|
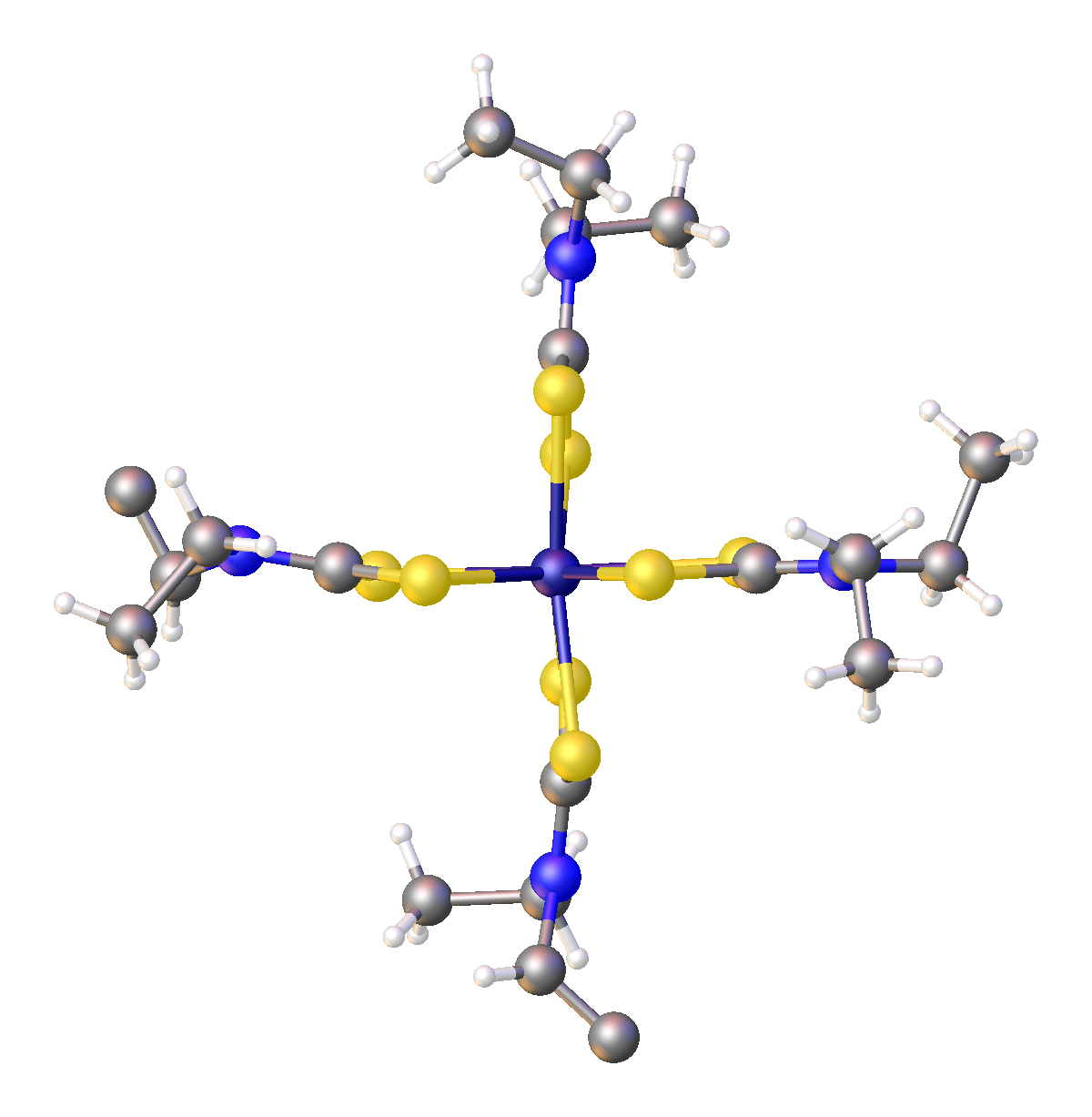
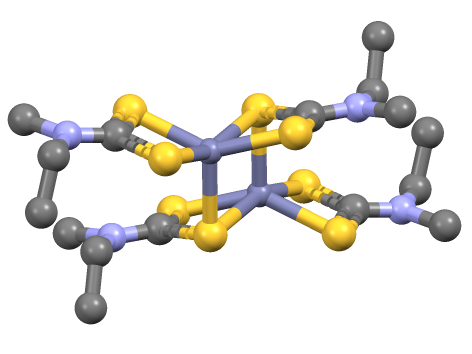
Iron Bis(diethyldithiocarbamate)
Iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) is a coordination complex with the formula where Et = ethyl (). A red solid, iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) is representative of several ferrous dithiocarbamates with diverse substituents in place of ethyl. In terms of structure, the species is dimeric, consisting of a pair of pentacoordinate iron(II) centers. It is structurally related to zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate). Reactions The complex reacts with a variety of reagents with concomitant formation of mono-iron derivatives. It adds 9,10-phenanthroline (phen) to give the blue-octahedral complex . 3,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dithiete reacts to give the Fe(IV) dithiolene complex . Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide add to give the nitrosyl complex and the carbonyl complex {{chem2, Fe(S2CNEt2)2(CO)2, respectively. Related compounds * Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) References Iron compounds Iron shows the characteristic chemical properties of the transition metals, namely the abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing chemical compound, compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A Ligand#Polydentate and polyhapto ligand motifs and nomenclature, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Group
In organic chemistry, an ethyl group (abbr. Et) is an alkyl substituent with the formula , derived from ethane (). ''Ethyl'' is used in the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...'s nomenclature of organic chemistry for a saturated two-carbon moiety in a molecule, while the prefix "''eth-''" is used to indicate the presence of two carbon atoms in the molecule. Ethylation Ethylation is the formation of a compound by introduction of the ethyl group. The most widely practiced example of this reaction is the ethylation of benzene with ethylene to yield ethylbenzene, a precursor to styrene, which is a precursor to polystyrene. Approximately 24.7 million tons of ethylbenzene were produced in 1999. :: Many ethyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Dithiocarbamate Complexes
193px, Structure of iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate). Transition metal dithiocarbamate complexes are coordination complexes containing one or more dithiocarbamate ligand, which are typically abbreviated R2dtc−. Many complexes are known. Several homoleptic derivatives have the formula M(R2dtc)n where n = 2 and 3. Ligand characteristics Dithiocarbamate anions are bidentate ligands that are classified as L-X ligand in the Covalent bond classification method. In the usual electron counting method, they are three-electron ligands. With respect to HSAB theory, they are classified as soft. Because of the pi-donor properties of the amino substituent, the two sulfur centers show enhanced basicity relative to dithiocarboxylates. This situation is represented by the zwitterionic resonance structure that depicts a positive charge on N and negative charges on both sulfurs. This N to C pi-bonding results in partial double bond character for the C-N bond. Consequently, barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a coordination complex of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide, the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, and other industrial applications. Applications Known as ziram in agriculture, it was introduced in the United States in 1960 as a broad-spectrum fungicide. It was used to address scab on apples and pears, leaf curl in peaches, and anthracnose and blight in tomatoes. In 1981, additional uses for ziram were approved, including the prevention of leaf blight and scab on almonds, shot-hole in apricots, brown rot and leaf spot in cherries, and scab and anthracnose in pecans. Ziram also began to be used on residential ornaments as a bird and mammal repellent. As a protectant fungicide, it is active on the plant’s surface where it forms a chemical barrier between the plant and a fungus. A protectant fungicide is not absorbed into the plant and must be applied prior to infection. Ziram can either be direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenanthroline
1,10-Phenanthroline (phen) is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The 1,10 refers to the location of the nitrogen atoms that replace CH's in the hydrocarbon called phenanthrene. Abbreviated "phen", or sometimes "o-phen" for ortho-phenanthroline, it is used as a ligand in coordination chemistry, forming strong complexes with most metal ions.Luman, C.R. and Castellano, F.N. (2003) "Phenanthroline Ligands" in Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II. Elsevier. . It is often sold as the monohydrate. Synthesis Phenanthroline can be prepared by two successive Skraup reactions of glycerol with ''o''-phenylenediamine, catalyzed by sulfuric acid, and an oxidizing agent, traditionally aqueous arsenic acid or nitrobenzene. Dehydration of glycerol gives acrolein which condenses with the amine followed by a cyclization. Reactions Oxidation of 1,10-phenanthroline with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids gives 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dithiete
3,4-Bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dithiete is the organofluorine compound with the formula , a yellow liquid. It is a stable 1,2-dithiete. It arises by the reaction of hexafluoro-2-butyne with molten sulfur. Bonding Being planar with six pi-electrons, the compound is considered to be aromatic. This description is supported by an electron diffraction study, which reveals an elongated C=C distance of 1.40 Å and shortened C-S distances of 1.73 Å. Reactions The compound tends to dimerize at room temperature, but the dimer cracks at higher temperature back to the dithiete. It is used to prepare metal dithiolene complexes. It reacts with low valent metal complexes by oxidative addition Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidat ...: : : References {{DEFAULTSORT:Bis(trifluoromethyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithiolene Complex
Dithiolene metal complexes are complexes containing 1,2-dithiolene ligands. 1,2-Dithiolene ligands, a particular case of 1,2-dichalcogenolene species along with 1,2-diselenolene derivatives, are unsaturated bidentate ligand wherein the two donor atoms are sulfur. 1,2-Dithiolene metal complexes are often referred to as "metal dithiolenes", "metallodithiolenes" or "dithiolene complexes". Most molybdenum- and tungsten-containing proteins have dithiolene-like moieties at their active sites, which feature the so-called molybdopterin cofactor bound to the Mo or W. Dithiolene metal complexes have been studied since the 1960s when they were first popularized by Gerhard N. Schrauzer and Volker P. Mayweg, who prepared nickel bis(stilbene-1,2-dithiolate) () by the reaction of nickel sulfide and diphenylacetylene. The structural, spectroscopic, and electrochemical properties of many related complexes have been described. Structure Dithiolene metal complexes can be found in coordination co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. It was proclaimed the " Molecule of the Year" in 1992. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide's role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Its impact extends beyond biology, with applications in medicine, such as the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosyl Complex
Sodium nitroprusside, a medicinally significant metal nitrosyl-pentacyanoferrate (Fe-III) compound, used to treat complexes that contain nitric oxide">hypertension. Metal nitrosyl complexes are complex (chemistry)">complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal. Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand. Bonding and structure Most complexes containing the NO ligand can be viewed as derivatives of the nitrosyl cation, NO+. The nitrosyl cation is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide, thus the bonding between a nitrosyl ligand and a metal follows the same principles as the bonding in carbonyl complexes. The nitrosyl cation serves as a two-electron donor to the metal and accepts electrons from the metal via back-bonding. The compounds Co(NO)(CO)3 and Ni(CO)4 illustrate the analogy between NO+ and CO. In an electron-counting sense, two linear NO ligands are equivalent to three CO groups. This trend is illustrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Complex
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such as aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid), as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, such that carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides, chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Tris(diethyldithiocarbamate)
Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with diethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (Et = ethyl). It is a black solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Synthesis, structure, bonding Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s are typically are prepared by salt metathesis reactions. Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is an octahedral coordination complex of iron(III) with idealized D3 symmetry. The phenomenon of spin crossover (SCO) was first reported in 1931 by Cambi ''et al.'' who observed anomalous magnetic behavior for the tris(N,N-dialkyldithiocarbamatoiron(III) complexes. The magnetism of these complexes are sensitive to the nature of the amine substituents as well as to temperature. This behavior is consistent with an equilibrium between two or more spin states. In the case of Fe(Et2dtc)3, X-ray crystallography reveals that the Fe-S bonds are 231 pm at 79K but 356 pm at 297 K. These data indicate a low-spin configuration at low temperatures a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |