|
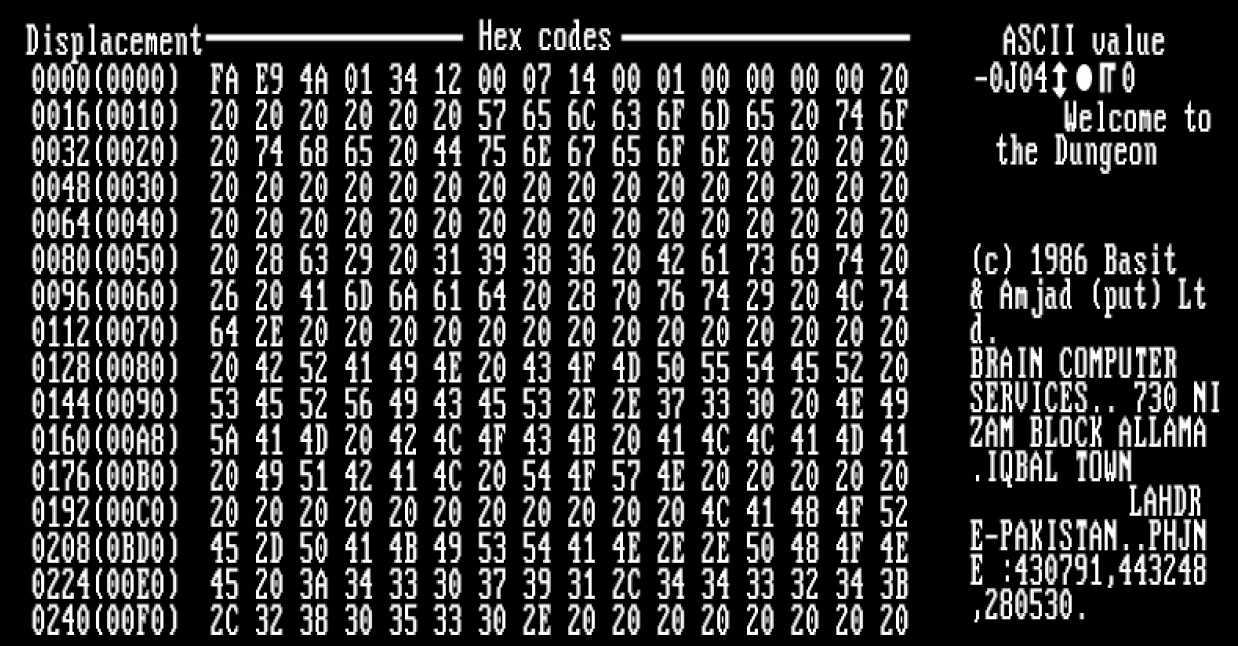
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a type of malware that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and Code injection, inserting its own Computer language, code into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a Computer program, host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. By contrast, a computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the Computer program, host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering (security), social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of vulnerability (computing), security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cybersecurity
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and networks from threats that can lead to unauthorized information disclosure, theft or damage to hardware, software, or data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the services they provide. The significance of the field stems from the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards. Its importance is further amplified by the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most significant new challenges facing the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societies they support. Security is particularly crucial for systems that govern large-scale sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Creeper (program)
Creeper was the first computer worm, while Reaper was the first antivirus software, designed to eliminate Creeper. Creeper Creeper was an experimental computer program written by Bob Thomas at BBN Technologies, BBN in 1971. Its original iteration was designed to move between Digital Equipment Corporation, DEC PDP-10 mainframe computers running the TENEX (operating system), TENEX operating system using the ARPANET, with a later version by Ray Tomlinson designed to copy itself between computers rather than simply move. This self-replicating version of Creeper is generally accepted to be the first computer worm. Creeper was a test created to demonstrate the possibility of a self-replicating computer program that could spread to other computers. The program was not actively Malware, malicious software as it caused no damage to data, the only effect being a message it output to the teletype reading "I'M THE CREEPER : CATCH ME IF YOU CAN" [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Dortmund
TU Dortmund University () is a technical university in Dortmund, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany with over 35,000 students, and over 6,000 staff including 300 professors, offering around 80 Bachelor's and master's degree programs. It is situated in the Ruhr area, the fourth largest urban area in Europe. The university pioneered the Internet in Germany, and contributed to machine learning (in particular, to support-vector machines, and RapidMiner). History The University of Dortmund (German: ''Universität Dortmund'') was founded in 1968, during the decline of the coal and steel industry in the Ruhr region. Its establishment was seen as an important move in the economic change (''Strukturwandel'') from heavy industry to technology. The university's main areas of research are the natural sciences, engineering, pedagogy/teacher training in a wide spectrum of subjects, special education, and journalism. The University of Dortmund was originally designed to be a technical university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diplom
A ''Diplom'' (, from ) is an academic degree in the German-speaking countries Germany, Austria, and Switzerland and a similarly named degree in some other European countries including Albania, Bulgaria, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Estonia, Finland, Poland, Russia, and Ukraine and only for engineers in France, Greece, Hungary, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, and Brazil. History The Diplom originates from the French Diplôme (''Diplôme de l'ordre impérial de la légion d'honneur'') describing a certificate devised during the Second French Empire to bestow honours upon outstanding citizens and soldiers of the imperial French army to promote them into the Legion of Honour since 1862. The Magister degree was the original graduate degree at German-speaking universities. In Germany the Diplom dates back to the pre-republican period: In October 1899 the engineering degree ''Diplom'' was announced by a ''supreme decree'' of the German emperor Wilhelm II in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Assembler (computer Programming)
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an '' assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book ''The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Digit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Self-replication
Self-replication is any behavior of a dynamical system that yields construction of an identical or similar copy of itself. Biological cells, given suitable environments, reproduce by cell division. During cell division, DNA is replicated and can be transmitted to offspring during reproduction. Biological viruses can replicate, but only by commandeering the reproductive machinery of cells through a process of infection. Harmful prion proteins can replicate by converting normal proteins into rogue forms. Computer viruses reproduce using the hardware and software already present on computers. Self-replication in robotics has been an area of research and a subject of interest in science fiction. Any self-replicating mechanism which does not make a perfect copy (mutation) will experience genetic variation and will create variants of itself. These variants will be subject to natural selection, since some will be better at surviving in their current environment than others and will o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Automata
An automaton (; : automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions. Some automata, such as bellstrikers in mechanical clocks, are designed to give the illusion to the casual observer that they are operating under their own power or will, like a mechanical robot. The term has long been commonly associated with automated puppets that resemble moving humans or animals, built to impress and/or to entertain people. Animatronics are a modern type of automata with electronics, often used for the portrayal of characters or creatures in films and in theme park attractions. Etymology The word ' is the latinization of the Ancient Greek (), which means "acting of one's own will". It was first used by Homer to describe an automatic door opening, or automatic movement of wheeled tripods. It is more often used to describe non-electronic moving machines, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC, U of I, Illinois, or University of Illinois) is a public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Champaign–Urbana metropolitan area, Illinois, United States. Established in 1867, it is the founding campus and Flagship#Colleges and universities in the United States, flagship institution of the University of Illinois System. With over 59,000 students, the University of Illinois is one of the List of United States public university campuses by enrollment, largest public universities by enrollment in the United States. The university contains 16 schools and colleges and offers more than 150 undergraduate and over 100 graduate programs of study. The university holds 651 buildings on and its annual operating budget in 2016 was over $2 billion. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign also operates Research Park at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, a research park home to innova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John Von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, integrating Basic research, pure and Applied science#Applied research, applied sciences and making major contributions to many fields, including mathematics, physics, economics, computing, and statistics. He was a pioneer in building the mathematical framework of quantum physics, in the development of functional analysis, and in game theory, introducing or codifying concepts including Cellular automaton, cellular automata, the Von Neumann universal constructor, universal constructor and the Computer, digital computer. His analysis of the structure of self-replication preceded the discovery of the structure of DNA. During World War II, von Neumann worked on the Manhattan Project. He developed the mathematical models behind the explosive lense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Register
''The Register'' (often also called El Reg) is a British Technology journalism, technology news website co-founded in 1994 by Mike Magee (journalist), Mike Magee and John Lettice. The online newspaper's Nameplate_(publishing), masthead Logo, sublogo is "''Biting the hand that feeds IT''." The publication's primary focus is information technology news and opinions. Situation Publishing Ltd is the site's publisher. Drew Cullen is an owner and Linus Birtles is the managing director. Andrew Orlowski was the executive editor before leaving the website in May 2019. History ''The Register'' was founded in London as an email newsletter called ''Chip Connection''. In 1998 ''The Register'' became a daily online news source. Magee left in 2001 to start competing publications ''The Inquirer'', and later the ''IT Examiner'' and ''TechEye''. In 2002, ''The Register'' expanded to have a presence in London and San Francisco, creating ''The Register USA'' at theregus.com through a joint ventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |