Social peer-to-peer processes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a  Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional
Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional
 ''Unstructured peer-to-peer networks'' do not impose a particular structure on the overlay network by design, but rather are formed by nodes that randomly form connections to each other. ( Gnutella,
''Unstructured peer-to-peer networks'' do not impose a particular structure on the overlay network by design, but rather are formed by nodes that randomly form connections to each other. ( Gnutella,
 However, in order to route traffic efficiently through the network, nodes in a structured overlay must maintain lists of neighbors that satisfy specific criteria. This makes them less robust in networks with a high rate of ''churn'' (i.e. with large numbers of nodes frequently joining and leaving the network). More recent evaluation of P2P resource discovery solutions under real workloads have pointed out several issues in DHT-based solutions such as high cost of advertising/discovering resources and static and dynamic load imbalance.
Notable distributed networks that use DHTs include Tixati, an alternative to BitTorrent's distributed tracker, the Kad network, the Storm botnet, and the YaCy. Some prominent research projects include the Chord project,
However, in order to route traffic efficiently through the network, nodes in a structured overlay must maintain lists of neighbors that satisfy specific criteria. This makes them less robust in networks with a high rate of ''churn'' (i.e. with large numbers of nodes frequently joining and leaving the network). More recent evaluation of P2P resource discovery solutions under real workloads have pointed out several issues in DHT-based solutions such as high cost of advertising/discovering resources and static and dynamic load imbalance.
Notable distributed networks that use DHTs include Tixati, an alternative to BitTorrent's distributed tracker, the Kad network, the Storm botnet, and the YaCy. Some prominent research projects include the Chord project,
 There are both advantages and disadvantages in P2P networks related to the topic of data
There are both advantages and disadvantages in P2P networks related to the topic of data
 Dat is a distributed version-controlled publishing platform. I2P, is an overlay network used to browse the Internet anonymously. Unlike the related I2P, the Tor network is not itself peer-to-peer; however, it can enable peer-to-peer applications to be built on top of it via onion services. The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol and network designed to create a content-addressable, peer-to-peer method of storing and sharing
Dat is a distributed version-controlled publishing platform. I2P, is an overlay network used to browse the Internet anonymously. Unlike the related I2P, the Tor network is not itself peer-to-peer; however, it can enable peer-to-peer applications to be built on top of it via onion services. The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol and network designed to create a content-addressable, peer-to-peer method of storing and sharing
 Cooperation among a community of participants is key to the continued success of P2P systems aimed at casual human users; these reach their full potential only when large numbers of nodes contribute resources. But in current practice, P2P networks often contain large numbers of users who utilize resources shared by other nodes, but who do not share anything themselves (often referred to as the "freeloader problem").
Freeloading can have a profound impact on the network and in some cases can cause the community to collapse. In these types of networks "users have natural disincentives to cooperate because cooperation consumes their own resources and may degrade their own performance".Feldman, M., Lai, K., Stoica, I., & Chuang, J. (2004, May). Robust incentive techniques for peer-to-peer networks. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM conference on Electronic commerce (pp. 102-111). ACM. Studying the social attributes of P2P networks is challenging due to large populations of turnover, asymmetry of interest and zero-cost identity. A variety of incentive mechanisms have been implemented to encourage or even force nodes to contribute resources.
Some researchers have explored the benefits of enabling virtual communities to self-organize and introduce incentives for resource sharing and cooperation, arguing that the social aspect missing from today's P2P systems should be seen both as a goal and a means for self-organized virtual communities to be built and fostered. Ongoing research efforts for designing effective incentive mechanisms in P2P systems, based on principles from game theory, are beginning to take on a more psychological and information-processing direction.
Cooperation among a community of participants is key to the continued success of P2P systems aimed at casual human users; these reach their full potential only when large numbers of nodes contribute resources. But in current practice, P2P networks often contain large numbers of users who utilize resources shared by other nodes, but who do not share anything themselves (often referred to as the "freeloader problem").
Freeloading can have a profound impact on the network and in some cases can cause the community to collapse. In these types of networks "users have natural disincentives to cooperate because cooperation consumes their own resources and may degrade their own performance".Feldman, M., Lai, K., Stoica, I., & Chuang, J. (2004, May). Robust incentive techniques for peer-to-peer networks. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM conference on Electronic commerce (pp. 102-111). ACM. Studying the social attributes of P2P networks is challenging due to large populations of turnover, asymmetry of interest and zero-cost identity. A variety of incentive mechanisms have been implemented to encourage or even force nodes to contribute resources.
Some researchers have explored the benefits of enabling virtual communities to self-organize and introduce incentives for resource sharing and cooperation, arguing that the social aspect missing from today's P2P systems should be seen both as a goal and a means for self-organized virtual communities to be built and fostered. Ongoing research efforts for designing effective incentive mechanisms in P2P systems, based on principles from game theory, are beginning to take on a more psychological and information-processing direction.
"Free-rider detection and punishment in BitTorrent based P2P networks"
International Advanced Computing Conference, 2014.
P2P-VoD Streaming: Design Issues & User Experience Challenges
Springer Proceedings, June 2014
of P2P terminology
Foundation of Peer-to-Peer Computing
Special Issue, Elsevier Journal of Computer Communication, (Ed) Javed I. Khan and Adam Wierzbicki, Volume 31, Issue 2, February 2008 * * Marling Engle & J. I. Khan
Vulnerabilities of P2P systems and a critical look at their solutions
, May 2006 * Stephanos Androutsellis-Theotokis and Diomidis Spinellis
. ACM Computing Surveys, 36(4):335–371, December 2004. * Biddle, Peter, Paul England, Marcus Peinado, and Bryan Willman
The Darknet and the Future of Content Distribution
. In ''2002 ACM Workshop on Digital Rights Management'', November 2002. * John F. Buford, Heather Yu, Eng Keong Lu
P2P Networking and Applications
, Morgan Kaufmann, December 2008 * Djamal-Eddine Meddour, Mubashar Mushtaq, and Toufik Ahmed,
Open Issues in P2P Multimedia Streaming
", in the proceedings of the 1st Multimedia Communications Workshop MULTICOMM 2006 held in conjunction with IEEE ICC 2006 pp 43–48, June 2006, Istanbul, Turkey. * Detlef Schoder and Kai Fischbach,
Core Concepts in Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Networking
". In: Subramanian, R.; Goodman, B. (eds.): ''P2P Computing: The Evolution of a Disruptive Technology'', Idea Group Inc, Hershey. 2005 * Ramesh Subramanian and Brian Goodman (eds),
Peer-to-Peer Computing: Evolution of a Disruptive Technology
', , Idea Group Inc., Hershey, PA, United States, 2005. * Shuman Ghosemajumder
Advanced Peer-Based Technology Business Models
. MIT Sloan School of Management, 2002. * Silverthorne, Sean.
Music Downloads: Pirates- or Customers?
''. Harvard Business School Working Knowledge, 2004.
Glasnost
test P2P traffic shaping ( Max Planck Institute for Software Systems) {{DEFAULTSORT:Peer-To-Peer File sharing networks File sharing Software engineering terminology
distributed application
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different computer network, networked computers.
The components of a distribu ...
architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent
In mathematics, two set (mathematics), sets or class (mathematics), classes ''A'' and ''B'' are equinumerous if there exists a one-to-one correspondence (or bijection) between them, that is, if there exists a function (mathematics), function from ...
participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of nodes. In addition, a personal area network (PAN) is also in nature a type of decentralized peer-to-peer network typically between two devices.
client–server model
The client–server model is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks or workloads between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and service requesters, called clients. Often clients and servers communicate ov ...
in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided.
While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
file sharing system Napster, originally released in 1999. P2P is used in many protocols such as BitTorrent
BitTorrent is a Protocol (computing), communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a Decentralised system, decentralized manner. The protocol is d ...
file sharing over the Internet and in personal networks like Miracast displaying and Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is li ...
radio. The concept has inspired new structures and philosophies in many areas of human interaction. In such social contexts, peer-to-peer as a meme refers to the egalitarian social network
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of Dyad (sociology), dyadic ties, and other Social relation, social interactions between actors. The social network per ...
ing that has emerged throughout society, enabled by Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
technologies in general.
Development
While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the concept was popularized byfile sharing
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digital media, such as computer programs, multimedia (audio, images and video), documents or electronic books. Common methods of storage, transmission and dispersion include ...
systems such as the music-sharing application Napster. The peer-to-peer movement allowed millions of Internet users to connect "directly, forming groups and collaborating to become user-created search engines, virtual supercomputers, and filesystems". The basic concept of peer-to-peer computing was envisioned in earlier software systems and networking discussions, reaching back to principles stated in the first Request for Comments
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development and standards-setting bodies for the Internet, most prominently the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). An RFC is authored by individuals or ...
, RFC 1.
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow a ...
's vision for the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
was close to a P2P network in that it assumed each user of the web would be an active editor and contributor, creating and linking content to form an interlinked "web" of links. The early Internet was more open than the present day, where two machines connected to the Internet could send packets to each other without firewalls and other security measures. This contrasts with the broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), ...
-like structure of the web as it has developed over the years. As a precursor to the Internet, ARPANET
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first computer networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the tec ...
was a successful peer-to-peer network where "every participating node could request and serve content". However, ARPANET was not self-organized, and it could not "provide any means for context or content-based routing beyond 'simple' address-based routing."
Therefore, Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Elli ...
, a distributed messaging system that is often described as an early peer-to-peer architecture, was established. It was developed in 1979 as a system that enforces a decentralized model of control. The basic model is a client–server model from the user or client perspective that offers a self-organizing approach to newsgroup servers. However, news servers communicate with one another as peers to propagate Usenet news articles over the entire group of network servers. The same consideration applies to SMTP email in the sense that the core email-relaying network of mail transfer agents has a peer-to-peer character, while the periphery of Email clients and their direct connections is strictly a client-server relationship.
In May 1999, with millions more people on the Internet, Shawn Fanning
Shawn Fanning (born November 22, 1980) is an American computer programmer, entrepreneur, and angel investor. He developed Napster, one of the first popular peer-to-peer file sharing, peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing platforms, in 1999. The populari ...
introduced the music and file-sharing application called Napster. Napster was the beginning of peer-to-peer networks, as we know them today, where "participating users establish a virtual network, entirely independent from the physical network, without having to obey any administrative authorities or restrictions".
Architecture
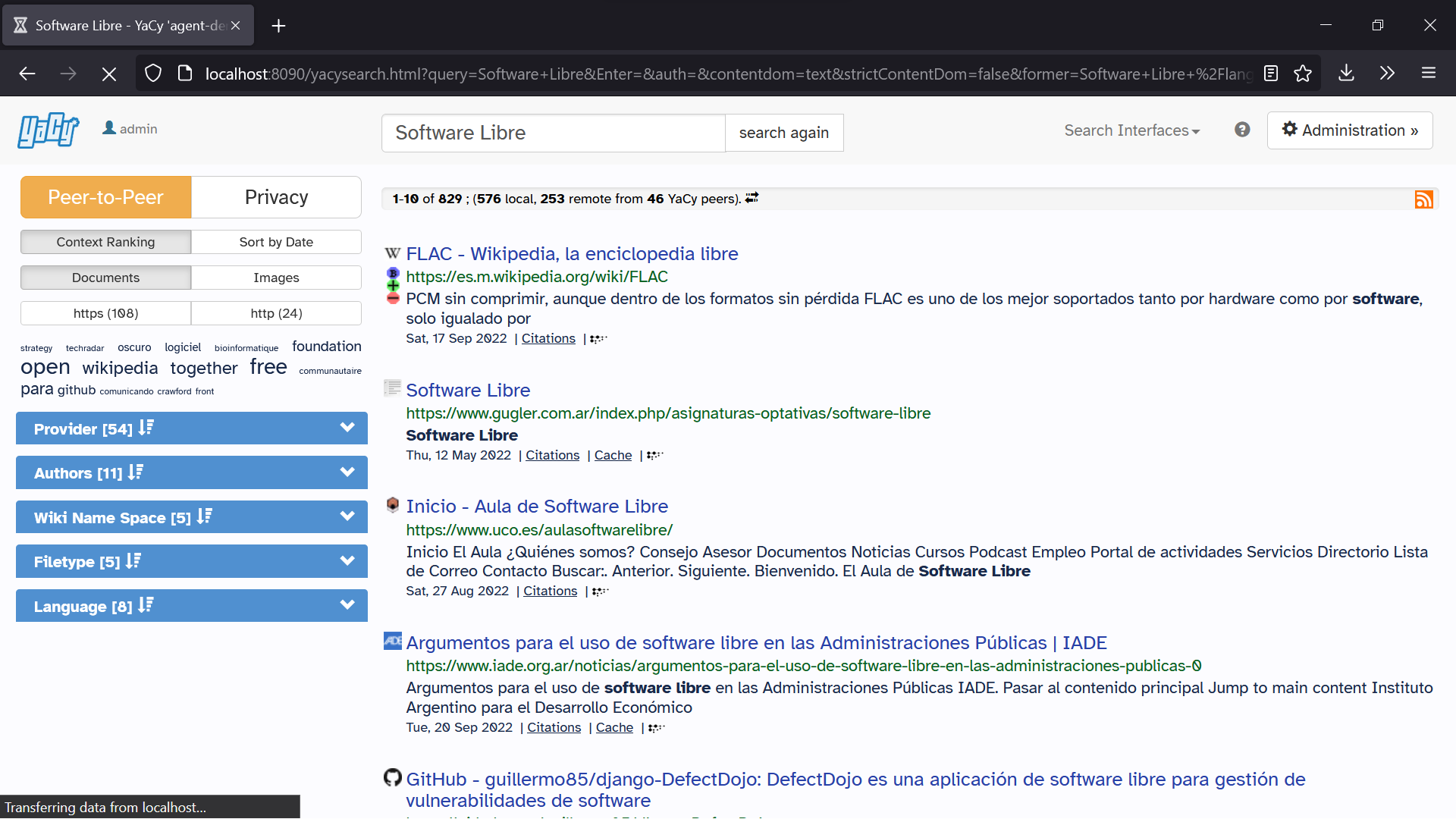
A peer-to-peer network is designed around the notion of equal '' peer'' nodes simultaneously functioning as both "clients" and "servers" to the other nodes on the network. This model of network arrangement differs from the client–server model where communication is usually to and from a central server. A typical example of a file transfer that uses the client-server model is theFile Transfer Protocol
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and d ...
(FTP) service in which the client and server programs are distinct: the clients initiate the transfer, and the servers satisfy these requests.
Routing and resource discovery
Peer-to-peer networks generally implement some form of virtual overlay network on top of the physical network topology, where the nodes in the overlay form asubset
In mathematics, a Set (mathematics), set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all Element (mathematics), elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ''A''. It is possible for ''A'' and ''B'' to be equal; if they a ...
of the nodes in the physical network. Data is still exchanged directly over the underlying TCP/IP
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the suite are ...
network, but at the application layer
An application layer is an abstraction layer that specifies the shared communication protocols and interface methods used by hosts in a communications network. An ''application layer'' abstraction is specified in both the Internet Protocol Su ...
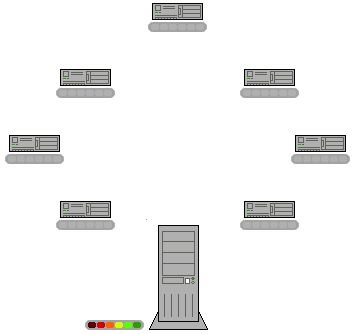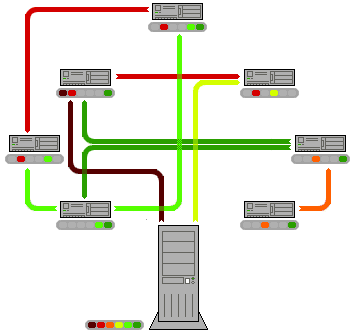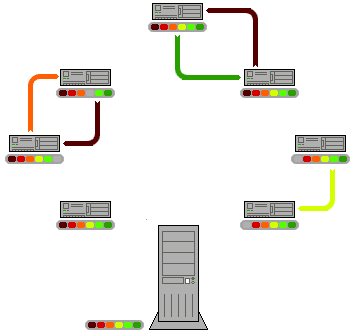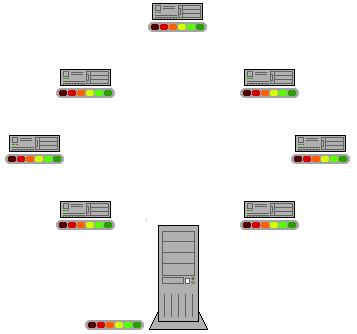
peers can communicate with each other directly, via the logical overlay links (each of which corresponds to a path through the underlying physical network). Overlays are used for indexing and peer discovery, and make the P2P system independent from the physical network topology. Based on how the nodes are linked to each other within the overlay network, and how resources are indexed and located, we can classify networks as ''unstructured'' or ''structured'' (or as a hybrid between the two).
Unstructured networks
 ''Unstructured peer-to-peer networks'' do not impose a particular structure on the overlay network by design, but rather are formed by nodes that randomly form connections to each other. ( Gnutella,
''Unstructured peer-to-peer networks'' do not impose a particular structure on the overlay network by design, but rather are formed by nodes that randomly form connections to each other. ( Gnutella, Gossip
Gossip is idle talk or rumor, especially about the personal or private affairs of others; the act is also known as dishing or tattling.
Etymology
The word is from Old English ''godsibb'', from ''god (word), god'' and ''sibb'', the term for the ...
, and Kazaa are examples of unstructured P2P protocols).
Because there is no structure globally imposed upon them, unstructured networks are easy to build and allow for localized optimizations to different regions of the overlay. Also, because the role of all peers in the network is the same, unstructured networks are highly robust in the face of high rates of "churn"—that is, when large numbers of peers are frequently joining and leaving the network.
However, the primary limitations of unstructured networks also arise from this lack of structure. In particular, when a peer wants to find a desired piece of data in the network, the search query must be flooded through the network to find as many peers as possible that share the data. Flooding causes a very high amount of signaling traffic in the network, uses more CPU/memory (by requiring every peer to process all search queries), and does not ensure that search queries will always be resolved. Furthermore, since there is no correlation between a peer and the content managed by it, there is no guarantee that flooding will find a peer that has the desired data. Popular content is likely to be available at several peers and any peer searching for it is likely to find the same thing. But if a peer is looking for rare data shared by only a few other peers, then it is highly unlikely that the search will be successful.
Structured networks
In ''structured peer-to-peer networks'' the overlay is organized into a specific topology, and the protocol ensures that any node can efficiently search the network for a file/resource, even if the resource is extremely rare. The most common type of structured P2P networks implement adistributed hash table
A distributed hash table (DHT) is a Distributed computing, distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table. Key–value pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node (networking), node can efficiently retrieve the ...
(DHT), in which a variant of consistent hashing is used to assign ownership of each file to a particular peer. This enables peers to search for resources on the network using a hash table
In computer science, a hash table is a data structure that implements an associative array, also called a dictionary or simply map; an associative array is an abstract data type that maps Unique key, keys to Value (computer science), values. ...
: that is, (''key'', ''value'') pairs are stored in the DHT, and any participating node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key.
Kademlia
Kademlia is a distributed hash table for decentralized peer-to-peer computer networks designed by Petar Maymounkov and David Mazières in 2002. It specifies the structure of the network and the exchange of information through node (networking), no ...
, PAST storage utility, P-Grid, a self-organized and emerging overlay network, and CoopNet content distribution system. DHT-based networks have also been widely utilized for accomplishing efficient resource discovery for grid computing
Grid computing is the use of widely distributed computer resources to reach a common goal. A computing grid can be thought of as a distributed system with non-interactive workloads that involve many files. Grid computing is distinguished fro ...
systems, as it aids in resource management and scheduling of applications.
Hybrid models
Hybrid models are a combination of peer-to-peer and client–server models. A common hybrid model is to have a central server that helps peers find each other.Spotify
Spotify (; ) is a List of companies of Sweden, Swedish Music streaming service, audio streaming and media service provider founded on 23 April 2006 by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon. , it is one of the largest providers of music streaming services ...
was an example of a hybrid model ntil 2014 There are a variety of hybrid models, all of which make trade-offs between the centralized functionality provided by a structured server/client network and the node equality afforded by the pure peer-to-peer unstructured networks. Currently, hybrid models have better performance than either pure unstructured networks or pure structured networks because certain functions, such as searching, do require a centralized functionality but benefit from the decentralized aggregation of nodes provided by unstructured networks.
CoopNet content distribution system
CoopNet (Cooperative Networking) was a proposed system for off-loading serving to peers who have recentlydownload
In computer networks, download means to ''receive'' data from a remote system, typically a server such as a web server, an FTP server, an email server, or other similar systems. This contrasts with uploading, where data is ''sent to'' a remote ...
ed content, proposed by computer scientists Venkata N. Padmanabhan and Kunwadee Sripanidkulchai, working at Microsoft Research
Microsoft Research (MSR) is the research subsidiary of Microsoft. It was created in 1991 by Richard Rashid, Bill Gates and Nathan Myhrvold with the intent to advance state-of-the-art computing and solve difficult world problems through technologi ...
and Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institu ...
. When a server experiences an increase in load it redirects incoming peers to other peers who have agreed to mirror
A mirror, also known as a looking glass, is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror forms an image of whatever is in front of it, which is then focused through the lens of the eye or a camera ...
the content, thus off-loading balance from the server. All of the information is retained at the server. This system makes use of the fact that the bottleneck is most likely in the outgoing bandwidth than the CPU, hence its server-centric design. It assigns peers to other peers who are 'close in IP' to its neighbors ame prefix rangein an attempt to use locality. If multiple peers are found with the same file it designates that the node choose the fastest of its neighbors. Streaming media
Streaming media refers to multimedia delivered through a Computer network, network for playback using a Media player (disambiguation), media player. Media is transferred in a ''stream'' of Network packet, packets from a Server (computing), ...
is transmitted by having clients cache the previous stream, and then transmit it piece-wise to new nodes.
Security and trust
Peer-to-peer systems pose unique challenges from acomputer security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, n ...
perspective. Like any other form of software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
, P2P applications can contain vulnerabilities. What makes this particularly dangerous for P2P software, however, is that peer-to-peer applications act as servers as well as clients, meaning that they can be more vulnerable to remote exploits.
Routing attacks
Since each node plays a role in routing traffic through the network, malicious users can perform a variety of "routing attacks", ordenial of service
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host co ...
attacks. Examples of common routing attacks include "incorrect lookup routing" whereby malicious nodes deliberately forward requests incorrectly or return false results, "incorrect routing updates" where malicious nodes corrupt the routing tables of neighboring nodes by sending them false information, and "incorrect routing network partition" where when new nodes are joining they bootstrap via a malicious node, which places the new node in a partition of the network that is populated by other malicious nodes.
Corrupted data and malware
The prevalence ofmalware
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to caus ...
varies between different peer-to-peer protocols. Studies analyzing the spread of malware on P2P networks found, for example, that 63% of the answered download requests on the gnutella network contained some form of malware, whereas only 3% of the content on OpenFT contained malware. In both cases, the top three most common types of malware accounted for the large majority of cases (99% in gnutella, and 65% in OpenFT). Another study analyzing traffic on the Kazaa network found that 15% of the 500,000 file sample taken were infected by one or more of the 365 different computer viruses that were tested for.
Corrupted data can also be distributed on P2P networks by modifying files that are already being shared on the network. For example, on the FastTrack network, the RIAA
The Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) is a trade organization that represents the music recording industry in the United States. Its members consist of record labels and distributors that the RIAA says "create, manufacture, and/o ...
managed to introduce faked chunks into downloads and downloaded files (mostly MP3 files). Files infected with the RIAA virus were unusable afterwards and contained malicious code. The RIAA is also known to have uploaded fake music and movies to P2P networks in order to deter illegal file sharing. Consequently, the P2P networks of today have seen an enormous increase of their security and file verification mechanisms. Modern hashing, chunk verification and different encryption methods have made most networks resistant to almost any type of attack, even when major parts of the respective network have been replaced by faked or nonfunctional hosts.
Resilient and scalable computer networks
The decentralized nature of P2P networks increases robustness because it removes thesingle point of failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that would Cascading failure, stop the entire system from working if it were to fail. The term single point of failure implies that there is not a backup or redundant option that would enab ...
that can be inherent in a client–server based system. As nodes arrive and demand on the system increases, the total capacity of the system also increases, and the likelihood of failure decreases. If one peer on the network fails to function properly, the whole network is not compromised or damaged. In contrast, in a typical client–server architecture, clients share only their demands with the system, but not their resources. In this case, as more clients join the system, fewer resources are available to serve each client, and if the central server fails, the entire network is taken down.
Distributed storage and search
 There are both advantages and disadvantages in P2P networks related to the topic of data
There are both advantages and disadvantages in P2P networks related to the topic of data backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back ...
, recovery, and availability. In a centralized network, the system administrators are the only forces controlling the availability of files being shared. If the administrators decide to no longer distribute a file, they simply have to remove it from their servers, and it will no longer be available to users. Along with leaving the users powerless in deciding what is distributed throughout the community, this makes the entire system vulnerable to threats and requests from the government and other large forces.
For example, YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
has been pressured by the RIAA
The Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) is a trade organization that represents the music recording industry in the United States. Its members consist of record labels and distributors that the RIAA says "create, manufacture, and/o ...
, MPAA, and entertainment industry to filter out copyrighted content. Although server-client networks are able to monitor and manage content availability, they can have more stability in the availability of the content they choose to host. A client should not have trouble accessing obscure content that is being shared on a stable centralized network. P2P networks, however, are more unreliable in sharing unpopular files because sharing files in a P2P network requires that at least one node in the network has the requested data, and that node must be able to connect to the node requesting the data. This requirement is occasionally hard to meet because users may delete or stop sharing data at any point.
In a P2P network, the community of users is entirely responsible for deciding which content is available. Unpopular files eventually disappear and become unavailable as fewer people share them. Popular files, however, are highly and easily distributed. Popular files on a P2P network are more stable and available than files on central networks. In a centralized network, a simple loss of connection between the server and clients can cause a failure, but in P2P networks, the connections between every node must be lost to cause a data-sharing failure. In a centralized system, the administrators are responsible for all data recovery and backups, while in P2P systems, each node requires its backup system. Because of the lack of central authority in P2P networks, forces such as the recording industry, RIAA
The Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) is a trade organization that represents the music recording industry in the United States. Its members consist of record labels and distributors that the RIAA says "create, manufacture, and/o ...
, MPAA, and the government are unable to delete or stop the sharing of content on P2P systems.
Applications
Content delivery
In P2P networks, clients both provide and use resources. This means that unlike client–server systems, the content-serving capacity of peer-to-peer networks can actually ''increase'' as more users begin to access the content (especially with protocols such asBitTorrent
BitTorrent is a Protocol (computing), communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a Decentralised system, decentralized manner. The protocol is d ...
that require users to share, refer a performance measurement study). This property is one of the major advantages of using P2P networks because it makes the setup and running costs very small for the original content distributor.
File-sharing networks
Peer-to-peer file sharing networks such as Gnutella, G2, and the eDonkey network have been useful in popularizing peer-to-peer technologies. These advancements have paved the way for Peer-to-peer content delivery networks and services, including distributed caching systems like Correli Caches to enhance performance. Furthermore, peer-to-peer networks have made possible the software publication and distribution, enabling efficient sharing of Linux distribution and various games throughfile sharing
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digital media, such as computer programs, multimedia (audio, images and video), documents or electronic books. Common methods of storage, transmission and dispersion include ...
networks.
Copyright infringements
Peer-to-peer networking involves data transfer from one user to another without using an intermediate server. Companies developing P2P applications have been involved in numerous legal cases, primarily in the United States, over conflicts withcopyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, ...
law. Two major cases are '' Grokster vs RIAA'' and '' MGM Studios, Inc. v. Grokster, Ltd.''. In the last case, the Court unanimously held that defendant peer-to-peer file sharing companies Grokster and Streamcast could be sued for inducing copyright infringement.
Multimedia
The P2PTV and PDTP protocols are used in various peer-to-peer applications. Some proprietary multimedia applications leverage a peer-to-peer network in conjunction with streaming servers to stream audio and video to their clients. Peercasting is employed for multicasting streams. Additionally, a project called LionShare, undertaken byPennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsyl ...
, MIT, and Simon Fraser University
Simon Fraser University (SFU) is a Public university, public research university in British Columbia, Canada. It maintains three campuses in Greater Vancouver, respectively located in Burnaby (main campus), Surrey, British Columbia, Surrey, and ...
, aims to facilitate file sharing among educational institutions globally. Another notable program, Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was ...
, enables users to create anonymous and autonomous web portals that are distributed via a peer-to-peer network.
Other P2P applications
 Dat is a distributed version-controlled publishing platform. I2P, is an overlay network used to browse the Internet anonymously. Unlike the related I2P, the Tor network is not itself peer-to-peer; however, it can enable peer-to-peer applications to be built on top of it via onion services. The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol and network designed to create a content-addressable, peer-to-peer method of storing and sharing
Dat is a distributed version-controlled publishing platform. I2P, is an overlay network used to browse the Internet anonymously. Unlike the related I2P, the Tor network is not itself peer-to-peer; however, it can enable peer-to-peer applications to be built on top of it via onion services. The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol and network designed to create a content-addressable, peer-to-peer method of storing and sharing hypermedia
Hypermedia, an extension of hypertext, is a nonlinear medium of information that includes graphics, audio, video, plain text and hyperlinks. This designation contrasts with the broader term ''multimedia'', which may include non-interactive linear ...
distribution protocol, with nodes in the IPFS network forming a distributed file system
A clustered file system (CFS) is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously Mount (computing), mounted on multiple Server (computing), servers. There are several approaches to computer cluster, clustering, most of which do not emplo ...
. Jami is a peer-to-peer chat and SIP app. JXTA is a peer-to-peer protocol designed for the Java platform
Java is a set of computer software and specifications that provides a software platform for developing application software and deploying it in a cross-platform computing environment. Java is used in a wide variety of computing platforms fr ...
. Netsukuku is a Wireless community network designed to be independent from the Internet. Open Garden is a connection-sharing application that shares Internet access with other devices using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
Resilio Sync is a directory-syncing app. Research includes projects such as the Chord project, the PAST storage utility, the P-Grid, and the CoopNet content distribution system. Secure Scuttlebutt is a peer-to-peer gossip protocol capable of supporting many different types of applications, primarily social networking. Syncthing is also a directory-syncing app. Tradepal l and M-commerce applications are designed to power real-time marketplaces. The U.S. Department of Defense is conducting research on P2P networks as part of its modern network warfare strategy. In May 2003, Anthony Tether, then director of DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
, testified that the United States military uses P2P networks. WebTorrent is a P2P streaming
Streaming media refers to multimedia delivered through a network for playback using a media player. Media is transferred in a ''stream'' of packets from a server to a client and is rendered in real-time; this contrasts with file downl ...
torrent client in JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have ...
for use in web browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's scr ...
s, as well as in the WebTorrent Desktop standalone version that bridges WebTorrent and BitTorrent
BitTorrent is a Protocol (computing), communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a Decentralised system, decentralized manner. The protocol is d ...
serverless networks. Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
, in Windows 10
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. The successor to Windows 8.1, it was Software release cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on July 2 ...
, uses a proprietary peer-to-peer technology called "Delivery Optimization" to deploy operating system updates using end-users' PCs either on the local network or other PCs. According to Microsoft's Channel 9, this led to a 30%-50% reduction in Internet bandwidth usage. Artisoft's LANtastic was built as a peer-to-peer operating system where machines can function as both servers and workstations simultaneously. Hotline Communications Hotline Client was built with decentralized servers and tracker software dedicated to any type of files and continues to operate today. Cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency (colloquially crypto) is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Individual coin ownership records ...
are peer-to-peer-based digital currencies that use blockchains
* List of cryptocurrencies
* List of blockchains
Social implications
Incentivizing resource sharing and cooperation
 Cooperation among a community of participants is key to the continued success of P2P systems aimed at casual human users; these reach their full potential only when large numbers of nodes contribute resources. But in current practice, P2P networks often contain large numbers of users who utilize resources shared by other nodes, but who do not share anything themselves (often referred to as the "freeloader problem").
Freeloading can have a profound impact on the network and in some cases can cause the community to collapse. In these types of networks "users have natural disincentives to cooperate because cooperation consumes their own resources and may degrade their own performance".Feldman, M., Lai, K., Stoica, I., & Chuang, J. (2004, May). Robust incentive techniques for peer-to-peer networks. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM conference on Electronic commerce (pp. 102-111). ACM. Studying the social attributes of P2P networks is challenging due to large populations of turnover, asymmetry of interest and zero-cost identity. A variety of incentive mechanisms have been implemented to encourage or even force nodes to contribute resources.
Some researchers have explored the benefits of enabling virtual communities to self-organize and introduce incentives for resource sharing and cooperation, arguing that the social aspect missing from today's P2P systems should be seen both as a goal and a means for self-organized virtual communities to be built and fostered. Ongoing research efforts for designing effective incentive mechanisms in P2P systems, based on principles from game theory, are beginning to take on a more psychological and information-processing direction.
Cooperation among a community of participants is key to the continued success of P2P systems aimed at casual human users; these reach their full potential only when large numbers of nodes contribute resources. But in current practice, P2P networks often contain large numbers of users who utilize resources shared by other nodes, but who do not share anything themselves (often referred to as the "freeloader problem").
Freeloading can have a profound impact on the network and in some cases can cause the community to collapse. In these types of networks "users have natural disincentives to cooperate because cooperation consumes their own resources and may degrade their own performance".Feldman, M., Lai, K., Stoica, I., & Chuang, J. (2004, May). Robust incentive techniques for peer-to-peer networks. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM conference on Electronic commerce (pp. 102-111). ACM. Studying the social attributes of P2P networks is challenging due to large populations of turnover, asymmetry of interest and zero-cost identity. A variety of incentive mechanisms have been implemented to encourage or even force nodes to contribute resources.
Some researchers have explored the benefits of enabling virtual communities to self-organize and introduce incentives for resource sharing and cooperation, arguing that the social aspect missing from today's P2P systems should be seen both as a goal and a means for self-organized virtual communities to be built and fostered. Ongoing research efforts for designing effective incentive mechanisms in P2P systems, based on principles from game theory, are beginning to take on a more psychological and information-processing direction.
Privacy and anonymity
Some peer-to-peer networks (e.g.Freenet
Hyphanet (until mid-2023: Freenet) is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, Anonymity application, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free soft ...
) place a heavy emphasis on privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
and anonymity
Anonymity describes situations where the acting person's identity is unknown. Anonymity may be created unintentionally through the loss of identifying information due to the passage of time or a destructive event, or intentionally if a person cho ...
—that is, ensuring that the contents of communications are hidden from eavesdroppers, and that the identities/locations of the participants are concealed. Public key cryptography
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic al ...
can be used to provide encryption
In Cryptography law, cryptography, encryption (more specifically, Code, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the inf ...
, data validation
In computing, data validation or input validation is the process of ensuring data has undergone data cleansing to confirm it has data quality, that is, that it is both correct and useful. It uses routines, often called "validation rules", "valida ...
, authorization, and authentication for data/messages. Onion routing
Onion routing is a technique for anonymous communication over a computer network. In an onion network, messages are encapsulated in layers of encryption, analogous to the layers of an onion. The encrypted data is transmitted through a series o ...
and other mix network protocols (e.g. Tarzan) can be used to provide anonymity.
Perpetrators of live streaming sexual abuse and other cybercrimes have used peer-to-peer platforms to carry out activities with anonymity.
Political implications
Intellectual property law and illegal sharing
Although peer-to-peer networks can be used for legitimate purposes, rights holders have targeted peer-to-peer over the involvement with sharing copyrighted material. Peer-to-peer networking involves data transfer from one user to another without using an intermediate server. Companies developing P2P applications have been involved in numerous legal cases, primarily in the United States, primarily over issues surroundingcopyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, ...
law. Two major cases are '' Grokster vs RIAA'' and '' MGM Studios, Inc. v. Grokster, Ltd.'' In both of the cases the file sharing technology was ruled to be legal as long as the developers had no ability to prevent the sharing of the copyrighted material.
To establish criminal liability for the copyright infringement on peer-to-peer systems, the government must prove that the defendant infringed a copyright willingly for the purpose of personal financial gain or commercial advantage. Fair use
Fair use is a Legal doctrine, doctrine in United States law that permits limited use of copyrighted material without having to first acquire permission from the copyright holder. Fair use is one of the limitations to copyright intended to bal ...
exceptions allow limited use of copyrighted material to be downloaded without acquiring permission from the rights holders. These documents are usually news reporting or under the lines of research and scholarly work. Controversies have developed over the concern of illegitimate use of peer-to-peer networks regarding public safety and national security. When a file is downloaded through a peer-to-peer network, it is impossible to know who created the file or what users are connected to the network at a given time. Trustworthiness of sources is a potential security threat that can be seen with peer-to-peer systems.
A study ordered by the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
found that illegal downloading ''may'' lead to an increase in overall video game sales because newer games charge for extra features or levels. The paper concluded that piracy had a negative financial impact on movies, music, and literature. The study relied on self-reported data about game purchases and use of illegal download sites. Pains were taken to remove effects of false and misremembered responses.
Network neutrality
Peer-to-peer applications present one of the core issues in the network neutrality controversy. Internet service providers ( ISPs) have been known to throttle P2P file-sharing traffic due to its high- bandwidth usage. Compared to Web browsing, e-mail or many other uses of the internet, where data is only transferred in short intervals and relative small quantities, P2P file-sharing often consists of relatively heavy bandwidth usage due to ongoing file transfers and swarm/network coordination packets. In October 2007,Comcast
Comcast Corporation, formerly known as Comcast Holdings,Before the AT&T Broadband, AT&T merger in 2001, the parent company was Comcast Holdings Corporation. Comcast Holdings Corporation now refers to a subsidiary of Comcast Corporation, not th ...
, one of the largest broadband Internet providers in the United States, started blocking P2P applications such as BitTorrent
BitTorrent is a Protocol (computing), communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a Decentralised system, decentralized manner. The protocol is d ...
. Their rationale was that P2P is mostly used to share illegal content, and their infrastructure is not designed for continuous, high-bandwidth traffic.
Critics point out that P2P networking has legitimate legal uses, and that this is another way that large providers are trying to control use and content on the Internet, and direct people towards a client–server-based application architecture. The client–server model provides financial barriers-to-entry to small publishers and individuals, and can be less efficient for sharing large files. As a reaction to this bandwidth throttling, several P2P applications started implementing protocol obfuscation, such as the BitTorrent protocol encryption. Techniques for achieving "protocol obfuscation" involves removing otherwise easily identifiable properties of protocols, such as deterministic byte sequences and packet sizes, by making the data look as if it were random. The ISP's solution to the high bandwidth is P2P caching
Peer-to-peer caching (P2P caching) is a computer network traffic management technology used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to accelerate content delivered over peer-to-peer (P2P) networks while reducing related bandwidth costs.
P2P Cache (c ...
, where an ISP stores the part of files most accessed by P2P clients in order to save access to the Internet.
Current research
Researchers have used computer simulations to aid in understanding and evaluating the complex behaviors of individuals within the network. "Networking research often relies on simulation in order to test and evaluate new ideas. An important requirement of this process is that results must be reproducible so that other researchers can replicate, validate, and extend existing work."Basu, A., Fleming, S., Stanier, J., Naicken, S., Wakeman, I., & Gurbani, V. K. (2013). The state of peer-to-peer network simulators. ACM Computing Surveys, 45(4), 46. If the research cannot be reproduced, then the opportunity for further research is hindered. "Even though new simulators continue to be released, the research community tends towards only a handful of open-source simulators. The demand for features in simulators, as shown by our criteria and survey, is high. Therefore, the community should work together to get these features in open-source software. This would reduce the need for custom simulators, and hence increase repeatability and reputability of experiments." Popular simulators that were widely used in the past are NS2, OMNeT++, SimPy, NetLogo, PlanetLab, ProtoPeer, QTM, PeerSim, ONE, P2PStrmSim, PlanetSim, GNUSim, and Bharambe. Besides all the above stated facts, there has also been work done on ns-2 open source network simulators. One research issue related to free rider detection and punishment has been explored using ns-2 simulator here.A Bhakuni, P Sharma, R Kausha"Free-rider detection and punishment in BitTorrent based P2P networks"
International Advanced Computing Conference, 2014.
See also
References
External links
* Ghosh Debjani, Rajan Payas, Pandey MayanP2P-VoD Streaming: Design Issues & User Experience Challenges
Springer Proceedings, June 2014
of P2P terminology
Foundation of Peer-to-Peer Computing
Special Issue, Elsevier Journal of Computer Communication, (Ed) Javed I. Khan and Adam Wierzbicki, Volume 31, Issue 2, February 2008 * * Marling Engle & J. I. Khan
Vulnerabilities of P2P systems and a critical look at their solutions
, May 2006 * Stephanos Androutsellis-Theotokis and Diomidis Spinellis
. ACM Computing Surveys, 36(4):335–371, December 2004. * Biddle, Peter, Paul England, Marcus Peinado, and Bryan Willman
The Darknet and the Future of Content Distribution
. In ''2002 ACM Workshop on Digital Rights Management'', November 2002. * John F. Buford, Heather Yu, Eng Keong Lu
P2P Networking and Applications
, Morgan Kaufmann, December 2008 * Djamal-Eddine Meddour, Mubashar Mushtaq, and Toufik Ahmed,
Open Issues in P2P Multimedia Streaming
", in the proceedings of the 1st Multimedia Communications Workshop MULTICOMM 2006 held in conjunction with IEEE ICC 2006 pp 43–48, June 2006, Istanbul, Turkey. * Detlef Schoder and Kai Fischbach,
Core Concepts in Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Networking
". In: Subramanian, R.; Goodman, B. (eds.): ''P2P Computing: The Evolution of a Disruptive Technology'', Idea Group Inc, Hershey. 2005 * Ramesh Subramanian and Brian Goodman (eds),
Peer-to-Peer Computing: Evolution of a Disruptive Technology
', , Idea Group Inc., Hershey, PA, United States, 2005. * Shuman Ghosemajumder
Advanced Peer-Based Technology Business Models
. MIT Sloan School of Management, 2002. * Silverthorne, Sean.
Music Downloads: Pirates- or Customers?
''. Harvard Business School Working Knowledge, 2004.
Glasnost
test P2P traffic shaping ( Max Planck Institute for Software Systems) {{DEFAULTSORT:Peer-To-Peer File sharing networks File sharing Software engineering terminology