Treaty of Saint Germain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (french: Traité de Saint-Germain-en-Laye) was signed on 10 September 1919 by the victorious
 The treaty declared that the Austro-Hungarian Empire was to be dissolved. According to article 177 Austria, along with the other
The treaty declared that the Austro-Hungarian Empire was to be dissolved. According to article 177 Austria, along with the other
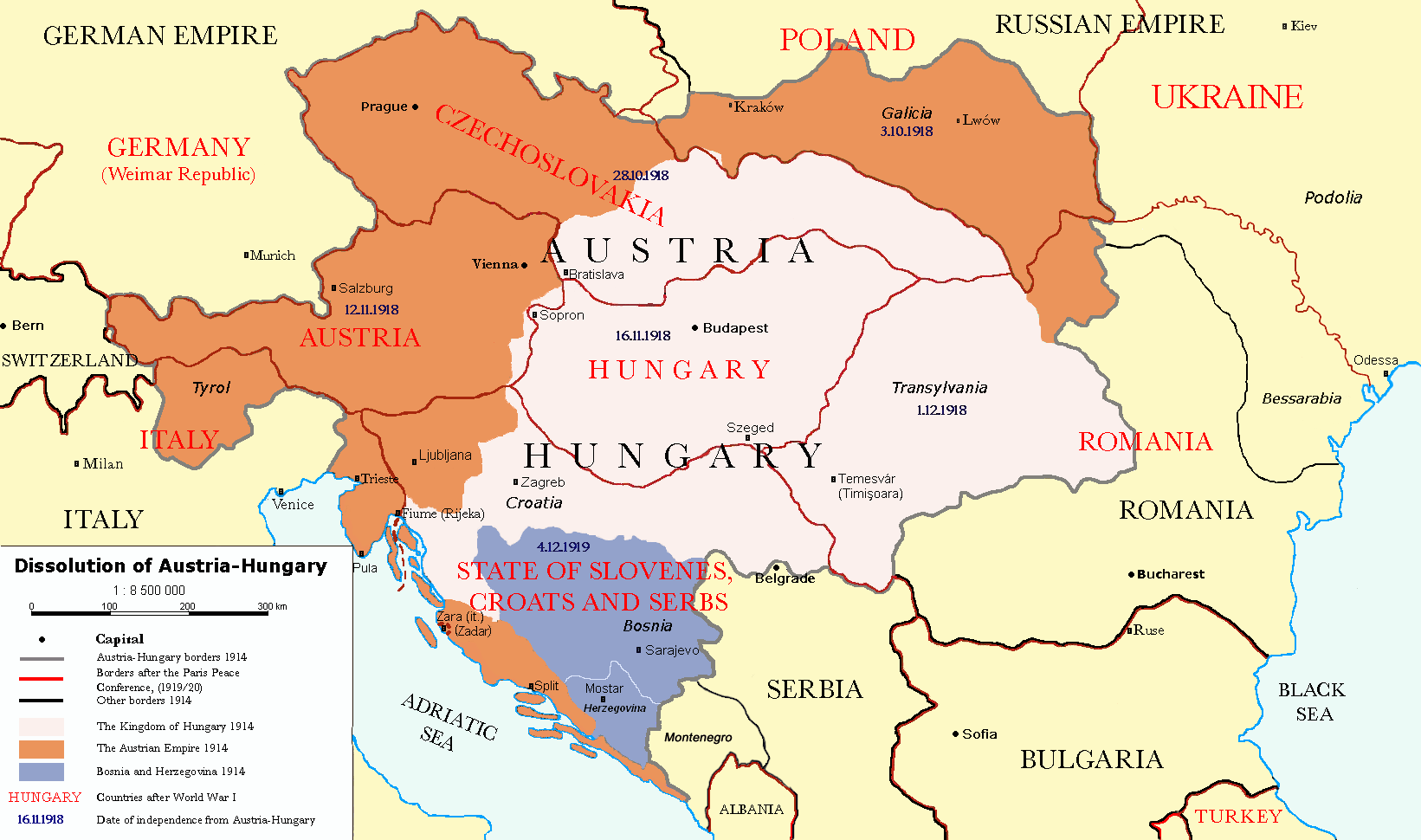 *The Lands of the Bohemian Crown, i.e. the
*The Lands of the Bohemian Crown, i.e. the
Animated map of Europe at the end of the First World War
from the website of the
A full text of the treaty, with signatories
{{Authority control Aftermath of World War I in Austria Partition (politics) Peace treaties of Austria Treaties of the Republic of German-Austria World War I treaties Treaties concluded in 1919 History of Austria-Hungary Treaties of the United Kingdom (1801–1922) Treaties of the French Third Republic Treaties of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946) Treaties of the United States Treaties of the Empire of Japan Treaties of Belgium Treaties of the Republic of China (1912–1949) Treaties of Cuba Treaties of Czechoslovakia Treaties of the Kingdom of Greece Treaties of Nicaragua Treaties of Panama Treaties of the Second Polish Republic Treaties of the Portuguese First Republic Treaties of the Kingdom of Romania Great Union (Romania) Treaties of Thailand Treaties of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia Greater Romania Territorial evolution of Romania Dissolution of Austria-Hungary September 1919 events 1919 in France Austria–Czechoslovakia relations
Allies of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoma ...
on the one hand and by the Republic of German-Austria on the other. Like the Treaty of Trianon with Hungary and the Treaty of Versailles with Germany, it contained the Covenant
Covenant may refer to:
Religion
* Covenant (religion), a formal alliance or agreement made by God with a religious community or with humanity in general
** Covenant (biblical), in the Hebrew Bible
** Covenant in Mormonism, a sacred agreement ...
of the League of Nations and as a result was not ratified by the United States but was followed by the US–Austrian Peace Treaty of 1921.
The treaty signing ceremony took place at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a former royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the ''département'' of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the ''musée d'Archéologie nationale'' (Natio ...
.
Background
As a preamble, on 21 October 1918, 208 German-speaking delegates of the Austrian Imperial Council had convened in a "provisional national assembly of German-Austria" at the Lower Austrian Landtag. When the collapse of theAustro-Hungarian Army
The Austro-Hungarian Army (, literally "Ground Forces of the Austro-Hungarians"; , literally "Imperial and Royal Army") was the ground force of the Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy from 1867 to 1918. It was composed of three parts: the joint arm ...
culminated at the Battle of Vittorio Veneto
The Battle of Vittorio Veneto was fought from 24 October to 3 November 1918 (with an armistice taking effect 24 hours later) near Vittorio Veneto on the Italian Front during World War I. After having thoroughly defeated Austro-Hungarian troop ...
, the Social Democrat Karl Renner was elected German-Austrian State Chancellor on 30 October. In the course of the Aster Revolution
The Aster Revolution or Chrysanthemum Revolution ( hu, Őszirózsás forradalom) was a revolution in Hungary led by Count Mihály Károlyi in the aftermath of World War I which resulted in the foundation of the short-lived First Hungarian Peopl ...
on 31 October, the newly established Hungarian People's Republic under Minister President Mihály Károlyi declared the real union with Austria terminated.
With the Armistice of Villa Giusti
The Armistice of Villa Giusti or Padua ended warfare between Italy and Austria-Hungary on the Italian Front during World War I. The armistice was signed on 3 November 1918 in the Villa Giusti, outside Padua in the Veneto, Northern Italy, and ...
on 3 November 1918, the fate of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
was sealed. On 11 November 1918 Emperor Charles I of Austria
Charles I or Karl I (german: Karl Franz Josef Ludwig Hubert Georg Otto Maria, hu, Károly Ferenc József Lajos Hubert György Ottó Mária; 17 August 18871 April 1922) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary (as Charles IV, ), King of Croatia, ...
officially declared to "relinquish every participation in the administration", one day later the provisional assembly declared German-Austria a democratic republic and part of the German Republic. However, on the territory of the Cisleithania
Cisleithania, also ''Zisleithanien'' sl, Cislajtanija hu, Ciszlajtánia cs, Předlitavsko sk, Predlitavsko pl, Przedlitawia sh-Cyrl-Latn, Цислајтанија, Cislajtanija ro, Cisleithania uk, Цислейтанія, Tsysleitaniia it, Cislei ...
n ("Austrian") half of the former empire, the newly established states of Czechoslovakia, Poland, and the Yugoslav Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (the "successor states") had been proclaimed. Moreover, South Tyrol and Trentino were occupied by Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional It ...
forces and Yugoslav troops entered the former Duchy of Carinthia, leading to violent fights.
An Austrian Constitutional Assembly election was held on 16 February 1919. The Assembly re-elected Karl Renner state chancellor and enacted the Habsburg Law
The Habsburg Law (''Habsburgergesetz'' (in full, the Law concerning the Expulsion and the Takeover of the Assets of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine) ''Gesetz vom 3. April 1919 betreffend die Landesverweisung und die Übernahme des Vermögens des H ...
concerning the banishment of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine. When Chancellor Renner arrived at Saint-Germain in May 1919, he and the Austrian delegation found themselves excluded from the negotiations led by French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau. Upon an Allied ultimatum, Renner signed the treaty on 10 September. The Treaty of Trianon in June 1920 between Hungary and the Allies completed the disposition of the former Dual Monarchy.
Provisions
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
, accepted responsibility for starting the war. The new Republic of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine States of Austria, states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, th ...
, consisting of most of the German-speaking Danubian and Alpine provinces in former Cisleithania
Cisleithania, also ''Zisleithanien'' sl, Cislajtanija hu, Ciszlajtánia cs, Předlitavsko sk, Predlitavsko pl, Przedlitawia sh-Cyrl-Latn, Цислајтанија, Cislajtanija ro, Cisleithania uk, Цислейтанія, Tsysleitaniia it, Cislei ...
, recognized the independence of Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Poland, and the Kingdom of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. The treaty included 'war reparations' of large sums of money, directed towards the Allies (however the exact amount has never been defined and collected from Austria), as well as provisions for the liquidation of the Austro-Hungarian Bank
The Austro-Hungarian Bank (german: Oesterreichisch-ungarische Bank, hu, Osztrák–Magyar Bank, cs, Rakousko-uherská banka, pl, Bank Austriacko-Węgierski, hr, Austro-Ugarska banka) was the central bank of the Habsburg Monarchy in the 19th a ...
.
Territory
Cisleithanian Austria had to face significant territorial losses, amounting to over 60 percent of the prewar Austrian Empire's territory: *The Lands of the Bohemian Crown, i.e. the
*The Lands of the Bohemian Crown, i.e. the Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohe ...
and Moravia crownlands (including small adjacent Lower Austria
Lower Austria (german: Niederösterreich; Austro-Bavarian: ''Niedaöstareich'', ''Niedaestareich'') is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Since 1986, the capital of Lower Austria has been Sankt P� ...
n territories around Feldsberg
Valtice (; german: Feldsberg) is a town in Břeclav District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 3,600 inhabitants. It is known as part of Lednice–Valtice Cultural Landscape, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The town ce ...
and Gmünd) formed the core of the newly created state of Czechoslovakia. The Austrian Silesia
Austrian Silesia, (historically also ''Oesterreichisch-Schlesien, Oesterreichisch Schlesien, österreichisch Schlesien''); cs, Rakouské Slezsko; pl, Śląsk Austriacki officially the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia, (historically ''Herzogth ...
province which was the subject of the Polish–Czechoslovak War
The Poland–Czechoslovakia War, also known mostly in Czech sources as the Seven-day war ( cs, Sedmidenní válka) was a military confrontation between Czechoslovakia and Poland over the territory of Cieszyn Silesia in early 1919.
After a vai ...
of January 1919, was split between Czech Silesia
Czech Silesia (, also , ; cs, České Slezsko; szl, Czeski Ślōnsk; sli, Tschechisch-Schläsing; german: Tschechisch-Schlesien; pl, Śląsk Czeski) is the part of the historical region of Silesia now in the Czech Republic. Czech Silesia is ...
and Polish Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( pl, Śląsk Cieszyński ; cs, Těšínské Slezsko or ; german: Teschener Schlesien or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český Tě ...
, and incorporated into the Silesian Voivodeship. These cessions concerned a large German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
-speaking population in German Bohemia
The Province of German Bohemia (german: Provinz Deutschböhmen ; cs, Německé Čechy) was a province in Bohemia, now the Czech Republic, established for a short period of time after the First World War, as part of the Republic of German-Austria. ...
and Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and sk, Sudety) is the historical German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the b ...
.
*The former Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria
The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria,, ; pl, Królestwo Galicji i Lodomerii, ; uk, Королівство Галичини та Володимирії, Korolivstvo Halychyny ta Volodymyrii; la, Rēgnum Galiciae et Lodomeriae also known as ...
, made up of the territory the Habsburg monarchy had annexed in the 1772 First Partition of Poland, fell back to the re-established Polish Republic.
*The adjacent Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
in the east passed to the Kingdom of Romania.
*The southern half of the former Tyrolean crownland up to the Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass (german: link=no, Brennerpass , shortly ; it, Passo del Brennero ) is a mountain pass through the Alps which forms the border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Eastern Alpine range and has ...
, including predominantly Southern Bavarian-speaking South Tyrol and the present-day Trentino province, together with the Carinthian Canal Valley around Tarvisio fell to Italy, as well as the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. I ...
(Gorizia and Gradisca
The Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca (german: Gefürstete Grafschaft Görz und Gradisca; it, Principesca Contea di Gorizia e Gradisca; sl, Poknežena grofija Goriška in Gradiščanska), historically sometimes shortened to and spelled " ...
, the Imperial Free City of Trieste
The Imperial Free City of Trieste and its Territory (german: Reichsunmittelbare Stadt Triest und ihr Gebiet, it, Città Imperiale di Trieste e Dintorni) was a possession of the Habsburg monarchy in the Holy Roman Empire from the 14th century to 18 ...
, and Istria as recognized by the Treaty of Rapallo in 1920).
*The main part of the former Kingdom of Dalmatia, the Duchy of Carniola and Lower Styria with the Carinthian Mieß (Meža
The Meža ( Slovene) or Mieß (German; ) is a river in the Austrian state of Carinthia and in Slovenia, a right tributary of the Drava. It is long, of which are in Slovenia. Its catchment area is , of which in Slovenia.
Name
The Meža River was ...
) Valley and Gemeinde Seeland ( Jezersko) was ceded to the Yugoslav Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, contrary to what was stipulated by the 1915 London Pact. Also Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
was given to it. The affiliation of the Southern Carinthian territory with its Slovene-speaking share of population was to be decided in a Carinthian Plebiscite
The Carinthian plebiscite (german: Kärntner Volksabstimmung, sl, Koroški plebiscit) was held on 10 October 1920 in the area in southern Carinthia predominantly settled by Carinthian Slovenes. It determined the final border between the Republi ...
.
*Austria-Hungary's only overseas possession, its concession in Tianjin, was turned over to China.
*The predominantly German- and Croatian-speaking western parts of the Hungarian counties of Moson
Moson (German: Wieselburg, Slovak: Mošon) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary, situated mostly on the right (south) side of the Danube river. Its territory is now divided between Austria and Hungary, except a s ...
, Sopron
Sopron (; german: Ödenburg, ; sl, Šopron) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fertő.
History
Ancient times-13th century
When the area that is today Western Hungary was a province of the Roman Empire, a ...
and Vas were awarded to Austria. The Uprising in West Hungary led to a plebiscite which resulted in the transition of Sopron and its surrounding 8 villages back to Hungary. Subsequently, other villages were returned or exchanged between Austria and Hungary up to 1923. In the end, the territories finally gained from Hungary were organised as a state of Austria named Burgenland
Burgenland (; hu, Őrvidék; hr, Gradišće; Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland;'' Slovene: ''Gradiščanska'') is the easternmost and least populous state of Austria. It consists of two statutory cities and seven rural districts, with a total of ...
.
The Allies had explicitly committed themselves to the cause of the minority peoples of Austria-Hungary late in the war. Indeed, U. S. Secretary of State Robert Lansing
Robert Lansing (; October 17, 1864 – October 30, 1928) was an American lawyer and diplomat who served as Counselor to the State Department at the outbreak of World War I, and then as United States Secretary of State under President Woodrow Wi ...
had effectively ended what slim chance existed for Austria-Hungary to survive the war when he told Vienna that since the Allies were now committed to the Czechs, Slovaks and South Slavs, autonomy for the nationalities–the tenth of the Fourteen Points–was no longer enough. Reflecting this, the Allies not only allowed the minority peoples to help create new states (Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia), recreate former states (Poland), or join their ethnic brethren in existing nation-states (Romania, Italy), but allowed the successor states to absorb significant blocks of German-inhabited territory. In addition the negotiators on the Allied side, particularly Wilson, did not understand when speaking of self-determination that no convenient line could be drawn to separate intermingled nationalities, and that in further cases, irredentists
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent sta ...
would claim that some German or Hungarian-inhabited territories had actually been theirs. This was as well rendered by the fact that in just a few cases were plebiscites allowed regarding the disputed territories to ascertain the wishes of the local populaces.
Politics and military
Article 88 of the treaty required Austria to refrain from directly or indirectly compromising its independence, which meant that Austria could not enter into political or economic union with theGerman Reich
German ''Reich'' (lit. German Realm, German Empire, from german: Deutsches Reich, ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty ...
without the agreement of the council of the League of Nations. Accordingly, the new republic's initial self-chosen name of German-Austria (german: Deutschösterreich) had to be changed to Austria. Many Austrians would come to find this term harsh (especially among the Austrian Germans being a vast majority who would support a single German nation state), due to Austria's later economic weakness, which was caused by loss of land. Because of all these reasons, Austria would later lead to support for the idea of ''Anschluss
The (, or , ), also known as the (, en, Annexation of Austria), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the Nazi Germany, German Reich on 13 March 1938.
The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a "Ger ...
'' (political union) with Nazi Germany.
Conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
was abolished and the Austrian Army
The Austrian Armed Forces (german: Bundesheer, lit=Federal Army) are the combined military forces of the Republic of Austria.
The military consists of 22,050 active-duty personnel and 125,600 reservists. The military budget is 0.74% of nat ...
was limited to a force of 30,000 volunteers. There were numerous provisions dealing with Danubian
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
navigation, the transfer of railways, and other details involved in the breakup of a great empire into several small independent states.
The vast reduction of population, territory and resources of the new Austria relative to the old empire wreaked havoc on the economy of the old nation, most notably in Vienna, an imperial capital now without an empire to support it. For a time, the country's very unity was called into question.
See also
*Aftermath of World War I
The aftermath of World War I saw drastic political, cultural, economic, and social change across Eurasia, Africa, and even in areas outside those that were directly involved. Four empires collapsed due to the war, old countries were abolished, ne ...
* Minority Treaties
* Paris Peace Conference, 1919
* Treaty of Trianon
* US–Austrian Peace Treaty (1921)
Notes
External links
Animated map of Europe at the end of the First World War
from the website of the
Australasian Legal Information Institute
The Australasian Legal Information Institute (AustLII) is an institution operated jointly by the Faculties of Law of the University of Technology Sydney and the University of New South Wales. Its public policy purpose is to improve access to just ...
, hosted by UNSW
The University of New South Wales (UNSW), also known as UNSW Sydney, is a public research university based in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It is one of the founding members of Group of Eight, a coalition of Australian research-intensive ...
and UTS
A full text of the treaty, with signatories
{{Authority control Aftermath of World War I in Austria Partition (politics) Peace treaties of Austria Treaties of the Republic of German-Austria World War I treaties Treaties concluded in 1919 History of Austria-Hungary Treaties of the United Kingdom (1801–1922) Treaties of the French Third Republic Treaties of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946) Treaties of the United States Treaties of the Empire of Japan Treaties of Belgium Treaties of the Republic of China (1912–1949) Treaties of Cuba Treaties of Czechoslovakia Treaties of the Kingdom of Greece Treaties of Nicaragua Treaties of Panama Treaties of the Second Polish Republic Treaties of the Portuguese First Republic Treaties of the Kingdom of Romania Great Union (Romania) Treaties of Thailand Treaties of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia Greater Romania Territorial evolution of Romania Dissolution of Austria-Hungary September 1919 events 1919 in France Austria–Czechoslovakia relations