Science Of Photography on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The science of photography is the use of
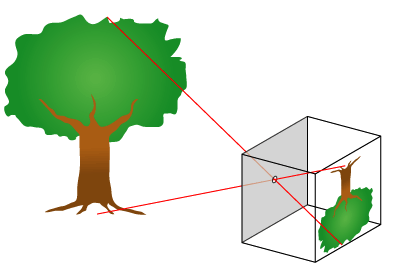 The fundamental technology of most photography, whether digital or analog, is the camera obscura effect and its ability to transform of a three dimensional scene into a two dimensional image. At its most basic, a camera obscura consists of a darkened box, with a very small hole in one side, which projects an image from the outside world onto the opposite side. This form is often referred to as a
The fundamental technology of most photography, whether digital or analog, is the camera obscura effect and its ability to transform of a three dimensional scene into a two dimensional image. At its most basic, a camera obscura consists of a darkened box, with a very small hole in one side, which projects an image from the outside world onto the opposite side. This form is often referred to as a
 Light trails are another photographic effect where motion blur is used. Photographs of the lines of light visible in long exposure photos of roads at night are one example of the effect.
This is caused by the cars moving along the road during the exposure. The same principle is used to create star trail photographs.
Generally, motion blur is something that is to be avoided, and this can be done in several different ways. The simplest way is to limit the shutter time so that there is very little movement of the image during the time the shutter is open. At longer
Light trails are another photographic effect where motion blur is used. Photographs of the lines of light visible in long exposure photos of roads at night are one example of the effect.
This is caused by the cars moving along the road during the exposure. The same principle is used to create star trail photographs.
Generally, motion blur is something that is to be avoided, and this can be done in several different ways. The simplest way is to limit the shutter time so that there is very little movement of the image during the time the shutter is open. At longer
 Black-and-white film has a "shiny" side and a "dull" side. The dull side is the
Black-and-white film has a "shiny" side and a "dull" side. The dull side is the
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
and physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
in all aspects of photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
. This applies to the camera, its lenses, physical operation of the camera, electronic camera internals, and the process of developing film
A film, also known as a movie or motion picture, is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, emotions, or atmosphere through the use of moving images that are generally, sinc ...
in order to take and develop pictures properly.
Optics
Camera obscura
 The fundamental technology of most photography, whether digital or analog, is the camera obscura effect and its ability to transform of a three dimensional scene into a two dimensional image. At its most basic, a camera obscura consists of a darkened box, with a very small hole in one side, which projects an image from the outside world onto the opposite side. This form is often referred to as a
The fundamental technology of most photography, whether digital or analog, is the camera obscura effect and its ability to transform of a three dimensional scene into a two dimensional image. At its most basic, a camera obscura consists of a darkened box, with a very small hole in one side, which projects an image from the outside world onto the opposite side. This form is often referred to as a pinhole camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera without a lens but with a tiny aperture (the so-called ''Pinhole (optics), pinhole'')—effectively a light-proof box with a small hole in one side. Light from a scene passes through the aperture and projects a ...
.
When aided by a lens, the hole in the camera doesn't have to be tiny to create a sharp and distinct image, and the exposure time can be decreased, which allows cameras to be handheld.
Lenses
A photographic lens is usually composed of several lens elements, which combine to reduce the effects ofchromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the ...
, coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
, spherical aberration, and other aberrations. A simple example is the three-element Cooke triplet
The ''Cooke triplet'' is a photographic lens designed and patented in 1893 by Dennis Taylor who was employed as chief engineer by T. Cooke & Sons of York. It was the first lens system that allowed the elimination of most of the optical distort ...
, still in use over a century after it was first designed, but many current photographic lenses are much more complex.
Using a smaller aperture can reduce most, but not all aberrations. They can also be reduced dramatically by using an aspheric element, but these are more complex to grind than spherical or cylindrical lenses. However, with modern manufacturing techniques the extra cost of manufacturing aspherical lenses is decreasing, and small aspherical lenses can now be made by molding, allowing their use in inexpensive consumer cameras. Fresnel lens
A Fresnel lens ( ; ; or ) is a type of composite compact lens (optics), lens which reduces the amount of material required compared to a conventional lens by dividing the lens into a set of concentric annular sections.
The simpler Dioptrics, d ...
es are not common in photography are used in some cases due to their very low weight. The recently developed Fiber-coupled monocentric lens consists of spheres constructed of concentric hemispherical shells of different glasses tied to the focal plane by bundles of optical fibers. Monocentric lenses are also not used in cameras because the technology was just debuted in October 2013 at the Frontiers in Optics Conference in Orlando, Florida.
All lens design is a compromise between numerous factors, including cost. Zoom lenses (i.e. lenses of variable focal length) involve additional compromises and therefore normally do not match the performance of prime lens
In film and photography, a prime lens is a fixed focal length photographic lens (as opposed to a zoom lens), typically with a maximum aperture from f2.8 to f1.2. The term can also mean the primary lens in a combination lens system.
Confusion ...
es.
When a camera lens is focused to project an object some distance away onto the film or detector, the objects that are closer in distance, relative to the distant object, are also ''approximately'' in focus. The range of distances that are nearly in focus is called the depth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus (optics), focus in an image captured with a camera. See also the closely related depth of focus.
Factors affecting depth ...
. Depth of field generally increases with decreasing aperture diameter (increasing f-number). The unfocused blur outside the depth of field is sometimes used for artistic effect in photography. The subjective appearance of this blur is known as bokeh.
If the camera lens is focused at or beyond its hyperfocal distance, then the depth of field becomes large, covering everything from half the hyperfocal distance to infinity
Infinity is something which is boundless, endless, or larger than any natural number. It is denoted by \infty, called the infinity symbol.
From the time of the Ancient Greek mathematics, ancient Greeks, the Infinity (philosophy), philosophic ...
. This effect is used to make " focus free" or fixed-focus cameras.
Aberration
Aberrations are the blurring and distorting properties of an optical system. A high quality lens will produce a smaller amount of aberrations. Spherical aberration occurs due to the increasedrefraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one transmission medium, medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commo ...
of light rays that occurs when rays strike a lens, or a reflection of light rays that occurs when rays strike a mirror near its edge in comparison with those that strike nearer the center. This is dependent on the focal length of a spherical lens and the distance from its center. It is compensated by designing a multi-lens system or by using an aspheric lens
An aspheric lens or asphere (often labeled ''ASPH'' on eye pieces) is a lens whose surface profiles are not portions of a sphere or cylinder. In photography, a lens assembly that includes an aspheric element is often called an aspherical lens.
...
.
Chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the ...
is caused by a lens having a different refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
for different wavelengths
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same '' phase'' on ...
of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
and the dependence of the optical properties on color
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though co ...
. Blue light will generally bend more than red light. There are higher order chromatic aberrations, such as the dependence of magnification on color. Chromatic aberration is compensated by using a lens made out of materials carefully designed to cancel out chromatic aberrations.
Curved focal surface is the dependence of the first order focus on the position on the film or CCD. This can be compensated with a multiple lens optical design, but curving the film has also been used.
Focus
Focus
Focus (: foci or focuses) may refer to:
Arts
* Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in East Australia Film
*Focus (2001 film), ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based on the Arthur Miller novel
*Focus (2015 ...
is the tendency for light rays to reach the same place on the image sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
or film, independent of where they pass through the lens. For clear pictures, the focus is adjusted for distance, because at a different object distance the rays reach different parts of the lens with different angles. In modern photography, focusing is often accomplished automatically.
The autofocus
An autofocus (AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus on an automatically or manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system h ...
system in modern SLRs use a sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a devi ...
in the mirrorbox to measure contrast. The sensor's signal is analyzed by an application-specific integrated circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficienc ...
(ASIC), and the ASIC tries to maximize the contrast pattern by moving lens elements. The ASICs in modern cameras also have special algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for per ...
for predicting motion, and other advanced features.
Diffraction limit
Since light propagates as waves, the patterns it produces on the film are subject to the wave phenomenon known asdiffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
, which limits the image resolution to features on the order of several times the wavelength of light. Diffraction is the main effect limiting the sharpness of optical images from lenses that are stopped down to small apertures (high f-numbers), while aberrations are the limiting effect at large apertures (low f-numbers). Since diffraction cannot be eliminated, the best possible lens for a given operating condition (aperture setting) is one that produces an image whose quality is limited only by diffraction. Such a lens is said to be ''diffraction limited''.
The diffraction-limited optical spot size on the CCD or film is proportional to the f-number
An f-number is a measure of the light-gathering ability of an optical system such as a camera lens. It is calculated by dividing the system's focal length by the diameter of the entrance pupil ("clear aperture").Smith, Warren ''Modern Optical ...
(about equal to the f-number times the wavelength of light, which is near 0.0005 mm), making the overall detail in a photograph proportional to the size of the film, or CCD divided by the f-number. For a 35 mm camera with , this limit corresponds to about 6,000 resolution elements across the width of the film (36 mm / (11 * 0.0005 mm) = 6,500.
The finite spot size caused by diffraction can also be expressed as a criterion for distinguishing distant objects: two distant point sources can only produce separate images on the film or sensor if their angular separation exceeds the wavelength of light divided by the width of the open aperture of the camera lens.
Chemical processes
Gelatin silver
The gelatin silver process is the most commonly used chemical process in black-and-white photography, and is the fundamental chemical process for modern analog color photography. As such, films and printing papers available for analog photography rarely rely on any other chemical process to record an image.Daguerreotypes
Daguerreotype (; ) was the first publicly available photographic process; it was widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process.Collodion process and the ambrotype
The collodion process is an early photographic process. The collodion process, mostly synonymous with the "collodion wet plate process", requires the photographic material to be coated, sensitized, exposed and developed within the span of about fifteen minutes, necessitating a portable darkroom for use in the field. Collodion is normally used in its wet form, but can also be used in dry form, at the cost of greatly increased exposure time. The latter made the dry form unsuitable for the usual portraiture work of most professional photographers of the 19th century. The use of the dry form was therefore mostly confined to landscape photography and other special applications where minutes-long exposure times were tolerable.Cyanotypes
Cyanotype is a photographic printing process that produces a cyan-blue print. Engineers used the process well into the 20th century as a simple and low-cost process to produce copies of drawings, referred to as blueprints. The process uses two chemicals: ferric ammonium citrate and potassium ferricyanide.Platinum and palladium processes
Platinum prints, also called platinotypes, are photographic prints made by a monochrome printing process involving platinum.Gum bichromate
Gum bichromate is a 19th-century photographic printing process based on the light sensitivity of dichromates. It is capable of rendering painterly images from photographic negatives. Gum printing is traditionally a multi-layered printing process, but satisfactory results may be obtained from a single pass. Any color can be used for gum printing, so natural-color photographs are also possible by using this technique in layers.C-prints and color film
A chromogenic print, also known as a C-print or C-type print, a silver halide print, or a dye coupler print, is aphotographic print
Photographic printing is the process of producing a final image on paper for viewing, using chemically sensitized paper. The paper is exposed to a photographic negative, a positive transparency (or ''slide''), or a digital image file projected ...
made from a color negative, transparency or digital image
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as pixels, each with '' finite'', '' discrete quantities'' of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions f ...
, and developed using a chromogenic process. They are composed of three layers of gelatin, each containing an emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally Miscibility, immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloi ...
of silver halide
A silver halide (or silver salt) is one of the chemical compounds that can form between the Chemical element, element silver (Ag) and one of the halogens. In particular, bromine (Br), chlorine (Cl), iodine (I) and fluorine (F) may each combine wit ...
, which is used as a light-sensitive material, and a different dye coupler
Dye coupler is present in Chromogen, chromogenic photographic film, film and photographic paper, paper used in photography, primarily color photography. When a color developer Redox, reduces ionized (exposed) silver halide crystals, the developer ...
of subtractive color
Subtractive color or subtractive color mixing predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and pigments are ...
which together, when developed, form a full-color image.
Digital sensors
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, 2] medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging.Practical applications
Law of reciprocity
: Exposure ∝ Aperture Area × Exposure Time × Scene Luminance The law of reciprocity describes how light intensity and duration trade off to make an exposure—it defines the relationship betweenshutter speed
In photography, shutter speed or exposure time is the length of time that the film or digital sensor inside the camera is exposed to light (that is, when the camera's shutter (photography), shutter is open) when taking a photograph.
The am ...
and aperture
In optics, the aperture of an optical system (including a system consisting of a single lens) is the hole or opening that primarily limits light propagated through the system. More specifically, the entrance pupil as the front side image o ...
, for a given total exposure. Changes to any of these elements are often measured in units known as "stops"; a stop is equal to a factor of two.
Halving the amount light exposing the film can be achieved either by:
# Closing the aperture by one stop
# Decreasing the shutter time (increasing the shutter speed) by one stop
# Cutting the scene lighting by half
Likewise, doubling the amount of light exposing the film can be achieved by the opposite of one of these operations.
The luminance of the scene, as measured on a reflected light meter
A light meter (or illuminometer) is a device used to measure the amount of light. In photography, an exposure meter is a light meter coupled to either a Digital data, digital or analog calculator which displays the correct shutter speed and f-nu ...
, also affects the exposure proportionately. The amount of light required for proper exposure depends on the film speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system introduced in 1974. A closely related system, also known as IS ...
; which can be varied in stops or fractions of stops. With either of these changes, the aperture or shutter speed can be adjusted by an equal number of stops to get to a suitable exposure.
Light is most easily controlled through the use of the camera's aperture (measure in f-stops), but it can also be regulated by adjusting the shutter speed
In photography, shutter speed or exposure time is the length of time that the film or digital sensor inside the camera is exposed to light (that is, when the camera's shutter (photography), shutter is open) when taking a photograph.
The am ...
. Using faster or slower film
A film, also known as a movie or motion picture, is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, emotions, or atmosphere through the use of moving images that are generally, sinc ...
is not usually something that can be done quickly, at least using roll film. Large format
Large format photography refers to any imaging format of or larger. Large format is larger than "medium format", the or size of Hasselblad, Mamiya, Rollei, Kowa, and Pentax cameras (using 120 film, 120- and 220-roll film), and much la ...
cameras use individual sheets of film and each sheet could be a different speed. Also, if you're using a larger format camera with a polaroid back, you can switch between backs containing different speed polaroids. Digital camera
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in Digital data storage, digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Dig ...
s can easily adjust the film speed they are simulating by adjusting the exposure index, and many digital cameras can do so automatically in response to exposure measurements.
For example, starting with an exposure of 1/60 at , the depth-of-field could be made shallower by opening up the aperture to , an increase in exposure of 4 stops. To compensate, the shutter speed would need to be increased as well by 4 stops, that is, adjust exposure time down to 1/1000. Closing down the aperture limits the resolution due to the diffraction limit
In optics, any optical instrument or systema microscope, telescope, or camerahas a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of res ...
.
The reciprocity law specifies the total exposure, but the response of a photographic material to a constant total exposure may not remain constant for very long exposures in very faint light, such as photographing a starry sky, or very short exposures in very bright light, such as photographing the sun. This is known as ''reciprocity failure'' of the material (film, paper, or sensor).
Motion blur
Motion blur
Motion blur is the apparent streaking of moving objects in a photograph or a sequence of frames, such as a film or animation. It results when the image being recorded changes during the recording of a single exposure, due to rapid movement or l ...
is caused when either the camera or the subject moves during the exposure. This causes a distinctive streaky appearance to the moving object or the entire picture (in the case of camera shake).
Motion blur can be used artistically to create the feeling of speed or motion, as with running water. An example of this is the technique of "panning
Pan or PAN may refer to:
Food
* Pan (cooking), a piece of cooking equipment
* Harina P.A.N., a pre-cooked corn meal
* Pan or Paan, a North Indian term for betel
Prefix
* ''Pan-'', a prefix meaning "all", "of everything", or "involving all ...
", where the camera is moved so it follows the subject, which is usually fast moving, such as a car. Done correctly, this will give an image of a clear subject, but the background will have motion blur, giving the feeling of movement. This is one of the more difficult photographic techniques to master, as the movement must be smooth, and at the correct speed. A subject that gets closer or further away from the camera may further cause focusing difficulties.
focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
s, the same movement of the camera body will cause more motion of the image, so a shorter shutter time is needed. A commonly cited rule of thumb is that the shutter speed in seconds should be about the reciprocal of the 35 mm equivalent focal length of the lens in millimeters. For example, a 50 mm lens should be used at a minimum speed of 1/50 sec, and a 300 mm lens at 1/300 of a second. This can cause difficulties when used in low light scenarios, since exposure also decreases with shutter time.
Motion blur due to subject movement can usually be prevented by using a faster shutter speed. The exact shutter speed will depend on the speed at which the subject is moving. For example, a very fast shutter speed will be needed to "freeze" the rotors of a helicopter, whereas a slower shutter speed will be sufficient to freeze a runner.
A tripod
A tripod is a portable three-legged frame or stand, used as a platform for supporting the weight and maintaining the stability of some other object. The three-legged (triangular stance) design provides good stability against gravitational loads ...
may be used to avoid motion blur due to camera shake. This will stabilize the camera during the exposure. A tripod is recommended for exposure times more than about 1/15 seconds. There are additional techniques which, in conjunction with use of a tripod, ensure that the camera remains very still. These may employ use of a remote actuator, such as a cable release or infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
remote switch to activate the shutter, so as to avoid the movement normally caused when the shutter release button is pressed directly. The use of a "self timer" (a timed release mechanism that automatically trips the shutter release after an interval of time) can serve the same purpose. Most modern single-lens reflex camera
In photography, a single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a type of camera that uses a mirror and prism system to allow photographers to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. SLRs became the dominant design for professional a ...
(SLR) have a mirror lock-up feature that eliminates the small amount of shake produced by the mirror flipping up.
Film grain resolution
 Black-and-white film has a "shiny" side and a "dull" side. The dull side is the
Black-and-white film has a "shiny" side and a "dull" side. The dull side is the emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally Miscibility, immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloi ...
, a gelatin that suspends an array of silver halide
A silver halide (or silver salt) is one of the chemical compounds that can form between the Chemical element, element silver (Ag) and one of the halogens. In particular, bromine (Br), chlorine (Cl), iodine (I) and fluorine (F) may each combine wit ...
crystals. These crystals contain silver grains that determine how sensitive the film is to light exposure, and how fine or grainy the negative the print will look. Larger grains mean faster exposure but a grainier appearance; smaller grains are finer looking but take more exposure to activate. The graininess of film is represented by its ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
factor; generally a multiple of 10 or 100. Lower numbers produce finer grain but slower film, and vice versa.
Contribution to noise (grain)
Quantum efficiency
Light comes in particles and the energy of a light-particle (thephoton
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
) is the frequency of the light times the Planck constant
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, denoted by h, is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics: a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant, and the wavelength of a ...
. A fundamental property of any photographic method is how it collects the light on its photographic plate
Photographic plates preceded film as the primary medium for capturing images in photography. These plates, made of metal or glass and coated with a light-sensitive emulsion, were integral to early photographic processes such as heliography, d ...
or electronic detector.
CCDs and other photodiodes
Photodiodes are back-biased semiconductor diodes, in which an intrinsic layer with very few charge carriers prevents electric currents from flowing. Depending on the material, photons have enough energy to raise oneelectron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
from the upper full band to the lowest empty band. The electron and the "hole", or the empty space where it was, are then free to move in the electric field and carry current, which can be measured. The fraction of incident photons that produce carrier pairs depends largely on the semiconductor material.
Photomultiplier tubes
Photomultiplier A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal.
Kinds of photomultiplier include:
* Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for sh ...
tubes are vacuum phototube
A phototube or photoelectric cell is a type of gas filled tube, gas-filled or vacuum tube that is sensitive to light. Such a tube is more correctly called a 'photoemissive cell' to distinguish it from photovoltaic or photoconductive cells. Photo ...
s that amplify light by accelerating the photoelectrons to knock more electrons free from a series of electrodes. They are among the most sensitive light detectors but are not well suited to photography.
Aliasing
Aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is a phenomenon that a reconstructed signal from samples of the original signal contains low frequency components that are not present in the original one. This is caused when, in the ori ...
can occur in optical and chemical processing, but it is more common and easily understood in digital processing. It occurs whenever an optical or digital image is sampled or re-sampled at a rate which is too low for its resolution. Some digital cameras and scanners have anti-aliasing filters to reduce aliasing by intentionally blurring the image to match the sampling rate. It is common for film developing equipment used to make prints of different sizes to increase the graininess of the smaller size prints by aliasing.
It is usually desirable to suppress both noises such as grain and details of the real object that are too small to be represented at the sampling rate.
See also
*Astrophotography
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1839, but it was no ...
* Underwater photography
* Infrared photography
In infrared photography, the photographic film or image sensor used is sensitive to infrared light. The part of the spectrum used is referred to as near-infrared to distinguish it from far-infrared, which is the domain of thermal imaging. Wav ...
* Ultraviolet photography
* Silver bromide
Silver bromide (AgBr), a soft, pale-yellow, water-insoluble salt well known (along with other silver halides) for its unusual sensitivity to light. This property has allowed silver halides to become the basis of modern photographic materials. AgB ...
* Photographic processing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image i ...
* Image editing
Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are Digital photography, digital photographs, traditional Photographic processing, photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known ...
* Highlight headroom
References
{{photography subject Photography, science of Photography