satellite image on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are
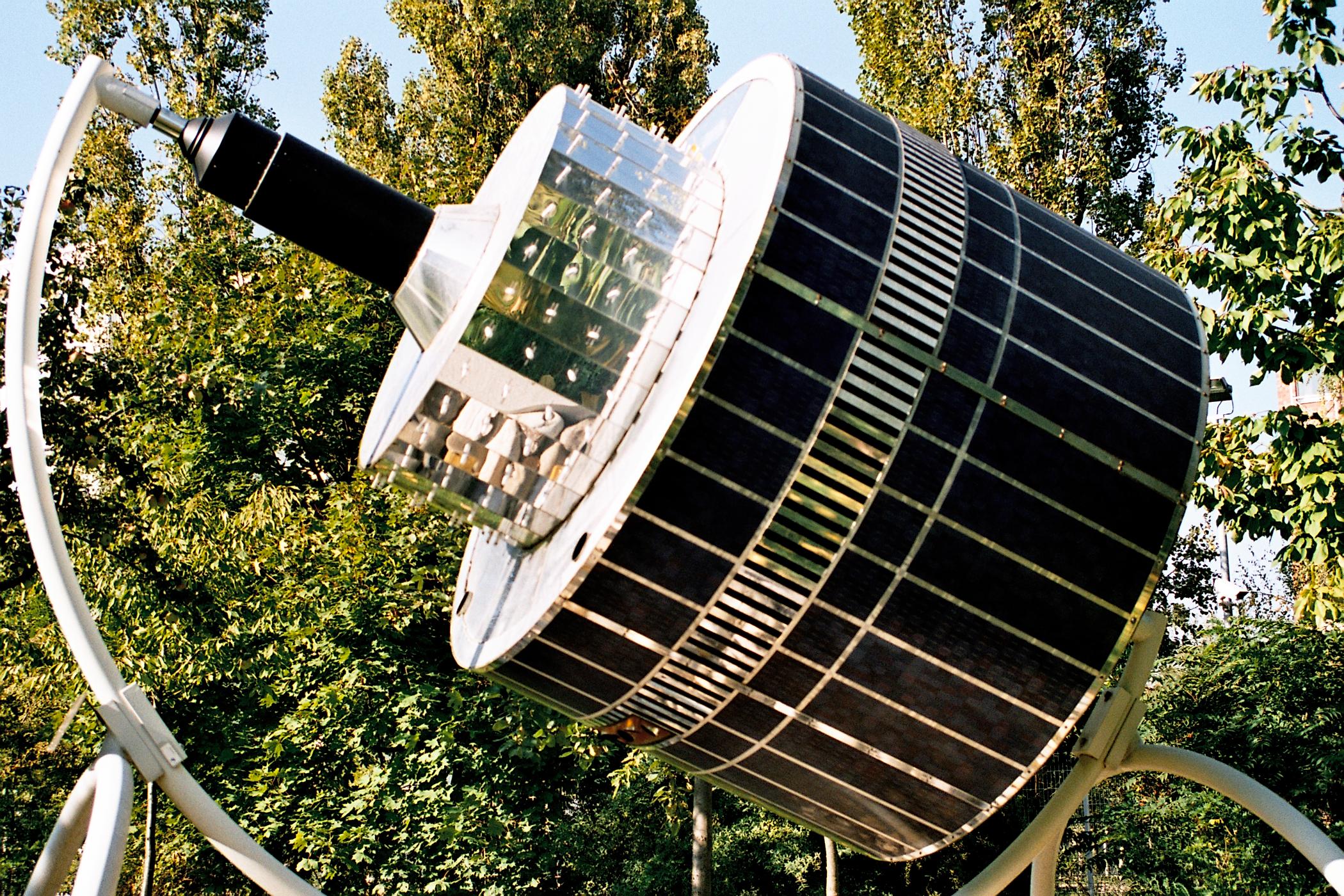 The '' Meteosat''-2 geostationary weather satellite began operationally to supply imagery data on 16 August 1981. Eumetsat has operated the Meteosats since 1987.
*The '' Meteosat visible and infrared imager (MVIRI)'', three-channel imager: visible, infrared and water vapour; It operates on the first generation Meteosat, Meteosat-7 being still active.
*The 12-channel ''Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI)'' includes similar channels to those used by MVIRI, providing continuity in climate data over three decades; Meteosat Second Generation (MSG).
*The ''Flexible Combined Imager (FCI)'' on Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) will also include similar channels, meaning that all three generations will have provided over 60 years of climate data.
The '' Meteosat''-2 geostationary weather satellite began operationally to supply imagery data on 16 August 1981. Eumetsat has operated the Meteosats since 1987.
*The '' Meteosat visible and infrared imager (MVIRI)'', three-channel imager: visible, infrared and water vapour; It operates on the first generation Meteosat, Meteosat-7 being still active.
*The 12-channel ''Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI)'' includes similar channels to those used by MVIRI, providing continuity in climate data over three decades; Meteosat Second Generation (MSG).
*The ''Flexible Combined Imager (FCI)'' on Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) will also include similar channels, meaning that all three generations will have provided over 60 years of climate data.
Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI)
which provides high-resolution images of the Earth. The AHI can capture images in 16 different spectral bands, allowing for detailed observation of weather patterns, clouds, and environmental phenomena.

 ''Pléiades''
''Pléiades''
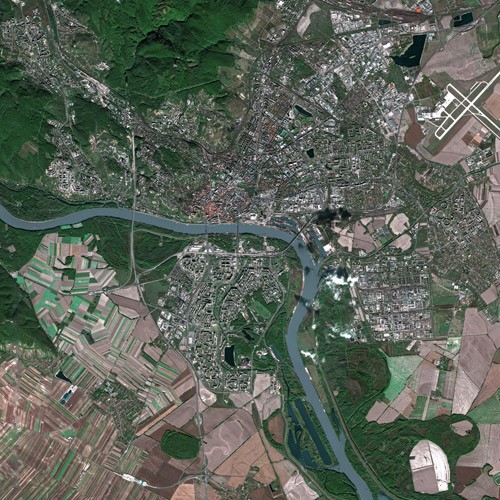

 The 3 SPOT satellites in orbit (Spot 5, 6, 7) provide very high resolution images – 1.5 m for Panchromatic channel, 6m for Multi-spectral (R,G,B,NIR). Spot Image also distributes multiresolution data from other optical satellites, in particular from Formosat-2 (
The 3 SPOT satellites in orbit (Spot 5, 6, 7) provide very high resolution images – 1.5 m for Panchromatic channel, 6m for Multi-spectral (R,G,B,NIR). Spot Image also distributes multiresolution data from other optical satellites, in particular from Formosat-2 (
"With 2 More Cubesats in Orbit, Earth-imaging Startup Planet Labs Ships Next Batch of 28 to Wallops"
''spacenews.com'', 26 November 2013. Retrieved on 26 November 2013.Bradshaw, Tim
''ft.com'', 26 November 2013. Retrieved on 26 November 2013. SkySat is a constellation of sub-metre resolution Earth observation satellites that provide imagery, high-definition video and analytics services. Planet acquired the satellites with their purchase of Terra Bella (formerly Skybox Imaging), a Mountain View, California-based company founded in 2009 by Dan Berkenstock, Julian Mann, John Fenwick, and Ching-Yu Hu, from Google in 2017. The SkySat satellites are based on using inexpensive automotive grade electronics and fast commercially available processors, but scaled up to approximately the size of a minifridge. The satellites are approximately long, compared to approximately for a 3U CubeSat, and weigh .
 Because the total area of the land on Earth is so large and because resolution is relatively high, satellite databases are huge and
Because the total area of the land on Earth is so large and because resolution is relatively high, satellite databases are huge and
ESA Envisat Meris – 300m
– the most detailed image of the entire Earth to date, made by the European Space Agency's Envisat Meris.
Blue Marble: Next Generation
– a detailed true-color image of the entire Earth.
World Wind
– an open source 3D Earth-viewing software developed by
 Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are image
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di ...
s of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell images by licensing them to governments and businesses such as Apple Maps and Google Maps
Google Maps is a web mapping platform and consumer application offered by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360° interactive panorama, interactive panoramic views of streets (Google Street View, Street View ...
.
History
The first images from space were taken on sub-orbital flights. The US-launched V-2 flight on October 24, 1946, took one image every 1.5 seconds. With an apogee of 65 miles (105 km), these photos were from five times higher than the previous record, the 13.7 miles (22 km) by the Explorer II balloon mission in 1935. The first satellite (orbital) photographs of Earth were made on August 14, 1959, by the U.S. Explorer 6. The first satellite photographs of theMoon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
might have been made on October 6, 1959, by the Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
satellite Luna 3, on a mission to photograph the far side of the Moon. The Blue Marble photograph was taken from space in 1972, and has become very popular in the media and among the public. Also in 1972 the United States started the Landsat program
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint National Aeronautics and Space Administration, NASA / United States Geological Survey, USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Landsa ...
, the largest program for acquisition of imagery of Earth from space. In 1977, the first real time satellite imagery was acquired by the United States' KH-11
The KH-11 KENNEN (later renamed CRYSTAL,p.199-200 then Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System, and codenamed 1010 and Key Hole) is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 19 ...
satellite system. The most recent Landsat satellite, Landsat 9, was launched on 27 September 2021.
All satellite images produced by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
are published by NASA Earth Observatory and are freely available to the public. Several other countries have satellite imaging programs, and a collaborative European effort launched the ERS and Envisat satellites carrying various sensors. There are also private companies that provide commercial satellite imagery. In the early 21st century satellite imagery became widely available when affordable, easy to use software with access to satellite imagery databases was offered by several companies and organizations.
Satellite image applications
Satellite images have numerous applications in a variety of fields. *Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
: They guide meteorologists in forecasting patterns, tracking storms, and understanding climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
* Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology.
It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of to ...
: By measuring sea temperatures and monitoring ecosystems, satellite images unlock insights into our oceans' health and global climate.
* Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
and fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
: Satellite data helps locate fish populations, assess crop health, and optimize resource use for a thriving agricultural and fishing industry.
* Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
: Conservation efforts leverage satellite technology to map habitats, monitor ecosystem changes, and protect endangered species.
* Forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and Natural environment, environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and ...
: Satellite data empowers sustainable forestry by tracking deforestation, assessing fire risks, and managing resources effectively.
* Landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or human-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes th ...
: Analyzing land use patterns with satellite images supports urban planning and facilitates sustainable development initiatives.
Less mainstream uses include anomaly hunting, a criticized investigation technique involving the search of satellite images for unexplained phenomena.
The spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
of satellite images is diverse, including visible light, near-infrared light, infrared light and radar, and many others. This wide range of light frequencies can provide researchers with large volumes of useful and rich information. In addition to the satellite applications mentioned above, these data can serve as powerful educational tools, advance scientific research and promote a deeper understanding of our environment. This shows that satellite imagery provides rich information and can promote global development.
Data characteristics
There are five types of resolution when discussing satellite imagery in remote sensing: spatial, spectral, temporal, radiometric and geometric. Campbell (2002) defines these as follows: * Spatial resolution is defined as thepixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
size of an image representing the size of the surface area (i.e. m2) being measured on the ground, determined by the sensors' instantaneous field of view (IFOV).
* Spectral resolution is defined by the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
interval size (i.e. the size of discrete segments of the electromagnetic spectrum) and the number of intervals that the sensor is measuring.
* Temporal resolution is defined by the amount of time (e.g. days) that passes between imagery collection periods for a given surface location.
*Radiometric resolution is defined as the ability of an imaging system to record many levels of brightness (e.g. contrast) and to the effective bit-depth of the sensor (number of grayscale levels) and is typically expressed as 8-bit (0–255), 11-bit (0–2047), 12-bit (0–4095) or 16-bit (0–65,535).
* Geometric resolution refers to the satellite sensor's ability to effectively image a portion of the Earth's surface in a single pixel and is typically expressed in terms of ground sample distance (GSD). GSD is a term containing the overall optical and systemic noise sources and is useful for comparing how well one sensor can "see" an object on the ground within a single pixel. For example, the GSD of Landsat is ≈30m, which means the smallest unit that maps to a single pixel within an image is ≈30m x 30m. The latest commercial satellite (GeoEye 1) has a GSD of 0.41 m. This compares to a 0.3 m resolution obtained by some early military film based reconnaissance satellites such as Corona.
The resolution of satellite images varies depending on the instrument used and the altitude of the satellite's orbit. For example, the Landsat archive offers repeated imagery at 30 meter resolution for the planet, but most of it has not been processed from the raw data. Landsat 7 has an average return period of 16 days. For many smaller areas, images with resolution as fine as 41 cm can be available.
Satellite imagery is sometimes supplemented with aerial photography
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other flight, airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography.
Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wi ...
, which has higher resolution, but is more expensive per square meter. Satellite imagery can be combined with vector or raster data in a GIS provided that the imagery has been spatially rectified so that it will properly align with other data sets.
Imaging satellites
Public domain
Satellite imaging of the Earth surface is of sufficient public utility that many countries maintain satellite imaging programs. The United States has led the way in making these data freely available for scientific use. Some of the more popular programs are listed below, recently followed by theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
's Sentinel constellation.
CORONA
The '' CORONA'' program was a series of American strategic reconnaissance satellites produced and operated by theCentral Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
(CIA) Directorate of Science & Technology with substantial assistance from the U.S. Air Force. The type of imagery is wet film panoramic and it used two cameras (AFT&FWD) for capturing stereographic imagery.
Landsat
'' Landsat'' is the oldest continuous Earth-observing satellite imaging program. Optical Landsat imagery has been collected at 30 m resolution since the early 1980s. Beginning with Landsat 5, thermal infrared imagery was also collected (at coarser spatial resolution than the optical data). The Landsat 7, Landsat 8, and Landsat 9 satellites are currently in orbit.MODIS
'' MODIS'' has collected near-daily satellite imagery of the earth in 36 spectral bands since 2000. MODIS is on board the NASA Terra and Aqua satellites.Sentinel
The ESA is currently developing the '' Sentinel'' constellation of satellites. Currently, 7 missions are planned, each for a different application. Sentinel-1 (SAR imaging),Sentinel-2
Sentinel-2 is an Earth observation mission from the Copernicus Programme that acquires optical imagery at high spatial resolution (10 m to 60 m) over land and coastal waters. The mission's Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B satellites were joined in or ...
(decameter optical imaging for land surfaces), and Sentinel-3 (hectometer optical and thermal imaging for land and water) have already been launched.
ASTER
The '' ASTER'' is an imaging instrument onboard Terra, the flagship satellite of NASA's Earth Observing System (EOS) launched in December 1999. ASTER is a cooperative effort between NASA, Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), and Japan Space Systems (J-spacesystems). ASTER data is used to create detailed maps of land surface temperature, reflectance, and elevation. The coordinated system of EOS satellites, including Terra, is a major component of NASA's Science Mission Directorate and the Earth Science Division. The goal of NASA Earth Science is to develop a scientific understanding of the Earth as an integrated system, its response to change, and to better predict variability and trends in climate, weather, and natural hazards. * Land surface climatology—investigation of land surface parameters, surface temperature, etc., to understand land-surface interaction and energy and moisture fluxes * Vegetation and ecosystem dynamics—investigations of vegetation and soil distribution and their changes to estimate biological productivity, understand land-atmosphere interactions, and detect ecosystem change * Volcano monitoring—monitoring of eruptions and precursor events, such as gas emissions, eruption plumes, development of lava lakes, eruptive history and eruptive potential * Hazard monitoring—observation of the extent and effects of wildfires, flooding,coastal erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of Wind wave, waves, Ocean current, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts ...
, earthquake damage, and tsunami damage
* Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and drainage basin sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydro ...
—understanding global energy and hydrologic processes and their relationship to global change; included is evapotranspiration from plants
* Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth ...
and soils—the detailed composition and geomorphologic mapping of surface soils and bedrocks to study land surface processes and Earth's history
* Land surface and land cover change—monitoring desertification, deforestation, and urbanization; providing data for conservation managers to monitor protected areas, national parks, and wilderness areas
Meteosat
 The '' Meteosat''-2 geostationary weather satellite began operationally to supply imagery data on 16 August 1981. Eumetsat has operated the Meteosats since 1987.
*The '' Meteosat visible and infrared imager (MVIRI)'', three-channel imager: visible, infrared and water vapour; It operates on the first generation Meteosat, Meteosat-7 being still active.
*The 12-channel ''Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI)'' includes similar channels to those used by MVIRI, providing continuity in climate data over three decades; Meteosat Second Generation (MSG).
*The ''Flexible Combined Imager (FCI)'' on Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) will also include similar channels, meaning that all three generations will have provided over 60 years of climate data.
The '' Meteosat''-2 geostationary weather satellite began operationally to supply imagery data on 16 August 1981. Eumetsat has operated the Meteosats since 1987.
*The '' Meteosat visible and infrared imager (MVIRI)'', three-channel imager: visible, infrared and water vapour; It operates on the first generation Meteosat, Meteosat-7 being still active.
*The 12-channel ''Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI)'' includes similar channels to those used by MVIRI, providing continuity in climate data over three decades; Meteosat Second Generation (MSG).
*The ''Flexible Combined Imager (FCI)'' on Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) will also include similar channels, meaning that all three generations will have provided over 60 years of climate data.
Himawari
The Himawari satellite series represents a significant leap forward in meteorological observation and environmental monitoring. With their advanced imaging technology and frequent data updates, Himawari-8 and Himawari-9 have become indispensable tools for weather forecasting, disaster management, and climate research, benefiting not only Japan but the entire Asia-Pacific region. *Frequent Updates:These satellites can provide full-disk images of the Asia-Pacific region every 10 minutes, and even more frequently( every 2.5 minutes) for specific areas (Japan), ensuring that meteorologists have up-to-date information for accurate weather forecasting. * Spectral Bands: **Visible Light Bands (0.47 μm, 0.51 μm, 0.64 μm): These bands are used for daytime cloud, land, and ocean surface observations. They provide high-resolution images that are critical for tracking cloud movements and assessing weather conditions. **Near-Infrared Bands (0.86 μm, 1.6 μm, 2.3 μm, 6.9 μm, 7.3 μm, 8.6 μm, 9.6 μm, 11.2 μm, 13.3 μm): These bands help in distinguishing between different types of clouds, vegetation, and surface features. They are particularly useful for detecting fog, ice, and snow. **Infrared Bands (3.9 μm, 6.2 μm, 10.4 μm, 12.4 μm): The remaining bands cover the thermal infrared spectrum. These bands are crucial for measuring cloud-top temperatures, sea surface temperatures, and atmospheric water vapor content. They enable continuous monitoring of weather patterns. *Advanced Imaging Technology: Himawari-8 and Himawari-9 are equipped with thAdvanced Himawari Imager (AHI)
which provides high-resolution images of the Earth. The AHI can capture images in 16 different spectral bands, allowing for detailed observation of weather patterns, clouds, and environmental phenomena.
Private domain
Several satellites are built and maintained by private companies, as follows.GeoEye
GeoEye's GeoEye-1 satellite was launched on September 6, 2008. The GeoEye-1 satellite has high resolution imaging system and is able to collect images with a ground resolution of 0.41 meters (16 inches) in panchromatic or black and white mode. It collects multispectral or color imagery at 1.65-meter resolution or about 64 inches.
Maxar
Maxar's WorldView-2 satellite provides high resolution commercial satellite imagery with 0.46 m spatial resolution (panchromatic only). The 0.46 meters resolution of WorldView-2's panchromatic images allows the satellite to distinguish between objects on the ground that are at least 46 cm apart. Similarly Maxar's QuickBird satellite provides 0.6 meter resolution (at nadir) panchromatic images. Maxar's WorldView-3 satellite provides high resolution commercial satellite imagery with 0.31 m spatial resolution. WVIII also carries a short wave infrared sensor and an atmospheric sensor.Airbus Intelligence
 ''Pléiades''
''Pléiades'' constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
is composed of two very-high-resolution (50 centimeters pan & 2.1 meter spectral) optical Earth-imaging satellites. ''Pléiades-HR 1A'' and ''Pléiades-HR 1B'' provide the coverage of Earth's surface with a repeat cycle of 26 days. Designed as a dual civil/military system, Pléiades will meet the space imagery requirements of Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an defense as well as civil and commercial needs.
is the advanced optical constellation, with four identical 30-cm resolution satellites with fast reactivity.
Spot Image

 The 3 SPOT satellites in orbit (Spot 5, 6, 7) provide very high resolution images – 1.5 m for Panchromatic channel, 6m for Multi-spectral (R,G,B,NIR). Spot Image also distributes multiresolution data from other optical satellites, in particular from Formosat-2 (
The 3 SPOT satellites in orbit (Spot 5, 6, 7) provide very high resolution images – 1.5 m for Panchromatic channel, 6m for Multi-spectral (R,G,B,NIR). Spot Image also distributes multiresolution data from other optical satellites, in particular from Formosat-2 (Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
) and Kompsat-2 (South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
) and from radar satellites (TerraSar-X, ERS, Envisat, Radarsat). Spot Image is also the exclusive distributor of data from the high resolution Pleiades satellites with a resolution of 0.50 meter or about 20 inches. The launches occurred in 2011 and 2012, respectively. The company also offers infrastructures for receiving and processing, as well as added value options.
Planet Labs
Planet Labs operates three satellite imagery constellations, RapidEye, Dove and SkySat. In 2015, Planet acquired BlackBridge, and its constellation of five RapidEye satellites, launched in August 2008. The RapidEye constellation contains identical multispectral sensors which are equally calibrated. Therefore, an image from one satellite will be equivalent to an image from any of the other four, allowing for a large amount of imagery to be collected (4 million km2 per day), and daily revisit to an area. Each travel on the same orbital plane at 630 km, and deliver images in 5 meter pixel size. RapidEye satellite imagery is especially suited for agricultural, environmental, cartographic and disaster management applications. The company not only offers their imagery, but consults their customers to create services and solutions based on analysis of this imagery. The RapidEye constellation was retired by Planet in April 2020. Planet's Dove satellites are CubeSats that weigh , in length, width and height, orbit at a height of about and provide imagery with a resolution of and are used for environmental, humanitarian, and business applications.Werner, Debra"With 2 More Cubesats in Orbit, Earth-imaging Startup Planet Labs Ships Next Batch of 28 to Wallops"
''spacenews.com'', 26 November 2013. Retrieved on 26 November 2013.Bradshaw, Tim
''ft.com'', 26 November 2013. Retrieved on 26 November 2013. SkySat is a constellation of sub-metre resolution Earth observation satellites that provide imagery, high-definition video and analytics services. Planet acquired the satellites with their purchase of Terra Bella (formerly Skybox Imaging), a Mountain View, California-based company founded in 2009 by Dan Berkenstock, Julian Mann, John Fenwick, and Ching-Yu Hu, from Google in 2017. The SkySat satellites are based on using inexpensive automotive grade electronics and fast commercially available processors, but scaled up to approximately the size of a minifridge. The satellites are approximately long, compared to approximately for a 3U CubeSat, and weigh .
ImageSat International
Earth Resource Observation Satellites, better known as "EROS" satellites, are lightweight, low earth orbiting, high-resolution satellites designed for fast maneuvering between imaging targets. In the commercial high-resolution satellite market, EROS is the smallest very high resolution satellite; it is very agile and thus enables very high performances. The satellites are deployed in a circular Sun-synchronous near polar orbit at an altitude of 510 km (± 40 km). EROS satellites imagery applications are primarily for intelligence, homeland security and national development purposes but also employed in a wide range of civilian applications, including: mapping, border control, infrastructure planning, agricultural monitoring, environmental monitoring, disaster response, training and simulations, etc. EROS A – a high resolution satellite with 1.9–1.2m resolution panchromatic was launched on December 5, 2000. EROS B – the second generation of Very High Resolution satellites with 70 cm resolution panchromatic, was launched on April 25, 2006. EROS C2 – the third generation of Very High Resolution satellites with 30 cm. resolution panchromatic, was launched in 2021. EROS C3 – the third generation of Very High Resolution satellites with 30 cm. resolution panchromatic and multispectral, was launched in 2023.China Siwei
GaoJing-1 / SuperView-1 (01, 02, 03, 04) is a commercial constellation of Chinese remote sensing satellites controlled by China Siwei Surveying and Mapping Technology Co. Ltd. The four satellites operate from an altitude of 530 km and are phased 90° from each other on the same orbit, providing 0.5m panchromatic resolution and 2m multispectral resolution on a swath of 12 km.Disadvantages
 Because the total area of the land on Earth is so large and because resolution is relatively high, satellite databases are huge and
Because the total area of the land on Earth is so large and because resolution is relatively high, satellite databases are huge and image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
(creating useful images from the raw data) is time-consuming. Preprocessing, such as image destriping, is often required. Depending on the sensor used, weather conditions can affect image quality. For example, it is difficult to obtain images for areas of frequent cloud cover such as mountaintops. For such reasons, publicly available satellite image datasets are typically processed for visual or scientific commercial use by third parties.
Commercial satellite companies do not place their imagery into the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
and do not sell their imagery; instead, one must acquire a license
A license (American English) or licence (Commonwealth English) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another part ...
to use their imagery. Thus, the ability to legally make derivative works from commercial satellite imagery is diminished.
Privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
concerns have been brought up by some who wish not to have their property shown from above. Google Maps responds to such concerns in their FAQ with the following statement: "We understand your privacy concerns... The images that Google Maps displays are no different from what can be seen by anyone who flies over or drives by a specific geographic location."
Using
Satellite images are used in many fields of activity — agriculture, geological and hydrological research, forestry, environmental protection, territorial planning, educational, intelligence and military purposes. Such images can be made in the visible part of the spectrum, as well as in the ultraviolet, infrared and other parts of the range. There are also various terrain maps made using radar surveys. Currently, the decryption and analysis of satellite images is increasingly performed using automated software systems such as ERDAS Imagine or ENVI. At the beginning of the development of this industry, some of the types of image enhancements commissioned by the US government were performed by contractor firms. For example, ESL Incorporated has developed one of the first two-dimensional Fourier transforms for digital image processing. Satellite image analysis is actively used to protect the environment, for example, the "Visual satellite search for illegal landfills" method has identified more than 200 unauthorized municipal solid and household waste landfills on the territory of 5 subjects of the Russian Federation ,Bezugly, T. A. "Visual satellite search of illegal landfills": an algorithm for searching illegal landfills of solid household and construction waste using satellite images / T. A. Bezugly. Chelyabinsk : ANO "Center of Ecopathology", 2022. 49 p., URL: https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=49202156.See also
*Aerial photography
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other flight, airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography.
Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wi ...
* Earth observation satellite
* Moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
* Reconnaissance satellite
* Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
* Shuttle Radar Topography Mission
* Timeline of first images of Earth from space
* Virtual globe
** NASA World Wind
* Weather satellite
References
External links
ESA Envisat Meris – 300m
– the most detailed image of the entire Earth to date, made by the European Space Agency's Envisat Meris.
Blue Marble: Next Generation
– a detailed true-color image of the entire Earth.
World Wind
– an open source 3D Earth-viewing software developed by
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
that accesses NASA JPL database
{{DEFAULTSORT:Satellite Imagery
Earth observation satellites
Geographic data and information
Photography by genre