Roman province on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of
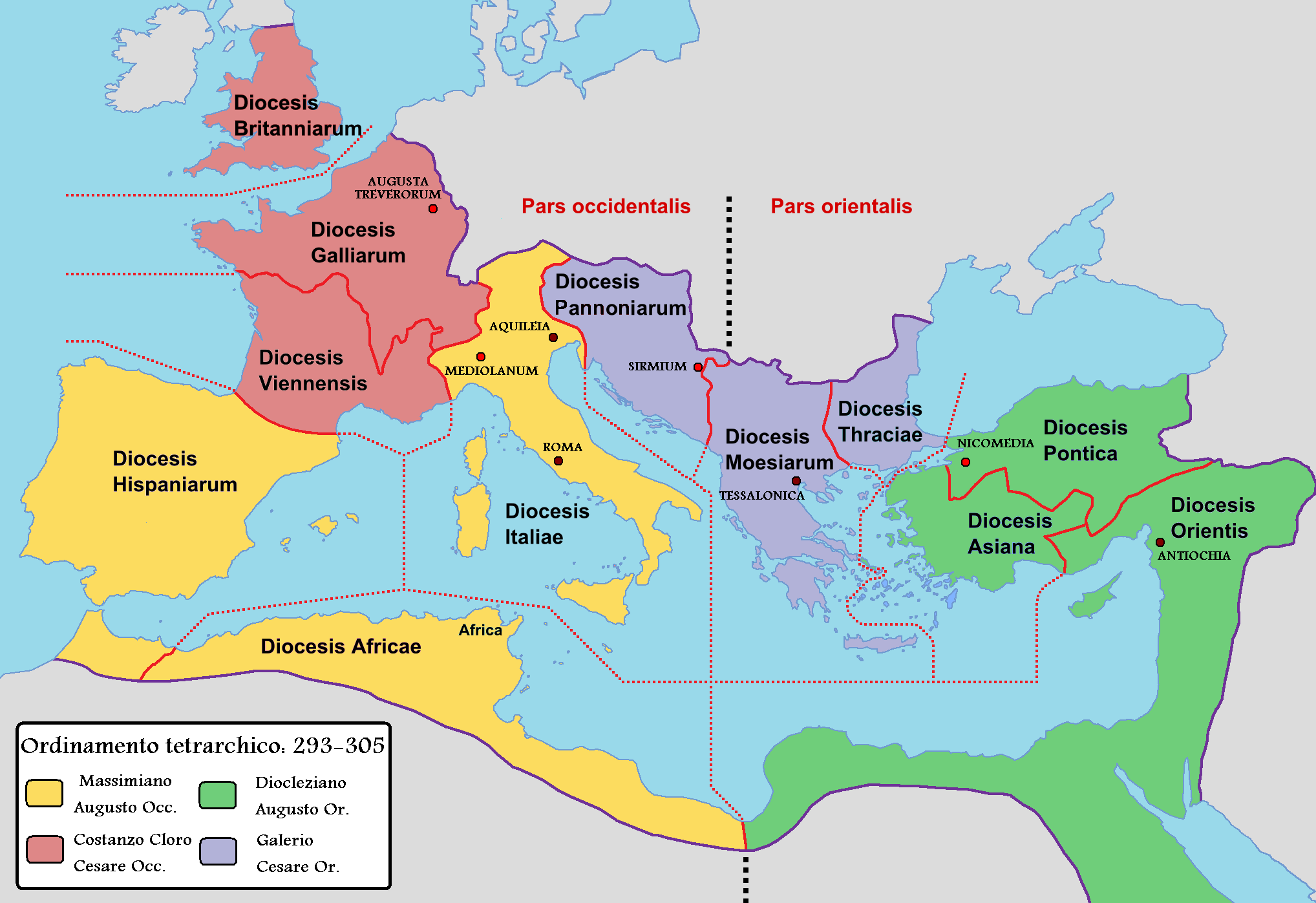 The emperor Diocletian introduced a radical reform known as the ''
The emperor Diocletian introduced a radical reform known as the ''

Map of the Roman Empire in the year 300
* https://web.archive.org/web/20060409205643/http://www.ancientlibrary.com/smith-dgra/ {{Authority control Ancient Roman provinces, Historical regions Provinces
 The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
and later the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
.
For centuries it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the imperial prefectures).
History
A province was the basic and, until theTetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
(from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy.
During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of senatorial
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the e ...
rank, usually former consuls
A consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the consul's own country, as well as to facilitate trade and friendship between the people ...
or former praetors
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected ''magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge variou ...
. A later exception was the province of Egypt, which was incorporated by Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
after the death of Cleopatra and was ruled by a governor of only equestrian
The word equestrian is a reference to equestrianism, or horseback riding, derived from Latin ' and ', "horse".
Horseback riding (or Riding in British English)
Examples of this are:
* Equestrian sports
*Equestrian order, one of the upper classes i ...
rank, perhaps as a discouragement to senatorial ambition. That exception was unique but not contrary to Roman law, as Egypt was considered Augustus's personal property, following the tradition of the kings of the earlier Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
.
Republican period
TheEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
word ''province'' comes from the Latin word ''provincia''. The Latin term ''provincia'' had an equivalent in eastern, Greek-speaking parts of the Greco-Roman world. In the Greek language, a province was called an ''eparchy'' ( el, , ''eparchia''), with a governor called an ''eparch'' ( el, , ''eparchos'').
Emergence
The Latin , during the middle republic, referred not to a territory, but to a task assigned to a Roman magistrate. That task might require using the military command powers of ''imperium
In ancient Rome, ''imperium'' was a form of authority held by a citizen to control a military or governmental entity. It is distinct from '' auctoritas'' and '' potestas'', different and generally inferior types of power in the Roman Republic a ...
'' but otherwise could even be a task assigned to a junior magistrates without ''imperium'': for example, the treasury was the of a quaestor and the civil jurisdiction of the urban praetor
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge vari ...
was the . In the middle and late republican authors like Plautus, Terence, and Cicero, the word referred something akin to a modern ministerial portfolio: "when... the senate assigned to the various magistrates... what they were doing was more like allocating a portfolio than putting people in charge of geographic areas".
The first commanders dispatched with were for the purpose of waging war and to command an army. However, merely that a ''provincia'' was assigned did not mean the Romans made that territory theirs. For example, Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus
Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus (fl. late 3rd to early 2nd century BC) was a Roman military officer and Senator who was elected Roman consul twice, and appointed dictator once. He fought in the Second Punic War and the First and Second Macedonian ...
in 211 BC received Macedonia as his ''provincia'' but the republic did not annex the kingdom, even as Macedonia was continuously assigned until 205 BC with the end of the First Macedonian war
The First Macedonian War (214–205 BC) was fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218–201 BC) against Carthage. The ...
. Even though the Second and Third Macedonian war
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman ...
s saw the Macedonian province revived, the senate settled affairs in the region by abolishing Macedonia and replacing it with four client republics. Macedonia only came under direct Roman administration in the aftermath of the Fourth Macedonian war
The Fourth Macedonian War (150–148 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by the pretender Andriscus, and the Roman Republic. It was the last of the Macedonian Wars, and was the last war to seriously threaten Roman control of Greece until the Fi ...
in 148 BC. Similarly, assignment of various in Hispania was not accompanied by the creation of any regular administration of the area; indeed, even though two praetors were assigned to Hispania regularly from 196 BC, no systematic settlement of the region occurred for nearly thirty years and what administration occurred was ''ad hoc'' and emerged from military necessities.
In the middle republic, the administration of a territory – whether taxation or jurisdictrion – had basically no relationship with whether that place was assigned as a ''provincia'' by the senate. Rome would even intervene on territorial disputes which were part of no ''provincia'' at all and were not administered by Rome. The territorial province, called a "permanent" ''provincia'' in the scholarship, emerged only gradually.
Permanent ''provincia''
The acquisition of territories, however, through the middle republic created the recurrent task of defending and administering some place. The first "permanent" was that of Sicily, created after the First Punic War. In the immediate aftermath, a quaestor was sent to Sicily to look out for Roman interests but eventually, praetors were dispatched as well. The sources differ as to when sending a praetor became normal: Appian reports 241 BC; Solinus indicates 227 BC instead. Regardless, the change likely reflected Roman unease about Carthaginian power: quaestors could not command armies or fleets; praetors could and initially seem to have held largely garrison duties. This first province started a permanent shift in Roman thinking about . Instead of being a task of military expansion, it became a recurrent defensive assignment to oversee conquered territories. These defensive assignments, with few opportunities to gain glory, were less desirable and therefore became regularly assigned to the praetors. Only around 180 BC did provinces take on a more geographically defined position when a border was established to separate the two commanders assigned to Hispania on the riverBaetis
''Baetis'' is a genus of mayflies of the family Baetidae, known as the blue-winged olive to anglers. There are at least 150 described species in ''Baetis''. They are distributed worldwide, with the most variety in North America and norther ...
. Later provinces, once campaigns were complete, were all largely defined geographically. Once this division of permanent and temporary emerged, magistrates assigned to permanent provinces also came under pressures to achieve as much as possible during their terms. Whenever a military crisis occurred near some province, it was normally reassigned to one of the consuls; praetors were left with the garrison duties. In the permanent provinces, the Roman commanders were initially not intended as administrators. However, the presence of the commander with forces sufficient to coerce compliance made him an obvious place to seek final judgement. A governor's legal jurisdiction thus grew from the demands of the provincial inhabitants for authoritative settlement of disputes.
In the absence of opportunities for conquest and with little oversight for their activities, many praetorian governors settled on extorting the provincials. This profiteering threatened Roman control by unnecessarily angering the province's subject populations and was regardless dishonourable. It eventually drew a reaction from the senate, which reacted with laws to rein in the governors. After initial experimentation with ''ad hoc'' panels of inquest, various laws were passed, such as the '' lex Calpurnia de repetundis'' in 149 BC, which established a permanent court to try corruption cases; troubles with corruption and laws reacting to it continued through the republican era. By the end of the republic, a multitude of laws had been passed on how a governor would complete his task, requiring presence in the province, regulating how he could requisition goods from provincial communities, limiting the number of years he could serve in the province, etc.
Assignment
Prior to 123 BC, the senate assigned consular provinces as it wished, usually in its first meeting of the consular year. The specific provinces to be assigned were normally determined by lot or by mutual agreement among the commanders; only extraordinarily did the senate assign a command (outside of sortition). But in 123 or 122 BC, the tribuneGaius Sempronius Gracchus
Gaius Sempronius Gracchus ( – 121 BC) was a reformist Roman politician in the 2nd century BC. He is most famous for his tribunate for the years 123 and 122 BC, in which he proposed a wide set of laws, including laws to establish ...
passed the ''lex Sempronia de provinciis consularibus'', which required the senate to select the consular provinces before the consular elections and made this announcement immune from tribunician veto. The law had the effect of, over time, abolishing the temporary , as it was not always realistic for the senate to anticipate the theatres of war some six months in advance. Instead, the senate chose to assign consuls to permanent provinces near expected trouble spots. From 200 to 124 BC, only 22 per cent of recorded consular were permanent provinces; between 122 and 53 BC, this rose to 60 per cent.
While many of the provinces had been assigned to sitting praetors in the earlier part of the second century, with new praetorships created to fill empty provincial commands, by the start of the first century it had become uncommon for praetors to hold provincial commands during their formal annual term. Instead they generally took command as promagistrate
In ancient Rome a promagistrate ( la, pro magistratu) was an ex-consul or ex- praetor whose '' imperium'' (the power to command an army) was extended at the end of his annual term of office or later. They were called proconsuls and propraetors. T ...
after the end of their term. The use of prorogation was due to an insufficient number of praetors, which was for two reasons: more provinces needed commands and the increased number of permanent jury courts ('' quaestiones perpetuae''), each of which had a praetor as president, exacerbated this issue. Praetors during the second century were normally prorogued ''pro praetore'', but starting with the Spanish provinces and expanding by 167 BC, praetors were more commonly prorogued with the augmented rank '' pro consule''; by the end of the republic, all governors acted ''pro consule''.
Also important was the assertion of popular authority over the assignment of provincial commands. This started with Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important refor ...
, who had an allied tribune introduce a law transferring to him the already-taken province of Numidia (then held by Quintus Caecilius Metellus), allowing Marius to assume command of the Jugurthine War
The Jugurthine War ( la, Bellum Iugurthinum; 112–106 BC) was an armed conflict between the Roman Republic and king Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. Jugurtha was the nephew and adopte ...
. This innovation destabilised the system of assigning provincial commands, exacerbated internal political tensions, and later allowed ambitious politicians to assemble for themselves enormous commands which the senate would never have approved: the Pompeian ''lex Gabinia'' of 67 BC granted Pompey all land within 50 miles of the Mediterranean; Caesar's Gallic command that encompassed three normal provinces.
Late Republican period
In the late Republican period, Roman authorities generally preferred that a majority of people in Rome's provinces venerated, respected, and worshipped gods from Rome proper and Roman Italy to an extent, alongside normal services done in honor of their "traditional" gods.Transition to empire
The increasing practices of prorogation and statutorily-defined "super commands" driven by political tactics undermined the republican constitutional principle of annually-elected magistracies. This allowed the powerful men to amass disproportionate wealth and military power through their provincial commands, which was one of the major factors in the transition from a republic to an imperial autocracy. The senate attempted to push back against these commands in many instances: it preferred to break up any large war into multiple territorially separated commands; for similar reasons, it opposed the ''lex Gabinia'' which gavePompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
an overlapping command over large portions of the Mediterranean. The senate, which had long acted as a check on aristocratic ambitions, was unable to stop these immense commands, which culminated eventually with the reduction of the number of meaningfully-independent governors during the triumviral period to three men and, with the end of the republic, to one man.
Early imperial period
During his sixth and seventh consulships (28 and 27 BC), Augustus began a process which saw the republic return to "normality": he shared the ''fasces'' that year with his consular colleague month-by-month and announced the abolition of the triumvirate by the end of the year in accordance with promises to do so at the close of the civil wars. At the start of 27 BC, Augustus formally had a provincial command over all of Rome's provinces. That year, in his "first settlement", he ostentatiously returned his control of them and their attached armies to the senate, likely by declaring that the task assigned to him either by the ''lex Titia
The ''lex Titia'' was a Roman law passed on 27 November 43 BC that established the Triumvirate of Octavian, Mark Antony and Marcus Aemilius Lepidus for five years until the end of 38 BC. The triumvirate established by the law was then re ...
'' creating the Triumvirate or that the war on Cleopatra and Antony was complete. In return, at a carefully-managed meeting of the senate, he was given commands over Spain, Gaul, Syria, Cilicia, Cyprus, and Egypt to hold for ten years; these provinces contained 22 of the 28 extant Roman legions (over 80 per cent) and contained all prospective military theatres.
The provinces that were assigned to Augustus became known as imperial provinces and the remaining provinces, largely demilitarised and confined to the older republican conquests, became known as public or senatorial provinces, as their commanders were still assigned by the senate on an annual basis consistent with tradition. Because no one man could command in practically all the border-regions of the empire at once, Augustus appointed subordinate legate
Legate may refer to:
*Legatus, a higher ranking general officer of the Roman army drawn from among the senatorial class
:*Legatus Augusti pro praetore, a provincial governor in the Roman Imperial period
*A member of a legation
*A representative, ...
s for each of the provinces with the title ''legatus Augusti pro praetore
A ''legatus Augusti pro praetore'' (literally: "envoy of the emperor – acting for the praetor") was the official title of the governor or general of some Imperial provincess of the Roman Empire during the Principate era, normally the larger ones ...
''. These lieutenant ''legati'' probably held ''imperium'' but, due to their lack of an independent command, were unable to triumph and could be replaced by their superior (Augustus) at any time. These arrangements were likely based on the precedent of Pompey's proconsulship over the Spanish provinces after 55 BC entirely through legates, while he stayed in the vicinity of Rome. In contrast, the public provinces continued to be governed by proconsuls with formally independent commands. In only three of the public provinces were there any armies: Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Illyricum, and Macedonia; after Augustus' Balkan wars, only Africa retained a legion.
To make this monopolisation of military commands palatable, Augustus separated prestige from military importance and inverted it. The title ''pro praetore'' had gone out of use by the end of the republic and was regardless in inferior status to a proconsul. More radically, Egypt (which was sufficiently powerful that a commander there could start a rebellion against the emperor) was commanded by an equestrian prefect, "a very low title indeed" as prefects were normally low-ranking officers and equestrians were not normally part of the elite. In Augustus' "second settlement" of 23 BC, he gave up his continual holding of the consulship in exchange for a general proconsulship – with a special dispensation from the law that nullified ''imperium'' within the city of Rome – over the imperial provinces. He also gave himself, through the senate, a general grant of ''imperium maius'', which gave him priority over the ordinary governors of the public provinces, allowing him to interfere in their affairs.
Within the public and imperial provinces there also existed distinctions of rank. In the public provinces, the provinces of Africa and Asia were given only to ex-consuls; ex-praetors received the others. The imperial provinces eventually produced a three-tier system with prefects and procurators, legates ''pro praetore'' who were ex-praetors, and legates ''pro praetore'' who were ex-consuls. The public provinces' governors normally served only one year; the imperial provinces' governors on the other hand normally served several years before rotating out. The extent to which the emperor exercised control over all the provinces increased during the imperial period: Tiberius, for example, once reprimanded legates in the imperial provinces for failing to forward financial reports to the senate; by the reign of Claudius, however, the senatorial provinces' proconsuls were regularly issued with orders directly from the emperor.
Late imperial period
tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
'' (AD 284–305), with a western and an eastern senior emperor styled ''Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
'', each seconded by a junior emperor (and designated successor) styled ''caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
''. Each of these four defended and administered a quarter of the empire. In the 290s, Diocletian divided the empire anew into almost a hundred provinces, including Roman Italy. Their governors were hierarchically ranked, from the proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
In the Roman Republic, military command, or ...
s of Africa Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
through those governed by '' consulares'' and ''corrector
A corrector (English plural ''correctors'', Latin plural ''correctores'') is a person or object practicing correction, usually by removing or rectifying errors.
The word is originally a Roman title, ''corrector'', derived from the Latin verb '' ...
es'' to the '' praesides''. The provinces in turn were grouped into (originally twelve) dioceses
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, headed usually by a ''vicarius
''Vicarius'' is a Latin word, meaning ''substitute'' or ''deputy''. It is the root of the English word "vicar".
History
Originally, in ancient Rome, this office was equivalent to the later English " vice-" (as in "deputy"), used as part of th ...
'', who oversaw their affairs. Only the proconsuls and the urban prefect
The ''praefectus urbanus'', also called ''praefectus urbi'' or urban prefect in English, was prefect of the city of Rome, and later also of Constantinople. The office originated under the Roman kings, continued during the Republic and Empire, and ...
of Rome (and later Constantinople) were exempt from this, and were directly subordinated to the tetrarchs.
Although the Caesars were soon eliminated from the picture, the four administrative resorts were restored in 318 by Emperor Constantine I, in the form of praetorian prefectures, whose holders generally rotated frequently, as in the usual magistracies but without a colleague. Constantine also created a new capital, named after him as Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, which was sometimes called 'New Rome' because it became the permanent seat of the government. In Italy itself, Rome had not been the imperial residence for some time and 286 Diocletian formally moved the seat of government to Mediolanum
Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in northern Italy. The city was settled by the Insubres around 600 BC, conquered by the Romans in 222 BC, and ...
(modern Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
), while taking up residence himself in Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocleti ...
. During the 4th century, the administrative structure was modified several times, including repeated experiments with Eastern-Western co-emperors.
Detailed information on the arrangements during this period is contained in the '' Notitia Dignitatum'' (Record of Offices), a document dating from the early 5th century. Most data is drawn from this authentic imperial source, as the names of the areas governed and titles of the governors are given there. There are however debates about the source of some data recorded in the ', and it seems clear that some of its own sources are earlier than others. Some scholars compare this with the list of military territories under the '' duces'', in charge of border garrisons on so-called '' limites'', and the higher ranking ', with more mobile forces, and the later, even higher ''magistri militum''.
Justinian I made the next great changes in 534–536 by abolishing, in some provinces, the strict separation of civil and military authority that Diocletian had established.This process was continued on a larger scale with the creation of extraordinary Exarchate
An exarchate is any territorial jurisdiction, either secular or ecclesiastical, whose ruler is called an exarch. The term originates from the Greek word ''arkhos'', meaning a leader, ruler, or chief. Byzantine Emperor Justinian I created the firs ...
s in the 580s and culminated with the adoption of the military theme system
Theme or themes may refer to:
* Theme (arts), the unifying subject or idea of the type of visual work
* Theme (Byzantine district), an administrative district in the Byzantine Empire governed by a Strategos
* Theme (computing), a custom graphical ...
in the 640s, which replaced the older administrative arrangements entirely. Some scholars use the reorganization of the empire into themata in this period as one of the demarcations between the Dominate
The Dominate, also known as the late Roman Empire, is the name sometimes given to the " despotic" later phase of imperial government in the ancient Roman Empire. It followed the earlier period known as the "Principate". Until the empire was reuni ...
and the Byzantine (or the Later Roman) period.
List of provinces
Republican provinces
* 241 BC –Sicilia
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
(Sicily) taken over from the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
and annexed at the end of the First Punic War
* 237 BC – Sardinia and Corsica
The Province of Sardinia and Corsica ( la, Provincia Sardinia et Corsica) was an ancient Roman province including the islands of Sardinia and Corsica.
Pre-Roman times
The Nuragic civilization flourished in Sardinia from 1800 to 500 BC. The ...
; these two islands were taken over from the Carthaginians and annexed soon after the Mercenary War
The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian contro ...
, in 238 BC and 237 BC respectively
* 197 BC – Hispania Citerior; along the east coast of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
; part of the territories taken over from the Carthaginians
* 197 BC – Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania ( ...
; along the southern coast of the Iberian Peninsula; part of the territories taken over from the Carthaginians in the Second Punic War
* 147 BC – Macedonia was annexed after the Achaean War
The Achaean War of 146 BC was fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek Achaean League, an alliance of Achaean and other Peloponnesian states in ancient Greece. It was the final stage of Rome's conquest of mainland Greece, taking place jus ...
* 146 BC – Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
(modern-day Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, eastern Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and western Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
); created after the destruction of Carthage in the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War (149–146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in modern northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 ...
* 129 BC – Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
, formerly the Attalid kingdom, in western Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
(now in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
), bequeathed to Rome by its last king, Attalus III
Attalus III ( el, Ἄτταλος Γ΄) Philometor Euergetes ( – 133 BC) was the last Attalid king of Pergamon, ruling from 138 BC to 133 BC.
Biography
Attalus III was the son of king Eumenes II and his queen Stratonice of Pergamon, and ...
, in 133 BC.
* 120 BC – Gallia Narbonensis (southern France); prior to its annexation it was called Gallia Transalpina
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the ...
(Gallia on the other side of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
) to distinguish it from Gallia Cisalpina
Cisalpine Gaul ( la, Gallia Cisalpina, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the part of Italy inhabited by Celts (Gauls) during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC.
After its conquest by the Roman Republic in the 200s BC it was con ...
(Gaul on this same side of the Alps, in northern Italy). It was annexed following attacks on the allied Greek city of Massalia (Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Fra ...
).
* 67 BC – Crete and Cyrenaica
Crete and Cyrenaica ( la, Provincia Creta et Cyrenaica, Ancient Greek ) was a senatorial province of the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire, established in 67 BC. It comprised the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in present-day L ...
; Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
was bequeathed to Rome in 78 BC. However, it was not organised as a province. It was incorporated into the province of Creta et Cyrenae when Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
was annexed in 67 BC.
* 63 BC – Bithynia et Pontus
Bithynia and Pontus ( la, Provincia Bithynia et Pontus, Ancient Greek ) was the name of a province of the Roman Empire on the Black Sea coast of Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). It was formed during the late Roman Republic by the amalgamation o ...
; the Kingdom of Bithynia Bithynia ( grc-gre, Βιθυνία) was a Hellenistic kingdom centred in the historical region of Bithynia, which seems to have been established in the fourth century BC. In the midst of the Wars of the Diadochi, Zipoites assumed the title of king ...
(in North-western Anatolia) was bequeathed to Rome by its last king, Nicomedes IV
Nicomedes IV Philopator ( grc-gre, Νικομήδης Φιλοπάτωρ) was the king of Bithynia from c. 94 BC to 74 BC. (''numbered as III. not IV.'') He was the first son and successor of Nicomedes III of Bithynia.
Life
Memnon of Heraclea wro ...
, in 74 BC. It was organised as a Roman province at the end of the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
(73–63 BC) by Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
, who incorporated the western part of the defeated Kingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( grc-gre, Πόντος ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty (of Persian origin), which possibly may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemen ...
into it in 63 BC.
* 63 BC – Syria; Pompey deposed the last Seleucid king Philip II Philoromaeus
Philip II Philoromaeus ( grc, Φίλιππος ὁ Φιλορωμαῖος, "Friend of the Romans") or Barypous (Βαρύπους, "Heavy-foot"), a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, was the son of the Seleucid king Philip I Philadelphus, ...
, creating the province of Syria.
* 63 BC – Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
; Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
was created as a province in the sense of area of military command in 102 BC in a campaign against piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
. The Romans controlled only a small area. In 74 BC Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
and Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
(to the east) were added to the small Roman possessions in Cilicia. Cilicia came fully under Roman control at the end of the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
(73–63 BC), reorganised by Pompey in 63 BC.
* 58 BC – Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
was annexed after the death of its last king Ptolemy of Cyprus
Ptolemy of Cyprus was the king of Cyprus c. 80-58 BC. He was the younger brother of Ptolemy XII Auletes, king of Egypt, and, like him, an illegitimate son of Ptolemy IX Lathyros. He was also the uncle of Cleopatra VII.
Reign over Cyprus
He appear ...
and added to the province of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
, creating the province of Cilicia et Cyprus.
* 46 BC – Africa Nova
Numidia was a Roman province on the North African coast, comprising roughly the territory of north-east Algeria.
History
The people of the area were first identified as Numidians by Polybius around the 2nd century BC, although they were often ...
(Eastern Numidia – Algeria), Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
annexed Eastern Numidia and the new province called ''Africa Nova'' (new Africa) to distinguish it from the older province of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, created in 146 BC, which became known as ''Africa Vetus'' (old Africa). Western Numidia was annexed and added to the province of ''Africa Nova'' in 40 BC. The territory remained the direct part of the Roman Empire except for a brief period when Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
restored Juba II
Juba II or Juba of Mauretania (Latin: ''Gaius Iulius Iuba''; grc, Ἰóβας, Ἰóβα or ;Roller, Duane W. (2003) ''The World of Juba II and Kleopatra Selene'' "Routledge (UK)". pp. 1–3. . c. 48 BC – AD 23) was the son of Juba I and client ...
(son of Juba I
Juba I of Numidia ( lat, IVBA, xpu, ywbʿy; –46BC) was a king of Numidia (reigned 60–46 BC). He was the son and successor to Hiempsal II.
Biography
In 81 BC Hiempsal had been driven from his throne; soon afterwards, Pompey was sent to Af ...
) as a client king (30–25 BC).
Cisalpine Gaul (in northern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
) was occupied by Rome in the 220s BC and became considered geographically and ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' part of Roman Italy, but remained politically and ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' separated. It was legally merged into the administrative unit of Roman Italy in 42 BC by the triumvir Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
as a ratification of Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
's unpublished acts (''Acta Caesaris'').
Provinces of the Principate
Under Augustus
* 30 BC – Aegyptus, taken over byAugustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
after his defeat of Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
and Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
in 30 BC. It was the first imperial province in that it was Augustus' own domain as the Egyptians recognised him as their new pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the ...
. Its proper initial name was Alexandrea et Aegyptus. It was governed by Augustus' ''praefectus'', Alexandreae et Aegypti.
* 27 BC – Achaia
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaïa'' ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwestern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. T ...
(southern and central Greece), Augustus separated it from Macedonia (senatorial propraetorial province)
* 27 BC – Hispania Tarraconensis; former Hispania Citerior (northern, central and eastern Spain), created with the reorganisation of the provinces in Hispania by Augustus (imperial proconsular province).
* 27 BC – Lusitania (Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
and Extremadura
Extremadura (; ext, Estremaúra; pt, Estremadura; Fala: ''Extremaúra'') is an autonomous community of Spain. Its capital city is Mérida, and its largest city is Badajoz. Located in the central-western part of the Iberian Peninsula, it ...
in Spain), created with the reorganisation of the provinces in Hispania by Augustus (imperial proconsular province)
* 27 BC – Illyricum, Augustus conquered Illyria and southern Pannonia in 35–33 BC. Created as a senatorial province in 27 BC. Northern Pannonia was conquered during the Pannonian War (14–10 BC). Subdivided into Dalmatia (a new name for Illyria) and Pannonia, which were officially called Upper and Lower Illyricum respectively in 9 BC, towards the end of the Batonian War. Initially a senatorial province, it became an imperial ''propraetorial'' province in 11 BC, during the Pannonian War. It was dissolved and the new provinces of Dalmatia and Pannonia were created during the reign of Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
(69–79). In 107, Pannonia was divided into Pannonia Superior
Pannonia Superior, lit. Upper Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Carnuntum. It was one on the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pan ...
and Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia ...
– imperial provinces (proconsular and ''propraetorial'' respectively).
* 27 BC or 16–13 BC – Aquitania (south-western France) province created in the territories in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
conquered by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
; there is uncertainty as to whether it was created with Augustus’ first visit and the first census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses in ...
on Gaul or during Augustus' visit in 16–13 (imperial proconsular province)
* 27 BC or 16–13 BC – Gallia Lugdunensis
Gallia Lugdunensis (French: ''Gaule Lyonnaise'') was a province of the Roman Empire in what is now the modern country of France, part of the Celtic territory of Gaul formerly known as Celtica. It is named after its capital Lugdunum (today's Lyon) ...
(central and part of northern France) province created in the territories in Gaul conquered by Julius Caesar; there is uncertainty as to whether it was created with Augustus’ first visit and the first census on Gaul or during Augustus’ visit in 16–13 (imperial proconsular province)
* 25 BC – Galatia (central Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, Turkey), formerly a client kingdom, it was annexed by Augustus when Amyntas, its last king, died (imperial propraetorial province)
* 25 BC – Africa Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. The client kingdom of Numidia under king Juba II
Juba II or Juba of Mauretania (Latin: ''Gaius Iulius Iuba''; grc, Ἰóβας, Ἰóβα or ;Roller, Duane W. (2003) ''The World of Juba II and Kleopatra Selene'' "Routledge (UK)". pp. 1–3. . c. 48 BC – AD 23) was the son of Juba I and client ...
(30 - 25 BC), previously between 46 - 30 BC the province ''Africa Nova'', was abolished, and merged with the province ''Africa Vetus'', creating the province ''Africa Proconsularis'' (except territory of ''Western Numidia'').
* 22 BC – Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, a ...
(Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
south of the Rhine river, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, part of northern France and Germany west of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
; there is uncertainty as to whether it was created with Augustus’ first visit and the first census on Gaul or during Augustus' visit in 16–13 (imperial proconsular province)
* 15 BC – Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
(imperial ''procuratorial'' province)
* 14 BC – Hispania Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basic di ...
; former Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania ( ...
(southern Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
); created with the reorganisation of the provinces in Hispania by Augustus (senatorial ''propraetorial'' province). The name derives from Betis, the Latin name for the Guadalquivir
The Guadalquivir (, also , , ) is the fifth-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula and the second-longest river with its entire length in Spain. The Guadalquivir is the only major navigable river in Spain. Currently it is navigable from the Gul ...
River.
* 7 BC – Germania Antiqua, lost after three Roman legions were routed in 9 AD
* AD 6? – Moesia (on the east and south bank of the River Danube part of modern Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
, the north part of North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
, northern Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
), Conquered in 28 BC, originally it was a military district under the province of Macedonia. The first mention of a provincial governor was for 6 AD, at the beginning of the Batonian War. In 85 Moesia was divided into Moesia Superior and Moesia Inferior (imperial proconsular provinces).
* AD 6 – Judaea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous so ...
, imperial ''procuratorial province'', created after the deposition of ethnarch Herod Archelaus
Herod Archelaus (, ''Hērōidēs Archelaos''; 23 BC – ) was ethnarch of Samaria, Judea, and Idumea, including the cities Caesarea and Jaffa, for a period of nine years (). He was the son of Herod the Great and Malthace the Samar ...
, formed initially from the territory of Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first ...
, Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
, and Idumea
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east ...
. Reverted to the status of client kingdom under king Herod Agrippa
Herod Agrippa (Roman name Marcus Julius Agrippa; born around 11–10 BC – in Caesarea), also known as Herod II or Agrippa I (), was a grandson of Herod the Great and King of Judea from AD 41 to 44. He was the father of Herod Agrippa II, th ...
in AD 41 by Claudius and became province again after Agrippa's death in AD 44, enlarged by territories of Galilee and Peraea
Peraia, and Peraea or Peræa (from grc, ἡ περαία, ''hē peraia'', "land across") in Classical Antiquity referred to "a community's territory lying 'opposite', predominantly (but not exclusively) a mainland possession of an island state" a ...
; renamed Syria Palaestina by Hadrian in AD 135 and upgraded to proconsular province.
Under Tiberius
* AD 17 –Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
(central Anatolia – Turkey); imperial ''propraetorial'' (later proconsular) province, created after the death of its last client king Archelaus.
Under Claudius
* AD 42 –Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana (Latin for "Tangerine Mauretania") was a Roman province, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia (or Chella ...
(northern Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
); after the death of Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
, the last king of Mauretania, in AD 40, his kingdom was annexed. It was begun by Caligula and was completed by Claudius with the defeat of the rebels. In AD 42, Claudius divided it into two provinces (imperial ''procuratorial'' province).
* AD 42 – Mauretania Caesariensis, (western and central Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
), after the death of Ptolemy, the last king of Mauretania, in AD 40, his kingdom was annexed. It was begun by Caligula and was completed by Claudius with the defeat of the rebels. In AD 42 Claudius divided it into two provinces( imperial ''procuratorial'' province).
* AD 41/53 – Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, ...
(central Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, north-eastern Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
and part of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
), it was incorporated into the empire in 16 BC. It was called a province, but it remained a client kingdom under the control of an imperial procurator. It was turned into a proper province during the reign of Claudius (41–54) (imperial ''propraetorial'' province).
* AD 43 – Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
; Claudius initiated the invasion of Britannia. Up to AD 60, the Romans controlled the area south of a line from the River Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between t ...
to the Severn Estuary
The Severn Estuary ( cy, Aber Hafren) is the estuary of the River Severn, flowing into the Bristol Channel between South West England and South Wales. Its high tidal range, approximately , means that it has been at the centre of discussions in t ...
. Wales was finally subdued in 78. In 78–84 Agricola
Agricola, the Latin word for farmer, may also refer to:
People Cognomen or given name
:''In chronological order''
* Gnaeus Julius Agricola (40–93), Roman governor of Britannia (AD 77–85)
* Sextus Calpurnius Agricola, Roman governor of the mi ...
conquered the north of England and Scotland. Scotland was then abandoned (imperial proconsular province). In 197 Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
divided Britannia into Britannia Superior and Britannia Inferior. Imperial provinces (proconsular and ''propraetorial'' respectively).
* AD 43 – Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
annexed by Claudius (in 74 AD merged with Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
to form Lycia et Pamphylia
Lycia et Pamphylia was the name of a province of the Roman empire, located in southern Anatolia. It was created by the emperor Vespasian (69–79), who merged Lycia and Pamphylia into a single administrative unit. In 43 AD, the emperor Claudius ...
).
* AD 46 – Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek D ...
(Thrace, north-eastern Greece, south-eastern Bulgaria and European Turkey), it was annexed by Claudius (imperial ''procuratorial'' province).
* AD 47? – Alpes Atrectianae et Poeninae (between Italy and Switzerland), Augustus subdued its inhabitants, the Salassi, in 15 BC. It was incorporated into Raetia. The date of the creation of the province is uncertain. It is usually set at the date of Claudius' foundation of Forum Claudii Vallensium (Martigny), which became its capital (imperial ''procuratorial'' province).
Under Nero
* AD 62 –Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
(the eastern half of the Kingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( grc-gre, Πόντος ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty (of Persian origin), which possibly may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemen ...
) together with Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
annexed, later incorporated in the province of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
(probably under Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
).
* AD 63 – Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (, ''Vasíleio toú Kimmerikoú Vospórou''), was an ancient Greco-Scythian state located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporus, ...
incorporated as part of the Roman province of Moesia Inferior. In 68 AD Galba restored the Bosporan Kingdom as a client kingdom.
* AD 63? – Alpes Maritimae
The Alpes Maritimae (; English: 'Maritime Alps') were a small province of the Roman Empire founded in 63 AD by Nero. It was one of the three provinces straddling the Alps between modern France and Italy, along with the Alpes Graiae et Poeninae a ...
(on the French Alps
The French Alps are the portions of the Alps mountain range that stand within France, located in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur regions. While some of the ranges of the French Alps are entirely in France, others, such as ...
), created as a protectorate by Augustus, it probably became a province under Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 unti ...
when Alpes Cottiae became a province (imperial ''procuratorial'' province)
* AD 63 – Alpes Cottiae (between France and Italy), in 14 BC it became a nominal prefecture which was run by the ruling dynasty of the Cotii. It was named after the king, Marcus Julius Cottius. It became a province in 63 (imperial ''procuratorial'' province).
Under Vespasian
* AD 72 –Commagene
Commagene ( grc-gre, Κομμαγηνή) was an ancient Greco-Iranian kingdom ruled by a Hellenized branch of the Iranian Orontid dynasty that had ruled over Armenia. The kingdom was located in and around the ancient city of Samosata, which s ...
, its last client king Antiochus IV was deposed and Commagene was annexed to Syria.
* AD 72 – Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia ( hy, Փոքր Հայք, ''Pokr Hayk''; la, Armenia Minor, Greek: Mikre Armenia, Μικρή Αρμενία), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian–populated regions primarily to the west and n ...
, its last client king Aristobulus of Chalcis
Aristobulus V of Chalcis ( grc-gre, Ἀριστόβουλος) was a son of Herod of Chalcis and his first wife Mariamne. Herod of Chalcis, ruler of Chalcis in Iturea, was a grandson of Herod the Great through his father, Aristobulus IV. Mariamne ...
was deposed and Lesser Armenia was annexed to Syria.
* AD 72 – Western mountainous parts of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
, formed into three client kingdoms established by Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, were disestablished, and merged with the imperial province of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coa ...
.
* AD 74 – Lycia et Pamphylia
Lycia et Pamphylia was the name of a province of the Roman empire, located in southern Anatolia. It was created by the emperor Vespasian (69–79), who merged Lycia and Pamphylia into a single administrative unit. In 43 AD, the emperor Claudius ...
. Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
(reigned AD 69–79) merged Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
, annexed by Claudius, and Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
which had been a part of the province of Galatia.
Under Domitian
* AD 83/84 – Germania Superior (southern Germany) The push into southern Germany up to theAgri Decumates
The ''Agri Decumates'' or ''Decumates Agri'' ("Decumatian Fields") were a region of the Roman Empire's provinces of Germania Superior and Raetia, covering the Black Forest, Swabian Jura, and Franconian Jura areas between the Rhine, Main, and Da ...
by Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
created the necessity to create this province, which had been a military district in Gallia Belgica when it was restricted to the west bank of the River Rhine (imperial proconsular province).
* AD 83/84 – Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agripp ...
(Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
south of the River Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, part of Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, and part of Germany west of the Rhine) originally a military district under Gallia Belgica, created when Germania Superior was created (imperial proconsular province).
* AD 92 – Chalcis was annexed to Syria after the death of its last ruler, tetrarch Aristobulus of Chalcis
Aristobulus V of Chalcis ( grc-gre, Ἀριστόβουλος) was a son of Herod of Chalcis and his first wife Mariamne. Herod of Chalcis, ruler of Chalcis in Iturea, was a grandson of Herod the Great through his father, Aristobulus IV. Mariamne ...
.
Under Trajan
* AD 100 – Territories of Iturea,Trachonitis
The Lajat (/ALA-LC: ''al-Lajāʾ''), also spelled ''Lejat'', ''Lajah'', ''el-Leja'' or ''Laja'', is the largest lava field in southern Syria, spanning some 900 square kilometers. Located about southeast of Damascus, the Lajat borders the Hauran ...
, Batanea
Batanaea or Batanea (the Hellenized/Latinised form of Bashan) was an area of the Biblical Holy Land, north-east of the Jordan River, to the west of Trachonitis. History
Bataneaea was one of the four post-Exile divisions of the area of Bashan.
...
, Gaulanitis
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
, Auranitis and Paneas
Banias or Banyas ( ar, بانياس الحولة; he, בניאס, label=Modern Hebrew; Judeo-Aramaic, Medieval Hebrew: פמייס, etc.; grc, Πανεάς) is a site in the Golan Heights near a natural spring, once associated with the Greek g ...
were annexed to Syria after the death of king Herod Agrippa II
Herod Agrippa II (; AD 27/28 – or 100), officially named Marcus Julius Agrippa and sometimes shortened to Agrippa, was the last ruler from the Herodian dynasty, reigning over territories outside of Judea as a Roman client. Agrippa II fled ...
.
* AD 106 – Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, formerly the Kingdom of Nabataea, it was annexed without resistance by Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
(imperial ''propraetorial'' province)
* AD 107 – Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
"Trajana" (the Romanian regions of south-eastern Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, the Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
, and Oltenia
Oltenia (, also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions, with the alternative Latin names ''Wallachia Minor'', ''Wallachia Alutana'', ''Wallachia Caesarea'' between 1718 and 1739) is a historical province and geographical region of Romania ...
), conquered by Trajan in the Dacian Wars (imperial proconsular province). Divided into Dacia Superior and Dacia Inferior
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today ...
in 158 by Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
. Divided into three provinces ( Tres Daciae) in 166 by Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
: Porolissensis, Apulensis and Malvensis (imperial ''procuratorial'' provinces). Abandoned by Aurelian in 271.
* AD 103/114 - Epirus Nova
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinric ...
(in western Greece and southern Albania), Epirus was originally under the province of Macedonia. It was placed under Achaia in 27 BC except for its northernmost part, which remained part of Macedonia. It became a separate province under Trajan, sometime between 103 and 114 AD, and was renamed Epirus Nova (New Epirus) (imperial ''procuratorial'' province).
* AD 114 – Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
, annexed by Trajan, who deposed its client king. In 118 Hadrian restored this client kingdom
* AD 116 – Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
(Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
) seized from the Parthians and annexed by Trajan, who invaded the Parthian Empire in late 115. Given back to the Parthians by Hadrian in 118. In 198 Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
conquered a small area in the north and named it Mesopotamia. It was attacked twice by the Persians (imperial ''praefectorial'' province).
* AD 116 – Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
, Trajan suppressed a revolt by Assyrians in Mesopotamia and created the province. Hadrian relinquished it in 118.
Under Septimius Severus
* AD 193 – Numidia, was separated fromAfrica Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
by Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
(imperial propraetorial province).
* AD 194 – Syria Coele and Syria Phoenice, Septimius Severus divided Syria into these two units in the north and the south respectively. Imperial provinces (proconsular and propraetorial respectively).
Under Caracalla
* AD 214 –Osrhoene
Osroene or Osrhoene (; grc-gre, Ὀσροηνή) was an ancient region and state in Upper Mesopotamia. The ''Kingdom of Osroene'', also known as the "Kingdom of Edessa" ( syc, ܡܠܟܘܬܐ ܕܒܝܬ ܐܘܪܗܝ / "Kingdom of Urhay"), according t ...
, this kingdom (in northern Mesopotamia, in parts of today's Iraq, Syria and Turkey) was annexed.
Under Aurelian
* AD 271 – Dacia Aureliana (most of Bulgaria and Serbia) created by Aurelian in the territory of the former Moesia Superior after his evacuation of Dacia Trajana beyond the River Danube. :Many of the above provinces were under Roman military control or under the rule of Roman clients for a long time before being officially constituted as civil provinces. Only the date of the official formation of the province is marked above, not the date of conquest.Provinces of the late empire
Primary sources for lists of provinces
Early Roman Empire provinces
* ''Germania'' (ca. 100) * ''Geography'' (Ptolemy) (ca. 140)Late Roman Empire provinces
* ''Laterculus Veronensis
The ''Laterculus Veronensis'' or Verona List is a list of Roman provinces and barbarian peoples from the time of the emperors Diocletian and Constantine I, most likely from AD 314.
The list is transmitted only in a 7th-century manuscript preserve ...
'' (ca. 310)
* '' Notitia dignitatum'' (ca. 400–420)
* ''Laterculus A ''laterculus'' was, in late antiquity or the early medieval period, an inscribed tile, stone or terracotta tablet used for publishing certain kinds of information in list or calendar form. The term thus came to be used for the content represented ...
Polemii Silvii'' (ca. 430)
* '' Synecdemus'' (ca. 520)
See also
*Ancient geography
The history of geography includes many histories of geography which have differed over time and between different cultural and political groups. In more recent developments, geography has become a distinct academic discipline. 'Geography' deriv ...
* Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
* Early world maps
The earliest known world maps date to classical antiquity, the oldest examples of the 6th to 5th centuries BCE still based on the flat Earth paradigm.
World maps assuming a spherical Earth first appear in the Hellenistic period.
The developments ...
* Ecumene
The ecumene ( US spelling) or oecumene ( UK spelling; grc-gre, οἰκουμένη, oikouménē, inhabited) is an ancient Greek term for the known, the inhabited, or the habitable world. In Greek antiquity, it referred to the portions of the worl ...
* Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
* History of cartography
The history of cartography refers to the development and consequences of cartography, or mapmaking technology, throughout human history. Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans to explain and navi ...
* History of the Mediterranean region
The history of the Mediterranean region and of the cultures and people of the Mediterranean Basin is important for understanding the origin and development of the Mesopotamian, Egyptian, Canaanite, Phoenician, Hebrew, Carthaginian, Minoan, G ...
* Latin spelling and pronunciation
* List of Graeco-Roman geographers
;Pre-Hellenistic Classical Greece
*Homer
* Anaximander
* Hecataeus of Miletus
* Massaliote Periplus
* Scylax of Caryanda (6th century BC)
*Herodotus
;Hellenistic period
* Pytheas (died c. 310 BC)
*''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' (3rd or 4th centur ...
* List of historical maps
The following is a list of notable extant historical maps.
Early world maps
*Babylonian Map of the World (flat-earth diagram on a clay tablet, c. 600 BC)
*'' Tabula Rogeriana'' (1154)
* Psalter world map (1260)
*''Tabula Peutingeriana'' (126 ...
* Local government (ancient Roman)
The Romans used provincial and local governments to govern conquered territories without having to rule them directly.
Although Rome ruled a vast empire, it needed strikingly few imperial officials to run it. This relatively light ruling admini ...
References
Citations
Sources
; Modern sources * * ** ** * * * * * * ; Other sources * * *External links
Map of the Roman Empire in the year 300
* https://web.archive.org/web/20060409205643/http://www.ancientlibrary.com/smith-dgra/ {{Authority control Ancient Roman provinces, Historical regions Provinces