Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3 or Global Goal 3), regarding "
Good Health and
Well-being
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
", is one of the 17
Sustainable Development Goals established by the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
in 2015. The official wording is: "To ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages''.''"
[United Nations (2015) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 25th September 2015, Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/70/1
The targets of SDG 3 cover and focus on various aspects of healthy life and healthy lifestyle. Progress towards the targets is measured using twenty-one indicators.
SDG 3 has 13 targets and 28 indicators to measure progress toward targets. The first nine targets are "outcome targets". Those are: reduction of
maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
; ending all preventable
deaths under five years of age; fight
communicable diseases; ensure reduction of mortality from
non-communicable diseases
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, most heart diseases, most cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, oste ...
and promote
mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental hea ...
; prevent and treat
substance abuse; reduce
road injuries and deaths; grant universal access to
sexual and reproductive care,
family planning and education; achieve
universal health coverage; and reduce illnesses and deaths from
hazardous chemicals and
pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
. The four "means to achieving" SDG 3 targets are: implement the
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control
The World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) is a treaty adopted by the 56th World Health Assembly held in Geneva, Switzerland on 21 May 2003. It became the first World Health Organization treaty adopted under ...
; support research, development and universal access to affordable
vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. s and medicines; increase health financing and support
health workforce in
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
; and improve early warning systems for global health risks.
[Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina (2018)]
Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
" (SDG 3) ''SDG-Tracker.org, website''
SDG 3 aims to achieve
universal health coverage, that seeks equitable access of healthcare services to all men and women. It proposes to end the preventable death of newborns, infants and children under five (
child mortality) and end
epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
s.
Good health is essential to
sustainable development and the
2030 Agenda
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
. It focuses on broader
economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
and
social inequalities
Social inequality occurs when resources in a given society are distributed unevenly, typically through norms of allocation, that engender specific patterns along lines of socially defined categories of persons. It posses and creates gender c ...
,
urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
,
climate crisis
''Climate crisis'' is a term describing global warming and climate change, and their impacts. The term and the alternative term ''climate emergency'' have been used to describe the threat of global warming to humanity (and their planet), and to u ...
, continuing burden of HIV and other
infectious diseases, not forgetting emerging challenges such as
non-communicable disease
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, most heart diseases, most cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, ...
s.
Considering the global pandemic of
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly ...
, there is a need to give significant attention towards the realization of good health and well being on a global scale.
Background

Ensuring that every child survives and thrives depends on a combination of high-impact interventions – including quality
antenatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
, delivery and
postnatal
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal perio ...
care for mothers and their newborns, prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV,
immunisation to protect children from infectious diseases and access to adequate and nutritious food.
The
UNDP
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
reports that "every 2 seconds, someone aged 30 to 70 years dies prematurely from noncommunicable diseases -
cardiovascular disease,
chronic respiratory disease,
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
or
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
."
According to statistics, globally, "2.4 million children died in the first month of life in 2019 – approximately 6,700
neonatal deaths every day – with about a third of all neonatal deaths occurring within the first day after birth, and close to three-quarters occurring within the first week of life".
Lack of access to quality healthcare is one of the major factors behind the figures and regional data revealing that
neonatal mortality
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion o ...
was highest in
sub-Saharan Africa and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
which post 27 and 25 deaths per 1,000 live births, respectively, in 2019.
Significant steps have been made in increasing
life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
and reducing some of the common causes of
child and
maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
. Between 2000 and 2016, the worldwide under-five mortality rate decreased by 47% (from 78 deaths per 1,000 live births to 41 deaths per 1,000 live births).
Still, the number of children dying under age five is extremely high: 5.6 million in 2016 alone.
New-borns account for a growing number of these deaths, and poorer children are at the greatest risk of under-five
mortality due to a number of factors.
SDG 3 aims to reduce under-five mortality to as low as 25 per 1,000 live births. But if current trends continue, more than 60 countries will miss the SDG
neonatal mortality target for 2030. About half of these countries would not reach the target even by 2050.
Between 2000 and 2016, the worldwide under-five death rate decreased by 47 percent (from 78 deaths per 1,000 live births to 41 deaths per 1,000 live births).
As mentioned earlier, the number of children dying under age five is extremely high: 5.6 million in 2016 alone.
Reports by
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to ...
,
WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
, the
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
and
UNDESA
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Econ ...
indicate that sixty million children under five will die between 2017 and 2030 despite the fact that the number of children dying in 2016 was low (5.6m) compared to 2000 (9.9m). SDG 3 also aims to reduce maternal mortality to less than 70 deaths per 100,000 live births.
Though the maternal mortality ratio declined by 37 per cent between 2000 and 2015, there were approximately 303,000 maternal deaths worldwide in 2015, most from preventable causes.
Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to clean water and sanitation and on reducing
malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
,
tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
,
polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe s ...
and the spread of
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
.
Advances in technologies such as the internet have enabled the digitization of health records and easier access to online medical resources for doctors and health workers, leading to improvements in patient treatment and outcomes.
Targets, indicators, and progress
The UN has defined 13 Targets and 28 Indicators for SDG 3. The main data source and maps for the indicators for SDG 3 come from
Our World in Data's SDG Tracker.
[Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina (2018)]
Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
" (SDG 3) ''SDG-Tracker.org, website'' The targets of SDG 3 cover a wide range of issues including reduction of maternal mortality (Target 3.1), ending all
preventable deaths
Preventable causes of death are causes of death related to risk factors which could have been avoided. The World Health Organization has traditionally classified death according to the primary type of disease or injury. However, causes of deat ...
under five years of age (Target 3.2), fight
communicable diseases (Target 3.3), ensure a reduction of mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote
mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental hea ...
(Target 3.4), prevent and treat
substance abuse (Target 3.5), reduce road injuries and deaths (Target 3.6), grant universal access to
sexual and reproductive health
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, healthcare, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual wellbeing during all stages of their life.
The term can also be further de ...
care,
family planning and education (Target 3.7), achieve
universal health coverage (Target 3.8), reduce illnesses and deaths from
hazardous chemicals and
pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
(Target 3.9), implement the
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control
The World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) is a treaty adopted by the 56th World Health Assembly held in Geneva, Switzerland on 21 May 2003. It became the first World Health Organization treaty adopted under ...
(Target 3.a), support research, development and universal access to affordable
vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. s and medicines (Target 3.b), increase health financing and support
health workforce in developing countries (Target 3.c) and improve
early warning system
An early warning system is a warning system that can be implemented as a chain of information communication systems and comprises sensors, event detection and decision subsystems for early identification of hazards. They work together to forec ...
s for global health risks (Target 3.d).
Target 3.1: Reduce maternal mortality

The full text of Target 3.1 is: "By 2030, reduce the global
maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births".
[United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/71/313
* Indicator 3.1.1:
Maternal mortality ratio
The maternal mortality ratio is a key performance indicator (KPI) for efforts to improve the health and safety of mothers before, during, and after childbirth per country worldwide. Often referred to as MMR, it is the annual number of female death ...
. The maternal mortality ratio refers to the number of women who die from pregnancy-related causes while pregnant or within 42 days of pregnancy termination per 100,000 live births.
* Indicator 3.1.2: Percentage of births attended by personnel trained to give the necessary supervision, care, and advice to women during pregnancy, labour, and the postpartum period; to conduct deliveries on their own; and to care for newborns
The unequal status of women and girls, lack of decision-making powers, knowledge and finances remain underlying causes for the inability or delay in seeking
health care which ends up increasing maternal mortality rates.
[United Nations (2017]
HLPF Thematic Review of SDG3
New York,
Target 3.1 aims to reduce maternal mortality to less than 70 deaths per 100,000 live births.
Though the maternal mortality ratio declined by 37 percent between 2000 and 2015, there were approximately 303,000 maternal deaths worldwide in 2015, most from preventable causes.
In 2015,
maternal health
Maternal health is the health of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. In most cases, maternal health encompasses the health care dimensions of family planning, preconception, prenatal, and postnatal care in order to ens ...
conditions were also the leading cause of death among girls aged 15–19.
Data for girls of greatest concern – those aged between 10 and 14 years is currently unavailable. Key strategies for meeting SDG 3 will be to reduce
adolescent pregnancy (which is strongly linked to
gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
), provide better data for all women and girls, and achieve universal coverage of skilled birth attendants.
Target 3.2: End all preventable deaths under five years of age

The full text of Target 3.2 is: "By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age, with all countries aiming to reduce
neonatal mortality
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion o ...
to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under‑5 mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births."
* Indicator 3.2.1:
Under-5 mortality rate. The under-5 mortality rate measures the number of children per 1,000 live births who die before their fifth birthday.
* Indicator 3.2.2: Neonatal mortality rate. The neonatal mortality rate is defined as the share of newborns per 1,000 live births in a given year who die before reaching 28 days of age.
Globally, the risk for children dying before age five was reduced by 44 per cent since 2000, reaching 43 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2015. Still, a large number of preventable deaths remain, with about 16,000 children under the age of five dying every day in 2015.
The neonatal mortality rate declined from 31 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2000 to 19 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2015. Though neonatal mortality is decreasing, the proportion of the global under-five mortality is increasing, signalling a need to ramp up focus on antenatal care programs.
The
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
in 2020 results in fewer women and their babies having access to lifesaving care.
This is because many healthcare facilities are even more short-staffed and under-equipped than usual. This can negatively impact the under-five mortality rate as well as the neonatal mortality rate.
[BMGF (2020]
Covid-19 A Global Perspective - 2020 Goalkeepers Report
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Seattle, USA
Target 3.3: Fight communicable diseases

The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of
AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and
neglected tropical diseases and combat
hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases."
* Indicator 3.3.1: Number of new HIV infections per 1,000 uninfected population
* Indicator 3.3.2:
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
per 100,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.3:
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
incidence per 1,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.4:
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
incidence per 100,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.5: Number of people requiring interventions against neglected
tropical disease
Tropical diseases are diseases that are prevalent in or unique to tropical and subtropical regions. The diseases are less prevalent in temperate climates, due in part to the occurrence of a cold season, which controls the insect population by for ...
Target 3.3 proposes to end the preventable death of newborns and children under five and to end
epidemics such as
AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and
water-borne diseases
Waterborne diseases are conditions (meaning adverse effects on human health, such as death, disability, illness or disorders) caused by pathogenic micro-organisms that are transmitted in water. These diseases can be spread while bathing, washing ...
, for example.

Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to
clean water and sanitation and on reducing malaria, tuberculosis,
polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe s ...
, and the spread of HIV/AIDS. From 2000 to 2016, new HIV infections declined by 66 percent for children under 15 and by 45 percent among adolescents aged 15–19.
However, current trends mean that 1 out of 4 countries still will not meet the SDG target to end AIDS among children under 5, and 3 out of 4 will not meet the target to end AIDS among adolescents.
Overall, AIDS remains the leading cause of death among women aged between 15 and 49 years as approximately 1800 young people being newly infected with HIV every day. This underscores]the importance of ensuring that young people can fully exercise their rights to access
sexual and reproductive health
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, healthcare, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual wellbeing during all stages of their life.
The term can also be further de ...
and HIV information.
In 2015, there were an estimated 10.4 million new Tuberculosis cases (1 million of which were under age 15), corresponding to 142 cases per 100,000 population, the malaria incidence rate was 91 per 1000 persons at risk, representing a 41% decrease globally between while deaths attributed to hepatitis are estimated to be around 1.3 million.
With regards to HIV infections, people living with HIV are at increased risk of death due to
Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19 in the year 2020. Also, disruptions to health services can result in people not getting
antiretroviral therapy (ART), which would result in more deaths.
Target 3.4: Reduce mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote mental health
The full text of Target 3.4 is: "By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from
non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and
well-being
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
."
* Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to
cardiovascular disease,
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
,
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
or
chronic respiratory disease
* Indicator 3.4.2:
Suicide mortality rate
Deaths caused by the four main
NCDs were 17.7 million from cardiovascular diseases, 8.8 million from
cancers
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
, 3.9 million from chronic respiratory diseases, and 1.6 million from
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
. The risk of dying from the four main NCDs between ages 30 and 70 decreased from 23% in 2000 to 19% in 2015
Target 3.5: Prevent and treat substance abuse
The full text of Target 3.5 is: "Strengthen the prevention and treatment of
substance abuse, including
narcotic drug abuse and
harmful use of alcohol."
* Indicator 3.5.1: Coverage of treatment interventions (
pharmacological
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemica ...
,
psychosocial
The psychosocial approach looks at individuals in the context of the combined influence that psychological factors and the surrounding social environment have on their physical and mental wellness and their ability to function. This approach is ...
and
rehabilitation and aftercare services) for substance use disorders
* Indicator 3.5.2: Harmful use of alcohol, defined according to the national context as alcohol
per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
consumption (aged 15 years and older) within a calendar year in litres of pure alcohol.
In 2016, worldwide consumption of alcohol was projected to be 6.4 litres per person aged 15 and older. Consumption is increasing in the Western
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
and
South-East Asia Regions, while remaining relatively stable in others. The available data is inadequate and much further work is needed to improve the measurement of treatment coverage for alcohol and drug use disorders.

Target 3.6: Reduce road injuries and deaths
The full text of Target 3.6 is: "By 2020, halve (50% less) the number of global deaths and injuries from
road traffic accidents."
Target 3.6 has only one Indicator: Indicator 3.6.1 is the Death rate due to road traffic injuries.
The need for improvements in safer infrastructure and government regulation continues. In countries with great success, such as Sweden that boasts a 66% reduction in injury and deaths from 1990 to 2015, tough government regulation has been key.
In November 2009, at the request of the
UN General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Cur ...
, the first Global Ministerial Conference on
road safety
Road traffic safety refers to the methods and measures used to prevent road users from being killed or seriously injured. Typical road users include pedestrians, cyclists, motorists, vehicle passengers, horse riders, and passengers of on-roa ...
was hosted by the
Government of the Russian Federation
The Government of Russia exercises executive power in the Russian Federation. The members of the government are the prime minister, the deputy prime ministers, and the federal ministers. It has its legal basis in the Constitution of the Russia ...
. Following the success of the conference, the
Decade of Action for Road Safety 2011-2020 declared in March 2010 by the United Nations General Assembly. In February 2020, the third global ministerial conference on Road Safety was held in
Stockholm, Sweden. The outcome of the conference was the Stockholm Declaration that set a global target of reducing road
traffic deaths and
injuries
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or o ...
by 50% by 2030. In August 2020, the United Nations ratified the Stockholm Declaration declaring 2021-2030 the Second Decade of action for Road Safety.

Target 3.7: Universal access to sexual and reproductive care, family planning and education
The full text of Target 3.7 is: "By 2030, ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services, including for
family planning, information and education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programs."
* Indicator 3.7.1: Percentage of married women ages 15–49 years whose need for family planning is satisfied with modern methods of contraception.
* Indicator 3.7.2: Adolescent birth rate (aged 10–14 years; aged 15–19 years) per 1,000 women in that age group.
Half of the women in developing countries have received the health care they need, and the need for family planning is increasing exponentially as the population grows. While needs are being addressed gradually, more than 225 million women have an unmet need for
contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
. There is a slight increase in the proportion of women of reproductive age who were married or in-union who had access to modern family planning methods, from 74.5% in 2000 to 76.7% in 2017.
In 2017, an estimated 13 million births will be to girls under age 20 with almost 1.8 billion adolescents and youth globally, investing in their health and well-being is essential to achieving the 2030 agenda.
In West Africa, the number of women using contraceptives more than doubled between 2011 and 2020.
Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage
The full text of Target 3.8 is: "Achieve
universal health coverage, including
financial risk protection, access to quality
essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable
essential medicines
Essential medicines, as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), are the medicines that "satisfy the priority health care needs of the population". These are the medications to which people should have access at all times in sufficient a ...
and vaccines for all."
* Indicator 3.8.1: Coverage of essential health services.
* Indicator 3.8.2: Proportion of population with large household expenditures on health as a share of total household expenditure or income
Through the lens of leaving no one behind, Universal Health Coverage (UHC) includes migrants and
refugees, many of whom may not have legal status or are unaccounted, in financial risk protection schemes and access to equitable health services.
Primary health care
Primary health care, or PHC, refers to "essential health care" that is based on scientifically sound and socially acceptable methods and technology. This makes universal health care accessible to all individuals and families in a community. PHC in ...
(PHC) is the most important pathway to achieve universal health coverage.
This because it can address more than 80 percent of a person's health needs and is accessible and affordable. In 2020, the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
resulted in a reduction in the "Universal Health Coverage Effective Coverage Index" (an index which assesses whether people in a country have access to essential health services).
Target 3.9: Reduce illnesses and deaths from hazardous chemicals and pollution
The full text of Target 3.9 is: "By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination."
* Indicator 3.9.1: Mortality rate attributed to the household (indoor) and ambient (outdoor) air pollution.
* Indicator 3.9.2: Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, sanitation, and lack of hygiene.
* Indicator 3.9.3: Mortality rate attributed to unintentional
poisoning
A poison can be any substance that is harmful to the body. It can be swallowed, inhaled, injected or absorbed through the skin. Poisoning is the harmful effect that occurs when too much of that substance has been taken. Poisoning is not to ...
.
Household air pollution is estimated to cause half of all pneumonia deaths among children under age five. The global mortality rate from unintentional poisonings decreased by 33% between the years 2000 and 2015 but still causes 108,000 deaths annually.

Target 3.a: Implement the WHO framework convention on tobacco control
The full text of Target 3.a is: "Strengthen the implementation of the
World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries, as appropriate."
Target 3.a has only one Indicator: Indicator 3.a.1 is the "age-standardized
prevalence of current tobacco use among persons aged 15 years and older".
The
WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
Framework Convention on Tobacco Control has been ratified by 180 Parties representing 90% of the global population. More than 80% of Parties have either adopted new or strengthened their existing tobacco control laws and regulations.
In 2019 the global average value for the "age-standardized smoking prevalence among ages 15 and older" was 17%, down from nearly 25% in 1990, which is a positive development.
The COVID-19 pandemic might accelerate this trend because people might stop buying tobacco if their income drops. Also, people have learned that smokers are more likely to get seriously ill or die from
Coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19, which might cause them to smoke less.
Target 3.b: Support research, development and universal access to affordable vaccines and medicines

The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the
Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health The Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health was adopted by the WTO Ministerial Conference of 2001 in Doha on November 14, 2001. It reaffirmed flexibility of TRIPS member states in circumventing patent rights for better access to es ...
, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the
regarding flexibilities to protect public health, and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all."
* Indicator 3.b.1: Proportion of the target population covered by all vaccines included in their national program.
* Indicator 3.b.2: Total net
official development assistance (ODA) to medical research and basic health sectors.
* Indicator 3.b.3: Proportion of health facilities that have a core set of relevant essential medicines available and affordable on a sustainable basis.
The current landscape of health research and development (R&D) is insufficiently aligned with global health demands and needs. As little as 1% of all funding for health R&D is allocated to diseases that are predominantly incident in developing countries.
SDG 3 aims to achieve universal health coverage, including access to essential medicines and vaccines.
2016 rates for the third dose of the
pertussis vaccine (DTP3) and the first dose of the
measles vaccine
Measles vaccine protects against becoming infected with measles. Nearly all of those who do not develop immunity after a single dose develop it after a second dose. When rate of vaccination within a population is greater than 92%, outbreaks o ...
(MCV1) reached 86 per cent and 85 per cent, respectively. Yet about 20 million children did not receive DTP3 and about 21 million did not receive MCV1.
Around two in five countries will need to accelerate progress in order to reach SDG targets for immunization.
Immunization averts an estimated 2 million-3 million deaths every year. In 2016, global coverage rates for the third dose of the
diphtheria, tetanus-pertussis vaccine (DTP3) and the first dose of measles-containing vaccine (MCV1) reached 86 per cent and 85 per cent, respectively, up from 72 per cent for each in 2000. Despite this increased coverage, about 20 million children did not receive three doses of DTP and about 21 million missed the first dose of MCV.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the gradual progress made in the past years with immunization, faces a huge decline. With highly contagious diseases like
measles, this poses a bigger risk to the world's children.
However, some of the affected countries have already implemented measures to respond and combat this disruption. By combining health campaigns (for vaccines, deworming pills, bed nets, etc.) communities can receive several services all at the same time instead of one by one. This can increase coverage while minimizing exposure during the pandemic.
Another viable route to attain this Target is to accelerate COVID-19 vaccination opportunities to people who are often underserved by community vaccination programmes, for example prisoners. Experts have called for people in prisons to be prioritised for the national COVID-19 vaccination strategy, given their risk profile of underlying chronic conditions, age and living environment.

Target 3.c: Increase health financing and support health workforce in developing countries
The full text of Target 3.c is: "Substantially increase health financing and the recruitment, development, training and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in the least developed countries and small island developing states."
Target 3.c has only one Indicator: Indicator 3.c.1 is the Health worker density and distribution.
The joint
ITU/
WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
initiative "Be Healthy Be Mobile" utilizes mobile technology to help countries combat growing burden of non-
communicable diseases by bringing mobile health services to scale within national
health systems and providing technical expertise on implementing mobile health interventions.

Target 3.d: Improve early warning systems for global health risks
The full text of Target 3.d is: "Strengthen the capacity of all countries, in particular developing countries, for early warning,
risk reduction and management of national and global health risks."
* Indicator 3.d.1:
International Health Regulations
The International Health Regulations (IHR), first adopted by the World Health Assembly in 1969 and last revised in 2005, are a legally binding rules that only apply to the WHO that is an instrument that aims for international collaboration "to pr ...
(IHR) capacity and
health emergency preparedness
* Indicator 3.d.2: Percentage of bloodstream infections due to selected antimicrobial resistant organisms.
The 2016 IHR review process acknowledged the need to include migration and mobile populations in epidemic and
pandemic preparedness and response plans. Pandemic preparedness and
global health security require across the board upscaling of IHR implementation.
Custodian agencies
Custodian agencies are in charge of reporting on the following indicators:
* Indicators 3.1.1, 3.2.1, 3.2.2, 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.5.2, 3.6.1, 3.8.2, 3.9.1, 3.9.2, 3.9.3, 3.b.3, 3.c.1, 3.d.1 and 3.d.2:
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO).
* Indicator 3.1.2:
United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF)
* Indicator 3.3.1:
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS) (, ONUSIDA) is the main advocate for accelerated, comprehensive and coordinated global action on the HIV/ AIDS pandemic.
The mission of UNAIDS is to lead, strengthen and support an ...
* Indicators 3.3.2, 3.3.3, 3.3.4 and 3.3.5:
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to ...
.
* Indicator 3.5.1:
the World Health Organisation and
the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime.
* Indicators 3.7.1 and 3.7.2:
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Ec ...
.
* Indicators 3.8.1 and 3.b.1:
WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
and
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to ...
.
* Indicator 3.b.2:
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Monitoring
An annual report is prepared by the
Secretary-General of the United Nations
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or SG) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
The role of the secretary-g ...
evaluating the progress towards the
Sustainable Development Goals.
[United Nations Economic and Social Council (2020]
Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020 In 2017, the
UN's High Level Political Forum published a thematic review of SDG 3.
Investing in
multi-stakeholder partnerships to remove barriers to equitable health services which are responsive to increasingly diverse population health needs, and to reach those most further behind first is essential for the
2030 Agenda
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
for Sustainable Development. Strong commitment by
UN Member States and the
international community to ensuring good health and
wellbeing
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
is achieved is therefore emphasised.
Challenges
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
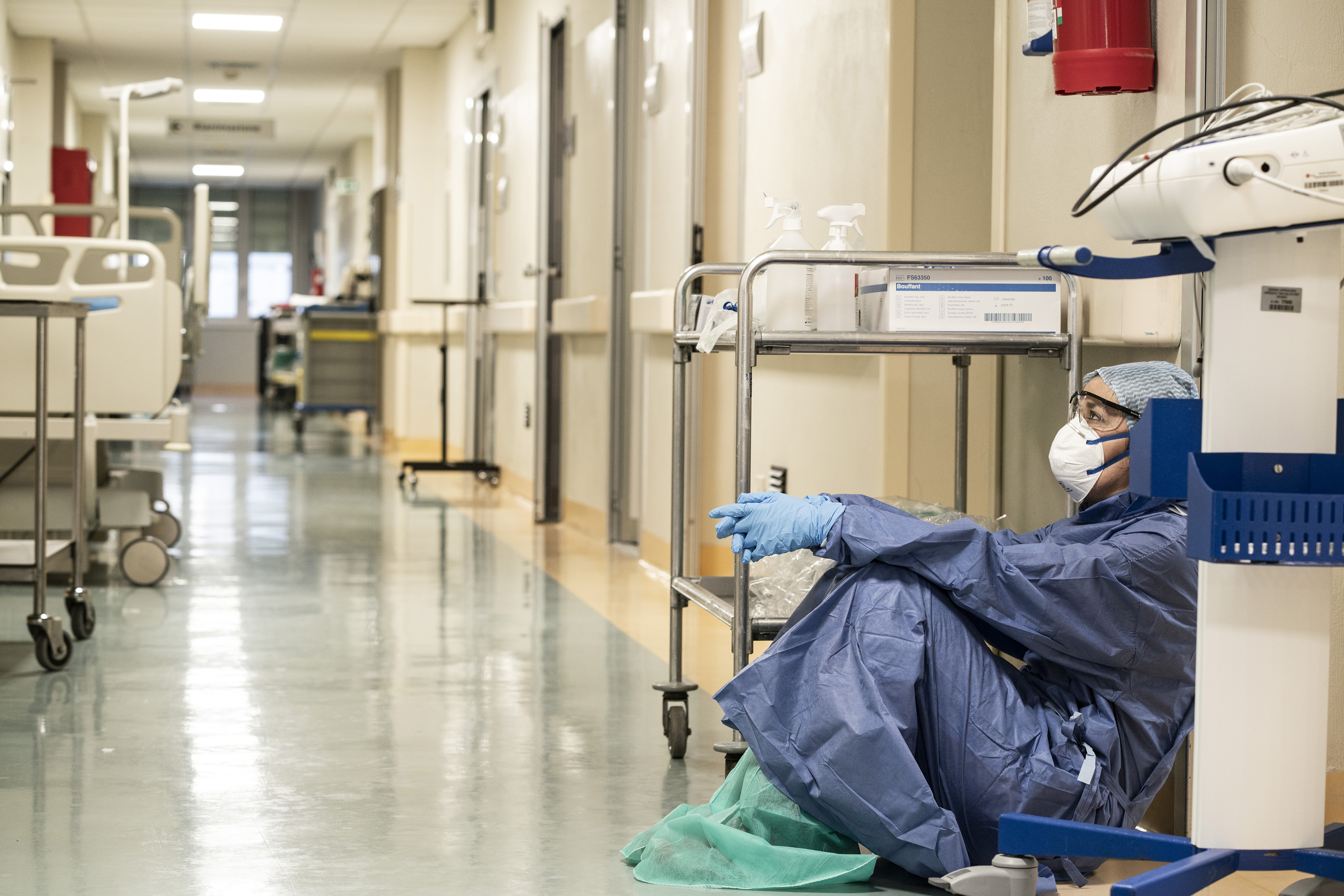

The
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
is a serious threat to the progress of SDG 3 aimed to ensure healthy lives and well-being for all. As the pandemic spread worldwide, the lockdown had over 70 countries putting a hold on various health services such as child vaccination, family planning, and cancer screening. The pandemic has also led to overloading and overcrowding of health facilities and many people became afraid of visiting for fear of being infected.
Most non-COVID-19 diseases have been either neglected or interrupted and healthcare systems are in turn stretched beyond their capacity and capabilities to provide adequate care. This is a great reverse in decades of improvement and has reiterated the need for governments to prioritize issues of healthy living and well-being and work towards the goal of SDG 3.
The governments of countries who already suffer from health workers shortage and other healthcare systems should take advantage of the lessons learnt during this crisis and build up resilience to combat future health pandemics and achieve progress towards Universal Health Coverage.
Links with other SDGs
SDG 3 is interwoven throughout the 2030 Agenda, with its targets directly linking to targets in other goals. Among these are targets of
SDG 2
Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2 or Global Goal 2) aims to achieve "zero hunger". It is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is: "End hunger, achieve food security and im ...
; 2.2 (end all forms of malnutrition),
SDG 4; 4.1 (free, equitable and good-quality secondary education), 4.2 (good-quality early childhood development), 4.7 (knowledge and skills for sustainable development),
SDG 5; 5.2 (eliminate all forms of violence against women and girls in the public and private spheres), 5.3 (eliminate all harmful practices, including
female genital mutilation), 5.6 (universal access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights),
SDG 6; 6.1(access to drinking water), 6.2 (access to sanitation),
SDG 7; 7.1 (access to modern energy services),
SDG 9; 9.5 (enhance scientific research /increase number of R&D workers),
SDG 11
Sustainable Development Goal 11 (SDG 11 or Global Goal 11), titled "sustainable cities and communities", is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. The official mission of SDG 11 is t ...
; 11.6 (air quality and municipal waste),
SDG 13; 13.1 (resilience to natural disasters), and
SDG 16; 16.1 (reduce violence and related death rates).
Organizations
Organizations dedicated to good health and well-being include:
*
The Global Fund to Fight AIDS
* Joint United Nations Program on
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
(
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS) (, ONUSIDA) is the main advocate for accelerated, comprehensive and coordinated global action on the HIV/AIDS pandemic.
The mission of UNAIDS is to lead, strengthen and support an ...
)
*
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
*
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO)
*
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to ...
*
Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA)
*
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention by combining the ...
(UNODC)
*
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
*
UN Women
The United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women, also known as UN Women, is a United Nations entity working for gender equality and the empowerment of women. UN Women advocates for the rights of women and girls, and foc ...
*
Gavi the Vaccine Alliance
*
Vodafone Foundation
*
Doctors Without Borders
Doctor or The Doctor may refer to:
Personal titles
* Doctor (title), the holder of an accredited academic degree
* A medical practitioner, including:
** Physician
** Surgeon
** Dentist
** Veterinary physician
** Optometrist
*Other roles
** ...
Red Cross InternationalMedical IMPACT*
Partners in Health
Partners In Health (PIH) is an international nonprofit public health organization founded in 1987 by Paul Farmer, Ophelia Dahl, Thomas J. White, Todd McCormack, and Jim Yong Kim.
Partners in Health provides healthcare in the poorest areas of de ...
PanAfricareThe Global Health Network
US Based Organizations
In the US there are over seventy-two thousand tax-exempt organizations working on issues related to UN SDG 3, according to data filed with the
Internal Revenue Service –IRS and aggregated by X4Impact. X4Impact, with the support of the Rockefeller Foundation, Ford Foundation, Hewlett Foundation,
and Giving Tech Labs, created a free online interactive too
Health and Well-being in the US This online tool enables users to see health-related indicators nationally and by state, as well as relevant information for over seventy-two thousand tax-exempt organizations in the US working on issues related to UN SDG 3. The nonprofit data in the tool is updated every 15 days while the indicators are updated annually.
References
External links
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 3“Global Goals” Campaign - SDG 3SDG-Track.org - SDG 3UN SDG 3 in the US{{Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainable development
Sustainable Development Goals
 Ensuring that every child survives and thrives depends on a combination of high-impact interventions – including quality
Ensuring that every child survives and thrives depends on a combination of high-impact interventions – including quality  The full text of Target 3.1 is: "By 2030, reduce the global
The full text of Target 3.1 is: "By 2030, reduce the global 
 The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat
The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat  Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to clean water and sanitation and on reducing malaria, tuberculosis,
Similarly, progress has been made on increasing access to clean water and sanitation and on reducing malaria, tuberculosis, 

 The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the
The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the 

 The
The