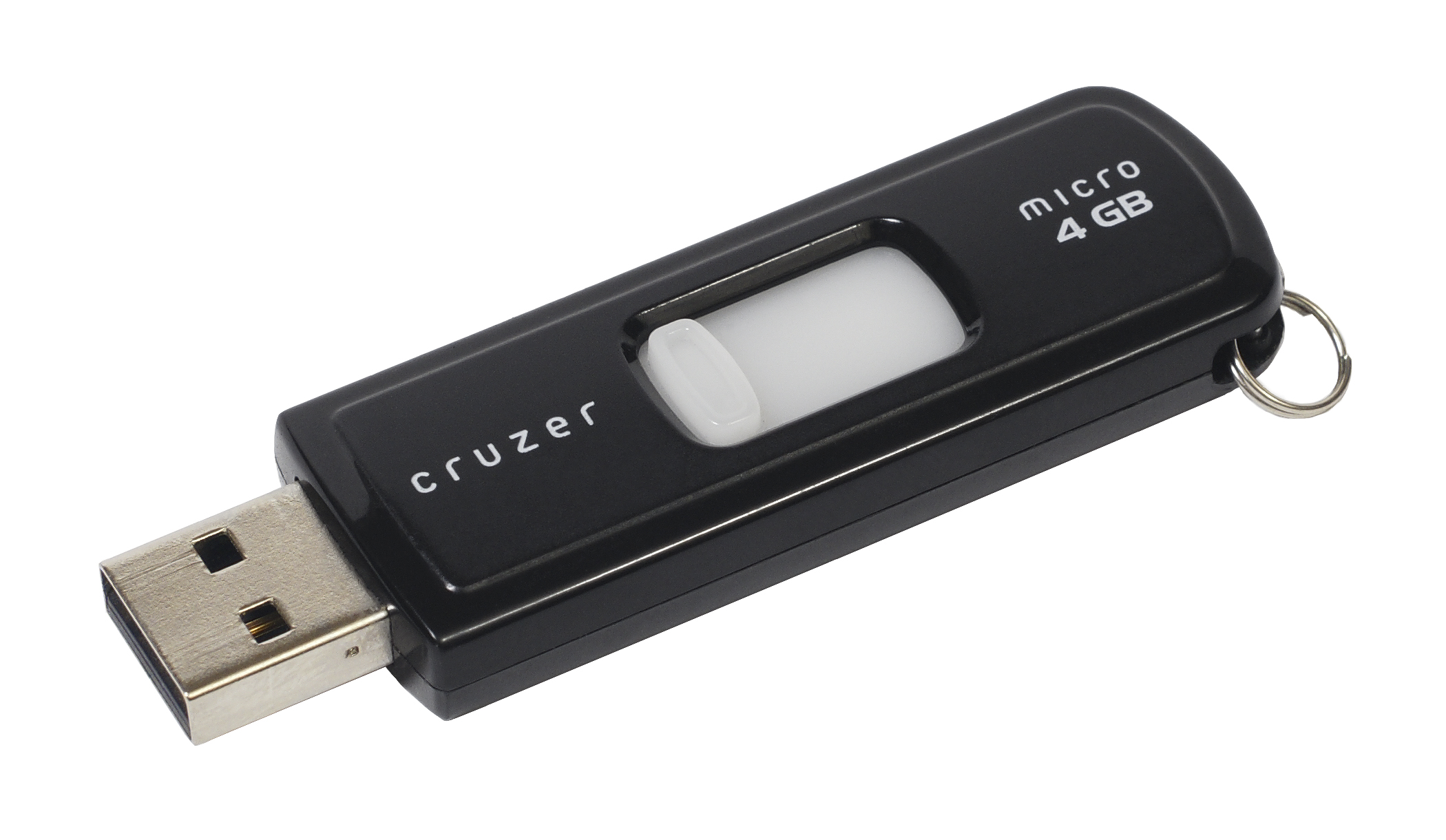



A flash drive (also thumb drive, memory stick, and pen drive/pendrive) is a
data storage device that includes
flash memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
with an integrated
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
interface. A typical USB drive is removable, rewritable, and smaller than an
optical disc
An optical disc is a flat, usuallyNon-circular optical discs exist for fashion purposes; see shaped compact disc. disc-shaped object that stores information in the form of physical variations on its surface that can be read with the aid o ...
, and usually weighs less than . Since first offered for sale in late 2000, the storage capacities of USB drives range from 8
megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB. The unit prefix ''mega'' is a multiplier of (106) in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes ...
s to 256
gigabyte
The gigabyte () is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The SI prefix, prefix ''giga-, giga'' means 109 in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is one billion bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte i ...
s (GB), 512 GB and 1
terabyte (TB).
As of 2024, 4 TB flash drives were the largest currently in production. Some allow up to 100,000 write/erase cycles, depending on the exact type of memory chip used, and are thought to physically last between 10 and 100 years under normal circumstances (
shelf storage time).
Common uses of USB flash drives are for storage, supplementary
back-ups, and transferring of
computer file
A computer file is a System resource, resource for recording Data (computing), data on a Computer data storage, computer storage device, primarily identified by its filename. Just as words can be written on paper, so too can data be written to a ...
s. Compared with
floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a ...
s or
CDs, they are smaller, faster, have significantly more capacity, and are more durable due to a lack of moving parts. Additionally, they are less vulnerable to
electromagnetic interference than floppy disks, and are unharmed by surface scratches (unlike CDs). However, as with any flash storage, data loss from
bit leaking due to prolonged lack of electrical power and the possibility of spontaneous
controller failure
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. On ...
due to poor manufacturing could make it unsuitable for long-term
archiving of data. The ability to retain data is affected by the controller's
firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
, internal
data redundancy
In computer main memory, auxiliary storage and computer buses, data redundancy is the existence of data that is additional to the actual data and permits correction of errors in stored or transmitted data. The additional data can simply be a com ...
, and
error correction
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunications, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communi ...
algorithms.
Until about 2005, most desktop and laptop computers were supplied with floppy disk drives in addition to USB ports, but floppy disk drives became obsolete after widespread adoption of USB ports and the larger USB drive capacity compared to the "
1.44 megabyte" 3.5-inch floppy disk.
USB flash drives use the
USB mass storage device class standard, supported natively by modern
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s such as
Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
,
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, and other
Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
systems, as well as many
BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
boot ROMs. USB drives with USB 2.0 support can store more data and transfer faster than much larger optical disc drives like CD-RW or DVD-RW drives and can be read by many other systems such as the
Xbox One
The Xbox One is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. Announced in May 2013, it is the successor to Xbox 360 and the third console in the Xbox#Consoles, Xbox series. It was first released in North America, parts of Europe, Austra ...
,
PlayStation 4, DVD players, automobile entertainment systems, and in a number of handheld devices such as smartphones and tablet computers, though the electronically similar
SD card
Secure Digital (SD) is a proprietary, non-volatile, flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA). Owing to their compact size, SD cards have been widely adopted in a variety of portable consumer electronics, including dig ...
is better suited for those devices, due to their standardized form factor, which allows the card to be housed inside a device without protruding.
A flash drive consists of a small
printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
carrying the circuit elements and a USB connector, insulated electrically and protected inside a plastic, metal, or rubberized case, which can be carried in a pocket or on a key chain, for example. Some are equipped with an
I/O indication
LED that lights up or blinks upon access. The USB connector may be protected by a removable cap or by retracting into the body of the drive, although it is not likely to be damaged if unprotected. Most flash drives use a standard type-A USB connection allowing connection with a port on a personal computer, but drives for other interfaces also exist (e.g. micro-USB and USB-C ports). USB flash drives draw power from the computer via the USB connection. Some devices combine the functionality of a
portable media player
A portable media player (PMP) or digital audio player (DAP) is a portable consumer electronics device capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, and video files. Normally they refer to small, Electric battery, batter ...
with USB flash storage; they require a battery only when used to play music on the go.
History
The basis for USB flash drives is
flash memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
, a type of
floating-gate semiconductor memory
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) memory cells on a si ...
invented by
Fujio Masuoka in the early 1980s. Flash memory uses
floating-gate MOSFET transistors as
memory cells.
Multiple individuals have staked a claim to having invented the USB flash drive. On April 5, 1999,
Amir Ban,
Dov Moran, and
Oron Ogdan of
M-Systems, an
Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
i company, filed a patent application entitled "Architecture for a Universal Serial Bus-Based PC Flash Disk".
The patent was subsequently granted on November 14, 2000, and these individuals have often been recognized as the inventors of the USB flash drive. Also in 1999,
Shimon Shmueli, an engineer at IBM, submitted an invention disclosure asserting that he had invented the USB flash drive.
A Singaporean company named
Trek 2000 International is the first company known to have sold a USB flash drive, and has also maintained that it is the original inventor of the device. Finally
Pua Khein-Seng, a Malaysian engineer, has also been recognized by some as a possible inventor of the device.
Given these competing inventor claims, patent disputes involving the USB flash drive have arisen over the years. Both
Trek 2000 International and
Netac Technology have accused others of infringing their patents on the USB flash drive. However, the question of who was the first to invent the USB flash drive has multiple claims persists. Netac Technology got the basic American copyright on December 7, 2004. And in the lawsuit, the PNY company paid 1,000 million dollars to Netac.
Technology improvements
Flash drives are often measured by the rate at which they transfer data. Transfer rates may be given in megabytes per second (MB/s), megabits per second (Mbit/s), or in optical drive multipliers such as "180X" (180 times 150
KiB/s). File transfer rates vary considerably among devices. Second generation flash drives have claimed to read at up to 30 MB/s and write at about half that rate, which was about 20 times faster than the theoretical transfer rate achievable by the previous model, USB 1.1, which is limited to 12 Mbit/s (1.5 MB/s) with accounted overhead. The effective transfer rate of a device is significantly affected by the data access pattern.
By 2002, USB flash drives had
USB 2.0 connectivity, which has 480
Mbit/s as the transfer rate upper bound; after accounting for the protocol overhead That same year, Intel sparked widespread use of second generation USB by including them within its laptops.
By 2010, the maximum available storage capacity for the devices had reached upwards of 128 GB.
was slow to appear in laptops. Through 2010, the majority of laptop models still contained only USB 2.0.
In January 2013, tech company Kingston, released a flash drive with 1 TB of storage. The first
USB 3.1 type-C flash drives, with read/write speeds of around 530 MB/s, were announced in March 2015. By July 2016, flash drives with 8 to 256 GB capacity were sold more frequently than those with capacities between 512 GB and 1 TB.
In 2017, Kingston Technology announced the release of a 2-TB flash drive. In 2018, SanDisk announced a 1 TB USB-C flash drive, the smallest of its kind.
On a USB flash drive, one end of the device is fitted with a single
Standard-A USB plug; some flash drives additionally offer a
micro USB or USB-C plug, facilitating data transfers between different devices.
Technology

On a USB flash drive, one end of the device is fitted with a single
USB plug; some flash drives additionally offer a
micro USB plug, facilitating data transfers between different devices.
Inside the casing is a small printed circuit board, which has some power circuitry and a small number of
surface-mounted integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s (ICs). Typically, one of these ICs provides an interface between the USB connector and the onboard memory, while the other is the
flash memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
. Drives typically use the
USB mass storage device class to communicate with the host.
Flash memory
Flash memory combines a number of older technologies, with lower cost, lower power consumption and small size made possible by advances in
semiconductor device fabrication technology. The memory storage is based on earlier
EPROM and
EEPROM technologies. These had limited capacity, were slow for both reading and writing, required complex high-voltage drive circuitry, and could be re-written only after erasing the entire contents of the chip.
Hardware designers later developed EEPROMs with the erasure region broken up into smaller "fields" that could be erased individually without affecting the others. Altering the contents of a particular memory location involved copying the entire field into an off-chip buffer memory, erasing the field, modifying the data as required in the buffer, and re-writing it into the same field. This required considerable computer support, and PC-based EEPROM flash memory systems often carried their own dedicated microprocessor system. Flash drives are more or less a miniaturized version of this.
The development of high-speed serial data interfaces such as USB made semiconductor memory systems with serially accessed storage viable, and the simultaneous development of small, high-speed, low-power microprocessor systems allowed this to be incorporated into extremely compact systems. Serial access requires far fewer electrical connections for the memory chips than
parallel access, simplifying the manufacture of multi-
gigabyte
The gigabyte () is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The SI prefix, prefix ''giga-, giga'' means 109 in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is one billion bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte i ...
drives.
Computers access flash memory systems very much like hard disk drives, where the
controller system has full control over where information is actually stored. The actual EEPROM writing and erasure processes are, however, still very similar to the earlier systems described above.
Many low-cost
MP3 players simply add extra software and a battery to a standard flash memory control microprocessor so it can also serve as a music playback decoder. Most of these players can also be used as a conventional flash drive, for storing files of any type.
Essential components

There are typically five parts to a flash drive:
* USB plug provides a physical interface to the host computer. Some USB flash drives use USB plug that does not protect the contacts, with the possibility of plugging it into the USB port in the wrong orientation, if the connector type is not symmetrical.
* USB mass storage controller a small
microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
with a small amount of on-chip
ROM and
RAM.
*
NAND flash memory chip(s) stores data (NAND flash is typically also used in
digital camera
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in Digital data storage, digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Dig ...
s).
*
Crystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator Electrical circuit, circuit that uses a piezoelectricity, piezoelectric crystal as a frequency selective surface, frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep trac ...
produces the device's main
clock signal and controls the device's data output through a
phase-locked loop.
* Cover typically made of plastic or metal, protecting the electronics against mechanical stress and even possible short circuits.
Additional components
The typical device may also include:
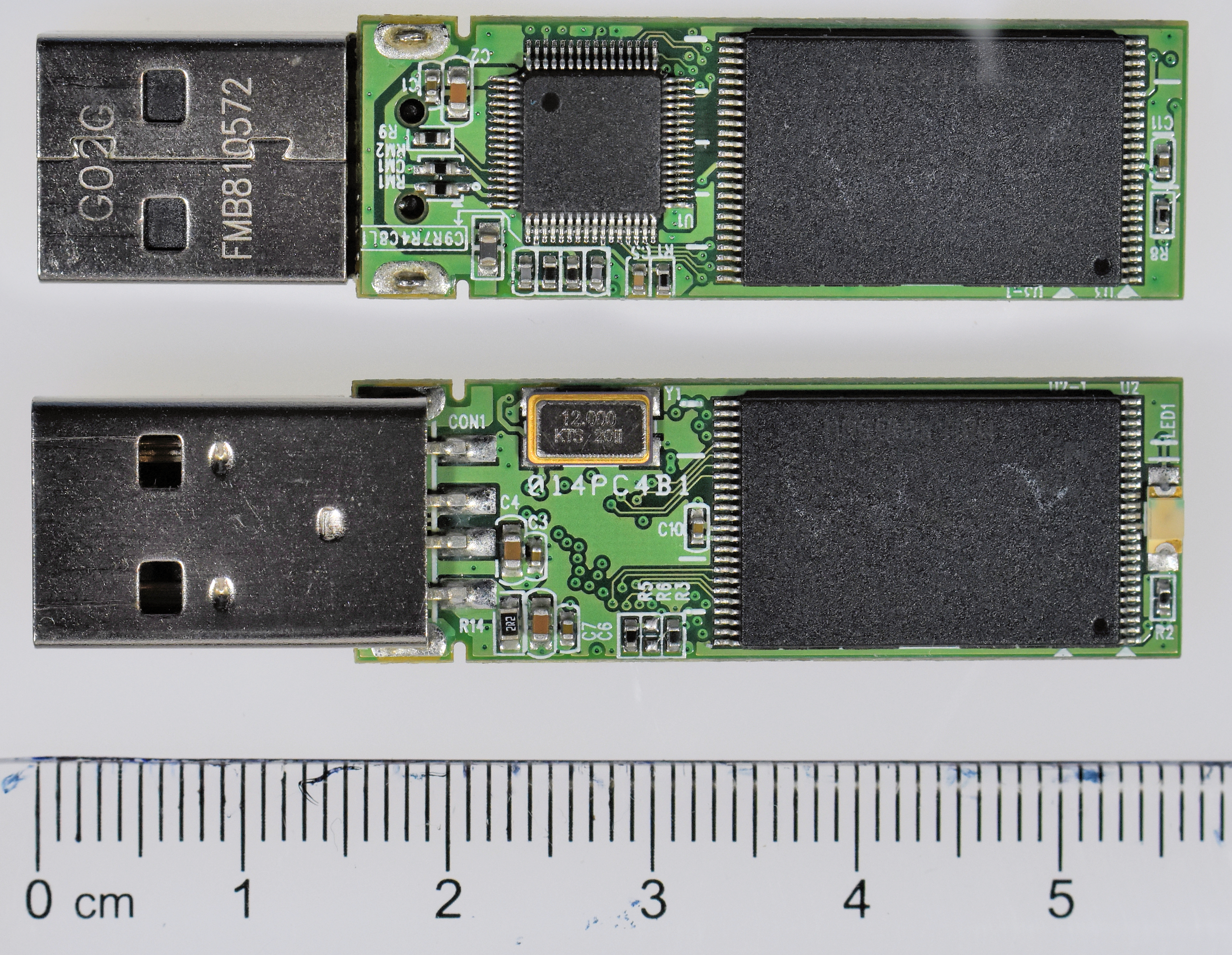
*
Jumpers
Jumper or Jumpers may refer to:
Clothing
*Jumper (sweater), is a long-sleeve article of clothing; also called a top, pullover, or sweater
**A waist-length top garment of dense wool, part of the Royal Navy uniform and the Uniforms of the United St ...
and test pins – for testing during the flash drive's manufacturing or loading code into its
microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
.
*
LEDs – indicate data transfers or data reads and writes.
*
Write-protect switches – Enable or disable writing of data into memory.
* Unpopulated space – provides space to include a second memory chip. Having this second space allows the manufacturer to use a single printed circuit board for more than one storage size device.
* USB connector cover or cap – reduces the risk of damage, prevents the entry of dirt or other contaminants, and improves overall device appearance. Some flash drives use retractable USB connectors instead. Others have a swivel arrangement so that the connector can be protected without removing anything.
* Transport aid – the cap or the body often contains a hole suitable for connection to a
key chain or
lanyard. Connecting the cap, rather than the body, can allow the drive itself to be lost.
* Some drives offer expandable storage via an internal
memory card slot, much like a memory
card reader.
Size and style of packaging
Most USB flash drives weigh less than . While some manufacturers are competing for the smallest size, with the biggest memory, offering drives only a few millimeters larger than the USB plug itself, some manufacturers differentiate their products by using elaborate housings, which are often bulky and make the drive difficult to connect to the USB port. Because the
USB port connectors on a computer housing are often closely spaced, plugging a flash drive into a USB port may block an adjacent port. Such devices may carry the USB logo only if sold with a separate extension cable. Such cables are USB-compatible but do not conform to the USB standard.
USB flash drives have been integrated into other commonly carried items, such as watches, pens, laser pointers, and even the
Swiss Army Knife; others have been fitted with novelty cases such as toy cars or
Lego
Lego (, ; ; stylised as LEGO) is a line of plastic construction toys manufactured by the Lego Group, a privately held company based in Billund, Denmark. Lego consists of variously coloured interlocking plastic bricks made of acrylonitri ...
bricks. USB flash drives with images of dragons, cats or aliens are very popular in Asia. The small size, robustness and cheapness of USB flash drives make them an increasingly popular peripheral for
case modding
Case modification, commonly referred to as case modding, is the modification of a computer case or a video game console chassis. Modifying a computer case in any non-standard way is considered a case mod. Modding is done, particularly by Compute ...
.
File system
Most flash drives ship preformatted with the
FAT32, or
exFAT file systems. The
ubiquity of the FAT32 file system allows the drive to be accessed on virtually any host device with USB support. Also, standard FAT
maintenance utilities (e.g.,
ScanDisk) can be used to repair or retrieve
corrupted data. However, because a flash drive appears as a USB-connected
hard drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
to the host system, the drive can be
reformatted to any file system supported by the host operating system.
Defragmenting
Flash drives can be
defragmented. There is a widespread opinion that defragmenting brings little advantage (as there is no mechanical head that moves from fragment to fragment), and that defragmenting shortens the life of the drive by making many unnecessary writes. However, some sources claim that defragmenting a flash drive can improve performance (mostly due to improved caching of the clustered data), and the additional wear on flash drives may not be significant.
Even distribution
Some file systems are designed to distribute usage over an entire memory device without concentrating usage on any part (e.g., for a directory) to prolong the life of simple flash memory devices. Some USB flash drives have this '
wear leveling' feature built into the software controller to prolong device life, while others do not, so it is not necessarily helpful to install one of these file systems.
Hard disk drive
Sectors are 512 bytes long, for compatibility with hard disk drives, and the first sector can contain a
master boot record
A master boot record (MBR) is a type of boot sector in the first block of disk partitioning, partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept ...
and a
partition table. Therefore, USB flash units can be partitioned just like hard disk drives.
Longevity
The memory in flash drives was commonly engineered with
multi-level cell (MLC) based memory that is good for around 3,000-5,000 program-erase cycles. Nowadays Triple-level Cell (TLC) is also often used, which has up to 500 write cycles per physical sector, while some high-end flash drives have
single-level cell (SLC) based memory that is good for around 30,000 writes. There is virtually no limit to the number of reads from such flash memory, so a well-worn USB drive may be write-protected to help ensure the life of individual cells.
Estimation of flash memory endurance is a challenging subject that depends on the
SLC/
MLC/
TLC memory type, size of the flash memory chips, and actual usage pattern. As a result, a USB flash drive can last from a few days to several hundred years.
Regardless of the endurance of the memory itself, the USB connector hardware is specified to withstand only around 1,500 insert-removal cycles.
Counterfeit products
Counterfeit USB flash drives are sometimes sold with claims of having higher capacities than they actually possess. These are typically low-capacity USB drives with modified flash memory controller
firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
that emulates larger capacity drives (for example, a 2 GB drive being marketed as a 64 GB drive). When plugged into a computer, they report being the larger capacity they were sold as, but when data is written to them, either the write fails, the drive freezes up, or it overwrites existing data. Software tools exist to check and detect fake USB drives,
and in some cases it is possible to repair these devices to remove the false capacity information and use its real storage limit.
File transfer speeds
Transfer speeds are technically determined by the slowest of three factors: the USB version used, the speed in which the USB controller device can read and write data onto the flash memory, and the speed of the
hardware bus, especially in the case of add-on USB ports.
USB flash drives usually specify their read and write speeds in megabytes per second (MB/s); read speed is usually faster. These speeds are for optimal conditions; real-world speeds are usually slower. In particular, circumstances that often lead to speeds much lower than advertised are transfer (particularly writing) of many small files rather than a few very large ones, and mixed reading and writing to the same device.
In a typical well-conducted review of a number of high-performance USB 3.0 drives, a drive that could read large files at 68 MB/s and write at 46 MB/s, could only manage 14 MB/s and 0.3 MB/s with many small files. When combining streaming reads and writes the speed of another drive, the drive could read at 92 MB/s and write at 70 MB/s, was 8 MB/s. These differences differ radically from one drive to another; some could write small files 10% faster than for large ones. The examples given are chosen to illustrate extremes.
Uses
Personal data transport
The most common use of flash drives is to transport and store personal files, such as documents, pictures and videos. Individuals also store medical information on flash drives for emergencies and disaster preparation.
Secure storage of data, application and software files
With wide deployment of flash drives in various environments (secured or otherwise), data and information security remain critical issues.
Biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics and features. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used t ...
and
encryption
In Cryptography law, cryptography, encryption (more specifically, Code, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the inf ...
are becoming the norm as data security needs increase;
on-the-fly encryption systems are particularly useful in this regard, as they can transparently encrypt large amounts of data. In some cases, a
secure USB drive may use a hardware-based encryption mechanism that uses a hardware module instead of software for strongly encrypting data.
IEEE 1667 is an attempt to create a generic authentication platform for USB drives. It is supported in
Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, ...
and Windows Vista (Service Pack 2 with a hotfix).
Computer forensics and law enforcement
A recent development for the use of a USB Flash Drive as an application carrier is to carry the
Computer Online Forensic Evidence Extractor (COFEE) application developed by
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
. COFEE is a set of applications designed to search for and extract
digital evidence
In evidence law, digital evidence or electronic evidence is any probative information stored or transmitted in digital form that a party to a court case may use at trial. Before accepting digital evidence a court will determine if the evid ...
on computers confiscated from suspects. Forensic software is required not to alter in any way the information stored on the computer being examined. Other forensic suites run from
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold b ...
or
DVD-ROM, but cannot store data on the media they are run from (although they can write to other attached devices, such as
external drives or
memory sticks).
Updating motherboard firmware
Motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It ho ...
firmware (including
BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
and
UEFI) can be updated using USB flash drives. Usually, new firmware is downloaded and placed onto a
FAT16- or
FAT32-formatted USB flash drive connected to a system which is to be updated, and the path to the new firmware image is selected within the update component of system's firmware. Some motherboard manufacturers also allow such updates without the need to enter the system's firmware update component, making it possible to easily recover systems with corrupted firmware.
In addition,
HP has introduced a ''USB floppy drive key'', an ordinary USB flash drive with the capacity to emulate floppy drives, allowing it to be used for updating system firmware where direct use of USB flash drives is not supported. The desired mode of operation, regular USB mass storage device or floppy drive emulation, is selected via sliding a switch on the device's housing.
Booting operating systems
Most current PC firmware permits
booting
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via Computer hardware, hardware such as a physical button on the computer or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) h ...
from a USB drive, allowing the launch of an operating system from a
bootable flash drive. Such a configuration is known as a
Live USB.
Original flash memory designs had very limited estimated lifetimes. The failure mechanism for flash memory cells is analogous to a
metal fatigue
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striation (fatigue), striati ...
mode; the device fails by refusing to write new data to specific cells that have been subject to many read-write cycles over the device's lifetime. Premature failure of a "live USB" could be circumvented by using a flash drive with a write-lock switch as a
WORM device, identical to a
live CD. Originally, this potential failure mode limited the use of "live USB" system to special-purpose applications or temporary tasks, such as:
* Loading a minimal, hardened
kernel for embedded applications (e.g., network router, firewall).
* Bootstrapping an operating system install or
disk cloning operation, often across a network.
* Maintenance tasks, such as virus scanning or low-level data repair, without the primary host operating system loaded.
, newer flash memory designs have much higher estimated lifetimes. Several manufacturers are now offering warranties of 5 years or more. Such warranties should make the device more attractive for more applications. By reducing the probability of the device's premature failure, flash memory devices can now be considered for use where a magnetic disk would normally have been required. Flash drives have also experienced an exponential growth in their storage capacity over time (following the
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
growth curve). As of 2013, single-packaged devices with capacities of 1
TB are readily available,
and devices with 16 GB capacity are very economical. Storage capacities in this range have traditionally been considered to offer adequate space, because they allow enough space for both the operating system software and some free space for the user's data.
Operating system installation media
Installers of some operating systems can be stored to a flash drive instead of a CD or DVD, including various
Linux distribution
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is oft ...
s,
Windows 7 and newer versions, and
macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
. In particular,
Mac OS X 10.7 is distributed only online, through the
Mac App Store
The Mac App Store (also known as the App Store) is a digital distribution platform for macOS apps, often referred to as Mac apps, created and maintained by Apple. The platform was announced on October 20, 2010, at Apple's "Back to the Mac" eve ...
, or on flash drives; for a
MacBook Air with
Boot Camp and no external optical drive, a flash drive can be used to run installation of Windows or Linux from USB, a process that can be automated via the use of tools like the
Universal USB Installer or
Rufus.
However, for installation of Windows 7 and later versions, using USB flash drive with hard disk drive emulation as detected in PC's firmware is recommended in order to boot from it. Transcend is the only manufacturer of USB flash drives containing such a feature.
Furthermore, for installation of
Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
, using a USB flash drive with a storage limit of at most 2 GB is recommended in order to boot from it.
Windows ReadyBoost
In
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft W ...
and later versions,
ReadyBoost feature allows flash drives (from 4 GB in case of Windows Vista) to augment operating system memory.
Application carriers
Flash drives are used to carry
applications that run on the host computer
without requiring installation. While any standalone application can in principle be used this way, many programs store data, configuration information, etc. on the hard drive and
registry of the host computer.
The
U3 company works with drive makers (parent company
SanDisk as well as others) to deliver custom versions of applications designed for
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
from a special flash drive; U3-compatible devices are designed to autoload a menu when plugged into a computer running Windows. Applications must be modified for the U3 platform not to leave any data on the host machine. U3 also provides a software framework for
independent software vendors interested in their platform.
Ceedo is an alternative product that does not require Windows applications to be modified in order for them to be carried and run on the drive.
Similarly, other
application virtualization
Application virtualization is a software technology that encapsulates computer programs from the underlying operating system on which they are executed. A fully virtualized application is not installed in the traditional sense, although it is sti ...
solutions and
portable application creators, such as
VMware ThinApp (for Windows) or RUNZ (for Linux) can be used to run software from a flash drive without installation.
In October 2010,
Apple Inc. released their newest iteration of the
MacBook Air, which had the system's restore files contained on a USB hard drive rather than the traditional install CDs, because the Air did not include an optical drive.
A wide range of
portable applications, which are all free of charge, and able to run off a computer running Windows without storing anything on the host computer's drives or registry, can be found in the
list of portable software.
Backup
Some
value-added resellers are now using a flash drive as part of small-business
turnkey solutions (e.g.,
point-of-sale systems). The drive is used as a
backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back ...
medium: at the close of business each night, the drive is inserted, and a
database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
backup is saved to the drive. Alternatively, the drive can be left inserted through the business day, and data regularly updated. In either case, the drive is removed at night and taken offsite.
* This is simple for the end-user, and more likely to be done.
* The drive is small and convenient, and more likely to be carried off-site for safety.
* The drives are less fragile mechanically and magnetically than tapes.
* The capacity is often large enough for several backup images of critical data.
* Flash drives are cheaper than many other backup systems.
Flash drives also have disadvantages. They are easy to lose and facilitate unauthorized backups. A lesser setback for flash drives is that they have only one tenth the capacity of hard drives manufactured around their time of distribution.
Password Reset Disk
Password Reset Disk is a feature of the Windows operating system. If a user sets up a Password Reset Disk, it can be used to reset the password on the computer it was set up on.
Audio players

Many companies make small solid-state
digital audio players, essentially producing flash drives with sound output and a simple user interface. Examples include the
Creative MuVo,
Philips GoGear and the first generation
iPod shuffle. Some of these players are true USB flash drives as well as music players; others do not support general-purpose data storage. Other applications requiring storage, such as
digital voice or sound recording, can also be combined with flash drive functionality.
Many of the smallest players are powered by a permanently fitted rechargeable battery, charged from the USB interface. Fancier devices that function as a digital audio player have a USB host port (type A female typically).
Media storage and marketing

Digital audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital signal (signal processing), digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical sampling (signal processing), ...
files can be transported from one computer to another like any other file, and played on a compatible
media player (with caveats for
DRM-locked files). In addition, many home
Hi-Fi
High fidelity (hi-fi or, rarely, HiFi) is the high-quality reproduction of sound. It is popular with audiophiles and home audio enthusiasts. Ideally, high-fidelity equipment has inaudible noise and distortion, and a flat (neutral, uncolored) ...
and
car stereo head units are now equipped with a USB port. This allows a USB flash drive containing media files in a variety of formats to be played directly on devices which support the format. Some LCD monitors for consumer HDTV viewing have a dedicated USB port through which music and video files can also be played without use of a personal computer.
Artists have sold or given away USB flash drives, with the first instance believed to be in 2004 when the German punk band
Wizo released the ''Stick EP'', only as a USB drive. In addition to five high-
bitrate MP3s, it also included a video, pictures, lyrics, and
guitar tablature. Subsequently, artists including
Nine Inch Nails
Nine Inch Nails, commonly abbreviated as NIN (stylized as NIИ), is an American industrial rock band formed in Cleveland, Ohio in 1988. Its members are the singer-songwriter, multi-instrumentalist and producer Trent Reznor and his frequent col ...
and
Kylie Minogue
Kylie Ann Minogue (; born 28 May 1968) is an Australian singer, songwriter, and actress. Frequently referred to as the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, Princess of Pop", she has achieved recognition in both the music industry and fas ...
have released music and promotional material on USB flash drives. The first USB album to be released in the UK was ''
Kiss Does... Rave'', a
compilation album
A compilation album comprises Album#Tracks, tracks, which may be previously released or unreleased, usually from several separate recordings by either one Performing arts#Performers, performer or by several performers. If the recordings are from ...
released by the
Kiss Network in April 2007.
Brand and product promotion

The availability of inexpensive flash drives has enabled them to be used for
promotional and
marketing
Marketing is the act of acquiring, satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of Business administration, business management and commerce.
Marketing is usually conducted by the seller, typically a retailer or ma ...
purposes, particularly within technical and computer-industry circles (e.g., technology
trade shows). They may be given away for free, sold at less than wholesale price, or included as a bonus with another purchased product.
Usually, such drives will be custom-stamped with a company's
logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name that it represents, as in ...
, as a form of
advertising
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a Product (business), product or Service (economics), service. Advertising aims to present a product or service in terms of utility, advantages, and qualities of int ...
. The drive may be blank, or preloaded with graphics, documentation, web links,
Flash animation
Animation is a filmmaking technique whereby still images are manipulated to create moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animati ...
or other
multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms, such as Text (literary theory), writing, Sound, audio, images, animations, or video, into a single presentation. T ...
, and free or demonstration software. Some preloaded drives are read-only, while others are configured with both read-only and user-writable segments. Such dual-partition drives are more expensive.
Flash drives can be set up to automatically launch stored presentations, websites, articles, and any other software immediately on insertion of the drive using the Microsoft Windows
AutoRun feature.
[USB flash drive auto run setup]
, article from Flashbay.com Autorunning software this way does not work on all computers, and it is normally disabled by security-conscious users.
Arcades
In the
arcade game
An arcade game or coin-op game is a coin-operated entertainment machine typically installed in public businesses such as restaurants, bars and amusement arcades. Most arcade games are presented as primarily game of skill, games of skill and in ...
''
In the Groove'' and more commonly ''
In The Groove 2'', flash drives are used to transfer high scores,
screenshots, dance edits, and combos throughout sessions. As of software revision 21 (R21), players can also store custom songs and play them on any machine on which this feature is enabled. While use of flash drives is common, the drive must be
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
compatible.
In the arcade games ''
Pump it Up NX2'' and ''
Pump it Up NXA'', a specially produced flash drive is used as a "save file" for unlocked songs, as well as for progressing in the WorldMax and Brain Shower sections of the game.
In the arcade game ''
Dance Dance Revolution X'', an exclusive USB flash drive was made by Konami for the purpose of the link feature from its Sony PlayStation 2 counterpart. However, any USB flash drive can be used in this arcade game.
Conveniences
Flash drives use little power, have no fragile moving parts, and for most capacities are small and light. Data stored on flash drives is impervious to mechanical shock, magnetic fields,
scratches and dust. These properties make them suitable for transporting data from place to place and keeping the data readily at hand.
Flash drives also store data densely compared to many removable media. In mid-2009, 256 GB drives became available, with the ability to hold many times more data than a
DVD (54 DVDs) or even a
Blu-ray
Blu-ray (Blu-ray Disc or BD) is a digital optical disc data storage format designed to supersede the DVD format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released worldwide on June 20, 2006, capable of storing several hours of high-defin ...
(10 BDs).
[Baker, Jeff (July 20, 2009) , MobileWhack.com]
Flash drives implement the
USB mass storage device class so that most modern
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s can read and write to them without installing
device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
s. The flash drives present a simple block-structured logical unit to the host operating system, hiding the individual complex implementation details of the various underlying flash memory devices. The operating system can use any
file system or block addressing scheme. Some computers can
boot up from flash drives.
Specially manufactured flash drives are available that have a tough rubber or metal casing designed to be waterproof and virtually "unbreakable". These flash drives retain their memory after being submerged in water, and even through a machine wash. Leaving such a flash drive out to dry completely before allowing current to run through it has been known to result in a working drive with no future problems.
Channel Five's ''
Gadget Show'' cooked one of these flash drives with propane, froze it with
dry ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and Sublimation (phase transition), sublimes directly from the solid state to the gas ...
, submerged it in various acidic liquids, ran over it with a
Jeep
Jeep is an American automobile brand, now owned by multi-national corporation Stellantis. Jeep has been part of Chrysler since 1987, when Chrysler acquired the Jeep brand, along with other assets, from its previous owner, American Motors Co ...
and fired it against a wall with a mortar. A company specializing in recovering lost data from computer drives managed to recover all the data on the drive. All data on the other removable storage devices tested, using optical or magnetic technologies, were destroyed.
Comparison with other portable storage

Tape
The applications of current
data tape cartridges hardly overlap those of flash drives: on tape, cost per gigabyte is very low for large volumes, but the individual drives and media are expensive. Media have a very high capacity and very fast transfer speeds, but store data
sequentially and are very slow for random access of data. While disk-based backup is now the primary medium of choice for most companies, tape backup is still popular for taking data off-site for worst-case scenarios and for very large volumes (more than a few hundreds of TB). See
LTO tapes.
Floppy disk

Floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a ...
drives are rarely fitted to modern computers and are obsolete for normal purposes, although internal and external drives can be fitted if required. Floppy disks may be the method of choice for transferring data to and from very old computers without USB or
booting
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via Computer hardware, hardware such as a physical button on the computer or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) h ...
from floppy disks, and so they are sometimes used to change the firmware on, for example,
BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
chips. Devices with removable storage like older
Yamaha music keyboards are also dependent on floppy disks, which require computers to process them. Newer devices are built with USB flash drive support.
Floppy disk hardware emulators exist which effectively utilize the internal connections and physical attributes of a floppy disk drive to utilize a device where a USB flash drive emulates the storage space of a floppy disk in a solid state form, and can be divided into a number of individual virtual floppy
disk images using individual data channels.
Optical media
The various writable and re-writable forms of
CD and
DVD are portable storage media supported by the vast majority of computers as of 2008. CD-R, DVD-R, and DVD+R can be written to only once, RW varieties up to about 1,000 erase/write cycles, while modern NAND-based flash drives often last for 500,000 or more erase/write cycles.
DVD-RAM discs are the most suitable optical discs for data storage involving much rewriting.
Optical storage devices are among the cheapest methods of mass data storage after the hard drive. They are slower than their flash-based counterparts. Standard 120 mm optical discs are larger than flash drives and more subject to damage. Smaller optical media do exist, such as
business card CD-Rs which have the same dimensions as a credit card, and the slightly less convenient but higher capacity 80 mm recordable
MiniCD and
Mini DVD. The small discs are more expensive than the standard size, and do not work in all drives.
Universal Disk Format (UDF) version 1.50 and above has facilities to support rewritable discs like sparing tables and virtual
allocation tables, spreading usage over the entire surface of a disc and maximising life, but many older operating systems do not support this format. Packet-writing utilities such as DirectCD and
InCD are available but produce discs that are not universally readable (although based on the
UDF standard). The
Mount Rainier
Mount Rainier ( ), also known as Tahoma, is a large active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range of the Pacific Northwest in the United States. The mountain is located in Mount Rainier National Park about south-southeast of Seattle. With an off ...
standard addresses this shortcoming in CD-RW media by running the older file systems on top of it and performing defect management for those standards, but it requires support from both the CD/DVD burner and the
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
. Many drives made today do not support Mount Rainier, and many older operating systems such as Windows XP and below, and Linux kernels older than 2.6.2, do not support it (later versions do). Essentially CDs/DVDs are a good way to record a great deal of information cheaply and have the advantage of being readable by most standalone players, but they are poor at making ongoing small changes to a large collection of information. Flash drives' ability to do this is their major advantage over optical media.
Flash memory cards
 Flash memory card
Flash memory cards, e.g.,
Secure Digital cards, are available in various formats and capacities, and are used by many consumer devices. However, while virtually all PCs have USB ports, allowing the use of USB flash drives, memory card readers are not commonly supplied as standard equipment (particularly with desktop computers). Although inexpensive card readers are available that read many common formats, this results in two pieces of portable equipment (card plus reader) rather than one.
Some manufacturers, aiming at a "best of both worlds" solution, have produced card readers that approach the size and form of USB flash drives (e.g.,
Kingston MobileLite,
SanDisk MobileMate) These readers are limited to a specific subset of memory card formats (such as SD,
microSD, or
Memory Stick), and often completely enclose the card, offering durability and portability approaching, if not quite equal to, that of a flash drive. Although the combined cost of a mini-reader and a memory card is usually slightly higher than a USB flash drive of comparable capacity, the reader + card solution offers additional flexibility of use, and virtually "unlimited" capacity. The ubiquity of
SD cards is such that, circa 2011, due to
economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in ...
, their price is now less than an equivalent-capacity USB flash drive, even with the added cost of a USB SD card reader.
An additional advantage of memory cards is that many consumer devices (e.g.,
digital camera
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in Digital data storage, digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Dig ...
s,
portable music players) cannot make use of USB flash drives (even if the device has a USB port), whereas the memory cards used by the devices can be read by PCs with a card reader.
External hard disk
Particularly with the advent of USB,
external hard disks have become widely available and inexpensive. External hard disk drives currently cost less per gigabyte than flash drives and are available in larger capacities. Some hard drives support alternative and faster interfaces than USB 2.0 (e.g.,
Thunderbolt,
FireWire
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony a ...
and
eSATA). For consecutive sector writes and reads (for example, from an unfragmented file), most hard drives can provide a much higher sustained data rate than current NAND flash memory, though
mechanical latencies seriously impact hard drive performance.
Unlike solid-state memory, hard drives are susceptible to damage by shock (e.g., a short fall) and vibration, have limitations on use at high altitude, and although shielded by their casings, are vulnerable when exposed to strong magnetic fields. In terms of overall mass, hard drives are usually larger and heavier than flash drives; however, hard disks sometimes weigh less per unit of storage. Like flash drives, hard disks also suffer from file
fragmentation, which can reduce access speed.
External solid-state drive
Compared to external
solid-state drives, USB flash drives are usually built using lower-cost and lower-performance
flash memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
, resulting in lower overall performance.
Obsolete devices
Audio tape cassettes and high-capacity floppy disks (e.g.,
Imation SuperDisk), and other forms of drives with removable magnetic media, such as the Iomega
Zip drive and
Jaz drives, are now largely obsolete and rarely used. There are products in today's market that will emulate these legacy drives for both tape and disk (SCSI1/SCSI2, SASI, Magneto optic, Ricoh ZIP, Jaz, IBM3590/ Fujitsu 3490E and Bernoulli for example) in state-of-the-art Compact Flash storage devices – CF2SCSI.
Encryption and security
As highly portable media, USB flash drives are easily lost or stolen. All USB flash drives can have their contents encrypted using third-party disk encryption software, which can often be run directly from the USB drive without installation (for example,
FreeOTFE), although some, such as BitLocker, require the user to have administrative rights on every computer it is run on.
Archiving software can achieve a similar result by creating encrypted
ZIP or
RAR files.
Some manufacturers have produced USB flash drives which use hardware-based encryption as part of the design,
removing the need for third-party encryption software. In limited circumstances these drives have been
shown to have security problems, and are typically more expensive than software-based systems, which are available for free.
A minority of flash drives support
biometric fingerprinting to confirm the user's identity. As of mid-, this was an expensive alternative to standard password protection offered on many new USB flash storage devices. Most fingerprint scanning drives rely upon the host operating system to validate the fingerprint via a software driver, often restricting the drive to
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
computers. However, there are USB drives with fingerprint scanners which use controllers that allow access to protected data without any authentication.
Some manufacturers deploy
physical authentication tokens in the form of a flash drive. These are used to control access to a sensitive system by containing encryption keys or, more commonly, communicating with security software on the target machine. The system is designed so the target machine will not operate except when the flash drive device is plugged into it. Some of these "PC lock" devices also function as normal flash drives when plugged into other machines.
Controversies
Criticisms
Failures
Like all flash memory devices, flash drives can sustain only a limited number of write and erase cycles before the drive fails. This should be a consideration when using a flash drive to run application software or an operating system. To address this, as well as space limitations, some developers have produced special versions of operating systems (such as
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
in
Live USB) or commonplace applications (such as
Mozilla Firefox) designed to run from flash drives. These are typically optimized for size and configured to place temporary or intermediate files in the computer's main RAM rather than store them temporarily on the flash drive.
When used in the same manner as external rotating drives (hard drives, optical drives, or floppy drives), i.e. in ignorance of their technology, USB drives'
failure
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. On ...
is more likely to be sudden: while rotating drives ''can'' fail instantaneously, they more frequently give some indication (noises, slowness) that they are about to fail, often with enough advance warning that data can be removed before total failure. USB drives give little or no advance warning of failure. Furthermore, when internal wear-leveling is applied to prolong life of the flash drive, once failure of even part of the memory occurs it can be difficult or impossible to use the remainder of the drive, which differs from magnetic media, where bad sectors can be marked permanently not to be used.
Most USB flash drives do not include a
write protection mechanism. This feature, which gradually became less common, consists of a switch on the housing of the drive itself, that prevents the host computer from writing or modifying data on the drive. For example, write protection makes a device suitable for repairing
virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
-contaminated host computers without the risk of infecting a USB flash drive itself. In contrast to
SD card
Secure Digital (SD) is a proprietary, non-volatile, flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA). Owing to their compact size, SD cards have been widely adopted in a variety of portable consumer electronics, including dig ...
s, write protection on USB flash drives (when available) is connected to the drive circuitry, and is handled by the drive itself instead of the host (on SD cards handling of the write-protection notch is optional).
A drawback to the small physical size of flash drives is that they are easily misplaced or otherwise lost. This is a particular problem if they contain sensitive data (see
data security
Data security or data protection means protecting digital data, such as those in a database, from destructive forces and from the unwanted actions of unauthorized users, such as a cyberattack or a data breach.
Technologies
Disk encryption
...
). As a consequence, some manufacturers have added encryption hardware to their drives, although
software encryption systems which can be used in conjunction with any
mass storage
In computing, mass storage refers to the storage of large amounts of data in a persisting and machine-readable fashion. In general, the term ''mass'' in ''mass storage'' is used to mean ''large'' in relation to contemporaneous hard disk drive ...
medium will achieve the same result. Most drives can be attached to keychains or lanyards. The USB plug is usually retractable or fitted with a removable protective cap.
Security threats
USB killer
Similar in appearance to a USB flash drive, a USB killer is a circuit which charges its
capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s to a high voltage using the power supply pins of a
USB port, then discharges that voltage through the data pins. This standalone device can instantly and permanently damage or destroy any host hardware that it is connected to.
"Handmade" USB drives
"Handmade" USB drives, containing movies and other related content, have also been reported.
Current and future developments

Semiconductor corporations have worked to reduce the cost of the components in a flash drive by integrating various flash drive functions in a single chip, thereby reducing the part-count and overall package-cost.
Flash drive capacities on the market increase continually. High speed has become a standard for modern flash drives. Capacities exceeding 256 GB were available on the market as early as 2009.
attempted to introduce a ''
USB FlashCard'', which would be a compact USB flash drive intended to replace various kinds of flash memory cards. Pretec introduced a similar card, which also plugs into any USB port, but is just one quarter the thickness of the Lexar model.
Until 2008, SanDisk manufactured a product called SD Plus, which was a
SecureDigital card with a USB connector.
SanDisk introduced a
digital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures, such as access control technologies, can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted works. DRM ...
technology called
FlashCP that they had purchased in 2005 to control the storage and usage of copyrighted materials on flash drives, primarily for use by students.
See also
*
Glossary of computer hardware terms
*
Memristor
A memristor (; a portmanteau of ''memory resistor'') is a non-linear two-terminal electrical component relating electric charge and magnetic flux linkage. It was described and named in 1971 by Leon Chua, completing a theoretical quartet of ...
*
Microdrive
*
Nonvolatile BIOS memory
*
Sneakernet
*
USB dead drop
*
USB Flash Drive Alliance
*
Disk enclosure
A disk enclosure is a specialized casing designed to hold and power hard disk drives or solid state drives while providing a mechanism to allow them to communicate to one or more separate computers.
Drive enclosures provide power to the drives ...
*
External storage
In computing, external storage refers to non-volatile memory, non-volatile (secondary) computer data storage, data storage outside a computer's own internal computer hardware, hardware, and thus can be readily disconnected and accessed elsewhere ...
*
BadUSB
Explanatory notes
References
External links
{{commons and cat
2000 in computing
2000 in technology
Computer-related introductions in 2000
Solid-state computer storage
Flash drive
Office equipment


 A flash drive (also thumb drive, memory stick, and pen drive/pendrive) is a data storage device that includes
A flash drive (also thumb drive, memory stick, and pen drive/pendrive) is a data storage device that includes  There are typically five parts to a flash drive:
* USB plug provides a physical interface to the host computer. Some USB flash drives use USB plug that does not protect the contacts, with the possibility of plugging it into the USB port in the wrong orientation, if the connector type is not symmetrical.
* USB mass storage controller a small
There are typically five parts to a flash drive:
* USB plug provides a physical interface to the host computer. Some USB flash drives use USB plug that does not protect the contacts, with the possibility of plugging it into the USB port in the wrong orientation, if the connector type is not symmetrical.
* USB mass storage controller a small  *
*  Many companies make small solid-state digital audio players, essentially producing flash drives with sound output and a simple user interface. Examples include the Creative MuVo, Philips GoGear and the first generation iPod shuffle. Some of these players are true USB flash drives as well as music players; others do not support general-purpose data storage. Other applications requiring storage, such as digital voice or sound recording, can also be combined with flash drive functionality.
Many of the smallest players are powered by a permanently fitted rechargeable battery, charged from the USB interface. Fancier devices that function as a digital audio player have a USB host port (type A female typically).
Many companies make small solid-state digital audio players, essentially producing flash drives with sound output and a simple user interface. Examples include the Creative MuVo, Philips GoGear and the first generation iPod shuffle. Some of these players are true USB flash drives as well as music players; others do not support general-purpose data storage. Other applications requiring storage, such as digital voice or sound recording, can also be combined with flash drive functionality.
Many of the smallest players are powered by a permanently fitted rechargeable battery, charged from the USB interface. Fancier devices that function as a digital audio player have a USB host port (type A female typically).

 The availability of inexpensive flash drives has enabled them to be used for promotional and
The availability of inexpensive flash drives has enabled them to be used for promotional and 

 Flash memory cards, e.g., Secure Digital cards, are available in various formats and capacities, and are used by many consumer devices. However, while virtually all PCs have USB ports, allowing the use of USB flash drives, memory card readers are not commonly supplied as standard equipment (particularly with desktop computers). Although inexpensive card readers are available that read many common formats, this results in two pieces of portable equipment (card plus reader) rather than one.
Some manufacturers, aiming at a "best of both worlds" solution, have produced card readers that approach the size and form of USB flash drives (e.g., Kingston MobileLite, SanDisk MobileMate) These readers are limited to a specific subset of memory card formats (such as SD, microSD, or Memory Stick), and often completely enclose the card, offering durability and portability approaching, if not quite equal to, that of a flash drive. Although the combined cost of a mini-reader and a memory card is usually slightly higher than a USB flash drive of comparable capacity, the reader + card solution offers additional flexibility of use, and virtually "unlimited" capacity. The ubiquity of SD cards is such that, circa 2011, due to
Flash memory cards, e.g., Secure Digital cards, are available in various formats and capacities, and are used by many consumer devices. However, while virtually all PCs have USB ports, allowing the use of USB flash drives, memory card readers are not commonly supplied as standard equipment (particularly with desktop computers). Although inexpensive card readers are available that read many common formats, this results in two pieces of portable equipment (card plus reader) rather than one.
Some manufacturers, aiming at a "best of both worlds" solution, have produced card readers that approach the size and form of USB flash drives (e.g., Kingston MobileLite, SanDisk MobileMate) These readers are limited to a specific subset of memory card formats (such as SD, microSD, or Memory Stick), and often completely enclose the card, offering durability and portability approaching, if not quite equal to, that of a flash drive. Although the combined cost of a mini-reader and a memory card is usually slightly higher than a USB flash drive of comparable capacity, the reader + card solution offers additional flexibility of use, and virtually "unlimited" capacity. The ubiquity of SD cards is such that, circa 2011, due to  Semiconductor corporations have worked to reduce the cost of the components in a flash drive by integrating various flash drive functions in a single chip, thereby reducing the part-count and overall package-cost.
Flash drive capacities on the market increase continually. High speed has become a standard for modern flash drives. Capacities exceeding 256 GB were available on the market as early as 2009.
Lexar attempted to introduce a '' USB FlashCard'', which would be a compact USB flash drive intended to replace various kinds of flash memory cards. Pretec introduced a similar card, which also plugs into any USB port, but is just one quarter the thickness of the Lexar model. Until 2008, SanDisk manufactured a product called SD Plus, which was a SecureDigital card with a USB connector.
SanDisk introduced a
Semiconductor corporations have worked to reduce the cost of the components in a flash drive by integrating various flash drive functions in a single chip, thereby reducing the part-count and overall package-cost.
Flash drive capacities on the market increase continually. High speed has become a standard for modern flash drives. Capacities exceeding 256 GB were available on the market as early as 2009.
Lexar attempted to introduce a '' USB FlashCard'', which would be a compact USB flash drive intended to replace various kinds of flash memory cards. Pretec introduced a similar card, which also plugs into any USB port, but is just one quarter the thickness of the Lexar model. Until 2008, SanDisk manufactured a product called SD Plus, which was a SecureDigital card with a USB connector.
SanDisk introduced a