The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is
one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the
Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Western States, the Far West, the Western territories, and the West) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau.
As American settlement i ...
, with the
Midwestern and
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau. Located on the East Coast of the United States, ...
to its north and the
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
and
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
to its south.
Historically, the South was defined as all states south of the 18th-century
Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, sometimes referred to as Mason and Dixon's Line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states: Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. It was Surveying, surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason ...
, the
Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
, and the
36°30′ parallel.
[The South](_blank)
. ''Britannica''. Retrieved June 5, 2021. Within the South are different
subregions such as the
Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, ...
,
South Central,
Upper South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, ...
, and
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
.
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
,
Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
,
Washington, D.C., and
Northern Virginia
Northern Virginia, locally referred to as NOVA or NoVA, comprises several County (United States), counties and independent city (United States), independent cities in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. ...
have become more culturally, economically, and politically aligned in certain aspects with the Northeastern United States and are sometimes identified as part of the Northeast or
Mid-Atlantic. The U.S. Census Bureau continues to define all four places as formally being in the South.
To account for cultural variations across the region, some scholars have proposed definitions of the South that do not coincide neatly with state boundaries. The South does not precisely correspond to the entire
geographic south of the United States, but primarily includes the
south-central and
southeastern states. For example, California, which is geographically in the southwestern part of the country, is not considered part of the South; however, the geographically southeastern state of
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
is.
The politics and economy of the region were historically dominated by a small rural elite. The historical and cultural development of the South has been profoundly influenced by the institution of
slave labor, especially in the Deep South and coastal plain areas, from the early 1600s to mid-1800s. This includes the presence of a large proportion of African Americans within the population, support for the doctrine of
states' rights
In United States, American politics of the United States, political discourse, states' rights are political powers held for the state governments of the United States, state governments rather than the federal government of the United States, ...
, and legacy of racism magnified by the Civil War and
Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
(1865–1877). Following effects included thousands of
lynchings, a
segregated system of separate schools and public facilities established from
Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
that remained until the 1960s, and the widespread use of
poll taxes and other methods to deny black and poor people the ability to vote or hold office until the 1960s. Scholars have characterized pockets of the Southern United States as being
authoritarian enclaves from Reconstruction until the
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
.
The South, being home to some of the most racially diverse areas in the United States, is known for having developed its own distinct
culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, with different customs, fashion,
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
,
musical styles, and
cuisines, which have distinguished it in many ways from other areas of the United States. Sociological research indicates that Southern collective identity stems from political, historical, demographic, and cultural distinctiveness from the rest of the United States; however, this has declined since around the late 20th century, with many Southern areas becoming a melting pot of cultures and people. When looked at broadly, studies have shown that Southerners tend to be more
conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
than most non-Southerners, with
liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, the right to private property, and equality before the law. ...
being mostly predominant in places with a
Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
majority or urban areas in the South.
The region contains almost all of the
Bible Belt, an area of high
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
church attendance, especially
evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
churches such as the
Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist organization, the largest Protestant, and the second-largest Chr ...
. In the 21st century, it is the fastest-growing region in the United States, with
Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
being the region's largest city.
Geography
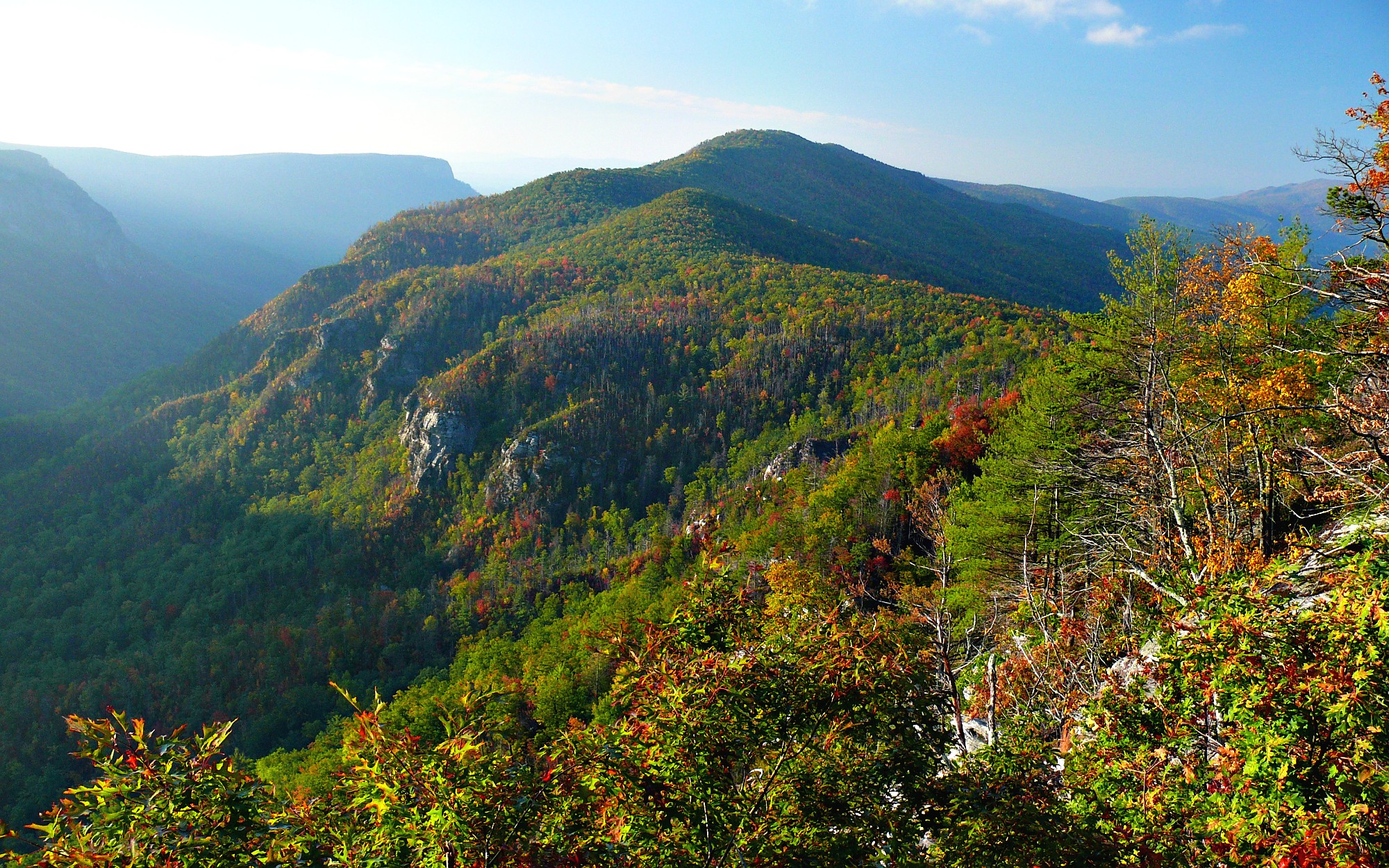










The South is a diverse meteorological region with numerous climatic zones, including
temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
,
sub-tropical,
tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
, and
arid—though the South generally has a reputation as hot and humid, with long summers and short, mild winters. Most of the South—except for the areas of higher elevations and areas near the western, southern, and some northern fringes—falls in the
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
zone. Crops grow readily in the South due to its climate consistently providing growing seasons of at least six months before the first frost. Some common environments include
bayous and swamplands, the southern
pine forests, the warm temperate montane forest of the Appalachians, the savannas of the southern Great Plains, and the
subtropical jungle and maritime forests along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts. Unique flora include various species of magnolia, rhododendron, cane, palm, and oak, among others.
Fauna of the region is also diverse, encompassing a plethora of
amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
species, reptiles such as the
green anole, the venomous
cottonmouth snake, and the
American alligator, mammals like the
American black bear
The American black bear (''Ursus americanus''), or simply black bear, is a species of medium-sized bear which is Endemism, endemic to North America. It is the continent's smallest and most widely distributed bear species. It is an omnivore, with ...
, the
swamp rabbit, and the
nine-banded armadillo
The nine-banded armadillo (''Dasypus novemcinctus''), also called the nine-banded long-nosed armadillo or common long-nosed armadillo, is a species of armadillo native to North America, North, Central America, Central, and South America, making ...
, and birds such as the
roseate spoonbill and the extinct but symbolic
carolina parakeet.
The question of how to define the boundaries and subregions of the South has long been the focus of research and debate. As defined by the
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
,
the Southern region of the United States includes sixteen states and the District of Columbia. As of 2010, an estimated 114,555,744 people, or thirty-seven percent of all U.S. residents, lived in the South, the nation's most populous region. The Census Bureau defines three smaller divisions:
* The
South Atlantic states: Delaware, the District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia and West Virginia.
* The
East South Central states: Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi and Tennessee.
* The
West South Central states: Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma and Texas.
A survey conducted by social geographers in 2010 selected thirteen states as the
cultural South: Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia and West Virginia. The
Council of State Governments, an organization for communication and coordination between states, includes the same thirteen states as well as Texas and Missouri in its South regional office.
Other terms related to the South include:
* The
Old South: Can mean either southern states that were among the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
(Virginia, Delaware, Maryland, Georgia, North Carolina and South Carolina) or all southern slave states before 1860 (which also includes Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Missouri, Arkansas, Louisiana and Texas).
* The
New South: All southern states following the American Civil War, post–
Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
.
*
Southeastern United States: Usually includes
the Carolinas,
the Virginias,
Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
,
Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
,
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
,
Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
,
Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
and Florida.
*
Southern Appalachia: Mainly refers to areas situated in the southern
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
, namely
Eastern Kentucky,
East Tennessee,
Western North Carolina
Western North Carolina (often abbreviated as WNC) is the region of North Carolina which includes the Appalachian Mountains; it is often known geographically as the state's Mountain Region. It contains the highest mountains in the Eastern United S ...
,
Western Maryland,
West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
,
Southwest Virginia,
North Georgia and
Northwestern South Carolina.
*
Upper South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, ...
: Usually includes Kentucky, Virginia, West Virginia,
Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
,
North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
and on rare occasions Missouri, Maryland and Delaware. When combined with the southern Appalachian Mountains, it is sometimes referred to as "
Greater Appalachia" following
Ulster Protestant migrations to the United States in the 18th and 19th centuries.
*
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
: Various definitions, usually includes Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi and South Carolina.
*
Border States: Includes Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. These were southern slave states on or near the border of the Confederacy that did not secede or only partially seceded from the U.S. in the 1860s. Large numbers of residents who joined both the Union and Confederate armed forces. Kentucky and Missouri had Confederate state governments with the
Confederate government of Missouri and the
Confederate government of Kentucky
The Confederate government of Kentucky was a government-in-exile, shadow government established for the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Kentucky by a self-constituted group of Confederate States of America, Confederate sympathizer ...
. The Confederacy controlled more than half of Kentucky and the southern portion of Missouri early in the war but were in-exile after 1862 and were represented in the Confederate Congress and by stars on the Confederate battle flag. West Virginia formed in 1863, after the western region of Virginia broke away to protest the Old Dominion's joining of the Confederacy, but residents of the new state were about evenly divided on supporting the Union or Confederacy.
*
Dixie: Nickname applied to Southern U.S. region, various definitions include certain areas more than others, but most commonly associated with the eleven former Confederate States.
*
Solid South: Electoral voting bloc largely controlled by the Democratic Party from 1877 to 1964, largely resulting from
disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction era in the late 19th century. Disfranchisement effectively denied most of the black and sometimes poor white population from voting or holding public office during this time period.
*
Gulf Coast: Includes Gulf coasts of Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, Texas and Alabama.
*
Tidewater: Low-lying
Atlantic coastal plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
regions of Maryland, Delaware, Virginia and North Carolina.
*
Mid-South: Various definitions, includes states within the Census Bureau of the East and West South Central United States.
In another informal definition, Tennessee, Arkansas, and Mississippi are included, with adjoining areas of other states.
Historically, the South was defined as all states south of the 18th-century
Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, sometimes referred to as Mason and Dixon's Line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states: Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. It was Surveying, surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason ...
, the
Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
, and the
36°30′ parallel.
Newer definitions of the South today are harder to define, due to cultural and sub-regional differences throughout the region; however, definitions usually refer to states that are in the southeastern and south-central geographic regions of the United States.
Although not included in the Census definition, two
U.S. territories located southeast of Florida (
Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
and the
U.S. Virgin Islands) are sometimes included as part of the Southern United States. The
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is a Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation that regulates civil aviation in t ...
includes Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands as part of the South, as does the
Agricultural Research Service and the
U.S. National Park Service.
History
Native American culture
The first well-dated evidence of human occupation in the south United States occurs around 9500 BC with the appearance of the earliest documented Americans, who are now referred to as
Paleo-Indians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
.
Paleoindians were hunter-gatherers that roamed in bands and frequently hunted
megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
. Several cultural stages, such as Archaic (–1000 BC) and the Woodland ( – AD 1000), preceded what the Europeans found at the end of the 15th centurythe
Mississippian culture.
The Mississippian culture was a complex,
mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Southeastern United States from approximately 800 AD to 1500 AD. Natives had elaborate and lengthy trading routes connecting their main residential and ceremonial centers extending through the river valleys and from the East Coast to the Great Lakes.
Some noted explorers who encountered and described the Mississippian culture, by then in decline, included
Pánfilo de Narváez (1528),
Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1497 – 21 May 1542) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, ...
(1540), and
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (1699).
Native American descendants of the mound-builders include
Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
,
Apalachee,
Caddo,
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; , or ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern ...
,
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, United States. Their traditional territory was in northern Mississippi, northwestern and northern Alabama, western Tennessee and southwestern Kentucky. Their language is ...
,
Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
,
Creek,
Guale,
Hitchiti,
Houma, and
Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, ...
peoples, all of whom still reside in the South.
Other peoples whose ancestral links to the Mississippian culture are less clear, but those who were in the region before the European incursion include the
Catawba and the
Powhatan.
European colonization

The arrival of European settlers caused a massive
population decline in Native Americans, due to Europeans unknowingly spreading
diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
that the natives had no immunities towards, numerous violent conflicts, and forcibly relocating them.
The predominant culture of the original Southern states was
English. In the 17th century, most voluntary immigrants were of English origin and settled chiefly along the eastern coast but had pushed as far inland as the
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
by the 18th century. The majority of early English settlers were
indentured servant
Indentured servitude is a form of Work (human activity), labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as paymen ...
s, who gained freedom after working off their passage. The wealthier men, typically members of the English
landed gentry
The landed gentry, or the gentry (sometimes collectively known as the squirearchy), is a largely historical Irish and British social class of landowners who could live entirely from rental income, or at least had a country estate. It is t ...
,
who paid their way received land grants known as
headrights to encourage settlement.
The Spanish and French established settlements in
Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
,
Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, and
Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
. The Spanish settled Florida in the 16th century, reaching a peak in the late 17th century, but the population was small because the Spaniards were relatively uninterested in agriculture, and Florida had no mineral resources.
There were regional differences in the Southern colonies, with the three main regions of
Tidewater, the
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
, and
Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
. The first region to be settled was Tidewater, containing the low-lying plains of southeast
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
,
northeastern North Carolina, southern
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
and the
Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
.
The next region to be settled was the Deep South, beginning in
Province of Carolina and later the
Province of Georgia. The last region to be settled was Appalachia, also settled by the
Scotch-Irish.
King
Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651 and King of England, Scotland, and King of Ireland, Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest su ...
granted the
Charter of Carolina in 1663 for land south of the British
Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia was a British Empire, British colonial settlement in North America from 1606 to 1776.
The first effort to create an English settlement in the area was chartered in 1584 and established in 1585; the resulting Roanoke Colo ...
and north of
Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida () was the first major European land-claim and attempted settlement-area in northern America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and th ...
. He granted the land to eight
lords proprietor. Charles granted the land in return for their financial and political assistance in
restoring him to the throne in 1660.
The granted lands included all or part of the present-day U.S. states of North Carolina, Tennessee, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and Florida.
In the British colonies, immigration began in 1607 and continued until the outbreak of the Revolution in 1775. Settlers cleared land, built houses and outbuildings, and on their own farms. The Southern rich owned large
plantations that dominated export agriculture and used slaves. Many were involved in the labor-intensive cultivation of tobacco, the first cash crop of Virginia. Tobacco exhausted the soil quickly, requiring that farmers regularly clear new fields. They used old fields as pasture, and for crops such as corn wheat, or allowed them to grow into woodlots.
In the mid-to-late-18th century, large groups of
Ulster Scots (later called the
Scotch-Irish) and people from the
Anglo-Scottish border
The Anglo-Scottish border runs for between Marshall Meadows Bay on the east coast and the Solway Firth in the west, separating Scotland and England.
The Firth of Forth was the border between the Picto- Gaelic Kingdom of Alba and the Angli ...
region immigrated and settled in the back country of
Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
and the
Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
. They were the largest group of non-English immigrants from the
British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
before the
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
.
[ David Hackett Fischer, '' Albion's Seed: Four British Folkways in America'', New York: Oxford University Press, 1989, pp. 361–368] In the
1980 census, 34% of Southerners reported that they were of English ancestry; English was the largest reported European ancestry in every Southern state by a large margin.
The early colonists engaged in
warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
, trade, and cultural exchanges. Those living in the backcountry were more likely to encounter
Creek Indians,
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; , or ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern ...
, and
Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
s and other regional native groups.
The oldest university in the South, the
College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (abbreviated as W&M) is a public university, public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. Founded in 1693 under a royal charter issued by King William III of England, William III and Queen ...
, was founded in 1693 in Virginia; it pioneered in the teaching of
political economy
Political or comparative economy is a branch of political science and economics studying economic systems (e.g. Marketplace, markets and national economies) and their governance by political systems (e.g. law, institutions, and government). Wi ...
and educated future U.S. Presidents
Jefferson,
Monroe and
Tyler, all from Virginia. Indeed, the entire region dominated politics in the
First Party System era: for example, four of the first five presidents
Washington, Jefferson,
Madison and Monroewere from Virginia. The two oldest public universities are also in the South: the
University of North Carolina
The University of North Carolina is the Public university, public university system for the state of North Carolina. Overseeing the state's 16 public universities and the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics, it is commonly referre ...
(1789) and the
University of Georgia
The University of Georgia (UGA or Georgia) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia, United States. Chartered in 1785, it is the oldest public university in th ...
(1785).
Instituting slavery
 Slavery was legal
Slavery was legal in all of the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
prior to the
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
in 1776. Britain had
slave island colonies in the Caribbean, including
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
,
Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
,
Nevis
Nevis ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute the Saint Kitts and Nevis, Federation of Saint Kitts ...
, and
Antigua
Antigua ( ; ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the local population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the most populous island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua ...
, which provided a steady flow of profits from the slave labor that produced sugar. The
Southern Colonies differed in that the proportion of their populations that were African American slaves was much higher than in the
Middle Colonies and
New England Colonies, as shown on the map.
According to
Bertram Wyatt-Brown, "Bondage was an answer to an economic need. The South was not founded to create slavery; slavery was recruited to perpetuate the South." The
Barbados Slave Code of 1661 served as the basis for the slave codes adopted in the
British American colonies of the
Province of Carolina and the
Province of Georgia. In other colonies where the slaves codes were not an exact copy, such as the
Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia was a British Empire, British colonial settlement in North America from 1606 to 1776.
The first effort to create an English settlement in the area was chartered in 1584 and established in 1585; the resulting Roanoke Colo ...
and the
Province of Maryland
The Province of Maryland was an Kingdom of England, English and later British colonization of the Americas, British colony in North America from 1634 until 1776, when the province was one of the Thirteen Colonies that joined in supporting the A ...
, the influence of the Barbados Slave Code can be traced throughout various provisions.
[Sweet Negotiations: Sugar, Slavery, and Plantation Agriculture in Early Barbados]
Chapter 6 ''The Expansion of Barbados'', p. 112
American Revolution


During the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, the Southern colonies helped embrace the
Patriot cause. Virginia would provide leaders such as commander-in-chief
George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
, and the author of the Declaration of Independence,
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
.
In 1780 and 1781, the British largely halted reconquest of the northern states and concentrated on the south, where they were told there was a large Loyalist population ready to leap to arms once the royal forces arrived. The British took control of Savannah and Charleston, capturing a large American army in the process, and set up a network of bases inland. Although there were
Loyalists within the Southern colonies, they were concentrated in larger coastal cities and were not great enough in number to overcome the revolutionaries. The British forces at the
Battle of Monck's Corner and the
Battle of Lenud's Ferry consisted entirely of Loyalists with the exception of the commanding officer (
Banastre Tarleton). Both white and black Loyalists fought for the British at the
Battle of Kemp's Landing in Virginia. Led by
Nathanael Greene
Major general (United States), Major General Nathanael Greene (August 7, 1742 – June 19, 1786) was an American military officer and planter who served in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. He emerge ...
and other generals, the Americans engaged in
Fabian tactics designed to wear down the British invasion force and to neutralize its strong points one by one. There were numerous battles large and small, with each side claiming some victories.
By 1781, however, British
General Cornwallis moved north to Virginia, where an approaching army forced him to fortify and await rescue by the British Navy. The British Navy did arrive, but so did a stronger French fleet, and Cornwallis was trapped. American and French armies, led by George Washington, forced Cornwallis to surrender his entire army in
Yorktown, Virginia
Yorktown is a town in York County, Virginia, United States. It is the county seat of York County, one of the eight original shires formed in Colony of Virginia, colonial Virginia in 1682. Yorktown's population was 195 as of the 2010 census, while ...
, in October 1781, effectively winning the North American part of the war.
The Revolution provided a shock to slavery in the South and other regions of the new country. Thousands of slaves took advantage of wartime disruption to find their own freedom, catalyzed by the British Governor Dunmore of Virginia's promise of freedom for service. Many others were removed by Loyalist owners and became slaves elsewhere in the British Empire. Between 1770 and 1790, there was a sharp decline in the percentage of blacks – from 61% to 44% in South Carolina and from 45% to 36% in Georgia. In addition, some slaveholders were inspired to free their slaves after the Revolution. They were moved by the principles of the Revolution, along with Quaker and Methodist preachers who worked to encourage slaveholders to free their slaves. Planters such as George Washington often freed slaves by their wills. In the
Upper South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, ...
, more than 10% of all blacks were free by 1810, a significant expansion from pre-war proportions of less than 1% free.
Antebellum years

Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
became dominant in the lower South after 1800. After the invention of the
cotton gin
A cotton gin—meaning "cotton engine"—is a machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds, enabling much greater productivity than manual cotton separation.. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); ...
, short staple cotton could be grown more widely. This led to an explosion of cotton cultivation, especially in the frontier uplands of Georgia, Alabama and other parts of the Deep South, as well as riverfront areas of the Mississippi Delta. Migrants poured into those areas in the early decades of the 19th century, when county population figures rose and fell as swells of people kept moving west. The expansion of cotton cultivation required more slave labor, and the institution became even more deeply an integral part of the South's economy.
With the opening up of frontier lands after the government forced most Native Americans to move west of the Mississippi, there was a major migration of both whites and blacks to those territories. From the 1820s through the 1850s, more than one million enslaved Africans were transported to the Deep South in forced migration, two-thirds of them by slave traders and the others by masters who moved there. Planters in the Upper South sold slaves in excess of their needs as they shifted from tobacco to mixed agriculture. Many enslaved families were broken up, as planters preferred mostly strong males for field work.
Two major political issues that festered in the first half of the 19th century caused political alignment along sectional lines, strengthened the identities of North and South as distinct regions with certain strongly opposed interests, and fed the arguments over states' rights that culminated in secession and the Civil War. One of these issues concerned the protective tariffs enacted to assist the growth of the manufacturing sector, primarily in the North. In 1832, in resistance to federal legislation increasing tariffs, South Carolina passed an ordinance of
nullification, a procedure in which a state would, in effect, repeal a Federal law. Soon a naval flotilla was sent to
Charleston harbor, and the threat of landing ground troops was used to compel the collection of tariffs. A compromise was reached by which the tariffs would be gradually reduced, but the underlying argument over states' rights continued to escalate in the following decades.
The second issue concerned slavery, primarily the question of whether slavery would be permitted in newly admitted states. The issue was initially finessed by political compromises designed to balance the number of "free" and "slave" states. The issue resurfaced in a more virulent form, however, around the time of the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
, which raised the stakes by adding new territories primarily on the Southern side of the imaginary geographic divide. Congress opposed allowing slavery in these territories.
Before the Civil War, the number of immigrants arriving at Southern ports began to increase, although the North continued to receive the most immigrants.
Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
were among the first settlers in Charleston, along with the largest number of Orthodox Jews outside of New York City. Numerous Irish immigrants settled in New Orleans, establishing a distinct
ethnic enclave now known as the
Irish Channel. Germans also went to New Orleans and its environs, resulting in a large area north of the city (along the Mississippi) becoming known as the German Coast. Still greater numbers immigrated to Texas (especially after 1848), where many bought land and were farmers. Many more German immigrants arrived in Texas after the Civil War, where they created the brewing industry in Houston and elsewhere, became grocers in numerous cities, and also established wide areas of farming.
By 1840,
New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
was the wealthiest city in the country and the third largest in population. The success of the city was based on the growth of international trade associated with products being shipped to and from the interior of the country down the Mississippi River. New Orleans also had the largest slave market in the country, as traders brought slaves by ship and overland to sell to planters across the Deep South. The city was a cosmopolitan port with a variety of jobs that attracted more immigrants than other areas of the South. Because of lack of investment, however, construction of railroads to span the region lagged behind the North. People relied most heavily on river traffic for getting their crops to market and for transportation.
Native American removal
Between 1830 and 1850, Native Americans were removed from their home states in the South and Eastern United States and were sent to Oklahoma.
Civil War

By 1856, the South had lost control of Congress, and was no longer able to silence calls for an end to slaverywhich came mostly from the more populated,
free states of the North. The Republican Party, founded in 1854, pledged to stop the spread of slavery beyond those states where it already existed. After Abraham Lincoln was elected the first Republican president in 1860, seven cotton states declared their secession and formed the
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an List of historical unrecognized states and dependencies, unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United State ...
before Lincoln was inaugurated. The United States government, both outgoing and incoming, refused to recognize the Confederacy, and when the new Confederate President
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the only President of the Confederate States of America, president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the Unite ...
ordered his troops to open fire on
Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a historical Coastal defense and fortification#Sea forts, sea fort located near Charleston, South Carolina. Constructed on an artificial island at the entrance of Charleston Harbor in 1829, the fort was built in response to the W ...
in April 1861, war broke out. Only the state of
Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
attempted to remain neutral, and it could only do so briefly. When Lincoln called for troops to suppress what he referred to as "combinations too powerful to be suppressed by the ordinary" judicial or martial means, four more states decided to secede and join the Confederacy (which then moved its capital to Richmond, Virginia). Although the Confederacy had large supplies of captured munitions and many volunteers, it was slower than the Union in dealing with the border states. While the Upland South
border states of Kentucky, Missouri, West Virginia, Maryland, and Delaware, as well as the
District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
, continued to permit
slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
during the Civil War, they remained with the
Union though Kentucky and Missouri both had rival Confederate governments that formed that were admitted and recognized by the Confederacy. Though early in the war, the Confederacy controlled more than half of Kentucky and the southern portion of Missouri. By March 1862, the Union largely controlled all the border state areas, had shut down all commercial traffic from all Confederate ports, had prevented European recognition of the Confederate government, and was poised to seize New Orleans. The rugged mountainous
East Tennessee region
attempted to rejoin the Union as a new state, having opposed secession and slavery compared to most of Tennessee.
[Eric Lacy, ''Vanquished Volunteers: East Tennessee Sectionalism from Statehood to Secession'' (Johnson City, Tenn.: East Tennessee State University Press, 1965), pp. 122–126, 217–233.]
In the four years of war 1861–65 the South was the primary battleground, with all but two of the major battles taking place on Southern soil. Union forces led numerous campaigns into the western Confederacy, controlling the border states in 1861, the Tennessee River, the Cumberland River and New Orleans in 1862, and the Mississippi River in 1863. In the East, however, the Confederate Army under
Robert E. Lee beat off attack after attack in its defense of their capital at Richmond. But when Lee tried to move north, he was repulsed (and nearly captured) at Sharpsburg (1862) and Gettysburg (1863).

The Confederacy had the resources for a short war, but was unable to finance or supply a longer war. It reversed the traditional low-tariff policy of the South by imposing a new 15% tax on all imports from the Union. The
Union blockade stopped most commerce from entering the South, and smugglers avoided the tax, so the Confederate tariff produced too little revenue to finance the war. Inflated currency was the solution, but that created distrust of the Richmond government. Because of low investment in railroads, the Southern transportation system depended primarily on river and coastal traffic by boat; both were shut down by the
Union Navy. The small railroad system virtually collapsed, so that by 1864 internal travel was so difficult that the Confederate economy was crippled.
The Confederate cause was hopeless by the time Atlanta fell and
William T. Sherman marched through Georgia in late 1864, but the rebels fought on until Lee's army surrendered in April 1865. Once the Confederate forces surrendered, the region moved into the
Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
(1865–1877), in a partially successful attempt to rebuild the destroyed region and grant civil rights to freed slaves.
Southerners who were against the Confederate cause during the Civil War were known as
Southern Unionists
In the United States, Southern Unionists were white Southerners living in the Confederate States of America and the Southern Border states (American Civil War), Border States opposed to secession. Many fought for the Union (American Civil War), ...
. They were also known as Union Loyalists or Lincoln's Loyalists. Within the eleven Confederate states, states such as Tennessee (especially
East Tennessee), Virginia (which included
West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
at the time), and North Carolina were home to the largest populations of Unionists. Many areas of
Southern Appalachia harbored pro-Union sentiment as well. As many as 100,000 men living in states under Confederate control would serve in the
Union Army or pro-Union guerrilla groups. Although Southern Unionists came from all classes, most differed socially, culturally, and economically from the regions dominant pre-war
planter class.
The South suffered more than the North overall, as the Union strategy of attrition warfare meant that Lee could not replace his casualties, and the total war waged by Sherman, Sheridan and other Union armies devastated the infrastructure and caused widespread poverty and distress. The Confederacy suffered military losses of 95,000 soldiers killed in action and 165,000 who died of disease, for a total of 260,000, out of a total white Southern population at the time of around 5.5 million. Based on 1860 census figures, 8% of all white males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including 6% in the North and about 18% in the South. Northern military deaths were greater than Southern military deaths in absolute numbers, but were two-thirds smaller in terms of proportion of the population affected.
Reconstruction and Jim Crow era
After the Civil War, the South was devastated in terms of infrastructure and economy. Because of states' reluctance to grant voting rights to freedmen, Congress instituted Reconstruction governments. It established military districts and governors to rule over the South until new governments could be established. Many white Southerners who had actively supported the Confederacy were temporarily disenfranchised. Rebuilding was difficult as people grappled with the effects of a new labor economy of a free market in the midst of a widespread
agricultural depression. In addition, the limited infrastructure the South had was mostly destroyed by the war. At the same time, the North was rapidly industrializing. To avoid the social effects of the war, most of the Southern states initially passed
black codes. During Reconstruction, these were mostly legally nullified by federal law and anti-Confederate legislatures, which existed for a short time during Reconstruction.
There were thousands of people on the move, as African Americans tried to reunite families separated by slave sales, and sometimes migrated for better opportunities in towns or other states. Other freed people moved from plantation areas to cities or towns for a chance to get different jobs. At the same time, whites returned from refuges to reclaim plantations or town dwellings. In some areas, many whites returned to the land to farm for a while. Some freedpeople left the South altogether for states such as Ohio and Indiana, and later, Kansas. Thousands of others joined the migration to new opportunities in the Mississippi and Arkansas Delta bottomlands, and Texas.

With passage of the
13th Amendment to the
Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
(which outlawed slavery), the
14th Amendment (which granted full U.S. citizenship to African Americans) and the
15th Amendment (which extended the right to vote to African American males), African Americans in the South were made free citizens and were given the right to vote. Under Federal protection, white and black
Republicans formed constitutional conventions and state governments. Among their accomplishments were creating the first public education systems in Southern states, and providing for welfare through orphanages, hospitals and similar institutions.
Northerners came south to participate in politics and business. Some were representatives of the
Freedmen's Bureau and other agencies of Reconstruction; some were
humanitarians with the intent to help black people. Some were adventurers who hoped to benefit themselves by questionable methods. They were all condemned with the pejorative term of
carpetbagger. Some Southerners would also take advantage of the disrupted environment and made money off various schemes, including bonds and financing for railroads. White Southerners who supported Reconstruction policies and efforts became known as
scalawags.
Secret
vigilante organizations such as the
Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
an organization sworn to perpetuate
white supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
had arisen quickly after the war's end in the 1860s, and used
lynching
Lynching is an extrajudicial killing by a group. It is most often used to characterize informal public executions by a mob in order to punish an alleged or convicted transgressor or to intimidate others. It can also be an extreme form of i ...
, physical attacks, house burnings and other forms of intimidation to keep African Americans from exercising their political rights. Although the first Klan was disrupted by prosecution by the Federal government in the early 1870s, other groups persisted. By the mid-to-late-1870s, some upper class Southerners created increasing resistance to the altered social structure.
Paramilitary organizations such as the
White League in
Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
(1874), the
Red Shirts in
Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
(1875) and rifle clubs, all "White Line" organizations, used organized violence against
Republicans, both black and white, to remove Republicans from political office, repress and bar black voting, and restore the
Democratic Party to power. In 1876 white Democrats regained power in most of the state legislatures. They began to pass laws designed to strip African Americans and
Poor White
Poor White is a sociocultural classification used to describe economically disadvantaged Whites in the English-speaking world, especially White Americans with low incomes.
In the United States, Poor White is the historical classification f ...
s from the voter registration rolls. The success of late-19th century interracial coalitions in several states inspired a reaction among some white Democrats, who worked harder to prevent both groups from voting.
Despite discrimination, many blacks became property owners in areas that were still developing. For instance, 90% of the Mississippi's bottomlands were still frontier and undeveloped after the war. By the end of the century, two-thirds of the farmers in Mississippi's Delta bottomlands were black. They had cleared the land themselves and often made money in early years by selling off timber. Tens of thousands of migrants went to the Delta, both to work as laborers to clear timber for lumber companies, and many to develop their own farms. Nonetheless, the long agricultural depression, along with disenfranchisement and lack of access to credit, led to many blacks in the Delta losing their property by 1910 and becoming sharecroppers or landless workers over the following decade. More than two generations of free African Americans lost their stake in property.
Nearly all Southerners, black and white, suffered economically as a result of the Civil War. Within a few years cotton production and harvest was back to pre-war levels, but low prices through much of the 19th century hampered recovery. They encouraged immigration by Chinese and Italian laborers into the Mississippi Delta. While the first Chinese entered as indentured laborers from
Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, the majority came in the early 20th century. Neither group stayed long at rural farm labor. The Chinese became merchants and established stores in small towns throughout the Delta, establishing a place between white and black.
Migrations continued in the late 19th and early 20th centuries among both blacks and whites. In the last two decades of the 19th century about 141,000 blacks left the South, and more after 1900, totaling a loss of 537,000. After that the movement increased in what became known as the Great Migration from 1910 to 1940, and the Second Great Migration through 1970. Even more whites left the South, some going to California for opportunities and others heading to Northern industrial cities after 1900. Between 1880 and 1910, the loss of whites totaled 1,243,000. Five million more left between 1940 and 1970.
From 1890 to 1908, ten of the eleven former Confederate states, along with Oklahoma upon statehood, passed disenfranchising constitutions or amendments that introduced voter registration barrierssuch as
poll taxes, residency requirements and
literacy teststhat were hard for minorities to meet. Most African Americans, most Mexican Americans, and tens of thousands of poor whites were disenfranchised, losing the vote for decades. In some states,
grandfather clauses temporarily exempted white illiterates from literacy tests. The numbers of voters dropped drastically throughout the former Confederacy as a result. This can be seen via the feature "Turnout in Presidential and Midterm Elections" at the University of Texas' ''Politics: Barriers to Voting''. Alabama, which had established universal white suffrage in 1819 when it became a state, also substantially reduced voting by poor whites.
Democrat-controlled legislatures passed
Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
to segregate public facilities and services, including transportation.
While African Americans, poor whites and civil rights groups started litigation against such provisions in the early 20th century, for decades
Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
decisions overturning such provisions were rapidly followed by new state laws with new devices to restrict voting. Most blacks in the former Confederacy and Oklahoma could not vote until 1965, after passage of the Voting Rights Act and Federal enforcement to ensure people could register. Despite increases in the eligible voting population with the inclusion of women, blacks, and those eighteen and over throughout this period, turnout in ex-Confederate states remained below the national average throughout the 20th century. Not until the late 1960s did all American citizens regain protected civil rights by passage of legislation following the leadership of the
American Civil Rights Movement.
Historian
William Chafe has explored the defensive techniques developed inside the African American community to avoid the worst features of Jim Crow as expressed in the legal system, unbalanced economic power, and intimidation and psychological pressure. Chafe says "protective socialization by blacks themselves" was created inside the community to accommodate white-imposed sanctions while subtly encouraging challenges to those sanctions. Known as "walking the tightrope", such efforts at bringing about change were only slightly effective before the 1920s, but did build the foundation that younger African Americans deployed in their aggressive, large-scale activism during the civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s.
1880s through 1930s
At the end of the 19th century, white Democrats in the South had created state constitutions that were hostile to industry and business development, with anti-industrial laws extensive from the time new constitutions were adopted in the 1890s. Banks were few and small; there was little access to credit. Traditional agriculture persisted across the region. Especially in Alabama and Florida, rural minorities held control in many state legislatures long after population had shifted to industrializing cities, and legislators resisted business and modernizing interests: Alabama refused to redistrict between 1901 and 1972, long after major population and economic shifts to cities. For decades Birmingham generated the majority of revenue for the state, for instance, but received little back in services or infrastructure.
In the late 19th century, Texas rapidly expanded its railroad network, creating a network of cities connected on a radial plan and linked to the port of Galveston. Strikes and labor unrest served as a reflection of increasing industry: "in 1885 Texas ranked ninth among forty states in number of workers involved in strikes (4,000); for the six-year period it ranked fifteenth. Seventy-five of the one hundred strikes, chiefly interstate strikes of telegraphers and railway workers, occurred in the year 1886."
By 1890,
Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
became the largest city in Texas, and by 1900 it had a population of more than 42,000, which more than doubled to over 92,000 a decade later. Dallas was the harnessmaking capital of the world and a center of other manufacturing. As an example of its ambitions, in 1907 Dallas built the
Praetorian Building, fifteen storeys tall and the first skyscraper west of the Mississippi, soon to be followed by other skyscrapers. Texas was transformed by a railroad network linking five important cities, among them Houston with its nearby port at Galveston, Dallas, Fort Worth, San Antonio, and El Paso. Each exceeded fifty thousand in population by 1920, with the major cities having three times that population.
Business interests were ignored by the Southern Democrat ruling class. Nonetheless, major new industries started developing in cities such as Atlanta, Georgia; Birmingham, Alabama; and Dallas, Fort Worth, and Houston, Texas. Growth began occurring at a geometric rate. Birmingham became a major steel producer and mining town, with major population growth in the early decades of the 20th century.
The first major oil well in the South was drilled at
Spindletop near
Beaumont, Texas
Beaumont is a city in the U.S. state of Texas. It is the county seat of Jefferson County, Texas, Jefferson County, within the Beaumont–Port Arthur metropolitan area, located in Southeast Texas on the Neches River about east of Houston (city ...
, on the morning of January 10, 1901. Other oil fields were later discovered nearby in Arkansas, Oklahoma, and under the
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
. The resulting "Oil Boom" permanently transformed the economy of the West South Central states and produced the richest economic expansion after the Civil War.
In the early 20th century, invasion of the
boll weevil devastated cotton crops in the South, producing an additional catalyst to African Americans' decisions to leave the South. From 1910 to 1970, more than 6.5 million African Americans left the South in the
Great Migration to Northern and Western cities, defecting from persistent
lynching
Lynching is an extrajudicial killing by a group. It is most often used to characterize informal public executions by a mob in order to punish an alleged or convicted transgressor or to intimidate others. It can also be an extreme form of i ...
, violence,
segregation, poor education, and inability to vote. Black migration transformed many Northern and Western cities, creating new cultures and music. Many African Americans, like other groups, became industrial workers; others started their own businesses within the communities. Southern whites also migrated to industrial cities like Chicago, Detroit,
Oakland, and Los Angeles, where they took jobs in the booming new auto and defense industry.
Later, the Southern economy was dealt additional blows by the
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
and the
Dust Bowl. After the
Wall Street Crash of 1929, the economy suffered significant reversals and millions were left unemployed. Beginning in 1934 and lasting until 1939, an ecological disaster of severe wind and drought caused an exodus from Texas and Arkansas, the
Oklahoma Panhandle region, and the surrounding plains, in which over 500,000
Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
were homeless, hungry and jobless. Thousands would leave the region to seek economic opportunities along the
West Coast.
President
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
noted the South as the "number one priority" in terms of need of assistance during the Great Depression. His administration created programs such as the
Tennessee Valley Authority in 1933 to provide rural electrification and stimulate development. Locked into low-productivity agriculture, the region's growth was slowed by limited industrial development, low levels of entrepreneurship, and the lack of capital investment.
1940s through late 20th century
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
marked a time of dramatic change within the South from an economic standpoint, as new industries and military bases were developed by the federal government, providing much-needed capital and infrastructure in many regions. People from all parts of the US came to the South for military training and work in the region's many bases and new industries. During and after the war millions of hard-scrabble farmers, both white and black, left agriculture for other occupations and urban jobs.
The United States began mobilizing for war in a major way in the spring of 1940. The warm weather of the South proved ideal for building 60% of the Army's new training camps and nearly half the new airfields. In all, 40% of spending on new military installations went to the South. For example, in 1940 the small town of 1500 people in
Starke, Florida
Starke is a city in and the county seat of Bradford County, Florida, United States. The population was 5,796 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The origin of the city's name is disputed. Starke may have been named in honor of local la ...
, became the base of
Camp Blanding. By March 1941, 20,000 men were constructing a permanent camp for 60,000 soldiers. Money flowed freely for the war effort, as over $4 billion went into military facilities in the South, and another $5 billion into defense plants. Major shipyards were built in Virginia, in Charleston, South Carolina, and along the Gulf Coast.
Huge warplane plants were opened in Dallas-Fort Worth and Georgia. The most secret and expensive operation was at
Oak Ridge, Tennessee, where unlimited amounts of locally generated electricity were used to prepare uranium for the atom bomb. The number of production workers doubled during the war. Most training centers, factories and shipyards were closed in 1945, but not all, and the families that left hardscrabble farms remained to find jobs in the growing urban South. The region had finally reached the take off stage into industrial and commercial growth, although its income and wage levels lagged well behind the national average. Nevertheless, as
George B. Tindall notes, the transformation was, "The demonstration of industrial potential, new habits of mind, and a recognition that industrialization demanded community services."
Per capita income jumped 140% from 1940 to 1945, compared to 100% elsewhere in the United States. Southern income rose from 59% to 65%. Dewey Grantham says the war, "brought an abrupt departure from the South's economic backwardness, poverty, and distinctive rural life, as the region moved perceptively closer to the mainstream of national economic and social life." Since 1970, the proportion of the
African American population living in the South stabilized and began slightly increasing.
Farming shifted from cotton and tobacco, to include cattle, rice,
soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
s,
corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
, and other foods. Industrial growth increased in the 1960s and greatly accelerated into the 1980s and 1990s. Several large urban areas in Texas, Georgia, and Florida grew to over four million people. Rapid expansion in industries such as autos, telecommunications, textiles, technology, banking, and aviation gave some states in the South an industrial strength to rival large states elsewhere in the country. By the 2000 census, the South (along with the West) was leading the nation in population growth. With this growth, however, has come long commute times and air pollution problems in cities such as Dallas, Houston, Atlanta, Austin, Charlotte, and others that rely on sprawling development and highway networks.
21st century
In the 21st century, and especially after the
2010 midterm elections, the Republican Party has largely dominated the South, both at the state and federal levels. As of 2024, Republicans control both houses of the
state legislatures of 10 out of the eleven former
Confederate States, the sole exception being the
Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, and the first elected legislative assembly in the New World. It was established on July 30, ...
. However, there are still some Democratic statewide officeholders in the South, such as Kentucky governor
Andy Beshear
Andrew Graham Beshear ( ; born November 29, 1977) is an American attorney and politician serving as the 63rd governor of Kentucky since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as the 50th attorney gen ...
, North Carolina governor
Josh Stein, Virginia's U.S. Senators
Mark Warner and
Tim Kaine, and Georgia's U.S. Senators
Raphael Warnock
Raphael Gamaliel Warnock ( ; born July 23, 1969) is an American politician and Baptists, Baptist pastor serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, junior United States Senate, United States senator from Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, ...
and
Jon Ossoff
Thomas Jonathan Ossoff ( ; born February 16, 1987) is an American politician serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, senior United States Senate, United States senator from Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia since 2021. A member of the ...
.
In 2019, Fortune 500 companies headquartered in Southern states included: Texas with 50, Virginia with 21, Florida with 18, Georgia with 17, North Carolina with 11, and Tennessee with 10. In 2022, Texas led the nation with the most Fortune 500 company headquarters with 53. This economic expansion has enabled parts of the South to report some of the lowest unemployment rates in the United States.
Even with certain southern states and areas doing well economically, many southern states and areas still have high poverty rates when compared to the U.S. nationally. In 2021, nine out of the ten
states with the highest poverty rates were in the South. Also, in 2023 all five states with
the lowest GDP per capita were in the South: Mississippi, West Virginia, Arkansas, Alabama, and South Carolina.
Modern economy
In the late 20th century, the South changed dramatically. It saw a boom in its
service economy, manufacturing base, high technology industries, and the financial sector. Texas in particular witnessed dramatic growth and population change with the dominance of the energy industry and tourism industries, such as the
Alamo Mission in
San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
. Tourism in Florida and along the Gulf Coast also grew steadily throughout the last decades of the 20th century.
Numerous new automobile production plants have opened in the region, or are soon to open, such as
Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz (), commonly referred to simply as Mercedes and occasionally as Benz, is a German automotive brand that was founded in 1926. Mercedes-Benz AG (a subsidiary of the Mercedes-Benz Group, established in 2019) is based in Stuttgart, ...
in
Tuscaloosa, Alabama
Tuscaloosa ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Tuscaloosa County, Alabama, Tuscaloosa County in west-central Alabama, United States, on the Black Warrior River where the Gulf Coastal Plain, Gulf Coastal and Piedmont (United States), Piedm ...
;
Hyundai in
Montgomery, Alabama
Montgomery is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Alabama. Named for Continental Army major general Richard Montgomery, it stands beside the Alabama River on the Gulf Coastal Plain. The population was 2 ...
; the
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, trading as BMW Group (commonly abbreviated to BMW (), sometimes anglicised as Bavarian Motor Works), is a German multinational manufacturer of vehicles and motorcycles headquartered in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Th ...
production plant in
Spartanburg, South Carolina
Spartanburg is a city in and the county seat of Spartanburg County, South Carolina, United States. The city had a population of 38,732 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List of municipalities in South Carolina, 11th ...
;
Toyota
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on August 28, 1937. Toyota is the List of manuf ...
plants in
Georgetown, Kentucky
Georgetown is a home rule-class city in Scott County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 37,086 at the 2020 census. It is the sixth-most populous city in Kentucky. It is the seat of its county. It was originally called Lebanon whe ...
,
Blue Springs, Mississippi and
San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
; the
GM manufacturing plant in
Spring Hill, Tennessee; a
Honda
commonly known as just Honda, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate automotive manufacturer headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Founded in October 1946 by Soichiro Honda, Honda has bee ...
factory in
Lincoln, Alabama; the
Nissan
is a Japanese multinational Automotive industry, automobile manufacturer headquartered in Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan. The company sells its vehicles under the ''Nissan'' and ''Infiniti'' brands, and formerly the ''Datsun'' brand, with in-house ...
North American headquarters in
Franklin, Tennessee
Franklin is a city in and the county seat of Williamson County, Tennessee, United States. About south of Nashville, Tennessee, Nashville, it is one of the principal cities of the Nashville metropolitan area and Middle Tennessee. As of 2020 Uni ...
, and factories in
Smyrna, Tennessee and
Canton, Mississippi
The city of Canton is the county seat of Madison County, Mississippi, United States, and is situated in the northern part of the Jackson, Mississippi metropolitan area, metropolitan area surrounding the state capital, Jackson, Mississippi, Jackso ...
; a
Kia factory in
West Point, Georgia; and the
Volkswagen Chattanooga Assembly Plant in Tennessee.
The two largest research parks in the country are located in the South:
Research Triangle Park in North Carolina (the world's largest) and the
Cummings Research Park in
Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is the List of municipalities in Alabama, most populous city in the U.S. state of Alabama. The population of the city is estimated to be 241,114 in 2024, making it the List of United States cities by population, 100th-most populous ...
(the world's fourth largest).
In medicine, the
Texas Medical Center in Houston has achieved international recognition in education, research, and patient care, especially in the fields of heart disease, cancer, and rehabilitation. In 1994 the Texas Medical Center was the largest medical center in the world including fourteen hospitals, two medical schools, four colleges of nursing, and six university systems. The University of Texas
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center is consistently ranked the No. 1 cancer research and treatment center in the United States.
Many major banking corporations have headquarters in the region.
Bank of America
The Bank of America Corporation (Bank of America) (often abbreviated BofA or BoA) is an American multinational investment banking, investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered at the Bank of America Corporate Center in ...
and
Truist Financial are in
Charlotte.
Wachovia was headquartered there before its purchase by
Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo & Company is an American multinational financial services company with a significant global presence. The company operates in 35 countries and serves over 70 million customers worldwide. It is a systemically important fi ...
.
Regions Financial Corporation is in
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
, as is
AmSouth Bancorporation, and previously
BBVA Compass before its acquisition by
PNC Financial Services.
Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
is the district headquarters of the
Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta.
Many corporations are headquartered in Atlanta and its surrounding area, such as
The Coca-Cola Company
The Coca-Cola Company is an American multinational corporation founded in 1892. It manufactures, sells and markets soft drinks including Coca-Cola, other non-alcoholic beverage concentrates and syrups, and alcoholic beverages. Its stock is lis ...
,
Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc. is a Major airlines of the United States, major airline in the United States headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, operating nine hubs, with Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport being its ...
, and
The Home Depot, and also many cable television networks, such as the
Turner Broadcasting System (
CNN,
TBS,
TNT,
Turner South,
Cartoon Network
Cartoon Network (CN) is an American cable television television channel, channel and the flagship property of the Cartoon Network, Inc., a sub-division of the Warner Bros. Discovery Networks division of Warner Bros. Discovery. It launched on ...
) and
The Weather Channel
The Weather Channel (TWC) is an American pay television television channel, channel owned by Weather Group, LLC, a subsidiary of Allen Media Group. The channel's headquarters are located in Atlanta, Georgia. Launched on May 2, 1982, the channel ...
.
Education
Southern
public schools in the past have ranked in the lower half of some national surveys. When allowance for race is considered, a 2007 US Government list of test scores often shows white fourth and eighth graders performing better than average for reading and math; while black fourth and eighth graders also performed better than average. This comparison does not hold across the board. Mississippi often scores lower than national averages, no matter how statistics are compared. Newer data from 2009 suggests that secondary school education in the South is on par nationally, with 72% of high schoolers graduating compared to 73% nationwide.
The Southern United States is home to some of the nation's largest and most prominent public and private institutions of higher education. Notable public colleges and universities in the South include:




*
University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a Public university#United States, public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia, United States. It was founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson and contains his The Lawn, Academical Village, a World H ...
*
Virginia Commonwealth University
*
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public university, public research university in Austin, Texas, United States. Founded in 1883, it is the flagship institution of the University of Texas System. With 53,082 stud ...
*
University of Houston
The University of Houston (; ) is a Public university, public research university in Houston, Texas, United States. It was established in 1927 as Houston Junior College, a coeducational institution and one of multiple junior colleges formed in ...
*
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC, UNC–Chapel Hill, or simply Carolina) is a public university, public research university in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, United States. Chartered in 1789, the university first began enrolli ...
*
Florida State University
Florida State University (FSU or Florida State) is a Public university, public research university in Tallahassee, Florida, United States. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida and a preeminent university in the s ...
*
University of North Carolina at Charlotte
*
Georgia State University
Georgia State University (Georgia State, State, or GSU) is a Public university, public research university in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. Founded in 1913, it is one of the University System of Georgia's four research universities. It is al ...
*
Georgia Tech
*
George Mason University
George Mason University (GMU) is a Public university, public research university in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. Located in Northern Virginia near Washington, D.C., the university is named in honor of George Mason, a Founding Father ...
*
University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida, United States. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida and a preem ...
*
University of Georgia
The University of Georgia (UGA or Georgia) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia, United States. Chartered in 1785, it is the oldest public university in th ...
*
Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, TA&M, or TAMU) is a public university, public, Land-grant university, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas, United States. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of ...
*
Florida A&M University
Florida Agricultural and Mechanical University (FAMU), commonly known as Florida A&M, is a Public university, public Historically black colleges and universities, historically black land-grant university in Tallahassee, Florida, United States. ...
*
North Carolina A&T State University
*
University of Tennessee
The University of Tennessee, Knoxville (or The University of Tennessee; UT; UT Knoxville; or colloquially UTK or Tennessee) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Knoxville, Tennessee, United St ...
*
College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (abbreviated as W&M) is a public university, public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. Founded in 1693 under a royal charter issued by King William III of England, William III and Queen ...
*
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State, North Carolina State, NC State University, or NCSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. Founded in 1887 and p ...
*
University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD i ...
*
University of Mississippi
The University of Mississippi (Epithet, byname Ole Miss) is a Public university, public research university in University, near Oxford, Mississippi, United States, with a University of Mississippi Medical Center, medical center in Jackson, Miss ...
*
Auburn University
Auburn University (AU or Auburn) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Auburn, Alabama, United States. With more than 26,800 undergraduate students, over 6,100 post-graduate students, and a tota ...
*
University of South Carolina
The University of South Carolina (USC, SC, or Carolina) is a Public university, public research university in Columbia, South Carolina, United States. Founded in 1801 as South Carolina College, It is the flagship of the University of South Car ...
*
James Madison University
James Madison University (JMU, Madison, or James Madison) is a public university, public research university in Harrisonburg, Virginia, United States. Founded in 1908, the institution was renamed in 1938 in honor of the fourth president of the ...
*
Virginia Tech
The Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, commonly referred to as Virginia Tech (VT), is a Public university, public Land-grant college, land-grant research university with its main campus in Blacksburg, Virginia, United States ...
*
Louisiana State University
Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, commonly referred to as Louisiana State University (LSU), is an American Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Baton Rouge, Louis ...
*
University of Alabama
The University of Alabama (informally known as Alabama, UA, the Capstone, or Bama) is a Public university, public research university in Tuscaloosa, Alabama, United States. Established in 1820 and opened to students in 1831, the University of ...
*
University of Alabama at Birmingham
*
University of Arkansas
The University of Arkansas (U of A, UArk, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Fayetteville, Arkansas, United States. It is the Flagship campus, flagship campus of the University of Arkan ...
*
University of Oklahoma
The University of Oklahoma (OU) is a Public university, public research university in Norman, Oklahoma, United States. Founded in 1890, it had existed in Oklahoma Territory near Indian Territory for 17 years before the two territories became the ...
*
University of Kentucky
The University of Kentucky (UK, UKY, or U of K) is a Public University, public Land-grant University, land-grant research university in Lexington, Kentucky, United States. Founded in 1865 by John Bryan Bowman as the Agricultural and Mechanical ...
*
University of Louisville
The University of Louisville (UofL) is a public university, public research university in Louisville, Kentucky, United States. It is part of the Kentucky state university system. Chartered in 1798 as the Jefferson Seminary, it became in the 19t ...
*
Virginia Military Institute
Notable private colleges and universities in the South include:
*
Duke University
Duke University is a Private university, private research university in Durham, North Carolina, United States. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity, North Carolina, Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1 ...
*
Rice University
William Marsh Rice University, commonly referred to as Rice University, is a Private university, private research university in Houston, Houston, Texas, United States. Established in 1912, the university spans 300 acres.
Rice University comp ...
*
Vanderbilt University
Vanderbilt University (informally Vandy or VU) is a private university, private research university in Nashville, Tennessee, United States. Founded in 1873, it was named in honor of shipping and railroad magnate Cornelius Vanderbilt, who provide ...
*
Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
*
George Washington University
The George Washington University (GW or GWU) is a Private university, private University charter#Federal, federally-chartered research university in Washington, D.C., United States. Originally named Columbian College, it was chartered in 1821 by ...
*
Georgetown University
Georgetown University is a private university, private Jesuit research university in Washington, D.C., United States. Founded by Bishop John Carroll (archbishop of Baltimore), John Carroll in 1789, it is the oldest Catholic higher education, Ca ...
*
Emory University
Emory University is a private university, private research university in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. It was founded in 1836 as Emory College by the Methodist Episcopal Church and named in honor of Methodist bishop John Emory. Its main campu ...
*
University of Miami
The University of Miami (UM, UMiami, Miami, U of M, and The U) is a private university, private research university in Coral Gables, Florida, United States. , the university enrolled 19,852 students in two colleges and ten schools across over ...
*
University of Richmond
The University of Richmond (UR or U of R) is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Richmond, Virginia, United States. It is a primarily undergraduate, residential institution with approxim ...
*
Liberty University
*
Tulane University
The Tulane University of Louisiana (commonly referred to as Tulane University) is a private research university in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. Founded as the Medical College of Louisiana in 1834 by a cohort of medical doctors, it b ...
*
Wake Forest University
Wake Forest University (WFU) is a private research university in Winston-Salem, North Carolina, United States. Founded in 1834, the university received its name from its original location in Wake Forest, north of Raleigh, North Carolina. The R ...
*
Southern Methodist University
*
Washington and Lee University
Washington and Lee University (Washington and Lee or W&L) is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Lexington, Virginia, United States. Established in 1749 as Augusta Academy, it is among ...
*
Davidson College
Davidson College is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Davidson, North Carolina, United States. It was established in 1837 by the Concord Presbytery and named after American Revolutiona ...
*
Berry College
*
Spelman College
Spelman College is a Private college, private, Historically black colleges and universities, historically black, Women's colleges in the United States, women's Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Atlanta, Georgia ...
*
Morehouse College
*
Howard University
Howard University is a private, historically black, federally chartered research university in Washington, D.C., United States. It is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity" and accredited by the Mid ...
*
Baylor University
Baylor University is a Private university, private Baptist research university in Waco, Texas, United States. It was chartered in 1845 by the last Congress of the Republic of Texas. Baylor is the oldest continuously operating university in Te ...
Culture

The American South is known for its
distinctive dialect and
accent. The predominant culture of the South is
English, and has its origins with the settlement of the region by large groups of people particularly from parts of
West Midlands,
southwest England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of the nine official regions of England, regions of England in the United Kingdom. Additionally, it is one of four regions that altogether make up Southern England. South West England con ...
, and
southeast England, such as
Sussex
Sussex (Help:IPA/English, /ˈsʌsɪks/; from the Old English ''Sūþseaxe''; lit. 'South Saxons'; 'Sussex') is an area within South East England that was historically a kingdom of Sussex, kingdom and, later, a Historic counties of England, ...
,
Shropshire
Shropshire (; abbreviated SalopAlso used officially as the name of the county from 1974–1980. The demonym for inhabitants of the county "Salopian" derives from this name.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West M ...
, and the
West Country who moved to the
Tidewater and the eastern parts of the
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
in the 17th and early 18th centuries. For example, the city of
Birmingham, Alabama
Birmingham ( ) is a city in the north central region of Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Jefferson County, Alabama, Jefferson County. The population was 200,733 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List ...
, is named after
Birmingham, England in the West Midlands.
Northern English,
Scots lowlanders and
Ulster-Scots (later called the
Scotch-Irish) who settled in
Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
and the
Upland South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, a ...
in the mid to late 18th century, and the many African people who were brought to the American South as slaves. Their descendants, identified as Black or African American people, compose the United States' second-largest racial minority, accounting for 12.1% of the total population according to the 2000 census. Despite
Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced racial segregation, " Jim Crow" being a pejorative term for an African American. The last of the ...
era
outflow to the North, the majority of the black population remains concentrated in Southern states and has heavily contributed to the cultural blend of religion, food, art, and music ''(see
spiritual,
blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
,
jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
,
R&B,
soul music
Soul music is a popular music genre that originated in African-American culture, African-American African-American neighborhood, communities throughout the United States in the late 1950s and early 1960s. Catchy rhythms, stressed by handclaps ...
,
country music
Country (also called country and western) is a popular music, music genre originating in the southern regions of the United States, both the American South and American southwest, the Southwest. First produced in the 1920s, country music is p ...
,
zydeco,
bluegrass and
rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock-n-roll, and rock 'n' roll) is a Genre (music), genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It Origins of rock and roll, originated from African ...
)'' that characterizes Southern culture today.
Overall, the South has had lower housing values, lower household incomes, and lower
cost of living
The cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living for an individual or a household. Changes in the cost of living over time can be measured in a cost-of-living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare t ...
than the rest of the United States. These factors, combined with the fact that Southerners have continued to maintain strong loyalty to family ties, has led some sociologists to label
white Southerners an ethnic or quasi-ethnic group, though this interpretation has been subject to criticism on the grounds that proponents of the view do not satisfactorily indicate how Southerners meet the criteria of ethnicity. In previous censuses, the largest ancestry group identified by Southerners was
English or mostly English,
with 19,618,370 self-reporting "English" as an ancestry on the 1980 census, followed by 12,709,872 listing "
Irish" and 11,054,127 "
Afro-American".
Almost a third of all Americans who claim English ancestry can be found in the American South, and over a quarter of all Southerners claim English descent as well.
Origins
The Southern
planter class originated from the
early modern
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
English
landed gentry
The landed gentry, or the gentry (sometimes collectively known as the squirearchy), is a largely historical Irish and British social class of landowners who could live entirely from rental income, or at least had a country estate. It is t ...
, who were aristocratic landowners but not
peers or "titled nobility". According to historian
G. E. Mingay, the gentry were landowners whose wealth "made possible a certain kind of education, a standard of comfort, and a degree of leisure and a common interest in ways of spending it". Leisure distinguished gentry from businessmen who gained their wealth through work. The gentry did not work; their income came largely from rents paid by
tenant farmers living on their estates. The concept of
Southern chivalry in the
Antebellum South originated from the gentry rank of
Gentleman
''Gentleman'' (Old French: ''gentilz hom'', gentle + man; abbreviated ''gent.'') is a term for a chivalrous, courteous, or honorable man. Originally, ''gentleman'' was the lowest rank of the landed gentry of England, ranking below an esquire ...
, acting as a
chivalric ideal of the white planter class supposedly descended from the
knights and
Cavaliers
The term ''Cavalier'' () was first used by Roundheads as a term of abuse for the wealthier royalist supporters of Charles I of England and his son Charles II of England, Charles II during the English Civil War, the Interregnum (England), Int ...
of the Medieval and colonial eras.
[ Genovese, Eugene D. "The Chivalric Tradition in the Old South." '' The Sewanee Review'', vol. 108, no. 2, 2000, pp. 188–205. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/27548832. Accessed 12 May 2024.]["The Plantation & Chivalry"]
'' USHistory.org''. Retrieved 12 May 2024.
Several Southern states (Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia) were among the British colonies that sent delegates to sign the
Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another state or failed state, or are breaka ...
and then fought against the government (Great Britain), along with the Middle and New England colonies, during the
Revolutionary War. The basis for much of Southern culture derives from these states being among the original
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
, and from much of the population of the colonial South having ancestral links to colonists who emigrated west. Southern manners and customs reflect the relationship with England that was held by the early population.
In 1765, London philanthropist Dr.
John Fothergill remarked on the cultural differences of the British American colonies southward from Maryland and those to the north, suggesting that the Southerners were marked by "idleness and extravagance". Fothergill suggested that Southerners were more similar to the people of the Caribbean than to the colonies to the north.
[ J. Hector St. John de Crèvecœur's 1782 '' Letters from an American Farmer'' described ]Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the List of municipalities in South Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of South Carolina's coastline on Charleston Harbor, an inlet of the Atla ...
, slaveholders as having "all that life affords most bewitching and pleasurable, without labour, without fatigue, hardly subjected to the trouble of wishing." He declared that although slavery had not yet been completely abolished in the Northern states, the lot of northern slaves was far "different... in every respect." Crèvecœur sought to portray Southerners as stuck in the social, cultural and economic remnants of colonialism, in contrast to the Northerners whom he considered to be representative of the distinctive culture of the new nation.[
Early in United States history, the contrasting characteristics of Southern states were acknowledged in a discussion between ]Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
and François-Jean de Chastellux. Jefferson ascribed the Southerners' "unsteady", "generous", "candid" traits to their climate, while De Chastellux claimed that Southerners' "indelible character which every nation acquires at the moment of its origin" would "always be aristocratic" not only because of slavery but also "vanity and sloth". A visiting French dignitary concurred in 1810 that American customs seemed "entirely changed" over the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
, and that Southern society resembled those of the Caribbean.
Religion
The South has had a majority of its population adhering to evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
ever since the early 1800s as a result of the Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Protestant religious revival during the late 18th to early 19th century in the United States. It spread religion through revivals and emotional preaching and sparked a number of reform movements. Revivals were a k ...
, The upper classes often stayed Episcopalian or Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
. The First Great Awakening starting in the 1740s and the Second Great Awakening ending in the 1850s generated large numbers of Methodist and Baptist converts. These denominations remain the two main Christian confessions in the South. By 1900, the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist organization, the largest Protestant, and the second-largest Chr ...
had become the largest Protestant denomination in the whole United States with its membership concentrated in rural areas of the South. Baptists
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
are the most common religious group, followed by Methodists, Pentecostals and other denominations. Roman Catholics historically were concentrated in Maryland, Louisiana, and Hispanic areas such as South Texas and South Florida and along the Gulf Coast. The great majority of black Southerners are either Baptist or Methodist. Statistics show that Southern states have the highest religious attendance figures of any region in the United States, constituting the so-called Bible Belt. Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
has been strong across the South since the late 19th century.
National and international influences
Apart from its climate, the living experience in the South increasingly resembles the rest of the nation. The arrival of millions of Northerners and Westerners, mainly since the late 20th century, has reshaped the culture of major metropolitan areas and coastal areas.
While Hispanics have long been a major factor in Texas, millions more have arrived in other Southern states during the 1990s and early 2000s bringing values not rooted in local traditions. Historian Raymond Mohl emphasizes the role of NAFTA in lowering trade barriers and facilitating large-scale population movements. He adds other factors such as ongoing economic crisis in Mexico, new more liberal immigration policies in the United States, labor recruitment and smuggling, that have produced a major flow of Mexican and Hispanic migration to the southeast. That region's low-wage, low-skill economy readily hired cheap, reliable, nonunion labor, without asking applicants too many questions about legal status. Richard J. Gonzales argues that the rise of La Raza (Mexican American community) in terms of numbers and influence in politics, education, and language and cultural rights will grow rapidly in Texas by 2030 when demographers predict Hispanics will outnumber Anglos in Texas. However thus far their political participation and the Latino vote have been low, so the potential political impact is much higher than the actual one thus far.
Scholars have suggested that collective identity and Southern distinctiveness are thus declining in the Deep South, particularly when defined against "an earlier South that was somehow more authentic, real, more unified and distinct".[ Edward L. Ayers, ''What Caused the Civil War? Reflections on the South and Southern History'' (2005) p. 46, 019535687X] On the other hand, Southerners have moved west in large numbers, especially to California and to the Midwest. Thus, journalist Michael Hirsh proposed that aspects of Southern culture have spread throughout a greater portion of the rest of the United States in a process termed " Southernization".[Michael Hirsh (April 25, 2008)]
"How the South Won (This) Civil War"
, ''Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly news magazine based in New York City. Founded as a weekly print magazine in 1933, it was widely distributed during the 20th century and has had many notable editors-in-chief. It is currently co-owned by Dev P ...
'', accessed November 22, 2008
Ethnicity
 The South has the largest
The South has the largest African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
population by region. The South has largely remained a black and white region while the other regions of the US have received larger amounts of Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
and Asian immigrants. However, the Hispanic population has seen rapid growth in certain areas of the South, particularly in South Florida
South Florida, sometimes colloquially shortened to SoFlo, is the Regions of the United States#Florida, southernmost region of the U.S. state of Florida. It is one of Florida's three most commonly referred to directional regions; the two others are ...
and South Texas. The Upland South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, economics, demographics, a ...
is heavily white, with few African Americans in this subregion of the South.
Sports
Football


American football
American football, referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron football, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular American football field, field with goalposts at e ...
is heavily considered the most popular team sport in most areas of the Southern United States.
The region is home to numerous decorated and historic college football
College football is gridiron football that is played by teams of amateur Student athlete, student-athletes at universities and colleges. It was through collegiate competition that gridiron football American football in the United States, firs ...
programs, particularly in the Southeastern Conference
The Southeastern Conference (SEC) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference whose member institutions are located primarily in the South Central United States, South Central and Southeastern United States. Its 16 members in ...
(known as the "SEC"), Atlantic Coast Conference
The Atlantic Coast Conference (ACC) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference in the United States. Headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, the ACC's eighteen member universities compete in the National Collegiate Athlet ...
(known as the "ACC"), and the Big 12 Conference
The Big 12 Conference is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference in the United States. It consists of 16 full-member universities (3 private universities and 13 public universities) in the states of Arizona, Colorado, Florida ...
. The SEC, consisting almost entirely of teams based in Southern states, is widely considered to be the strongest league in contemporary college football and includes the Alabama Crimson Tide, the program with the most national championships in the sport's modern history. The sport is also highly competitive and has a spectator following at the high school level, particularly in rural areas, where high school football games often serve as prominent community gatherings.
The first established professional football team based in the South were the Washington Redskins
The Washington Commanders are a professional American football team based in the Washington metropolitan area. The Commanders compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC East, East ...
, now called the Washington Commanders
The Washington Commanders are a professional American football team based in the Washington metropolitan area. The Commanders compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) East division ...
. They still retain a large following in most of Virginia and parts of Maryland. Later on, the National Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a Professional gridiron football, professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National ...
(NFL) and American Football League
The American Football League (AFL) was a major professional American football league that operated for ten seasons from 1960 until 1970, AFL–NFL merger, when it merged with the older National Football League (NFL), and became the American Foot ...
(AFL) began to expand many teams in the Southern US during the 1960s, with franchises like the Atlanta Falcons
The Atlanta Falcons are a professional American football team based in Atlanta. The Falcons compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC South, South division. The Falcons were founded o ...
, New Orleans Saints
The New Orleans Saints are a professional American football team based in New Orleans. The Saints compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC South, South division. Since 1975, the team ...
, Houston Oilers, Miami Dolphins, and the Dallas Cowboys
The Dallas Cowboys are a professional American football team based in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. The Cowboys compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC East, East division. T ...
. In later decades, NFL expansion into Southern states continued, with the Tampa Bay Buccaneers during the 1970s, along with the Carolina Panthers, Jacksonville Jaguars
The Jacksonville Jaguars are a professional American football team based in Jacksonville, Florida. The Jaguars compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) AFC South, South division. The team ...
, and Baltimore Ravens
The Baltimore Ravens are a professional American football team based in Baltimore. The Ravens compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) AFC North, North division. The team plays its home g ...
during the 1990s. The Houston Oilers were eventually replaced by the Houston Texans
The Houston Texans are a professional American football team based in Houston. The Texans compete in the National Football League as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) AFC South, South division. The team plays its home games at N ...
, after the Oilers relocated to Nashville
Nashville, often known as Music City, is the capital and List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County in Middle Tennessee, locat ...
to become the Tennessee Titans
The Tennessee Titans are a professional American football team based in Nashville, Tennessee. The Titans compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) AFC South, South division. They play the ...
.
Baseball
Baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball sport played between two team sport, teams of nine players each, taking turns batting (baseball), batting and Fielding (baseball), fielding. The game occurs over the course of several Pitch ...
has been played in the Southern United States dating back to the mid-19th century. It was traditionally more popular than American football until the 1980s and still accounts for the largest annual attendance amongst sports played in the South. The first mention of a baseball team in Houston was on April 11, 1861. During the late 19th century and early 20th century games were common, especially once the professional leagues such as the Texas League, the Dixie League, and the Southern League were organized.
The short-lived Louisville Colonels
The Louisville Colonels were a Major League Baseball team that played in the American Association (AA) throughout that league's ten-year existence from 1882 until 1891. They were known as the Louisville Eclipse from 1882 to 1884, and as th ...
were a part of the early National League and American Association, but ceased to exist in 1899. The first Southern Major League Baseball team after the Colonels appeared in 1962, when the Houston Colt .45s (known today as the Houston Astros
The Houston Astros are an American professional baseball team based in Houston. The Astros compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) American League West, West Division. They are one of two major leag ...
) were enfranchised. Later, the Atlanta Braves
The Atlanta Braves are an American professional baseball team based in the Atlanta metropolitan area. The Braves compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (baseball), National League (NL) National League Eas ...
came in 1966, followed by the Texas Rangers in 1972, and finally the Miami Marlins and Tampa Bay Rays in the 1990s.
College baseball
College baseball is baseball that is played by Student athlete, student-athletes at institutions of higher education. In the United States, college baseball is sanctioned mainly by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA); in Japan, ...
appears to be more well attended in the South than elsewhere, as teams like Florida State, Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
, LSU
Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, commonly referred to as Louisiana State University (LSU), is an American Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Baton Rouge, Louis ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, Mississippi State, Ole Miss, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
and Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
are commonly at the top of the NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates College athletics in the United States, student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, and Simon Fraser University, 1 in Canada. ...
's attendance. The South generally produces very successful collegiate baseball teams with Virginia, Vanderbilt, LSU, South Carolina, Florida and Coastal Carolina winning recent College World Series
The College World Series (CWS), officially the NCAA Men's College World Series (MCWS), is a baseball tournament held each June in Omaha, Nebraska. It is the culmination of the NCAA Division I baseball tournament—featuring 64 teams in the ...
Titles.
The following is a list of each MLB team in the Southern U.S. and the total fan attendance for 2019:
Auto racing
 The Southern states are commonly associated with
The Southern states are commonly associated with stock car racing
Stock car racing is a form of Auto racing, automobile racing run on oval track racing, oval tracks and road courses. It originally used Production vehicle, production-model cars, hence the name "stock car", but is now run using cars specifical ...
and its most prominent competition level NASCAR
The National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing, LLC (NASCAR) is an American auto racing sanctioning and operating company that is best known for stock car racing. It is considered to be one of the top ranked motorsports organizations in ...
, which is headquartered in Charlotte and Daytona Beach. The sport was developed in the South during the early 20th century, with stock car racing's historic mecca being Daytona Beach, where cars initially raced on the wide, flat beachfront, before the construction of Daytona International Speedway. Though the sport has attained a following throughout the United States, a majority of NASCAR races continue to take place at Southern tracks.
Basketball
Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
is very popular throughout the Southern United States as both a recreational and spectator sport, particularly in the states of Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
and North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
. Both states are home to several prominent college basketball
College basketball is basketball that is played by teams of Student athlete, student-athletes at universities and colleges. In the Higher education in the United States, United States, colleges and universities are governed by collegiate athle ...
programs, including the Kentucky Wildcats, Louisville Cardinals, Duke Blue Devils and North Carolina Tar Heels
The North Carolina Tar Heels (also Carolina Tar Heels) are the college sports in the United States, intercollegiate athletic teams that represent the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. The name Tar Heel is a nickname used to refer to ...
. Other southern teams, like the Florida Gators and Virginia Cavaliers have won national championships.
NBA teams based in the South include the San Antonio Spurs
The San Antonio Spurs are an American professional basketball team based in San Antonio. The Spurs compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southwest Division (NBA), Southwest Division of the Western Conference (NBA ...
, Houston Rockets
The Houston Rockets are an American professional basketball team based in Houston. The Rockets compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southwest Division (NBA), Southwest Division of the Western Conference (NBA) ...
, Oklahoma City Thunder
The Oklahoma City Thunder are an American professional basketball team based in Oklahoma City. The Thunder compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Northwest Division (NBA), Northwest Division of the Western Confer ...
, Dallas Mavericks
The Dallas Mavericks (often referred to as the Mavs) are an American professional basketball team based in Dallas. The Mavericks compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southwest Division (NBA), Southwest Divisi ...
, Washington Wizards, Charlotte Hornets
The Charlotte Hornets are an American professional basketball team based in Charlotte, North Carolina. The Hornets compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southeast Division of the Eastern Conference. The team ...
, Atlanta Hawks
The Atlanta Hawks are an American professional basketball team based in Atlanta. The Hawks compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southeast Division (NBA), Southeast Division of the Eastern Conference (NBA), Easte ...
, Orlando Magic, Memphis Grizzlies, New Orleans Pelicans
The New Orleans Pelicans are an American professional basketball team based in New Orleans. The Pelicans compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southwest Division (NBA), Southwest Division of the Western Confere ...
, and Miami Heat
The Miami Heat are an American professional basketball team based in Miami. The Heat compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southeast Division (NBA), Southeast Division of the Eastern Conference (NBA), Eastern C ...
. The Spurs and Heat in particular have become prominent within the NBA, with eight championships won by the two between 1999 and 2014.
Golf
Golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various Golf club, clubs to hit a Golf ball, ball into a series of holes on a golf course, course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standa ...
is a popular recreational sport in most areas of the South, with the region's warm climate allowing it to host many professional tournaments and numerous destination golf resorts, particularly in the state of Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
. The region is home to The Masters
The Masters Tournament (usually referred to as simply the Masters, or as the U.S. Masters outside North America) is one of the four men's major golf championships, men's major championships in Professional golf tours, professional golf. Schedul ...
which is played at Augusta National Golf Club in Augusta, Georgia
Augusta is a city on the central eastern border of the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. The city lies directly across the Savannah River from North Augusta, South Carolina at the head of its navigable portion. Augusta, the third mos ...
, and has become one of the professional game's most important tournaments. One of the four major championships in Hilton Head Island, in South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, is also home to a prominent American golf tournament and has several high-quality courses.
Soccer
In recent decades association football, known in the South as in the rest of the United States as "soccer", has become a popular sport at youth and collegiate levels throughout the region. The game has been historically widespread at the college level in the Atlantic coast states of Maryland, Virginia, and the Carolinas; which contain many of the nation's most successful college soccer programs. In particular, Virginia Cavaliers men's soccer, Virginia has won 7 NCAA National Championships, the third most of any school.
The establishment of Major League Soccer has led to professional soccer clubs in the Southern cities including FC Dallas, Houston Dynamo, D.C. United, Orlando City SC, Orlando City, Inter Miami CF, Inter Miami, Nashville SC, Atlanta United, Austin FC and Charlotte FC. The current United States second division soccer league, the USL Championship, was initially geographically based in the coastal Southeast around clubs in Charleston, Richmond, Charlotte, Wilmington, North Carolina, Wilmington, Raleigh, Virginia Beach, and Atlanta.
Major sports teams in the South
The Southern region is home to numerous professional sports franchises in the Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, "Big Four" leagues (NFL, NBA, NHL, and MLB), with many championships collectively among them. Professional sports leagues such as the National Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a Professional gridiron football, professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National ...
(NFL), Major League Baseball (MLB), National Basketball Association (NBA), Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA), National Hockey League (NHL), Major League Soccer (MLS), and National Women's Soccer League (NWSL), have team franchises in following cities/metropolitan areas of the region:
* Dallas-Fort Worth: Dallas Cowboys, Cowboys (NFL), Texas Rangers (baseball), Rangers (MLB), Dallas Mavericks, Mavericks (NBA), Dallas Stars, Stars (NHL), FC Dallas (MLS), Dallas Wings, Wings (WNBA)
* Washington, D.C.: Washington Commanders, Commanders (NFL), Washington Nationals, Nationals (MLB), Washington Wizards, Wizards (NBA), Washington Capitals, Capitals (NHL), D.C. United, United or the Eagles (MLS), Washington Mystics, Mystics (WNBA), Washington Spirit, Spirit (NWSL)
* Miami-Fort Lauderdale: Miami Dolphins, Dolphins (NFL), Miami Marlins, Marlins (MLB), Miami Heat, Heat (NBA), Florida Panthers, Panthers (NHL), Inter Miami, Inter or the Herons (MLS)
* Houston: Houston Texans, Texans (NFL), Houston Astros, Astros (MLB), Houston Rockets, Rockets (NBA), Houston Dynamo, Dynamo (MLS), Houston Dash, Dash (NWSL)
* Atlanta: Atlanta Falcons, Falcons (NFL), Atlanta Braves, Braves (MLB), Atlanta Hawks, Hawks (NBA), Atlanta United FC, United (MLS), Atlanta Dream, Dream (WNBA)
* Tampa Bay: Tampa Bay Buccaneers, Buccaneers (NFL), Tampa Bay Rays, Rays (MLB), Tampa Bay Lightning, Lightning (NHL)
* Baltimore: Baltimore Ravens, Ravens (NFL), Baltimore Orioles, Orioles (MLB)
* Charlotte: Carolina Panthers, Panthers (NFL), Charlotte Hornets, Hornets (NBA), Charlotte FC or the Crown (MLS)
* Nashville: Tennessee Titans, Titans (NFL), Nashville Predators, Predators (NHL), Nashville SC (MLS)
* New Orleans: New Orleans Saints, Saints (NFL), New Orleans Pelicans, Pelicans (NBA)
* Orlando: Orlando Magic, Magic (NBA), Orlando City SC or the Lions (MLS), Orlando Pride, Pride (NWSL)
* San Antonio: San Antonio Spurs, Spurs (NBA)
* Jacksonville: Jacksonville Jaguars, Jaguars (NFL)
* Oklahoma City: Oklahoma City Thunder, Thunder (NBA)
* Memphis: Memphis Grizzlies, Grizzlies (NBA)
* Raleigh: Carolina Hurricanes, Hurricanes (NHL)
* Austin: Austin FC (MLS)
* Cary, North Carolina: North Carolina Courage, Courage (NWSL)
* Louisville, Kentucky: Racing Louisville FC, Racing (NWSL)
Health
 The map on the right shows that life expectancy is lower overall in most Southern states compared to the rest of the country. Obesity rates, hypertension, and diabetes are higher relative to the rest of the nation.
A study reported that six Southern states have the worst incidence of sleep disturbances in the nation, attributing the disturbances to high rates of obesity and smoking.
The South has a higher percentage of obese people and diabetics when compared to national regional averages. The region also has the largest number of people dying from stroke complications and the highest rates of Dementia#Cognitive testing, cognitive decline. Life expectancy is lower and death rates are higher, when compared to national averages of other regions in the United States. This disparity reflects substantial divergence between the South and other regions since the middle of the 20th century.
The East South Central states, East South Central Census Division of the United States (made up of Kentucky, Tennessee, Mississippi, and Alabama) had the highest rate of inpatient hospital stays in 2012. The other divisions, West South Central (Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas and Louisiana) and South Atlantic (West Virginia, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Florida) ranked seventh and fifth. The South had a significantly higher rate of hospital discharges in 2005 than other regions of the United States, but the rate had declined to be closer to the overall national rate by 2011.
For cancer causes, the South, particularly an axis from West Virginia through Texas, leads the nation in adult obesity, adult smoking, low exercise, low fruit consumption, low vegetable consumption, all known cancer risk factors, which matches a similar high risk axis in "All Cancers Combined, Death Rates by State, 2011" from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The South is home to some of the nation's largest Academic medical centre, academic health systems, including the Johns Hopkins Hospital, Duke University Health System, Duke University Health, University of Florida Health, UNC Medical Center, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami Health, UT Health Science Center at Houston, Emory Healthcare, University of South Florida College of Medicine, University of South Florida Health, and others.
The map on the right shows that life expectancy is lower overall in most Southern states compared to the rest of the country. Obesity rates, hypertension, and diabetes are higher relative to the rest of the nation.
A study reported that six Southern states have the worst incidence of sleep disturbances in the nation, attributing the disturbances to high rates of obesity and smoking.
The South has a higher percentage of obese people and diabetics when compared to national regional averages. The region also has the largest number of people dying from stroke complications and the highest rates of Dementia#Cognitive testing, cognitive decline. Life expectancy is lower and death rates are higher, when compared to national averages of other regions in the United States. This disparity reflects substantial divergence between the South and other regions since the middle of the 20th century.
The East South Central states, East South Central Census Division of the United States (made up of Kentucky, Tennessee, Mississippi, and Alabama) had the highest rate of inpatient hospital stays in 2012. The other divisions, West South Central (Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas and Louisiana) and South Atlantic (West Virginia, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Florida) ranked seventh and fifth. The South had a significantly higher rate of hospital discharges in 2005 than other regions of the United States, but the rate had declined to be closer to the overall national rate by 2011.
For cancer causes, the South, particularly an axis from West Virginia through Texas, leads the nation in adult obesity, adult smoking, low exercise, low fruit consumption, low vegetable consumption, all known cancer risk factors, which matches a similar high risk axis in "All Cancers Combined, Death Rates by State, 2011" from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The South is home to some of the nation's largest Academic medical centre, academic health systems, including the Johns Hopkins Hospital, Duke University Health System, Duke University Health, University of Florida Health, UNC Medical Center, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami Health, UT Health Science Center at Houston, Emory Healthcare, University of South Florida College of Medicine, University of South Florida Health, and others.
Politics
In the first decades after Reconstruction era, Reconstruction in the 1880s and 1890s, white Democrats regained power in the state legislatures, and began to make voter registration more complicated, to reduce black voting. With a combination of intimidation, fraud and violence by paramilitary groups, they suppressed black voting and turned Republicans out of office. From 1890 to 1908, ten of eleven states ratified new constitutions or amendments that effectively disenfranchised most black voters and many poor white voters. This disenfranchisement persisted for six decades into the 20th century, depriving blacks and poor whites of all political representation. Because they could not vote, they could not sit on juries. They had no one to represent their interests, resulting in state legislatures consistently underfunding programs and services, such as schools, for blacks and poor whites. Scholars have characterized pockets of the Southern United States as being "authoritarian enclaves" from Reconstruction to the Civil Rights Act. Increasing support for civil rights legislation by the national Democratic Party beginning in 1948 caused segregationist Southern Democrats to nominate Strom Thurmond on a third-party "Dixiecrat" ticket in 1948. These Dixiecrats returned to the party by 1950, but Southern Democrats held off Republican inroads in the suburbs by arguing that only they could defend the region from the onslaught of northern liberals and the civil rights movement. In response to the ''Brown v. Board of Education'' ruling of 1954, 101 Southern congressmen (19 senators, 82 House members of which 99 were Southern Democrats and 2 were Republicans) in 1956 denounced the Brown decisions as a "clear abuse of judicial power [that] climaxes a trend in the federal judiciary undertaking to legislate in derogation of the authority of Congress and to encroach upon the reserved rights of the states and the people." The manifesto lauded, "...those states which have declared the intention to resist enforced integration by any lawful means". It was signed by all Southern senators except Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, and Tennessee senators Albert Gore Sr. and Estes Kefauver. Virginia closed schools in Warren County, Virginia, Warren County, Prince Edward County, Virginia, Prince Edward County, Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, and Norfolk, Virginia, Norfolk rather than integrate, but no other state followed suit. Democratic governors Orval Faubus of Arkansas, Ross Barnett of Mississippi, John Connally of Texas, Lester Maddox of Georgia, and, especially, George Wallace of Alabama resisted integration and appealed to a rural and blue-collar electorate.
The northern Democrats' support of civil rights issues culminated when Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the
Increasing support for civil rights legislation by the national Democratic Party beginning in 1948 caused segregationist Southern Democrats to nominate Strom Thurmond on a third-party "Dixiecrat" ticket in 1948. These Dixiecrats returned to the party by 1950, but Southern Democrats held off Republican inroads in the suburbs by arguing that only they could defend the region from the onslaught of northern liberals and the civil rights movement. In response to the ''Brown v. Board of Education'' ruling of 1954, 101 Southern congressmen (19 senators, 82 House members of which 99 were Southern Democrats and 2 were Republicans) in 1956 denounced the Brown decisions as a "clear abuse of judicial power [that] climaxes a trend in the federal judiciary undertaking to legislate in derogation of the authority of Congress and to encroach upon the reserved rights of the states and the people." The manifesto lauded, "...those states which have declared the intention to resist enforced integration by any lawful means". It was signed by all Southern senators except Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, and Tennessee senators Albert Gore Sr. and Estes Kefauver. Virginia closed schools in Warren County, Virginia, Warren County, Prince Edward County, Virginia, Prince Edward County, Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, and Norfolk, Virginia, Norfolk rather than integrate, but no other state followed suit. Democratic governors Orval Faubus of Arkansas, Ross Barnett of Mississippi, John Connally of Texas, Lester Maddox of Georgia, and, especially, George Wallace of Alabama resisted integration and appealed to a rural and blue-collar electorate.
The northern Democrats' support of civil rights issues culminated when Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which ended legal segregation and provided federal enforcement of voting rights for blacks. In the 1964 United States presidential election, presidential election of 1964, Barry Goldwater's only electoral victories outside his home state of United States presidential election in Arizona, 1964, Arizona were in the states of the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
where few blacks could vote before the 1965 Voting Rights Act. Pockets of resistance to integration in public places broke out in violence during the 1960s by the shadowy Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
, which caused a backlash among moderates. Major resistance to school busing extended into the 1970s.
National Republicans such as Richard Nixon began to develop their Southern strategy to attract conservative white Southerners, especially the middle class and suburban voters, in addition to migrants from the North and traditional GOP pockets in Appalachia. The transition to a Republican stronghold in the South took decades. First, the states started voting Republican in presidential elections, except for native Southerners Jimmy Carter in 1976 and Bill Clinton in 1992 and 1996. Then the states began electing Republican senators and finally governors. Georgia was the last state to do so, with Sonny Perdue taking the governorship in 2002. In addition to its middle class and business base, Republicans cultivated the religious right and attracted strong majorities from the evangelical or Fundamentalist vote, mostly Southern Baptists, which had not been a distinct political force prior to 1980.
Decline of Southern liberalism during the 20th century
Southern liberals were an essential part of the New Deal coalition – without them Roosevelt lacked majorities in Congress. Typical leaders were Lyndon B. Johnson in Texas, Jim Folsom and John Sparkman in Alabama, Claude Pepper in Florida, Earl Long and Hale Boggs in Louisiana, and Estes Kefauver in Tennessee. They promoted subsidies for small farmers, and supported the nascent labor union movement. An essential condition for this north–south coalition was for northern liberals to ignore the problem of racism throughout the South and elsewhere in the country. After 1945, however, northern liberalsled especially by young Hubert Humphrey of Minnesotaincreasingly made civil rights a central issue. They convinced Truman to join them in 1948. The conservative Southern Democratsthe Dixiecratstook control of the state parties in half the region and ran Strom Thurmond for president against Truman. Thurmond carried only the Deep South, but that threat was enough to guarantee the national Democratic Party in 1952 and 1956 would not make civil rights a major issue. In 1956, 101 of the 128 southern congressmen and senators signed the Southern Manifesto denouncing forced desegregation. The labor movement in the South was divided, and lost its political influence. Southern liberals were in a quandary – most of them kept quiet or moderated their liberalism, others switched sides, and the rest continued on the liberal path. One by one, the last group was defeated; historian Numan V. Bartley states, "Indeed, the very word 'liberal' gradually disappeared from the southern political lexicon, except as a term of opprobrium."
Presidents from the South
 The South produced nine of the country's first twelve List of presidents of the United States, Presidents, including the Virginia Dynasty. After Zachary Taylor won the presidential election of 1848, no Southern politician was elected president until Woodrow Wilson in 1912. Andrew Johnson (of
The South produced nine of the country's first twelve List of presidents of the United States, Presidents, including the Virginia Dynasty. After Zachary Taylor won the presidential election of 1848, no Southern politician was elected president until Woodrow Wilson in 1912. Andrew Johnson (of Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
) who was List of vice presidents of the United States, vice president in 1865, became president after the death of Abraham Lincoln.
Out of the last eleven U.S. presidents, seven have Southern region ties: Lyndon B. Johnson (of Texas; 1963–69), Jimmy Carter (of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
; 1977–81), George H. W. Bush (of Texas; 1989–93), Bill Clinton (of Arkansas; 1993–2001), George W. Bush (of Texas; 2001–2009), Donald Trump (of Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
; 2017–2021, 2025–present), and Joe Biden (of Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
; 2021–2025). Johnson was a native of Texas, while Carter is from Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, and Clinton from Arkansas. While George H. W. Bush and George W. Bush began their political careers in Texas, they were both born in New England and have their ancestral roots in that region. Similarly, while Joe Biden was born in Pennsylvania, he grew up largely in Delaware (classified as a Southern state by the U.S. Census Bureau) and spent his entire political career there.
Other politicians and political movements
The South has produced various nationally known politicians and political movements. In 1948, a group of Democratic congressmen, led by Governor Strom Thurmond of South Carolina, split from the Democrats in reaction to an anti-segregation speech given by Minneapolis mayor and future senator Hubert Humphrey of Minnesota. They founded the States Rights Democratic or Dixiecrat Party. During that year's presidential election, the party ran Thurmond as its candidate and he carried four Deep South states.
In the 1968 United States presidential election, 1968 Presidential election, Alabama Governor George C. Wallace ran for president on the American Independent Party ticket. Wallace ran a "law and order" campaign similar to that of Republican candidate, Richard Nixon. Nixon's Southern Strategy of gaining electoral votes downplayed race issues and focused on culturally conservative values, such as family issues, patriotism, and cultural issues that appealed to Southern Baptists.
In United States elections, 1994, the 1994 mid-term elections, another Southern politician, Newt Gingrich, led the Republican Revolution, ushering in twelve years of GOP control of the House. Gingrich became Speaker of the United States House of Representatives in 1995 and served until his resignation in 1999. The incumbent Speaker of the House, Louisiana Republican Mike Johnson, is also from the South.
Except for Bob Dole from Kansas (1985–96) and John Thune from South Dakota (2025-present), nearly all the recent Republican Senate Leaders have all been Southerners: Howard Baker (1981–1985) of Tennessee, Trent Lott (1996–2003) of Mississippi, Bill Frist (2003–2006) of Tennessee, and Mitch McConnell (2007–2024) of Kentucky.
The Republican candidates for president have won the South in elections since 1972 United States presidential election, 1972, except for 1976 United States presidential election, 1976. The region is not, however, entirely monolithic, and every successful Democratic candidate has won at least 2 of the 11 former Confederate states. Barack Obama won Florida, Maryland, Delaware, North Carolina, and Virginia in 2008 but did not repeat his victory in North Carolina during his 2012 reelection campaign. Joe Biden also performed well for a modern Democrat in the South, winning Maryland, Delaware, Virginia, and Georgia, in the 2020 United States presidential election.
Political issues
As of 2025, all southern states except for Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia permit the death penalty.
Race relations
Native Americans
Native Americans have lived in what is now termed the American South for nearly 12,000 years. Increasing amounts of their land was taken until they were defeated by settlers in a series of conflicts ending in the War of 1812 and the Seminole Wars, and most of the surviving population was removed west to Indian Territory (now Oklahoma).
Civil rights movement
The South witnessed two major events in the lives of 20th century African Americans: the Great Migration and the American Civil Rights Movement. The Great Migration began during World War I, hitting its high point during World War II. During this migration, Black people left the South to find work in Northern factories and other sectors of the economy.
The migration also empowered the growing Civil Rights Movement. While the movement existed in all parts of the United States, its focus was against disenfranchisement and the Jim Crow laws in the South. Most of the major events in the movement occurred in the South, including the Montgomery bus boycott, the Mississippi Freedom Summer, the March on Selma, Alabama, and the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. In addition, some of the most important writings to come out of the movement were written in the South, such as King's "Letter from Birmingham Jail". Most of the civil rights landmarks can be found around the South. The Birmingham Civil Rights National Monument in Birmingham includes the Birmingham Civil Rights Institute which details Birmingham's role as the center of the Civil Rights Movement. The 16th Street Baptist Church served as a rallying point for coordinating and carrying out the Birmingham campaign as well as the adjacent Kelly Ingram Park. This park served as ground zero for the infamous children's protest that eventually led to the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
; it has since been rededicated as a place of "Revolution and Reconciliation" and is now the setting of moving sculptures related to the battle for Civil Rights in the city. Both Kelly Ingram Park and the 16th Street Baptist Church are centerpieces of the Birmingham Civil Rights District. The Martin Luther King Jr. National Historical Park in Atlanta includes a museum that chronicles the American Civil Rights Movement as well as Martin Luther King Jr.'s boyhood home on Auburn Avenue. Additionally, Ebenezer Baptist Church (Atlanta, Georgia), Ebenezer Baptist Church is located in the Sweet Auburn district as is the King Center, the location of Martin Luther and Coretta Scott King's gravesites.
Racial integration
During the 1950s and 1960s, the racial integration of all-white collegiate sports teams was high on the regional agenda. Involved in it were issues of racial equality, racism, and the alumni's demand for the top players who it needed to win high-profile games. The Atlantic Coast Conference
The Atlantic Coast Conference (ACC) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference in the United States. Headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, the ACC's eighteen member universities compete in the National Collegiate Athlet ...
(ACC) would take the lead. First, they started to schedule integrated teams from the North. The wake-up call came in 1966, when Don Haskins's University of Texas at El Paso#History, Texas Western College team with 1965–66 Texas Western Miners men's basketball team, five black starters, upset the all-white University of Kentucky team to win the NCAA national basketball championship. That happened at a time when there were no black varsity basketball teams in either the Southeastern Conference or the Southwest Conference. Finally ACC schools, typically under pressure from boosters and civil rights groups, integrated their sports teams. With an alumni base that dominated local and state politics, society and business, the ACC flagship schools were successful in their endeavoras historian Pamela Grundy argues, they had learned how to win:
: The widespread admiration that athletic ability inspired would help transform athletic fields from grounds of symbolic play to forces for social change, places where a wide range of citizens could publicly and at times effectively challenge the assumptions that cast them as unworthy of full participation in U.S. society. While athletic successes would not rid society of prejudice or stereotypeblack athletes would continue to confront racial slurs...[minority star players demonstrated] the discipline, intelligence, and poise to contend for position or influence in every arena of national life.
Congress ends segregation (1964) and guarantees voting rights (1965)
 The decisive action ending segregation came when Congress, in a bipartisan fashion, overcame Southern filibusters to pass the
The decisive action ending segregation came when Congress, in a bipartisan fashion, overcame Southern filibusters to pass the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. A complex interaction of factors came together unexpectedly in the period from 1954 to 1965 to make the momentous changes possible. The Supreme Court had taken the first initiative in Brown v. Board of Education (1954) making segregation of public schools unconstitutional. Enforcement was rapid in the North and border states but was deliberately stopped in the South by the movement called Massive Resistance, sponsored by rural segregationists who largely controlled the state legislatures. Southern liberals, who counseled moderation, were shouted down by both sides and had limited impact. Much more significant was the Civil Rights Movement, especially the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) headed by Martin Luther King Jr. It largely displaced the old, much more moderate NAACP in taking leadership roles. King organized massive demonstrations, that seized massive media attention in an era when network television news was an innovative and universally watched phenomenon. SCLC, student activists and smaller local organizations staged demonstrations across the South. National attention focused on Birmingham, Alabama, where protesters deliberately provoked Bull Connor and his police forces by using young teenagers as demonstrators – and Connor arrested 900 in one day alone. The next day Connor unleashed billy clubs, police dogs, and high-pressure water hoses to disperse and punish the young demonstrators with a brutality that horrified the nation. It was very bad for business and the image of a modernizing progressive urban South. President John F. Kennedy, who had been calling for moderation, threatened to use federal troops to restore order in Birmingham. The result in Birmingham was a compromise by which the new mayor opened the library, golf courses, and other city facilities to both races, against the backdrop of church bombings and assassinations.
Confrontations continued to escalate. In the summer of 1963, there were 800 demonstrations in 200 southern cities and towns, involving over 100,000 participants and 15,000 arrests. In Alabama in June 1963, Governor George Wallace escalated the crisis by defying court orders to admit the first two black students to the University of Alabama. Kennedy responded by sending Congress a comprehensive civil rights bill and ordered Attorney General Robert Kennedy to file federal lawsuits against segregated schools and to deny funds for discriminatory programs. Doctor King launched a massive march on Washington in August 1963, bringing out 200,000 demonstrators in front of the Lincoln Memorial, the largest political assembly in the nation's history. The Kennedy administration now gave full-fledged support to the civil rights movement, but powerful southern congressmen blocked any legislation. After Kennedy was assassinated President Lyndon Johnson called for immediate passage of Kennedy civil rights legislation as a memorial to the martyred president. Johnson formed a coalition with Northern Republicans that led to passage in the House, and with the help of Republican Senate leader Everett Dirksen with passage in the Senate early in 1964. For the first time in history, the southern filibuster was broken, and the Senate finally passed its version on June 19 by a vote of 73 to 27. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 was the most powerful affirmation of equal rights ever made by Congress. It guaranteed access to public accommodations such as restaurants and places of amusement, authorized the Justice Department to bring suits to desegregate facilities in schools, gave new powers to the Civil Rights Commission; and allowed federal funds to be cut off in cases of discrimination. Furthermore, racial, religious and gender discrimination was outlawed for businesses with 25 or more employees, as well as apartment houses. The South resisted until the last moment, but as soon as the new law was signed by President Johnson on July 2, 1964, it was widely accepted across the nation. There was only a scattering of diehard opposition, typified by restaurant owner Lester Maddox in Georgia, who became governor, but the great majority of restaurants and hotels in Georgia followed the new law as the business community realized that peaceful integration was the only way forward.
Since the enactment of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Voting Rights Act of 1965, black people have gone on to hold many offices within the Southern states. Black people have been elected or appointed as mayors or police chiefs in the cities of Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
, Baltimore, Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
, Charlotte, NC, Charlotte, Columbia, South Carolina, Columbia, Dover, Delaware, Dover, Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
, Jackson, Mississippi, Jackson, Jacksonville, Florida, Jacksonville, Memphis, Tennessee, Memphis, Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery, Nashville, Tennessee, Nashville, New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, Raleigh, Richmond, Virginia, Richmond, and Washington, D.C., Washington. They have also gone on to serve in both the U.S. Congress and state legislatures of Southern states.
New Great Migration
The Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s ended Jim Crow laws across the South and other areas of the United States. In recent decades, a second migration appears to be underway, this time with New Great Migration, African Americans from the North moving to the South in record numbers. While race relations are still a contentious issue in the South and most of the U.S., the region surpasses the rest of the country in many areas of integration and racial equality. According to 2003 report by researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee, Virginia Beach, Charlotte, Nashville, Tennessee, Nashville-Davidson, and Jacksonville, Florida, Jacksonville were the five most integrated of the nation's fifty largest cities, with Memphis, Tennessee, Memphis at number six. Southern states tend to have a low disparity in incarceration rates between blacks and whites relative to the rest of the country.
The New Great Migration is not evenly distributed throughout the South. The rise in net gain points to Atlanta, Charlotte, Dallas, and Houston being a growing hot spots for the migrants of The New Great Migration. The percentage of Black Americans who live in the South has been increasing since 1990, and the biggest gains have been in the region's large urban areas, according to census data. The Black population of metro Atlanta more than doubled between 1990 and 2020, surpassing 2 million in the most recent census. The Black population also more than doubled in metro Charlotte while Greater Houston and Dallas-Fort Worth both saw their Black populations surpass 1 million for the first time. Several smaller metro areas also saw sizable gains, including San Antonio;Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
, Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
and Texas. Other southern states, including Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
and Arkansas, have seen little net growth in the African American population from return migration.
Symbolism
The Flags of the Confederate States of America#Battle flag, Confederate battle flag is used as a symbol to identify the South, states' rights and Southern tradition.
Such groups as the League of the South have a high regard for the secession movement of 1860, citing a desire to protect and defend Southern heritage. Numerous political battles have erupted nationally and within the South over flying the Confederate flag over state capitols, and the naming of public buildings or highways after Confederate leaders, the prominence of certain statues and monuments, and the everyday display of Confederate insignia.
Other symbols of the South include the Bonnie Blue Flag, magnolia trees, and the song "Dixie (song), Dixie".
Population centers
The South was predominately rural up until the 1940s. Since the mid-20th century, the population has increasingly grown in urban and metropolitan areas. The following tables show the twenty largest cities, counties, metropolitan and combined statistical areas in the South. Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
is the largest city in the Southern United States.
Major cities





Major counties
Major metropolitan areas
* Asterisk indicates part of the metropolitan area is outside the states classified as Southern by the U.S. Census Bureau.
Major combined statistical areas
Southern states
Listed below are states that are defined by the United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau as the Southern United States. Washington, D.C. is located in the Southern United States region as defined by the Census Bureau, but serves as the capital city of the United States, and is not a state.
See also
* List of online encyclopedias of U.S. states
* ''Albion's Seed''
* Antebellum architecture
* Black Belt in the American South
* Black Southerners
* Cuisine of the Southern United States
* Culture of the Southern United States
* List of plantations in the United States
** Culture of honor (Southern United States)
* Lost Cause of the Confederacy
* Public health in American history
* Rice Belt
* Rural American history
* Southern American English
* Southern art
* Southern hip hop
* Southern hospitality
* Southernization
* Southern literature
* Southern rock
* Southern strategy
* White Southerners
References
Further reading
*
* Ayers, Edward L. ''What Caused the Civil War? Reflections on the South and Southern History'' (2005). .
*
*
*
* Cash, Wilbur J
''The Mind of the South''
(1941). .
* Cooper, Christopher A. and H. Gibbs Knotts, eds. ''The New Politics of North Carolina'' (U. of North Carolina Press, 2008)
* Davis, Donald, and Mark R. Stoll. ''Southern United States: An Environmental History'' (2006)
* Edwards, Laura F. "Southern History as U.S. History", ''Journal of Southern History'', 75 (Aug. 2009), 533–64.
* Flynt, J. Wayne ''Dixie's Forgotten People: The South's Poor Whites'' (1979). Deals with the 20th century.
* Frederickson, Kari. (2013). ''Cold War Dixie: Militarization and Modernization in the American South.'' Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press.
*
* Grantham, Dewey W. ''The South in modern America'' (2001) survey covers 1877–2000.
* Grantham, Dewey W. ''The Life and Death of the Solid South: A Political History'' (1992).
* Jensen, Jeffrey; Pardelli, Giuliana; Timmons, Jeffrey F. 2023.
Representation and Taxation in the American South, 1820–1910
'. Cambridge University Press.
* Johnson, Charles S. ''Statistical atlas of southern counties: listing and analysis of socio-economic indices of 1104 southern counties'' (1941)
excerpt
*
* V. O. Key Jr., Key, V. O.]
''Southern Politics in State and Nation''
(1951). Classic political analysis, state by state.
* Kirby, Jack Temple
''Rural Worlds Lost: The American South, 1920–1960''
(LSU Press, 1986). Major scholarly survey with detailed bibliography.
*
*
* McWhiney, Grady. ''Cracker Culture: Celtic Ways in the Old South'' (1988)
* Mark, Rebecca, and Rob Vaughan. ''The South: The Greenwood Encyclopedia of American Regional Cultures'' (2004)
*
* Odem, Mary E. and Elaine Lacy, eds. ''Latino Immigrants and the Transformation of the U.S. South'' (U of Georgia Press, 2009).
*
*
*
* Rivers, Larry E., and Canter Brown, eds. ''The Varieties of Women's Experiences: Portraits of Southern Women in the Post-Civil War Century'' (UP of Florida, 2010).
* Thornton III, J. Mills
''Archipelagoes of My South: Episodes in the Shaping of a Region, 1830–1965''
(2016)
* Tindall, George B
''The emergence of the new South, 1913–1945''
(1967)
*
*
*
*
* Wilson, Charles R., ed. (2006-2020) ''The New Encyclopedia of Southern Culture'' (University of North Carolina Press), complete in 24 volumes
online
*
* Woodward, C. Vann. ''Origins of the New South, 1877–1913: A History of the South'' (1951). .
*
External links
*
– multimedia collections from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC, UNC–Chapel Hill, or simply Carolina) is a public university, public research university in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, United States. Chartered in 1789, the university first began enrolli ...
Center for the Study of Southern Culture
– the research center at the University of Mississippi
The University of Mississippi (Epithet, byname Ole Miss) is a Public university, public research university in University, near Oxford, Mississippi, United States, with a University of Mississippi Medical Center, medical center in Jackson, Miss ...
, with a graduate program and undergraduate major in southern studies
*
*
{{Authority control
Southern United States,
Census regions of the United States
Cultural regions of the United States







 The South is a diverse meteorological region with numerous climatic zones, including
The South is a diverse meteorological region with numerous climatic zones, including  The arrival of European settlers caused a massive population decline in Native Americans, due to Europeans unknowingly spreading
The arrival of European settlers caused a massive population decline in Native Americans, due to Europeans unknowingly spreading  Slavery was legal in all of the
Slavery was legal in all of the 
 During the
During the 
 The Confederacy had the resources for a short war, but was unable to finance or supply a longer war. It reversed the traditional low-tariff policy of the South by imposing a new 15% tax on all imports from the Union. The Union blockade stopped most commerce from entering the South, and smugglers avoided the tax, so the Confederate tariff produced too little revenue to finance the war. Inflated currency was the solution, but that created distrust of the Richmond government. Because of low investment in railroads, the Southern transportation system depended primarily on river and coastal traffic by boat; both were shut down by the Union Navy. The small railroad system virtually collapsed, so that by 1864 internal travel was so difficult that the Confederate economy was crippled.
The Confederate cause was hopeless by the time Atlanta fell and William T. Sherman marched through Georgia in late 1864, but the rebels fought on until Lee's army surrendered in April 1865. Once the Confederate forces surrendered, the region moved into the
The Confederacy had the resources for a short war, but was unable to finance or supply a longer war. It reversed the traditional low-tariff policy of the South by imposing a new 15% tax on all imports from the Union. The Union blockade stopped most commerce from entering the South, and smugglers avoided the tax, so the Confederate tariff produced too little revenue to finance the war. Inflated currency was the solution, but that created distrust of the Richmond government. Because of low investment in railroads, the Southern transportation system depended primarily on river and coastal traffic by boat; both were shut down by the Union Navy. The small railroad system virtually collapsed, so that by 1864 internal travel was so difficult that the Confederate economy was crippled.
The Confederate cause was hopeless by the time Atlanta fell and William T. Sherman marched through Georgia in late 1864, but the rebels fought on until Lee's army surrendered in April 1865. Once the Confederate forces surrendered, the region moved into the  With passage of the 13th Amendment to the
With passage of the 13th Amendment to the 


 *
* 
 The American South is known for its distinctive dialect and accent. The predominant culture of the South is English, and has its origins with the settlement of the region by large groups of people particularly from parts of West Midlands,
The American South is known for its distinctive dialect and accent. The predominant culture of the South is English, and has its origins with the settlement of the region by large groups of people particularly from parts of West Midlands, 

 Increasing support for civil rights legislation by the national Democratic Party beginning in 1948 caused segregationist Southern Democrats to nominate Strom Thurmond on a third-party "Dixiecrat" ticket in 1948. These Dixiecrats returned to the party by 1950, but Southern Democrats held off Republican inroads in the suburbs by arguing that only they could defend the region from the onslaught of northern liberals and the civil rights movement. In response to the ''Brown v. Board of Education'' ruling of 1954, 101 Southern congressmen (19 senators, 82 House members of which 99 were Southern Democrats and 2 were Republicans) in 1956 denounced the Brown decisions as a "clear abuse of judicial power [that] climaxes a trend in the federal judiciary undertaking to legislate in derogation of the authority of Congress and to encroach upon the reserved rights of the states and the people." The manifesto lauded, "...those states which have declared the intention to resist enforced integration by any lawful means". It was signed by all Southern senators except Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, and Tennessee senators Albert Gore Sr. and Estes Kefauver. Virginia closed schools in Warren County, Virginia, Warren County, Prince Edward County, Virginia, Prince Edward County, Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, and Norfolk, Virginia, Norfolk rather than integrate, but no other state followed suit. Democratic governors Orval Faubus of Arkansas, Ross Barnett of Mississippi, John Connally of Texas, Lester Maddox of Georgia, and, especially, George Wallace of Alabama resisted integration and appealed to a rural and blue-collar electorate.
The northern Democrats' support of civil rights issues culminated when Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the
Increasing support for civil rights legislation by the national Democratic Party beginning in 1948 caused segregationist Southern Democrats to nominate Strom Thurmond on a third-party "Dixiecrat" ticket in 1948. These Dixiecrats returned to the party by 1950, but Southern Democrats held off Republican inroads in the suburbs by arguing that only they could defend the region from the onslaught of northern liberals and the civil rights movement. In response to the ''Brown v. Board of Education'' ruling of 1954, 101 Southern congressmen (19 senators, 82 House members of which 99 were Southern Democrats and 2 were Republicans) in 1956 denounced the Brown decisions as a "clear abuse of judicial power [that] climaxes a trend in the federal judiciary undertaking to legislate in derogation of the authority of Congress and to encroach upon the reserved rights of the states and the people." The manifesto lauded, "...those states which have declared the intention to resist enforced integration by any lawful means". It was signed by all Southern senators except Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, and Tennessee senators Albert Gore Sr. and Estes Kefauver. Virginia closed schools in Warren County, Virginia, Warren County, Prince Edward County, Virginia, Prince Edward County, Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, and Norfolk, Virginia, Norfolk rather than integrate, but no other state followed suit. Democratic governors Orval Faubus of Arkansas, Ross Barnett of Mississippi, John Connally of Texas, Lester Maddox of Georgia, and, especially, George Wallace of Alabama resisted integration and appealed to a rural and blue-collar electorate.
The northern Democrats' support of civil rights issues culminated when Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the  The South produced nine of the country's first twelve List of presidents of the United States, Presidents, including the Virginia Dynasty. After Zachary Taylor won the presidential election of 1848, no Southern politician was elected president until Woodrow Wilson in 1912. Andrew Johnson (of
The South produced nine of the country's first twelve List of presidents of the United States, Presidents, including the Virginia Dynasty. After Zachary Taylor won the presidential election of 1848, no Southern politician was elected president until Woodrow Wilson in 1912. Andrew Johnson (of  The decisive action ending segregation came when Congress, in a bipartisan fashion, overcame Southern filibusters to pass the
The decisive action ending segregation came when Congress, in a bipartisan fashion, overcame Southern filibusters to pass the 



