was the first European to reach New ...
on his voyage of discovery in the 1640s. In 1642 Tasman became the first known European to land on the shores of Tasmania. After landing at Blackman Bay and later raising the Dutch flag at North Bay, Tasman named the island ''Anthoonij van Diemenslandt'' (Anthony Van Diemen's land) in his patron's honour.
The demonym
A demonym (; ) or 'gentilic' () is a word that identifies a group of people ( inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place ( hamlet, village, town, city, region, ...
for inhabitants of Van Diemen's Land was "Van Diemonian", though contemporaries used the spelling "Vandemonian". Anthony Trollope
Anthony Trollope ( ; 24 April 1815 – 6 December 1882) was an English novelist and civil servant of the Victorian era. Among the best-known of his 47 novels are two series of six novels each collectively known as the ''Chronicles of Barsetshire ...
used the latter term; "They are (the Vandemonians) united in their declaration that the cessation of the coming of convicts has been their ruin."
In 1856, Van Diemen's Land was renamed ''Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
'', removing the unsavoury link the name Van Diemen's Land had with its penal settlements (and the "demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in folklore, mythology, religion, occultism, and literature; these beliefs are reflected in Media (communication), media including
f ...
" connotation). Tasmania was chosen as it honoured the explorer Abel Tasman, the first European to visit the island. Within 21 years the last penal settlement in Tasmania at Port Arthur was permanently closed in 1877.
History
Exploration
 In 1642, Abel Tasman discovered the western side of the island and named it on behalf of the Dutch. He sailed around the south to the east, landing at Blackman Bay and assumed it was part of the Australian mainland.
Between 1772 and 1798, recorded European visits were only to the southeastern portion of the island and it was not known to be an island until
In 1642, Abel Tasman discovered the western side of the island and named it on behalf of the Dutch. He sailed around the south to the east, landing at Blackman Bay and assumed it was part of the Australian mainland.
Between 1772 and 1798, recorded European visits were only to the southeastern portion of the island and it was not known to be an island until Matthew Flinders
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain Matthew Flinders (16 March 1774 – 19 July 1814) was a British Royal Navy officer, navigator and cartographer who led the first littoral zone, inshore circumnavigate, circumnavigation of mainland Australia, then ...
and George Bass
George Bass (; 30 January 1771 – after 5 February 1803) was a British naval surgeon and explorer of Australia.
Early life
Bass was born on 30 January 1771 at Aswarby, a hamlet near Sleaford, Lincolnshire, the son of a tenant farmer, George B ...
circumnavigated it in the sloop in 1798–1799.
In 1773, Tobias Furneaux
Captain Tobias Furneaux (21 August 173518 September 1781) was a British navigator and Royal Navy officer, who accompanied James Cook on his second voyage of exploration. He was one of the first men to circumnavigate the world in both direction ...
in , explored a great part of the south and east coasts of Van Diemen's Land and made the earliest British chart of the island. He discovered the opening to D'Entrecasteaux Channel and, at Bruny Island
Bruny Island is a coastal island of Tasmania, Australia, located at the mouths of the Derwent River and Huon River estuaries on Storm Bay on the Tasman Sea, south of Hobart. The island is separated from the mainland by the D'Entrecasteaux C ...
, named Adventure Bay for his ship.
In 1777, James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
took on water and wood in Tasmania and became cursorily acquainted with some indigenous peoples on his third voyage of discovery. Cook named the Furneaux Group
The Furneaux Group is a group of approximately 100 islands located at the eastern end of Bass Strait, between Victoria and Tasmania, Australia. The islands were named after British navigator Tobias Furneaux, who sighted the eastern side of ...
of islands at the eastern entrance to Bass Strait
Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria (Australia), Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The ...
and the group now known as the Low Archipelago.
From at least the settlement of New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, sealers and whalers operated in the surrounding waters and explored parts.
In January 1793, a French expedition under the command of Antoine Bruni d'Entrecasteaux
Antoine Raymond Joseph de Bruni, chevalier d'Entrecasteaux (; 8 November 1737 – 21 July 1793) was a French Navy officer, explorer and colonial administrator who served as the Governor of Isle de France (Mauritius), governor of Isle de Fran ...
anchored in Recherche Bay and a period of five weeks was spent in that area, carrying out explorations into both natural history
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
and geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
. A few months later, British East India Company Captain John Hayes, with the ships ''Duke of Clarence'' and ''Duchess'', resupplied with wood and water at Adventure Bay and explored and named the Derwent River and many surrounding features.
In 1802 and 1803, the French expedition commanded by Nicolas Baudin explored D'Entrecasteaux Channel and Maria Island and carried out charting of Bass Strait
Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria (Australia), Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The ...
. Baudin had been associated, like Peyroux, with the resettlement of the Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
from French Canada -- mostly from what is now called the New Brunswick–Nova Scotia area -- to Louisiana.
Early colonisation
Around 1784–1785, Henri Peyroux de la Coudrenière, a serial entrepreneur in colonial schemes, wrote a "memoir on the advantages to be gained for the Spanish crown by the settlement of Van Diemen's Land". After receiving no response from the Spanish government, Peyroux proposed it to the French government, as "Mémoire sur les avantages qui résulteraient d'une colonie puissante à la terre de Diémen" but nothing came of his scheme. Sealers and whalers based themselves on the Tasmanian islands from 1798. In August 1803,New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
Governor Philip King sent Lieutenant John Bowen to establish a small military outpost on the eastern shore of the Derwent River to forestall any claims to the island arising from the activities of the French explorers.
From 24 September 1804 until 4 February 1813, there were two administrative divisions in Van Diemen's Land, Cornwall County in the north and Buckingham County in the south. The border between the counties was defined as the 42nd parallel (now between Trial Harbour
Trial Harbour is a rural locality in the local government area (LGA) of West Coast Council, West Coast in the North-west and west LGA Region, North-west and west LGA region of Tasmania. The locality is about south-west of the town of Zeehan, Tas ...
and Friendly Beaches). Cornwall County was administered by William Paterson while Buckingham County was administered by David Collins.
Major-General Ralph Darling
General Sir Ralph Darling, GCH (1772 – 2 April 1858) was a British Army officer who served as Governor of New South Wales from 1825 to 1831. His period of governorship was unpopular, with Darling being broadly regarded as a tyrant. He introd ...
was appointed Governor of New South Wales in 1825. In the same year he visited Hobart Town. On 3 December of 1825, he proclaimed the establishment of the independent colony, of which he became governor for three days.
In 1836, the new governor, Sir John Franklin, sailed to Van Diemen's Land, together with William Hutchins (1792-1841), who was to become the colony's first Archdeacon.
In 1856, the colony was granted responsible self-government with its representative parliament, and the name of the island and colony was officially changed to Tasmania on 1 January 1856.
Penal colony
From the early 1800s to the 1853 abolition ofpenal transportation
Penal transportation (or simply transportation) was the relocation of convicted criminals, or other persons regarded as undesirable, to a distant place, often a colony, for a specified term; later, specifically established penal colonies bec ...
(known simply as "transportation"), Van Diemen's Land was the primary penal colony in Australia. Following the suspension of transportation to New South Wales, all transported convicts were sent to Van Diemen's Land. In total, some 73,000 convicts were transported to Van Diemen's Land or about 40% of all convicts sent to Australia.
Male convicts served their sentences as assigned labour to free settlers or in gangs assigned to public works. Only the most difficult convicts (mostly re-offenders) were sent to the Tasman Peninsula prison known as Port Arthur. Female convicts were assigned as servants in free settler households or sent to a female factory (women's workhouse prison). There were five female factories in Van Diemen's Land.
Convicts completing their sentences or earning their ticket-of-leave often promptly left Van Diemen's Land. Many settled in the new free colony of Victoria, to the dismay of the free settlers in towns such as Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
.
On 6 August 1829, the brig
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square rig, square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the l ...
, a government-owned vessel used to transport goods, people, and convicts, set sail from Hobart Town for Macquarie Harbour Penal Station on a routine voyage carrying supplies and convicts. While the ship was becalmed in Recherche Bay, convicts allowed on deck attacked their guards and took control of the brig. The mutineers marooned officers, soldiers, and convicts who did not join the mutiny without supplies. The convicts then sailed the ''Cyprus'' to Canton, China, where they scuttled her and claimed to be castaways from another vessel. On the way, ''Cyprus'' visited Japan during the height of the period of severe Japanese restrictions on the entry of foreigners, the first Australian ship to do so.
Tensions sometimes ran high between the settlers and the "Vandemonians" as they were termed, particularly during the Victorian gold rush
The Victorian gold rush was a period in the history of Victoria, Australia, approximately between 1851 and the late 1860s. It led to a period of extreme prosperity for the Australian colony and an influx of population growth and financial capi ...
when a flood of settlers from Van Diemen's Land rushed to the Victorian goldfields.
Complaints from Victorians about recently released convicts from Van Diemen's Land re-offending in Victoria was one of the contributing reasons for the eventual abolition of transportation to Van Diemen's Land in 1853.
Demographics
Population summary
According to the 1851 Census of Van Diemen's Land, there was a total population of 70,130 individuals, with 62.85% being males and 37.14% being females. Non-convicts, i.e. free people, comprised 75.6% of the population andconvicts
A convict is "a person found Guilt (law), guilty of a crime and Sentence (law), sentenced by a court" or "a person serving a sentence in prison". Convicts are often also known as "prisoners" or "inmates" or by the slang term "con", while a commo ...
, 24.3%, which was an increase since the 1848 Census. Of the males who were not a part of the Military, or convicts on public works, 71% were free and 28.57% were bond. Of the females who were not part of the Military, or convicts on public works, 84.15% were free and 15.84% were bond.
Religion
Popular culture
Film
* The 2008 film ''The Last Confession of Alexander Pearce
''The Last Confession of Alexander Pearce'' is a 2008 Australian-Irish film directed by Michael James Rowland starring Irish actors Adrian Dunbar as Philip Conolly and Ciarán McMenamin as bushranger Alexander Pearce and an ensemble Australian cas ...
'' tells the true story of Alexander Pearce through his final confession to fellow Irishman and colonial priest Philip Conolly. The film was nominated for a Rose d'Or, an Irish Film and Television Award, an Australian Film Institute Award and won an IF Award in 2009.
* The 2009 film ''Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania during the European exploration of Australia, European exploration and colonisation of Australia in the 19th century. The Aboriginal Tasmanians, Aboriginal-inhabited island wa ...
'' follows the story of the infamous Irish convict Alexander Pearce and his escape with seven other convicts.
* The 2011 Australian drama film '' The Hunter,'' about a shadowy corporation that sends a mercenary to Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
to track down a thylacine
The thylacine (; binomial name ''Thylacinus cynocephalus''), also commonly known as the Tasmanian tiger or Tasmanian wolf, was a carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmani ...
, a supposedly extinct animal whose genetic code holds the secret to a dangerous weapon.
* The 2013 ABC telemovie '' The Outlaw Michael Howe'' is set in Van Diemen's Land and tells the story of bushranger Michael Howe's convict-led rebellion.
* The 2018 film '' Black '47'' directed by Lance Daly and set in Ireland during the Great Irish Famine
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact o ...
depicts a judgement imposed on a farmer for theft by a judge in the province of Connemara
Connemara ( ; ) is a region on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of western County Galway, in the west of Ireland. The area has a strong association with traditional Irish culture and contains much of the Connacht Irish-speaking Gaeltacht, ...
, which includes six months of hard labour and subsequent penal transportation to Van Diemen's Land.
* The 2018 film'' The Nightingale'' is set in Van Diemen's Land in 1825 and depicts a female Irish convict taking revenge for the murder of her family by the colonial forces of Australia as the Black War
The Black War was a period of violent conflict between British colonists and Aboriginal Tasmanians in Tasmania from the mid-1820s to 1832 that precipitated the near-extermination of the indigenous population. The conflict was fought largely as ...
breaks out.
Music
* U2 recorded the song "Van Diemen's Land" for their 1988 album ''Rattle and Hum
''Rattle and Hum'' is a hybrid live/studio album by Irish rock band U2, and a companion rockumentary film directed by Phil Joanou. The album was produced by Jimmy Iovine and was released on 10 October 1988, while the film was distributed by ...
'', with lyrics expressing the plight of a man facing transportation.
* Tom Russell sets Van Diemen's Land as the ship's destination in his song "Isaac Lewis" on the album "Modern Art".
* In the traditional Irish folk song " The Black Velvet Band", the protagonist is found guilty of stealing a watch and is sent to Van Diemen's Land as punishment.
* The song "Van Diemen's Land" in the album titled "Parcel of Rogues" with vocals by Barbara Dickson
Barbara Ruth Dickson (born 27 September 1947) is a Scottish singer and actress whose hits include " I Know Him So Well" (a chart-topping duet with Elaine Paige), " Answer Me" and " January February". Dickson has placed fifteen albums on the UK ...
is about an Irish man caught for poaching and transported to Van Diemen's Land and the hardships he has living there.
* Russell Morris released an album titled "Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania during the European exploration of Australia, European exploration and colonisation of Australia in the 19th century. The Aboriginal Tasmanians, Aboriginal-inhabited island wa ...
" in Australia in 2014. The title track describes the voyage of a convict being transported to Van Diemen's Land and was released with a video shot in Tasmania.
* The Roud Folk Song Index
The Roud Folk Song Index is a database of around 250,000 references to nearly 25,000 songs collected from oral tradition in the English language from all over the world. It is compiled by Steve Roud. Roud's Index is a combination of the Broadsid ...
includes two different English transportation ballads with the title Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania during the European exploration of Australia, European exploration and colonisation of Australia in the 19th century. The Aboriginal Tasmanians, Aboriginal-inhabited island wa ...
, both about a poacher sentenced to transportation to the penal colony.
* The album "Fred Holstein: A Collection" includes Fred Holstein's version of the classic folk song "Maggie May" ( Maggie May (folk song), which is different from Rod Stewart's Maggie May). In his version, the prostitute and thief Maggie May is transported to "Van Diemen's cruel shore."
* Ewan McColl recorded the transportation song "Van Diemen's Land," releasing it on the Riverside Records long-playing album "Scots Streets Songs," and also released the song as a 45-rpm single.
* ''The Fields Of Athenrye'': Depicting a young girl saying goodbye to her partner as he's being transported to Van Diemen's land for stealing "Trevelyan's corn"
Literature
 *
* Emily Dickinson
Emily Elizabeth Dickinson (December 10, 1830 – May 15, 1886) was an American poet. Little-known during her life, she has since been regarded as one of the most important figures in American poetry. Dickinson was born in Amherst, Massac ...
's 1890 poem, "If you were coming in the fall" makes reference to Van Diemen's land with the line "Subtracting, til my fingers dropped, Into Van Dieman's Land.".
* The novel, '' The Broad Arrow: Being Passages from the History of Maida Gwynnham, a Lifer'' (published in 1859 in London and in 1860 in Hobart) was written in the penal colony, under the pen name Oliné Keese.Caroline Woolmer Leaky, ''Index of Significant Tasmanian Women'', Department of Premier and Cabinet, Government of Tasmania. * Australian winner of the Nobel Prize for Literature Patrick White's novel '' A Fringe of Leaves'' places much of the novel's beginnings in Van Diemen's Land. * Van Diemen's Land is the setting of
Richard Flanagan
Richard Miller Flanagan (born 1961) is an Australian writer, who won the 2014 Man Booker Prize for his novel ''The Narrow Road to the Deep North (novel), The Narrow Road to the Deep North'' and the 2024 Baillie Gifford Prize for ''Question 7'', ...
's novels '' Gould's Book of Fish: A Novel in Twelve Fish'' (2002) and ''Wanting'' (2008).
* Brendan Whiting's book ''Victims of Tyranny'', gives an account of the lives of the Irish rebels, the Fitzgerald convict brothers who were sent to help open up the north of Van Diemen's Land in 1805, under the leadership of the explorer Colonel William Paterson.
* In Cormac McCarthy
Cormac McCarthy (born Charles Joseph McCarthy Jr.; July 20, 1933 – June 13, 2023) was an American author who wrote twelve novels, two plays, five screenplays, and three short stories, spanning the Western, post-apocalyptic, and Southern Got ...
's novel '' Blood Meridian'', one of the characters in the Glanton Gang of scalpers in 1850s Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
is a "Vandiemenlander" named Bathcat. Born in Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
he later went to Australia to hunt aborigines, and eventually came to Mexico, where he uses those skills on the Apache
The Apache ( ) are several Southern Athabaskan language-speaking peoples of the Southwestern United States, Southwest, the Southern Plains and Northern Mexico. They are linguistically related to the Navajo. They migrated from the Athabascan ho ...
s.
* From ''The Potato Factory'' by Bryce Courtenay
Arthur Bryce Courtenay, (14 August 1933 – 22 November 2012) was a South African-Australian advertising director and novelist. He is one of Australia's best-selling authors, notable for his book '' The Power of One''.
Background and early ye ...
(1995), "... subtracting till my fingers dropped; into Van Diemen's Land." This is a quote from Emily Dickinson's Poem "If You Were Coming in the Fall". Two of the main characters in Cortenay's novel are transported Van Diemen's Land as convicts and another travels there, where around half of the novel takes place.
* In the novel ''The Convicts'' by Iain Lawrence, young Tom Tin is sent to Van Diemen's Land on charges of murder.
* In the novel ''The Terror'' by Dan Simmons
Dan Simmons (born April 4, 1948) is an American science fiction and horror writer. He is the author of the Hyperion Cantos and the Ilium/Olympos cycles, among other works that span the science fiction, horror, and fantasy genres, sometimes ...
(2007). In this novel about the ill-fated exploration by and to discover the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic ...
. The ships left England in May 1846 and were never heard from again, although since then much has been discovered about the fate of the 129 officers and crew. References are made to Van Diemen's Land during the chapters devoted to Francis Crozier.
* Van Diemen's Land is the setting of the novel '' English Passengers'' by Matthew Kneale (2000), which tells the story of three eccentric Englishmen who in 1857 set sail for the island in search of the Garden of Eden. The story runs parallel with the narrative of a young Tasmanian who tells the struggle of the indigenous population and the desperate battle against the invading British colonists.
* Christopher Koch's novel '' Out of Ireland'' (1999) describes life as a convict in Van Diemen's Land.
* Marcus Clarke used historical events as the basis for his fictional ''For the Term of his Natural Life
''For the Term of His Natural Life'' is a story written by Marcus Clarke and published in ''The Australian Journal'' between 1870 and 1872 (as ''His Natural Life''). It was published as a novel in 1874 and is the best known novelisation of life ...
'' (1870), the story of a gentleman, falsely convicted of murder, who is transported to Van Diemen's Land.
* Julian Stockwin's nautical fiction series, ''The Kydd Series'', includes the book ''Command'' (2006) in which Thomas Kydd takes a ship to Van Diemen's Land, at the behest of then governor of New South Wales, Philip Gidley King
Captain Philip Gidley King (23 April 1758 – 3 September 1808) was a Royal Navy officer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of New South Wales from 1800 to 1806. When the First Fleet arrived in January 1788, King was detai ...
, for the purpose of preventing French explorers from establishing a French settlement on the island.
* "The Exiles" by Christina Baker Kline (2020) tells the story of "transportation" to Van Dieman's Land and the hardship, oppression, opportunity and hope of three women at the centre of the story.
See also
*Cape Grim massacre
The Cape Grim massacre was an attack on 10 February 1828 in which a group of Aboriginal Tasmanians gathering food at a beach in the north-west of Tasmania is said to have been ambushed and shot by four Van Diemen's Land Company (VDLC) workers, w ...
* Cyprus mutiny
* Colony of Tasmania
The Colony of Tasmania (more commonly referred to simply as "Tasmania") was a British colony that existed on the island of Tasmania from 1856 until 1901, when it federated together with the five other Australian colonies to form the Commonweal ...
* Governors of Tasmania
* Van Diemen's Land Company
* Apostolic Vicariate of New Holland and Van Diemen's Land (Catholic missionary jurisdiction)
Notes
References
* Alexandra, Rieck (editor) (2005) '' The Companion to Tasmanian History'' Centre for Tasmanian Historical Studies, University of Tasmania, Hobart. . * Boyce, James (2008), ''Van Diemen's Land''. Black Inc., Melbourne. . * Robson, L.L. (1983) ''A history of Tasmania. Volume 1. Van Diemen's Land from the earliest times to 1855'' Melbourne, Oxford University Press. . * Robson, L.L. (1991) ''A history of Tasmania. Volume II. Colony and state from 1856 to the 1980s'' Melbourne, Oxford University Press. .External links
Constitution Act 1855, establishing an elected parliament in the colony
{{Authority control Former penal colonies Colonial history of Tasmania States and territories established in 1825 1825 establishments in Australia States and territories disestablished in 1856 1856 disestablishments in Oceania