|
Social Peer-to-peer Processes
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of nodes. In addition, a personal area network (PAN) is also in nature a type of decentralized peer-to-peer network typically between two devices. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the Internet file sharing system Napster, originally released in 1999. P2P is used in many protocols su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of Dyad (sociology), dyadic ties, and other Social relation, social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities along with a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine dynamics of networks. For instance, social network analysis has been used in studying the spread of misinformation on social media platforms or analyzing the influence of key figures in social networks. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mail Transfer Agent
Within the Internet email system, a message transfer agent (MTA), mail transfer agent, or mail relay is software that transfers electronic mail messages from one computer to another using the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. In some contexts, the alternative names mail server, mail exchanger, or MX host are used to describe an MTA. Messages exchanged across networks are passed between mail servers, including any attached data files (such as images, multimedia, or documents). These servers often keep mailboxes for email. Access to this email by end users is typically either by webmail or an email client. Operation A message transfer agent receives mail from either another MTA, a mail submission agent (MSA), or a mail user agent (MUA). The transmission details are specified by the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). When a recipient mailbox of a message is not hosted locally, the message is relayed, that is, forwarded to another MTA. Every time an MTA receives an email message, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMTP
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages. User-level email clients typically use SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for relaying, and typically submit outgoing email to the mail server on port 465 or 587 per . For retrieving messages, IMAP (which replaced the older POP3) is standard, but proprietary servers also often implement proprietary protocols, e.g., Exchange ActiveSync. SMTP's origins began in 1980, building on concepts implemented on the ARPANET since 1971. It has been updated, modified and extended multiple times. The protocol version in common use today has extensible structure with various extensions for authentication, encryption, binary data transfer, and internationalized email addresses. SMTP servers commonly use the Transmission Control Protocol on port number 25 (between ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News Server
A news server is a collection of software used to handle Usenet articles. It may also refer to a computer itself which is primarily or solely used for handling Usenet. Access to Usenet is only available through news server providers. Articles and posts End users often use the term "posting" to refer to a single message or file posted to Usenet. For articles containing plain text, this is synonymous with an article. For binary content such as pictures and files, it is often necessary to split the content among multiple articles. Typically through the use of numbered Subject: headers, the multiple-article postings are automatically reassembled into a single unit by the newsreader. Most servers do not distinguish between single and multiple-part postings, dealing only at the level of the individual component articles. Headers and overviews Each news article contains a complete set of header lines, but in common use the term "headers" is also used when referring to the News Over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis (computing), Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980.''From Usenet to CoWebs: interacting with social information spaces'', Christopher Lueg, Danyel Fisher, Springer (2003), , Users read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more topic categories, known as Usenet newsgroup, newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are Threaded discussion, threaded, as with web forums and BBSes, though posts are stored on the server sequentially. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARPANET
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first computer networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the technical foundation of the Internet. The ARPANET was established by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (now DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense. Building on the ideas of J. C. R. Licklider, Robert Taylor (computer scientist), Bob Taylor initiated the ARPANET project in 1966 to enable resource sharing between remote computers. Taylor appointed Lawrence Roberts (scientist), Larry Roberts as program manager. Roberts made the key decisions about the request for proposal to build the network. He incorporated Donald Davies' concepts and designs for packet switching, and sought input from Paul Baran on dynamic routing. In 1969, ARPA awarded the contract to build the Interface Message Processors (IMPs) for the network to Bolt Berane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a :wikt:one-to-many, one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio, which came into popular use around 1920 with the spread of vacuum tube radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. Before this, most implementations of electronic communication (early radio, telephone, and telegraph) were wikt:one-to-one, one-to-one, with the message intended for a single recipient. The term ''broadcasting'' evolved from its use as the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about. It was later adopted for describing the widespread distribution of information by printed materials or by telegraph. Examples applying it to "one-to-many" radio transmissions of an individual station to multiple listeners appeared as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while at CERN in 1989 and opened to the public in 1993. It was conceived as a "universal linked information system". Documents and other media content are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
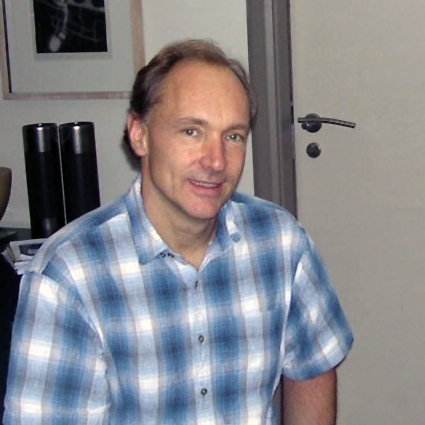
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow at the University of Oxford and a professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on 12 March 1989 and implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and Server (computing), server via the Internet in mid-November. He devised and implemented the first Web browser and Web server and helped foster the Web's subsequent development. He is the founder and emeritus director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which oversees the continued development of the Web. He co-founded (with Rosemary Leith) the World Wide Web Foundation. In April 2009, he was elected as Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Request For Comments
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development and standards-setting bodies for the Internet, most prominently the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). An RFC is authored by individuals or groups of engineers and computer scientists in the form of a memorandum describing methods, behaviors, research, or innovations applicable to the working of the Internet and Internet-connected systems. It is submitted either for peer review or to convey new concepts, information, or, occasionally, engineering humor. The IETF adopts some of the proposals published as RFCs as Internet Standards. However, many RFCs are informational or experimental in nature and are not standards. The RFC system was invented by Steve Crocker in 1969 to help record unofficial notes on the development of ARPANET. RFCs have since become official documents of Internet specifications, communications protocols, procedures, and events. According to Crocker, the docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |