Tamil language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tamil (, , , also written as ''Tamizhil'' according to linguistic pronunciation) is a
 Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The earliest records in Old Tamil are short inscriptions from 300 BCE to 700 CE. These inscriptions are written in a variant of the
Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The earliest records in Old Tamil are short inscriptions from 300 BCE to 700 CE. These inscriptions are written in a variant of the
 The evolution of
The evolution of
Indianmalaysian.com. Retrieved 28 July 2013. A large community of Pakistani Tamils speakers exists in
Tamil Hindus in Karachi
''Pakistan Hindu Post'' as well as Christians and Muslims – including some Tamil-speaking Muslim refugees from Sri Lanka.Raman, B. (15 July 2002
''The Hindu Business Line'' There are about 100 Tamil Hindu families in Madrasi Para colony in Karachi. They speak impeccable Tamil along with Urdu, Punjabi and Sindhi. Many in
''The Hindu''. 28 October 2005.

"Tamil dialects"
in ''Tamil language''. Encyclopædia Britannica Online For example,
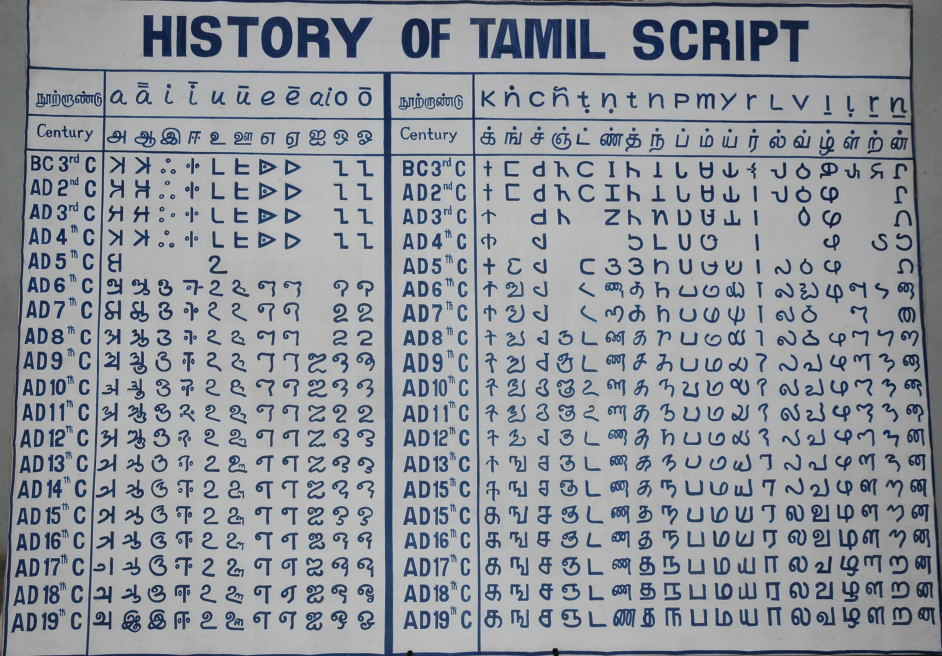
 After Tamil Brahmi fell out of use, Tamil was written using a script called amongst others such as Grantha and
After Tamil Brahmi fell out of use, Tamil was written using a script called amongst others such as Grantha and
''Tamil and English Dictionary''
based on J.P. Fabricius ''Malabar-English Dictionary'', 3rd and 4th Edition Revised and Enlarged by David Bexell. Evangelical Lutheran Mission Publishing House, Tranquebar; called Tranquebar Dictionary. * *
Tamil language
at ''
Tamil language and literature
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Tamil Language Agglutinative languages Classical Language in India Dravidian languages Languages of Andhra Pradesh Languages of Indonesia Languages of Karnataka Languages of Kerala Languages of Malaysia Languages of Mauritius Languages of Puducherry Languages of South Africa Languages of Singapore Languages of Sri Lanka Languages of Tamil Nadu Languages of Telangana Official languages of India Subject–object–verb languages Languages attested from the 1st millennium BC Articles containing video clips
Dravidian language
The Dravidian languages are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia.
The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (i ...
natively spoken by the Tamil people
The Tamils ( ), also known by their endonym Tamilar, are a Dravidian ethnic group who natively speak the Tamil language and trace their ancestry mainly to the southern part of the Indian subcontinent. The Tamil language is one of the longe ...
of South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
. It is one of the longest-surviving classical language
According to the definition by George L. Hart, a classical language is any language with an independent literary tradition and a large body of ancient written literature.
Classical languages are usually extinct languages. Those that are still ...
s in the world,. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). attested since 300 BCE.: "...the most acceptable periodisation which has so far been suggested for the development of Tamil writing seems to me to be that of A Chidambaranatha Chettiar (1907–1967): 1. Sangam Literature – 200BC to AD 200; 2. Post Sangam literature – AD 200 – AD 600; 3. Early Medieval literature – AD 600 to AD 1200; 4. Later Medieval literature – AD 1200 to AD 1800; 5. Pre-Modern literature – AD 1800 to 1900" at p. 610
Tamil was the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
for early maritime traders in South India, with Tamil inscriptions found outside of the Indian subcontinent, such as Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. The language has a well-documented history with literary works like Sangam literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil language, Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam''), historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil language, Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cā ...
, consisting of over 2,000 poems. Tamil script evolved from Tamil Brahmi, and later, the vatteluttu script was used until the current script was standardized. The language has a distinct grammatical structure, with agglutinative morphology that allows for complex word formations.
Tamil is the official language of the state of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
and union territory of Puducherry in India. It is also one of the official languages of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
. Tamil-speaking diaspora communities exist in several countries across the world. Tamil was the first to be recognized as a classical language of India by the Central Government
A central government is the government that is a controlling power over a unitary state. Another distinct but sovereign political entity is a federal government, which may have distinct powers at various levels of government, authorized or deleg ...
in 2004.
Etymology
The earliest extant Tamil literary works and their commentaries celebrate the Pandiyan Kings for the organization of long-term Tamil Sangams, which researched, developed and made amendments to the Tamil language. Although the name of the language which was developed by these Tamil Sangams is mentioned as Tamil, the period when the name "Tamil" came to be applied to the language is unclear, as is the precise etymology of the name. The earliest attested use of the name is found in Tholkappiyam, which is dated as early as the 2nd century BCE. TheHathigumpha inscription
The Hathigumpha Inscription (pronounced: ɦɑːt̪ʰiːgumpʰɑː) is a seventeen line inscription in a Prakrit language incised in Brahmi script in a cavern called Hathigumpha in Udayagiri hills, near Bhubaneswar in Odisha, India. Dated betwe ...
, inscribed around a similar period (150 BCE) by Kharavela, the Jain king of Kalinga, also refers to a ''Tamira Samghatta'' (''Tamil confederacy'').
The Samavayanga Sutra, dated to the 3rd century BCE contains a reference to a Tamil script named 'Damili'.
Southworth suggests that the name comes from > "self-speak", or "our own speech". Kamil Zvelebil
Kamil Václav Zvelebil (November 17, 1927 – January 17, 2009) was a Czech scholar in Indian literature and linguistics, notably Tamil, Sanskrit, Dravidian linguistics and literature and philology.
Life and career
Zvelebil studied at the C ...
suggests an etymology of , with meaning "self" or "one's self", and "" having the connotation of "unfolding sound". Alternatively, he suggests a derivation of < < * < *, meaning in origin "the proper process (of speaking)". However, this is deemed unlikely by Southworth due to the contemporary use of the compound 'centamiḻ', which means refined speech in the earliest literature.
The Tamil Lexicon of the University of Madras
The University of Madras is a public university, public State university (India), state university in Chennai (Madras), Tamil Nadu, India. Established in 1857, it is one of the oldest and most prominent universities in India, incorporated by an ...
defines the word "Tamil" as "sweetness". S. V. Subramanian suggests the meaning "sweet sound", from ''tam'' – "sweet" and ''il'' – "sound".
David Shulman cites Cuntaramurti's ''Tevaram'', in which he writes to Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
, "Do you know proper Tamil?" and ascribes it the meaning "Do you know how to behave properly as a male lover should? Can you understand the hints and implicit meaning that a proficient lover ought to be able to decipher?" He also states that at some point in history, Tamil meant something like "knowing how to love", in a poetic sense, and that to "know Tamil" could also mean "to be a civilized being".
Classification
''Tamil'' belongs to the southern branch of theDravidian languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia.
The most commonly spoken Dravidian l ...
, a family of around 26 languages native to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. It is also classified as being part of a Tamil language family that, alongside Tamil proper, includes the languages of about 35 ethno-linguistic groups such as the Irula and Yerukula languages (see SIL Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
).
The closest major relative of Tamil is Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
; the two began diverging around the 9th century CE. Although many of the differences between Tamil and Malayalam demonstrate a pre-historic divergence of the western dialect, the process of separation into a distinct language, Malayalam, was not completed until sometime in the 13th or 14th century.
Additionally Kannada is also relatively close to the Tamil language and shares the format of the formal ancient Tamil language. While there are some variations from the Tamil language, Kannada still preserves a lot from its roots. As part of the southern family of Indian languages and situated relatively close to the northern parts of India, Kannada also shares some Sanskrit words, similar to Malayalam. Many of the formerly used words in Tamil have been preserved with little change in Kannada. This shows a relative parallel to Tamil, even as Tamil has undergone some changes in modern ways of speaking.
History
Legendary origins
According to Hindu legend, Tamil or in personification form Tamil Thāi (Mother Tamil) was created by LordShiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
. Murugan
Kartikeya (/ kɑɾt̪ɪkejə/; ), also known as Skanda ( /skən̪d̪ə/), Subrahmanya (/ sʊbɾəɦməɲjə/, /ɕʊ-/), Shanmukha ( /ɕɑnmʊkʰə/) and Murugan (/ mʊɾʊgən/), is the Hindu god of war. He is generally described as the ...
, revered as the Tamil God, along with sage Agastya
Agastya was a revered Indian sage of Hinduism. In the Indian tradition, he is a noted recluse and an influential scholar in diverse languages of the Indian subcontinent. He is regarded in some traditions to be a Chiranjivi. He and his wife ...
, brought it to the people.
Historical origins
Tamil, like other Dravidian languages, ultimately descends from theProto-Dravidian language
Proto-Dravidian is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Dravidian languages native to the Indian subcontinent. It is thought to have differentiated into Proto-North Dravidian, Proto-Central Dravidian, and Proto-South Dravi ...
, which was most likely spoken around the third millennium BCE, possibly in the region around the lower Godavari
The Godavari (, �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga River and drains the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharash ...
river basin. The material evidence suggests that the speakers of Proto-Dravidian were of the culture associated with the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
complexes of South India, but it has also been related to the Harappan civilization.
Scholars categorise the attested history of the language into three periods: Old Tamil (300 BCE–700 CE), Middle Tamil (700–1600) and Modern Tamil (1600–present).
Brahmi script
About 60,000 of the approximately 10,000 inscriptions found by theArchaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexander ...
in India are in Tamil Nadu. Of them, most are in Tamil, with only about 5 percent in other languages.
In 2004, a number of skeletons were found buried in earthenware urns dating from at least 696 BCE in Adichanallur. Some of these urns contained writing in Tamil Brahmi script, and some contained skeletons of Tamil origin. Between 2017 and 2018, 5,820 artifacts have been found in Keezhadi. These were sent to Beta Analytic in Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
, Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, for Accelerator Mass Spectrometry
Accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is a form of mass spectrometry that accelerates ions to extraordinarily high kinetic energies before mass analysis. The special strength of AMS among the different methods of mass spectrometry is its ability t ...
(AMS) dating. One sample containing Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions was claimed to be dated to around 580 BCE.
John Guy states that Tamil was the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
for early maritime traders from India. Tamil language inscriptions written in Brahmi script have been discovered in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and on trade goods in Thailand and Egypt. In November 2007, an excavation at Quseir-al-Qadim revealed Egyptian pottery dating back to first century BCE with ancient Tamil Brahmi inscriptions. There are a number of apparent Tamil loanwords in Biblical Hebrew dating to before 500 BCE, the oldest attestation of the language.Rabin, C. ''Proceedings of the Second International Conference Seminar of Tamil Studies'', p. 438
Old Tamil
 Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The earliest records in Old Tamil are short inscriptions from 300 BCE to 700 CE. These inscriptions are written in a variant of the
Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The earliest records in Old Tamil are short inscriptions from 300 BCE to 700 CE. These inscriptions are written in a variant of the Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
called Tamil-Brahmi. The earliest long text in Old Tamil is the ''Tolkāppiyam
''Tolkāppiyam'', also romanised as ''Tholkaappiyam'' ( , ''lit.'' "ancient poem"), is the oldest extant Tamil grammar text and the oldest extant long work of Tamil literature. It is the earliest Tamil text mentioning Gods, perhaps linked to ...
'', an early work on Tamil grammar and poetics, whose oldest layers could be as old as the late 2nd century BCE. Many literary works in Old Tamil have also survived. These include a corpus of 2,381 poems collectively known as Sangam literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil language, Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam''), historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil language, Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cā ...
. These poems are usually dated to between the 1st century BCE and 5th century CE.
Middle Tamil
 The evolution of
The evolution of Old Tamil
Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning from the 3rd century BCE to the seventh century CE. Prior to Old Tamil, the period of Tamil linguistic development is termed as Proto-Tamil. After the Old Tamil period, Tamil becomes Middl ...
into Middle Tamil, which is generally taken to have been completed by the 8th century, was characterised by a number of phonological and grammatical changes. In phonological terms, the most important shifts were the virtual disappearance of the aytam (ஃ), an old phoneme, the coalescence of the alveolar and dental nasals, and the transformation of the alveolar plosive
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or simply a stop, is a pulmonic consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases.
The occlusion may be made with the tongue tip or blade (, ), tongue body (, ), lip ...
into a rhotic. In grammar, the most important change was the emergence of the present tense. The present tense evolved out of the verb ' (), meaning "to be possible" or "to befall". In Old Tamil, this verb was used as an aspect marker to indicate that an action was micro-durative, non-sustained or non-lasting, usually in combination with a time marker such as ' (). In Middle Tamil, this usage evolved into a present tense marker – ' () – which combined the old aspect and time markers.
Modern Tamil
The Nannūl remains the standard normative grammar for modern literary Tamil, which therefore continues to be based on Middle Tamil of the 13th century rather than on Modern Tamil. Colloquial spoken Tamil, in contrast, shows a number of changes. The negative conjugation of verbs, for example, has fallen out of use in Modern Tamil – instead, negation is expressed either morphologically or syntactically. Modern spoken Tamil also shows a number of sound changes, in particular, a tendency to lower high vowels in initial and medial positions, and the disappearance of vowels between plosives and between a plosive and rhotic. Contact with European languages affected written and spoken Tamil. Changes in written Tamil include the use of European-style punctuation and the use of consonant clusters that were not permitted in Middle Tamil. The syntax of written Tamil has also changed, with the introduction of new aspectual auxiliaries and more complex sentence structures, and with the emergence of a more rigid word order that resembles the syntactic argument structure of English. In 1578, Portuguese Christian missionaries published a Tamil prayer book in old Tamil script named '' Thambiran Vanakkam'', thus making Tamil the first Indian language to be printed and published. The '' Tamil Lexicon'', published by theUniversity of Madras
The University of Madras is a public university, public State university (India), state university in Chennai (Madras), Tamil Nadu, India. Established in 1857, it is one of the oldest and most prominent universities in India, incorporated by an ...
, was one of the earliest dictionaries published in Indian languages.
A strong strain of linguistic purism
Linguistic purism or linguistic protectionism is a concept with two common meanings: one with respect to foreign languages and the other with respect to the internal variants of a language (dialects).
The first meaning is the historical trend ...
emerged in the early 20th century, culminating in the Pure Tamil Movement which called for removal of all Sanskritic elements from Tamil. It received some support from Dravidian parties
Dravidian parties include an array of List of political parties in India, regional political parties in the States and union territories of India, state of Tamil Nadu, India, which trace their origins and ideologies either directly or indirect ...
. This led to the replacement of a significant number of Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
loanwords by Tamil equivalents, though many others remain.
According to a 2001 survey, there were 1,863 newspapers published in Tamil, of which 353 were dailies.
Geographic distribution
Tamil is the primary language of the majority of the people residing inTamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
, Puducherry, (in India) and in the Northern and Eastern provinces of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
. The language is spoken among small minority groups in other states of India which include Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
, Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
, Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
, Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
, Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India comprising 572 islands, of which only 38 are inhabited. The islands are grouped into two main clusters: the northern Andaman Islands and the southern Nicobar Islands, separated by a ...
in India and in certain regions of Sri Lanka such as Colombo
Colombo, ( ; , ; , ), is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. The Colombo metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 within the municipal limits. It is the ...
and the hill country. Tamil or dialects of it were used widely in the state of Kerala as the major language of administration, literature and common usage until the 12th century CE. Tamil was also used widely in inscriptions found in southern Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
districts of Chittoor and Nellore until the 12th century CE. Tamil was used for inscriptions from the 10th through 14th centuries in southern Karnataka districts such as Kolar
Kolar may refer to:
Places India
* Kolar, Karnataka, a city in India
**Kolar Assembly constituency
*Kolar district, in Karnataka, India
*Kolar Gold Fields, former gold mines in Karnataka, India
**KGF (disambiguation)
**Kolar Gold Field Assembly co ...
, Mysore
Mysore ( ), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the ...
, Mandya
Mandya is a city in the state of Karnataka. It is the headquarter of Mandya district,
Sugar factories contribute to the major economic output. It is also called Sugar City (Kannada: ''Sakkare Nagara'') because sugarcane is a major crop grown ...
and Bengaluru
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
.
There are currently sizeable Tamil-speaking populations descended from colonial-era migrants in Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
, Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, Indonesia, Thailand, Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
, Brunei
Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. Apart from its coastline on the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak, with ...
, and Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
. Tamil is used as one of the languages of education in Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, along with English, Malay and Mandarin.Tamil SchoolsIndianmalaysian.com. Retrieved 28 July 2013. A large community of Pakistani Tamils speakers exists in
Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a popul ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, which includes Tamil-speaking HindusSunny, Sanjesh (21 September 2010Tamil Hindus in Karachi
''Pakistan Hindu Post'' as well as Christians and Muslims – including some Tamil-speaking Muslim refugees from Sri Lanka.Raman, B. (15 July 2002
''The Hindu Business Line'' There are about 100 Tamil Hindu families in Madrasi Para colony in Karachi. They speak impeccable Tamil along with Urdu, Punjabi and Sindhi. Many in
Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
, Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
, Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
, Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; i ...
, and Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
have Tamil origins, but only a small number speak the language. In Reunion where the Tamil language was forbidden to be learnt and used in public space by France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
it is now being relearnt by students and adults. Tamil is also spoken by migrants from Sri Lanka and India in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
.
Status
Official Status
Tamil is theofficial language
An official language is defined by the Cambridge English Dictionary as, "the language or one of the languages that is accepted by a country's government, is taught in schools, used in the courts of law, etc." Depending on the decree, establishmen ...
of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and one of the 22 languages under schedule 8 of the constitution of India. It is one of the official languages of the union territories of Puducherry and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India comprising 572 islands, of which only 38 are inhabited. The islands are grouped into two main clusters: the northern Andaman Islands and the southern Nicobar Islands, separated by a ...
. Tamil is also one of the official languages of Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
. Tamil is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka, along with Sinhala. It was once given nominal official status in the Indian state of Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
, purportedly as a rebuff to Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
, though there was no attested Tamil-speaking population in the state, and was later replaced by Punjabi, in 2010.
In addition, with the creation in October 2004 of a legal status for classical languages by the Government of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union t ...
and following a political campaign supported by several Tamil associations, Tamil became the first legally recognised Classical language
According to the definition by George L. Hart, a classical language is any language with an independent literary tradition and a large body of ancient written literature.
Classical languages are usually extinct languages. Those that are still ...
of India. The recognition was announced by the contemporaneous President of India
The president of India (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, and the commander-in-chief, supreme commander of the Indian Armed ...
, Abdul Kalam
Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalam ( ; 15 October 193127 July 2015) was an Indian Aerospace engineering, aerospace scientist and statesman who served as the president of India from 2002 to 2007.
Born and raised in a Muslim family in Ramesw ...
, who was a Tami himself, in a joint sitting of both houses of the Indian Parliament
The Parliament of India (ISO: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Government of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People). The President o ...
on 6 June 2004."Sanskrit to be declared classical language"''The Hindu''. 28 October 2005.
Education
In Malaysia, 543 primary education government schools are available fully in Tamil as the medium of instruction. The establishment of Tamil-medium schools has been in process inMyanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
to provide education completely in Tamil language by the Tamils who settled there 200 years ago. Tamil language is available as a course in some local school boards and major universities in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and the month of January has been declared "Tamil Heritage Month" by the Parliament of Canada
The Parliament of Canada () is the Canadian federalism, federal legislature of Canada. The Monarchy of Canada, Crown, along with two chambers: the Senate of Canada, Senate and the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons, form the Bicameral ...
. Tamil enjoys a special status of protection under Article 6(b), Chapter 1 of the Constitution of South Africa
The Constitution of South Africa is the supreme law of the Republic of South Africa. It provides the legal foundation for the existence of the republic, it sets out the human rights and duties of its citizens, and defines the structure of t ...
and is taught as a subject in schools in KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN) is a Provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the government merged the Zulu people, Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu language, Zulu) and ...
province. Recently, it has been rolled out as a subject of study in schools in the French overseas department
The overseas departments and regions of France (, ; DROM) are the five departments and regions of the French Republic which are located outside European France (also known as "metropolitan France"). These overseas entities have exactly the same ...
of Réunion
Réunion (; ; ; known as before 1848) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France. Part of the Mascarene Islands, it is located approximately east of the isl ...
.
Mass Media
Tamil language paper media such asnewspaper
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as poli ...
s are very common with a 2001 survey claiming there were 1,863 newspapers published in Tamil, of which 353 were dailies. Tamil language digital media is also abundant with films being especially common.
Dialects

Region-specific variations
The socio-linguistic situation of Tamil is characterised bydiglossia
In linguistics, diglossia ( , ) is where two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled "L" or "low" v ...
: there are two separate registers varying by socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement used by economics, economists and sociology, sociologsts. The measurement combines a person's work experience and their or their family's access to economic resources and social position in relation t ...
, a high register and a low one. Tamil dialects are primarily differentiated from each other by the fact that they have undergone different phonological changes and sound shifts in evolving from Old Tamil. For example, the word for "here"—' in ''Centamil'' (the classic variety)—has evolved into ' in the Kongu dialect of Coimbatore
Coimbatore (Tamil: kōyamputtūr, ), also known as Kovai (), is one of the major Metropolitan cities of India, metropolitan cities in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of the Noyy ...
, ''inga'' in the dialects of Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also known as Thanjai, previously known as Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the 12th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of southern Indian religion, art ...
and Palakkad
Palakkad (), Renaming of cities in India, also known as Palghat, historically known as Palakkattussery, is a city and a municipality in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of P ...
, and ' in some dialects of Sri Lanka. Old Tamil's ' (where ' means place) is the source of ' in the dialect of Tirunelveli
Tirunelveli (), also known as Nellai and historically (during British rule) as Tinnevelly, is a major city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirunelveli District. It is the fourth-largest munici ...
, Old Tamil ' is the source of ' in the dialect of Madurai
Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District, which is ...
, and ' in some northern dialects. Even now, in the Coimbatore area, it is common to hear "" meaning "that place". Although Tamil dialects do not differ significantly in their vocabulary, there are a few exceptions. The dialects spoken in Sri Lanka retain many words and grammatical forms that are not in everyday use in India, and use many other words slightly differently. Tamil dialects include Central Tamil dialect
The Central Tamil dialect is a dialect of Tamil spoken in the districts of Thanjavur, Tiruvarur, Nagapattinam, Mayiladuthurai, Perambalur and Tiruchirapalli in central Tamil Nadu, India and to some extent, in the neighbouring Cuddalore and ...
, Kongu Tamil
Kongu Tamil or Kovai Tamil (also called Kongalam, Kongu Pechu, Coimbatore Tamil) is the dialect of Tamil language that is spoken by the people in Kongu Nadu, which is the western region of Tamil Nadu. It is originally known as "Kangee"` or "Kong ...
, Madras Bashai
Madras Bashai (Tamil: , ) is a Variety (linguistics), variety of the Tamil language spoken by native people in the city of Chennai (previously known as Madras) in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. In the past it was sometimes considered a pidgin, ...
, Madurai Tamil, Nellai Tamil
Tirunelveli Tamil also known as Nellai Tamil or Pandya Nadu, ThenPaandi Tamil is one of the dialects of Tamil language, Tamil which is spoken in the districts of Tirunelveli, Tenkasi, Thoothukudi, Kanyakumari and some parts of Virudhunagar as wel ...
, Kumari Tamil in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
; Batticaloa Tamil dialect, Jaffna Tamil dialect, Negombo Tamil dialect in Sri Lanka; and Malaysian Tamil in Malaysia. Sankethi dialect in Karnataka has been heavily influenced by Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
.
Loanword variations
The dialect of the district ofPalakkad
Palakkad (), Renaming of cities in India, also known as Palghat, historically known as Palakkattussery, is a city and a municipality in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of P ...
in Kerala has many Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
loanwords, has been influenced by Malayalam's syntax, and has a distinctive Malayalam accent. Similarly, Tamil spoken in Kanyakumari District has more unique words and phonetic style than Tamil spoken at other parts of Tamil Nadu. The words and phonetics are so different that a person from Kanyakumari district is easily identifiable by their spoken Tamil. Hebbar and Mandyam dialects, spoken by groups of Tamil Vaishnavites who migrated to Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
in the 11th century, retain many features of the ''Vaishnava paribasai'', a special form of Tamil developed in the 9th and 10th centuries that reflect Vaishnavite religious and spiritual values. Several caste
A caste is a Essentialism, fixed social group into which an individual is born within a particular system of social stratification: a caste system. Within such a system, individuals are expected to marry exclusively within the same caste (en ...
s have their own sociolect
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language ( non-standard dialect, restricted register) or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, age group, or other social group.
Sociolects involve both passive acquisit ...
s which most members of that caste traditionally used regardless of where they come from. It is often possible to identify a person's caste by their speech.Krishnamurti, Bhadriraju (2013"Tamil dialects"
in ''Tamil language''. Encyclopædia Britannica Online For example,
Tamil Brahmin
Tamil Brahmins are an ethnoreligious community of Tamil-speaking Hindu Brahmins, predominantly living in Tamil Nadu, though they number significantly in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Telangana in addition to other regions of India. The ...
s tend to speak a variety of dialects that are all collectively known as Brahmin Tamil. These dialects tend to have softer consonants (with consonant deletion also common). These dialects also tend to have many Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
loanwords. Tamil in Sri Lanka incorporates loan words
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
from Portuguese, Dutch, and English.
Spoken and literary variants
In addition to its dialects, Tamil exhibits different forms: a classical literary style modelled on the ancient language ('), a modern literary and formal style ('), and a moderncolloquial
Colloquialism (also called ''colloquial language'', ''colloquial speech'', ''everyday language'', or ''general parlance'') is the linguistic style used for casual and informal communication. It is the most common form of speech in conversation amo ...
form ('). These styles shade into each other, forming a stylistic continuum. For example, it is possible to write ' with a vocabulary drawn from ', or to use forms associated with one of the other variants while speaking '.
In modern times, ' is generally used in formal writing and speech. For instance, it is the language of textbooks, of much of Tamil literature
Tamil literature includes a collection of literary works that have come from a tradition spanning more than two thousand years. The oldest extant works show signs of maturity indicating an even longer period of evolution. Contributors to the T ...
and of public speaking and debate. In recent times, however, ' has been making inroads into areas that have traditionally been considered the province of '. Most contemporary cinema, theatre and popular entertainment on television and radio, for example, is in ', and many politicians use it to bring themselves closer to their audience. The increasing use of ' in modern times has led to the emergence of unofficial 'standard' spoken dialects. In India, the 'standard' ', rather than on any one dialect, but has been significantly influenced by the dialects of Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also known as Thanjai, previously known as Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the 12th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of southern Indian religion, art ...
and Madurai
Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District, which is ...
. In Sri Lanka, the standard is based on the dialect of Jaffna
Jaffna (, ; , ) is the capital city of the Northern Province, Sri Lanka, Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jaffna District located on a Jaffna Peninsula, peninsula of the same name. With a population o ...
.
Lexical Differences
There are some words that are only used in Literary Tamil such as: ''annai'' (mother), ''a:rava:ram'' (din and bustle), ''ali'' (offer), ''tarmam'' (charity), ''iyalum'' (possible), ''illam'' (house), ''kata'' (cross), and ''karpi'' (teach). There are also some words only used in Colloquial Tamil and these include: ''Le:cu'' (easy), ''rompa'' (much), ''vantava:''lam ''(unpleasant facts)'', ''va:ttiya:r'' (boss/leader), ''tatave'' (times/occasion).Comparative Text
Writing system

 After Tamil Brahmi fell out of use, Tamil was written using a script called amongst others such as Grantha and
After Tamil Brahmi fell out of use, Tamil was written using a script called amongst others such as Grantha and Pallava
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of South India, the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The Pallavas played a crucial role in shaping in particular southern Indian history and heritage. The ...
. The current Tamil script
The Tamil script ( ) is an abugida script that is used by Tamils and Tamil language, Tamil speakers in India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Singapore and elsewhere to write the Tamil language. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. ...
consists of 12 vowel
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness a ...
s, 18 consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
s and one special character, the '' āytam''. The vowels and consonants combine to form 216 compound characters, giving a total of 247 characters (12 + 18 + 1 + (12 × 18)). All consonants have an inherent vowel ''a'', as with other Indic scripts
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used b ...
. This inherent vowel is removed by adding a tittle
The tittle or superscript dot is the dot on top of lowercase ''i'' and ''j''. In English writing the tittle is a diacritic which only appears as part of these glyphs, but diacritic dots can appear over other letters in various languages. In mos ...
called a ', to the consonantal sign. For example, is ''ṉa'' (with the inherent ''a'') and is ''ṉ'' (without a vowel). Many Indic scripts have a similar sign, generically called virama
Virama ( ्, ) is a Sanskrit phonological concept to suppress the inherent vowel that otherwise occurs with every consonant letter, commonly used as a generic term for a codepoint in Unicode, representing either
# halanta, hasanta or explicit vir ...
, but the Tamil script is somewhat different in that it nearly always uses a visible ''puḷḷi'' to indicate a 'dead consonant' (a consonant without a vowel). In other Indic scripts, it is generally preferred to use a ligature or a half form to write a syllable or a cluster containing a dead consonant, although writing it with a visible virama is also possible. The Tamil script does not differentiate voiced and unvoiced plosive
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or simply a stop, is a pulmonic consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases.
The occlusion may be made with the tongue tip or blade (, ), tongue body (, ), lip ...
s. Instead, plosives are articulated with voice depending on their position in a word, in accordance with the rules of Tamil phonology
Tamil phonology is characterised by the presence of "true-subapical" retroflex consonants and multiple rhotic consonants. Its script does not distinguish between voiced and unvoiced consonants; phonetically, voice is assigned depending on a ...
.
In addition to the standard characters, six characters taken from the Grantha script
The Grantha script (; ; ) is a classical South Indian Brahmic script, found particularly in Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Originating from the Pallava script, the Grantha script is related to Tamil and Vatteluttu scripts. The modern Malayalam script ...
, which was used in the Tamil region to write Sanskrit, are sometimes used to represent sounds not native to Tamil, that is, words adopted from Sanskrit, Prakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Ind ...
, and other languages. The traditional system prescribed by classical grammars for writing loan-words, which involves respelling them in accordance with Tamil phonology, remains, but is not always consistently applied. ISO 15919
ISO 15919 is an international standard for the romanization of Indic scripts. Published in 2001, it is part of a series of romanization standards by the International Organization for Standardization.
Overview
Relation to other systems
...
is an international standard for the transliteration of Tamil and other Indic scripts
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used b ...
into Latin characters. It uses diacritics to map the much larger set of Brahmic consonants and vowels to Latin script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
, and thus the alphabets of various languages, including English.
Numerals and symbols
Apart from the usual numerals, Tamil has numerals for 10, 100 and 1000. Symbols for day, month, year, debit, credit, as above, rupee, and numeral are present as well. Tamil also uses several historical fractional signs.Phonology
, , , , and are only found in loanwords and may be considered marginal phonemes, though they are traditionally not seen as fully phonemic. Tamil has twodiphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of ...
s: and , the latter of which is restricted to a few lexical items.
Phonotactics
Tamil has noconsonant cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster, consonant sequence or consonant compound is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word ''splits''. In the education fie ...
s at the beginning of words and the consonant clusters which do occur are: /mp/, /rt/, /ɳʈ/, /Ƞk/, /ṇt/, /ll/, /ɭɭ/, /pp/, /cc/, /tt/, /kk/, /rr/, /ɾk/, /mm/, and /nn/.
Grammar
Tamil employsagglutinative
In linguistics, agglutination is a morphological process in which words are formed by stringing together morphemes (word parts), each of which corresponds to a single syntactic feature. Languages that use agglutination widely are called agglu ...
grammar, where suffixes are used to mark noun class
In linguistics, a noun class is a particular category of nouns. A noun may belong to a given class because of the characteristic features of its referent, such as gender, animacy, shape, but such designations are often clearly conventional. Some ...
, number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
, and case
Case or CASE may refer to:
Instances
* Instantiation (disambiguation), a realization of a concept, theme, or design
* Special case, an instance that differs in a certain way from others of the type
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of relate ...
, verb tense and other grammatical categories. Tamil's standard metalinguistic terminology and scholarly vocabulary is itself Tamil, as opposed to the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
that is standard for most Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east ...
.
Much of Tamil grammar is extensively described in the oldest known grammar book for Tamil, the ''Tolkāppiyam
''Tolkāppiyam'', also romanised as ''Tholkaappiyam'' ( , ''lit.'' "ancient poem"), is the oldest extant Tamil grammar text and the oldest extant long work of Tamil literature. It is the earliest Tamil text mentioning Gods, perhaps linked to ...
''. Modern Tamil writing is largely based on the 13th-century grammar ' which restated and clarified the rules of the ''Tolkāppiyam'', with some modifications. Traditional Tamil grammar consists of five parts, namely ', ', ', ', '. Of these, the last two are mostly applied in poetry.
Tamil words consist of a lexical root to which one or more affix
In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. The main two categories are Morphological derivation, derivational and inflectional affixes. Derivational affixes, such as ''un-'', ''-ation' ...
es are attached. Most Tamil affixes are suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can ca ...
es. Tamil suffixes can be derivational suffixes, which either change the part of speech of the word or its meaning, or inflection
In linguistic Morphology (linguistics), morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical category, grammatical categories such as grammatical tense, ...
al suffixes, which mark categories such as person
A person (: people or persons, depending on context) is a being who has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations suc ...
, number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
, mood, tense, etc. There is no absolute limit on the length and extent of agglutination
In linguistics, agglutination is a morphology (linguistics), morphological process in which words are formed by stringing together morphemes (word parts), each of which corresponds to a single Syntax, syntactic feature. Languages that use agglu ...
, which can lead to long words with many suffixes, which would require several words or a sentence in English. To give an example, the word ''pōkamuṭiyātavarkaḷukkāka'' (போகமுடியாதவர்களுக்காக) means "for the sake of those who cannot go" and consists of the following morpheme
A morpheme is any of the smallest meaningful constituents within a linguistic expression and particularly within a word. Many words are themselves standalone morphemes, while other words contain multiple morphemes; in linguistic terminology, this ...
s:
Morphology
Tamil nouns (and pronouns) are classified into two super-classes (')—the "rational" ('), and the "irrational" (')—which include a total of five classes (''pāl'', which literally means "gender"). Humans anddeities
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
are classified as "rational", and all other nouns (animals, objects, abstract nouns) are classified as irrational. The "rational" nouns and pronouns belong to one of three classes (''pāl'')—masculine singular, feminine singular, and rational plural. The "irrational" nouns and pronouns belong to one of two classes: irrational singular and irrational plural. The ''pāl'' is often indicated through suffixes. The plural form for rational nouns may be used as an honorific
An honorific is a title that conveys esteem, courtesy, or respect for position or rank when used in addressing or referring to a person. Sometimes, the term "honorific" is used in a more specific sense to refer to an Honorary title (academic), h ...
, gender-neutral, singular form.
Suffixes are used to perform the functions of cases or postposition
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complemen ...
s. Traditional grammarians tried to group the various suffixes into eight cases corresponding to the cases used in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
. These were the nominative
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case, or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb, or (in Latin and formal variants of E ...
, accusative
In grammar, the accusative case (abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to receive the direct object of a transitive verb.
In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: "me", "him", "her", " ...
, dative
In grammar, the dative case (abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob a drink". In this exampl ...
, sociative, genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can ...
, instrumental
An instrumental or instrumental song is music without any vocals, although it might include some inarticulate vocals, such as shouted backup vocals in a big band setting. Through Semantic change, semantic widening, a broader sense of the word s ...
, locative
In grammar, the locative case ( ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which indicates a location. In languages using it, the locative case may perform a function which in English would be expressed with such prepositions as "in", "on", "at", and " ...
, and ablative
In grammar, the ablative case (pronounced ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical case for nouns, pronouns, and adjectives in the grammars of various languages. It is used to indicate motion away from something, make comparisons, and serve various o ...
. Modern grammarians argue that this classification is artificial, and that Tamil usage is best understood if each suffix or combination of suffixes is seen as marking a separate case. Tamil nouns can take one of four prefixes
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the word to which it is affixed.
Prefixes, like other affixes, can b ...
: ''i'', ''a'', ''u'', and ''e'' which are functionally equivalent to the demonstrative
Demonstratives (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) are words, such as ''this'' and ''that'', used to indicate which entities are being referred to and to distinguish those entities from others. They are typically deictic, their meaning ...
s in English. For example, the word ''vazhi'' (வழி) meaning "way" can take these to produce ''ivvazhi'' (இவ்வழி) "this way", ''avvazhi'' (அவ்வழி) "that way", ''uvvazhi'' (உவ்வழி) "the medial way" and ''evvazhi'' (எவ்வழி) "which way".
Tamil verbs are also inflected through the use of suffixes. A typical Tamil verb form will have a number of suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can ca ...
es, which show person, number, mood, tense, and voice.
* Person and number are indicated by suffixing the oblique case
In grammar, an oblique ( abbreviated ; from ) or objective case ( abbr. ) is a nominal case other than the nominative case and, sometimes, the vocative.
A noun or pronoun in the oblique case can generally appear in any role except as subject, ...
of the relevant pronoun. The suffixes to indicate tenses and voice are formed from grammatical particle
In grammar, the term ''particle'' ( abbreviated ) has a traditional meaning, as a part of speech that cannot be inflected, and a modern meaning, as a function word (functor) associated with another word or phrase in order to impart meaning. Alth ...
s, which are added to the stem.
* Tamil has two voices. The first indicates that the subject of the sentence ''undergoes'' or ''is the object of'' the action named by the verb stem, and the second indicates that the subject of the sentence ''directs'' the action referred to by the verb stem.
* Tamil has three simple tenses—past, present, and future—indicated by the suffixes, as well as a series of perfects indicated by compound suffixes. Mood is implicit in Tamil, and is normally reflected by the same morpheme
A morpheme is any of the smallest meaningful constituents within a linguistic expression and particularly within a word. Many words are themselves standalone morphemes, while other words contain multiple morphemes; in linguistic terminology, this ...
s which mark tense categories. Tamil verbs also mark evidentiality
In linguistics, evidentiality is, broadly, the indication of the nature of evidence for a given statement; that is, whether evidence exists for the statement and if so, what kind. An evidential (also verificational or validational) is the particul ...
, through the addition of the hearsay clitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic ( , backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a ...
''.'' Verb inflection is shown below using example ''aḻintukkoṇṭiruntēṉ''; (அழிந்துக்கொண்டிருந்தேன்); "(I) was being destroyed".
Traditional grammars of Tamil do not distinguish between adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of ...
s and adverb An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by ...
s, including both of them under the category ''uriccol'', although modern grammarians tend to distinguish between them on morphological and syntactical grounds. Tamil has many ideophones that act as adverbs indicating the way the object in a given state "says" or "sounds".
Tamil does not have articles. Definiteness and indefiniteness are either indicated by special grammatical devices, such as using the number "one" as an indefinite article, or by the context. In the first person plural, Tamil makes a distinction between inclusive pronouns ' (we), ' (our) that include the addressee and exclusive pronouns ' (we), ' (our) that do not.
Syntax
Tamil is a consistentlyhead-final
In linguistics, head directionality is a proposed Principles and parameters, parameter that classifies languages according to whether they are head-initial (the head (linguistics), head of a phrase precedes its Complement (linguistics), complement ...
language. The verb comes at the end of the clause, with a typical word order of subject–object–verb (SOV). However, word order in Tamil is also flexible, so that surface permutations of the SOV order are possible with different pragmatic effects. Tamil has postposition
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complemen ...
s rather than prepositions
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complemen ...
. Demonstratives and modifiers precede the noun within the noun phrase. Subordinate clauses precede the verb of the matrix clause.
Tamil is a null-subject language
In linguistic typology, a null-subject language is a language whose grammar permits an independent clause to lack an explicit subject; such a clause is then said to have a null subject.
In the principles and parameters framework, the null s ...
. Not all Tamil sentences have subjects, verbs, and objects. It is possible to construct grammatically valid and meaningful sentences which lack one or more of the three. For example, a sentence may only have a verb—such as ' ("completed")—or only a subject and object, without a verb such as ' ("That smy house"). Tamil does not have a copula (a linking verb equivalent to the word ''is''). The word is included in the translations only to convey the meaning more easily.
Vocabulary
The vocabulary of Tamil is mainly Dravidian. A strong sense oflinguistic purism
Linguistic purism or linguistic protectionism is a concept with two common meanings: one with respect to foreign languages and the other with respect to the internal variants of a language (dialects).
The first meaning is the historical trend ...
is found in Modern Tamil, which opposes the use of foreign loanwords. Nonetheless, a number of words used in classical and modern Tamil are loanwords from the languages of neighbouring groups, or with whom the Tamils had trading links, including Malay (e.g. "sago" from Malay ), Chinese (for example, "skiff" from Chinese san-pan) and Greek (for example, from Greek ὥρα). In more modern times, Tamil has imported words from Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
and Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
, reflecting groups that have influenced the Tamil area at times, and from neighbouring languages such as Telugu, Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
, and Sinhala. During the modern period, words have also been adapted from European languages, such as Portuguese, French, and English.
The strongest effect of purism in Tamil has been on words taken from Sanskrit. During its history, Tamil, along with other Dravidian languages like Telugu, Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
, Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
etc., was influenced by Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
in terms of vocabulary, grammar and literary styles,"Literature in all Dravidian languages owes a great deal to Sanskrit, the magic wand whose touch raised each of the languages from a level of patois to that of a literary idiom" (Sastri 1955, p. 309); Trautmann, Thomas R. (2006). ''Languages and nations: the Dravidian proof in colonial Madras''. Berkeley: University of California Press. "The author endeavours to demonstrate that the entire Sangam poetic corpus follows the "Kavya" form of Sanskrit poetry" – .Takahashi, Takanobu. (1995). ''Tamil love poetry and poetics''. Brill's Indological Library, v. 9. Leiden: E. J. Brill, pp. 16, 18. . reflecting the increased trend of Sanskritisation
Sanskritisation (or Sanskritization) is a term in sociology which refers to the process by which castes or tribes placed lower in the caste hierarchy seek upward mobility by emulating the rituals and practices of the dominant castes or upper c ...
in the Tamil country. Tamil vocabulary never became quite as heavily Sanskritised as that of the other Dravidian languages, and unlike in those languages, it was and remains possible to express complex ideas (including in science, art, religion and law) without the use of Sanskrit loan words. In addition, Sanskritisation was actively resisted by a number of authors of the late medieval period, culminating in the 20th century in a movement called '' '' (meaning "pure Tamil movement"), led by Parithimaar Kalaignar and Maraimalai Adigal
Maraimalai Adigal (15 July 1876 – 15 September 1950) was a Tamil Saivite writer, orator and father of the Tanittamil Iyakkam movement. He authored more than 100 books, including works on original poems and dramas and notable research works o ...
, which sought to remove the accumulated influence of Sanskrit on Tamil. As a result of this, Tamil in formal documents, literature and public speeches has seen a marked decline in the use Sanskrit loan words in the past few decades, under some estimates having fallen from 40 to 50% to about 20%. As a result, the Prakrit and Sanskrit loan words used in modern Tamil are, unlike in some other Dravidian languages, restricted mainly to some spiritual terminology and abstract noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an object or subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example ...
s.
In the 20th century, institutions and learned bodies have, with government support, generated technical dictionaries for Tamil containing neologism
In linguistics, a neologism (; also known as a coinage) is any newly formed word, term, or phrase that has achieved popular or institutional recognition and is becoming accepted into mainstream language. Most definitively, a word can be considered ...
s and words derived from Tamil roots to replace loan words from English and other languages. the language had a listed vocabulary of over 470,000 unique words, including those from old literary sources. In November 2019, the state government issued an order to add 9,000 new words to the vocabulary.
Influence
Words of Tamil origin occur in other languages. A notable example of a word in worldwide use with Dravidian (not specifically Tamil) etymology is '' orange'', via Sanskrit from a Dravidian predecessor of Tamil 'fragrant fruit'. One suggestion as to the origin of the word ''anaconda'' is the Tamil 'having killed an elephant'. Examples in English include ''cheroot'' ( meaning 'rolled up'), ''mango'' (from ), ''mulligatawny'' (from 'pepper water'), ''pariah'' (from ), ''curry'' (from ),"curry, n.2", ''The Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd ed. 1989. OED Online. Oxford University Press. 14 August 2009 ''catamaran'' (from 'bundled logs'), and ''congee'' (from 'rice porridge' or 'gruel').Sample text
The following is a sample text in literary Tamil of Article 1 of theUniversal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal D ...
. The first line is the Tamil script
The Tamil script ( ) is an abugida script that is used by Tamils and Tamil language, Tamil speakers in India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Singapore and elsewhere to write the Tamil language. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. ...
; the second is romanized Tamil; the third is the International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation ...
; the fourth is the gloss.
See also
* List of countries where Tamil is an official language *List of languages by first written accounts
This is a list of languages arranged by age of the oldest existing text recording a complete sentence in the language. It does not include undeciphered writing systems, though there are various claims without wide acceptance, which, if substanti ...
* Tamil keyboard
The Tamil language, Tamil keyboard layout, keyboard is used in computers and mobile devices to input text in the Tamil script.
The keyboard layout approved by the Government of Tamil Nadu is Tamil 99. The InScript keyboard is the keyboard layout ...
* Tamil population by cities
* Tamil population by nation
* Tamil Loanwords in other languages
* Tamil Shorthand
* Geolinguistics
Geolinguistics has been identified by some as being a branch of linguistics and by others as being an offshoot of language geography which is further defined in terms of being a branch of human geography. When seen as a branch of linguistics, geol ...
* Language geography
Language geography is the branch of human geography that studies the geographic distribution of language(s) or its constituent elements. Linguistic geography can also refer to studies of how people talk about the landscape. For example, toponym ...
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Fabricius, Johann Philip (1933 and 1972)''Tamil and English Dictionary''
based on J.P. Fabricius ''Malabar-English Dictionary'', 3rd and 4th Edition Revised and Enlarged by David Bexell. Evangelical Lutheran Mission Publishing House, Tranquebar; called Tranquebar Dictionary. * *
External links
Tamil language
at ''
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
''
Tamil language and literature
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Tamil Language Agglutinative languages Classical Language in India Dravidian languages Languages of Andhra Pradesh Languages of Indonesia Languages of Karnataka Languages of Kerala Languages of Malaysia Languages of Mauritius Languages of Puducherry Languages of South Africa Languages of Singapore Languages of Sri Lanka Languages of Tamil Nadu Languages of Telangana Official languages of India Subject–object–verb languages Languages attested from the 1st millennium BC Articles containing video clips