The United States dollar (
symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
:
$;
currency code: USD) is the official
currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
of the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and
several other countries. The
Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the
Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100
cents, and authorized the
minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of
Federal Reserve Notes, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color.
The U.S. dollar was originally defined under a
bimetallic standard of (0.7734375 troy ounces) fine silver or, from
1834, fine gold, or $20.67 per
troy ounce. The
Gold Standard Act of 1900 linked the dollar solely to gold. From 1934, its equivalence to gold was revised to $35 per
troy ounce. In 1971 all links to gold were repealed. The U.S. dollar became an important international
reserve currency after the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, and displaced the
pound sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
as the world's primary reserve currency by the
Bretton Woods Agreement towards the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The dollar is the
most widely used currency in
international transactions, and a
free-floating currency. It is also the official currency in several countries and the
''de facto'' currency in many others, with
Federal Reserve Notes (and, in a few cases, U.S. coins) used in circulation.
The
monetary policy of the United States is conducted by the
Federal Reserve System, which acts as the nation's
central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
. As of February 10, 2021, currency in circulation amounted to , of which is in Federal Reserve Notes (the remaining is in the form of
coins
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
and older-style
United States Notes). As of January 1, 2025, the Federal Reserve estimated that the total amount of currency in circulation was approximately .
Overview
In the Constitution
Article I,
Section 8 of the
U.S. Constitution provides that
Congress has the power "to
coin money". Laws implementing this power are currently codified in
Title 31 of the
U.S. Code, under Section 5112, which prescribes the forms in which the United States dollars should be issued.
[''Denominations, specifications, and design of coins''. .] These coins are both designated in the section as
legal tender in payment of debts.
The
Sacagawea dollar is one example of the
copper alloy dollar, in contrast to the
American Silver Eagle which is pure
silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
. Section 5112 also provides for the
minting and
issuance of other coins, which have values ranging from
one cent (
U.S. Penny) to 100 dollars.
These other coins are more fully described in
Coins of the United States dollar.
Article I, Section 9 of the Constitution provides that "a regular Statement and Account of the Receipts and Expenditures of all public Money shall be published from time to time", which is further specified by Section 331 of Title 31 of the U.S. Code. The sums of money reported in the "Statements" are currently expressed in U.S. dollars, thus the U.S. dollar may be described as the
unit of account
In economics, unit of account is one of the functions of money. A unit of account is a standard numerical monetary unit of measurement of the market value of goods, services, and other transactions. Also known as a "measure" or "standard" of ...
of the United States. "Dollar" is one of the first words of Section 9, in which the term refers to the
Spanish milled dollar, or the coin worth eight
Spanish reales.
Coinage Act
In 1792, the
U.S. Congress passed the
Coinage Act, of which Section 9 authorized the production of various coins, including:
[ U.S. Congress. 1792. ]
Coinage Act of 1792
'. 2nd Congress, 1st Session. Sec. 9, ch. 16. Retrieved June 6, 2020.Section 20 of the Act designates the United States dollar as the
unit of currency of the United States:
Decimal units
Unlike the Spanish milled dollar, the
Continental Congress and the Coinage Act prescribed a
decimal system of units to go with the unit dollar, as follows:
the mill, or one-thousandth of a dollar; the cent, or one-hundredth of a dollar; the dime, or one-tenth of a dollar; and the eagle, or ten dollars. The current relevance of these units:
* Only the
cent (¢) is used as an everyday division of the dollar, with the ubiquitous exception of vehicle fuel pricing.
* ''
Dime'' is used solely as the name of the
coin
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
with the value of ten cents.
* The
mill (₥) is relatively unknown but before the middle of the 20th century was familiar in matters of
sales taxes. It is ubiquitous in prices of
gasoline and diesel fuels, which are usually in the form of $''xx.xx''9 per
gallon (e.g., $3.599, commonly written as $).
* The
eagle is also largely unknown to the general public.
This term was used in the ''Coinage Act of 1792'' for the denomination of ten dollars and subsequently in naming gold coins.
The Spanish peso, or dollar, was historically divided into eight
reales (colloquially, ''bits'') – hence ''pieces of eight''. Americans also learned counting in non-decimal ''bits'' of cents before 1857 when Mexican ''bits'' were more frequently encountered than American cents; in fact this practice survived in
New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is the List of stock exchanges, largest stock excha ...
quotations until 2001.
In 1854,
Secretary of the Treasury
The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal a ...
James Guthrie proposed creating $100, $50, and $25 gold coins, to be referred to as a ''
union'', ''
half union'', and ''quarter union'', respectively, thus implying a denomination of 1 Union = $100. However, no such coins were ever struck, and only patterns for the $50 half union exist.
When currently issued in circulating form, denominations less than or equal to a dollar are emitted as
U.S. coins, while denominations greater than or equal to a dollar are emitted as
Federal Reserve Notes, disregarding the following special cases:
* Gold coins issued for
circulation until the 1930s, up to the value of $20 (known as the ''
double eagle'')
* Bullion or commemorative
gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
,
silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
,
platinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name origina ...
, and
palladium coins valued up to $100 as legal tender (though worth far more as
bullion).
* Civil War paper currency issue in denominations below $1, i.e. fractional currency, sometimes pejoratively referred to as ''
shinplasters''.
Etymology
In the 16th century, Count
Hieronymus Schlick of
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
began minting coins known as ''joachimstalers'', named for
Joachimstal, the valley in which the silver was mined. In turn, the valley's name is titled after Saint
Joachim, whereby ''thal'' or ''tal'', a cognate of the English word , is
German for 'valley.'
["Ask US." '' National Geographic''. June 2002. p. 1.] The ''joachimstaler'' was later shortened to the German ''
taler'', a word that eventually found its way into many languages, including:
''tolar'' (
Czech,
Slovak and
Slovenian); ''daler'' (
Danish and
Swedish); ''talar'' (
Polish);
''dalar'' and ''daler'' (
Norwegian); ''daler'' or ''daalder'' (
Dutch);
''
talari'' (
Ethiopian);
''tallér'' (
Hungarian);
''tallero'' (
Italian);
''دولار'' (
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
); and ''
dollar'' (
English).
Though the
Dutch pioneered in modern-day
New York in the 17th century the use and the counting of money in silver dollars in the form of German-Dutch ''
reichsthalers'' and native Dutch ''
leeuwendaalders'' ('lion dollars'), it was the ubiquitous
Spanish American eight-real coin which became exclusively known as the ''dollar'' since the 18th century.
Nicknames
The
colloquialism ''
buck(s)'' (much like the British ''quid'' for the
pound sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
) is often used to refer to dollars of various nations, including the U.S. dollar. This term, dating to the 18th century, may have originated with the colonial
leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffal ...
trade, or it may also have originated from a
poker
Poker is a family of Card game#Comparing games, comparing card games in which Card player, players betting (poker), wager over which poker hand, hand is best according to that specific game's rules. It is played worldwide, with varying rules i ...
term.
''Greenback'' is another nickname, originally applied specifically to the 19th-century
Demand Note dollars, which were printed black and green on the backside, created by
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
to finance the
North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
for the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
. It is still used to refer to the U.S. dollar (but not to the dollars of other countries). The term ''greenback'' is also used by the financial press in other countries, such as
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
,
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
,
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
,
and
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
.
Other well-known names of the dollar as a whole in denominations include ''greenmail'', ''green'', and ''dead presidents'', the latter of which referring to the deceased presidents pictured on most bills. Dollars in general have also been known as ''bones'' (e.g. "twenty bones" = $20). The newer designs, with portraits displayed in the main body of the obverse (rather than in
cameo insets), upon paper color-coded by denomination, are sometimes referred to as ''bigface'' notes or ''
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce ...
money''.
''
Piastre'' was the original French word for the U.S. dollar, used for example in the French text of the
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
. Though the U.S. dollar is called ''dollar'' in Modern French, the term ''piastre'' is still used among the speakers of
Cajun French and
New England French, as well as speakers in
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
and other
French Caribbean islands.
Nicknames specific to denomination:
* The
quarter dollar coin is known as ''two bits'', alluding the dollar's origins as the "piece of eight" (bits or ''reales'').
* The
$1 bill is nicknamed ''buck'' or ''single''.
* The infrequently-used
$2 bill is sometimes called ''deuce'', ''Tom'', or ''Jefferson'' (after
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
).
* The
$5 bill is sometimes called ''Lincoln'' (after
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
), ''fin'', ''fiver'', or ''five-spot''.
* The
$10 bill is sometimes called ''sawbuck'', ''ten-spot'', or ''Hamilton'' (after
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first U.S. secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795 dur ...
).
* The
$20 bill is sometimes called ''double sawbuck'', ''Jackson'' (after
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
), or ''
double eagle''.
* The
$50 bill is sometimes called a ''yardstick'', or a ''grant'', after President
Ulysses S. Grant.
* The
$100 bill is called ''Benjamin'', ''Benji'', ''Ben'', or ''Franklin'', referring to its portrait of
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
. Other nicknames include ''C-note'' (C being the
Roman numeral
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, ea ...
for 100), ''century note'', or ''bill'' (e.g. ''two bills'' = $200).
* Amounts or multiples of $1,000 are sometimes called ''
grand'' in colloquial speech, abbreviated in written form to ''G'', ''K'', or ''k'' (from
''kilo''; e.g. $10k = $10,000). Likewise, a ''large'' or ''stack'' can also refer to a multiple of $1,000 (e.g. "fifty large" = $50,000).
Dollar sign

The symbol , usually written before the numerical amount, is used for the U.S. dollar (as well as for many other currencies). The sign was perhaps the result of a late 18th-century evolution of the
scribal abbreviation ''p
s'' for the
peso, the common name for the Spanish dollars that were in wide circulation in the
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The ''p'' and the ''s'' eventually came to be written over each other giving rise to ''$''.
Another popular explanation is that it is derived from the
Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules are the promontory, promontories that flank the entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar. The northern Pillar, Calpe Mons, is the Rock of Gibraltar. A corresponding North African peak not being predominant, the identity of ...
on the
Spanish coat of arms of the Spanish dollar. These
Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules are the promontory, promontories that flank the entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar. The northern Pillar, Calpe Mons, is the Rock of Gibraltar. A corresponding North African peak not being predominant, the identity of ...
on the silver Spanish dollar coins take the form of two vertical bars (, , ) and a swinging cloth band in the shape of an ''S''.
Yet another explanation suggests that the dollar sign was formed from the capital letters ''U'' and ''S'' written or printed one on top of the other. This theory, popularized by novelist
Ayn Rand in ''
Atlas Shrugged'', does not consider the fact that the symbol was already in use before the formation of the United States.
History
Origins: the Spanish dollar
The U.S. dollar was introduced at par with the Spanish-American silver dollar (or ''Spanish peso'', ''Spanish milled dollar'', ''eight-real coin'', ''piece-of-eight''). The latter was produced from the rich silver mine output of
Spanish America, was minted in
Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
,
Potosí (Bolivia),
Lima
Lima ( ; ), founded in 1535 as the Ciudad de los Reyes (, Spanish for "City of Biblical Magi, Kings"), is the capital and largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rive ...
(Peru), and elsewhere, and was in wide circulation throughout the Americas, Asia, and Europe from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The minting of machine-milled Spanish dollars since 1732 boosted its worldwide reputation as a trade coin and positioned it to be the model for the new currency of the United States.
Even after the
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bull ...
commenced issuing coins in 1792, locally minted ''dollars'' and ''cents'' were less abundant in circulation than
Spanish American ''pesos'' and ''reales''; hence Spanish, Mexican, and American dollars all remained legal tender in the United States until the
Coinage Act of 1857. In particular, colonists' familiarity with the Spanish two-''real quarter peso'' was the reason for issuing a quasi-decimal
25-cent quarter dollar coin rather than a 20-cent coin.
For the relationship between the
Spanish dollar and the individual state colonial currencies, see
Connecticut pound,
Delaware pound,
Georgia pound,
Maryland pound,
Massachusetts pound,
New Hampshire pound,
New Jersey pound,
New York pound,
North Carolina pound,
Pennsylvania pound,
Rhode Island pound,
South Carolina pound, and
Virginia pound.
Coinage Act of 1792

On July 6, 1785, the
Continental Congress resolved that the money unit of the United States, the dollar, would contain 375.64
grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and le ...
of fine silver; on August 8, 1786, the Continental Congress continued that definition and further resolved that the money of account, corresponding with the division of coins, would proceed in a
decimal ratio, with the sub-units being mills at 0.001 of a dollar, cents at 0.010 of a dollar, and dimes at 0.100 of a dollar.
After the adoption of the
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
, the U.S. dollar was defined by the
Coinage Act of 1792. It specified a "dollar" based on the
Spanish milled dollar to contain
grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
s of fine silver, or of "standard silver" of fineness 371.25/416 = 89.24%; as well as an "eagle" to contain grains of fine gold, or of 22
karat or 91.67% fine gold.
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first U.S. secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795 dur ...
arrived at these numbers based on a treasury assay of the average fine silver content of a selection of worn
Spanish dollars, which came out to be 371 grains. Combined with the prevailing gold-silver ratio of 15, the standard for gold was calculated at 371/15 = 24.73 grains fine gold or 26.98 grains 22K gold. Rounding the latter to 27.0 grains finalized the dollar's standard to 24.75 grains of fine gold or 24.75×15 = 371.25 grains = 24.0566 grams = 0.7735 troy ounces of fine silver.
The same coinage act also set the value of an eagle at 10 dollars, and the dollar at eagle. It called for silver coins in denominations of 1, , , , and dollar, as well as gold coins in denominations of 1, and eagle. The value of gold or silver contained in the dollar was then converted into relative value in the economy for the buying and selling of goods. This allowed the value of things to remain fairly constant over time, except for the influx and outflux of gold and silver in the nation's economy.
Though a
Spanish dollar freshly minted after 1772 theoretically contained 417.7 grains of silver of fineness 130/144 (or 377.1 grains fine silver), reliable assays of the period in fact confirmed a fine silver content of for the average Spanish dollar in circulation.
The new U.S. silver dollar of therefore compared favorably and was received at par with the Spanish dollar for foreign payments, and after 1803 the
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bull ...
had to suspend making this coin out of its limited resources since it failed to stay in domestic circulation. It was only after Mexican independence in 1821 when their peso's fine silver content of 377.1 grains was firmly upheld, which the U.S. later had to compete with using a heavier
Trade dollar coin.
Design
The early currency of the United States did not exhibit faces of presidents, as is the custom now; although today, by law, only the portrait of a deceased individual may appear on United States currency. In fact, the newly formed government was against having portraits of leaders on the currency, a practice compared to the policies of European monarchs. The currency as we know it today did not get the faces they currently have until after the early 20th century; before that "heads" side of coinage used profile faces and striding, seated, and standing figures from Greek and Roman mythology and composite Native Americans. The last coins to be converted to profiles of historic Americans were the dime (1946), the half Dollar (1948), and the Dollar (1971).
Continental currency

After the
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
became independent. Freed from British monetary regulations, they each issued
£sd paper money to pay for military expenses. The
Continental Congress also began issuing "Continental Currency" denominated in Spanish dollars. For its value relative to states' currencies, see
Early American currency.
Continental currency
depreciated badly during the war, giving rise to the famous phrase "not worth a continental". A primary problem was that monetary policy was not coordinated between Congress and the states, which continued to issue bills of credit. Additionally, neither Congress nor the governments of the several states had the will or the means to retire the bills from circulation through taxation or the sale of bonds. The currency was ultimately replaced by the silver dollar at the rate of 1 silver dollar to 1000 continental dollars. This resulted in the clause "No state shall... make anything but gold and silver coin a tender in payment of debts" being written into the
United States Constitution article 1, section 10.
Silver and gold standards, 19th century
From implementation of the 1792
Mint Act to the 1900 implementation of the
gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
, the dollar was on a
bimetallic silver-and-gold standard, defined as either 371.25
grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and le ...
(24.056 g) of fine silver or 24.75 grains of fine gold (gold-silver ratio 15).
Subsequent to the
Coinage Act of 1834 the dollar's fine gold equivalent was revised to 23.2 grains; it was slightly adjusted to in 1837 (gold-silver ratio ≈16). The same act also resolved the difficulty in minting the "standard silver" of 89.24% fineness by revising the dollar's alloy to 412.5 grains, 90% silver, still containing 371.25 grains fine silver. Gold was also revised to 90% fineness: 25.8 grains gross, 23.22 grains fine gold.
Following the rise in the price of silver during the
California Gold Rush
The California gold rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the U ...
and the disappearance of circulating silver coins, the
Coinage Act of 1853 reduced the standard for silver coins less than $1 from 412.5 grains to , 90% silver per 100 cents (slightly revised to 25.0 g, 90% silver in 1873). The Act also limited the
free silver right of individuals to convert
bullion into only one coin, the silver dollar of 412.5 grains; smaller coins of lower standard can only be produced by the
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bull ...
using its own bullion.
Summary and
links to coins issued in the 19th century:
* In base metal:
1/2 cent,
1 cent,
5 cents.
* In silver:
half dime,
dime,
quarter dollar,
half dollar,
silver dollar.
* In gold:
gold $1,
$2.50 quarter eagle,
$5 half eagle,
$10 eagle,
$20 double eagle.
* Less common denominations:
bronze 2 cents,
nickel 3 cents,
silver 3 cents,
silver 20 cents,
gold $3.
Note issues, 19th century

In order to finance the
War of 1812, Congress authorized the issuance of
Treasury Notes, interest-bearing short-term debt that could be used to pay public dues. While they were intended to serve as debt, they did function "to a limited extent" as money. Treasury Notes were again printed to help resolve the reduction in public revenues resulting from the
Panic of 1837
The Panic of 1837 was a financial crisis in the United States that began a major depression (economics), depression which lasted until the mid-1840s. Profits, prices, and wages dropped, westward expansion was stalled, unemployment rose, and pes ...
and the
Panic of 1857, as well as to help finance the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
and the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
.
Paper money was issued again in 1862 without the backing of precious metals due to the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
. In addition to Treasury Notes, Congress in 1861 authorized the Treasury to borrow $50 million in the form of
Demand Notes, which did not bear interest but could be redeemed on demand for precious metals. However, by December 1861, the
Union government's supply of specie was outstripped by demand for redemption and they were forced to suspend redemption temporarily. In February 1862 Congress passed the
''Legal Tender Act of 1862'', issuing
United States Notes, which were not redeemable on demand and bore no interest, but were
legal tender, meaning that creditors had to accept them at face value for any payment except for import tariffs and interest on public debts. However, silver and gold coins continued to be issued, resulting in the depreciation of the newly printed notes through
Gresham's law. In 1869, Supreme Court ruled in
Hepburn v. Griswold that Congress could not require creditors to accept United States Notes, but overturned that ruling the next year in the
Legal Tender Cases. In 1875, Congress passed the ''
Specie Payment Resumption Act'', requiring the Treasury to allow U.S. Notes to be redeemed for gold after January 1, 1879.
Gold standard, 20th century
Though the dollar came under the
gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
''de jure'' only after 1900, the
bimetallic era was ended ''de facto'' when the
Coinage Act of 1873 suspended the minting of the standard
silver dollar of , the only fully legal tender coin that individuals could convert bullion into in unlimited (or
Free silver) quantities, and right at the onset of the
silver rush from the
Comstock Lode in the 1870s. This was the so-called "Crime of '73".
The ''
Gold Standard Act'' of 1900 repealed the U.S. dollar's historic link to silver and defined it solely as of fine gold (or $20.67 per
troy ounce of 480 grains). In 1933, gold coins were confiscated by
Executive Order 6102 under
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
, and in 1934 the standard was changed to $35 per troy ounce fine gold, or per dollar.
After 1968 a series of revisions to the gold peg was implemented, culminating in the
Nixon Shock of August 15, 1971, which suddenly ended the convertibility of dollars to gold. The U.S. dollar has since floated freely on the
foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, ...
s.
Federal Reserve Notes, 20th century to present
Congress continued to issue paper money after the Civil War, the latest of which is the
Federal Reserve Note that was authorized by the
Federal Reserve Act of 1913. Since the discontinuation of all other types of notes (Gold Certificates in 1933, Silver Certificates in 1963, and United States Notes in 1971), U.S. dollar notes have since been issued exclusively as
Federal Reserve Notes.
Emergence as reserve currency

The U.S. dollar first emerged as an important international
reserve currency in the 1920s, displacing the British
pound sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
as it emerged from the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
relatively unscathed and since the United States was a significant recipient of wartime gold inflows. After the United States emerged as an even stronger global
superpower
Superpower describes a sovereign state or supranational union that holds a dominant position characterized by the ability to Sphere of influence, exert influence and Power projection, project power on a global scale. This is done through the comb ...
during the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the
Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 established the U.S. dollar as the world's primary reserve currency and the only post-war currency linked to gold. Despite all links to gold being severed in 1971, the dollar continues to be the world's foremost reserve currency for international trade to this day.
The Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 also defined the post-World War II monetary order and relations among modern-day
independent states, by setting up a system of rules, institutions, and procedures to regulate the
international monetary system. The agreement founded the
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
and other institutions of the modern-day
World Bank Group
The World Bank Group (WBG) is a family of five international organizations that make leveraged loans to developing countries. It is the largest and best-known development bank in the world and an observer at the United Nations Development Group ...
, establishing the infrastructure for conducting international payments and accessing the global capital markets using the U.S. dollar.
The
monetary policy of the United States is conducted by the
Federal Reserve System, which acts as the nation's
central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
. It was founded in 1913 under the
Federal Reserve Act
The Federal Reserve Act was passed by the 63rd United States Congress and signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson on December 23, 1913. The law created the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States.
After Dem ...
in order to furnish an elastic currency for the United States and to supervise its banking system, particularly in the aftermath of the
Panic of 1907.
For most of the post-war period, the
U.S. government has financed its own spending by borrowing heavily from the dollar-lubricated global capital markets, in debts denominated in its own currency and at minimal interest rates. This ability to borrow heavily without facing a significant
balance of payments crisis has been described as the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
's
exorbitant privilege.
Coins
The
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bull ...
has issued legal tender coins every year from 1792 to the present. From 1934 to the present, the only denominations produced for circulation have been the familiar penny, nickel, dime, quarter, half dollar, and dollar.
Gold and silver coins have been previously minted for general circulation from the 18th to the 20th centuries. The last gold coins were minted in 1933. The last 90% silver coins were minted in 1964, and the last 40% silver half dollar was minted in 1970.
The
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bull ...
currently produces circulating coins at the
Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
and
Denver Mints, and commemorative and proof coins for collectors at the
San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
and
West Point Mints. Mint mark conventions for these and for past mint branches are discussed in ''
Coins of the United States dollar#Mint marks''.
The
one-dollar coin has never been in popular circulation from 1794 to present, despite several attempts to increase their usage since the 1970s, the most important reason of which is the continued production and popularity of the
one-dollar bill.
Half dollar coins were commonly used currency since inception in 1794, but has fallen out of use from the mid-1960s when all silver half dollars began to be hoarded.
The
nickel is the only coin whose size and composition (5 grams, 75% copper, and 25% nickel) is still in use from 1865 to today, except for wartime 1942–1945
Jefferson nickels which contained silver.
Due to the penny's low value, some
efforts have been made to eliminate the penny as circulating coinage.
For a discussion of other discontinued and canceled denominations, see ''
Obsolete denominations of United States currency'' and ''
Canceled denominations of United States currency''.
Collector coins
Collector coins are technically legal tender at face value but are usually worth far more due to their numismatic value or for their precious metal content. These include:
*
American Eagle bullion coins
**
American Silver Eagle $1 (1
troy oz) Silver bullion coin 1986–present
**
American Gold Eagle $5 ( troy oz), $10 ( troy oz), $25 ( troy oz), and $50 (1 troy oz) Gold bullion coin 1986–present
**
American Platinum Eagle $10 ( troy oz), $25 ( troy oz), $50 ( troy oz), and $100 (1 troy oz) Platinum bullion coin 1997–present
**
American Palladium Eagle $25 (1 troy oz) Palladium bullion coin 2017–present
*
United States commemorative coins—special issue coins, among these:
**
$50.00 (Half Union) minted for the
Panama-Pacific International Exposition (1915)
**Silver proof sets minted since 1992 with dimes, quarters and half-dollars made of silver rather than the standard copper-nickel
**
Presidential dollar coins proof sets minted since 2007
Banknotes
The
U.S. Constitution provides that Congress shall have the power to "borrow money on the credit of the United States." Congress has exercised that power by authorizing
Federal Reserve Banks to issue
Federal Reserve Notes. Those notes are "obligations of the United States" and "shall be redeemed in lawful money on demand at the Treasury Department of the United States, in the city of Washington, District of Columbia, or at any Federal Reserve bank". Federal Reserve Notes are designated by law as "
legal tender" for the payment of debts. Congress has also authorized the issuance of
more than 10 other types of banknotes, including the
United States Note and the
Federal Reserve Bank Note. The Federal Reserve Note is the only type that remains in circulation since the 1970s.
Federal Reserve Notes are printed by the
Bureau of Engraving and Printing and are made from
cotton fiber paper (as opposed to
wood fiber used to make common paper). The "
large-sized notes" issued before 1928 measured , while
small-sized notes introduced that year measure . The dimensions of the modern (small-size) U.S. currency is identical to the size of
Philippine peso banknotes issued under United States administration after 1903, which had proven highly successful. The American large-note bills became known as "horse blankets" or "saddle blankets".
Currently printed denominations are
$1,
$2,
$5,
$10,
$20,
$50, and
$100. Notes above the $100 denomination stopped being printed in 1946 and were officially withdrawn from circulation in 1969. These notes were used primarily in inter-bank transactions or by
organized crime
Organized crime is a category of transnational organized crime, transnational, national, or local group of centralized enterprises run to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally thought of as a f ...
; it was the latter usage that prompted President
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
to issue an executive order in 1969 halting their use. With the advent of electronic banking, they became less necessary. Notes in denominations of
$500,
$1,000,
$5,000,
$10,000 (discontinued, but still legal tender);
$100,000 were all produced at one time; see
large denomination bills in U.S. currency for details. With the exception of the $100,000 bill (which was only issued as a Series 1934 Gold Certificate and was never publicly circulated; thus it is illegal to own), these notes are now collectors' items and are worth more than their face value to collectors.
Though still predominantly green, the post-2004 series incorporate other colors to better distinguish different denominations. As a result of a 2008 decision in an accessibility lawsuit filed by the
American Council of the Blind, the
Bureau of Engraving and Printing is planning to implement a raised tactile feature in the next redesign of each note, except the $1 and the current version of the $100 bill. It also plans larger, higher-contrast numerals, more color differences, and distribution of currency readers to assist the visually impaired during the transition period.
Countries that use US dollar
Official users
These countries and territories use the US dollar as the official currency:
*
** including 5 territories:
***
***
***
***
***
**
United States Minor Outlying Islands
The United States Minor Outlying Islands is a statistical designation applying to the minor outlying islands and groups of islands that comprise eight United States insular areas in the Pacific Ocean (Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Isla ...
*
Compact of Free Association
**
**
**
*
(alongside
Ecuadorian centavo coins)
*
*
(alongside
Liberian dollar)
*
(alongside
Panamanian balboa coins)
*
(alongside
Timor-Leste centavo coins)
*
British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or alternatively referred to as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are the fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom that, ...
:
**
**
*
Dutch Caribbean
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the New World territories, colonies, and countries (former and current) of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea, mainly the norther ...
:
**
**
**
Unofficial users
These countries and territories widely accept the US dollar unofficially as a secondary currency:
* , official currency is
Cambodian riel
* , official currency is
Honduran lempira
* , official currency is
Lebanese Pound
* , official currency is
Venezuelan Bolivar
* , official currency is
Zimbabwe Gold
*
British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or alternatively referred to as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are the fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom that, ...
:
** , official currency is the
Pound sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
*
Dutch Caribbean
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the New World territories, colonies, and countries (former and current) of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea, mainly the norther ...
:
** , official currency is
Caribbean guilder
*
Overseas France
Overseas France (, also ) consists of 13 France, French territories outside Europe, mostly the remnants of the French colonial empire that remained a part of the French state under various statuses after decolonisation. Most are part of the E ...
:
** , official currency is the
euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
Monetary policy

The
Federal Reserve Act
The Federal Reserve Act was passed by the 63rd United States Congress and signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson on December 23, 1913. The law created the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States.
After Dem ...
created the
Federal Reserve System in 1913 as the
central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
of the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. Its primary task is
to conduct the nation's
monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the U.S. economy. It is also tasked to promote the stability of the financial system and regulate financial institutions, and to act as
lender of last resort
In public finance, a lender of last resort (LOLR) is a financial entity, generally a central bank, that acts as the provider of liquidity to a financial institution which finds itself unable to obtain sufficient liquidity in the interbank ...
.
The
Monetary policy of the United States is conducted by the
Federal Open Market Committee, which is composed of the
Federal Reserve Board of Governors and 5 out of the 12 Federal Reserve Bank presidents, and is implemented by all twelve regional
Federal Reserve Banks.
Monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
refers to actions made by central banks that determine the size and growth rate of the
money supply available in the economy, and which would result in desired objectives like low inflation, low unemployment, and stable financial systems. The economy's aggregate
money supply is the total of
* M0 money, or Monetary Base – "dollars" in currency and
bank money balances credited to the central bank's depositors, which are backed by the central bank's assets,
* plus M1, M2, M3 money – "dollars" in the form of
bank money balances credited to banks' depositors, which are backed by the bank's assets and investments.
The FOMC influences the level of money available to the economy by the following means:
* Reserve requirements – specifies a required minimum percentage of deposits in a
commercial bank that should be held as a reserve (i.e. as deposits with the Federal Reserve), with the rest available to loan or invest. Higher requirements mean less money loaned or invested, helping keep inflation in check. Raising the
federal funds rate earned on those reserves also helps achieve this objective.
* Open market operations – the Federal Reserve buys or sells
US Treasury bonds and other securities held by banks in exchange for reserves; more reserves increase a bank's capacity to loan or invest elsewhere.
* Discount window lending – banks can borrow from the Federal Reserve.
Monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
directly affects interest rates; it indirectly affects stock prices, wealth, and currency exchange rates. Through these channels, monetary policy influences spending, investment, production, employment, and inflation in the United States. Effective
monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
complements
fiscal policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variab ...
to support economic growth.
The adjusted monetary base has increased from approximately $400 billion in 1994, to $800 billion in 2005, and to over $3 trillion in 2013.
When the Federal Reserve makes a purchase, it credits the seller's reserve account (with the Federal Reserve). This money is not transferred from any existing funds—it is at this point that the Federal Reserve has created new
high-powered money. Commercial banks then decide how much money to keep in deposit with the Federal Reserve and how much to hold as physical currency. In the latter case, the Federal Reserve places an order for printed money from the U.S. Treasury Department. The Treasury Department, in turn, sends these requests to the Bureau of Engraving and Printing (to print new
dollar bills) and the Bureau of the Mint (to stamp the coins).
The Federal Reserve's monetary policy objectives to keep prices stable and unemployment low is often called the ''dual mandate''. This replaces past practices under a
gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
where the main concern is the gold equivalent of the local currency, or under a gold exchange standard where the concern is fixing the exchange rate versus another gold-convertible currency (previously practiced worldwide under the
Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 via fixed exchange rates to the U.S. dollar).
International use as reserve currency

Ascendancy
The primary currency used for global trade between
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
,
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, and
the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.'' Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sin ...
has historically been the Spanish-American
silver dollar, which created a global
silver standard system from the 16th to 19th centuries, due to abundant silver supplies in
Spanish America.
The U.S. dollar itself was derived from this coin. The
Spanish dollar was later displaced by the British
pound sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
in the advent of the international
gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
in the last quarter of the 19th century.
The U.S. dollar began to displace the
pound sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
as international
reserve currency from the 1920s since it emerged from the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
relatively unscathed and since the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
was a significant recipient of wartime gold inflows.
After the U.S. emerged as an even stronger global
superpower
Superpower describes a sovereign state or supranational union that holds a dominant position characterized by the ability to Sphere of influence, exert influence and Power projection, project power on a global scale. This is done through the comb ...
during the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the
Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 established the post-war international monetary system, with the U.S. dollar ascending to become the world's primary
reserve currency for international trade, and the only post-war currency linked to gold at $35 per
troy ounce.
As international reserve currency
The U.S. dollar is joined by the world's other major currencies – the
euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
,
pound sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
,
Japanese yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro.
Th ...
and Chinese
renminbi
The renminbi ( ; currency symbol, symbol: Yen and yuan sign, ¥; ISO 4217, ISO code: CNY; abbreviation: RMB), also known as the Chinese yuan, is the official currency of the China, People's Republic of China. The renminbi is issued by the Peop ...
– in the currency basket of the
special drawing rights of the
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
. Central banks worldwide have huge reserves of U.S. dollars in their holdings and are significant buyers of
U.S. treasury bills and notes.
Foreign companies, entities, and private individuals hold U.S. dollars in foreign deposit accounts called
eurodollars (not to be confused with the
euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
), which are outside the jurisdiction of the
Federal Reserve System. Private individuals also hold dollars outside the banking system mostly in the form of
US$100 bills, of which 80% of its supply is held overseas.
The
United States Department of the Treasury
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the Treasury, national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States. It is one of 15 current United States federal executive departments, U.S. government departments.
...
exercises considerable oversight over the
SWIFT financial transfers network, and consequently has a huge sway on the global
financial transaction
A financial transaction is an Contract, agreement, or communication, between a buyer and seller to exchange goods, Service (economics), services, or assets for payment. Any transaction involves a change in the status of the finances of two or mo ...
s systems, with the ability to impose sanctions on foreign entities and individuals.
In the global markets
The U.S. dollar is predominantly the standard currency unit in which goods are quoted and traded, and with which payments are settled, in the global
commodity markets. The
U.S. Dollar Index is an important indicator of the dollar's strength or weakness versus a basket of six foreign currencies.
The
United States Government
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the Federation#Federal governments, national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct ...
is capable of borrowing trillions of dollars from the global capital markets in U.S. dollars issued by the
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of ...
, which is itself under U.S. government purview, at minimal interest rates, and with virtually zero default risk. In contrast, foreign governments and corporations incapable of raising money in their own local currencies are forced to issue debt denominated in U.S. dollars, along with its consequent higher interest rates and risks of default. The United States's ability to borrow in its own currency without facing a significant balance of payments crisis has been frequently described as its
exorbitant privilege.
A frequent topic of debate is whether the
strong dollar policy of the United States is indeed in America's own best interests, as well as in the best interest of the
international community
The international community is a term used in geopolitics and international relations to refer to a broad group of people and governments of the world.
Usage
Aside from its use as a general descriptor, the term is typically used to imply the ...
.
Currencies fixed to the U.S. dollar
For a more exhaustive discussion of countries using the U.S. dollar as official or customary currency, or using currencies which are pegged to the U.S. dollar, see ''
International use of the U.S. dollar#Dollarization and fixed exchange rates'' and ''
Currency substitution#US dollar''.
Countries using the U.S. dollar as their official currency include:
* In the Americas:
Panama
Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a country in Latin America at the southern end of Central America, bordering South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and ...
,
Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
,
El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
,
British Virgin Islands
The British Virgin Islands (BVI), officially the Virgin Islands, are a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean, to the east of Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands, US Virgin Islands and north-west ...
,
Turks and Caicos Islands, and the
Caribbean Netherlands
The Caribbean Netherlands (, ) is a geographic region of the Netherlands located outside of Europe, in the Caribbean, consisting of three special municipalities. These are the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba (island), Saba,"Bonair ...
.
* The constituent states of the former
Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands:
Palau
Palau, officially the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. The Republic of Palau consists of approximately 340 islands and is the western part of the Caroline Islands ...
, the
Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (, abbreviated FSM), or simply Micronesia, is an island country in Micronesia, a region of Oceania. The federation encompasses the majority of the Caroline Islands (excluding Palau) and consists of four Admin ...
, and the
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The territory consists of 29 c ...
.
* Others:
Timor-Leste.
Among the countries using the U.S. dollar together with other foreign currencies and their local currency are
Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
and
Zimbabwe
file:Zimbabwe, relief map.jpg, upright=1.22, Zimbabwe, relief map
Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Bots ...
.
Currencies pegged to the U.S. dollar include:
* In the Caribbean: the
Bahamian dollar,
Barbadian dollar,
Belize dollar,
Bermudian dollar,
Cayman Islands dollar,
Eastern Caribbean dollar,
Netherlands Antillean guilder and the
Aruban florin.
* The currencies of five oil-producing Arab countries: the
Saudi riyal,
United Arab Emirates dirham,
Omani rial,
Qatari riyal and the
Bahraini dinar.
* Others: the
Hong Kong dollar,
Macanese pataca,
Jordanian dinar,
Lebanese pound.
Value
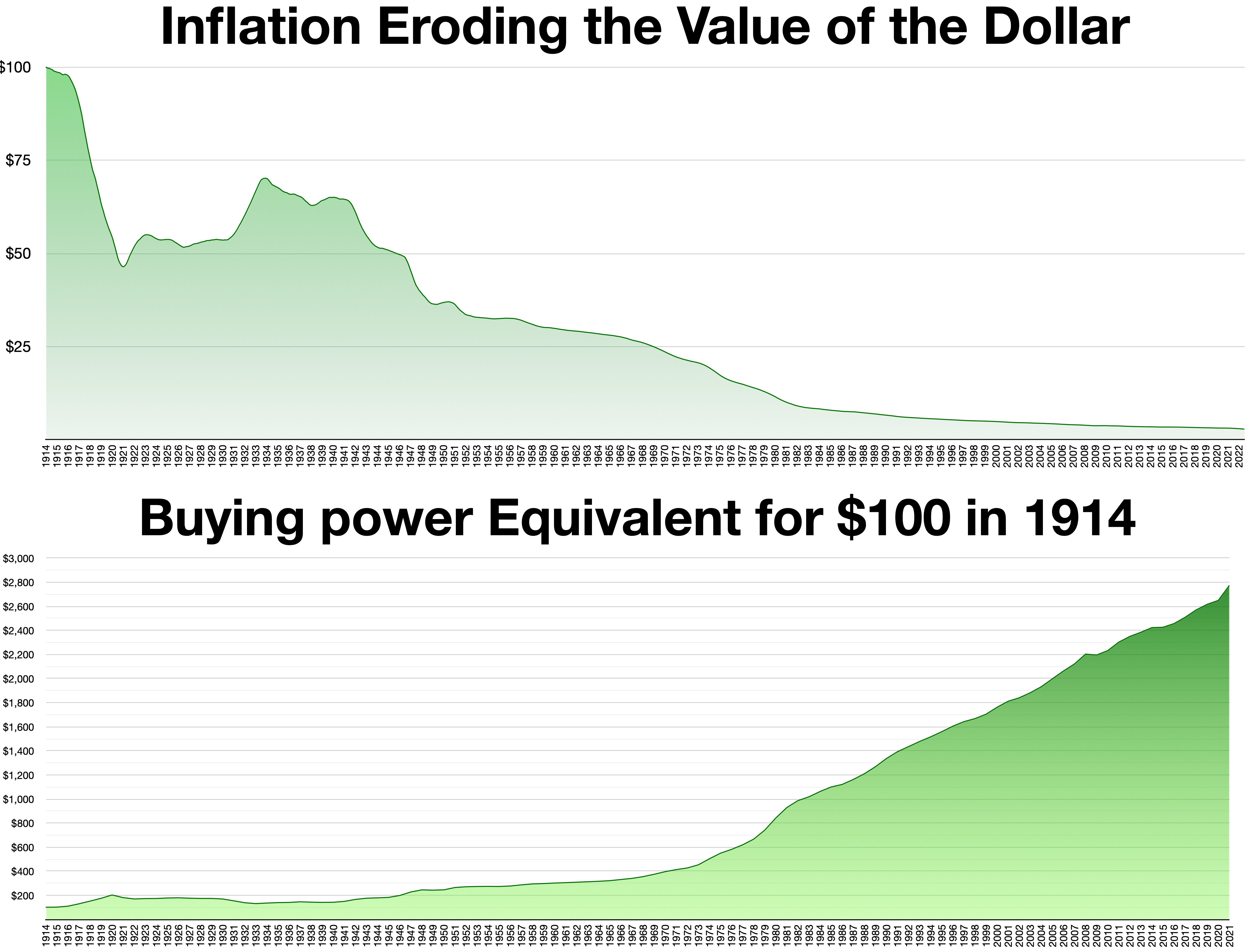
The 6th paragraph of
Section 8 of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution provides that the U.S. Congress shall have the power to "coin money" and to "regulate the value" of domestic and foreign coins. Congress exercised those powers when it enacted the
Coinage Act of 1792. That Act provided for the minting of the
first U.S. dollar and it declared that the U.S. dollar shall have "the value of a
Spanish milled dollar as the same is now current".
The table above shows the equivalent amount of goods that, in a particular year, could be purchased with $1. The table shows that from 1774 through 2012 the U.S. dollar has lost about 97.0% of its buying power.
The decline in the value of the U.S. dollar corresponds to
price inflation, which is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. A
consumer price index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a statistical estimate of the level of prices of goods and services bought for consumption purposes by households. It is calculated as the weighted average price of a market basket of Goods, consumer goods and ...
(CPI) is a measure estimating the average price of consumer goods and services purchased by households. The
United States Consumer Price Index, published by the
Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
, is a measure estimating the average price of consumer goods and services in the United States. It reflects inflation as experienced by consumers in their day-to-day living expenses. A graph showing the U.S. CPI relative to 1982–1984 and the annual year-over-year change in CPI is shown at right.
The value of the U.S. dollar declined significantly during wartime, especially during the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, World War I, and World War II. The
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of ...
, which was established in 1913, was designed to furnish an "elastic" currency subject to "substantial changes of quantity over short periods", which differed significantly from previous forms of
high-powered money such as gold, national banknotes, and silver coins. Over the very long run, the prior gold standard kept prices stable—for instance, the price level and the value of the U.S. dollar in 1914 were not very different from the price level in the 1880s. The Federal Reserve initially succeeded in maintaining the value of the U.S. dollar and price stability, reversing the inflation caused by the First World War and stabilizing the value of the dollar during the 1920s, before presiding over a 30% deflation in U.S. prices in the 1930s.
Under the
Bretton Woods system established after World War II, the value of gold was fixed to $35 per ounce, and the value of the U.S. dollar was thus anchored to the value of gold. Rising government spending in the 1960s, however, led to doubts about the ability of the United States to maintain this convertibility, gold stocks dwindled as banks and international investors began to convert dollars to gold, and as a result, the value of the dollar began to decline. Facing an emerging
currency crisis and the imminent danger that the United States would no longer be able to redeem dollars for gold, gold convertibility was finally terminated in 1971 by
President Nixon, resulting in the "
Nixon shock".
The value of the U.S. dollar was therefore no longer anchored to gold, and it fell upon the Federal Reserve to maintain the value of the U.S. currency. The Federal Reserve, however, continued to increase the money supply, resulting in
stagflation and a rapidly declining value of the U.S. dollar in the 1970s. This was largely due to the prevailing economic view at the time that inflation and real economic growth were linked (the
Phillips curve), and so inflation was regarded as relatively benign.
Between 1965 and 1981, the U.S. dollar lost two thirds of its value.
In 1979,
President Carter appointed
Paul Volcker Chairman of the Federal Reserve
The chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System is the head of the Federal Reserve, and is the active executive officer of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. The chairman presides at meetings of the Board.
...
. The Federal Reserve tightened the money supply and inflation was substantially lower in the 1980s, and hence the value of the U.S. dollar stabilized.
Over the thirty-year period from 1981 to 2009, the U.S. dollar lost over half its value.
This is because the Federal Reserve has targeted not zero inflation, but a low, stable rate of inflation—between 1987 and 1997, the rate of inflation was approximately 3.5%, and between 1997 and 2007 it was approximately 2%. The so-called "
Great Moderation" of economic conditions since the 1970s is credited to monetary policy targeting price stability.
There is an ongoing debate about whether central banks should target zero inflation (which would mean a constant value for the U.S. dollar over time) or low, stable inflation (which would mean a continuously but slowly declining value of the dollar over time, as is the case now). Although some economists are in favor of a zero inflation policy and therefore a constant value for the U.S. dollar,
others contend that such a policy limits the ability of the central bank to control
interest rates and stimulate the economy when needed.
Pegged currencies
*
Aruban florin (lower value)
*
Bahamian dollar (at par)
*
Bahraini dinar (higher value)
*
Barbadian dollar (lower value)
*
Belarusian ruble (alongside Euro and Russian ruble in currency basket)
*
Belize dollar (lower value)
*
Bermudian dollar (at par)
*
Bolivian boliviano (lower value)
*
Cambodian riel (lower value)
*
Cayman Islands dollar (higher value)
*
Costa Rican colón (lower value)
*
Cuban peso (lower value)
*
Eastern Caribbean dollar (lower value)
*
Ecuadorian centavo coins (at par)
*
Eritrean nakfa (lower value)
*
Guatemalan quetzal (lower value)
*
Haitian gourde (lower value)
*
Honduran lempira (lower value)
*
Hong Kong dollar (narrow band)
*
Iraqi dinar (lower value)
*
Jordanian dinar (higher value)
*
Kuwaiti dinar (higher value)
*
Lebanese pound (lower value)
*
Netherlands Antillean guilder (lower value, to be replaced by
Caribbean guilder in 2025)
*
Nicaraguan córdoba (lower value)
*
Nigerian naira (lower value)
*
Omani rial (higher value)
*
Panamanian balboa (at par)
*
Qatari riyal (lower value)
*
Saudi riyal (lower value)
*
Sierra Leonean leone (lower value)
*
Timor-Leste centavo coins (at par)
*
Trinidad and Tobago dollar (lower value)
*
United Arab Emirates dirham (lower value)
*
Yemeni rial (lower value)
Currencies formerly with pegs (incomplete list)
*
Argentine austral (1985–1991: fluctuating peg to USD)
*
Argentine peso (1991–2002: 1/USD)
*
Chinese yuan
The renminbi ( ; currency symbol, symbol: Yen and yuan sign, ¥; ISO 4217, ISO code: CNY; abbreviation: RMB), also known as the Chinese yuan, is the official currency of the China, People's Republic of China. The renminbi is issued by the Peop ...
(until 2005: 1/USD)
*
Indonesian rupiah (until 1997: 1/USD)
*
Malaysian ringgit (1998–2005: 3.80/USD)
*
Mexican peso
The Mexican peso (Currency symbol, symbol: $; ISO 4217, currency code: MXN; also abbreviated Mex$ to distinguish it from peso, other peso-denominated currencies; referred to as the peso, Mexican peso, or colloquially varo) is the official curre ...
(1933–1948: 8.65/USD, 1954–1976: 12.5/USD)
*
South Korean won (until 1997: 1/USD)
*
Thai baht (until 1997: 1/USD)
Obsolete currencies with USD peg
*
Salvadoran colón (lower value)
*
Zimbabwean bond coins and
bond notes (at par)
Exchange rates
Historical exchange rates
Current exchange rates
See also
*
Counterfeit United States currency
*
Dedollarisation
*
Currency substitution
*
International use of the U.S. dollar
*
List of the largest trading partners of the United States
*
Monetary policy of the United States
*
Petrodollar recycling
Petrodollar recycling is the international spending or investment of a country's revenues from petroleum exports ("petrodollars"). It generally refers to the phenomenon of major List of countries by oil exports, petroleum-exporting states, mai ...
*
Strong dollar policy
*
U.S. Dollar Index
*
Virtual currency
Notes
References
Further reading
*
External links
U.S. Bureau of Engraving and Printing
American Currency Exhibit at the San Francisco Federal Reserve Bank
Relative values of the U.S. dollar, from 1774 to presentSummary of BEP Production StatisticsThe U.S. Currency Education Program
Images of U.S. currency and coins
U.S. Currency Education Program page with images of all current banknotesU.S. Mint: Image Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States Dollar
Currencies introduced in 1792
Currencies of dependent territories of the United Kingdom
Currencies of Timor-Leste
Dollar
Currencies of El Salvador
Currencies of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Dollar
Currencies of Zimbabwe
Historical currencies of the United States
1792 establishments in the United States
Currencies of Africa
Circulating currencies
Dollar
Currencies of Oceania
Currencies of Asia
 The symbol , usually written before the numerical amount, is used for the U.S. dollar (as well as for many other currencies). The sign was perhaps the result of a late 18th-century evolution of the scribal abbreviation ''ps'' for the peso, the common name for the Spanish dollars that were in wide circulation in the
The symbol , usually written before the numerical amount, is used for the U.S. dollar (as well as for many other currencies). The sign was perhaps the result of a late 18th-century evolution of the scribal abbreviation ''ps'' for the peso, the common name for the Spanish dollars that were in wide circulation in the  On July 6, 1785, the Continental Congress resolved that the money unit of the United States, the dollar, would contain 375.64
On July 6, 1785, the Continental Congress resolved that the money unit of the United States, the dollar, would contain 375.64  After the
After the  In order to finance the War of 1812, Congress authorized the issuance of Treasury Notes, interest-bearing short-term debt that could be used to pay public dues. While they were intended to serve as debt, they did function "to a limited extent" as money. Treasury Notes were again printed to help resolve the reduction in public revenues resulting from the
In order to finance the War of 1812, Congress authorized the issuance of Treasury Notes, interest-bearing short-term debt that could be used to pay public dues. While they were intended to serve as debt, they did function "to a limited extent" as money. Treasury Notes were again printed to help resolve the reduction in public revenues resulting from the  The U.S. dollar first emerged as an important international reserve currency in the 1920s, displacing the British
The U.S. dollar first emerged as an important international reserve currency in the 1920s, displacing the British  The
The  The 6th paragraph of Section 8 of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution provides that the U.S. Congress shall have the power to "coin money" and to "regulate the value" of domestic and foreign coins. Congress exercised those powers when it enacted the Coinage Act of 1792. That Act provided for the minting of the first U.S. dollar and it declared that the U.S. dollar shall have "the value of a Spanish milled dollar as the same is now current".
The table above shows the equivalent amount of goods that, in a particular year, could be purchased with $1. The table shows that from 1774 through 2012 the U.S. dollar has lost about 97.0% of its buying power.
The decline in the value of the U.S. dollar corresponds to price inflation, which is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. A
The 6th paragraph of Section 8 of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution provides that the U.S. Congress shall have the power to "coin money" and to "regulate the value" of domestic and foreign coins. Congress exercised those powers when it enacted the Coinage Act of 1792. That Act provided for the minting of the first U.S. dollar and it declared that the U.S. dollar shall have "the value of a Spanish milled dollar as the same is now current".
The table above shows the equivalent amount of goods that, in a particular year, could be purchased with $1. The table shows that from 1774 through 2012 the U.S. dollar has lost about 97.0% of its buying power.
The decline in the value of the U.S. dollar corresponds to price inflation, which is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. A