Transition Metal Dithiocarbamate Complexes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
193px, Structure of iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate).
Transition metal dithiocarbamate complexes are
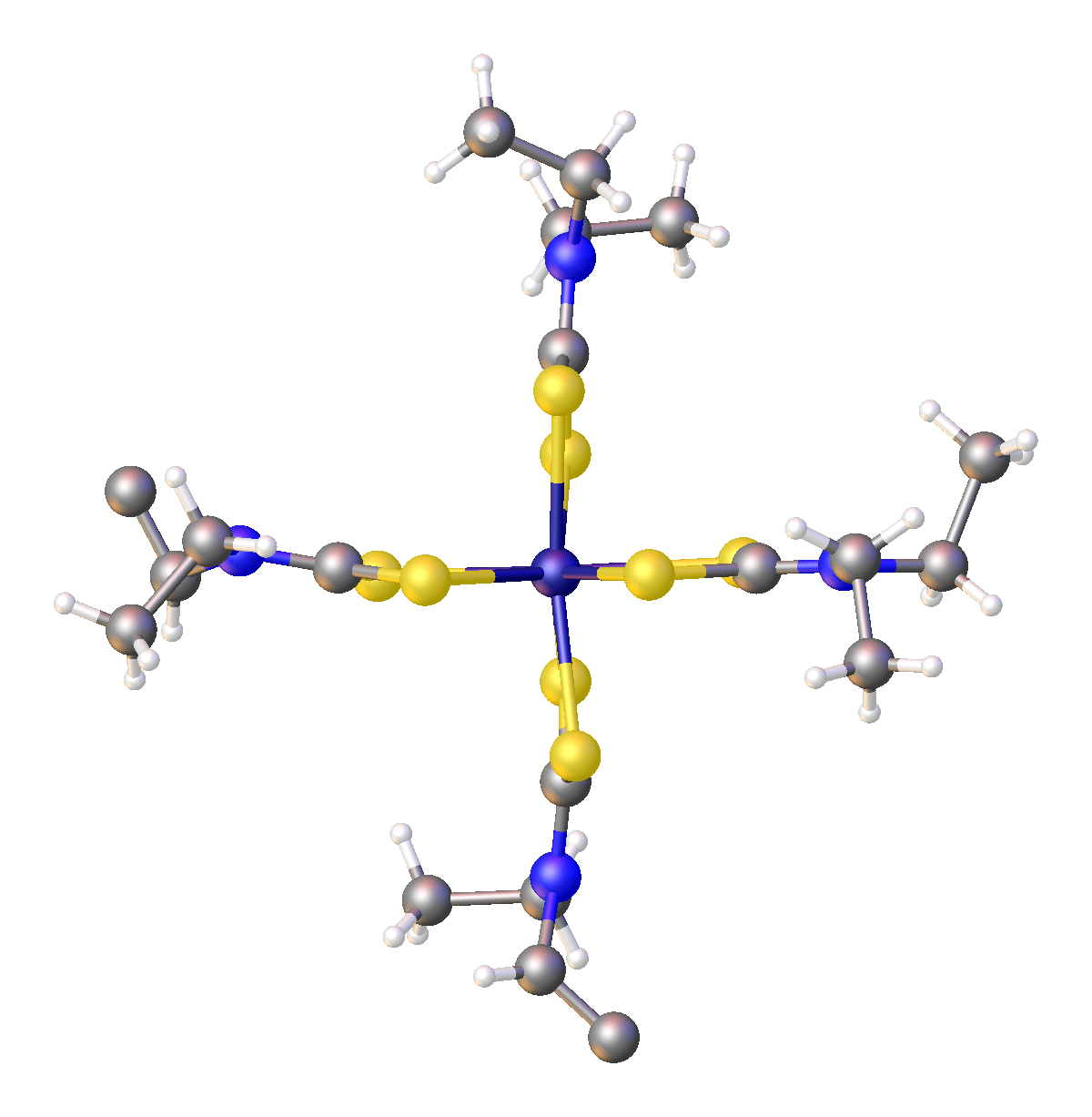 ;Bis complexes
* nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), palladium bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), platinum bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), all square-planar complexes
* copper bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), a square-planar complex
;Tris complexes
* vanadium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* chromium tris(diethylditiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* manganese tris(dimthylthtiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), ruthenium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), osmium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
* cobalt tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), rhodium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), iridium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
;Tetrakis complexes
* titanium tetrakis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
* molybdenum tetrakis(diethyldithiocarbamate)
;Dimetallic complexes
* iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), pentacoordinate Fe dimer
*
;Bis complexes
* nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), palladium bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), platinum bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), all square-planar complexes
* copper bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), a square-planar complex
;Tris complexes
* vanadium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* chromium tris(diethylditiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* manganese tris(dimthylthtiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), ruthenium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), osmium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
* cobalt tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), rhodium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), iridium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
;Tetrakis complexes
* titanium tetrakis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
* molybdenum tetrakis(diethyldithiocarbamate)
;Dimetallic complexes
* iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), pentacoordinate Fe dimer
*
coordination complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ' ...
es containing one or more dithiocarbamate
In organic chemistry, a dithiocarbamate is a chemical compound with the general formula . It contains the functional group with the Chemical structure, structure . It is the analog of a carbamate in which both oxygen atoms are replaced by sulfur ...
ligand, which are typically abbreviated R2dtc−. Many complexes are known. Several homoleptic derivatives have the formula M(R2dtc)n where n = 2 and 3.
Ligand characteristics
Dithiocarbamate anions are bidentate ligands that are classified as L-X ligand in the Covalent bond classification method. In the usual electron counting method, they are three-electron ligands. With respect toHSAB theory
HSAB is an acronym for "hard and soft (Lewis) acids and bases". HSAB is widely used in chemistry for explaining the stability of compounds, reaction mechanisms and pathways. It assigns the terms 'hard' or 'soft', and 'acid' or 'base' to chemical ...
, they are classified as soft.
Because of the pi-donor properties of the amino substituent, the two sulfur centers show enhanced basicity relative to dithiocarboxylates. This situation is represented by the zwitterionic resonance structure that depicts a positive charge on N and negative charges on both sulfurs. This N to C pi-bonding results in partial double bond character for the C-N bond. Consequently, barriers to rotational about this bond are elevated. Another consequence of their high basicity, dithiocarbamates often stabilize complexes in some uncharacteristically high oxidation state (e.g., Fe(IV), Co(IV), Ni(III), Cu(III)).
Dithiocarbamate salts are easily synthesized. Many primary and secondary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s react with carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula and structure . It is also considered as the anhydride of thiocarbonic acid. It is a colorless, flammable, neurotoxic liquid that is used as ...
and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
to form dithiocarbamate salts:
:R2NH + CS2 + NaOH → R2NCS2−Na+ + H2O
A wide variety of secondary amines give the corresponding dtc ligand. Popular amines include dimethylamine
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around ...
(Me2NH), diethylamine
Diethylamine is an organic compound with the formula . It is classified as a secondary amine. It is a flammable, volatile weakly alkaline liquid that is miscible with most solvents. It is a colorless liquid, but commercial samples often appear br ...
(Et2NH), and pyrrolidine
Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)4NH. It is a cyclic secondary amine, also classified as a saturated heterocycle. It is a colourless liquid that is miscible with water and most ...
((CH2)4NH). Complexes of , derived from the parent dithiocarbamic acid have been reported.
Related ligands
Dithiocarbamates are classified as derivatives of dithiocarbamic acid. Their properties as ligands resemble the conjugate bases of many related "1,1-dithioacids": * Diorganothiophosphates, (RO)2PS2− * Dithiocarboxylates, RCS2− *Xanthate
A xanthate is a Salt (chemistry), salt or ester of a xanthic acid. The formula of the salt of xanthic acid is (where R is organyl group and M is usually Sodium, Na or Potassium, K). Xanthate also refers to the anion . The formula of a xanthic a ...
s, ROCS2−
*Thioxanthate In chemistry, a thioxanthate is an organosulfur compound with the formula RSCS2X. When X is an alkali metal, the thioxanthate is a salt. When X is a transition metal, the thioxanthate is a ligand, and when X is an organic group, the compounds are ...
s, RSCS2−
Synthetic methods
Commonly, metal dithiocarbamates are prepared bysalt metathesis reaction
A salt metathesis reaction (also called a double displacement reaction, double replacement reaction, or double decomposition) is a type of chemical reaction in which two ionic compounds in aqueous solution exchange their component ions to form two ...
s using alkali metal dithiocarbamates:
:NiCl2 + 2NaS2CNMe2 → Ni(S2CNMe2)2 + 2NaCl
In some cases, the dithiocarbamate serves as a reductant, followed by its complexation.
A complementary method entails oxidative addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidat ...
of thiuram disulfide
Thiuram disulfides are a class of organosulfur compounds with the formula (R2NCSS)2. Many examples are known, but popular ones include R = Me and R = Et. They are disulfides obtained by oxidation of the dithiocarbamates. These compounds are use ...
s to low-valent metal complexes:
:Mo(CO)6 + 2 2CNMe2sub>2 → Mo(S2CNMe2)4 + 6CO
Metal amido complexes, such as tetrakis(dimethylamido)titanium, react with carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula and structure . It is also considered as the anhydride of thiocarbonic acid. It is a colorless, flammable, neurotoxic liquid that is used as ...
:
:Ti(NMe2)4 + 4CS2 → Ti(S2CNMe2)4
Homoleptic complexes
 ;Bis complexes
* nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), palladium bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), platinum bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), all square-planar complexes
* copper bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), a square-planar complex
;Tris complexes
* vanadium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* chromium tris(diethylditiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* manganese tris(dimthylthtiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), ruthenium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), osmium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
* cobalt tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), rhodium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), iridium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
;Tetrakis complexes
* titanium tetrakis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
* molybdenum tetrakis(diethyldithiocarbamate)
;Dimetallic complexes
* iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), pentacoordinate Fe dimer
*
;Bis complexes
* nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), palladium bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), platinum bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate), all square-planar complexes
* copper bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), a square-planar complex
;Tris complexes
* vanadium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* chromium tris(diethylditiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* manganese tris(dimthylthtiocarbamate), an octahedral complex
* iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), ruthenium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), osmium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
* cobalt tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), rhodium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), iridium tris(diethyldithiocarbamate), all octahedral complexes
;Tetrakis complexes
* titanium tetrakis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
* molybdenum tetrakis(diethyldithiocarbamate)
;Dimetallic complexes
* iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate), pentacoordinate Fe dimer
* zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a coordination complex of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide, the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, and other industrial applications.
Applications
Known as ziram ...
, pentacoordinate Zn dimer
* dicobalt pentakis(diethyldithiocarbamate) cation, with a pair of octahedral Co(III) centers
* diruthenium pentakis(diethyldithiocarbamate) cation, with a pair of octahedral Ru(III) centers, two isomers
Reactions
Dithiocarbamate complexes do not undergo characteristic reactions. They can be removed from complexes by oxidation, as illustrated by the iodination of the iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate): : They degrade to metal sulfides upon heating.Applications
Dtc complexes find several applications: *herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
s in the form of the iron and zinc derivatives Ferbam
Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with dimethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNMe2)3 (Me = methyl). It is marketed as a fungicide.
Synthesis, structure, bonding
Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s are typi ...
and Zineb
Zineb is the chemical compound with the formula n. Structurally, it is classified as a coordination polymer and a dithiocarbamate complex. This pale yellow solid is used as fungicide.
Production and applications
It is produced by treating ethyle ...
, respectively
* vulcanization accelerators, zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a coordination complex of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide, the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, and other industrial applications.
Applications
Known as ziram ...
.
* medicine, iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) as a nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
scavenger.
* lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, ...
s. Metal thiocarbamates are also used in metal-to-metal lubrication proposes, mainly as an anti-oxidation or anti-extreme pressure (EP) additive. 1-2% of such compounds can be added to internal combustion engine lubricant to increase extreme pressure performance in high operational temperatures.
References
{{Coordination complexes Dithiocarbamates