Strapdown Inertial Guidance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 An inertial navigation system (INS; also inertial guidance system, inertial instrument) is a
An inertial navigation system (INS; also inertial guidance system, inertial instrument) is a
DGON / IEEE ISA
with about 200 international attendees is held annually in October in Germany. Th
publications of all DGON ISA conferences over the last more than 60 years
are accessible.
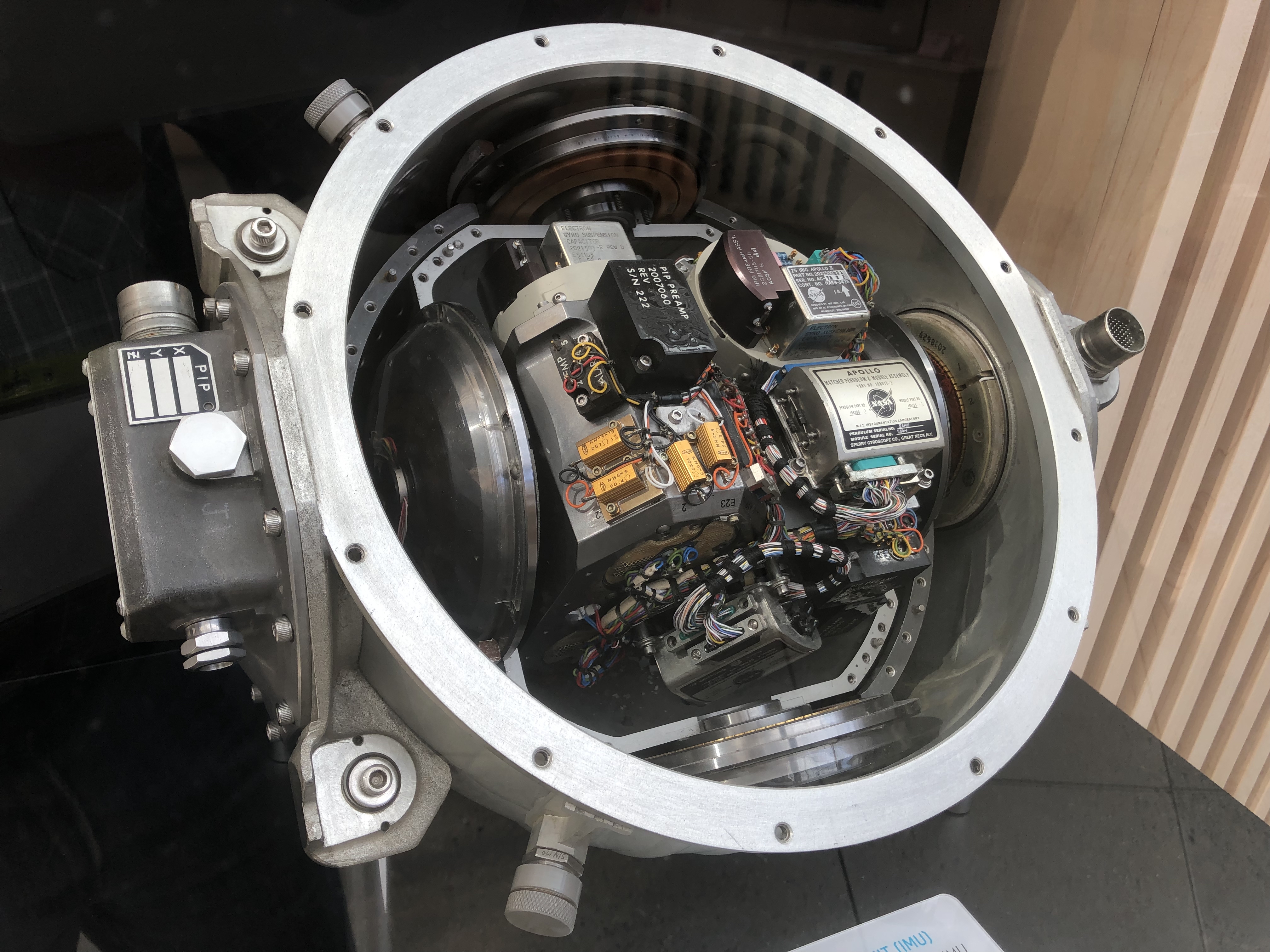 In February 1961 NASA awarded MIT a contract for preliminary design study of a guidance and navigation system for the
In February 1961 NASA awarded MIT a contract for preliminary design study of a guidance and navigation system for the

 INSs contain
INSs contain
 Some systems place the linear accelerometers on a gimballed gyrostabilized platform. The
Some systems place the linear accelerometers on a gimballed gyrostabilized platform. The
Safran
manufactures large numbers of HRG base
inertial navigation systems
dedicated to a wide range of applications.
 These products include "tuning fork gyros". Here, the gyro is designed as an electronically driven tuning fork, often fabricated out of a single piece of quartz or silicon. Such gyros operate in accordance with the dynamic theory that when an angle rate is applied to a translating body, a
These products include "tuning fork gyros". Here, the gyro is designed as an electronically driven tuning fork, often fabricated out of a single piece of quartz or silicon. Such gyros operate in accordance with the dynamic theory that when an angle rate is applied to a translating body, a
 MEMS gyroscopes typically rely on the Coriolis effect to measure angular velocity. It consists of a resonating proof mass mounted in silicon. The gyroscope is, unlike an accelerometer, an active sensor. The proof mass is pushed back and forth by driving combs. A rotation of the gyroscope generates a Coriolis force that is acting on the mass which results in a motion in a different direction. The motion in this direction is measured by electrodes and represents the rate of turn.
MEMS gyroscopes typically rely on the Coriolis effect to measure angular velocity. It consists of a resonating proof mass mounted in silicon. The gyroscope is, unlike an accelerometer, an active sensor. The proof mass is pushed back and forth by driving combs. A rotation of the gyroscope generates a Coriolis force that is acting on the mass which results in a motion in a different direction. The motion in this direction is measured by electrodes and represents the rate of turn.
 A ring laser gyro (RLG) splits a beam of
A ring laser gyro (RLG) splits a beam of
 The basic, open-loop accelerometer consists of a mass attached to a spring. The mass is constrained to move only in line with the spring. Acceleration causes deflection of the mass and the offset distance is measured. The acceleration is derived from the values of deflection distance, mass and the spring constant. The system must also be damped to avoid oscillation. A closed-loop accelerometer achieves higher performance by using a feedback loop to cancel the deflection, thus keeping the mass nearly stationary. Whenever the mass deflects, the feedback loop causes an electric coil to apply an equally negative force on the mass, canceling the motion. Acceleration is derived from the amount of negative force applied. Because the mass barely moves, the effects of non-linearities of the spring and damping system are greatly reduced. In addition, this accelerometer provides for increased bandwidth beyond the natural frequency of the sensing element.
Both types of accelerometers have been manufactured as integrated micro-machinery on silicon chips.
The basic, open-loop accelerometer consists of a mass attached to a spring. The mass is constrained to move only in line with the spring. Acceleration causes deflection of the mass and the offset distance is measured. The acceleration is derived from the values of deflection distance, mass and the spring constant. The system must also be damped to avoid oscillation. A closed-loop accelerometer achieves higher performance by using a feedback loop to cancel the deflection, thus keeping the mass nearly stationary. Whenever the mass deflects, the feedback loop causes an electric coil to apply an equally negative force on the mass, canceling the motion. Acceleration is derived from the amount of negative force applied. Because the mass barely moves, the effects of non-linearities of the spring and damping system are greatly reduced. In addition, this accelerometer provides for increased bandwidth beyond the natural frequency of the sensing element.
Both types of accelerometers have been manufactured as integrated micro-machinery on silicon chips.
Micro-PNT adds a highly accurate master timing clock integrated into an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) chip, making it a Timing & Inertial Measurement Unit chip. A TIMU chip integrates 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer and 3-axis magnetometer together with a highly accurate master timing clock, so that it can simultaneously measure the motion tracked and combine that with timing from the synchronized clock.
 Where f is specific force, is angular rate, a is acceleration, R is position, and V are velocity, is the angular velocity of the earth, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h are the NED location parameters. Also, super/subscripts of E, I and B are representing variables in the Earth centered, inertial or body reference frame, respectively and C is a transformation of reference frames.
Where f is specific force, is angular rate, a is acceleration, R is position, and V are velocity, is the angular velocity of the earth, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h are the NED location parameters. Also, super/subscripts of E, I and B are representing variables in the Earth centered, inertial or body reference frame, respectively and C is a transformation of reference frames.
Ferranti Inertial Navigation System (INAS)
Inertial Navigation System
Principle of operation of an accelerometer
Overview of inertial instrument types
Oxford Technical Solutions Inertial Navigation Guide
Listing of open-source Inertial Navigation system
Impact of inertial sensor errors on Inertial Navigation System position and attitude errors
Introduction to Inertial Navigation Systems in UAV/Drone Applications
{{Use dmy dates, date=July 2022 Geodesy Aircraft instruments Aerospace engineering Avionics Spacecraft components Missile guidance Navigational equipment Technology systems Navigational aids Inertial navigation

navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navig ...
device that uses motion sensors (accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (tha ...
s), rotation sensors (gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in ...
s) and a computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
to continuously calculate by dead reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating the current position of a moving object by using a previously determined position, or fix, and incorporating estimates of speed, heading (or direction or course), and elapsed time. T ...
the position, the orientation, and the velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
(direction and speed of movement) of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter
An altimeter or an altitude meter is an instrument used to measure the altitude of an object above a fixed level. The measurement of altitude is called altimetry, which is related to the term bathymetry, the measurement of depth under water.
Ty ...
and sometimes by magnetic sensors (magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, ...
s) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robot
A mobile robot is an automatic machine that is capable of locomotion.Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Lanzon, A.,Group Coordinated Control of Networked Mobile Robots with Applications to Object Transportation IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 202 ...
s and on vehicles such as ship
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally disti ...
s, aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
, submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
s, guided missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of Propulsion, self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a targ ...
s, and spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous.
Design
Inertial navigation is a self-contained navigation technique in which measurements provided by accelerometers and gyroscopes are used to track the position and orientation of an object relative to a known starting point, orientation and velocity. Inertial measurement units (IMUs) typically contain three orthogonal rate-gyroscopes and three orthogonal accelerometers, measuring angular velocity and linear acceleration respectively. By processing signals from these devices it is possible to track the position and orientation of a device. An inertial navigation system includes at least a computer and a platform or module containingaccelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (tha ...
s, gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in ...
s, or other motion-sensing devices. The INS is initially provided with its position and velocity from another source (a human operator, a GPS satellite receiver, etc.) accompanied with the initial orientation and thereafter computes its own updated position and velocity by integrating information received from the motion sensors. The advantage of an INS is that it requires no external references in order to determine its position, orientation, or velocity once it has been initialized.
An INS can detect a change in its geographic position (a move east or north, for example), a change in its velocity (speed and direction of movement) and a change in its orientation (rotation about an axis). It does this by measuring the linear acceleration and angular velocity applied to the system. Since it requires no external reference (after initialization), it is immune to jamming and deception.
Gyroscopes measure the angular displacement of the sensor frame with respect to the inertial reference frame
In classical physics and special relativity, an inertial frame of reference (also called an inertial space or a Galilean reference frame) is a frame of reference in which objects exhibit inertia: they remain at rest or in uniform motion relative ...
. By using the original orientation of the system in the inertial reference frame as the initial condition
In mathematics and particularly in dynamic systems, an initial condition, in some contexts called a seed value, is a value of an evolving variable at some point in time designated as the initial time (typically denoted ''t'' = 0). Fo ...
and integrating the angular displacement, the system's current orientation is known at all times. This can be thought of as the ability of a blindfolded passenger in a car to feel the car turn left and right or tilt up and down as the car ascends or descends hills. Based on this information alone, the passenger knows what direction the car is facing, but not how fast or slow it is moving, or whether it is sliding sideways.
Accelerometers measure the linear acceleration of the moving vehicle in the sensor or body frame, but in directions that can only be measured relative to the moving system (since the accelerometers are fixed to the system and rotate with the system, but are not aware of their own orientation). This can be thought of as the ability of a blindfolded passenger in a car to feel themself pressed back into their seat as the vehicle accelerates forward or pulled forward as it slows down; and feel themself pressed down into their seat as the vehicle accelerates up a hill or rise up out of their seat as the car passes over the crest of a hill and begins to descend. Based on this information alone, they know how the vehicle is accelerating relative to itself; that is, whether it is accelerating forward, backward, left, right, up (toward the car's ceiling), or down (toward the car's floor), measured relative to the car, but not the direction relative to the Earth, since they did not know what direction the car was facing relative to the Earth when they felt the accelerations.
However, by tracking both the current angular velocity
In physics, angular velocity (symbol or \vec, the lowercase Greek letter omega), also known as the angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time, i ...
of the system and the current linear acceleration of the system measured relative to the moving system, it is possible to determine the linear acceleration of the system in the inertial reference frame. Performing integration on the inertial accelerations (using the original velocity as the initial conditions) using the correct kinematic equations yields the inertial velocities of the system and integration again (using the original position as the initial condition) yields the inertial position. In our example, if the blindfolded passenger knew how the car was pointed and what its velocity was before they were blindfolded, and if they are able to keep track of both how the car has turned and how it has accelerated and decelerated since, then they can accurately know the current orientation, position, and velocity of the car at any time.
Uses
Inertial navigation is used in a wide range of applications including the navigation of aircraft, tactical and strategic missiles, spacecraft, submarines and ships. It is also embedded in some mobile phones for purposes of mobile phone location and tracking. Recent advances in the construction ofmicroelectromechanical systems
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices ...
(MEMS) have made it possible to manufacture small and light inertial navigation systems. These advances have widened the range of possible applications to include areas such as human and animal motion capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mocap or mo-cap, for short) is the process of recording high-resolution motion (physics), movement of objects or people into a computer system. It is used in Military science, military, entertainment, sports ...
.
Inertial navigation systems are used in many different moving objects. However, their cost and complexity place constraints on the environments in which they are practical for use.
To support the use of inertial technology in the best way, already in 1965 a technical working group for Inertial Sensors had been established in Germany to bring together the users, the manufacturers and the researchers of inertial sensors. This working group has been continuously developed and today it is known as DGON ISA Inertial Sensors and Application Symposium, the leading conference for inertial technologies for more than 60 years. This SymposiuDGON / IEEE ISA
with about 200 international attendees is held annually in October in Germany. Th
publications of all DGON ISA conferences over the last more than 60 years
are accessible.
Drift rate
All inertial navigation systems suffer from integration drift: small errors in the measurement of acceleration and angular velocity are integrated into progressively larger errors in velocity, which are compounded into still greater errors in position.''Inertial navigation systems analysis'', Kenneth R. Britting, Wiley-Interscience, 1971. Since the new position is calculated from the previous calculated position and the measured acceleration and angular velocity, these errors accumulate roughly proportionally to the time since the initial position was input. Even the best accelerometers, with a standard error of 10 micro-g, would accumulate a 50-meter (164-ft) error within 17 minutes. Therefore, the position must be periodically corrected by input from some other type of navigation system. Accordingly, inertial navigation is usually used to supplement other navigation systems, providing a higher degree of accuracy than is possible with the use of any single system. For example, if, in terrestrial use, the inertially tracked velocity is intermittently updated to zero by stopping, the position will remain precise for a much longer time, a so-called ''zero velocity update''. In aerospace particularly, other measurement systems are used to determine INS inaccuracies, e.g. the Honeywell LaseRefV inertial navigation systems usesGPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geol ...
and air data computer
An air data computer (ADC) or central air data computer (CADC) computes altitude, vertical speed, air speed, and Mach number from pressure and temperature inputs. It is an essential avionics component found in modern aircraft. This computer, ra ...
outputs to maintain required navigation performance
Required navigation performance (RNP) is a type of performance-based navigation (PBN) that allows an aircraft to fly a specific path between two 3D-defined points in space.
Navigation precision
Area navigation, Area navigation (RNAV) and RNP s ...
. The navigation error rises with the lower sensitivity of the sensors used. Currently, devices combining different sensors are being developed, e.g. attitude and heading reference system. Because the navigation error is mainly influenced by the numerical integration
In analysis, numerical integration comprises a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral.
The term numerical quadrature (often abbreviated to quadrature) is more or less a synonym for "numerical integr ...
of angular rates and accelerations, the pressure reference system
Pressure reference system (PRS) is an enhancement of the inertial reference system and attitude and heading reference system designed to provide position angles measurements which are stable in time and do not suffer from long term drift caused ...
was developed to use one numerical integration of the angular rate measurements.
Estimation theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of Statistical parameter, parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such ...
in general and Kalman filtering
In statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering (also known as linear quadratic estimation) is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, to produce estimates of unk ...
in particular,''Applied Optimal Estimation'', Arthur Gelb (Editor), M.I.T. Press, 1974. provide a theoretical framework for combining information from various sensors. One of the most common alternative sensors is a satellite navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geopositioning. A satellite navigation system with global coverage is termed global navigation satellite system (GNSS). , four global systems are ope ...
radio such as GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geol ...
, which can be used for all kinds of vehicles with direct sky visibility. Indoor applications can use pedometer
A pedometer, or step-counter, is a device, usually portable and electronic or electromechanical, that counts each step a person takes by detecting the motion of the person's hands or hips. Because the distance of each person's step varies, an ...
s, distance measurement equipment, or other kinds of position sensor A position sensor is a sensor that detects an object's position. A position sensor may indicate the absolute position of the object (its location) or its relative position (displacement) in terms of linear travel, rotational angle or three-dimension ...
s. By properly combining the information from an INS and other systems (GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geol ...
), the errors in position and velocity are stable
A stable is a building in which working animals are kept, especially horses or oxen. The building is usually divided into stalls, and may include storage for equipment and feed.
Styles
There are many different types of stables in use tod ...
. Furthermore, INS can be used as a short-term fallback while GPS signals are unavailable, for example when a vehicle passes through a tunnel.
In 2011, GPS jamming at the civilian level became a governmental concern. The relative ease in ability to jam these systems has motivated the military to reduce navigation dependence on GPS technology. Because inertial navigation sensors do not depend on radio signals unlike GPS, they cannot be jammed. In 2012, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory reported a method to merge measurements from 10 pairs of MEMS gyroscope
A vibrating structure gyroscope (VSG), defined by the IEEE as a Coriolis vibratory gyroscope (CVG), is a gyroscope that uses a vibrating (as opposed to rotating) structure as its orientation reference. A vibrating structure gyroscope functions ...
and accelerometers (plus occasional GPS), reducing the positional error by two thirds for a projectile. The algorithm can correct for systemic biases in individual sensors, using both GPS and a heuristic based on the gun-firing acceleration force. If one sensor consistently over or underestimates distance, the system can adjust the corrupted sensor's contributions to the final calculation.
History
Inertial navigation systems were originally developed forrocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
s. American rocketry pioneer Robert Goddard
Robert Hutchings Goddard (October 5, 1882 – August 10, 1945) was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket, which was successfully lau ...
experimented with rudimentary gyroscopic
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rot ...
systems. Goddard's systems were of great interest to contemporary German pioneers including Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( ; ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German–American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and '' Allgemeine SS'', the leading figure in the development of ...
. The systems entered more widespread use with the advent of spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
, guided missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of Propulsion, self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a targ ...
s, and commercial airliner
An airliner is a type of airplane for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. The modern and most common variant of the airliner is a long, tube shaped, and jet powered aircraft. The largest ...
s.
Early German World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
V2 guidance systems combined two gyroscopes and a lateral accelerometer with a simple analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses physical phenomena such as Electrical network, electrical, Mechanics, mechanical, or Hydraulics, hydraulic quantities behaving according to the math ...
to adjust the azimuth
An azimuth (; from ) is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north, in a local or observer-centric spherical coordinate system.
Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer ( origin) to a point ...
for the rocket in flight. Analog computer signals were used to drive four graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
rudders in the rocket exhaust for flight control. The GN&C (Guidance, Navigation, and Control) system for the V2 provided many innovations as an integrated platform with closed loop guidance. At the end of the war von Braun engineered the surrender of 500 of his top rocket scientists, along with plans and test vehicles, to the Americans. They arrived at Fort Bliss, Texas
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
in 1945 under the provisions of Operation Paperclip
The Operation Paperclip was a secret United States intelligence program in which more than 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians were taken from former Nazi Germany to the US for government employment after the end of World War I ...
and were subsequently moved to Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is the List of municipalities in Alabama, most populous city in the U.S. state of Alabama. The population of the city is estimated to be 241,114 in 2024, making it the List of United States cities by population, 100th-most populous ...
, in 1950 where they worked for U.S. Army rocket research programs.
In the early 1950s, the US government wanted to insulate itself against over-dependency on the German team for military applications, including the development of a fully domestic missile guidance program. The MIT Instrumentation Laboratory (later to become the Charles Stark Draper Laboratory
Draper Laboratory is an American non-profit research and development organization, headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts; its official name is The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Inc. The laboratory specializes in the design, development, an ...
, Inc.) was chosen by the Air Force Western Development Division to provide a self-contained guidance system backup to Convair in San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
for the new Atlas intercontinental ballistic missile (Construction and testing were completed by Arma Division of AmBosch Arma). The technical monitor for the MIT task was engineer Jim Fletcher, who later served as NASA Administrator. The Atlas guidance system was to be a combination of an on-board autonomous system and a ground-based tracking and command system. The self-contained system finally prevailed in ballistic missile applications for obvious reasons. In space exploration, a mixture of the two remains.
In the summer of 1952, Dr. Richard Battin and Dr. J. Halcombe "Hal" Laning, Jr., researched computational based solutions to guidance and undertook the initial analytical work on the Atlas inertial guidance in 1954. Other key figures at Convair were Charlie Bossart, the Chief Engineer, and Walter Schweidetzky, head of the guidance group. Schweidetzky had worked with von Braun at Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, ) is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in north-eastern Germany. It is part of the ''Amt (country subdivision), Amt'' (collective municipality) of Used ...
during World War II.
The initial Delta guidance system assessed the difference in position from a reference trajectory. A velocity to be gained (VGO) calculation is made to correct the current trajectory with the objective of driving VGO to zero. The mathematics of this approach were fundamentally valid, but dropped because of the challenges in accurate inertial guidance and analog computing power. The challenges faced by the Delta efforts were overcome by the Q system (see Q-guidance) of guidance. The Q system's revolution was to bind the challenges of missile guidance (and associated equations of motion) in the matrix Q. The Q matrix represents the partial derivatives of the velocity with respect to the position vector. A key feature of this approach allowed for the components of the vector cross product (v, xdv, /dt) to be used as the basic autopilot rate signals—a technique that became known as ''cross-product steering''. The Q-system was presented at the first Technical Symposium on Ballistic Missiles held at the Ramo-Wooldridge Corporation in Los Angeles on 21 and 22 June 1956. The Q system was classified information through the 1960s. Derivations of this guidance are used for today's missiles.
Guidance in human spaceflight
 In February 1961 NASA awarded MIT a contract for preliminary design study of a guidance and navigation system for the
In February 1961 NASA awarded MIT a contract for preliminary design study of a guidance and navigation system for the Apollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
. MIT and the Delco Electronics Div. of General Motors Corp. were awarded the joint contract for design and production of the Apollo Guidance and Navigation systems for the Command Module and the Lunar Module. Delco produced the IMUs (Inertial Measurement Unit
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the Orientation (geometry), orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, an ...
s) for these systems, Kollsman Instrument Corp. produced the Optical Systems, and the Apollo Guidance Computer
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidanc ...
was built by Raytheon
Raytheon is a business unit of RTX Corporation and is a major U.S. defense contractor and industrial corporation with manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. Founded in 1922, it merged in 2020 with Unite ...
under subcontract.
For the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
, open loop
In control theory, an open-loop controller, also called a non-feedback controller, is a control loop part of a control system in which the control action ("input" to the system) is independent of the "process output", which is the process varia ...
guidance was used to guide the Shuttle from lift-off until Solid Rocket Booster (SRB) separation. After SRB separation the primary Space Shuttle guidance is named PEG (Powered Explicit Guidance). PEG takes into account both the Q system and the predictor-corrector attributes of the original "Delta" System (PEG Guidance). Although many updates to the Shuttle's navigation system had taken place over the last 30 years (ex. GPS in the OI-22 build), the guidance core of the Shuttle GN&C system had evolved little. Within a crewed system, there is a human interface needed for the guidance system. As astronauts are the customer for the system, many new teams were formed that touch GN&C as it is a primary interface to "fly" the vehicle.
Early use in aircraft inertial guidance
One example of a popular INS for commercial aircraft was the Delco Carousel, which provided partial automation of navigation in the days before completeflight management system
A flight management system (FMS) is a fundamental component of a modern airliner's avionics. An FMS is a specialized computer system that automates a wide variety of in-flight tasks, reducing the workload on the flight crew to the point that mod ...
s became commonplace. The Carousel allowed pilots to enter 9 waypoints at a time and then guided the aircraft from one waypoint to the next using an INS to determine aircraft position and velocity. Boeing Corporation subcontracted the Delco Electronics Div. of General Motors to design and build the first production Carousel systems for the early models (-100, -200 and -300) of the 747 aircraft. The 747 utilized three Carousel systems operating in concert for reliability purposes. The Carousel system and derivatives thereof were subsequently adopted for use in many other commercial and military aircraft. The USAF C-141 was the first military aircraft to utilize the Carousel in a dual system configuration, followed by the C-5A which utilized the triple INS configuration, similar to the 747. The KC-135A fleet was fitted with a single Carousel IV-E system that could operate as a stand-alone INS or can be aided by the AN/APN-81 or AN/APN-218 Doppler radar
A Doppler radar is a specialized radar that uses the Doppler effect to produce velocity data about objects at a distance. It does this by bouncing a microwave signal off a desired target and analyzing how the object's motion has altered the fre ...
. Some special-mission variants of the C-135 were fitted with dual Carousel IV-E INSs. ARINC Characteristic 704 defines the INS used in commercial air transport.
Details
Inertial Measurement Unit
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the Orientation (geometry), orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, an ...
s (IMUs) which have angular and linear accelerometers (for changes in position); some IMUs include a gyroscopic element (for maintaining an absolute angular reference).
Angular accelerometers measure how the vehicle is rotating in space. Generally, there is at least one sensor for each of the three axes: pitch (nose up and down), yaw (nose left and right) and roll (clockwise or counter-clockwise from the cockpit).
Linear accelerometers measure non-gravitational accelerationsEshbach's Handbook of Engineering Fundamentals By Ovid W. Eshbach, Byron pg 9 of the vehicle. Since it can move in three axes (up and down, left and right, forward and back), there is a linear accelerometer for each axis.
A computer continually calculates the vehicle's current position. First, for each of the six degrees of freedom
In many scientific fields, the degrees of freedom of a system is the number of parameters of the system that may vary independently. For example, a point in the plane has two degrees of freedom for translation: its two coordinates; a non-infinite ...
(x,y,z and θx, θy and θz), it integrates over time the sensed acceleration, together with an estimate of gravity, to calculate the current velocity. Then it integrates the velocity to calculate the current position.
Inertial guidance is difficult without computers. The desire to use inertial guidance in the Minuteman missile and Project Apollo
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
drove early attempts to miniaturize computers.
Inertial guidance systems are now usually combined with satellite navigation system
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
s through a digital filtering system. The inertial system provides short term data, while the satellite system corrects accumulated errors of the inertial system.
An inertial guidance system that will operate near the surface of the earth must incorporate Schuler tuning Schuler, also Schüler, Shuler, and Shuhler, is a surname. The German language, German word ''Schüler'' directly translates to the English word ''scholar'' and has the meaning "pupil" in German. Notable people with the surname include:
* Adon Shule ...
so that its platform will continue pointing towards the center of the Earth as a vehicle moves from place to place.
Basic schemes
Gimballed gyrostabilized platforms
 Some systems place the linear accelerometers on a gimballed gyrostabilized platform. The
Some systems place the linear accelerometers on a gimballed gyrostabilized platform. The gimbal
A gimbal is a pivoted support that permits rotation of an object about an axis. A set of three gimbals, one mounted on the other with orthogonal pivot axes, may be used to allow an object mounted on the innermost gimbal to remain independent of ...
s are a set of three rings, each with a pair of bearings initially at right angles. They let the platform twist about any rotational axis (or, rather, they let the platform keep the same orientation while the vehicle rotates around it). There are two gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in ...
s (usually) on the platform.
Two gyroscopes are used to cancel gyroscopic precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In othe ...
, the tendency of a gyroscope to twist at right angles to an input torque. By mounting a pair of gyroscopes (of the same rotational inertia and spinning at the same speed in opposite directions) at right angles the precessions are cancelled and the platform will resist twisting.
This system allows a vehicle's roll, pitch and yaw angles to be measured directly at the bearings of the gimbals. Relatively simple electronic circuits can be used to add up the linear accelerations, because the directions of the linear accelerometers do not change.
The big disadvantage of this scheme is that it uses many expensive precision mechanical parts. It also has moving parts
Machines include both fixed and moving parts. The moving parts have controlled and constrained motions.
Moving parts are machine components excluding any moving fluids, such as fuel, coolant or hydraulic fluid. Moving parts also do not include ...
that can wear out or jam and is vulnerable to gimbal lock
Gimbal lock is the loss of one degree of freedom (mechanics), degree of freedom in a multi-dimensional mechanism at certain alignments of the axes. In a three-dimensional three-gimbal mechanism, gimbal lock occurs when the axes of two of the gi ...
. The primary guidance system of the Apollo spacecraft
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft ...
used a three-axis gyrostabilized platform, feeding data to the Apollo Guidance Computer
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidanc ...
. Maneuvers had to be carefully planned to avoid gimbal lock.
Fluid-suspended gyrostabilized platforms
Gimbal lock constrains maneuvering and it would be beneficial to eliminate the slip rings and bearings of the gimbals. Therefore, some systems use fluid bearings or a flotation chamber to mount a gyrostabilized platform. These systems can have very high precisions (e.g.,Advanced Inertial Reference Sphere
The Advanced Inertial Reference Sphere (AIRS) is a highly accurate inertial navigation system designed for use in the LGM-118 Peacekeeper ICBM, which was intended for precision nuclear strikes against Soviet missile silos.
Details
AIRS is a flu ...
). Like all gyrostabilized platforms, this system runs well with relatively slow, low-power computers.
The fluid bearings are pads with holes through which pressurized inert gas (such as helium) or oil presses against the spherical shell of the platform. The fluid bearings are very slippery and the spherical platform can turn freely. There are usually four bearing pads, mounted in a tetrahedral arrangement to support the platform.
In premium systems, the angular sensors are usually specialized transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
coils made in a strip on a flexible printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
. Several coil strips are mounted on great circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.
Discussion
Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spher ...
s around the spherical shell of the gyrostabilized platform. Electronics outside the platform uses similar strip-shaped transformers to read the varying magnetic fields produced by the transformers wrapped around the spherical platform. Whenever a magnetic field changes shape, or moves, it will cut the wires of the coils on the external transformer strips. The cutting generates an electric current in the external strip-shaped coils and electronics can measure that current to derive angles.
Cheap systems sometimes use bar code
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, Machine-readable data, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly ref ...
s to sense orientations and use solar cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect.
s or a single transformer to power the platform. Some small missiles have powered the platform with light from a window or optic fibers to the motor. A research topic is to suspend the platform with pressure from exhaust gases. Data is returned to the outside world via the transformers, or sometimes LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresp ...
s communicating with external photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ...
s.
Strapdown systems
Lightweight digital computers permit the system to eliminate the gimbals, creating ''strapdown'' systems, so called because their sensors are simply strapped to the vehicle. This reduces the cost, eliminatesgimbal lock
Gimbal lock is the loss of one degree of freedom (mechanics), degree of freedom in a multi-dimensional mechanism at certain alignments of the axes. In a three-dimensional three-gimbal mechanism, gimbal lock occurs when the axes of two of the gi ...
, removes the need for some calibrations and increases the reliability by eliminating some of the moving parts. Angular rate sensors called ''rate gyros'' measure the angular velocity of the vehicle.
A strapdown system needs a dynamic measurement range several hundred times that required by a gimballed system. That is, it must integrate the vehicle's attitude changes in pitch, roll and yaw, as well as gross movements. Gimballed systems could usually do well with update rates of 50–60 Hz. However, strapdown systems normally update about 2000 Hz. The higher rate is needed to let the navigation system integrate the angular rate into an attitude accurately.
The data updating algorithms (''direction cosines'' or quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. The algebra of quater ...
s) involved are too complex to be accurately performed except by digital electronics. However, digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', wh ...
s are now so inexpensive and fast that rate gyro systems can now be practically used and mass-produced. The Apollo lunar module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed s ...
used a strapdown system in its backup Abort Guidance System (AGS).
Strapdown systems are nowadays commonly used in commercial and military applications (aircraft, ships, ROVs, missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
s, etc.). State-of-the-art strapdown systems are based upon ring laser gyroscopes, fibre optic gyrocopes or hemispherical resonator gyroscopes. They are using digital electronics and advanced digital filtering techniques such as Kalman filter
In statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering (also known as linear quadratic estimation) is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, to produce estimates of unk ...
.
Motion-based alignment
The orientation of a gyroscope system can sometimes also be inferred simply from its position history (e.g., GPS). This is, in particular, the case with planes and cars, where the velocity vector usually implies the orientation of the vehicle body. For example,Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building automation, industrial automa ...
's ''Align in Motion'' is an initialization process where the initialization occurs while the aircraft is moving, in the air or on the ground. This is accomplished using GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geol ...
and an inertial reasonableness test, thereby allowing commercial data integrity requirements to be met. This process has been FAA certified to recover pure INS performance equivalent to stationary alignment procedures for civilian flight times up to 18 hours.
It avoids the need for gyroscope batteries on aircraft.
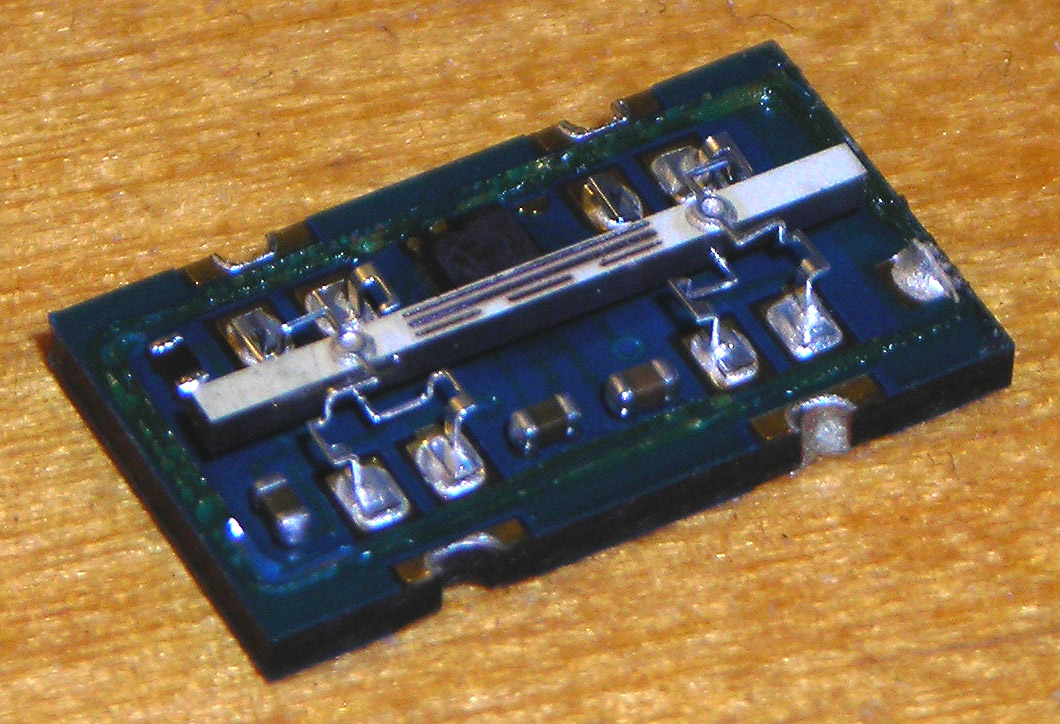
Vibrating gyros
Less-expensive navigation systems, intended for use in automobiles, may use avibrating structure gyroscope
A vibrating structure gyroscope (VSG), defined by the IEEE as a Coriolis vibratory gyroscope (CVG), is a gyroscope that uses a vibrating (as opposed to rotating) structure as its orientation reference. A vibrating structure gyroscope functions ...
to detect changes in heading and the odometer pickup to measure distance covered along the vehicle's track. This type of system is much less accurate than a higher-end INS, but it is adequate for the typical automobile application where GPS is the primary navigation system and dead reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating the current position of a moving object by using a previously determined position, or fix, and incorporating estimates of speed, heading (or direction or course), and elapsed time. T ...
is only needed to fill gaps in GPS coverage when buildings or terrain block the satellite signals.
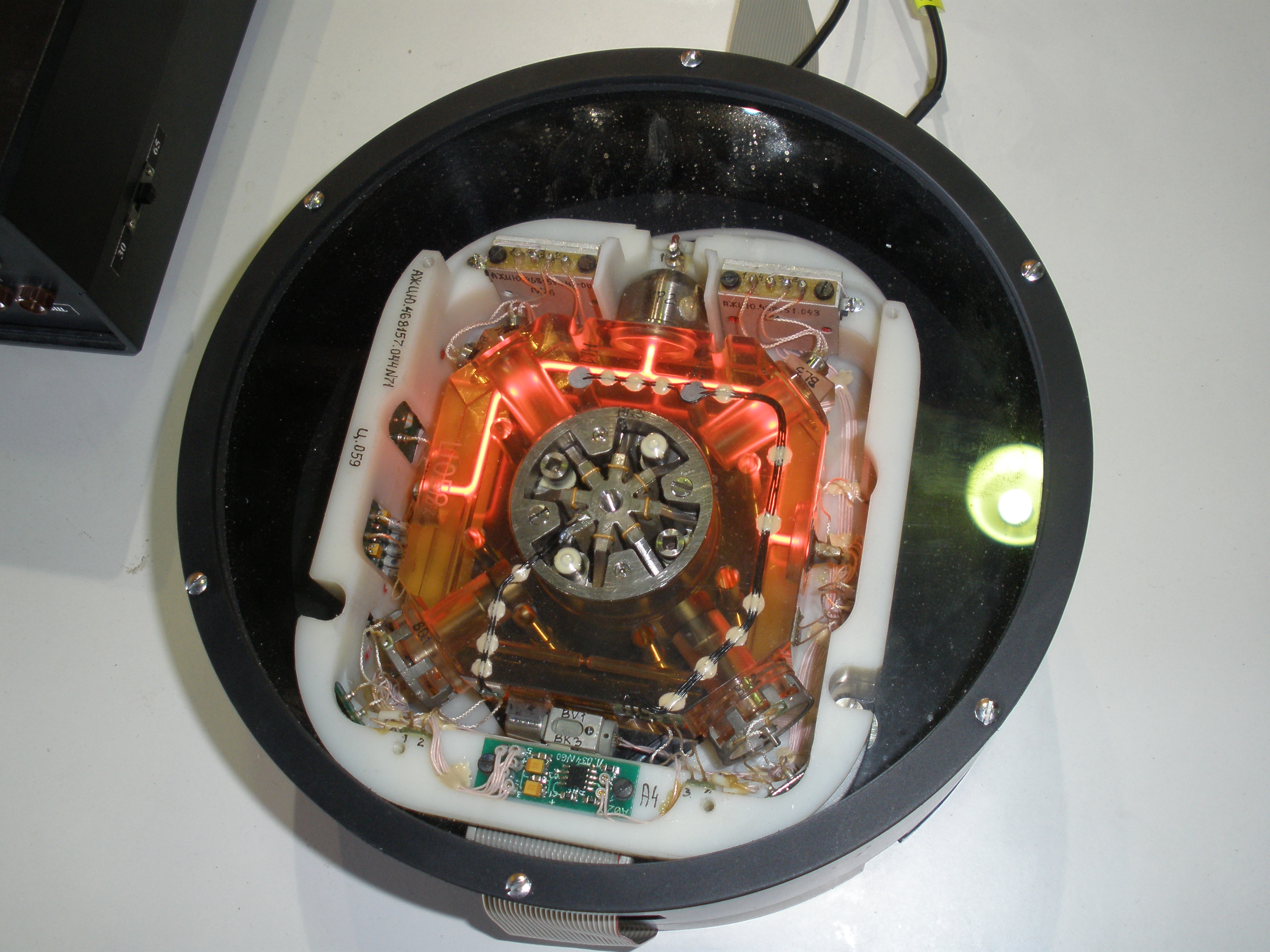
Hemispherical resonator gyros
If a standing wave is induced in a hemispheric resonant structure and then the resonant structure is rotated, the spherical harmonic standing wave rotates through an angle different from the quartz resonator structure due to the Coriolis force. The movement of the outer case with respect to the standing wave pattern is proportional to the total rotation angle and can be sensed by appropriate electronics. The system resonators are machined fromfused quartz
Fused quartz, fused silica or quartz glass is a glass consisting of almost pure silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) in amorphous (non-crystalline) form. This differs from all other commercial glasses, such as soda-lime glass, lead glass, or borosi ...
due to its excellent mechanical properties. The electrodes that drive and sense the standing waves are deposited directly onto separate quartz structures that surround the resonator. These gyros can operate in either a whole angle mode (which gives them nearly unlimited rate capability) or a force rebalance mode that holds the standing wave in a fixed orientation with respect to the gyro housing (which gives them much better accuracy).
This system has almost no moving parts and is very accurate. However it is still relatively expensive due to the cost of the precision ground and polished hollow quartz hemispheres. Northrop Grumman currently manufactures IMUs (inertial measurement unit
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the Orientation (geometry), orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, an ...
s) for spacecraft that use HRGs. These IMUs have demonstrated extremely high reliability since their initial use in 1996Safran
manufactures large numbers of HRG base
inertial navigation systems
dedicated to a wide range of applications.
Quartz rate sensors
 These products include "tuning fork gyros". Here, the gyro is designed as an electronically driven tuning fork, often fabricated out of a single piece of quartz or silicon. Such gyros operate in accordance with the dynamic theory that when an angle rate is applied to a translating body, a
These products include "tuning fork gyros". Here, the gyro is designed as an electronically driven tuning fork, often fabricated out of a single piece of quartz or silicon. Such gyros operate in accordance with the dynamic theory that when an angle rate is applied to a translating body, a Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motio ...
is generated.
This system is usually integrated on a silicon chip. It has two mass-balanced quartz tuning forks, arranged "handle-to-handle" so forces cancel. Aluminum electrodes evaporated onto the forks and the underlying chip both drive and sense the motion. The system is both manufacturable and inexpensive. Since quartz is dimensionally stable, the system can be accurate.
As the forks are twisted about the axis of the handle, the vibration of the tines tends to continue in the same plane of motion. This motion has to be resisted by electrostatic forces from the electrodes under the tines. By measuring the difference in capacitance between the two tines of a fork, the system can determine the rate of angular motion.
Current state-of-the-art non-military technology () can build small solid-state sensors that can measure human body movements. These devices have no moving parts and weigh about .
Solid-state devices using the same physical principles are used for image stabilization
Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce motion blur, blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure (photography), exposure.
Generally, it compensates for panning (camera), pan an ...
in small cameras or camcorders. These can be extremely small, around and are built with microelectromechanical systems
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices ...
(MEMS) technologies.
MHD sensor
Sensors based on magnetohydrodynamic principles can be used to measure angular velocities.MEMS gyroscope
 MEMS gyroscopes typically rely on the Coriolis effect to measure angular velocity. It consists of a resonating proof mass mounted in silicon. The gyroscope is, unlike an accelerometer, an active sensor. The proof mass is pushed back and forth by driving combs. A rotation of the gyroscope generates a Coriolis force that is acting on the mass which results in a motion in a different direction. The motion in this direction is measured by electrodes and represents the rate of turn.
MEMS gyroscopes typically rely on the Coriolis effect to measure angular velocity. It consists of a resonating proof mass mounted in silicon. The gyroscope is, unlike an accelerometer, an active sensor. The proof mass is pushed back and forth by driving combs. A rotation of the gyroscope generates a Coriolis force that is acting on the mass which results in a motion in a different direction. The motion in this direction is measured by electrodes and represents the rate of turn.
Ring laser gyros
 A ring laser gyro (RLG) splits a beam of
A ring laser gyro (RLG) splits a beam of laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
light into two beams in opposite directions through narrow tunnels in a closed circular optical path around the perimeter of a triangular block of temperature-stable Cervit glass with reflecting mirrors placed in each corner. When the gyro is rotating at some angular rate, the distance traveled by each beam will differ—the shorter path being opposite to the rotation. The phase shift between the two beams can be measured by an interferometer and is proportional to the rate of rotation (Sagnac effect
The Sagnac effect, also called Sagnac interference, named after French physicist Georges Sagnac, is a phenomenon encountered in interferometry that is elicited by rotation. The Sagnac effect manifests itself in a setup called a ring interferomete ...
).
In practice, at low rotation rates the output frequency can drop to zero as the result of backscatter
In physics, backscatter (or backscattering) is the reflection of waves, particles, or signals back to the direction from which they came. It is usually a diffuse reflection due to scattering, as opposed to specular reflection as from a mirror, ...
ing causing the beams to synchronise and lock together. This is known as a ''lock-in'', or ''laser-lock''. The result is that there is no change in the interference pattern and therefore no measurement change.
To unlock the counter-rotating light beams, laser gyros either have independent light paths for the two directions (usually in fiber optic gyros), or the laser gyro is mounted on a piezo-electric dither motor that rapidly vibrates the laser ring back and forth about its input axis through the lock-in region to decouple the light waves.
The shaker is the most accurate, because both light beams use exactly the same path. Thus laser gyros retain moving parts, but they do not move as far.
Fiber optic gyros
A more recent variation on the optical gyroscope, the fiber optic gyroscope (FOG), uses an external laser and two beams going opposite directions (counter-propagating) in long spools (several kilometers) of fiber optic filament, with the phase difference of the two beams compared after their travel through the spools of fiber. The basic mechanism, monochromatic laser light travelling in opposite paths and theSagnac effect
The Sagnac effect, also called Sagnac interference, named after French physicist Georges Sagnac, is a phenomenon encountered in interferometry that is elicited by rotation. The Sagnac effect manifests itself in a setup called a ring interferomete ...
, is the same in a FOG and a RLG, but the engineering details are substantially different in the FOG compared to earlier laser gyros.
Precise winding of the fiber-optic coil is required to ensure the paths taken by the light in opposite directions are as similar as possible. The FOG requires more complex calibrations than a laser ring gyro making the development and manufacture of FOG's more technically challenging that for a RLG. However FOG's do not suffer from laser lock at low speeds and do not need to contain any moving parts, increasing the maximum potential accuracy and lifespan of a FOG over an equivalent RLG.
Pendular accelerometers
TIMU sensors
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
's Microsystems Technology Office (MTO) department is working on a Micro-PNT (Micro-Technology for Positioning, Navigation and Timing) program to design Timing & Inertial Measurement Unit (TIMU) chips that do absolute position tracking on a single chip without GPS-aided navigation.Extreme Miniaturization: Seven Devices, One Chip to Navigate without GPSMicro-PNT adds a highly accurate master timing clock integrated into an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) chip, making it a Timing & Inertial Measurement Unit chip. A TIMU chip integrates 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer and 3-axis magnetometer together with a highly accurate master timing clock, so that it can simultaneously measure the motion tracked and combine that with timing from the synchronized clock.
Method
In one form, the navigational system of equations acquires linear and angular measurements from the inertial and body frame, respectively and calculates the final attitude and position in the NED frame of reference.See also
* * * * Quantum compassReferences
Further reading
* * *External links
Ferranti Inertial Navigation System (INAS)
Inertial Navigation System
Principle of operation of an accelerometer
Overview of inertial instrument types
Oxford Technical Solutions Inertial Navigation Guide
Listing of open-source Inertial Navigation system
Impact of inertial sensor errors on Inertial Navigation System position and attitude errors
Introduction to Inertial Navigation Systems in UAV/Drone Applications
{{Use dmy dates, date=July 2022 Geodesy Aircraft instruments Aerospace engineering Avionics Spacecraft components Missile guidance Navigational equipment Technology systems Navigational aids Inertial navigation