Rust is a
general-purpose programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
emphasizing
performance
A performance is an act or process of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Performance has evolved glo ...
,
type safety, and
concurrency. It enforces
memory safety, meaning that all
references
A reference is a relationship between Object (philosophy), objects in which one object designates, or acts as a means by which to connect to or link to, another object. The first object in this relation is said to ''refer to'' the second object. ...
point to valid memory. It does so without a conventional
garbage collector; instead, memory safety errors and
data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the
object lifetime of references
at compile time.
Rust does not enforce a
programming paradigm
A programming paradigm is a relatively high-level way to conceptualize and structure the implementation of a computer program. A programming language can be classified as supporting one or more paradigms.
Paradigms are separated along and descri ...
, but was influenced by ideas from
functional programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarat ...
, including
immutability,
higher-order function In mathematics and computer science, a higher-order function (HOF) is a function that does at least one of the following:
* takes one or more functions as arguments (i.e. a procedural parameter, which is a parameter of a procedure that is itself ...
s,
algebraic data types, and
pattern matching. It also supports
object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and impl ...
via structs,
enums, traits, and methods. It is popular for
systems programming.
Software developer Graydon Hoare created Rust as a personal project while working at
Mozilla Research in 2006. Mozilla officially sponsored the project in 2009. In the years following the first stable release in May 2015, Rust was adopted by companies including
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
,
Discord,
Dropbox,
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
(
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
),
Meta, and
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
. In December 2022, it became the first language other than
C and
assembly to be supported in the development of the
Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ...
.
Rust has been noted for its rapid adoption, and has been studied in
programming language theory
Programming language theory (PLT) is a branch of computer science that deals with the design, implementation, analysis, characterization, and classification of formal languages known as programming languages. Programming language theory is clos ...
research.
History
2006–2009: Early years

Rust began as a personal project by
Mozilla employee Graydon Hoare in 2006.
Hoare started the project due to his frustration with a broken elevator in his apartment building.
[ Hoare has stated that Rust was named for the group of fungi that are "over-engineered for survival".][ During the time period between 2006 and 2009, Rust was not publicized to others at Mozilla and was written in Hoare's free time;]BETA
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represe ...
(1975), Mesa (1977), NIL (1981), Erlang (1987), Newsqueak
Newsqueak is a concurrent programming language for writing application software with interactive graphical user interfaces.
Newsqueak's syntax and semantics are influenced by the C (programming language), C language, but its approach to concurr ...
(1988), Napier (1988), Hermes (1990), Sather (1990), Alef (1992), and Limbo (1996) as influences, stating "many older languages rebetter than new ones", and describing the language as "technology from the past come to save the future from itself."[ Early Rust developer Manish Goregaokar similarly described Rust as being based on "mostly decades-old research."][
During the early years, the Rust ]compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primaril ...
was written in about 38,000 lines of OCaml
OCaml ( , formerly Objective Caml) is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, High-level programming language, high-level, Comparison of multi-paradigm programming languages, multi-paradigm programming language which extends the ...
.object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and impl ...
via an keyword (later removed),[ and a typestates system that would allow variables of a type to be tracked along with state changes (such as going from uninitialized to initialized).]
2009-2012: Mozilla sponsorship
Mozilla officially sponsored the Rust project in 2009.[ ]Brendan Eich
Brendan Eich ( ; born July 4, 1961) is an American computer programmer and technology executive. He created the JavaScript programming language and co-founded the Mozilla project, the Mozilla Foundation, and the Mozilla Corporation. He serve ...
and other executives, intrigued by the possibility of using Rust for a safe web browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's scr ...
engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ge ...
, placed engineers on the project including Patrick Walton, Niko Matsakis, Felix Klock, and Manish Goregaokar.[ A conference room taken by the project developers was dubbed "the nerd cave," with a sign placed outside the door.][
During this time period, work had shifted from the initial OCaml compiler to a self-hosting compiler, ''i.e.'', written in Rust, based on ]LLVM
LLVM, also called LLVM Core, is a target-independent optimizer and code generator. It can be used to develop a Compiler#Front end, frontend for any programming language and a Compiler#Back end, backend for any instruction set architecture. LLVM i ...
.[ The Rust logo was developed in 2011 based on a bicycle chainring.
The first public release, Rust 0.1 was released on January 20, 2012][
]
2012–2015: Evolution
The years from 2012 to 2015 were marked by substantial changes to the Rust type system
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a ''type'' (for example, integer, floating point, string) to every '' term'' (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Usu ...
, especially, removal of the typestate system, consolidation of other language features, and the removal of the garbage collector.[ Memory management through the ownership system was gradually consolidated and expanded to prevent memory-related bugs. By 2013, the garbage collector feature was rarely used, and was removed by the team in favor of the ownership system.][ Other changes during this time included the removal of pure functions, which were declared by an explicit annotation, in March 2013. Specialized syntax support for channels and various pointer types were removed to simplify the language.][
Rust's expansion and consolidation was influenced by developers coming from C++ (e.g., low-level performance of features), ]scripting language
In computing, a script is a relatively short and simple set of instructions that typically automation, automate an otherwise manual process. The act of writing a script is called scripting. A scripting language or script language is a programming ...
s (e.g., Cargo and package management), and functional programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarat ...
(e.g., type systems development).[
Graydon Hoare stepped down from Rust in 2013.][ This allowed it to evolve organically under a more federated governance structure, with a "core team" of initially six people,][ around 30-40 developers total across various other teams,][ and a ]Request for Comments
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development and standards-setting bodies for the Internet, most prominently the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). An RFC is authored by individuals or ...
(RFC) process for new language features added in March 2014.[ The core team would grow to nine people by 2016][ with over 1600 proposed RFCs.][
According to Andrew Binstock writing for '' Dr. Dobb's Journal'' in January 2014, while Rust was "widely viewed as a remarkably elegant language", adoption slowed because it radically changed from version to version. Rust development at this time was focused on finalizing the language features and moving towards 1.0 so it could begin promising ]backward compatibility
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with Input ...
.[
Six years after Mozilla sponsored its development, the first stable release, Rust 1.0, was published on May 15, 2015.][ A year after the release, the Rust compiler had accumulated over 1,400 contributors and there were over 5,000 third-party libraries published on the Rust package management website Crates.io.][
]
2015–2020: Servo and early adoption
 The development of the Servo browser engine continued in parallel with Rust, jointly funded by Mozilla and Samsung. The teams behind the two projects worked in close collaboration; new features in Rust were tested out by the Servo team, and new features in Servo were used to give feedback back to the Rust team.
The development of the Servo browser engine continued in parallel with Rust, jointly funded by Mozilla and Samsung. The teams behind the two projects worked in close collaboration; new features in Rust were tested out by the Servo team, and new features in Servo were used to give feedback back to the Rust team.[ The first version of Servo was released in 2016.][ The ]Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements curr ...
web browser shipped with Rust code as of 2016 (version 45),[ but components of Servo did not appear in Firefox until September 2017 (version 57) as part of the Gecko and Quantum projects.
Improvements were made to the Rust toolchain ecosystem during the years following 1.0 including Rustfmt, ]integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
integration,[ a regular compiler testing and release cycle,][ a community ]code of conduct
A code of conduct is a set of rules outlining the social norm, norms, rules, and responsibilities or proper practices of an individual party or an organization.
Companies' codes of conduct
A company code of conduct is a set of rules which is comm ...
, and community discussion organized through an IRC chat.[
The earliest adoption outside of Mozilla was by individual projects at Samsung, ]Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
(now Meta Platforms), Dropbox, and others including Tilde, Inc. (the company behind ember.js).[ ]Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Amazon that provides Software as a service, on-demand cloud computing computing platform, platforms and Application programming interface, APIs to individuals, companies, and gover ...
followed in 2020.[ Engineers cited performance, lack of a garbage collector, safety, and pleasantness of working in the language as reasons for the adoption, while acknowledging that it was a risky bet as Rust was new technology. Amazon developers cited the fact that Rust uses half as much electricity as similar code written in ]Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, behind only C,[ as found by a study at the University of Minho, NOVA University Lisbon, and the University of Coimbra.]
Since 2020: Mozilla layoffs and Rust Foundation
In August 2020, Mozilla laid off 250 of its 1,000 employees worldwide, as part of a corporate restructuring caused by the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. The team behind Servo was disbanded. The event raised concerns about the future of Rust, due to the overlap between the two projects. In the following week, the Rust Core Team acknowledged the severe impact of the layoffs and announced that plans for a Rust foundation were underway. The first goal of the foundation would be to take ownership of all trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a form of intellectual property that consists of a word, phrase, symbol, design, or a combination that identifies a Good (economics and accounting), product or Service (economics), service f ...
s and domain names, and take financial responsibility for their costs.
On February 8, 2021, the formation of the Rust Foundation was announced by five founding companies: Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Amazon that provides Software as a service, on-demand cloud computing computing platform, platforms and Application programming interface, APIs to individuals, companies, and gover ...
, Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, Huawei
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ("Huawei" sometimes stylized as "HUAWEI"; ; zh, c=华为, p= ) is a Chinese multinational corporationtechnology company in Longgang, Shenzhen, Longgang, Shenzhen, Guangdong. Its main product lines include teleco ...
, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
, and Mozilla. The foundation, led by Shane Miller for its first two years, offered $20,000 grants and other support for programmers working on major Rust features.[ In a ]blog
A blog (a Clipping (morphology), truncation of "weblog") is an informational website consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries also known as posts. Posts are typically displayed in Reverse chronology, reverse chronologic ...
post published on April 6, 2021, Google announced support for Rust within the Android Open Source Project as an alternative to C/C++.
On November 22, 2021, the Moderation Team, which was responsible for enforcing the community code of conduct, announced their resignation "in protest of the Core Team placing themselves unaccountable to anyone but themselves".White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
released a 19-page press report urging software development to move to memory-safe programming languages; specifically, moving away from C and C++ and encouraging languages like C#, Go, Java, Ruby, Swift, and Rust.
Syntax and features
Rust's syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituenc ...
is similar to that of C and C++,[ although many of its features were influenced by ]functional programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarat ...
languages such as OCaml
OCaml ( , formerly Objective Caml) is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, High-level programming language, high-level, Comparison of multi-paradigm programming languages, multi-paradigm programming language which extends the ...
. Hoare has described Rust as targeted at frustrated C++ developers and emphasized features such as safety, control of memory layout, and concurrency.[ Safety in Rust includes the guarantees of memory safety, type safety, and lack of data races.
]
Hello World program
Below is a "Hello, World!" program in Rust. The keyword denotes a function, and the macro (see ) prints the message to standard output Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object t ...
. Statements in Rust are separated by semicolons.
fn main()
Variables
Variables in Rust are defined through the keyword. The example below assigns a value to the variable with name and outputs its value.
fn main()
Variables are immutable by default, but adding the keyword allows the variable to be mutated. The following example uses , which denotes the start of a comment.
fn main()
Multiple expressions can define multiple variables with the same name, known as variable shadowing. Variable shadowing allows transforming variables without having to name the variables differently. The example below declares a new variable with the same name that is double the original value:
fn main()
Variable shadowing is also possible for values of different types. For example, going from a string to its length:
fn main()
Block expressions and control flow
A ''block expression'' is delimited by curly brackets. When the last expression inside a block does not end with a semicolon, the block evaluates to the value of that trailing expression:
fn main()
Trailing expressions of function bodies are used as the return value:
fn add_two(x: i32) -> i32
expressions
An conditional expression executes code based on whether the given value is . can be used for when the value evaluates to , and can be used for combining multiple expressions.
fn main()
and blocks can evaluate to a value, which can then be assigned to a variable:
fn main()
loops
while can be used to repeat a block of code while a condition is met.
fn main()
loops and iterators
For loop
In computer science, a for-loop or for loop is a control flow Statement (computer science), statement for specifying iteration. Specifically, a for-loop functions by running a section of code repeatedly until a certain condition has been satisfi ...
s in Rust loop over elements of a collection.
expressions work over any iterator type.
fn main()
In the above code, is a value of type which implements the trait. The code within the curly braces is applied to each element returned by the iterator.
Iterators can be combined with functions over iterators like , , and . For example, the following adds up all numbers between 1 and 100 that are multiples of 3:
(1..=100).filter(, &x, x % 3 0).sum()
and statements
More generally, the keyword allows repeating a portion of code until a occurs. may optionally exit the loop with a value. In the case of nested loops, labels denoted by can be used to break an outer loop rather than the innermost loop.
fn main()
Pattern matching
The and expressions can be used for pattern matching. For example, can be used to double an optional integer value if present, and return zero otherwise:
fn double(x: Option) -> u64
Equivalently, this can be written with and :
fn double(x: Option) -> u64
Types
Rust is strongly typed and statically typed
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a ''type'' (for example, integer, floating point, string) to every '' term'' (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Usu ...
, meaning that the types of all variables must be known at compilation time. Assigning a value of a particular type to a differently typed variable causes a compilation error. Type inference is used to determine the type of variables if unspecified.
The default integer type is , and the default floating point type is . If the type of a literal number is not explicitly provided, it is either inferred from the context or the default type is used.
Primitive types
Integer types in Rust are named based on the signedness
In computing, signedness is a property of data types representing numbers in computer programs. A numeric variable is ''signed'' if it can represent both positive and negative numbers, and ''unsigned'' if it can only represent non-negative num ...
and the number of bits the type takes. For example, is a signed integer that takes 32 bits of storage, whereas is unsigned and only takes 8 bits of storage. and take storage depending on the architecture of the computer that runs the code, for example, on computers with 32-bit architectures, both types will take up 32 bits of space.
By default, integer literals are in base-10, but different radices are supported with prefixes, for example, for binary number
A binary number is a number expressed in the Radix, base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" (zero) and "1" (one). A ''binary number'' may ...
s, for octal
Octal (base 8) is a numeral system with eight as the base.
In the decimal system, each place is a power of ten. For example:
: \mathbf_ = \mathbf \times 10^1 + \mathbf \times 10^0
In the octal system, each place is a power of eight. For ex ...
s, and for hexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbo ...
s. By default, integer literals default to as its type. Suffixes such as can be used to explicitly set the type of a literal. Byte literals such as are available to represent the ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
value (as a ) of a specific character.
The Boolean type is referred to as which can take a value of either or . A takes up 32 bits of space and represents a Unicode scalar value: a Unicode codepoint that is not a surrogate. IEEE 754
The IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE 754) is a technical standard for floating-point arithmetic originally established in 1985 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The standard #Design rationale, add ...
floating point numbers are supported with for single precision floats and for double precision floats.
Compound types
Compound types can contain multiple values. Tuples are fixed-size lists that can contain values whose types can be different. Arrays are fixed-size lists whose values are of the same type. Expressions of the tuple and array types can be written through listing the values, and can be accessed with or :
let tuple: (u32, i64) = (3, -3);
let array: 8; 5= , 2, 3, 4, 5
let tuple: (bool, bool) = (true, true);
let value = tuple.1; // -3
let value = array // 3
Arrays can also be constructed through copying a single value a number of times:
let array2: har; 10= '; 10
User-defined types
User-defined types are created with the or keywords. The keyword is used to denote a record type that groups multiple related values. s can take on different variants at runtime, with its capabilities similar to algebraic data types found in functional programming languages. Both records and enum variants can contain fields with different types. Alternative names, or aliases, for the same type can be defined with the keyword.
The keyword can define methods for a user-defined type. Data and functions are defined separately. Implementations fulfill a role similar to that of classes within other languages.
Standard library
Option values are handled using syntactic sugar, such as the if let construction, to access the inner value (in this case, a string):
fn main()
Pointers
Rust does not use null pointer
In computing, a null pointer (sometimes shortened to nullptr or null) or null reference is a value saved for indicating that the Pointer (computer programming), pointer or reference (computer science), reference does not refer to a valid Object (c ...
s to indicate a lack of data, as doing so can lead to null dereferencing. Accordingly, the basic & and &mut references are guaranteed to not be null. Rust instead uses Option for this purpose: Some(T) indicates that a value is present, and None is analogous to the null pointer. Option implements a "null pointer optimization", avoiding any spatial overhead for types that cannot have a null value (references or the NonZero types, for example).
Unlike references, the raw pointer types *const and *mut may be null; however, it is impossible to dereference them unless the code is explicitly declared unsafe through the use of an unsafe block. Unlike dereferencing, the creation of raw pointers is allowed inside of safe Rust code.
Type conversion
Ownership
Rust's ownership system consists of rules that ensure memory safety without using a garbage collector. At compile time, each value must be attached to a variable called the ''owner'' of that value, and every value must have exactly one owner. Values are moved between different owners through assignment or passing a value as a function parameter. Values can also be ''borrowed,'' meaning they are temporarily passed to a different function before being returned to the owner. With these rules, Rust can prevent the creation and use of dangling pointers:
fn print_string(s: String)
fn main()
Because of these ownership rules, Rust types are known as ''linear
In mathematics, the term ''linear'' is used in two distinct senses for two different properties:
* linearity of a '' function'' (or '' mapping'');
* linearity of a '' polynomial''.
An example of a linear function is the function defined by f(x) ...
'' or ''affine'' types, meaning each value can be used exactly once. This enforces a form of software fault isolation as the owner of a value is solely responsible for its correctness and deallocation.
Lifetimes
Object lifetime refers to the period of time during which a reference
A reference is a relationship between objects in which one object designates, or acts as a means by which to connect to or link to, another object. The first object in this relation is said to ''refer to'' the second object. It is called a ''nam ...
is valid; that is, the time between the object creation and destruction. These ''lifetimes'' are implicitly associated with all Rust reference types. While often inferred, they can also be indicated explicitly with named lifetime parameters (often denoted , , and so on).
Lifetimes in Rust can be thought of as lexically scoped, meaning that the duration of an object lifetime is inferred from the set of locations in the source code (i.e., function, line, and column numbers) for which a variable is valid. For example, a reference to a local variable has a lifetime corresponding to the block it is defined in:
fn main() // ------------------+
The borrow checker in the Rust compiler then enforces that references are only used in the locations of the source code where the associated lifetime is valid. In the example above, storing a reference to variable in is valid, as variable has a longer lifetime () than variable (). However, when has a shorter lifetime, the borrow checker would reject the program:
fn main() // ------------------+
Since the lifetime of the referenced variable () is shorter than the lifetime of the variable holding the reference (), the borrow checker errors, preventing from being used from outside its scope.
Lifetimes can be indicated using explicit ''lifetime parameters'' on function arguments. For example, the following code specifies that the reference returned by the function has the same lifetime as (and ''not'' necessarily the same lifetime as ):
fn remove_prefix<'a>(mut original: &'a str, prefix: &str) -> &'a str
When user-defined types hold references to data, they also need to use lifetime parameters. The example below parses some configuration options from a string and creates a struct containing the options. The function parse_config also showcases lifetime elision, which reduces the need for explicitly defining lifetime parameters.
use std::collections::HashMap;
// This struct has one lifetime parameter, 'src. The name is only used within the struct's definition.
# erive(Debug)struct Config<'src>
// The '_ lifetime parameter, in this case, refers to the anonymous lifetime attached to the type
// of the argument `config`.
fn parse_config(config: &str) -> Config<'_>
fn main()
In the compiler, ownership and lifetimes work together to prevent memory safety issues such as dangling pointers.
Polymorphism
Generics
Rust's more advanced features include the use of generic functions. A generic function is given generic parameters, which allow the same function to be applied to different variable types. This capability reduces duplicate code and is known as parametric polymorphism.
The following program calculates the sum of two things, for which addition is implemented using a generic function:
use std::ops::Add;
// sum is a generic function with one type parameter, T
fn sum(num1: T, num2: T) -> T
where
T: Add
At compile time, polymorphic functions like sum are instantiated with the specific types the code requires; in this case, sum of integers and sum of floats.
Generics can be used in functions to allow implementing a behavior for different types without repeating the same code. Generic functions can be written in relation to other generics, without knowing the actual type.
Traits
 Rust's type system supports a mechanism called traits, inspired by type classes in the
Rust's type system supports a mechanism called traits, inspired by type classes in the Haskell
Haskell () is a general-purpose, statically typed, purely functional programming language with type inference and lazy evaluation. Designed for teaching, research, and industrial applications, Haskell pioneered several programming language ...
language,[ to define shared behavior between different types. For example, the ]Add trait can be implemented for floats and integers, which can be added; and the Display or Debug traits can be implemented for any type that can be converted to a string. Traits can be used to provide a set of common behavior for different types without knowing the actual type. This facility is known as ad hoc polymorphism.
Generic functions can constrain the generic type to implement a particular trait or traits; for example, an add_one function might require the type to implement Add. This means that a generic function can be type-checked as soon as it is defined. The implementation of generics is similar to the typical implementation of C++ templates: a separate copy of the code is generated for each instantiation. This is called monomorphization and contrasts with the type erasure scheme typically used in Java and Haskell. Type erasure is also available via the keyword dyn (short for dynamic). Because monomorphization duplicates the code for each type used, it can result in more optimized code for specific-use cases, but compile time and size of the output binary are also increased.
In addition to defining methods for a user-defined type, the impl keyword can be used to implement a trait for a type. Traits can provide additional derived methods when implemented. For example, the trait Iterator requires that the next method be defined for the type. Once the next method is defined, the trait can provide common functional helper methods over the iterator, such as map or filter.
Trait objects
Rust traits are implemented using static dispatch, meaning that the type of all values is known at compile time; however, Rust also uses a feature known as ''trait objects'' to accomplish dynamic dispatch, a type of polymorphism where the implementation of a polymorphic operation is chosen at runtime. This allows for behavior similar to duck typing, where all data types that implement a given trait can be treated as functionally equivalent. Trait objects are declared using the syntax dyn Tr where Tr is a trait. Trait objects are dynamically sized, therefore they must be put behind a pointer, such as Box. The following example creates a list of objects where each object can be printed out using the Display trait:
use std::fmt::Display;
let v: Vec> = vec! Box::new(3),
Box::new(5.0),
Box::new("hi"),
for x in v
If an element in the list does not implement the Display trait, it will cause a compile-time error.
Memory safety
Rust is designed to be memory safe. It does not permit null pointers, dangling pointers, or data races.unsafe keyword. Unsafe code may also be used for low-level functionality, such as volatile memory access, architecture-specific intrinsics, type punning, and inline assembly.
Memory management
Rust does not use garbage collection. Memory and other resources are instead managed through the "resource acquisition is initialization" convention, with optional reference counting. Rust provides deterministic management of resources, with very low overhead. Values are allocated on the stack by default, and all dynamic allocations must be explicit.
The built-in reference types using the & symbol do not involve run-time reference counting. The safety and validity of the underlying pointers is verified at compile time, preventing dangling pointers and other forms of undefined behavior. Rust's type system separates shared, immutable references of the form &T from unique, mutable references of the form &mut T. A mutable reference can be coerced to an immutable reference, but not vice versa.
Macros
Macros allow generation and transformation of Rust code to reduce repetition. Macros come in two forms, with ''declarative macros'' defined through macro_rules!, and ''procedural macros'', which are defined in separate crates.
Declarative macros
A declarative macro (also called a "macro by example") is a macro, defined using the macro_rules! keyword, that uses pattern matching to determine its expansion.
Procedural macros
Procedural macros are Rust functions that run and modify the compiler's input token stream, before any other components are compiled. They are generally more flexible than declarative macros, but are more difficult to maintain due to their complexity.custom!(...)
* Derive macros # erive(CustomDerive)/code>
* Attribute macros # ustom_attribute/code>
Interface with C and C++
Rust has a foreign function interface (FFI) that can be used both to call code written in languages such as C from Rust and to call Rust code from those languages. , an external library called CXX exists for calling to or from C++. Rust and C differ in how they lay out structs in memory, so Rust structs may be given a # epr(C)/code> attribute, forcing the same layout as the equivalent C struct.
Ecosystem
The Rust ecosystem includes its compiler, its standard library
In computer programming, a standard library is the library (computing), library made available across Programming language implementation, implementations of a programming language. Often, a standard library is specified by its associated program ...
, and additional components for software development. Component installation is typically managed by , a Rust toolchain
A toolchain is a set of software development tools used to build and otherwise develop software. Often, the tools are executed sequentially and form a pipeline such that the output of one tool is the input for the next. Sometimes the term is us ...
installer developed by the Rust project.
Compiler
The Rust compiler, , translates Rust code into low-level LLVM IR. LLVM is then invoked as a subcomponent to apply optimizations and translate the resulting IR into object code
In computing, object code or object module is the product of an assembler or compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' ...
. A linker
Linker or linkers may refer to:
Computing
* Linker (computing), a computer program that takes one or more object files generated by a compiler or generated by an assembler and links them with libraries, generating an executable program or shar ...
is then used to combine the objects into a single executable image or binary file.
Other than LLVM, the compiler also supports using alternative backends such as GCC and Cranelift for code generation. The intention of those alternative backends is to increase platform coverage of Rust or to improve compilation times.
Standard library
The Rust standard library defines and implements many widely used custom data types, including core data structures such as , , and , as well as smart pointer types. Rust also provides a way to exclude most of the standard library using the attribute ; this enables applications, such as embedded devices, which want to remove dependency code or provide their own core data structures. Internally, the standard library is divided into three parts, , , and , where and are excluded by .
Cargo
Cargo is Rust's build system and package manager
A package manager or package management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner.
A package manager deals wi ...
. It downloads, compiles, distributes, and uploads packages—called ''crates''—that are maintained in an official registry. It also acts as a front-end for Clippy and other Rust components.
Rustfmt
Rustfmt is a code formatter for Rust. It formats whitespace and indentation to produce code in accordance with a common style
Style, or styles may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Style'' (2001 film), a Hindi film starring Sharman Joshi, Riya Sen, Sahil Khan and Shilpi Mudgal
* ''Style'' (2002 film), a Tamil drama film
* ''Style'' (2004 film), a Burmese film
* '' ...
, unless otherwise specified. It can be invoked as a standalone program, or from a Rust project through Cargo.
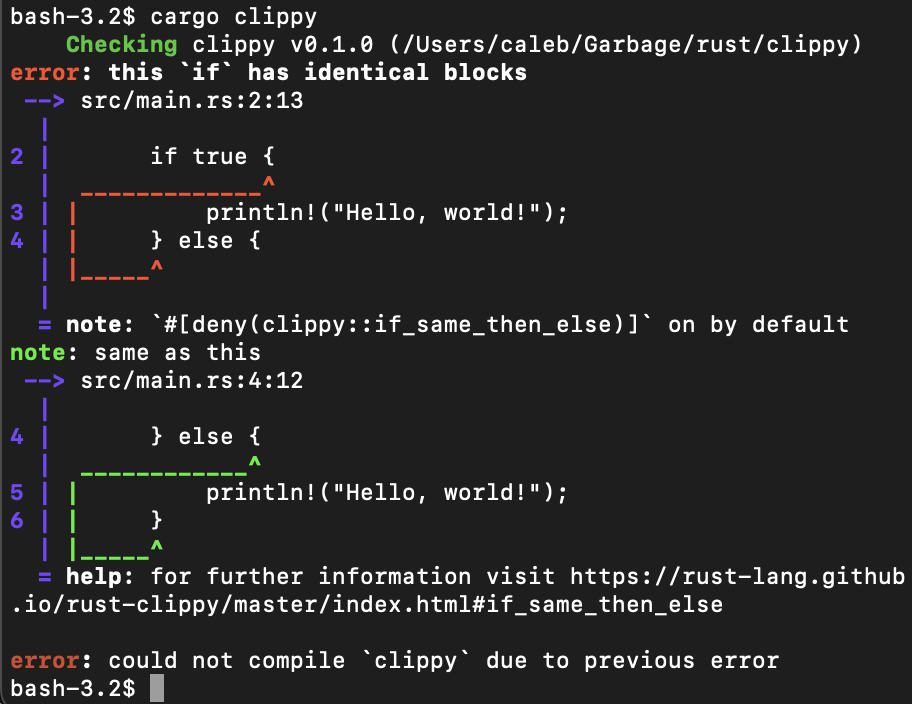
Clippy
Clippy is Rust's built-in linting tool to improve the correctness, performance, and readability of Rust code. , it has more than 700 rules.
Versioning system
Following Rust 1.0, new features are developed in ''nightly'' versions which are released daily. During each six-week release cycle, changes to nightly versions are released to beta, while changes from the previous beta version are released to a new stable version.
IDE support
''rust-analyzer'' is a collection of utilities that provides Integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
s (IDEs) and text editors with information about a Rust project through the Language Server Protocol. This enables features including autocompletion, and the display of compilation errors while editing.
Performance
Since it performs no garbage collection, Rust is often faster than other memory-safe languages.[ Most of Rust's memory safety guarantees impose no runtime overhead, with the exception of array indexing which is checked at runtime by default.][
Rust provides two "modes": safe and unsafe. Safe mode is the "normal" one, in which most Rust is written. In unsafe mode, the developer is responsible for the code's memory safety, which is used by developers for cases where the compiler is too restrictive.]parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a String (computer science), string of Symbol (formal), symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal gramm ...
. Static dispatch is used by default to eliminate method calls, except for methods called on dynamic trait objects. The compiler also uses inline expansion to eliminate function calls and statically-dispatched method invocations.
Since Rust uses LLVM
LLVM, also called LLVM Core, is a target-independent optimizer and code generator. It can be used to develop a Compiler#Front end, frontend for any programming language and a Compiler#Back end, backend for any instruction set architecture. LLVM i ...
, all performance improvements in LLVM apply to Rust also.[
]
Adoption
Rust is used in software across different domains. Components from the Servo browser engine (funded by Mozilla and Samsung) were incorporated in the Gecko browser engine underlying Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements curr ...
. In January 2023, Google (Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
) announced support for using third party Rust libraries in Chromium.
Rust is used in several backend software projects of large web service
A web service (WS) is either:
* a service offered by an electronic device to another electronic device, communicating with each other via the Internet, or
* a server running on a computer device, listening for requests at a particular port over a n ...
s. OpenDNS, a DNS resolution service owned by Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc. (using the trademark Cisco) is an American multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, s ...
, uses Rust internally. Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Amazon that provides Software as a service, on-demand cloud computing computing platform, platforms and Application programming interface, APIs to individuals, companies, and gover ...
uses Rust in "performance-sensitive components" of its several services. In 2019, AWS open-sourced Firecracker, a virtualization solution primarily written in Rust. Microsoft Azure IoT Edge, a platform used to run Azure services on IoT devices, has components implemented in Rust. Microsoft also uses Rust to run containerized modules with WebAssembly and Kubernetes. Cloudflare, a company providing content delivery network
A content delivery network (CDN) or content distribution network is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance ("speed") by distributing the service spat ...
services, used Rust to build a new web proxy named Pingora for increased performance and efficiency. The npm package manager used Rust for its production authentication service in 2019.
 In operating systems, the Rust for Linux project, launched in 2020, merged initial support into the
In operating systems, the Rust for Linux project, launched in 2020, merged initial support into the Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ...
version 6.1 in late 2022.[ The first drivers written in Rust were merged into the kernel for version 6.8.][ The Android developers used Rust in 2021 to rewrite existing components. ]Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
has rewritten parts of Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
in Rust. The r9 project aims to re-implement Plan 9 from Bell Labs
Plan 9 from Bell Labs is a distributed operating system which originated from the Computing Science Research Center (CSRC) at Bell Labs in the mid-1980s and built on UNIX concepts first developed there in the late 1960s. Since 2000, Plan 9 has ...
in Rust. Rust has been used in the development of new operating systems such as Redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is t ...
, a "Unix-like" operating system and microkernel
In computer science, a microkernel (often abbreviated as μ-kernel) is the near-minimum amount of software that can provide the mechanisms needed to implement an operating system (OS). These mechanisms include low-level address space management, ...
, Theseus, an experimental operating system with modular state management, and most of Fuchsia.JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have ...
and TypeScript
TypeScript (abbreviated as TS) is a high-level programming language that adds static typing with optional type annotations to JavaScript. It is designed for developing large applications and transpiles to JavaScript. It is developed by Micr ...
, is built on top of V8 using Rust and Tokio. Other notable adoptions in this space include Ruffle, an open-source SWF emulator, and Polkadot, an open source blockchain and cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency (colloquially crypto) is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Individual coin ownership record ...
platform.
Discord, an instant messaging software company, rewrote parts of its system in Rust for increased performance in 2020. In the same year, Dropbox announced that its file synchronization had been rewritten in Rust. Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
( Meta) used Rust to redesign its system that manages source code for internal projects.[
In the 2024 ]Stack Overflow
In software, a stack overflow occurs if the call stack pointer exceeds the stack bound. The call stack may consist of a limited amount of address space, often determined at the start of the program. The size of the call stack depends on many fa ...
Developer Survey, 12.6% of respondents had recently done extensive development in Rust.[
]
In academic research
Rust has been studied in academic research, both for properties of the language itself as well as the utility the language provides for writing software used for research. Its features around safety[ and performance have been examined.
In a journal article published to '' Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union'', astrophysicists Blanco-Cuaresma and Bolmont re-implemented programs responsible for simulating multi-planet systems in Rust, and found it to be a competitive programming language for its "speed and accuracy".][ Likewise, an article published on ]Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
shared several stories of bioinformaticians using Rust for its performance and safety.[ However, both articles have cited Rust's unique concepts, including its ownership system, being difficult to learn as one of the main drawbacks to adopting Rust.
]
Community
 According to one '' MIT Technology Review'' article, the Rust community was seen as "unusually friendly" to newcomers
According to one '' MIT Technology Review'' article, the Rust community was seen as "unusually friendly" to newcomers[ and particularly attracted people from the queer community, partly due to its ]code of conduct
A code of conduct is a set of rules outlining the social norm, norms, rules, and responsibilities or proper practices of an individual party or an organization.
Companies' codes of conduct
A company code of conduct is a set of rules which is comm ...
which outlined a set of expectations for Rust community members to follow.[ Inclusiveness of the community has been cited as an important factor for some Rust developers.][ Demographic data on the community has been collected and published by the Rust official blog.]
Rust Foundation
The Rust Foundation is a non-profit
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or so ...
membership organization incorporated in United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, with the primary purposes of backing the technical project as a legal entity
In law, a legal person is any person or legal entity that can do the things a human person is usually able to do in law – such as enter into contracts, lawsuit, sue and be sued, ownership, own property, and so on. The reason for the term "''le ...
and helping to manage the trademark and infrastructure assets.[
]
Governance teams
The Rust project is composed of ''teams'' that are responsible for different subareas of the development. The compiler team develops, manages, and optimizes compiler internals; and the language team designs new language features and helps implement them. The Rust project website lists 6 top-level teams . Representatives among teams form the Leadership council, which oversees the Rust project as a whole.
See also
* Comparison of programming languages
* History of programming languages
* List of programming languages
* List of programming languages by type
Notes
References
Book sources
*
*
*
*
*
Others
External links
*
*
{{Portal bar, Computer programming
Concurrent programming languages
Free and open source compilers
Free software projects
Functional languages
High-level programming languages
Mozilla
Multi-paradigm programming languages
Pattern matching programming languages
Procedural programming languages
Programming languages created in 2015
Software using the Apache license
Software using the MIT license
Statically typed programming languages
Systems programming languages
Articles with example Rust code
 The development of the Servo browser engine continued in parallel with Rust, jointly funded by Mozilla and Samsung. The teams behind the two projects worked in close collaboration; new features in Rust were tested out by the Servo team, and new features in Servo were used to give feedback back to the Rust team. The first version of Servo was released in 2016. The
The development of the Servo browser engine continued in parallel with Rust, jointly funded by Mozilla and Samsung. The teams behind the two projects worked in close collaboration; new features in Rust were tested out by the Servo team, and new features in Servo were used to give feedback back to the Rust team. The first version of Servo was released in 2016. The 

 In operating systems, the Rust for Linux project, launched in 2020, merged initial support into the Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ...
In operating systems, the Rust for Linux project, launched in 2020, merged initial support into the Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the k ... According to one '' MIT Technology Review'' article, the Rust community was seen as "unusually friendly" to newcomers and particularly attracted people from the queer community, partly due to its code of conduct
A code of conduct is a set of rules outlining the social norm, norms, rules, and responsibilities or proper practices of an individual party or an organization.
Companies' codes of conduct
A company code of conduct is a set of rules which is comm ...
According to one '' MIT Technology Review'' article, the Rust community was seen as "unusually friendly" to newcomers and particularly attracted people from the queer community, partly due to its code of conduct
A code of conduct is a set of rules outlining the social norm, norms, rules, and responsibilities or proper practices of an individual party or an organization.
Companies' codes of conduct
A company code of conduct is a set of rules which is comm ...