The Creation of Adam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''The Creation of Adam'' () is a
 In 1505, Michelangelo was invited back to Rome by the newly elected
In 1505, Michelangelo was invited back to Rome by the newly elected
on Mental Health & Illness.com. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
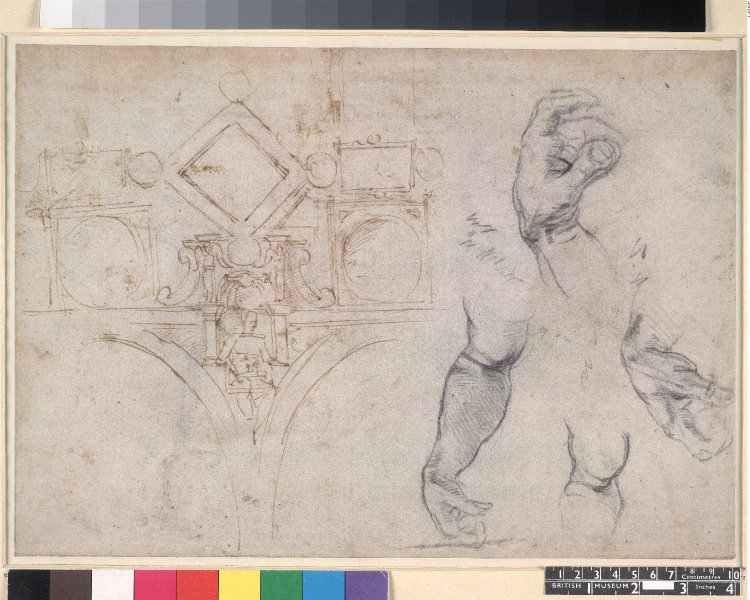
Studies of a Reclining Male Nude: Adam in the Fresco "The Creation of Man."
' It was created in 1511 in dark red chalk, over a stylus under drawing. Red chalk was Michelangelo's preferred medium at this period of time, as it could be shaved to a finer point than black chalk. Michelangelo used this fine point to create a scintillating skin surface, that was unique for this particular sketch, and is not seen in his later works. The recto drawing is 193 millimeters in height and 259 millimeters in width.
 In a well known study in red chalk in the British Museum, Adam is resting on earth, propped up by his forearm, with his thighs spread out and his torso slightly twisted to the side. Michelangelo employed a male model to capture this pose and used his red chalk to develop thick contours, in order to establish a definitive form, so every
In a well known study in red chalk in the British Museum, Adam is resting on earth, propped up by his forearm, with his thighs spread out and his torso slightly twisted to the side. Michelangelo employed a male model to capture this pose and used his red chalk to develop thick contours, in order to establish a definitive form, so every
Models of wax and clay used by Michelangelo in making his sculpture and paintings
{{DEFAULTSORT:Creation Of Adam 1512 paintings Paintings depicting Adam and Eve Paintings of gods Sistine Chapel ceiling Nude art
fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plast ...
painting by Italian artist Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was ins ...
, which forms part of the Sistine Chapel's ceiling, painted c. 1508–1512. It illustrates the Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of ...
creation narrative from the Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
in which God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
gives life to Adam
Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as " ...
, the first man
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromo ...
. The fresco is part of a complex iconographic scheme and is chronologically the fourth in the series of panels depicting episodes from Genesis.
The painting has been reproduced in countless imitations and parodies. Michelangelo's ''Creation of Adam'' is one of the most replicated religious paintings of all time.
History
 In 1505, Michelangelo was invited back to Rome by the newly elected
In 1505, Michelangelo was invited back to Rome by the newly elected Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or t ...
. He was commissioned to build the Pope's tomb, which was to include forty statues and be finished in five years.
Under the patronage of the Pope, Michelangelo experienced constant interruptions to his work on the tomb in order to accomplish numerous other tasks. Although Michelangelo worked on the tomb for 40 years, it was never finished to his satisfaction.Goldscheider, pp. 14–16. It is located in the Church of S. Pietro in Vincoli in Rome and is most famous for his central figure of ''Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu ( Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pr ...
'', completed in 1516. Of the other statues intended for the tomb, two known as the '' Rebellious Slave'' and the ''Dying Slave
The ''Dying Slave'' is a sculpture by the Italian Renaissance artist Michelangelo. Created between 1513 and 1516, it was to serve with another figure, the '' Rebellious Slave'', at the tomb of Pope Julius II. It is a marble figure 2.15 metres (7' ...
'', are now in the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
.
During the same period, Michelangelo painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, which took approximately four years to complete (1508–1512).Bartz and König, p. 134. According to Condivi's account, Bramante
Donato Bramante ( , , ; 1444 – 11 April 1514), born as Donato di Pascuccio d'Antonio and also known as Bramante Lazzari, was an Italian architect and painter. He introduced Renaissance architecture to Milan and the High Renaissance st ...
, who was working on the building of St Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter in the Vatican ( it, Basilica Papale di San Pietro in Vaticano), or simply Saint Peter's Basilica ( la, Basilica Sancti Petri), is a Church (building), church built in the Renaissance architecture, Renaissanc ...
, resented Michelangelo's commission for the Pope's tomb and convinced the Pope to commission him in a medium with which he was unfamiliar, in order that he might fail at the task.
Michelangelo was originally commissioned to paint the Twelve Apostles
In Christian theology and ecclesiology, the apostles, particularly the Twelve Apostles (also known as the Twelve Disciples or simply the Twelve), were the primary disciples of Jesus according to the New Testament. During the life and minist ...
on the triangular pendentives that supported the ceiling, and cover the central part of the ceiling with ornament.Goldscheider, pp. 12–14. Michelangelo persuaded Pope Julius to give him a free hand and proposed a different and more complex scheme, representing the Creation
Creation may refer to:
Religion
*''Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing
*Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it
*Creationism, the belief that ...
, the Fall of Man
The fall of man, the fall of Adam, or simply the Fall, is a term used in Christianity to describe the transition of the first man and woman from a state of innocent obedience to God to a state of guilty disobedience.
*
*
*
* The doctrine of the ...
, the Promise of Salvation through the prophets, and the genealogy of Christ. The work is part of a larger scheme of decoration within the chapel which represents much of the doctrine of the Catholic Church.
The composition stretches over 500 square metres of ceiling, and contains over 300 figures. At its centre are nine episodes from the Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
, divided into three groups: God's Creation of the Earth; God's Creation of Humankind and their fall from God's grace; and lastly, the state of Humanity as represented by Noah
Noah ''Nukh''; am, ኖህ, ''Noḥ''; ar, نُوح '; grc, Νῶε ''Nôe'' () is the tenth and last of the pre-Flood patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5� ...
and his family. On the pendentives supporting the ceiling are painted twelve men and women who prophesied the coming of Jesus; seven prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
s of Israel and five Sibyl
The sibyls (, singular ) were prophetesses or oracles in Ancient Greece.
The sibyls prophesied at holy sites.
A sibyl at Delphi has been dated to as early as the eleventh century BC by PausaniasPausanias 10.12.1 when he described local trad ...
s, prophetic women of the Classical world. Among the most famous paintings on the ceiling are ''The Creation of Adam'', ''Adam and Eve
Adam and Eve, according to the creation myth of the Abrahamic religions, were the first man and woman. They are central to the belief that humanity is in essence a single family, with everyone descended from a single pair of original ancestors. ...
in the Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan- Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the biblical paradise described in Genesis 2-3 and Ezekiel 28 ...
'', the ''Deluge'', the ''Prophet Jeremiah
Jeremiah, Modern: , Tiberian: ; el, Ἰερεμίας, Ieremíās; meaning "Yah shall raise" (c. 650 – c. 570 BC), also called Jeremias or the "weeping prophet", was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewis ...
'' and the ''Cumaean Sibyl
The Cumaean Sibyl was the priestess presiding over the Apollonian oracle at Cumae, a Greek colony located near Naples, Italy. The word ''sibyl'' comes (via Latin) from the ancient Greek word ''sibylla'', meaning prophetess. There were many siby ...
''.
Composition
God is depicted as an elderly white-bearded man, wrapped in a swirling cloak while Adam, on the lower left, is completelynaked
Nudity is the state of being in which a human is without clothing.
The loss of body hair was one of the physical characteristics that marked the biological evolution of modern humans from their hominin ancestors. Adaptations related to h ...
. God's right arm is outstretched to impart the spark of life from his own finger into that of Adam, whose left arm is extended in a pose mirroring God's, a reminder that man is created in the image and likeness of God ().
Many hypotheses have been formulated regarding the identity and meaning of the twelve figures around God. According to an interpretation that was first proposed by the English art critic Walter Pater
Walter Horatio Pater (4 August 1839 – 30 July 1894) was an English essayist, art critic and literary critic, and fiction writer, regarded as one of the great stylists. His first and most often reprinted book, ''Studies in the History of the Re ...
(1839–1894) and is now widely accepted, the person protected by God's left arm represents Eve, due to the figure's feminine appearance and gaze towards Adam, and the eleven other figures symbolically represent the souls of Adam and Eve's unborn progeny, the entire human race. This interpretation has been challenged, mainly on the grounds that the Catholic Church regards the teaching of the pre-existence
Pre-existence, preexistence, beforelife, or premortal existence, is the belief that each individual human soul existed before mortal conception, and at some point before birth enters or is placed into the body. Concepts of pre-existence can enc ...
of souls as heretical. Consequently, the figure behind God has also been suggested to be the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
, Sophia (the personification of wisdom mentioned in the Book of Wisdom
The Book of Wisdom, or the Wisdom of Solomon, is a Jewish work written in Greek and most likely composed in Alexandria, Egypt. Generally dated to the mid-first century BCE, the central theme of the work is "wisdom" itself, appearing under two ...
), the personified human soul, or "an angel of masculine build".
''The Creation of Adam'' is generally thought to depict the excerpt "God created man in His own image, in the image of God He created him" (). The inspiration for Michelangelo's treatment of the subject may come from a medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn ...
, "Veni Creator Spiritus
"Veni Creator Spiritus" (Come, Creator Spirit) is a traditional Christian hymn believed to have been written by Rabanus Maurus, a ninth-century German monk, teacher, and archbishop. When the original Latin text is used, it is normally sung in ...
", which asks the 'finger of the paternal right hand' (''digitus paternae dexterae'') to give the faithful speech.
Sources
Michelangelo's main source of inspiration for his Adam in his ''Creation of Adam'' may have been a cameo showing a nudeAugustus Caesar
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
riding sidesaddle on a Capricorn. This cameo is now at Alnwick Castle
Alnwick Castle () is a castle and country house in Alnwick in the English county of Northumberland. It is the seat of the 12th Duke of Northumberland, built following the Norman conquest and renovated and remodelled a number of times. It is a G ...
, Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land ...
. The cameo used to belong to cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**'' Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**'' Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, t ...
Domenico Grimani who lived in Rome while Michelangelo painted the ceiling. Evidence suggests that Michelangelo and Grimani were friends. This cameo offers an alternative theory for those scholars who have been dissatisfied with the theory that Michelangelo was mainly inspired by Lorenzo Ghiberti
Lorenzo Ghiberti (, , ; 1378 – 1 December 1455), born Lorenzo di Bartolo, was an Italian Renaissance sculptor from Florence, a key figure in the Early Renaissance, best known as the creator of two sets of bronze doors of the Florence Baptistery ...
's Adam in his ''Creation of Adam''.
Analysis
Several hypotheses have been put forward about the meaning of ''The Creation of Adams highly original composition, many of them taking Michelangelo's well-documented expertise in human anatomy as their starting point.Portrayal of the human brain
In 1990 inAnderson, Indiana
Anderson, named after Chief William Anderson, is a city in and the county seat of Madison County, Indiana, United States. It is the principal city of the Anderson, Indiana Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses Madison County. Anderson ...
, physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
Frank Meshberger noted in the ''Journal of the American Medical Association
''The Journal of the American Medical Association'' (''JAMA'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 48 times a year by the American Medical Association. It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering all aspects of b ...
'' that the background figures and shapes portrayed behind the figure of God appeared to be an anatomically accurate picture of the human brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of ...
.Pdfon Mental Health & Illness.com. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
sulci
Sulci or Sulki (in Greek , Steph. B., Ptol.; , Strabo; , Paus.), was one of the most considerable cities of ancient Sardinia, situated in the southwest corner of the island, on a small island, now called Isola di Sant'Antioco, which is, how ...
of the cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. ...
in the inner and outer surface of the brain, the brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
, the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
, the basilar artery, the pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The h ...
and the optic chiasm
In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma (; , ), is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrat ...
.
Portrayal of the birth process
Alternatively, it has been observed that the red cloth around God has the shape of a humanuterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
(one art historian has called it a "uterine mantle") and that the scarf hanging out, coloured green, could be a newly cut umbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologi ...
. In 2015 a group of Italian researchers published on '' Mayo Clinic Proceedings'' an article where the images of the mantle and the postpartum uterus were overlapped. According to Enrico Bruschini (2004), "This is an interesting hypothesis that presents the Creation scene as an idealised representation of the physical birth of man ("The Creation"). It explains the navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus, commonly known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. All placental mammals have a navel, altho ...
that appears on Adam
Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as " ...
, which is at first perplexing because he was created, not born of a woman."
Portrayal of Eve's Rib
Additionally, Deivis Campos notes in '' Clinical Anatomy Journal'' that the left side ofAdam
Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as " ...
’s torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a hu ...
contains an extra concealed rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
. Due to Michelangelo’s in-depth knowledge of human anatomy, he insinuates that this rib outline is intentional, and represents the rib of Eve.
Campos suggests that this extra rib inclusion was a way for Michelangelo to represent Adam and Eve being created side by side, which differs from the Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
tradition that states Eve was created after Adam. There is significant evidence that Michelangelo radically disagreed with many Catholic traditions and had a tumultuous relationship with the commissioner of the ceiling, Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or t ...
. Thus, Campos suggests that the rib inclusion was an intentional way to slight Pope Julius II and the Catholic Church, without having to admit fault, as very few people knew anything about human anatomy at the time and could challenge the piece.
Critical sketches

Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was ins ...
was a prolific draftsman
A drafter (also draughtsman / draughtswoman in British and Commonwealth English, draftsman / draftswoman or drafting technician in American and Canadian English) is an engineering technician who makes detailed technical drawings or plans for ...
, as he was trained in a Florentine workshop at a dynamic time in the art scene, when paper had become readily available in sufficient quantity. As follows, sketching was the first step in Michelangelo's artistic process, as it helped him plan his final paintings and sculptural pieces. Thus, Michelangelo's sketches provide a critical link between his creative vision and final compositions. This is especially evident through his sheets "filled with multiple figures and close studies of human anatomy."
Preliminary studies
Michelangelo completed two sketches in Rome in preparation for the ''Creation of Adam'' scene. They are both in theBritish Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
in London, revealing Michelangelo's in depth planning process for the Sistine Chapel ceiling composition, and his serious attention to perspective and shadowing.
The first is a ''Scheme for the Decoration of the Vault of the Sistine Chapel: Studies of Arms and Hands''. The right side of the page was sketched in 1508 with black chalk, and is a study of Adam's limp hand, before it is ignited with the gift of life from God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
, in the Creation of Adam scene. Michelangelo sketched this over a previous brown, lead point stylus
A stylus (plural styli or styluses) is a writing utensil or a small tool for some other form of marking or shaping, for example, in pottery. It can also be a computer accessory that is used to assist in navigating or providing more precision ...
study of the vaulted Sistine Chapel ceiling
The Sistine Chapel ceiling ( it, Soffitto della Cappella Sistina), painted in fresco by Michelangelo between 1508 and 1512, is a cornerstone work of High Renaissance art. The Sistine Chapel is the large papal chapel built within the Vatican ...
. The entire composition is 274 millimeters in height and 386 millimeters in width. The second sketch is titled Studies of a Reclining Male Nude: Adam in the Fresco "The Creation of Man."
' It was created in 1511 in dark red chalk, over a stylus under drawing. Red chalk was Michelangelo's preferred medium at this period of time, as it could be shaved to a finer point than black chalk. Michelangelo used this fine point to create a scintillating skin surface, that was unique for this particular sketch, and is not seen in his later works. The recto drawing is 193 millimeters in height and 259 millimeters in width.
''Studies of a Reclining Male Nude''
 In a well known study in red chalk in the British Museum, Adam is resting on earth, propped up by his forearm, with his thighs spread out and his torso slightly twisted to the side. Michelangelo employed a male model to capture this pose and used his red chalk to develop thick contours, in order to establish a definitive form, so every
In a well known study in red chalk in the British Museum, Adam is resting on earth, propped up by his forearm, with his thighs spread out and his torso slightly twisted to the side. Michelangelo employed a male model to capture this pose and used his red chalk to develop thick contours, in order to establish a definitive form, so every chapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type ...
visitor could clearly recognize the muscular body from standing on the floor, 68 feet below the ceiling
A ceiling is an overhead interior surface that covers the upper limits of a room. It is not generally considered a structural element, but a finished surface concealing the underside of the roof structure or the floor of a story above. Ceilings ...
.
In Michelangelo's final fresco on the ceiling
A ceiling is an overhead interior surface that covers the upper limits of a room. It is not generally considered a structural element, but a finished surface concealing the underside of the roof structure or the floor of a story above. Ceilings ...
, Adam is physically beautiful, but spiritually still incomplete. The sketch prefaces this story, as it is also incomplete in the sense that the only complete component of the drawing is Adam's twisted torso. Adam's other limbs bleed off of the trimmed page in immature form. However, the work is not “unfinished,” as it reached its purpose for Michelangelo, which was to work out the details of the torso in the medium of chalk, so he was confident in the composition when he began the actual, permanent fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plast ...
panel.
Context
Michelangelo heavily studied the human body and dissected numerouscadaver
A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Stud ...
s in his artistic career, and over time became captivated by the male torso. In his treatises on painting and sculpture, Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. H ...
, defined the male figure as a "geometrical and harmonious sum of its parts". Michelangelo however, felt that the torso was the powerhouse of the male body, and therefore warranted significant attention and mass in his art pieces. Thus, the torso in the ''Study'' represents an idealization of the male form, “symbolic of the perfection of God’s creation before the fall".
Sources
Michelangelo's inspiration for the torso in the British Museum sketch, is believed to be theBelvedere Torso
__NOTOC__
The Belvedere Torso is a tall fragmentary marble statue of a male nude, known to be in Rome from the 1430s, and signed prominently on the front of the base by "Apollonios, son of Nestor, Athenian", who is unmentioned in ancient literat ...
. The Belvedere Torso
__NOTOC__
The Belvedere Torso is a tall fragmentary marble statue of a male nude, known to be in Rome from the 1430s, and signed prominently on the front of the base by "Apollonios, son of Nestor, Athenian", who is unmentioned in ancient literat ...
is a fragmentary marble statue that is a 1st century BC Roman copy of an ancient Greek sculpture. Michelangelo historically used ancient, classical statuary as inspiration for the human physique in his great masterpieces. In 2015, the Belvedere Torso
__NOTOC__
The Belvedere Torso is a tall fragmentary marble statue of a male nude, known to be in Rome from the 1430s, and signed prominently on the front of the base by "Apollonios, son of Nestor, Athenian", who is unmentioned in ancient literat ...
was displayed with Michelangelo's sketch in the “Defining Beauty: The Body in Ancient Greek Art” show at the British Museum in London.
See also
* * Sistine Chapel of FootballReferences
External links
*Models of wax and clay used by Michelangelo in making his sculpture and paintings
{{DEFAULTSORT:Creation Of Adam 1512 paintings Paintings depicting Adam and Eve Paintings of gods Sistine Chapel ceiling Nude art