Subatomic Particle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 All of these have now been discovered by experiments, with the latest being the top quark (1995), tau neutrino (2000), and Higgs boson (2012).
Various extensions of the Standard Model predict the existence of an elementary graviton particle and many other elementary particles, but none have been discovered as of 2021.
All of these have now been discovered by experiments, with the latest being the top quark (1995), tau neutrino (2000), and Higgs boson (2012).
Various extensions of the Standard Model predict the existence of an elementary graviton particle and many other elementary particles, but none have been discovered as of 2021.
University of California: Particle Data Group.
{{Composition Quantum mechanics
physical sciences
Physical science is a branch of natural science that studies non-living systems, in contrast to life science. It in turn has many branches, each referred to as a "physical science", together called the "physical sciences".
Definition
Phy ...
, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, a ...
. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Since protons and ...
, or meson), or an elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. Particles currently thought to be elementary include electrons, the fundamental fermions ( quarks, leptons, ...
, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
, photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they alwa ...
, or muon). Particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
and nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies t ...
study these particles and how they interact.
Experiments show that light could behave like a stream of particles (called photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they alwa ...
s) as well as exhibiting wave-like properties. This led to the concept of wave–particle duality
Wave–particle duality is the concept in quantum mechanics that every particle or quantum entity may be described as either a particle or a wave. It expresses the inability of the classical physics, classical concepts "particle" or "wave" to fu ...
to reflect that quantum-scale behave like both particles and waves; they are sometimes called wavicles to reflect this.
Another concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. The wave–particle duality has been shown to apply not only to photons but to more massive particles as well.
Interactions of particles in the framework of quantum field theory are understood as creation and annihilation of '' quanta'' of corresponding fundamental interactions. This blends particle physics with field theory.
Even among particle physicists
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) a ...
, the exact definition of a particle has diverse descriptions. These professional attempts at the definition of a particle include:
* A particle is a collapsed wave function
* A particle is a quantum excitation of a field
* A particle is an irreducible representation of the Poincaré group
* A particle is an observed thing
Classification
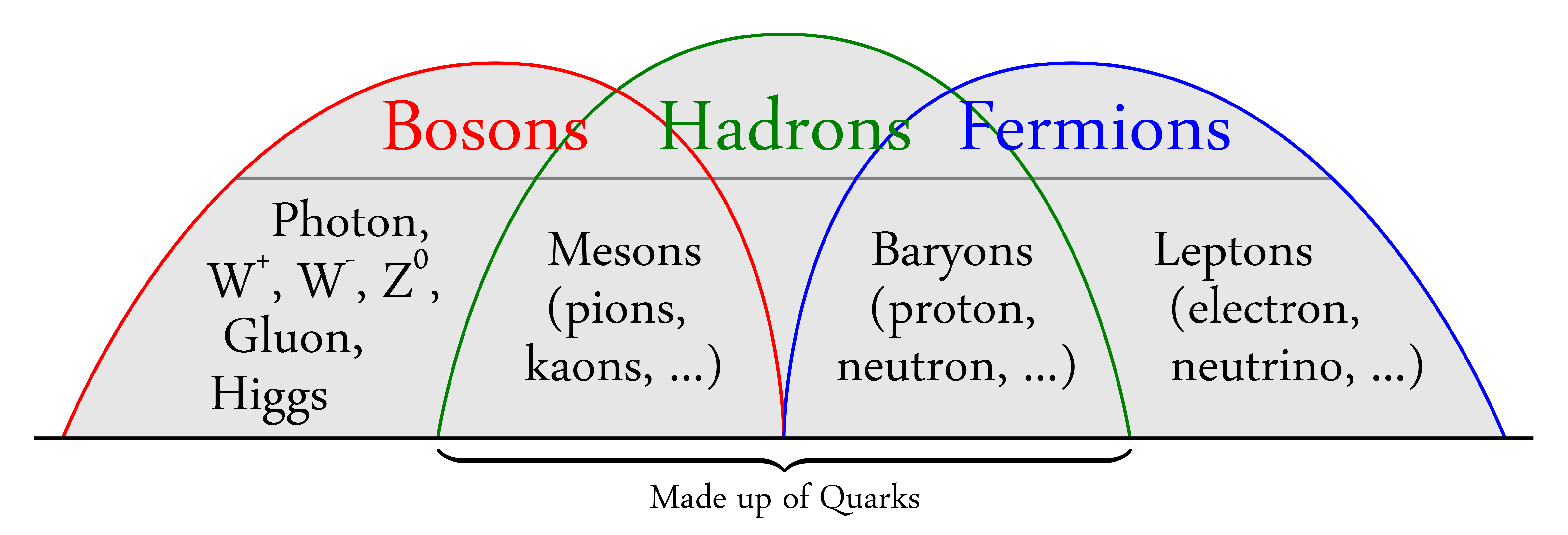
By composition
Subatomic particles are either "elementary", i.e. not made of multiple other particles, or "composite" and made of more than one elementary particle bound together. The elementary particles of the Standard Model are: * Six " flavors" of quarks: up, down, strange,charm
Charm may refer to:
Social science
* Charisma, a person or thing's pronounced ability to attract others
* Superficial charm, flattery, telling people what they want to hear
Science and technology
* Charm quark, a type of elementary particle
* Ch ...
, bottom, and top;
* Six types of leptons: electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
, electron neutrino, muon, muon neutrino, tau, tau neutrino;
* Twelve gauge bosons (force carriers): the photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they alwa ...
of electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
, the three W and Z bosons
In particle physics, the W and Z bosons are vector bosons that are together known as the weak bosons or more generally as the intermediate vector bosons. These elementary particles mediate the weak interaction; the respective symbols are , , an ...
of the weak force, and the eight gluons of the strong force;
* The Higgs boson.
Hadrons
The word hadron comes from Greek and was introduced in 1962 by L.B. Okun. Nearly all composite particles contain multiple quarks (and/or antiquarks) bound together by gluons (with a few exceptions with no quarks, such as positronium andmuonium
Muonium is an exotic atom made up of an antimuon and an electron,
which was discovered in 1960 by Vernon W. Hughes
and is given the chemical symbol Mu. During the muon's lifetime, muonium can undergo chemical reactions. Due to the mass diff ...
). Those containing few (≤ 5) quarks (including antiquarks) are called hadron
In particle physics, a hadron (; grc, ἁδρός, hadrós; "stout, thick") is a composite subatomic particle made of two or more quarks held together by the strong interaction. They are analogous to molecules that are held together by the ...
s.
Due to a property known as color confinement, quarks are never found singly but always occur in hadrons containing multiple quarks. The hadrons are divided by number of quarks (including antiquarks) into the baryons containing an odd number of quarks (almost always 3), of which the proton and neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Since protons and ...
(the two nucleons) are by far the best known; and the mesons containing an even number of quarks (almost always 2, one quark and one antiquark), of which the pions and kaons are the best known.
Except for the proton and neutron, all other hadrons are unstable and decay into other particles in microseconds or less.
A proton is made of two up quarks and one down quark, while the neutron is made of two down quarks and one up quark.
These commonly bind together into an atomic nucleus, e.g. a helium-4
Helium-4 () is a stable isotope of the element helium. It is by far the more abundant of the two naturally occurring isotopes of helium, making up about 99.99986% of the helium on Earth. Its nucleus is identical to an alpha particle, and cons ...
nucleus is composed of two protons and two neutrons.
Most hadrons do not live long enough to bind into nucleus-like composites; those that do (other than the proton and neutron) form exotic nuclei
A hypernucleus is similar to a conventional atomic nucleus, but contains at least one hyperon in addition to the normal protons and neutrons. Hyperons are a category of baryon particles that carry non-zero strangeness quantum number, which is c ...
.

By statistics
Any subatomic particle, like any particle in thethree-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informa ...
that obeys the laws
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vari ...
of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
, can be either a boson (with integer spin) or a fermion (with odd half-integer spin).
In the Standard Model, all the elementary fermions have spin 1/2, and are divided into the quarks
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All common ...
which carry color charge and therefore feel the strong interaction, and the leptons
In particle physics, a lepton is an elementary particle of half-integer spin (spin ) that does not undergo strong interactions. Two main classes of leptons exist: charged leptons (also known as the electron-like leptons or muons), and neutra ...
which do not.
The elementary bosons comprise the gauge bosons
In particle physics, a gauge boson is a bosonic elementary particle that acts as the force carrier for elementary fermions. Elementary particles, whose interactions are described by a gauge theory, interact with each other by the exchange of gauge ...
(photon, W and Z, gluons) with spin 1, while the Higgs boson is the only elementary particle with spin zero.
The hypothetical graviton is required theoretically to have spin 2, but is not part of the Standard Model. Some extensions such as supersymmetry predict additional elementary particles with spin 3/2, but none have been discovered as of 2021.
Due to the laws for spin of composite particles, the baryons (3 quarks) have spin either 1/2 or 3/2, and are therefore fermions; the mesons (2 quarks) have integer spin of either 0 or 1, and are therefore bosons.
By mass
Inspecial relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The law ...
, the energy of a particle at rest equals its mass times the speed of light squared, ''E'' = ''mc''2. That is, mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
can be expressed in terms of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of ...
and vice versa. If a particle has a frame of reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system whose origin, orientation, and scale are specified by a set of reference points― geometric points whose position is identified both math ...
in which it lies at rest, then it has a positive rest mass and is referred to as ''massive''.
All composite particles are massive. Baryons (meaning "heavy") tend to have greater mass than mesons (meaning "intermediate"), which in turn tend to be heavier than leptons (meaning "lightweight"), but the heaviest lepton (the tau particle
The tau (), also called the tau lepton, tau particle, tauon or tau electron, is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with negative electric charge and a spin of . Like the electron, the muon, and the three neutrinos, the tau is a l ...
) is heavier than the two lightest flavours of baryons ( nucleons). It is also certain that any particle with an electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons res ...
is massive.
When originally defined in the 1950s, the terms baryons, mesons and leptons referred to masses; however, after the quark model became accepted in the 1970s, it was recognised that baryons are composites of three quarks, mesons are composites of one quark and one antiquark, while leptons are elementary and are defined as the elementary fermions with no color charge.
All massless particles (particles whose invariant mass is zero) are elementary. These include the photon and gluon, although the latter cannot be isolated.
By decay
Most subatomic particles are not stable. All leptons, as well as baryons decay by either the strong force or weak force (except for the proton). Protons are not known to decay, although whether they are "truly" stable is unknown, as some very important Grand Unified Theories (GUTs) actually require it. The μ and τ muons, as well as their antiparticles, decay by the weak force. Neutrinos (and antineutrinos) do not decay, but a related phenomenon of neutrino oscillations is thought to exist even in vacuums. The electron and its antiparticle, the positron, are theoretically stable due tocharge conservation
In physics, charge conservation is the principle that the total electric charge in an isolated system never changes. The net quantity of electric charge, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge in the universe, is al ...
unless a lighter particle having magnitude of electric charge ''e'' exists (which is unlikely).
Its charge is not shown yet.
Other properties
All observable subatomic particles have their electric charge aninteger
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the languag ...
multiple of the elementary charge. The Standard Model's quarks have "non-integer" electric charges, namely, multiple of ''e'', but quarks (and other combinations with non-integer electric charge) cannot be isolated due to color confinement. For baryons, mesons, and their antiparticles the constituent quarks' charges sum up to an integer multiple of ''e''.
Through the work of Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
, Satyendra Nath Bose, Louis de Broglie, and many others, current scientific theory holds that ''all'' particles also have a wave nature. This has been verified not only for elementary particles but also for compound particles like atoms and even molecules. In fact, according to traditional formulations of non-relativistic quantum mechanics, wave–particle duality applies to all objects, even macroscopic ones; although the wave properties of macroscopic objects cannot be detected due to their small wavelengths.
Interactions between particles have been scrutinized for many centuries, and a few simple laws underpin how particles behave in collisions and interactions. The most fundamental of these are the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum, which let us make calculations of particle interactions on scales of magnitude that range from stars to quarks. These are the prerequisite basics of Newtonian mechanics, a series of statements and equations in '' Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica'', originally published in 1687.
Dividing an atom
The negatively charged electron has a mass equal to of that of ahydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
atom. The remainder of the hydrogen atom's mass comes from the positively charged proton. The atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of ever ...
of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus. Neutrons are neutral particles having a mass slightly greater than that of the proton. Different isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass num ...
s of the same element contain the same number of protons but differing numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope is the total number of nucleons (neutrons and protons collectively).
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
concerns itself with how electron sharing binds atoms into structures such as crystals and molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and b ...
s. The subatomic particles considered important in the understanding of chemistry are the electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
, the proton, and the neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Since protons and ...
. Nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies t ...
deals with how protons and neutrons arrange themselves in nuclei. The study of subatomic particles, atoms and molecules, and their structure and interactions, requires quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
. Analyzing processes that change the numbers and types of particles requires quantum field theory. The study of subatomic particles ''per se'' is called particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
. The term ''high-energy physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) a ...
'' is nearly synonymous to "particle physics" since creation of particles requires high energies: it occurs only as a result of cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s, or in particle accelerators. Particle phenomenology systematizes the knowledge about subatomic particles obtained from these experiments.Taiebyzadeh, Payam (2017). String Theory; A unified theory and inner dimension of elementary particles (BazDahm). Riverside, Iran: Shamloo Publications Center. .
History
The term "''subatomic'' particle" is largely a retronym of the 1960s, used to distinguish a large number ofbaryon
In particle physics, a baryon is a type of composite subatomic particle which contains an odd number of valence quarks (at least 3). Baryons belong to the hadron family of particles; hadrons are composed of quarks. Baryons are also classifie ...
s and mesons (which comprise hadron
In particle physics, a hadron (; grc, ἁδρός, hadrós; "stout, thick") is a composite subatomic particle made of two or more quarks held together by the strong interaction. They are analogous to molecules that are held together by the ...
s) from particles that are now thought to be truly elementary. Before that hadrons were usually classified as "elementary" because their composition was unknown.
A list of important discoveries follows:
See also
References
Further reading
General readers
* Feynman, R.P. & Weinberg, S. (1987). ''Elementary Particles and the Laws of Physics: The 1986 Dirac Memorial Lectures''. Cambridge Univ. Press. * * Oerter, Robert (2006). ''The Theory of Almost Everything: The Standard Model, the Unsung Triumph of Modern Physics''. Plume. * Schumm, Bruce A. (2004). ''Deep Down Things: The Breathtaking Beauty of Particle Physics''. Johns Hopkins University Press. . *Textbooks
* Coughlan, G.D., J.E. Dodd, and B.M. Gripaios (2006). ''The Ideas of Particle Physics: An Introduction for Scientists'', 3rd ed. Cambridge Univ. Press. An undergraduate text for those not majoring in physics. * *External links
University of California: Particle Data Group.
{{Composition Quantum mechanics